东营凹陷盐家地区沙四上亚段储层低渗成因机制及分类评价
马奔奔,操应长,王艳忠
(中国石油大学(华东) 地球科学与技术学院,山东 青岛,266580)
摘要:综合利用岩心观察、薄片鉴定、图像分析、压汞及岩石物性测试等多种技术方法,对东营凹陷盐家地区沙四上亚段近岸水下扇砂砾岩储层进行研究。以“储层成岩作用演化序列-储层孔隙结构”为约束进行地质历史时期储层物性的恢复,确定不同亚相或微相、不同岩性储层的低渗形成时间,分析沙四上亚段砂砾岩低渗储层成因机制。研究表明:储层的成岩作用具有强烈压实、多期溶解、多期胶结和灰泥组分重结晶的特征。沙四上亚段砂砾岩储层存在5种不同成因类型的低渗储层:Ⅰ类储层为压实低渗特低渗、灰泥重结晶超低渗型;Ⅱ类储层为压实低渗、胶结特低超低渗型;Ⅲ类储层为压实低渗、特低渗型;Ⅳ类储层为溶蚀改善物性,压实胶结低渗型;Ⅴ类储层为压实低渗,压实胶结特低超低渗型。根据致密史-成藏史关系以及试油结果分析可知:Ⅳ类储层为高渗成藏-现今低渗型,勘探潜力最好,为好储层;Ⅲ类储层为中渗成藏-现今特低渗型、勘探潜力中等,为较好储层;Ⅴ类储层为低渗成藏-现今超低渗,勘探潜力较差,为中等储层;Ⅰ类和Ⅱ类储层分别为特低渗成藏-现今非渗型和中渗成藏-现今非渗型,勘探潜力小,为较差储层。
关键词:低渗透储层;成因机制;近岸水下扇;沙四上亚段;东营凹陷
中图分类号:TE122.2 文献标志码:A 文章编号:1672-7207(2014)12-4277-15
Genetic mechanisms and classified evaluation of low permeability reservoirs of Es4s in Yanjia area, Dongying depression
MA Benben, CAO Yingchang, WANG Yanzhong
(School of Geosciences, China University of Petroleum, Qingdao 266580, China)
Abstract: By means of core observation, thin section identification, image analysis, mercury penetration, petro-physical property testing and other technical methods, the low permeability reservoirs in the near-shore subaqueous fan of Es4s were studied in the Yanjia area, Dongying depression. The diagenesis of low permeability reservoirs of Es4s was characterized by strong compaction, multistage of dissolution and cementation, and lime-mud matrix recrystallization. Confined by conditions of “reservoir diagenesis evolutionary sequence and reservoir pore structure”, physical properties of the reservoirs in geological history were restored. The geological time when reservoirs of different lithologies in different sub/micro-facies form low-permeability properties was determined based on the reservoir property evolutionary history. Genetic mechanisms of low permeability reservoirs of sandy conglomerate were investigated. The results show that there are five different genetic types of low permeability reservoirs. The characteristic of type Ⅰ reservoir is that its low permeability and extra-low permeability are caused by compaction, while its ultra-low permeability is caused by lime-mud matrix recrystallization. The characteristic of type Ⅱ reservoir is that its low permeability is caused by compaction, while its extra-low permeability and ultra-low permeability are caused by cementation. The characteristic of type Ⅲ reservoir is that its low permeability and extra-low permeability are caused by compaction. The characteristic of type Ⅳ reservoir is that its physical property is improved by dissolution, while its low permeability is caused by compaction and cementation; The characteristic of type Ⅴ reservoir is that its low permeability is caused by compaction, while its extra-low and ultra-low permeability are caused by compaction and cementation. According to a matching relationship between the reservoir compaction history and the hydrocarbon accumulation history as well as results from oil testing, type Ⅳ reservoir had high permeability in the hydrocarbon accumulation period and shows low permeability now, which is the best reservoir and has the best exploration potential. Type Ⅲ reservoir has medium permeability in the hydrocarbon accumulation period and shows extra-low permeability now, which is better reservoir and has medium exploration potential. Type Ⅴ reservoir has low permeability in the hydrocarbon accumulation period and shows ultra-low permeability now, which is medium reservoir and has poor exploration potential. Type Ⅰ reservoir had extra low permeability while Type Ⅱ low permeability reservoir has medium permeability in the hydrocarbon accumulation period. Both of these two types of reservoirs show impermeability now, which are poor reservoirs and have little exploration potential.
Key words: low permeability reservoirs; genetic mechanism; nearshore subaqueous fan; Es4s; Dongying depression
低渗透储层是指渗透率为0.1~50×10-3 μm2的一套储集体。随着对低渗透率储层油气勘探的不断深入,在普遍低孔隙度、低渗透率储层发育区常常可以找到相对优质的储集层段[1]。低渗透油气藏中的油气主要储集在这些优质储层中。因此,加强对低渗透储层特征的研究,明确低渗透储层的形成机制,寻找低孔隙度、低渗透率储层中相对优质储层的形成与分布规律,有利于对低渗储层的勘探开发及岩性油气藏的勘探。低渗透储层成因机制应包括储层物性主控因素和储层致密史-油气成藏史匹配关系2个方面。目前对低渗透储层物性主控因素的研究比较深入[2-7],而仅有少数学者对储层致密史-油藏成藏史的匹配关系进行了初步探讨。成藏关键时期储层物性很大程度上决定着油气能否大规模进入储层。先期中高渗充注成藏、后期致密化的低渗透储层与先期致密化、后期充注成藏的低渗透储层的勘探开发潜力存在较大差异[8]。因此,加强低渗透储层致密史-成藏史匹配关系的研究,对于勘探阶段钻前预测低渗透储层勘探潜力具有重要的指导意义。东营凹陷盐家地区沙四上亚段低渗透砂砾岩体发育,这类砂砾岩体紧邻烃源岩分布,成藏条件优越,勘探潜力大[9-10],并已获得较好的工业油流,如永936井3 793~3 808 m试油日产油7.6 t,盐222井3 985.8~ 4 194.6 m日产油17.7 t,并且2010年在民丰洼陷北带永920块沙四上亚段上报探明石油地质储量4176万t。但是,盐家地区沙四上亚段近岸水下扇砂砾岩在埋藏演化过程中经历了多期胶结作用、多期溶解作用和复杂交代作用,同时在埋藏演化过程中经历了多期油气充注作用[11]。成藏时期物性特征决定了现今砂砾岩油藏的分布规律。对成藏时期砂砾岩储层物性分布规律认识不清,直接影响了砂砾岩体油气下一步勘探部署。因此,作者综合运用钻井取心、岩石薄片、压汞测试、物性测试等资料,结合区域地质背景,明确盐家地区沙四上亚段近岸水下扇低渗透储层成因机制与形成时间,并针对不同成因类型的低渗透储层,结合储层物性演化史-油藏成藏史及试油试采成果等进行储层评价,为盐家地区沙四上亚段近岸水下扇低渗透储层的勘探开发提供一定的理论指导。
1 地质概况
图1所示为东营凹陷盐家地区构造位置(据文献[14]修改)。东营凹陷是济阳坳陷的一个次级构造单元,东接青坨子凸起,南部为鲁西隆起和广饶凸起,西邻林樊家凸起、高青凸起,北以陈家庄-滨县凸起为界,东西长90 km,南北宽65 km,面积5 850 km2,总体走向为北东向,剖面上具有北断南超的开阔型箕状凹陷特征[12]。盐家地区位于东营凹陷北带东段,西与胜坨油田相邻,东到青坨子凸起,南邻民丰洼陷,北至陈家庄凸起,是由陈南铲式扇形边界断层所控制的陡斜坡构造带,具有断坡陡峭、山高谷深、沟梁相间的古地貌[10, 13],自西向东发育盐16和盐18两大古冲沟(图1)。沙四上亚段沉积时期,受这种古构造背景的控制,季节性洪水携带大量粗碎屑物质沿古冲沟入湖,盐家地区北部陡坡带在边界断裂面上发育了多期近岸水下扇砂砾岩体。根据沉积特征和水动力条件,近岸水下扇可划分为扇根、扇中和扇缘3个亚相。扇根亚相主要发育主水道微相,岩性主要为杂基支撑砾岩,分选差,砾石多为次棱角状,沉积厚度大,垂向递变不明显,多期扇根间缺乏正常湖相泥岩;扇中亚相可进一步划分为辫状水道和水道间微相,辫状水道微相岩性主要为块状砾质砂岩和含砾砂岩、叠覆冲刷粗砂岩,分选中等偏差、杂基质量分数较低,颗粒支撑等;常见正粒序层理、冲刷面构造和强烈的同生变形构造;水道间微相岩性主要为典型浊积岩,厚度薄,粒度较小;扇中亚相多期正序砂砾岩层间多发育正常湖相泥岩(特别是生油岩)。扇缘亚相岩性主要为深灰色泥岩夹薄层砂岩、含砾砂岩,可见平行层理。

图1 东营凹陷盐家地区构造位置(据文献[14]修改)
Fig. 1 Structural setting of Yanjia area, Dongying depression (Revised by Ref. [14])
2 储层基本特征
2.1 岩石学特征
图2所示为盐家地区沙四上亚段近岸水下扇岩石组分三角图。东营凹陷民丰洼陷北部陡坡沙四上亚段近岸水下扇岩石类型主要有砾岩、砾质砂岩、含砾砂岩、砂岩和深灰色泥岩等。砾岩和砾质砂岩砾石成分复杂,以灰岩、花岗片麻岩为主;砾石主要为棱角状—次圆状,杂基支撑,杂基成分主要为灰泥。砂岩以岩屑质长石砂岩和长石质岩屑砂岩为主(图2)。石英质量分数10.00%~47.00%,平均为41.88%;长石质量分数10.00%~43.00%,平均为30.86%;岩屑质量分数8.00%~62.00%,平均为26.12%,其中岩屑成分复杂,类型多样,主要为变质岩岩屑;胶结物主要为碳酸盐和硅质胶结物,质量分数主要为3.00%~28.00%,平均为9.20%;杂基质量分数主要为3.00%~15.00%,平均为5.00%。分选系数主要为1.6~2.3,分选中等—差;磨圆以次棱角状-次圆状为主。总体上,盐家地区沙四上亚段砂砾岩结构成熟度和成分成熟度较低。

图2 盐家地区沙四上亚段近岸水下扇岩石组分三角图
Fig. 2 Ditrital composition of sandstone in near-shore subaqueous fan of Es4s in Yanjia area
2.2 储集空间及物性特征
图3所示为盐家地区沙四上亚段近岸水下扇储层物性分布特征。盐家地区沙四上亚段近岸水下扇砂砾岩储层储集空间以次生孔隙为主,孔隙类型主要以长石和岩屑的次生溶蚀孔隙为主,占孔隙类型的比例为67.5%。根据对盐家地区25口井1 400余个实测物性数据资料统计(来源于胜利油田地质科学研究院),孔隙度<15%的样品占总样品的82.3%,基本均为一般低孔及其以下储层;渗透率小于50×10-3 μm2的样品占总样品的86.9%,储层低孔低渗特征明显(图3)。
2.3 孔喉结构特征
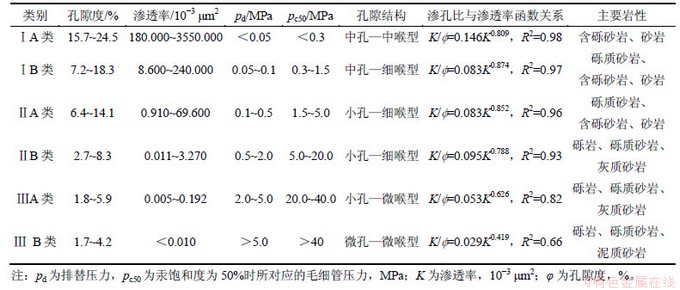
表1所示为盐家地区沙四上亚段近岸水下扇砂砾岩储层孔隙结构分类。综合利用压汞测试资料、储层物性、岩石铸体薄片等资料,选取与储层渗透率相关性较高的压汞参数Pd与Pc50,将近岸水下扇砂砾岩储层孔隙结构分为3个大类6个小类(表1):ⅠA类中孔-中喉型,对应中孔中高渗储层;ⅠB类中孔-细喉型,对应中低孔中低渗储层;ⅡA类小孔-细喉型,对应一般低孔特低孔、一般低渗特低渗储层;ⅡB类小孔-细喉型,对应特低超低孔、特低超低渗储层;ⅢA类小孔-微喉型,对应特低超低孔、超低渗储层;ⅢB类微孔-微喉型,对应超低孔超低渗储层。不同孔隙结构类型的储层,其渗孔比与渗透率函数关系不同(表1)。
3 成岩作用特征
东营凹陷盐家地区沙四上亚段近岸水下扇砂砾岩储层成岩作用具有强烈压实、多期溶解、多期胶结和和灰泥组分重结晶的特征。整体上,压实作用较为强烈,颗粒主要呈点-线接触到线接触,甚至呈凹凸接触或缝合接触;胶结作用以碳酸盐胶结为主,石英加大较为常见,并可见少量黄铁矿等胶结物;灰泥组分发生重结晶现象,而且随着埋深的增加,灰泥重结晶程度增加,到了深层甚至出现了交代颗粒的现象。溶解作用以长石和碳酸盐胶结物的溶解为主,可见石英颗粒及其加大边发生溶解。近岸水下扇不同亚(微)相沉积特征的差异性导致了埋藏过程中成岩作用的差异性。

图3 盐家地区沙四上亚段近岸水下扇储层物性分布特征
Fig. 3 Reservoir properties in near-shore subaqueous fan of Es4s in Yanjia area
表1 盐家地区沙四上亚段近岸水下扇砂砾岩储层孔隙结构分类
Table 1 Types of sandy conglomerate reservoirs in near-shore subaqueous fan of Es4s in Yanjia area
3.1 扇根成岩作用特征
图4所示为东营凹陷盐家地区沙四上亚段近岸水下扇扇根成岩作用特征。扇根亚相单层厚度大,岩性以杂基支撑砾岩为主,杂基质量分数高,颗粒呈漂浮状,分选较差。杂基不仅发育灰泥质,也发育砂质碎屑。扇根成岩作用主要为强压实作用(图4(a)),当杂基为灰泥质时,会发生杂基重结晶现象,而且随着埋深的增加,扇根重结晶程度增加,到了深层甚至出现了交代颗粒的现象(图4(b),4(c)和4(d))。扇根也可见一定的胶结作用,胶结物主要为碳酸盐矿物,充填孔隙及颗粒压实碎裂缝(图4(e))。统计数据显示,扇根碳酸盐胶结物总体上质量分数偏低,以0~5%为主,且主要发育干层。溶解作用主要为长石颗粒及碳酸盐胶结物的微弱溶解(图4(f)),未能形成较好的次生孔隙。
3.2 扇中成岩作用特征
3.2.1 扇中辫状水道微相成岩作用特征
扇中辫状水道微相岩性主要为砾质砂岩、含砾砂岩、砂岩等,整体上杂基质量分数偏低、分选中等,厚度适中,多期扇体之间常发育湖相泥岩。扇中亚相胶结物类型多样,主要为碳酸盐胶结及石英次生加大,少量黄铁矿及石膏等胶结物,质量分数上以碳酸盐胶结物为主,胶结程度上,既可见胶结强烈的储层,也可见胶结相对较弱的储层;溶解作用以长石溶解、碳酸盐胶结物溶解为主,可见少量石英及岩屑的溶解。胶结强烈的储层,溶解孔隙不发育,胶结物不仅充填粒间原生孔,而且强烈充填早期次生溶孔;而胶结偏弱的储层,不仅粒间原生孔发育,且溶解作用也较为强烈。
图5所示为东营凹陷盐家地区沙四上亚段近岸水下扇扇中成岩作用特征。盐家地区沙四上亚段近岸水下扇扇中辫状水道微相砂砾岩的胶结物质量分数与其距砂泥接触面距离有关:距离砂泥接触面较近的部位胶结物质量分数一般较高,溶解微弱;距砂泥接触面较远的部位胶结物质量分数相对偏低,溶解强烈(图5)。图6所示为东营凹陷盐家地区沙四上亚段胶结物质量分数与其距砂泥接触面距离关系。通过对盐家地区沙四上亚段大量近岸水下扇扇中辫状水道微相砂砾岩的胶结物质量分数与其距砂泥接触面距离统计,扇中距砂泥接触面距离在0.52 m以内部位胶结物质量分数一般大于10%,距砂泥接触面距离在0.52~1.20 m部位胶结物质量分数多在5%~10%之间,距砂泥接触面距离大于1.20 m的部位胶结物质量分数多小于5%(图6)。产生这种现象的原因是在碱性环境下,泥岩中蒙脱石向伊/蒙混层转化脱水和石膏脱水释放大量Ca2+,Mg2+和Fe2+等金属离子进入砂体内部,形成碳酸盐胶结物充填孔隙。金属离子浓度在砂泥接触处最大、向砂体内部逐渐降低,导致砂体边缘被致密胶结、储层孔隙被严重破坏,油气难以进入、后期酸性流体对其改造作用也受到抑制;而砂体内部碳酸盐胶结程度低、油气充注易于进入、抑制后期成岩作用,使得孔隙得以大量保存,最终形成砂泥岩界面处胶结强烈向砂体内部胶结程度逐渐变弱的现象。前人研究也表明,砂泥组合中泥岩的成岩演化对砂泥岩界面附近砂岩的孔隙演化有较大影响[15-18],如钟大康等[15]研究认为:深埋藏下(埋深大于2 500 m),在砂岩夹泥岩的情况下,砂泥岩界面附近胶结强于内部,导致砂泥岩界面附近的物性比砂岩内部差;漆滨汶等[17]研究认为在砂岩透镜体与钙质泥岩接触带内会形成一个致密的钙质结壳,使多数砂层物性变差。

图4 东营凹陷盐家地区沙四上亚段近岸水下扇扇根成岩作用特征
Fig. 4 Diagenetic characteristics of inner fan in near-shore subaqueous fan of Es4s in Yanjia area, Dongying depression
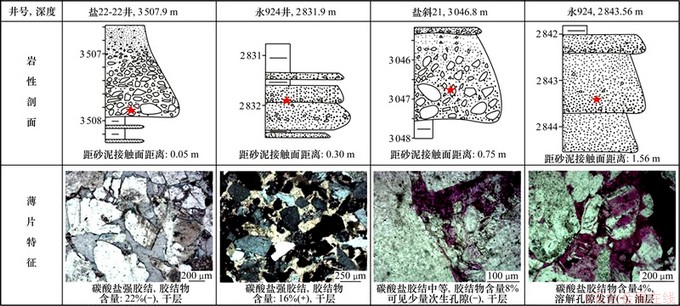
图5 东营凹陷盐家地区沙四上亚段近岸水下扇扇中成岩作用特征
Fig. 5 Diagenetic characteristics of middle fan in near-shore subaqueous fan of Es4s in Yanjia area, Dongying depression
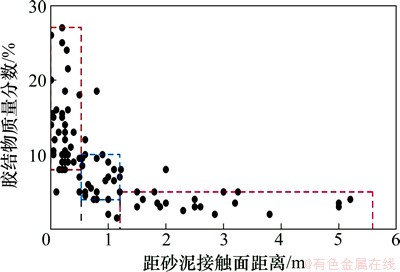
图6 东营凹陷盐家地区沙四上亚段胶结物质量分数与其距砂泥接触面距离关系
Fig. 6 Relationships between cement content of sand-conglomerate and distance from sand-mud boundary of middle fan of Es4s in Yanjia area, Dongying depression
3.2.2 扇中水道间微相成岩作用特征
扇中水道间微相岩性主要为砂岩、粉砂岩、泥岩等细粒沉积物,也可见少量含砾砂岩,总体上表现为砂泥互层的特征,砂岩分选偏差,杂基质量分数偏高。成岩作用主要发育胶结作用和交代作用。胶结作用较为强烈,胶结物质量分数多大于10%,胶结物主要为碳酸盐矿物,可见石英次生加大及少量黄铁矿;溶解作用主要为长石和碳酸盐胶结物的溶解,但溶解程度微弱。
3.3 扇缘成岩作用特征
扇缘亚相主要为厚层泥岩夹薄层泥质粉砂岩、砂岩及少量含砾砂岩。成岩作用特征和扇中近泥岩部位相似,主要表现为强胶结作用及交代作用,胶结物主要为碳酸盐胶结物,质量分数多大于10%,石英加大也较为发育,甚至可见两期加大,并可见少量黄铁矿胶结物;溶解作用微弱,主要为长石颗粒及碳酸盐胶结物的溶解。
4 近岸水下扇储层物性演化史
4.1 储层成岩作用演化序列
在成岩作用类型及特征分析的基础上,通过自生矿物的形态、交代切割关系、溶解充填关系以及流体包裹体均一温度等特征,确定盐家地区北带沙四上亚段成岩作用演化序列及发生时间。
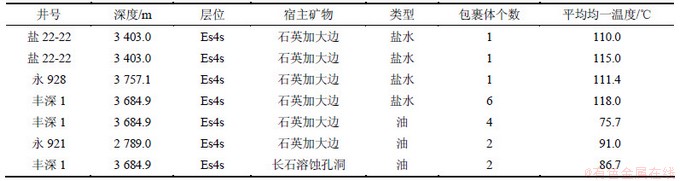
图7所示为盐家地区沙四上亚段主要胶结、交代、溶解作用及溶解充填现象。由碳酸盐胶结物交代石英加大边(图7(a)),可以推断碳酸盐胶结物形成晚于石英加大边。但是,石英具有多期加大的现象,说明石英可能具有晚期加大(图7(b))。通过碳酸盐胶结物充填长石溶解孔隙(图7(c))及碳酸盐胶结物的溶解(图7(d))现象,可推断储层经历了早期长石溶解和晚期以碳酸盐胶结物溶解为主的两期酸性溶解。表2所示为盐家地区沙四上亚段流体包裹体测试数据。长石在酸性环境下发生溶解作用的产物之一是SiO2,SiO2在酸性环境下会以石英次生加大的形式沉淀。盐家地区沙四上亚段流体包裹体数据表明[11],石英加大边中盐水包裹体平均均一温度为110~118 ℃,油包裹体平均均一温度为91 ℃,长石表面溶蚀孔洞中油包裹体平均均一温度为86.7 ℃(表2)。根据丰深1井埋藏史[19]可知石英加大边形成时间为距今约36 Ma,充分说明长石溶解和石英次生加大为同期成岩作用且发生的时间较早。
碳酸盐重结晶作用需要2个条件:1) 需要达到一定的温度和压力条件[20-24],Heydari等[25]认为碳酸盐重结晶作用在50~75 ℃开始,可持续到4 000多m;2) 需要有外来碱性高钙热液流体参与[20, 26-28]。扇根在持续压实作用下孔隙水在浅层已基本排出,灰泥杂基重结晶作用需要有外来流体的参与才能发生。因此,认为扇根灰泥杂基重结晶作用与碳酸盐胶结作用属于同期,也是在有外来碱性流体进入的条件下发生的。盐家地区沙四上亚段储层中黄铁矿胶结物相对比较发育,部分球粒状黄铁矿(图7(e))为早期胶结物,由黄铁矿交代石英次生加大边和碳酸盐胶结物的现象(图7(f)),可推断部分黄铁矿胶结物形成较晚。综合分析认为,盐家地区沙四上亚段近岸水下扇砂砾岩储层成岩作用演化序列为:压实作用/早期黄铁矿胶结→长石溶解/石英加大→石英溶解/碳酸盐胶结/灰泥杂基重结晶→碳酸盐溶解/石英加大→晚期黄铁矿胶结。

图7 盐家地区沙四上亚段主要胶结、交代、溶解作用及溶解充填现象
Fig. 7 Main kinds of cementation, metasomatism, dissolution and filling role of dissolution of Es4s in Yanjia area
表2 盐家地区沙四上亚段流体包裹体测试数据
Table 2 Test data of fluid inclusions of Es4s in Yanjia area
油气充注作为一种特殊的成岩流体对储层的成岩作用具有重要影响[29-31]:它一方面可提供一定量的有机酸,改变孔隙水化学组成,使地层流体 pH 降低;另一方面会限制流体活动,阻碍离子间的传递。可见油气充注一方面可促进酸溶性矿物的溶解甚至强烈溶解,另一方面会抑制自生矿物的形成以及矿物间的交代和转化。前人研究表明[32],盐家地区沙四上亚段共发生了2期油气充注,第1期油气充注发生时间早,主要发生在24.6~38.0 Ma,该时期油气成熟度Ro低(0.5%<Ro<1.0%),以充注油为主,充注量较少;第2期油气充注主要发生在0~6.0 Ma,,其中馆陶组沉积末期至明化镇组沉积末期(距今2.0 Ma)以充油为主,明化镇组末期至今充注少量凝析气。
王艳忠[11]通过埋藏演化史、有机质热演化、膏盐层脱水等综合分析,认为盐家地区沙四上亚段经历了酸碱交替的成岩环境演化:沙四上亚段地层具有含膏泥岩与深水油页岩共生的特征,沉积环境为深水碱性还原环境,原始地层水为碱性;沙四上亚段地层沉积之后至距今42.5 Ma(Es3x沉积时期),有机质尚未成熟,流体仍保持弱碱性;距今42.5 Ma(Es3x沉积时期)至距今32.0 Ma(Ed沉积初)为有机酸控制下的酸性环境;距今32.0 Ma(Ed沉积初)至距今24.6 Ma(Ed沉积末),有机酸发生脱羧,同时沙四下亚段顶部膏盐层脱出大量碱性水,使地层水pH呈碱性;距今24.6 Ma(Ed沉积末)至距今6.0 Ma(Ng沉积末),地层经历抬升及再沉降,在抬升过程中有机质再次生成有机酸,使地层水pH呈酸性;距今2.0 Ma左右,Es4s膏盐层发生脱水,地层流体呈弱碱性,至现今Es4s地层流体仍呈弱碱性(pH 7~8.5)。
综合以上分析,可以确定盐家地区沙四上亚段储层成岩作用演化序列以及油气充注时间,如图8所示。
4.2 地质历史时期物性演化史
以“储层成岩作用演化序列—储层孔隙结构”约束下的地质历史时期储层物性恢复方法[33]为指导,笔者以岩石铸体薄片为对象,结合储层埋藏史及成岩作用演化序列,利用图像分析技术精确求取不同成岩事件造成的储层孔隙度变化值,并采用反演回剥法恢复地质历史时期各主要成岩作用时期储层的孔隙度;然后,以储层现今孔隙结构类型及其对应下的铸体薄片特征为基准,结合成岩作用演化序列及不同成岩事件造成的储层孔隙度变化值,依次恢复地质历史时期各主要成岩阶段储层的孔隙结构类型;最后根据现今不同类型储层孔隙结构特征,确定地质历史时期特定阶段储层孔隙结构所属类型,并通过相应的孔隙结构类型储层的孔-渗函数关系(表1),计算地质历史时期储层渗透率,结果如图9所示。
通过地质历史时期储层物性的恢复,可以确定盐22-22井3 350.25 m细砂岩储层在距今约32.0 Ma成为低渗储层(K<50×10-3 μm2),在距今约30.5 Ma成为特低渗储层(K<10×10-3 μm2),在距今约28.0 Ma成为超低渗储层(K<1×10-3 μm2),在距今约26.0 Ma成为非渗储层(K<0.1×10-3 μm2),现今为非渗储层(图9)。因此,判断盐22-22井3 350.25 m细砂岩储层低渗、特低渗、超低渗以及非渗形成时间均位于第1期成藏期内。

图8 盐家地区沙四上亚段储层成岩作用序列—成藏史综合图
Fig. 8 Reservoir diagenesis sequence and hydrocarbon accumulation history of Es4s in yanjia area

图9 盐22-22井3 350.25 m细砂岩地质历史时期储层物性演化
Fig. 9 Reservoir properties evolution history of fine sandstone at depth of 3 350.25 m, Well Yan22-22
5 储层低渗成因机制及分类评价
针对盐家地区沙四上亚段近岸水下扇砂砾岩储层,采用上述物性恢复方法,对近岸水下扇不同亚相或微相、不同岩性地质历史时期储层物性进行恢复,并确定了不同类型储层(特/超)低渗成因机制与形成 时间。
依据沙四上亚段近岸水下扇不同亚相或微相、不同岩性储层物性演化表明,沙四上亚段近岸水下扇存在5种不同低渗成因类型的储层:Ⅰ类低渗储层为压实低渗特低渗、灰泥重结晶超低渗型;Ⅱ类低渗储层为压实低渗、胶结特低超低渗型;Ⅲ类低渗储层为压实低渗、特低渗型;Ⅳ类低渗储层为溶蚀改善物性,压实胶结低渗型;Ⅴ类低渗储层为压实低渗,压实胶结特低超低渗型(表2)。根据储层物性演化史-成藏史的匹配关系、储层含油性以及试油试采成果等,分析不同低渗成因类型储层的勘探潜力,并进行储层分类评价。
图10所示为AⅠ型低渗储层物性演化和低渗成因综合图。Ⅰ类储层为压实低渗特低渗、灰泥重结晶超低渗型(图10),主要分布在扇根大套杂基支撑砾岩中,分选差,原始物性差。沉积初期至距今42.5 Ma,早期的快速压实使物性快速降低,并导致储层形成一般低渗,距今32.0~42.5 Ma,在有机酸作用下发生微弱溶解,但溶解作用物性的增加远小于压实作用物性的减小,因此物性仍持续降低并导致储层形成特低渗;距今24.6~32.0 Ma,发生灰泥重结晶作用使物性进一步降低导致储层超低渗;距今24.6 Ma至现今,压实作用和灰泥重结晶作用持续增强,后期溶解作用微弱,物性持续降低。由于该类低渗储层在第1期油气成藏前已经形成一般低渗、特低渗,难以形成有效的早期油气充注,储层遭受严重破坏,现今为非渗储层,具小孔或微孔-微喉型孔隙结构。钻井取心为无显示-荧光含油级别,该类储层潜力小,为较差储层,如永920井3 580~3 587 m杂基支撑中砾岩储层,采取压裂措施后仍为干层。
图11所示为Ⅱ型低渗储层物性演化和低渗成因综合图。Ⅱ类储层为压实低渗、胶结特低超低渗型(图11),主要分布在扇中辫状水道中厚层砂砾岩距泥岩近部位、扇中水道间和扇缘薄层砂岩,分选中等,原始物性中等。沉积初期至距今42.5 Ma,成岩作用以压实作用为主,储层物性变差;距今32.0~42.5 Ma,在有机酸作用下发生溶解,但溶解作用物性的增加量小于压实作用物性的减小量,因此,物性仍持续降低并导致储层形成一般低渗;距今24.6~32.0 Ma,在碱性流体作用下发生碳酸盐胶结作用,并且早期油气充注过程要略早于碳酸盐胶结作用。在早期油气充注的过程中,油气首先充注构造高部位和物性更好的扇中辫状水道距泥岩较远部位,扇中辫状水道距泥岩较近部位、扇中水道间和扇缘薄层砂油气充注量有限,含油饱和度低。前人研究表明,烃类充注对储层成岩作用的抑制与含油饱和度有密切关系,只有在储层的孔隙完全或大部分被油气所占据,造成孔隙水呈不连续的孤立滞留状态,才可扼制成岩作用的继续进行,否则只要孔隙水尚能自由的运动,成岩作用就不会停止[34]。因此,扇中辫状水道距泥岩较近部位、扇中水道间和扇缘薄层砂油气充注对后期成岩作用的抑制有限。在碱性环境下,储层被碳酸盐致密胶结,从而迅速形成特低渗和超低渗。距今24.6 Ma至现今,后期酸性流体进入困难,对储层改造有限,储层压实作用持续增强,现今为非渗,具小孔或微孔-微喉型孔隙结构,为较差储层。如盐22-22井3 350~3 357 m粉细砂岩储层,试油结果为干层。
表2 盐家地区沙四上亚段近岸水下扇不同成因机制低渗透储层分类
Table 2 Genetic mechanism types of low-permeability reservoirs in near-shore subaqueous fan of Es4s in Yanjia area

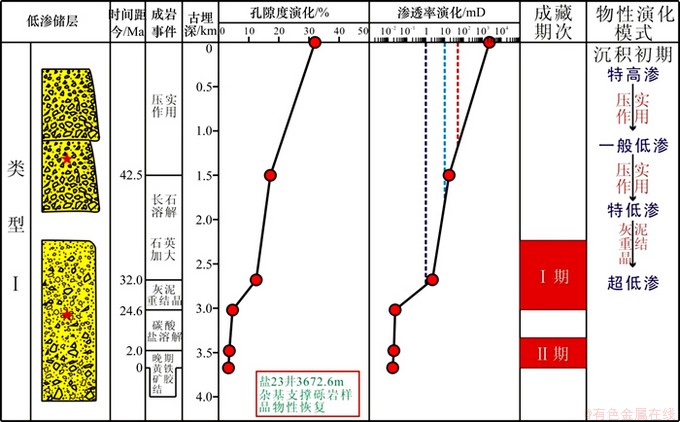
图10 A Ⅰ型低渗储层物性演化和低渗成因综合图
Fig. 10 Comprehensive diagram of properties evolution and genesis of low permeability of typeⅠ low permeability reservoirs

图11 Ⅰ-B Ⅱ型低渗储层物性演化和低渗成因综合图
Fig. 11 Ⅰ-B comprehensive diagram of properties evolution and genesis of low permeability of type Ⅱ low permeability reservoirs
图12所示为Ⅲ型低渗储层物性演化和低渗成因综合图。Ⅲ类储层为压实低渗、特低渗型(图12),主要分布在扇根颗粒支撑砾岩和扇中辫状水道中厚层砂砾岩的底部,分选中等,原始物性中等。距今32.0~42.5 Ma,成岩作用以压实作用为主,物性降低。距今32.0~42.5 Ma,在有机酸作用下发生微弱溶解,但溶解作用物性的增加要小于压实作用物性的减小,因此物性仍持续降低;距今24.6~32.0 Ma,发生第1期油气充注和碳酸盐胶结作用,由于早期油气充注时储层并未形成低渗,因此油气可部分充注储层。碱性金属离子浓度在砂泥界面处最大、向砂体内部逐渐降低,导致砂体边缘被致密胶结,中厚层砂砾岩的底部碳酸盐胶结作用并不强,持续的压实作用使物性降低并导致储层形成一般低渗。距今24.6 Ma至现今,压实作用持续增强,后期溶解作用微弱,物性持续降低,导致储层特低渗。由于该类储层第一期油气充注要早于一般低渗形成时间,早期油气可充注储层,后期只遭受一定程度的破坏,现今为特低渗储层,具中孔细喉或小孔细喉型孔隙结构,为较好储层。如盐22-22井3 505.1~3 514.3 m灰色油斑砾质砂岩储层,试油结果显示为低产油层,日产油3.37 t。
图13所示为Ⅳ型低渗储层物性演化和低渗成因综合图。Ⅳ类储层为溶蚀改善物性,压实和胶结作用低渗型(图13),主要分布在扇中辫状水道中厚层砂砾岩距泥岩远部位,分选较好,原始物性较好。沉积初期至距今42.5 Ma,成岩作用以压实作用为主,储层物性变差;距今32.0~42.5 Ma,在有机酸作用下发生溶解,使储层物性显著增加;距今24.6~32.0 Ma,发生早期油气充注,油气优先充注这些物性较好的储层且充注油气充注量相对较大,含油饱和度高。在后期的碱性环境下,油气充注有效抑制了碳酸盐胶结作用,使储层得以良好的保护,储层物性降低较少。距今2.0~24.6 Ma,发生第2期酸性溶解作用,但溶解作用物性的增加量要小于压实作用物性的减小量,在此期间储层形成一般低渗;距今2.0 Ma至现今,形成少量晚期黄铁矿胶结,现今为一般低渗储层,具中孔中喉或中孔细喉型孔隙结构,为好储层。如盐22井3 235.5~3 246.0 m油浸含砾砂岩储层,试油结果为油层,日产油9.29 t。
图14所示为Ⅴ型低渗储层物性演化和低渗成因综合图。Ⅴ类储层为压实低渗,压实胶结特低超低渗型(图14),主要分布在扇中辫状水道中厚层砂砾岩距泥岩较远部位。分选中等,原始物中等。沉积初期至距今42.5 Ma,主要发生早期的压实作用,使储层物性变差;距今32.0~42.5 Ma,在有机酸作用下发生溶解,但溶解作用物性的增加量要小于压实作用物性的减小量,因此,物性仍持续降低并导致储层形成一般低渗;距今24.6~32.0 Ma,在碱性流体作用下发生碳酸盐胶结作用,但胶结作用强度有限,压实和碳酸盐胶结共同作用导致储层形成特低渗;距今24.6~现今,第2期酸性溶解对储层的改善有限,主要以压实作用为主,物性仍持续降低并导致储层超低渗。由于该类储层在早期油气充注前已形成一般低渗储层,难以形成有效的油气充注,储层在后期成岩演化过程中遭受较大程度的破坏,现今为超低渗储层,具小孔细喉或小孔微喉型孔隙结构,为中等储层。如盐222井4 070~4 075 m砂砾岩储层,试油结果为油水同层,日产油0.5 t,日产水1.2 t。
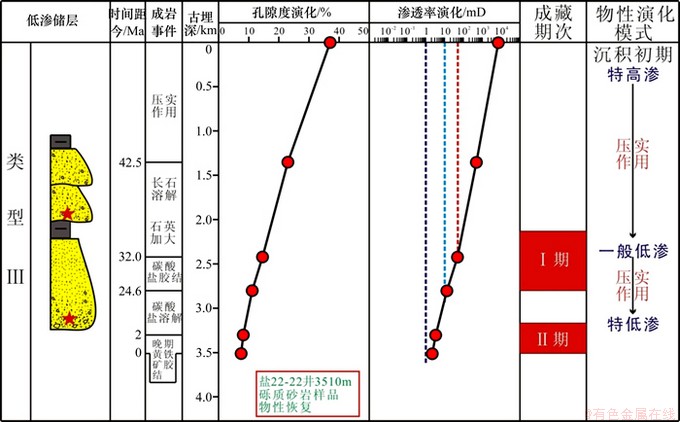
图12 Ⅰ-C Ⅲ型低渗储层物性演化和低渗成因综合图
Fig. 12 Ⅰ-C Comprehensive diagram of properties evolution and genesis of low permeability of type Ⅲ low permeability reservoirs

图13 Ⅰ-D Ⅳ型低渗储层物性演化和低渗成因综合图
Fig. 13 Ⅰ-D comprehensive diagram of properties evolution and genesis of low permeability of type Ⅳ low permeability reservoirs

图14 Ⅰ-E Ⅴ型低渗储层物性演化和低渗成因综合图
Fig. 14 Ⅰ-E comprehensive diagram of properties evolution and genesis of low permeability of type Ⅴ low permeability reservoirs
6 结论
1) 东营凹陷盐家地区沙四上亚段近岸水下扇砂砾岩储层埋藏较深,整体上物性较差,储层低渗特征明显。储层成岩作用具有强烈压实、多期溶解、多期胶结以及灰泥组分重结晶特征。
2) 盐家地区沙四上亚段近岸水下扇砂砾岩储层经历了多期酸碱交替的流体演化,其成岩演化序列为:开始沉积至距今42.5 Ma,地层流体呈弱碱性,成岩作用主要为早期压实作用,形成早期球粒状黄铁矿胶结物;距今32.0~42.5 Ma,地层流体呈酸性,发生长石溶解、石英加大;距今24.6~32.0 Ma,地层流体呈碱性,发生碳酸盐胶结、灰泥杂基重结晶和石英溶解,期间发生第1期油气充注;距今2.0~24.6 Ma,地层流体呈酸性,发生第2期酸性溶解、石英加大,其中距今6 Ma发生第2期油气充注;距今2 Ma至现今,地层流体呈弱碱性,发育晚期少量黄铁矿胶结。
3) 盐家地区沙四上亚段近岸水下扇存在5种不同成因机制的低渗储层:Ⅰ类储层为压实低渗特低渗、灰泥重结晶超低渗型;Ⅱ类储层为压实低渗、胶结特低超低渗型;Ⅲ类储层为压实低渗特低渗型;Ⅳ类储层为溶蚀改善物性,压实胶结低渗型;Ⅴ类储层为压实低渗,压实胶结特低超低渗型。根据致密史-成藏史关系以及试油结果分析可知,Ⅳ类储层为高渗成藏-现今低渗型,勘探潜力最好,为好储层;Ⅲ类储层为中渗成藏-现今特低渗型,勘探潜力中等,为较好储层;Ⅴ类储层为低渗成藏-现今超低渗,勘探潜力较差,为中等储层;Ⅰ类和Ⅱ类储层分别为特低渗成藏-现今非渗型和中渗成藏-现今非渗型,勘探潜力小,为较差储层。
参考文献:
[1] 杨晓萍, 赵文智, 邹才能, 等.低渗透储层成因机理及优质储层形成与分布[J].石油学报, 2007, 28(4): 57-61.
YANG Xiaoping, ZHAO Wenzhi, ZOU Caineng, et al. Origin of low-permeability reservoir and distribution of favorable reservoir[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2007, 28(4): 57-61.
[2] 高静乐, 宋广寿, 高辉, 等. 西峰油田庄40区块长6储层特低渗透成因与主控因素[J]. 沉积学报, 2008, 26(4): 640-646.
GAO Jingle, SONG Guangshou, GAO Hui, et al. Origin of extra low-permeability and controlling factors of Chang 6 Reservoir in Zhuang 40 Area of Xifeng Oil Field[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2008, 26(4): 640-646.
[3] 张哨楠, 丁晓琪. 鄂尔多斯盆地南部延长组致密砂岩储层特征及其成因[J]. 成都理工大学学报(自然科学版), 2010, 37(4): 386-390.
ZHANG Shaonan, DING Xiaoqi. Characters and causes of tight sandstones of Yanchang Formation in southern Ordos Basin, China[J]. Journal Of Chengdu University Of Technology (Science & Technology Edition), 2010, 37(4): 386-390.
[4] 董臣强, 洪太元, 王军. 准噶尔盆地腹部地区中生界低孔渗储层成因分析[J]. 油气地球物理, 2007, 5(3): 58-61.
DONG Chenqiang, HONG Taiyuan, WANG Jun. Analysis on the genetic of low porosity and permeability of Mesozoic in the hinterland of Jugar Basin[J]. Petroleum Geophysics, 2007, 5(3): 58-61.
[5] 高剑波, 庞雄奇, 王志欣, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地姬塬地区延长组碎屑岩储层低渗特征及含油性主控因素[J]. 中国石油大学学报(自然科学版), 2007, 31(1): 5-10.
GAO Jianbo, PANG Xiongqi, WANG Zhixin, et al. Characteristics and master control factors of petroliferous properties of low permeability clastic reservoirs of Yan-chang formation in the upper Triassic of Jiyuan area in Ordos Basin[J]. Journal of China University of Petroleum (Natural Science Edition), 2007, 31(1): 5-10.
[6] 南珺祥, 解丽琴, 刘绥保, 等. 鄂尔多斯苏里格气田二叠系低孔低渗储层成因[J]. 西北大学学报(自然科学版), 2005, 35(2): 207-211.
NAN Junxiang, XIE Liqin, LIU Suibao, et al. The contributing factors of lower porosity and permeability resevoir in perm ian in SuligeGas-field, Ordos Basin[J]. Journal of Northwest University (Natural Science Edition), 2005, 35(2): 207-211.
[7] 王键, 贾爱林, 魏铁军, 等. 长岭气田登娄库组低渗砂岩储层控制因素分析[J]. 天然气地球科学, 2011, 22(5): 828-830.
WANG Jian, JIA Ailin, WEI Tiejun, et al. Controlling factors of low permeability sandstone reservoirs in Denglouku formation of Changling gas field[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 2011, 22(5): 828-830.
[8] 操应长, 远光辉, 王艳忠, 等. 准噶尔盆地北三台地区清水河组低渗透储层成因机制[J]. 石油学报, 2012, 33(5): 758-770.
CAO Yingchang, YUAN Guanghui, WANG Yanzhong, et al. Genetic mechanisims of low permeability reservoirs of Qingshuihe Formation in Beisantai area, Junggar Basin[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2012, 33(5): 758-770.
[9] 万念明, 王艳忠, 操应长, 等. 东营凹陷民丰洼陷北带沙四段深层超压封存箱与油气成藏[J]. 沉积学报, 2010, 28(2): 395-400.
WAN Nianming, WANG Yanzhong, CAO Yingchang, et al. Overpressured fluid compartment and hydrocarbon accumulation of deep layer of Es4 in the north zone of Minfeng Sag, Dongying Depression[J]. Acta Sedimenologica Sinica, 2010, 28(2): 395-400.
[10] 隋风贵. 断陷湖盆陡坡带砂砾岩扇体成藏动力学特征[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2003, 24(4): 335-340.
SUI Fenggui. Characteristics of reservoiring dynamic on the sand-conglomerate fan bodies in the steep-slope belt of continental fault basin: A case study on Dongying Depression[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2003, 24(4): 335-340.
[11] 王艳忠. 东营凹陷北带古近系次生孔隙发育带成因机制及演化模式[D]. 青岛: 中国石油大学(华东)地球科学与技术学院学院, 2010: 51-87.
WANG Yanzhong. Genetic mechanism and evolution model of secondary pore development zone of Paleogene in the North Zone in Dongying Depression[D]. Qingdao: China University of Petroleum. Department of Geosciences, 2010: 51-87.
[12] 张永刚, 许卫平, 王国力, 等. 中国东部陆相断陷盆地油气成藏组合体[M]. 北京: 石油工业出版社, 2006: 127-131.
ZHANG Yonggang, XU Weiping, WANG Guoli, et al. Oil and gas accumulation assembly of continental fault basin in east China[M]. Beijing: Petroleum Industry Press, 2006: 127-131.
[13] 孔凡仙. 东营凹陷北带砂砾岩扇体勘探技术与实践[J]. 石油学报, 2000, 21(5): 27-31.
KONG Fanxian. Exploration technique and practice of sandy-conglomeratic fans in the northern part of Dongying depression[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2000, 21(5): 27-31.
[14] 宋明水, 李存磊, 张金亮. 东营凹陷盐家地区砂砾岩体沉积期次精细划分与对比[J]. 石油学报, 2012, 33(5): 781-782.
SONG Mingshui, LI Cunlei, ZHANG Jinliang. Fine division and correlation of conglomerate sedimentary cycles in Yanjia area of Dongying depression[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2012, 33(5): 781-782.
[15] 钟大康, 朱筱敏, 张琴. 不同埋深条件下砂泥岩互层中砂岩储层物性变化规律[J]. 地质学报, 2004, 78(6): 863-871.
ZHONG Dakang, ZHU Xiaomin, ZHANG Qin. Variation characteristics of sandstone reservoirs when sandstone and mudstone are interbedded at different buried depths[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2004, 78(6): 863-871.
[16] 李丕龙, 庞雄奇. 陆相断陷盆地隐蔽油气藏形成: 以济阳坳陷为例[M]. 北京: 石油工业出版社, 2004, 254-293.
LI Pilong, PANG Xiongqi. Formation of subtle reservoirs in continental fault basin: Based on the Jiyang Depression[M]. Beijing: Petroleum Industry Press, 2004: 254-293.
[17] 漆滨汶, 林春明, 邱桂强, 等. 东营凹陷古近系沙河街组砂岩透镜体钙质结壳形成机理及其对油气成藏的影响[J]. 古地理学报, 2006, 8(4): 522-529.
QI Binwen, LIN Chunming, QIU Guiqiang, et al. Formation mechanism of calcareous incrustation in lenticular sandbody of the Shahejie Formation of Paleogene and its influence on hydrocarbon accumulation in Dongying Sag[J]. Journal of Palaeogeography, 2006, 8(4): 522-529.
[18] 张永旺, 曾溅辉, 高霞, 等. 东营凹陷古近系储层碳酸盐胶结物分布特征及主控因素[J]. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版), 2009, 39(1): 17-22.
ZHANG Yongwang, ZENG Jianhui, GAO Xia, et al. Distribution characteristics and main controlling factors of carbonate cements in the Paleogene Reservoirs in Dongying Depression[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Earth Science Edition), 2009, 39(1): 17-22.
[19] 宋国奇, 金强, 王力, 等. 东营凹陷深层沙河街组天然气生成动力学研究[J]. 石油学报, 2009, 30(5): 672-677.
SONG Guoqi, JIN Qiang, WANG Li, et al. Study on kinetics for generating natural gas of Shahejie Formation in deep-buried sags of Dongying Depression[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2009, 30(5): 672-677.
[20] Hartig K A. Dolomite in permian paleosols of the Bravo Dome CO2 Field, USA: Permian reflux followed by late recrystallization at elevated temperature[J]. Journal of Sedimentary Research, 2011, 81: 248-265.
[21] 邓长瑜, 张秀莲, 陈建文, 等. 黔东南地区寒武系碳酸盐岩成岩作用分析[J]. 沉积学报, 2004, 22(4): 588-596.
DENG Changyu, ZHANG Xiulian, CHEN Jianwen, et al. The analysis of sequence stratigraphy and diagenesis for the carbonates of Cambrian in the southeast of Guizhou Province[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2004, 22(4): 588-596.
[22] Qilong F U. Early dolomitization and recrystallization of carbonate in an evaporitebasin: the Middle Devonian Ratner laminite in southern Saskatchewan, Canada[J]. Journal of the Geological Society, 2006, 163: 937-948.
[23] 郭成贤, 王正允, 王方平. 深水碳酸盐岩成岩作用的稳定同位素特征[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 1999, 20(2): 144-147.
GUO Chengxian, WANG Zhengyun, WANG Fangping. Stable isotopic characteristics of diagenesis in deep-water carbonate rocks[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 1999, 20(2): 144-147.
[24] 李秀华, 夏文杰. 砂岩中的杂基类型与鉴别标志[J]. 矿物岩石, 1986, 6(3): 32-40.
LI Xiuhua, XIA Wenjie. The types of matrix in sandstones and their recognitionalcriteria[J]. Minerals and Rocks, 1986, 6(3): 32-40.
[25] Heydari E, Wade W J. Massive recrystallization of low-Mg calcite at high temperatures in hydrocarbon source rocks: Implications for organic acids as factors in diagenesis[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 2002, 86(7): 1285-1303.
[26] 康玉柱. 塔里木盆地古生代海相碳酸盐岩储集岩特征[J]. 石油实验地质, 2007, 29(3): 217-223.
KANG Yuzhu. Reservoir rock characteristics of Paleozoic marine facies carbonate rock in the Tarimbasin[J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 2007, 29(3): 217-223.
[27] 朱东亚, 金之钧, 胡文瑄, 等. 塔里木盆地深部流体对碳酸盐岩储层影响[J]. 地质论评, 2008, 54(3): 348-357.
ZHU Dongya, JIN Zhijun, HU Wenxuan, et al. Effects of deep fluid on carbonates reservoir in Tarim Basin[J]. Geological Review, 2008, 54(3): 348-357.
[28] 刘树根, 马永生, 王国芝, 等. 四川盆地震旦系-下古生界优质储层形成与保存机理[J]. 油气地质与采收率, 2008, 15(1): 1-6.
LIU Shugen, MA Yongsheng, WANG Guozhi, et al. Formation and conservation mechanism of the high-quality reservoirs in Sinian-lower Palaeozoic in Sichuan Basin[J]. Petroleum Geology and Recovery Efficiency, 2008, 15(1): 1-6.
[29] 蔡进功, 张枝焕, 朱筱敏, 等. 东营凹陷烃类充注与储集层化学成岩作用[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2003, 30(3): 79-83.
CAI Jingong, ZHANG Zhihuan, ZHU Xiaomin, et al. Hydrocarbon filling and chemical diagenesis evolution of the clastic reservoir of the Paleogene in Dongying sag[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2003, 30(3): 79-83.
[30] 张枝焕, 胡文瑄, 曾溅辉, 等. 东营凹陷下第三系流体—岩石相互作用研究[J]. 沉积学报, 2000, 18(4): 560-565.
ZHANG Zhihuan, HU Wenxuan, ZENG Jianhui, et al. Study of fluid-rock interactions in Eogene formation in Dongying depression, Bohai Gulf Basin[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2000, 18(4): 560-565.
[31] 李艳霞, 刘洪军, 袁东山, 等. 石油充注对储层成岩矿物演化的影响[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2003, 24(3): 274-280.
LI Yanxia, LIU Hongjun, YUAN Dongshan, et al. Effect of oil charging on reservoirs diagenetic mineral evolution[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2003, 24(3): 274-280.
[32] 宋国奇, 蒋有录, 刘华, 等. 东营凹陷利津-民丰地区中深层裂解气成藏史[J]. 天然气工业, 2009, 29(4): 14-17.
SONG Guoqi, JIANG Youlu, LIU Hua, et al. Pooling history of cracked gas in middle-deep reservoirs in Lijin-Minfeng areas of the Dongying sag[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 2009, 29(4): 14-17.
[33] 操应长. 东营凹陷沙河街组碎屑岩储层纵向演化及其量化表征研究[R]. 东营: 胜利油田分公司地质科学研究院, 2010: 182-190.
CAO Yingchang. Vertical evolution and quantitative characterization of clastic reservoirs in Shahejie Formation. Dongying sag[R]. Dongying: Geological Science Research Institute of Shengli Oilfield, Sinopec, 2010: 182-190.
[34] 吴富强, 宁兴贤. 影响渤南洼陷深部储层次生孔隙形成的因素及其作用[J]. 沉积与特提斯地质, 2004, 24(2): 76-82.
WU Fuqiang, NING Xingxian. The controlling factors and processes for the formation of the secondary porosity of the deep-seated reservoir rocks in the Bonan depression, Shandong[J]. Sedimentary Geology and Tethyan Geology, 2001, 24(2): 76-82.
(编辑 陈爱华)
收稿日期:2014-03-10;修回日期:2014-06-23
基金项目(Foundation item):国家油气重大专项(2011ZX05006-003);国家自然科学基金资助项目(41102058,U1262203);中国石油大学(华东)优秀博士学位论文培育计划项目(LW140101A)(Project (2011ZX05006-003) supported by National key Oil & Gas Project; Project (41102058, U1262203) supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China; Project (LW140101A) supported by Excellent Doctoral Dissertation Program of China University of Petroleum)
通信作者:马奔奔(1988-),男,安徽毫州人,博士研究生,从事储层地质学研究;电话:15192667376;E-mail:mabenbenupc@163.com