DOI: 10.11817/j.issn.1672-7207.2016.05.026
东营凹陷盐家地区沙四段砂砾岩储层裂缝发育特征
袁静1,李春堂2,杨学君3,路智勇4,樊海琳5,张艳增4
(1. 中国石油大学(华东) 地球科学与技术学院,山东 青岛,266580;
2. 中石化华北油气分公司,河南 郑州,450000;
3. 中石油塔里木油田分公司勘探开发研究院,新疆 库尔勒,841000;
4. 中石化胜利油田分公司东辛采油厂,山东 东营,257000;
5. 中石油大庆油田分公司,黑龙江 大庆,163000)
摘要:通过岩心观察、薄片鉴定、成像测井及物性分析等手段对东营凹陷盐家地区沙四段近岸水下扇沉积砂砾岩储层裂缝发育特征进行研究。研究结果表明:研究区沙四段砂砾岩储层裂缝普遍发育,主要为构造裂缝和风化缝、成岩缝、超压缝、溶蚀缝等非构造裂缝。有效的构造裂缝主要形成于东营期末强烈的构造反转活动,为挤压应力作用下的产物,近东西走向;这些构造裂缝以斜交缝为主,裂缝线密度随岩石粒度变粗和单层厚度增大而明显减小,总体上以近岸水下扇中扇辫状沟道和沟道前缘的中粗砂岩构造裂缝最为发育。风化缝主要发育于沙四上亚段内扇近岸水下扇主沟道和中扇辫状沟道微相的花岗片麻质中粗砾石中,是其在风化带遭受风化破裂和差异溶蚀所致,这类裂缝多开启并与孔隙连通,常储集油气。成岩缝在本区主要为压裂缝和收缩缝,压裂缝主要表现为粒内压裂缝和粒缘缝,其发育程度与岩石粒级、碎屑颗粒成分以及填隙物含量关系密切,在中扇辫状沟道颗粒支撑的粗砂岩和中细砾岩中最为发育。研究区沙四段异常超压较为普遍,造成胶结致密砂砾岩储层超压裂缝较为发育。粒度较粗、颗粒支撑、单层厚度适中的中扇亚相辫状沟道砂砾岩中各类裂缝较为发育,与孔隙交织在一起构成连通性良好的孔隙-裂缝复合储集空间系统,是其成为近岸水下扇中最有利的储集相带的重要原因。
关键词:砂砾岩;近岸水下扇;构造裂缝;非构造裂缝;沙四段;东营凹陷
中图分类号:P558.21;TE122 文献标志码:A 文章编号:1672-7207(2016)05-1649-11
Development characteristics of glutenite reservoir fractures of the fourth member of Shahejie Formation in Yanjia area, Dongying sag
YUAN Jing1, LI Chuntang2, YANG Xuejun3, LU Zhiyong4, FAN Hailin5, ZHANG Yanzeng4
(1. School of Geosciences, China University of Petroleum, Qingdao 266580, China;
2. North China Oil & Gas Branch of Sinopec, Zhengzhou 450000, China;
3. Exploration and Development Research Institute, Petrochina Tarim Oilfield Branch, Korla 841000, China;
4. Dongxin Oil Production Plant, Sinopec Shengli Oilfield Branch, Dongying 257000, China;
5. Petrochina Daqing Oilfield Branch, Daqing 163000, China)
Abstract: Development characteristics of glutenite reservoir of nearshore subaqueous fan fractures of the fourth member of Shahejie Formation, Paleogene in Yanjia area of Dongying sag were studied based on the comprehensive analysis of cores, thin sections, FMI loggings and physical properties analysis. The results show that there are abundant structural fractures and non-structural fractures, such as weathering fractures, diagenetic fractures, overpressure fractures and dissolution fractures in the glutenite. Effective structural fractures in Yanjia area are induced by the compression stress, due to the intense structural inversion in the end of Dongying Formation stage. Most of these structural fractures are oblique. Linear fracture density decreases with the grain sizes coarsening and the layer thickening. Middle-coarse sandstone fractures are mostly developed in general. Weathering fractures are mostly open and connected with the pores in granite gneiss pebbles and cobbles of main channels and braided channels. Diagenetic fractures in Yanjia area mainly include crashed fractures and shrink fractures. Diagenetic compaction induces crashed fractures which include intra-grain fissures and grain edge fissures, common in grain supported coarse sand and conglomerate of braided channels, the development degree of which is closely related to the grain size, clastic particles component and the interstitial material content. Overpressure fractures are promoted by the available overpressure common in Yanjia area. Fractures are relatively well developed in braided channels of middle fan, which has coarser-grained and grain supporting texture and moderate layer thickness. The cracks and pores are intertwined forming pore-fracture complex reservoir space, which is the important cause of being the most favorable reservoir of nearshore subaqueous fan.
Key words: glutenite; nearshore subaqueous fan; structural fractures; non-structural fractures; characteristics; the fourth member of Shahejie Formation; Dongying sag
东营凹陷北部陡坡带沙河街组砂砾岩体油气藏是胜利油气区近年来的重点勘探目标之一,预测其剩余资源量在1.3×109 t以上,具有巨大的勘探潜力。盐家地区位于东营凹陷北部陡坡带东段,北邻陈家庄凸起,南接民丰洼陷(图1),勘探面积达1 500 km2,2009年探明石油地质储量为4.2×104 t,沙四段为其主力层段。该区发育多条规模较大的古冲沟,在沙四段沉积时期于古冲沟的下方发育了大量近岸水下扇相砂砾岩体。这些砂砾岩体物源来自北部陈家庄凸起的母岩风化产物,沿陡坡快速堆积,纵向上多期叠合,平面上交互叠置,与民丰洼陷沙三中下的优质烃源岩邻近,北部以扇根侧向封堵,南部为岩性尖灭,东西两侧不同期次砂砾岩体错层尖灭,含油叠合连片[1]。研究区沙四段砂砾岩体近物源、埋深大、遭受构造作用和成岩作用强烈,储集空间类型及特征复杂,基质物性普遍较差。这类岩石能否成为有效储层,断裂变形导致大规模裂缝形成是重要因素之一[2];同时,油田开发实践业已表明,裂缝发育程度对这类砂砾岩储层的产能有重要影响[3]。如天然裂缝较为发育的FS1井沙四下砂砾岩体气藏压裂后日产气8×104 m3,日产油50 m3,而该区块后继钻探的天然裂缝不发育的FS3井开发效果却不理想。由此可见:裂缝既是低渗透砂砾岩储层有效的储集空间,同时又是主要的渗流通道,裂缝发育规律研究对砂砾岩油藏既具有理论意义,又有应用价值。对裂缝特征的描述和分布预测,国内外学者提出了众多的研究思路和方法[4-9],但多集中于碳酸盐岩、低渗透砂岩和泥岩裂缝储层[10-13],而阐述砂砾岩裂缝发育特征和成因机理的报道尚不多见,大多是将裂缝作为砂砾岩储层储集空间之一与孔隙一起讨 论[14-16]。本文作者以盐家地区沙四段砂砾岩为研究对象,对FS1,FS2,FS3,F8,Y22,Y22-22,Y222和Y22-X1等8口取心井400多米岩心和476张薄片进行系统的描述与统计,并结合成像测井解释成果和物性分析等手段对其宏微观裂缝特征和成因展开讨论。
1 储层岩性、物性和储集空间类型
1.1 岩石学特征
岩心观察和薄片鉴定结果表明:盐家地区沙四段砂砾岩体储层主要岩石类型为不等粒砂岩、中粗砂岩、含砾砂岩、细砾岩和中砾岩等。砂岩类型主要为长石砂岩,其次为岩屑长石砂岩。岩屑平均质量分数为26.4%,受沙四段沉积时期陈家庄凸起主要出露太古界花岗片麻岩和古生界碳酸盐岩的影响,主要为花岗质变质岩碎屑和为碳酸盐岩碎屑。杂基一般为泥质,平均质量分数为5.25%,个别样品为泥灰质或泥云质。胶结物质量分数最高达33%,平均为7.2%,以白云石类和含铁方解石类为主,兼有自生石英、硬石膏、黄铁矿、菱铁矿等,反映其成岩演化阶段高、成岩作用复杂。盐家地区沙四段砾岩类常具有复杂的双模态结构或复模态结构。砾石多呈次棱~次圆状,分选较差。杂基含量较高,兼有杂基支撑和颗粒支撑。
1.2 物性特征
通过对FS1,F8和Y22-22等10余口井的岩心实测物性分析得知:盐家地区沙四段砂砾岩储层孔隙度一般为2.6%~16.5%,平均值为8.74%;渗透率一般为(0.065~278)×10-3 μm2,平均值为5.28×10-3 μm2。同时发现,岩性不同,储层的物性有较大的差异(图2)。砂岩和含砾砂岩的孔隙度分布范围为2%~17%,细砾岩和中粗砾岩的孔隙度分布范围略窄,为2.5%~13.5%,相同孔隙度分布范围内,砾岩渗透率分布范围比含砾砂岩和砂岩的更宽。结合宏微观观察发现:砾岩,尤其是中粗砾岩渗透率异常高样品通常有明显的裂缝发育,表明裂缝发育为砾岩渗透率提高起到了积极作用。
图1 研究区位置图
Fig. 1 Location of study area
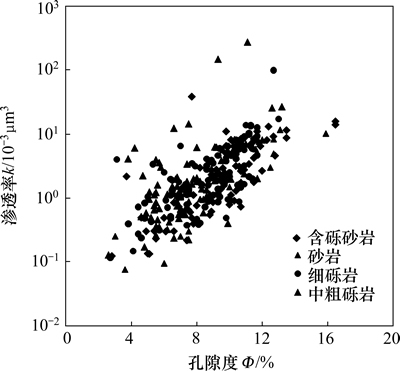
图2 盐家地区沙四段砂砾岩储层不同岩石类型物性特征
Fig. 2 Physical characteristics of different rock types in glutenite of the fourth member of Shahejie Formation in Yanjia area
根据沉积特征和水动力条件等,盐家地区沙四段近岸水下扇沉积相可分为内扇、中扇和外扇3个亚相。砂砾岩储层物性与沉积相带具有较密切的关系。以取心最长、最为系统的Y22-22井为例,对其主要储集相带储层岩心物性统计结果表明,内扇亚相物性整体较差,其中主沟道微相主要为大套杂基支撑中粗砾岩[17],孔隙度与渗透率平均值分别为6.8%和2.4×10-3 μm2,沟道侧缘由于岩性多为颗粒支撑砾岩、含砾中粗砂岩、细砂岩,孔隙度略高,平均为7%,但由于该微相沉积通常夹于大套主沟道砾岩沉积之中,层薄且连通性很差,平均渗透率仅为1.3×10-3 μm2。中扇亚相储层物性整体较好,其中辫状沟道微相主要发育颗粒支撑中粗砾岩、细砾岩和含砾中粗砂岩,孔、渗相对较好,平均值分别为8.6%和5.5×10-3 μm2;沟道前缘微相主要为灰色中细砂岩、含细砾中粗砂岩,颗粒分选较好,孔隙度高于辫状沟道微相,平均为9.3%,但由于层薄,且多夹于厚层沟道间微相泥岩和外扇泥岩沉积之间,渗透率略有下降,平均值为5×10-3 μm2。
1.3 储集空间特征
岩心观察、岩石薄片和扫描电镜观察表明:宏微观裂缝在盐家地区沙四段砂砾岩中发育广泛,孔隙和裂缝交织在一起,构成砂砾岩储层复杂的孔隙-裂缝复合储集空间系统(图3),不仅改善了砂砾岩储层的渗透性,也是有效的油气储集空间。综合分析认为:研究区沙四段砂砾岩不仅发育与断裂活动有关的构造裂缝,风化缝、成岩缝、超压缝和溶蚀缝等非构造裂缝也较为发育。
2 构造裂缝
2.1 发育特征
构造裂缝是指岩石在构造应力作用下形成的裂缝,研究区构造裂缝根据其充填特征可以分为2类。一类是被泥质、方解石类和(硬)石膏充填的裂缝,主要分布在局部层段的砂泥岩互层中,往往具有张裂缝的特征,与古地震成因的同沉积正断层(图4(a))伴生,有时则呈现出树枝状分叉和杏仁状组合(图4(b));另一类是未被充填的裂缝,在研究区沙四段砂砾岩中更为常见,通常表现为中高角度与层面相交或切穿粗砾(图4(c)),镜下通常表现为切穿砾石,有一定开度,并延伸数厘米以上,具有剪裂缝的特征,大多含油或见油迹(图4(d)和4(e)),是有效的油气储集空间。本次研究主要应用FMI 成像测井资料并结合岩心测量对未充填构造裂缝进行统计分析。
2.1.1 裂缝走向和倾向
全井眼地层微电阻率扫描成像测井(FMI)裂缝产状统计结果表明:研究区沙四段砂砾岩体高导缝主要倾向SE方向(图5(a)),走向为NE—SW方向(图5(b));高阻缝主要倾向有近S和近N 2个方向(图5(c)),走向近EW方向(图5(d))。
2.1.2 裂缝倾角
岩心裂缝描述及统计表明:盐家地区沙四段砂砾岩储层未被(完全)充填的构造裂缝以低角度缝(15°<裂缝倾角≤45°)和斜交缝(45°<裂缝倾角≤75°)为主,垂直缝(裂缝倾角>75°)仅占10.7%(图6)。

图3 盐家地区沙四段砂砾岩储层孔隙-裂缝复合储集空间系统
Fig. 3 Complex reservoir spaces of pores&fractures in glutenite of the fourth member of Shahejie Formation in Yanjia area

图4 盐家地区沙四段砂砾岩储层构造裂缝
Fig. 4 Structural fractures in glutenite of the fourth member of Shahejie Formation in Yanjia area
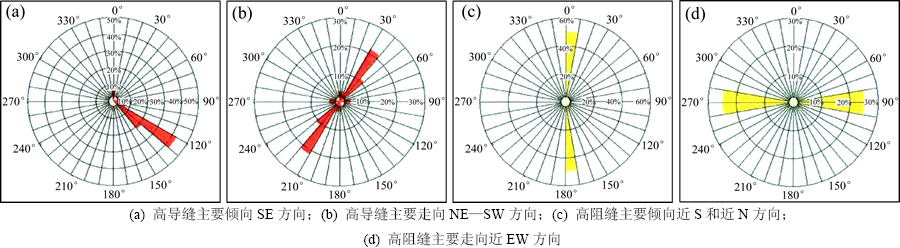
图5 Y22-22井成像测井裂缝产状统计
Fig. 5 Statistics of fractural occurrence with imaging logging of well Y22-22
2.1.3 裂缝线密度
岩心观察统计结果表明:盐家地区沙四段砂砾岩各主要岩石类型中以中粗砂岩裂缝最发育,平均裂缝线密度为5条/m;随砾石含量增多,粒度变粗,裂缝发育程度逐渐减弱;裂缝线密度的由大到小关系为:中粗砂岩(5条/m),含砾中粗砂岩(1.7条/m),细砾岩 (1.6条/m),中粗砾岩(1.4条/m)(图7)。这是因为不同岩类其力学性质不同,在受力破裂时裂缝发育情况不同[18-19]。裂缝的发育程度与岩石的脆性密切相关:本区岩石粒度越粗,杂基支撑者越多,胶结越疏松,岩石脆性越小,构造裂缝越不发育。进一步研究表明:研究区砂砾岩中构造裂缝线密度与单层厚度呈明显的负相关关系,即同一岩性的地层,单层厚度越大,构造裂缝越不发育(图8)。测井解释统计结果表明:研究区沙四段砂砾岩体不同岩性平均单层厚度以粗砾岩最大,为2.01 m;其次是细砾岩,平均为0.51 m;粗砂岩和含砾中粗砂岩相近,分别为0.39 m和0.33 m;各粒级岩石裂缝发育程度与上述认识基本吻合。

图6 盐家地区沙四段砂砾岩构造裂缝倾角分布直方图
Fig. 6 Dip angle distribution of structural fractures in glutenite in Yanjia area
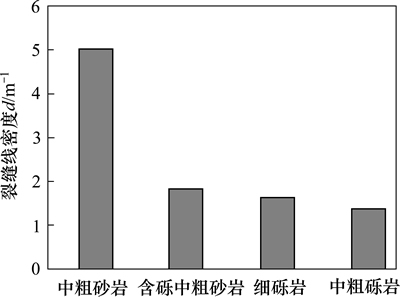
图7 盐家沙四段砂砾岩不同岩石类型中裂缝线密度
Fig. 7 Liner density of structural fractures in different rock types
2.2 成因
盐家地区地处坨胜永断裂带,且紧邻东营凹陷控盆断层陈南断层。前人研究表明:孔店组-沙四段沉积时期,由于郯庐断裂运动方式由左旋走滑运动向右旋走滑运动的转换,主要是SN向或NEE向拉伸应力场控制了东营凹陷发育[20],北部陡坡带东段主要由NWW陈南断层控制。沙三段-沙一段沉积时期,东营凹陷主要处于NW-SE 向拉伸应力场作用下,拉伸应力作用的结果主要是形成了大量的NE向同沉积断层[21-24],坨胜永断层即在这一时期形成,且活动性逐渐加强,同时形成大量走向NE-SW向的次生小断层和宏微观张裂缝。这些宏微观裂缝被同期泥质和后期成岩矿物,如碳酸盐类、硬石膏等自生矿物充填(图4(a)和(b)),表现为高导特征(图5(b))。

图8 盐家沙四段砂砾岩裂缝线密度与单层厚度关系
Fig. 8 Relationship between liner density of structural fractures and thickness of single layer
前人研究认为:受东营期末(≤25 Ma)郯庐断裂带由右旋走滑转为逆冲右旋走滑,构造应力场特征表现为NEE—SWW双向强挤压应力场叠加于NW—SE向的双向拉张应力场之上[24]。陈南断层发生构造正反转,尤以东段因走向NW或NNW与应力场方向近于垂直或大角度夹角而尤为显著。本研究根据井壁塌落、诱导缝产状及过井纵横波剖面结合分析得到的研究区现今水平最大主应力为近EW向,与上述研究成果相吻合。因此,认为东营期末的构造反转活动产生挤压型破裂和碎裂作用,是形成砂砾岩储层中走向近EW、切穿砾石等颗粒的剪裂缝的主要原因。这些裂缝形成时期与沙四下亚段烃源岩成熟并开始发生原油初次运移时期[25]匹配,因此成为流体渗流的通道。部分裂缝中的原油受地层抬升背景的影响转化为沥青质(图4(d)),更多的裂缝被后期埋藏成岩作用溶蚀扩大,对油气运移和储集具有重要意义(图4(c)~(e)),表现为高阻特征(图5(d))。在油气田开发过程中,可以针对构造裂缝走向采取压裂工艺使其进一步得到沟通,从而提高油气采收率。
3 非构造缝
非构造裂缝[7, 14, 26]是在非构造因素作用下,由沉积物(岩石)体积力、重力或成岩作用、油气源排烃等因素诱发形成的与构造应力无关或仅间接有关的裂缝类型。在盐家地区沙四段砂砾岩中,非构造缝包括风化缝、成岩缝、超压缝和溶蚀缝等类型。
3.1 风化缝
风化缝是在各种机械和化学风化作用以及与块体滑移有关的作用下形成的一种裂缝[26]。这种裂缝可在岩层中保留下来并在后期成岩过程中遭受溶蚀,从而增大储层孔隙度。一般认为风化缝等表生缝在碳酸盐岩中的意义较大,在其他岩类中对油气的储集意义不大[6]。然而对盐家地区沙四段近岸水下扇砂砾岩体岩心观察发现,内扇主沟道和中扇辫状沟道中粗砾岩中常见砾内树枝状和网络状风化缝(图9(a)),其中后者具有储集性能。
树枝状风化缝主要赋存于沙四下亚段砂砾岩体中的碳酸盐岩中粗砾中,主要表现为垂直(或近垂直)的树枝状缝,尾端常有分叉现象,受早成岩期碱性介质的影响[27],常被灰白色方解石致密充填而失去渗滤意义。网络状风化缝主要出现在沙四上亚段砂砾岩体中的花岗片麻岩质中粗砾中,有时可见褐色铁质充填物,应为其中不稳定含铁镁暗色矿物在岩石发生早期物理风化破裂后在饱和硅铝和酸性硅铝阶段受大气水的侵蚀而发生溶蚀的部分产物。这些网络状风化缝与上述不稳定暗色矿物在风化带中分解形成的溶蚀孔洞沟通,在埋藏成岩过程中进一步溶蚀扩大,并与基质孔隙连通,进而储集油气(图9(a)),增强了上述沉积相带的储集性能。
3.2 成岩缝
成岩缝是指岩层在成岩过程中由于压实作用、压溶作用、组分体积收缩等作用而产生的裂缝。盐家地区沙四段砂砾岩体中主要发育由压实作用和成岩收缩作用形成的压裂缝和收缩缝。
3.2.1 压裂缝
岩石内部颗粒由于受到上覆岩层压力常会因相互挤压而发生移动、变形、转动、溶解和破碎,形成粒内压裂缝、粒缘缝或粒间缝(图9(b))。这些压裂缝在盐家地区沙四段砂砾岩体颗粒支撑的中粗砂岩、砂砾岩和中细砾岩中广泛发育。它们通常会优先沿着长石解理面、石英微裂纹或其他薄弱面产生,一般局限在某个颗粒内或某几个颗粒边缘,规模较小,宽度较窄,延伸较短,不同颗粒内发育的压裂缝没有统一的方向,常以颗粒接触点为中心呈辐射状向颗粒内部消减(图9(c))。尽管它的产生以砂砾间孔隙的减少为代价,对孔隙度增加意义不大,但可以提高流体的渗流性,同基质孔隙和其他裂缝连通共同构成纵横交织的裂缝系统,不但改善深部砂砾岩储层的油气储集和渗流能力,也是有效的油气储集空间(图9(c))。

图9 东营凹陷盐家地区沙四段砂砾岩储层非构造裂缝
Fig. 9 Non-structural fractures in glutenite of the fourth member of Shahejie Formation in Yanjia area
岩心和微观观察表明:盐家地区沙四段砂砾岩中压裂缝的发育程度与岩石粒级、碎屑颗粒成分及填隙物含量有密切关系。压裂缝多发育于中扇辫状沟道中的颗粒支撑粗砂岩和中细砾岩中,被压裂的主要为长石、石英和某些刚性岩屑;且在粒级和碎屑颗粒成分构成相当的情况下,压裂缝发育程度与填隙物含量呈反比,即颗粒支撑者比杂基支撑者粒内压裂缝更为发育。这是因为,一方面,在一定的外力作用下,粗粒级颗粒所受的压强比细粒级颗粒的大很多,造成压裂缝在粗粒级岩石中发育[28]。另一方面,杂基支撑的岩石其颗粒之间没有接触,杂基相当于塑性介质,可以通过塑性流动缓冲应力,减少了作用于颗粒上的应力,颗粒不易发生破裂;颗粒支撑的砂岩和砾岩因其颗粒支撑点较少,颗粒接触点上的压强要比杂基支撑者和细砂岩、粉砂岩等高出几个数量级[26],易使粗颗粒局部受力超过破裂强度而沿平行压应力的方向破裂,形成压裂缝。若这种压裂缝在后期成岩环境中得以保存,则可成为油气良好的储集空间和渗流通道[28]。
形成压裂缝的应力既可以单独由纵向岩层压力提供,也可以由构造挤压提供。研究区东营期末处于正反转活动时期,为挤压应力背景,发育在盐家地区沙四段粗碎屑岩中的部分压裂缝不排除构造挤压成因。在该类油气田在开发过程中,可以通过压裂工艺使压裂缝进一步扩大,提高储层的渗流能力。
3.2.2 收缩缝
本文中所指的收缩缝是指碎屑岩在埋藏成岩过程中因组分体积缩小产生张应力而形成的拉张裂缝(图9(d))。盐家地区沙四段砂砾岩储层中的收缩缝一般顺层或沿组分分界面分布,延伸数毫米至数十厘米,断续出现,有的被沥青质完全或部分充填。它们主要发育于泥质岩类与砂砾岩层界面处、杂基支撑砂砾岩中砾石与基质交界处、砂岩和粉砂岩的泥质夹层或泥质岩屑中,从区域上看,主要分布于中扇沟道前缘和沟道间泥岩界面处。
本区沙四段砂砾岩储层收缩缝的成因机制主要是脱水作用和矿物相变作用。脱水作用是一种由于水下或地下失水而造成沉积物总体积减小的化学过程,包括黏土及凝胶或胶体悬浮物的失水和体积减小[6],可出现在页岩、粉砂岩、石灰岩、白云岩及细粒至粗粒的砂岩中,是造成细碎屑岩和中粗碎屑岩层间裂缝的重要原因,对油气储集和渗流具有积极影响。此外,砂砾岩中碳酸盐和黏土组分的矿物相变引起的体积减小也可以形成收缩缝,由此产生晶间和层内微缝隙。东营期末的构造反转活动造成地层大幅度抬升,因岩石组分的热胀冷缩率存在差异性,也是形成大颗粒和基质接触处成岩收缩缝的原因之一。
3.3 超压缝
地层形成异常高压的原因有多种,如欠压实作用、生烃作用、水热增压作用、黏土矿物脱水和构造挤压作用等。异常高压流体的存在使岩石中某一点的应力摩尔圆向左移动,并当流体压力达到异性数值的时候,可以使最小主应力(σ3)由正值(压应力)变为负值(张应力),从而在岩石内形成拉张裂缝[29],提高储集层的孔渗性能。微观观察表明,盐家地区沙四段砂砾岩储层超压缝规则性和方向性较差,呈线状或分支状延伸,可将颗粒破碎成网格状或炸裂状(图9(e)),开度很小,常见于较大的刚性颗粒内部,如石英颗粒中,或使颗粒相对较薄的边缘破碎。超压裂缝有时被有机质或方解石充填,表明其具有流体渗透性。
国内外很多学者研究了产生超压裂缝时的孔隙流体压力范围,一般认为,当孔隙流体压力超过上覆岩层静压力的85%时,会导致流体压裂上覆岩层,形成微裂缝[30]。根据对东营凹陷北带盐家地区各井的压力结构分析表明,该区沙四段储层压力系数一般在1.2~1.6之间,局部压力系数最高可达1.75,足以导致岩石破裂而产生超压裂缝。由于异常高压区是一个压力不断积累、释放,再积累、再释放的过程,在这种状态下形成的裂缝具有周期性开启和闭合的特点。这一过程的多次反复,会使大量油气从烃源岩中排出[6],并促使构造裂缝进一步发育。通过对钻井岩心的宏微观分析发现,超压缝在分布区域上与构造裂缝发育区叠合,表明已存在裂缝的沉积物或岩石的强度要比同类完整的沉积物或岩石的强度低得多。
3.4 溶蚀缝
盐家地区沙四段砂砾岩储层经历了强烈的成岩作用,现今处于中成岩A2亚期-B期,溶蚀作用具有多重溶解机理,主要是有机酸溶解作用、无机酸溶解作用、硫酸盐热化学氧化还原反应和油田水引起的溶解作用等酸性介质溶解机理和以石英为主要溶蚀对象的碱性介质溶解机理;溶解作用的动力机制包括循环热对流、断裂活动引起大气淡水淋滤和超压泄露[26]。溶蚀缝是孔隙水进入先成裂缝,对缝壁不稳定组分溶蚀,将其进一步扩大而成。因此,未被充填的溶蚀缝是有效的流体渗流通道和储集空间。在研究区砂砾岩储层中,溶蚀缝主要表现为沿砾石边缘的贴粒溶蚀(图9(f)),即流体沿碎屑颗粒边缘流动并溶解早期填隙物形成紧贴颗粒外缘发育的线状缝隙。其他形式裂缝,如砾石原生节理缝、泥岩收缩缝和颗粒压裂缝等经溶蚀改造形成的裂缝也可认为是溶蚀缝。
4 裂缝发育与储层质量
以Y22-22砂砾岩体为例,其主力产层为7小层(图10)。储层评价结果表明:全区除Y22-X8和Y22-X43井外,其余各井平均物性均在有效储层下限之上。其中Y22-42和Y22-X1井区主要发育内扇主沟道微 相,砂砾岩平均孔隙度为4%~6%,基质渗透率为(0.5~1.0)×10-3 μm2,岩心和微观观察表明,其裂缝类型主要为风化缝和成岩缝,为Ⅲ类储层;其他井区主要发育中扇辫状沟道微相,平均孔隙度为4%~10%,基质渗透率为(1~10)×10-3 μm2,岩心和薄片中构造缝和上述各类非裂缝均较为发育,为Ⅱ类储层。综合分析认为,粒度较粗、颗粒支撑、单层厚度适中的中扇亚相辫状沟道砂砾岩中各类裂缝较为发育,裂缝与孔隙交织在一起,构成了沟通良好的孔隙-裂缝复合储集空间系统,是其成为近岸水下扇中最有利的储集相带的重要原因。
5 结论
1) 盐家地区沙四段近岸水下扇砂砾岩储层裂缝普遍发育,主要包括构造裂缝和风化缝、成岩缝、超压缝和溶蚀缝等非构造裂缝。
2) 有效的构造裂缝主要形成于东营期末强烈的构造反转活动,为挤压应力作用下的斜交缝,且随岩性变粗,发育程度也逐渐减弱。风化缝是中粗砾岩储层中富有特色的储集空间类型,主要发育于内扇主沟道和中扇辫状沟道的花岗片麻质中粗砾石中,是这些粗碎屑在物源区中遭受风化破裂和差异溶蚀所致。成岩缝主要表现为压裂缝和收缩缝,尤以广泛分布于中扇辫状沟道颗粒支撑的粗砂岩和中细砾岩中的粒内压裂缝和粒缘缝这两类压裂缝为特征。研究区较为普遍的异常超压是沙四段致密砂砾岩储层发育超压裂缝的成因。
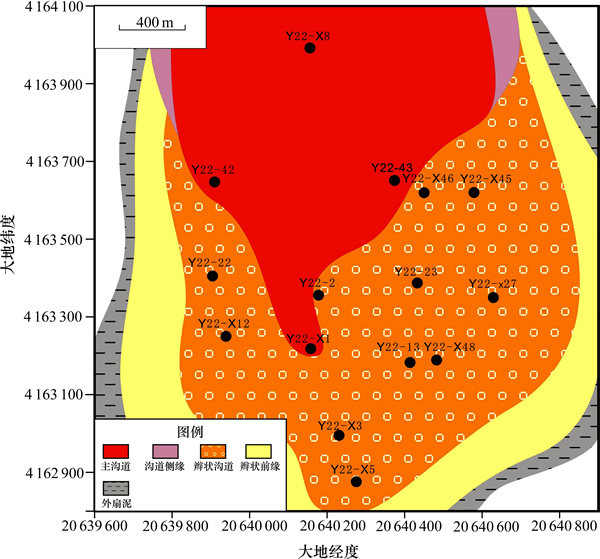
图10 Y22-22近岸水下扇沉积相平面图
Fig. 10 Sedimentary facies map of Y22-22 nearshore subaqueous fan
3) 中扇亚相辫状沟道砂砾岩中各类裂缝较为发育,裂缝与孔隙交织在一起,构成了沟通良好的孔隙-裂缝复合储集空间系统,是其成为近岸水下扇中最有利的储集相带的重要原因。
参考文献:
[1] 田美荣. 盐家地区沙四段上亚段砂砾岩体储层特征及成岩演化[J]. 油气地质与采收率, 2011, 18(2): 30-33, 48.
TIAN Meirong. Diagenesis evolution characteristics of glutenite reservoir in Yanjia area[J]. Petroleum Geology and Recovery Efficiency, 2011, 18(2): 30-33, 48.
[2] 付晓飞, 尚小钰, 孟令东. 低孔隙岩石中断裂带内部结构及与油气成藏[J]. 中南大学学报(自然科学报), 2013, 44(6): 2428-2438.
FU Xiaofei, SHANG Xiaoyu, MENG Lingdong. Internal structure of fault zone and oil/gas reservoir in low-porosity rock[J]. Journal of Central South University (Science and Technology), 2013, 44(6): 2428-2438.
[3] 肖丽华, 张磊, 田伟志, 等. 徐家围子断陷深层砂砾岩优质储层预测[J]. 中南大学学报(自然科学版), 2014, 45(4): 1174-1182.
XIAO Lihua, ZHANG Lei, TIAN Weizhi, et al. High-quality reservoir prediction of deep tight glutenites in Xujiaweizi Fault Depression[J] . Journal of Central South University (Science and Technology), 2014, 45(4): 1174-1182.
[4] BAI T P, DAVID D. Fracture spacing in layered rocks: a new explanation based on the stress transition[J]. Journal of Structural Geology, 2000, 22(1): 43-57.
[5] CONNOLLY P, COSGROVE J. Prediction of fracture-induced permeability and fluid flow in the crust using experimental stress data[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 1999, 83(5): 757-777.
[6] NELSON R A. Geologic analysis of naturally fractured reservoirs[M]. Texas: Gulf Publishing Company, 1985: 8-26.
[7] 郭璇, 钟建华, 徐小林, 等. 非构造裂缝的发育特征及成因机制[J]. 中国石油大学学报(自然科学版), 2004, 28(2): 6-11.
GUO Xuan, ZHONG Jianhua, XU Xiaolin, et al. The development characteristics and generation mechanism of nonstructural fractures[J]. Journal of China University of Petroleum (Edition of Natural Science), 2004, 28(2): 6-11.
[8] 宋惠珍, 贾承造, 欧阳健, 等. 裂缝性储集层研究理论与方法[M]. 北京: 石油工业出版社, 2001: 22.
SONG Huizhen, JIA Chengzao, OUYANG Jian, et al. Research theory and method of fractured reservoir[M]. Beijing: Publishing House of Oil Industry, 2001: 22.
[9] 曾联波, 漆家福, 王永秀. 低渗透储层构造裂缝的成因类型及其形成地质条件[J]. 石油学报, 2007, 28(4): 52-56.
ZENG Lianbo, QI Jiafu, WANG Yongxiu. Origin type of tectonic fractures and geological conditions in low permeability reservoirs[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2007, 28(4): 52-56.
[10] ERNSTSON K, RAMPINO M R, HILTL M. Cratered cobbles in Triassic Buntsandstein conglomerates in northeastern Spain: an indicator of shock deformation in the vicinity of large impacts[J]. Geology January, 2001, 29(1): 11-14.
[11] 王真. 丰深1 砂砾岩体裂缝发育特征及主控因素研究[J]. 中国石油大学胜利学院学报, 2008, 22(2): 6-8.
WANG Zhen. The development characteristics and master factor analysis of fracture of sand gravel body of well Feng sheng1[J]. Journal of Shengli College China University of Petroleum, 2008, 22(2): 6-8.
[12] 巩磊, 曾联波, 张本健, 等. 九龙山构造致密砾岩储层裂缝发育的控制因素[J]. 中国石油大学学报(自然科学版), 2012, 36(6): 6-12.
GONG Lei, ZENG Lianbo, ZHANG Benjian, et al. Control factors for fracture development in tight conglomerate reservoir of Jiulongshan structure[J]. Journal of China University of Petroleum (Edition of Natural Science), 2012, 36(6): 6-12.
[13] 张立松, 闫相祯, 杨秀娟, 等. 致密碎屑岩裂缝性储层发育定量预测[J]. 中南大学学报(自然科学版), 2014, 45(2): 501-506.
ZHANG Lisong, YAN Xiangzhen, YANG Xiujuan, et al. Quantitative prediction of natural fracture development for tight fractured clastic rock reservoir[J]. Journal of Central South University (Science and Technology), 2014, 45(2): 501-506.
[14] 文慧俭, 舒萍, 范传闻, 等. 兴城气田深层砾岩储层储集空间类型及控制因素[J]. 大庆石油学院学报, 2008, 32(3): 101-104.
WEN Huijian, SHU Ping, FAN Chuanwen, et al. Reservoir space type and control factors of the deep conglomerate reservoir in Xingcheng gas field [J]. Journal of Daqing Petroleum Institute, 2008, 32(3): 101-104.
[15] 王成, 官艳华, 肖利梅, 等. 松辽盆地北部深层砾岩储层特征[J]. 石油学报, 2006, 27(增刊): 52-56.
WANG Cheng, GUAN Yanhua, XIAO Limei, et al. Characteristics of deep conglomerate reservoir in northern Songliao Basin [J]. Petrolei Sinica, 2006, 27(Suppl): 52-56.
[16] 王勇, 钟建华, 马锋, 等. 济阳坳陷陡坡带深层砂砾岩体次生孔隙成因机制探讨[J]. 地质学报, 2008, 82(8): 1152-1159.
WANG Yong, ZHONG Jianhua, MA Feng, et al. The mechanism of secondary porosity in the deep-seated gravel reservoirs on the steep slope belt, Jiyang Depression[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2008, 82(8): 1152-1159.
[17] 袁静, 杨学君, 陈武杰, 等. 东营凹陷盐22块沙四上亚段砂砾岩粒度概率累积曲线特征[J]. 沉积学报, 2011, 29(3): 815-824.
YUAN Jing, YANG Xuejun, CHEN Wujie, et al. Probability cumulative grain size curves in sandy conglomerate of the upper Es4 in Yan 22 Block, Dongying Depression[J] .Acta Sedimentologica Sinica. 2011, 29(3): 815-824.
[18] 旷红伟, 刘俊奇, 覃汉生, 等. 束鹿凹陷古近系沙河街组第三段下部储层物性及其影响因素[J]. 沉积与特提斯地质, 2008, 28(1): 88-95.
KUANG Hongwei, LIU Junqi, QIN Hansheng, et al. Physical properties and influencing factors of the reservoir rocks in the lower part of the third member of the Palaeogene Shahejie Formation in the Shulu depression[J]. Sedimentary Geology and Tethyan Geology, 2008, 28(1): 88-95.
[19] 周文, 张银德, 闫长辉, 等. 泌阳凹陷安棚油田核三段储层裂缝成因、期次及分布研究[J]. 地学前缘, 2009, 16(4): 157-165.
ZHOU Wen, ZHANG Yinde, YAN Changhui, et al. Genesis, stages and distribution of the fractures in H3 reservoir in Anpeng oil field, Miyang sag [J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2009, 16(4): 157-165.
[20] 张鹏, 王良书, 丁增永, 等. 济阳坳陷中-新生代断裂发育特征及形成机制[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2006, 27(8): 467-474.
ZHANG Peng, WANG Liangshu, DING Zengyong, et al. Characteristics and formation mechanism of the faults in Mesozoic-Cenozoic in Jiyang Depression[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2006, 27(8): 467-474.
[21] 盛文波, 操应长, 刘晖, 等. 东营凹陷古近纪控盆断层演化特征及盆地结构类型[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2008, 29(3): 290-296, 289.
SHENG Wenbo, CAO Yingchang, LIU Hui, et al. Evolutionary characteristics of the Palaeogene basin-controlling boundary faults and types of basin architectures in the Dongying sag[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2008, 29(3): 290-296, 289.
[22] 阳怀忠, 任建业, 陆金波. 东营凹陷负反转构造样式及其运动学特征[J]. 地球科学: 中国地质大学学报, 2009, 34(3): 493-501.
YANG Huaizhong, REN Jianye, LU Jinbo. Tectonic styles and kinematic characteristics of negative inversion structure in Dongying Depression[J]. Earth Science: Journal of China University of Geosciences, 2009, 34(3): 493-501.
[23] 谢锐杰, 漆家福, 王永诗, 等. 渤海湾盆地东营凹陷北部地区新生代构造演化特征研究[J]. 石油实验地质, 2004, 26(5): 427-431.
XIE Ruijie, QI Jiafu, WANG Yongshi, et al. Characteristics of the Cenozoic structural evolution in the north of the Dongying sag, the Bohaiwan Basin[J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 2004, 26(5): 427-431.
[24] 侯旭波. 济阳坳陷构造反转特征及其与叠合盆地演化关系[D]. 青岛: 中国石油大学(华东)地球科学与技术学院, 2010: 72.
HOU Xubo. The development characteristics of structures inversion in Jiyang Depression and its relationship with the evolution of superimposed Basin[D]. Qingdao: China University of Petroleum (Huadong). School of Geosciences,2010: 72.
[25] 宋国奇, 蒋有录, 刘华, 等. 东营凹陷利津—民丰地区中深层裂解气成藏史[J]. 天然气工业, 2009, 29(4): 14-17, 38.
SONG Guoqi, JIANG Youlu, LIU Hua, et al. Pooling history of cracked gas in middle-deep reservoirs in Lijin-Minfeng areas of the Dongying sag[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 2009, 29(4): 14-17, 38.
[26] 王洪辉, 陆正元. 四川盆地中西部上三叠统砂岩非构造裂缝储层[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 1998, 19(1): 35-41.
WANG Honghui, LU Zhengyuan. Nontectonic fractured sandstone reservoirs of upper Triassic in middle-west Sichuan Basin[J]. Oil and Gas Geology, 1998, 19(1): 35-41.
[27] 袁静, 张善文, 乔俊, 等. 东营凹陷深层溶蚀孔隙的多重介质成因机理和动力机制[J]. 沉积学报, 2007, 25(6): 840-846.
YUAN Jing, ZHANG Shanwen, QIAO Jun, et al. Cause of formation and dynamical mechanisms in multiply medium of dissolved pores in deep formation of Dongying sag[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica. 2007, 25(6): 840-846.
[28] 郭沫贞, 朱国华, 寿建峰, 等. 碎屑岩压裂缝的特征、成因与油气勘探意义[J]. 沉积学报, 2006, 24(4): 483-487.
GUO Mozhen, ZHU Guohua, SHOU Jianfeng, et al. Origin and petroleum explorative significance of crushed fracture in clastic rock[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica. 2006, 24(4): 483-487.
[29] 曾联波, 漆家福, 王成刚, 等. 构造应力对裂缝形成与流体流动的影响[J]. 地学前缘(中国地质大学(北京); 北京大学), 2008, 15(3): 292-298.
ZENG Lianbo, QI Jiafu, WANG Chenggang, et al. The influence of tectonic stress on fracture formation and fluid flow[J]. Earth Science Frontiers (China University of Geosciences, Beijing; Peking University), 2008, 15(3): 292-298.
[30] 蒋凌志, 顾家裕, 郭彬程. 中国含油气盆地碎屑岩低渗透储层的特征及形成机理[J]. 沉积学报, 2004, 22(1): 13-18.
JIANG Lingzhi, GU Jiayu, GUO Bincheng. Characteristics and mechanism of low permeability clastic reservoir in Chinese petroliferous Basin[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2004, 22(1): 13-18.
(编辑 杨幼平)
收稿日期:2015-05-13;修回日期:2015-07-04
基金项目(Foundation item):国家科技重大专项(2011X05001) (Project(2011X05001) supported by the National Science and Technology Major Program of China)
通信作者:袁静,博士,教授,从事储层沉积学和储层地质学研究;E-mail: drjyuan@163.com