文章编号:1004-0609(2013)06-1611-07
化学气相沉积ZrC涂层的缺陷形成机制及控制
孙 威1,郝振华1,熊 翔1,李小斌2,李江鸿1
(1. 中南大学 粉末冶金国家重点实验室,长沙 410083;
2. 中南大学 冶金与环境学院,长沙 410083)
摘 要:为减少化学气相沉积(CVD) ZrC涂层的缺陷,提高涂层的性能和使用寿命,深入分析化学气相沉积过程中ZrC涂层的缺陷特征和形成机制,主要利用扫描电镜对CVD-ZrC涂层的表面和断口进行观察。结果表明:ZrC涂层中存在的3类典型缺陷,即裂纹、片状脱落和“蠕虫状”凸起,裂纹是在涂层生长过程或冷却过程中受到热应力形成的。片状脱落发生在薄膜边缘应力集中的局部区域,慢速沉积可以有效消除网状缺陷和面缺陷,也可有效抑制贯穿裂纹甚至片状剥落的出现;“蠕虫状”凸起形成于反应器进气口易形成紊流场的位置,该凸起起到了类似韧性相增韧和压应力增韧的双重效果。
关键词:化学气相沉积;碳化锆涂层;形成机理;缺陷控制
中图分类号:TG 407 文献标志码:A
Formation mechanism and control of defects for ZrC ceramic coatings by chemical vapor deposition
SUN Wei1, HAO Zhen-hua1, XIONG Xiang1, LI Xiao-bin2, LI Jiang-hong1
(1. State Key Laboratory of Powder Metallurgy, Central South University, Changsha 410083, China;
2. School of Metallurgical and Environment, Central South University, Changsha 410083, China)
Abstract: In order to reduce the defect and improve properties and service life of zirconium carbide (ZrC) coatings, the feature and forming mechanism of defect from chemical vapor deposition process were analyzed. ZrC coatings were prepared on carbon/carbon substrate using ZrCl4+C3H6+H2+Ar system. The results show that three types of defects, such as cracks, exfoliation and “vermicular” bulges were studied by surface and fracture SEM images. The defects characteristics and formation mechanism of defects were analyzed. The cracks were induced by growth and thermal stress. The results show that exfoliation always take place at edges of samples where the stress concentrates. Slow deposition is favorable to the coating defects control, especially to the plane-defects. “Vermicular” bulges take place at gas inlet where turbulent flow forms, which can improve the toughness of the coating.
Key words: chemical vapor deposition; ZrC coating; formation mechanism; defect control
碳化锆(ZrC)是一种过渡金属碳化物,具有较为优异的物理和化学性能,如高硬度、高熔点、良好的导电性,较好的耐化学腐蚀和抗热冲击性能等。在各应用领域中,ZrC陶瓷多以涂层或薄膜的形式存在并发挥极为重要的作用。例如,可利用ZrC薄膜的高硬度进行刀具表面改性[1];由于ZrC涂层的中子吸收截面低和阻挡放射性裂变产物释放的能力强,ZrC涂层可替代传统的SiC涂层制备新型的包覆燃料颗粒[2];ZrC的溢出功仅为3.5 eV,经ZrC薄膜涂覆的Mo、W尖锥具有更高发射电流的能力[3]。近年来,ZrC作为耐烧蚀防护涂层开创性应用到某些轻质高强复合材料的超高温防护体系中,如炭/炭复合材料[4-5]。
迄今为止,文献报道过的制备ZrC薄膜或涂层的主要方法包括热蒸镀[6]、溅射沉积[7]、离子束辅助沉积[8]、激光脉冲沉积[9]、液相脉冲放电沉积[10]和化学气相沉积[11]等。与前几种方法相比,化学气相沉积可以在较低的温度下制备出难熔金属ZrC涂层,同时不受基体的形状制,是最具工业应用前景的制备方法。然而,在化学气相沉积涂层过程中,或者由于反应剂、输送剂和载气的化学成分不纯,以及反应容器、衬底托架和各种管道材料的杂质,涂层内部会出现夹杂以及污染物;或者由于反应器内部不合理设计,影响了气体的混合程度和均匀性,造成涂层的不均匀沉积;或者由于生长过程以及制备冷却过程中所形成生长应力和热应力的影响,涂层会形成裂纹,界面分离,脱层等较为严重的破坏[12]。吴守军等[13]曾深入分析化学气相沉积碳化硅防氧化涂层网状缺陷和面缺陷形成机理,并从涂层沉积工艺角度出发,指出慢速沉积对面缺陷的控制有显著效果。本文作者根据化学气相沉积ZrC涂层缺陷的形貌特征,将缺陷类型细分为裂纹、片状脱落及未报道过的“蠕虫状”凸起,从气体界面反应、热应力集中、气流状态等方面分析这些缺陷产生的原因,并提出缺陷控制方法。本研究对于改进化学气相沉积设备及工艺条件,从根本上提高ZrC涂层的性能和使用寿命,具有重要的意义。
1 实验
图1所示为实验所用CVD反应系统示意图,主要由4部分构成:加热系统、送粉系统、供气系统和废气处理系统。加热系统采用超音频电磁感应加热方式,最大电功率为60 kW。加热炉外罩为石英材质,发热体为高纯石墨材质。用光电高温计、自动温控系统测量和调控反应温度。沉积基体置于发热体内部。
实验选用尺寸为d 30 mm×10 mm、密度为1.8 g/cm3的高纯石墨材料作为沉积基底。沉积之前,样品要经过抛光、去脂和酒精清洗。化学气相沉积ZrC所选用的系统为ZrCl4+C3H6+H2+Ar。其中,Ar作为载气和稀释气体;H2作为还原性气体;C3H6作为碳源气体;作为Zr源的固体粉末ZrCl4由特定的送粉装置直接送入沉积炉[12],再由Ar载入反应区生成ZrCl4蒸 气。在石墨基体表面生成ZrC的反应如下:
ZrCl4+H2→ZrClx+HCl (x=0, 1, 2, 3) (1)
C3H6→[C]+H2 (2)
ZrClx+[C]→ZrC+xCl (3)
Cl+H2→HCl (4)
实验所采用的沉积温度为1 300~1 600 ℃;压力为1×105 Pa;氩气流量约为400 mL/min;氢气流量约为300 mL/min;沉积时间为每次3 h;氢气与四氯化锆的摩尔比为10。
用JEOL JXA-840型扫描电镜(Scanning electron microscope, SEM)对涂层表面和断面进行显微结构观测。用INCA EDX型能谱分析仪(Energy-dispersive X-ray analyzer) 对涂层表面和断面进行微区成分分析。
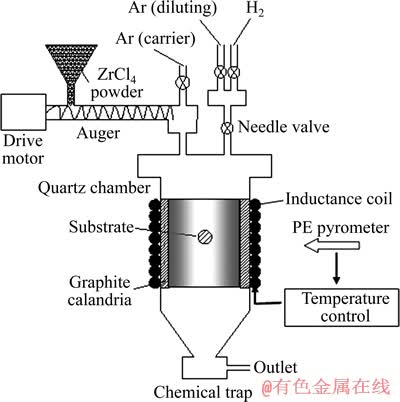
图1 CVD反应系统示意图
Fig. 1 Schematic diagram of CVD system
2 结果与讨论
2.1 ZrC涂层中的裂纹及形成机制
图2所示为ZrC涂层中裂纹的4种典型形态:网状裂纹、面缺陷、层间裂纹和贯穿裂纹。其中,网状裂纹、面缺陷是在涂层生长过程中形成的;贯穿裂纹主要是在制备完成冷却过程中受到热应力形成的;层间裂纹的形成可能发生在沉积过程中,也可能发生在冷却过程中。
从图2(a)中可以看出:涂层表面粗糙,存在大量彼此接触不良的球形团聚体。即使涂层表面平整,也存在大量成网状分布的未贯穿涂层的微细裂纹,即网状缺陷。在化学气相沉积ZrC的过程中,锆源气体和碳源气体会在基底界面处形成气体边界层。当边界层中气体过饱和度达到临界值,气体会转变为由Zr、C、Cl和H组成的液滴。当液滴由边界层中移动到温度较高的基底表面时,液滴中Cl和H的含量降低,形成化学计量的ZrC。当沉积温度较低时,形成的液滴很难相互融合为一体,而液滴向颗粒转变时,Cl和H的去除使颗粒浓缩,从而导致在颗粒的边界处形成沟槽。网状缺陷即为这些沟槽相互连接的结果。
如图2(b)所示的面缺陷是ZrC涂层内部呈层状排列所致。当反应气体过饱和度较高时,在基底材料界面层上沉积ZrC涂层的过程可分为3个阶段:在初始阶段,气体边界层中的过饱和度比临界值低,可以观察到细的晶粒内层。随着沉积过程的继续进行,过饱和度达到临界值,形成液滴。在内涂层表面继续沉积ZrC时,由于内涂层表面将被吸附的O、Cl和S所钝化,导致固相形核难于已钝化的内层表面进行,并且随着沉积的进行,将发生液相形核。由于从液滴转变而来的颗粒不能与已存在的内层融合为一体,因而涂层之间存在缺陷,即面缺陷。第三阶段是新形成的涂层表面会重新被O、Cl和S所钝化,从而重复第二阶段过程,于是涂层中形成周期性排列的面缺陷。
对于图2(a)和(d)中的表面及垂直涂层的贯穿裂纹则是由于涂层和基底复合材料热膨胀系数的不匹配,在制备完成后在涂层冷却过程中受到热应力形成的。值得注意的是,由于炭纤维在径向和轴向热膨胀系数差别很大,导致C/C复合材料在各个方向的热膨胀不一致。在平行于炭纤维的C/C复合材料的表面,很容易出现垂直于炭纤维横向裂纹;而在垂直于纤维布的平面沉积时,裂纹少些。把陶瓷/炭炭基体界面看作是在陶瓷基体中包含的圆球形金属颗粒,在颗粒半径趋近于无穷大的极限情形,通过数学处理将其演变为陶瓷/炭炭基底材料垂直界面裂纹的应力强度影响因子,然后讨论陶瓷和炭/炭基底的热膨胀系数性能差别对其影响[14]。
设圆形金属颗粒的半径为r,如图3所示,在金属颗粒内发生的本征应力为σ11和σ22,应变为ε11和ε22,则在金属颗粒外两侧沿X轴力距离内产生的应力场为

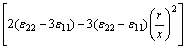 (5)
(5)
 (6)
(6)
和
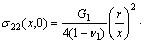
 (7)
(7)
式中:G1、ν1为陶瓷材料的剪切模量和泊松比。
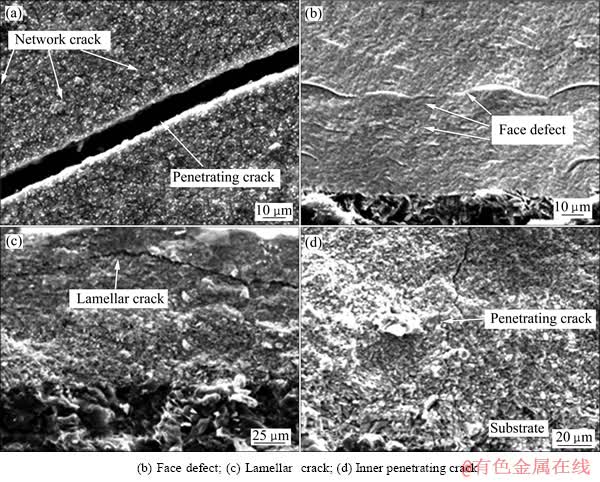

图2 ZrC涂层中的裂纹
Fig. 2 Different kinds of cracks in ZrC coatings
如果金属颗粒的本征应变使σ22(x,0)>0,并且这个应力足够大时,可以导致颗粒两侧的陶瓷相内开裂,而产生两个对称的微裂纹。根据文献[14],在微裂纹c端的应力强度因子K1可由下式决定。
 (8)
(8)
 (9)
(9)
 (10)
(10)
式中:c为基体加陶陶涂层的厚度。半裂纹垂直于界面并伸向陶瓷,其长度l,将图3 中的金属颗粒半径加大,令r趋向于∞,则成为图4所示的陶瓷涂层/炭炭基底界面,图4中界面的左侧对应于半径为∞的炭/炭基底,而其右侧则视为陶瓷涂层。当r→ ∞,则有c–r=l,代入得
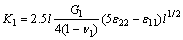 (11)
(11)
式(11)即为陶瓷/炭炭基底材料垂直于界面半裂纹的应力强度因子,在不同的条件下,本征应变ε11和ε12不同。在同样的温度变化的情况下,陶瓷涂层与炭炭基底将发生不同的热应变,它们的热应变之差即代表炭炭基底的本征应变。因此,基底的本征应变可近似为
 (12)
(12)
式中: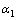 和
和 分别为陶瓷涂层和炭/炭基底的热膨胀系数,ΔT代表整个物体的温度变化。将式(12)代入式(11)可得到由热膨胀性质的差异在温度变化时在半裂纹顶端所产生的应力强度因子,则有
分别为陶瓷涂层和炭/炭基底的热膨胀系数,ΔT代表整个物体的温度变化。将式(12)代入式(11)可得到由热膨胀性质的差异在温度变化时在半裂纹顶端所产生的应力强度因子,则有
 (13)
(13)
缺陷易发生在厚涂层的边缘处,其原因是涂层或薄膜边缘容易发生应力集中,生成的裂纹不足以完全释放这些应力,而发生断裂。可见,垂直界面裂纹应力强度因子与陶瓷涂层和炭/炭基底的热膨胀系数差成正比,与温度差成正比。炭/炭基底的热膨胀系数小于陶瓷涂层的热膨胀系数,所以在相同的裂纹长度和温度变化的情况下,对于热膨胀系数相差较大,而且陶瓷涂层本身的剪切模量也较大的情况而言,计算的K1值很容易达到甚至超过陶瓷材料的宏观断裂韧性值,因此,这种裂纹很容易长大形成贯穿裂纹,甚至导致整个界面破坏。
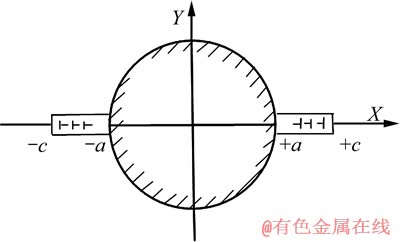
图3 圆形夹杂两侧对称的微裂纹
Fig. 3 Symmetrical micro-cracks along two sides of circular inclusion
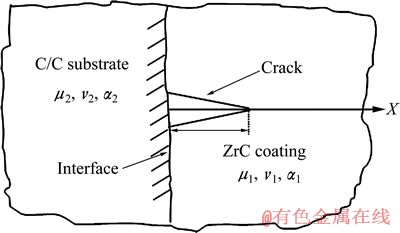
图4 ZrC陶瓷涂层/炭炭基底界面的垂直裂纹示意图
Fig. 4 Schematic diagram of vertical cracks between ZrC coatings and C/C substrate
2.2 ZrC陶瓷中的片状剥落及形成机制
化学气相沉积ZrC涂层存在“片状剥落”典型缺陷。如图 5(a)所示,涂层裂纹的周围弥散分布着许多条形凹坑,进一步放大显示这类缺陷是“月牙”或“镰刀”片状颗粒脱落、底部涂层裸露所致。这类缺陷易发生在厚边缘的边缘处。其原因是涂层或薄膜边缘容易发生应力集中,生成的裂纹不足以完全释放这些应力,而发生断裂。
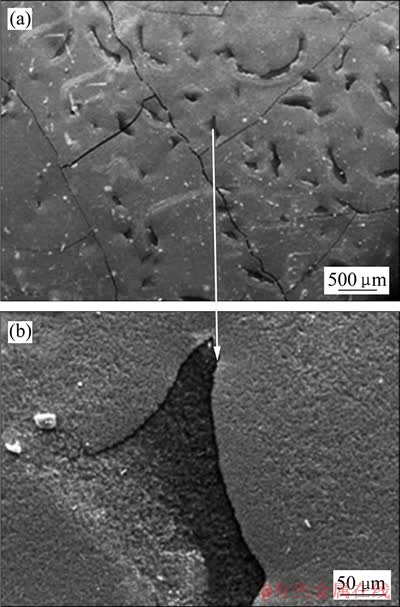
图5 ZrC涂层边缘典型的片状剥落形貌
Fig. 5 Morphologies of exfoliation on edge of ZrC coatings
慢速沉积可以有效消除网状缺陷和面缺陷,也可有效抑制贯穿裂纹甚至片状剥落的出现。这是由于慢速沉积一般选择使气相饱和度达到较低的条件,而当气相过饱和度达不到临界值,在基底材料的边界层将不会有液滴形成。沉积过程由液相形核转为固相形核。气相在较薄的边界层中扩散迅速,发生非自发形核。生成的ZrC颗粒细小,堆积致密。低的反应气体供给量使沉积过程沉积速率减小,因此,慢速沉积得到的涂层厚度相对较小,热应力容易释放,涂层微裂纹宽度较小。然而,在涂层厚度要求相同的条件下,慢速沉积会使生产周期延长、成本增加。
2.3 ZrC涂层中的“蠕虫状”凸起及形成机制
采用化学气相沉积制备的ZrC涂层中存在一种典型的非均匀形貌——“蠕虫状”凸起。图6所示为“蠕虫状”凸起的宏观形貌图。图6(a)中的凸起尺寸大约400~600 μm,多数呈椭圆状,部分呈环状、弓状。这些凸起不规则的分布在表面上,部分有桥连。凸起的脊梁呈现拱形特征。图6(b)中的凸起多呈不规则长条状,宽度约为200 μm,分布比较弥散。凸起的高度明显低于图6(a)中的凸起。图6(c)中的凸起尺寸更加细小,高度也更低。图6(d)中的凸起则基本消失,表面光滑,照片显示为黑白相间的特征,进一步放大照片显示,黑色区域表面要高于白色区域。凸起从图6(a)到(b)的变化趋势是尺寸和高度逐渐变小 。图6(e)是与图6(b)同一样品的截面形貌图,这些凸起使得涂层表面“此起彼伏”,呈波浪状,严重降低涂层的光滑度。能谱测试结果显示,凸起表面的含碳量要远远高于未凸起表面的。
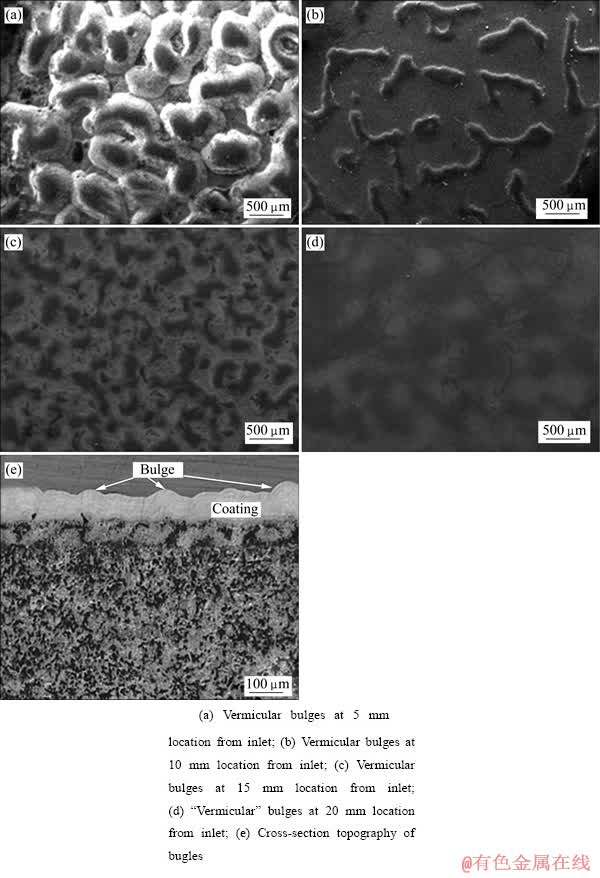
图6 ZrC涂层中“蠕虫状”凸起宏观形貌
Fig. 6 Morphologies of coral bulges of ZrC coatings
“蠕虫状”凸起主要形成在反应器进气口附近加热体内表面上,即图7中的红线框位置。此处由于反应器棱角结构对反应前驱气体在气流方向上的局部扰动,气体多为紊流态[15]。而处在紊流区的碳源气体、锆源气体,以及其他气体的混合、输送、扩散是不均匀的。其可能的趋势是部分反应源气体到达基体表面反应是扩散动力学控制,部分则可能是反应动力学控制。此外,锆源气体分子的密度远大于丙烯气体分子的,在相同力场作用下,丙烯气体易漂浮于上方。这些作用交织在一起使得紊流区的沉积反应与反应快慢极为复杂,包括生成热解炭的均质与非均质反应,生成的ZrC的均质和非均质反应等。此外,紊流区可能在一定程度上呈现出生成反应之间相互叠加的规律性,从而使表面生长较为规律的凸起。在图中l长度标定区域从左至右方向,气流流动逐渐向层流过渡,凸起尺寸越来越小,高度越来越低,即图6(a)~(d)所展示的形貌演变规律。气体流动处于紊流状态下,会影响沉积的均匀性和造成沉积缺陷,这是化学气相沉积中要极力避免的。
然而,值得注意的是,具有“蠕虫状”凸起的ZrC涂层往往不含有裂纹和片状剥落缺陷,其原因可能是由于凸起破坏了涂层的连续性,起到类似韧性相增韧和压应力增韧的双重效果。首先,这些凸起在垂直于涂层方向有更好的延性,会使裂纹钝化,裂纹尖端的应力集中可以得到释放。其次,紊流场中的不均匀快速沉积会在涂层中形成压应力,而裂纹的萌生和张开是由拉应力驱使的,这样裂纹扩展时,拉应力必须克服压应力而额外消耗能量。
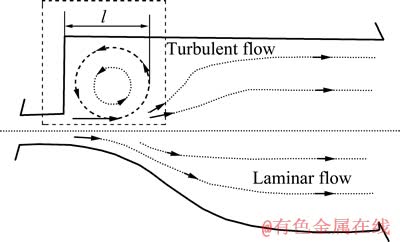
图7 反应管中气流状态示意图
Fig. 7 Schematic diagram of gas flow in reactor
3 结论
1) 化学气相沉积ZrC涂层易形成3种典型缺陷:裂纹、片状剥落和“蠕虫状”凸起。其中,裂纹包括网状裂纹、面缺陷、层间裂纹和贯穿裂纹。
2) 网状裂纹和面缺陷是在涂层生长过程中形成的,贯穿裂纹是在涂层制备完成后冷却过程受到热应力形成的。片状脱落发生在薄膜边缘应力集中的局部区域。慢速沉积可以有效消除网状缺陷和面缺陷,也可有效抑制贯穿裂纹甚至片状剥落的出现。
3) “蠕虫状”凸起形成于反应器进气口易形成紊流场的位置。该凸起起到了类似韧性相增韧和压应力增韧的双重效果。
REFERENCES
[1] 熊炳昆, 杨新民, 罗方承. 锆铪及其化合物应用[M]. 北京: 冶金工业出版社, 2002: 66-72.
XIONG Bin-kun, YANG Xin-ming, LUO Fang-cheng. Zirconium, hafnium and the application of their compounds[M]. Beijing: Metallurgy Industry Press, 2002: 66-72.
[2] 刘 岗, 李国栋, 熊 翔, 王雅雷, 陈招科. 固态输送ZrCl4低压化学气相沉积制备ZrC涂层的特征[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2012, 22(1): 171-178.
LIU Gang, LI Guo-dong, XIONG Xiang, WANG Ya-lei, CHEN Zhao-ke. Character of ZrC film prepared by transporting solid ZrCl4 during low pressure chemical vapor deposition[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2012, 22(1): 171-178.
[3] 李含雁, 丁明清, 冯进军. 敷ZrC的Mo Spindt 阵列阴极的发射性能[J]. 真空电子技术, 2006(3): 57-59.
LI Han-yan, DING Ming-qing, FENG Jin-jun. Field emission from Mo FEAs coated with ZrC films[J]. Vacuum Electronics, 2006(3): 57-59.
[4] SUN W, XIONG X, HUANG B Y. ZrC ablation protective coating for carbon/carbon composites[J]. Carbon, 2009, 47(14): 3368-3371.
[5] 郑湘林, 李国栋, 熊 翔, 孙 威. 常压化学气相沉积ZrC涂层动力学与组织结构[J]. 中南大学学报: 自然科学版, 2011, 42(7): 1912-1917.
ZHENG Xiang-lin, LI Guo-dong, XIONG Xiang, SUN Wei. Deposition kinetics and microstructure of APCVD ZrC coating[J]. Journal of Central South University: Science and Technology, 2011, 42(7): 1912-1917.
[6] TESSNER T C. Preparation and characterization of crystalline ZrC films[J]. Journal of Vaccum Science & Technology A, 1993, 11(1): 1-5.
[7] BALACEANU M, BRAIC M, BRAIC V. Surface chemistry of plasma deposited ZrC hard coatings[J]. Journal of Optoelectronics and Advanced Materials, 2005, 7(5): 2557-2560.
[8] HE X M, LI S, LI H B. High corrosion resistant ZrC films synthesized by ion-beam-assisted deposition[J]. Journal of Materials Research, 1999, 14(2): 615-618.
[9] WOO A J, BOURNE G, CRACIUM V. Mechanical properties of ZrC thin films grown by pulsed laser deposition[J]. Journal of Optoelectronics and Advanced Materials, 2006, 8(1): 20-23.
[10] 吴 锋, 揭晓华,陈玉明. 液中脉冲放电沉积ZrC陶瓷涂层的强化工艺及涂层性能的研究[J]. 材料研究与应用, 2007, 1(1): 15-18.
WU Feng, JIE Xiao-hua, CHEN Yu-ming. Study on the intensity process and the performance of the ZrC ceramic coating with electrical discharge in the liquid[J]. Materials Research and Application, 2007, 1(1): 15-18.
[11] KAZUHIRO S, SHOUHEI U, JUN A. Present status of ZrC coated fuel particle development for very high temperature reactors in JAEA[J]. Transactions of the American Nuclear Society, 2006, 94: 705.
[12] 孟广耀. 化学气相淀积与无机新材料[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 1984: 123-145.
MENG Guang-yao. Chemical vapor deposition and novel inorganic materials[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 1984: 123-145.
[13] SUN W, XIONG X, HUANG B Y. Preparation of ZrC nano-particles reinforced amorphous carbon composite coating by atmospheric pressure chemical vapor deposition[J]. Applied Surface Science, 2008, 255(16): 7142-7146.
[14] ZHANG W Z, ZENG Y, LEMUEL G, XIONG X, HUANG B Y. Preparation and oxidation property of ZrB2-MoSi2/SiC coating on carbon/carbon composites[J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2011, 21: 1583-1544.
[15] HELMAR V S, CHRIS R K, HARRY E A. On turbulent flows in cold-wall CVD reactors[J]. Journal of Crystal Growth, 2000, 212: 299-310.
(编辑 李艳红)
基金项目:国家重点基础研究发展计划资助项目(2011CB605805);中国博士后基金资助项目(20110491262)
收稿日期:2012-09-18;修订日期:2013-01-15
通信作者:孙 威,助理研究员,博士;电话:0731-88830363;E-mail: sunweimse@csu.edu.cn