DOI:10.19476/j.ysxb.1004.0609.2018.01.17
基于电化学热耦合模型的锂离子动力电池极化特性
李书国1,艾 亮2, 3,贾 明1, 2, 3,程 昀1,杜双龙1,蒋跃辉1
(1. 中南大学 冶金与环境学院,长沙 410083;
2. 湖南艾华集团股份有限公司,益阳 413000;
3. 全固态储能材料与器件湖南省重点实验室,益阳 413000)
摘 要:基于电化学热耦合模型,定量分析了磷酸铁锂动力电池不同倍率放电下正负极欧姆极化、浓差极化和活化极化。结果表明:1C放电初期,正极固相浓差极化波动最大,峰值达到147 mV;放电中期,各类型极化变化曲线较为平稳,活化极化最大,约为48 mV;放电末期,负极活化极化和负极固相浓差极化迅速增大;8C放电末期,正极固相浓差极化急剧增加,达到715 mV。提高放电倍率,活化极化的大幅增加是高倍率下极化严重的最主要原因,且负极活化极化的增加幅度比正极活化极化更大;而减小负极颗粒粒径可以有效减小负极活化极化。
关键词:锂离子电池;欧姆极化;浓差极化;活化极化;数值仿真
文章编号:1004-0609(2018)-01-0142-08 中图分类号:TM911 文献标志码:A
近年来,电动汽车不断发展,对动力电池高倍率充放电性能要求越来越高[1]。在实际应用中,由于内部极化,动力电池放电倍率越高,放电电压越低,所能释放的能量也越低[2]。根据极化形成机理,可将极化分解为电化学活化极化、浓差极化和欧姆极化[3]。因此,如何准确定量分析电池内部各类型极化,受到电极材料和电池优化设计工作者广泛关注[4-6]。
不同类型的极化可通过实验方法测定,如电极浓差极化可通过恒电流间歇滴定-电压弛豫技术[7-8]、静态法[9]等测定,但测定过程一般需要繁琐的实验步骤和重复性操作,且难以兼顾实际放电过程中多物理场的变化。随着计算机技术的发展和放电过程电池内部多物理场理论的成熟,快速发展的电池数值仿真可以有效解决该问题[10-12]。YAN等[13]建立LiCoO2电极微观结构模型,考察充放电过程微观结构对电极极化的影响,表明浓差极化主要取决于空间位置、扭曲率和孔隙率;活化极化受孔隙率、荷电状态及空间位置的影响较大,且在放电末期不同空间位置处活化过电势的差别增大,充电末期差别减小。微观结构模型虽然可以更好地研究电池内部极化在空间位置的分布特性,但模型计算效率低,且对计算机的性能要求高,不利于其推广应用。张凯等[14]基于准二维电化学模型讨论了LiMn2O4/石墨电池电极厚度、活性材料颗粒粒径对浓差极化的影响,洪树等[15]研究了全固态锂离子电池放电倍率、电解质的扩散系数以及电极厚度对浓差极化的影响。NYMAN等[16]给出不同类型极化的理论计算公式,并基于准二维电化学模型计算了混合脉冲循环过程中不同荷电状态下的过电势分布。RAJESWARI[17]基于准二维电化学模型,定量研究了LixC6/liquid electrolyte/Liy(NiaCobMnc)O2体系在3C和5C恒流放电中的正负极过电势分布,表明不同放电倍率下,不同极化类型的极化程度不同,但其模型计算过程未考虑温度变化对过电势的影响。
本文作者以磷酸铁锂动力电池为研究对象,基于COMSOL仿真平台,综合考虑动态参数变化,建立准二维电化学热耦合模型,定量分析1C恒流放电正负极极化,并比较提高放电倍率至3C、8C各类型极化的变化。以期能明晰造成高倍率极化严重的关键因素,进而为减小高倍率下电极极化提供理论指导。
1 模型建立
本实验中电化学模型建立的基础是多孔电极模型[18-19],多孔电极模型基于质量守恒、电化学动力学、电荷守恒和能量守恒构建。将电极活性材料假定为均一球形颗粒,按区域将磷酸铁锂电池分为5段,分别是负极集流体、负极、隔膜、正极和正极集流体,锂离子电池的电化学模型示意图如图1所示。
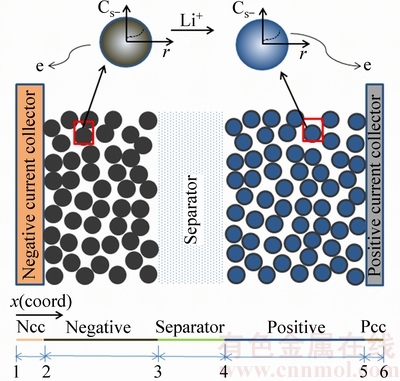
图1 锂离子电池的电化学模型示意图
Fig. 1 Schematic diagram of Li-ion battery model
1.1 质量守恒
锂离子电池放电过程中的质量守恒,包括固相质量守恒和液相质量守恒。采用菲克定律描述锂离子在固相活性颗粒中的传递过程,如式(1)所示,采用式(2)描述锂离子在液相溶解过程。
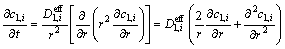 (1)
(1)
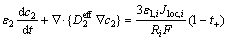 (2)
(2)
式中:c、D、r、ε、t、t+、F、Ri分别表示锂离子浓度、扩散系数、反应界面半径、体积分数、时间、离子迁移数、法拉第常数和正负极材料颗粒粒径;下标1、2、i分别代表固相、液相和不同电池组成;上标eff表示对参数进行Bruggeman修正,修正系数取值为1.5[20],即:
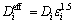 (3)
(3)
球形颗粒中心对称,且颗粒表面锂通量依据法拉第定律描述,即:
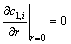 (4)
(4)
 (5)
(5)
式中:Jloc,i为局部电流密度。
1.2 电化学动力学
电化学反应只考虑锂离子在正负极活性材料之间的脱/嵌反应,而忽略副反应的发生,并用Butler-Volmer方程来解析这一反应过程,如式(6)所示。交换电流密度J0 是固/液两相中锂离子浓度的函数,计算方程如式(7)所示:
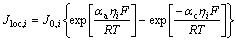 (6)
(6)
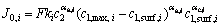 (7)
(7)
式中:αa、αc分别为阳极、阴极电极反应转化系数,R、T、η分别为摩尔气体常数、电池实际温度、局部活化过电势。下标surf表示活性材料颗粒表面,max表示最大值。
局部活化过电势等于固相和电解质电势差值减去热力学平衡电势Usurf,i,即:
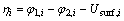 (8)
(8)
平衡电势Usurf,i的计算考虑了温度变化的影响,即:
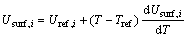 (9)
(9)
式中:Tref、Uref,i分别是参考温度和对应的开路电位, 表示电压温升系数。
表示电压温升系数。
值得注意的是,这里局部活化过电势与下文提及加权平均活化过电势不同,若未特别注明,文中活化过电势指的是加权平均活化过电势。
1.3 电荷守恒
电荷守恒包括固相电子电荷守恒和液相离子电荷守恒,如式(10)、(11)所示,根据欧姆定律计算电子电荷守恒,用浓溶液理论计算离子电荷守恒。
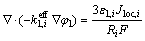 (10)
(10)
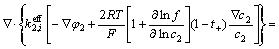
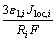 (11)
(11)
在隔膜与电极表面没有电子电荷通过,即
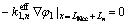
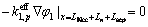 (12)
(12)
在集流体/电极界面锂离子通量为零,即
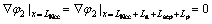 (13)
(13)
其中,L表示厚度。Ncc、n、sep、p、Pcc分别表示负极集流体、负极、隔膜、正极、正极集流体。
1.4 能量守恒
考虑到高倍率放电,电池内部温升对过电势的影响,以电化学模型中产生的热量为热源,建立传热模型计算电极内部的温度变化。并将热模型中的温度变化实时反馈到电化学模型中,从而实现电化学模型和热模型的耦合。在传热模型中,能量守恒表达式如下:
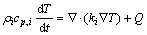 (14)
(14)
式中:cp,i为定压比热容;Q为放电过程中电池的总产热[20],用牛顿冷却定律和辐射定律表述锂离子电池热模型的边界条件,即:
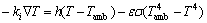 (15)
(15)
式中:k为材料导热系数,具体详见参考文献[21];h为自然换热系数,取值7.17 W/(K·m2)[22];σ为辐射常数;取值5.67×10-8 W/(m2·K4);ε为表面黑度,取值0.8[22]。
1.5 电池内部极化分布
电池内部极化可分为液相浓差极化、固相浓差极化、欧姆极化、活化极化4大类。不同类型极化受空间位置以及电流分布影响较大,为了方便说明和比较,下面统一采用平均过电势来描述不同类型过电势行为。具体计算表达式[16]见表1。
2 模型参数
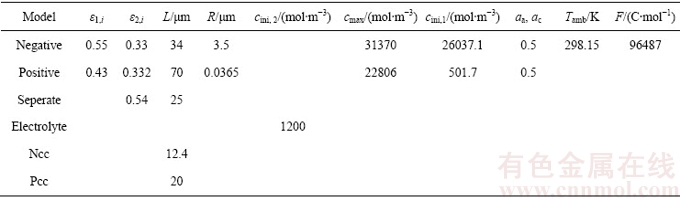
根据参数是否随温度或放电深度动态变化,可将模型参数可分为一般参数和动态响应参数。一般参数具体如表2所示,动态响应参数主要包括:1) 电极开路电压;2) 电极反应速率;3) 锂离子在固相中的扩散系数;4) 锂离子在液相中的扩散系数;5) 电解质活度相关的热力学因子;6) 锂离子传递系数;7) 电解质离子导电率。动态响应参数的具体表达式详见文献[23]。
3 结果与讨论
3.1 模型验证
锂离子电池是一个封闭的电化学系统,放电过程中电池内部电势、SOC、过电位等难以通过实验测量。因此,准二维电化学热耦合模型的有效性主要通过对比模拟所得放电曲线、温升与实际测量值来验证,模型的可靠性已在本课题组之前发表文献中得到多次验证[23-25]。
表1 不同类型过电势计算表达式
Table 1 Expressions for calculation of different overpotential
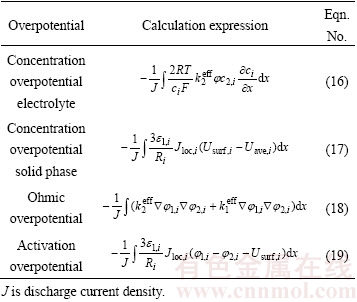
表2 电化学热耦合模型参数设置
Table 2 Parameters used in electrochemical-thermal model
3.2 1C放电过程正负极极化
电池放电过程中,电极极化涉及多孔电极中的固相浓差极化、液相浓差极化、欧姆极化和活化极化。图2(a)所示为1C恒流放电不同类型正极过电势随时间变化曲线。放电初期,不同类型过电势都有不同程度的波动,其中固相浓差极化波动最大,峰值达147 mV。放电600 s后不同类型过电势变化曲线开始趋于平稳,平稳阶段,欧姆极化约12 mV,活化极化约7 mV,固相和液相浓差极化相近且均小于0.1 mV。如图2 (b)所示,负极放电初期和放电中期极化变化曲线没有明显波动,其中活化过电势为40 mV左右,远大于其他3种类型过电势。当放电3130 s后,固相浓差极化和活化极化急剧增大,放电截止时刻分别达到266和172 mV。正极和负极总的欧姆极化和活化极化如图3所示。在放电中期,正负极欧姆极化之和为15 mV左右,活化极化为48 mV左右。综合来看,1C放电过程中,正负极液相浓差极化对放电的影响可以忽略不计。不同放电阶段占主导地位的极化类型不同,放电初期是正极固相浓差极化占主导,中期为活化极化占主导,后期为负极固相浓差极化占主导。
固相浓差过电势在正极放电初期和负极放电末期都有急剧变化,放电中期正极和负极浓差过电势均较小。从式(17)可看出,固相浓度过电势的大小由固相锂离子浓度梯度以及浓度梯度对平衡电势的影响共同决定。正负极平衡电势与荷电状态(State of charge,SOC)的关系曲线如图4所示,当SOC在[0.1,0.9]区间内变化时,正极活性材料的平衡电势几乎不变,SOC在此区间外时,SOC变化对正极平衡电势的影响较大。就负极而言,当SOC<0.1时,负极活性材料平衡电势随SOC减小而迅速增加。1C放电过程中,固相表面SOC与平均SOC的变化曲线如图5所示,可以看出放电初期正极表面SOC增加较快,平均SOC的增大速度较小,结合图4和图5可知,1C恒流放电初期,正极固相锂离子浓度较小,且分布不均匀,造成放电开始后正极浓差过电势波动范围较大,而当平均SOC达到0.1(385 s)时,正极浓差过电势接近于0。
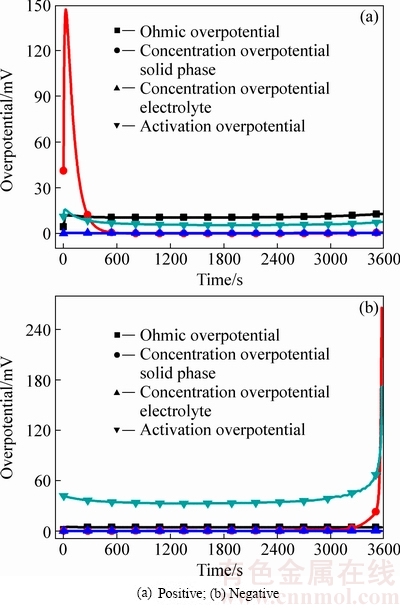
图2 1C恒流放电电极过电势变化
Fig. 2 Overpotential of electrodes at 1C rate discharge
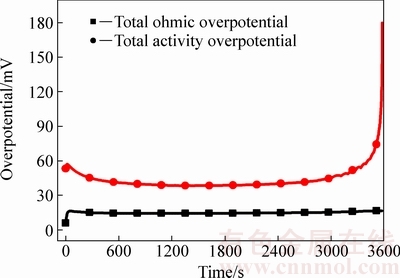
图3 1C恒流放电正极和负极总的欧姆过电势与活化过电势变化
Fig. 3 Changes of total ohmic and activation overpotential of positive and negative electrodes at 1C rate discharge
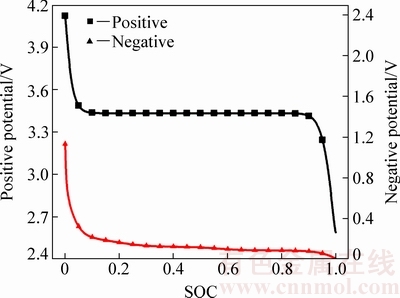
图4 正负极平衡电势随SOC变化曲线
Fig. 4 Equilibrium potential change of positive and negative electrodes with SOC
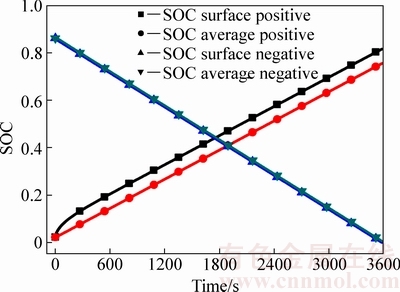
图5 1C放电正负极SOC变化
Fig. 5 SOC changes of positive and negative electrodes at 1C discharge rate
又由于1C放电时单位时间内从负极传输过来的锂离子浓度相对较小,锂离子在正极固相表面积累速度缓慢,放电截止时刻表面SOC未超过0.9,所以放电末期正极固相浓差极化没有明显变化。锂离子在负极活性材料内的扩散速度比在正极活性材料内的快[23],在整个放电过程中,活性材料颗粒表面SOC和平均SOC相差较小。但放电末期负极处于贫锂状态,接近完全放电状态,因此,即使电极内部锂离子浓度梯度较小,也表现出较大过电势。
3.3 高倍率放电正极极化变化
3C放电正极过电势如图6(a)所示,放电初期,固相浓差极化波动范围最大,峰值达到187 mV;在放电中期,欧姆过电势约38 mV,活化过电势约31 mV,其余极化较小;放电末期,固相扩散过电势迅速增加,放电截止时刻达到39 mV,其余类型极化较放电中期的变化较小。当8C放电时,放电初期固相浓差过电势峰值达到208 mV,较3C增加15 mV。在放电中期,欧姆过电势达到78 mV,基本随放电电流成正比增加,活化过电势呈现先减小后增大的趋势,其最小值为45 mV。欧姆极化与活化极化的差值增大,表明放电倍率越高,欧姆极化对正极极化的影响越大。放电末期,活化极化迅速增加,放电截止时达到115 mV,较3C放电截止时增加87 mV,表明随着放电倍率增加,放电后期正极活化极化对放电行为也会产生较大影响。图中也可看出,放电末期,固相浓差极化急剧增加,放电截止时达到715 mV,导致在404 s时提前达到放电截止条件。这主要是因为放电倍率越高,单位时间内从负极传输到正极锂离子越多,但锂离子在正极固相内扩散速度有限,正极固相内部浓度差越大,且放电末期活性材料表面接近满充状态(SOC>0.9)。正极液相浓差极化在3C、8C下对放电过程的影响均可忽略不计。与1C恒流放电相比,放电倍率增加正极各项极化均有不同程度的增加,另外,高倍率放电末期,固相浓差极化和活化极化的变化也不容忽视。
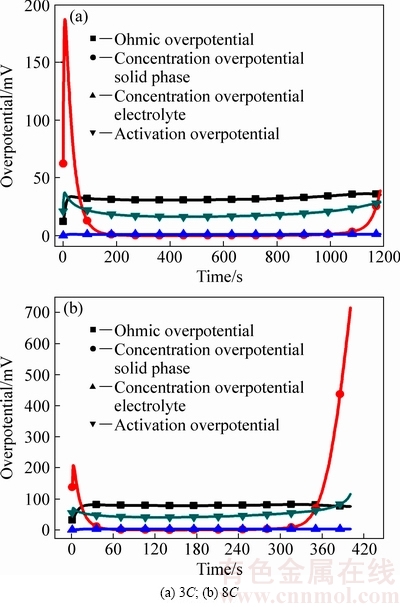
图6 不同倍率放电正极过电势变化
Fig. 6 Overpotential changes of positive electrode at different discharges
3.4 高倍率放电负极极化变化
3C放电负极过电势变化曲线如图7(a)所示,放电前期和中期,不同类型极化变化较小,其中活化极化最大,约为100 mV;放电末期,固相浓差极化激增至387 mV,较1C放电增加了121 mV。这是主要因为3C放电末期负极活性材料表面锂离子浓度枯竭较1C放电更为严重,且内部浓度差也较大所致。图7(b)所示为8C放电负极过电势变化曲线,活化极化占绝对主导地位,在226~255 mV之间波动,远大于其他类型极化。与3C相比,8C放电末期负极固相浓差极化没有急剧增加过程,这是因为8C放电末期时,表面SOC为0.08,平均SOC为0.11,该范围内,SOC对平衡电势的影响较小,所以浓差过电势较小。与正极欧姆极化类似,负极欧姆极化与放电电流成正比。综合来看,与1C相比,增加放电倍率,活化极化的变化最大,在放电中期,3C活化过电势约为1C相同阶段的2.5倍,8C约为3C相同阶段的2倍。
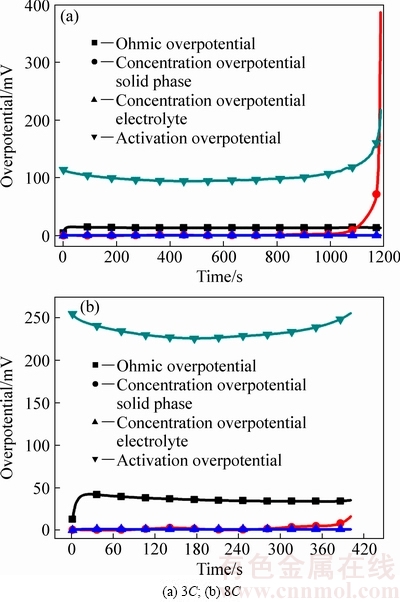
图7 不同倍率放电下负极过电势变化
Fig. 7 Overpotential of negative electrode at different discharges
综上所述,在高倍率放电条件下,活化极化,特别是负极活化极化的大幅增加是电极极化严重的主要原因。负极活化极化的本质是电子迁移速率高,而活性材料锂离子的脱出速率较低,导致正电荷积累,使得电极电势偏离平衡电势。因此,加快锂离子从负极固相材料脱出至电解液的过程,如减小颗粒粒径、提高锂离子在固相的扩散速率等措施都有利于降低负极活化极化,进而缓解高倍率放电极化严重的现象。就材料和电池优化设计而言,减小负极颗粒粒径,似乎最为简便。为了直观说明负极活性材料颗粒粒径对负极活化极化的影响,如图8所示,比较了8C恒流放电下不同负极固相颗粒粒径的负极活化极化。1Rn、0.5Rn、0.2Rn和0.1Rn分别表示表2中负极颗粒粒径的1倍、0.5倍、0.2倍和0.1倍。当固相粒径为0.5Rn时,活化极化为121~144 mV,较1Rn时的降低45%左右,当固相粒径为0.1Rn时,活化极化减小至30 mV左右,表明减小负极颗粒粒径可以明显降低负极活化极化。
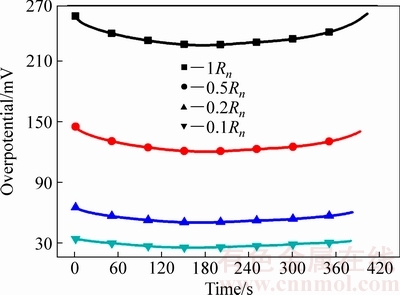
图8 8C放电不同负极颗粒粒径的活化过电势
Fig. 8 Activation overpotential with different active material particle sizes of negative electrode at 8C rate discharge
4 结论
1) 1C放电初期,正极固相浓差极化波动最大,峰值达到147 mV;放电中期,各类型极化趋于平稳,其中活化过电势最大,约为48 mV;放电末期,负极固相浓差极化和负极活化极化都急剧增加。
2) 提高放电倍率,各类型过电势都有不同程度增加,其中活化过电势,特别是负极活化过电势的大幅增加对电极极化的影响最大。放电前期和中期各类型极化变化趋势基本不变,但放电末期正极固相浓差极化急剧增加,8C放电截止时刻,达到715 mV,而8C放电末期,负极固相浓差极化没有急剧增加过程。
3) 固相颗粒粒径是影响活化极化的一个主要因素,8C放电下,当负极固相粒径为0.5Rn时,活化极化为121~144 mV,较1Rn时的降低45%左右,当固相粒径为0.1Rn时,活化极化减小至30 mV左右。
REFERENCES
[1] JIANG H R, LU Z, WU M C, CIUCCI F, ZHAO T S. Borophene: A promising anode material offering high specific capacity and high rate capability for lithium-ion batteries[J]. Nano Energy, 2016, 23: 97-104.
[2] HE C N, WU S, ZHAO N Q, SHI C S, LIU E Z, LI J J. Carbon-encapsulated Fe3O4 nanoparticles as a high-rate lithium ion battery anode material[J]. Acs Nano, 2013, 7(5): 4459-4469.
[3] HEUBNER C, SCHNEIDER M, MICHAELIS A. Investigation of charge transfer kinetics of Li-Intercalation in LiFePO4[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2015, 288: 115-120.
[4] ZHANG X D, BI Z Y, HE W, YANG G, LIU H, YUE Y Z. Fabricating high-energy quantum dots in ultra-thin LiFePO4 nanosheets using a multifunctional high-energy biomolecule—ATP[J]. Energy & Environmental Science, 2014, 7(7): 2285-2294.
[5] KASNATSCHEEW J, RODEHORST U, STREIPERT B, WIEMERS-MEYER S, JAKELSKI R, WAGNER R, LASKOVIC I C, WINTER M. Learning from overpotentials in lithium ion batteries: A case study on the LiNi1/3Co1/3Mn1/3O2 (NCM) cathode[J]. Journal of the Electrochemical Society, 2016, 163(14): 2943-2950.
[6] GUAN X M, LI G J, LI C Y, REN R M. Synthesis of porous nano/micro structured LiFePO4/C cathode materials for lithium-ion batteries by spray-drying method[J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2017, 27(1): 141-147.
[7] SUN J P, TANG K, YU X Q, HU J, LI H, HUANG X J. Overpotential and electrochemical impedance analysis on Cr2O3, thin film and powder electrode in rechargeable lithium batteries[J]. Solid State Ionics, 2008, 179(40): 2390-2395.
[8] WANG X J, YU X Q, Li H, YANG X Q, MCBREEN J, HUANG X J. Li-storage in LiFe1/4Mn1/4Co1/4Ni1/4PO4 solid solution[J]. Electrochemistry Communications, 2008, 10(9): 1347-1350.
[9] ARIYOSHI K, MAEDA Y, KAWAI T, OHZUKU T. Effect of primary particle pize upon polarization and cycling stability of 5-V lithium insertion material of Li[Ni1/2Mn3/2]O4[J]. Journal of the Electrochemical Society, 2011, 158(3): A281-A284.
[10] PARK M, ZHANG X C, CHUNG M, LESS G B, SASTRY A M. A review of conduction phenomena in Li-ion batteries[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2010, 195(24): 7904-7929.
[11] MAETINEZ-ROSAS E, VASQUEZ-MEDRANO R, FLOORES-TLACUAHUA C A. Modeling and simulation of lithium-ion batteries[J]. Computers & Chemical Engineering, 2011, 35(9): 1937-1948.
[12] JOKAR A, RAJABLOO B, DESILETS M, LACROIX M. Review of simplified Pseudo-two-Dimensional models of lithium-ion batteries[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2016, 327: 44-55.
[13] YAN B, LIM C, SONG Z B, ZHU L K. Analysis of polarization in realistic Li ion battery electrode microstructure using numerical simulation[J]. Electrochimica Acta, 2015, 185: 125-141.
[14] 张 凯, 汤依伟, 邹 忠, 宋文峰, 贾 明, 卢 海, 张治安. 锂离子电池LiMn2O4/石墨电极放电过程中浓差极化的仿真[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2013, 23(8): 2235-2242.
ZHANG K, TANG Y W, ZOU Z, SONG W F, JIA M, LU H, ZHANG Z A. Simulation of diffusion polarization in LiMn2O4/graphite Li-ion battery during discharge process[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2013, 23(8): 2235-2242.
[15] 洪 树, 汤依伟, 贾 明, 艾立华, 殷宝华, 李 劼. 基于电化学模型的全固态锂离子电池的放电行为[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2015, 25(8): 2176-2182.
HONG S, TANG Y W, JIA M, AI L H, YIN B H, LI J. Discharge behavior of all-solid-state Li-ion batteries based on electrochemical model[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2015, 25(8): 2176-2182.
[16] NYMAN A, ZAVALIS T G, ELGER R, BEHM M, LINDBERGH G. Analysis of the polarization in a Li-ion battery cell by numerical simulations[J]. Journal of the Electrochemical Society, 2010, 157(11): A1236-A1246.
[17] CHANDRASEKARAN R. Quantification of contributions to the cell overpotential during galvanostatic discharge of a lithium-ion cell[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2014, 262: 501-513.
[18] TIEDEMANN W. Maximum effective capacity in an ohmically limited porous electrode[J]. Journal of the Electrochemical Society, 1975, 122(11): 1482-1485.
[19] DOYLE M, NEWMAN J. Analysis of capacity–rate data for lithium batteries using simplified models of the discharge process[J]. Journal of Applied Electrochemistry, 1997, 27(7): 846-856.
[20] WU W, XIAO X R, HUANG X S. The effect of battery design parameters on heat generation and utilization in a Li-ion cell[J]. Electrochimica Acta, 2012, 83: 227-240.
[21] LAI Y Q, DU S L, AI L, AI L H, CHENG Y, TANG Y W, JIA M. Insight into heat generation of lithium ion batteries based on the electrochemical-thermal model at high discharge rates[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2015, 40(38): 13039-13049.
[22] KIM G H, PESARAN A, SPOTNITZ R. A three-dimensional thermal abuse model for lithium-ion cells[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2007, 170(2): 476-489.
[23] Li J, CHENG Y, JIA M, TANG Y W, LIN Y, ZHANG Z A, LIU Y X. An electrochemical-thermal model based on dynamic responses for lithium iron phosphate battery[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2014, 255: 130-143.
[24] DU S L, JIA M, CHENG Y, TANG Y W, ZHANG H L, AI L H, ZHANG K, LAI Y Q. Study on the thermal behaviors of power lithium iron phosphate (LFP) aluminum-laminated battery with different tab configurations[J]. International Journal of Thermal Sciences, 2015, 89(3): 327-336.
[25] TANG Y W, JIA M, AI L H, YIN B H, CHENG Y, LIU Y X. Capacity fade analysis of the lithium-ion power battery cycling process based on an electrochemical-thermal coupling model[J]. Energy Technology, 2015, 3(12): 1250-1259.
Polarization characteristics of lithium ion power battery based on electrochemical-thermal model
LI Shu-guo1, AI Liang2, 3, JIA Ming1, 2, 3, CHENG Yun1, DU Shuang-long1, JIANG Yue-hui1
(1. School of Metallurgy and Environment, Centre South University, Changsha 410083, China;
2. Aihua Group Co., Ltd., Yiyang 413000, China;
3. Hunan Provincial Key Laboratory of All-Solid-State Energy Storage Materials and Devices, Yiyang 413000, China)
Abstract: An electrochemical-thermal model was developed to quantitative analysis ohmic polarization, concentration polarization and activation polarization of positive and negative electrodes at different discharge rates. The results show that concentration polarization of positive is the main constituent part at the beginning of 1C rate discharge, which also shows the biggest fluctuation range. Various polarizations change less in the middle of 1C rate discharge, but at the end ohmic polarization and activation polarization of negative rapidly increase. Concentration polarization of solid phase in positive electrode increases dramatically to 715mV at the end of 8C rate discharge. The aggravation of activation polarization is the main cause of large polarization with discharge rate raised, and the activation polarization of negative electrode is worse than that of positive. It is effective to remit activation polarization of negative by reducing particle sizes of negative electrode.
Key words: lithium ion battery; ohmic polarization; concentration polarization; activation polarization; numerical simulation
Foundation item: Project(51774343) supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China
Received date: 2016-12-08; Accepted date: 2017-04-27
Corresponding author: JIA Ming; Tel: +86-13975127722; E-mail: jiamingsunmoon@aliyun.com
(编辑 龙怀中)
基金项目:国家自然科学基金资助项目(51774343)
收稿日期:2016-12-08;修订日期:2017-04-27
通信作者:贾 明,副教授,博士;电话:13975127722;E-mail:jiamingsunmoon@aliyun.com