表面改性处理钛增强纤维连接蛋白介导的 成骨细胞MG-63黏附和增殖
来源期刊:中国有色金属学报(英文版)2014年第4期
论文作者:周 征 戴 瑶 刘斌斌 夏磊磊 刘洪波 Pankaj VADGAMA 刘海蓉
文章页码:1065 - 1071
关键词:钛;表面改性;Outside-in信号传导;纤维连接蛋白;整合素
Key words:titanium; surface modification; Outside-in signaling; fibronectin; integrin
摘 要:采用化学抛光处理钛、阳极氧化和微弧氧化处理钛作为生物材料模型,研究成骨细胞MG-63在其表面的黏附和增殖机理。结果表明,阳极氧化和微弧氧化处理的钛表面通过促进MG-63细胞分泌纤维连接蛋白形成细胞外基质从而使其快速附着和伸展。另外,阳极氧化和微弧氧化处理的钛表面通过Outside-in信号传导通路,上调纤维连接蛋白及与其相关的整合素α5的转录水平,促进成骨细胞MG-63在其表面的增殖。
Abstract: An understanding of osteoblast adhesion and proliferation on biomaterials is crucial to optimizing the surfaces of artificial implants used in clinical practice. Polished, anodic oxidation (AO) and micro-arc oxidation (MAO) treated titanium (Ti) plates were used as model surfaces to study the adhesion of MG-63 cells. Cells were monitored for 0.5 and 4 h; faster adhesion and spreading of MG-63 cells were observed on the AO and MAO modified samples. Stimulated secretion of fibronectin (FN) influenced the adhesion rates. In addition, AO and MAO modified surfaces promoted cell proliferation through apparent up-regulation of FN and integrin α5 transcription via outside-in signaling. This strongly suggests that FN secretion by osteoblasts plays an essential role in enhanced cell adhesion, spreading and proliferation on these modified Ti surfaces.
Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 24(2014) 1065-1071
Zheng ZHOU1, Yao DAI 2, Bin-bin LIU2, Lei-lei XIA2, Hong-bo LIU2, Pankaj VADGAMA3, Hai-rong LIU2
1. College of Biology, Hunan University, Changsha 410082, China;
2. College of Materials Science and Engineering, Hunan University, Changsha 410082, China;
3. IRC in Biomedical Materials, Queen Mary University, London, UK
Received 28 April 2013; accepted 29 November 2013
Abstract: An understanding of osteoblast adhesion and proliferation on biomaterials is crucial to optimizing the surfaces of artificial implants used in clinical practice. Polished, anodic oxidation (AO) and micro-arc oxidation (MAO) treated titanium (Ti) plates were used as model surfaces to study the adhesion of MG-63 cells. Cells were monitored for 0.5 and 4 h; faster adhesion and spreading of MG-63 cells were observed on the AO and MAO modified samples. Stimulated secretion of fibronectin (FN) influenced the adhesion rates. In addition, AO and MAO modified surfaces promoted cell proliferation through apparent up-regulation of FN and integrin α5 transcription via outside-in signaling. This strongly suggests that FN secretion by osteoblasts plays an essential role in enhanced cell adhesion, spreading and proliferation on these modified Ti surfaces.
Key words: titanium; surface modification; Outside-in signaling; fibronectin; integrin
1 Introduction
Titanium is an ideal choice for the long-term replacement of hard tissue because of its excellent mechanical properties, corrosion resistance and biocompatibility. Enhancement of titanium bioactivity via surface modification has been reported for particular clinical applications [1,2]. Frequently used methods are anodic oxidation (AO) and micro-arc oxidation (MAO) [3,4]. Anodic oxidation produces vertically aligned TiO2 nanotubes on a titanium substrate, and micro-arc oxidation can provide titanium with a microporous calcium phosphate coating. Both modifications have been well tested in vivo and in vitro [5-7], and have exhibited benefits for osteoblast growth and a potential for future clinical application.
For the successful clinical use of biomaterial implants, cell/surface interactions are considered to be a key determinant [8]. Research is focused on establishing the relevant surface characteristics of biomaterials, such as chemical composition [9,10] and topography [11,12], to unravel the processes whereby biomaterials affect cell behavior. However, because of the complex and varied surface properties of biomaterials, and the application of different cell culture conditions, it is difficult to arrive at a general conclusion on how biomaterials regulate cell behavior [13]. Our mechanistic understanding of cell alteration on biomaterial surfaces remains incomplete [14]. The relationship between osteoblast behavior and titanium surface modification is the focus of study here, in order to provide further insight into cell/biomaterial interface. Moreover, the system has clinical relevance for hard tissue replacement.
Outside-in signaling is one of the most important processes mediating the interaction of cells and biomaterials. The cell, typically, uses integrins to transduce information from the extracellular matrix (ECM) to the cell interior [13,15], but such outside-in signaling also mediates the response to biomaterial surfaces [16,17]. This signaling exerts significant influence on cell adhesion and proliferation, and if we can fully understand this signaling function, we can also better control cell behavior through improved design biomaterials. An outside-in signaling study of the interaction of osteoblasts with AO or MAO modified titanium implants has not yet been reported.
The specific objective of this study is to understand the mechanism of outside-in signaling at osteoblasts cultured on AO or MAO modified titanium. Polished, AO and MAO treated Ti plates were used as the biomaterial models, and MG-63 cells, a human osteosarcoma cell line were used as the osteoblast model. Protein expression and gene transcription of fibronectin (FN) and collagen I (COLI), respectively, were observed by Western blot and RT-PCR assay. RT-PCR assay was also employed to examine the FN and COLI-related integrin transcription.
2 Experimental
2.1 Biomaterial preparation
Commercially available titanium plates (>99.9% purity, ASTM GR.1, Baoji INT Titanium Material Co., Ltd., China) of 2 mm×10 mm×10 mm were chemically polished and used for AO or MAO treatment. Scratches or blemishes on the plates were first removed using 400-grits SiC polishing paper, and chemical polishing was then carried out by using acid etch solution comprising HNO3 (65%-68% in mass fraction) and HF (40%) in volume ratio of 1:1. The samples were then ultrasonically cleaned using double distilled water (ddH2O) and ethanol (99.7%), respectively. Finally, the samples were dried at room temperature.
AO treatment of the titanium plates was performed in electrolyte solution containing NaF (0.138 mol/L) and H3PO4 (0.5 mol/L) according to a reported procedure [18]. A constant voltage of 10 V was also applied to the titanium plates for 20 min at 40 °C. All prepared samples were then ultrasonically cleaned with ddH2O and dried at room temperature.
MAO treatment of plates (prepared by Shanghai Institute of Ceramics, Chinese Academy of Sciences) was carried out in electrolyte solution comprising Ca(CH3COO)2 (0.1 mol/L) and Na2C3H5(OH)2PO4(0.1 mol/L) at 10 °C [19,20]. During this treatment, an AC voltage was applied for 4 min at 800 Hz and current density of 0.15 A/cm2. The MAO treated samples were cleaned by the same method as for AO treatment.
2.2 Surface analysis
The surface morphology of the specimens was observed using a field emission scanning electron microscope (FESEM, JSM6700F, JEOL, Japan).
2.3 Cell culture
A human osteoblast-like MG-63 cell line (purchased from the Center of Cell Resource, Shanghai Institutes for Biological Science, China) was used to evaluate the biological response to the samples. Cells were cultured in RPMI 1640 medium supplemented with 10% (v/v) fetal bovine serum and 1% (v/v) antibiotic (100 U/mL penicillin, and 100 g/mL streptomycin) at 37 °C in a humidified incubator (BB15, Thermo Scientific, USA) with an atmosphere of 5% CO2. All reagents were from Thermo Scientific, USA.
2.4 Cell morphology
Titanium samples were collected and washed twice with PBS prior to their use for MG-63 cell culture. Culture periods of 0.5 h and 4 h were used. For imaging, samples were pre-fixed with 3% glutaraldehyde for 30 min, and then dehydration gradients of ethanol and of hexamethyldisilazane were applied. The dehydrated specimens were observed by a field emission scanning electron microscope (FESEM, JSM6700F, JEOL, Japan).
2.5 AlamarBlue assay
AlamarBlue (Invitrogen, USA) assay of cell viability was carried out according to the protocol described previously [9].
2.6 Reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR)
Total RNA was extracted from MG-63 cells which had been cultured on polished Ti, AO and MAO treated Ti for either 4 h or 5 d using TRIzol reagent (Invitrogen, USA). The RNA was precipitated with isopropanol, washed with 75% ethanol and dissolved in RNase-free water.
Following DNase I (Fermentas, USA) treatment, the extracted RNA was used to produce cDNA using a reverse transcription kit (Fermentas, USA). PCR reactions were undertaken using a thermal cycle system (2720 Thermal Cycler, Applied Biosystems, USA) with the following programs: a denaturation step for 2 min at 94 °C followed by a sequence of 25-30 cycles at 94 °C for 30 s, 55-57 °C for 30 s and 72 °C for 60 s. The PCR products were detected using a gel image analysis system (2600R GIS, Tanon, China). Typically, five repeats were performed for every sample. The primers used in this study are listed in Table 1.
2.7 Western blotting assay
MG-63 cells were collected after they had been incubated with samples for 4 h and 5 d, respectively, and were washed once with PBS and once with washing buffer (10 mmol/L tris (pH 8.0), 150 mmol/L NaCl, 1 mmol/L EDTA (pH 8.0)). The cells were then lysed in 200 μL of lysis buffer which contained 20 mmol/L tris-HCl (pH 8.0), 30 mmol/L MgCl2, 2 mmol/L ethyleneglycol tetraacetic acid (EGTA), 10% glycerol, 1% CHAPS, 1.2 μL of 10% β-mercaptoethanol and 100 mmol/L phenylmethanesulfonyl fluoride (PMSF).
Table 1 Primer pairs used for RT-PCR

Proteins (~20 μg) were resolved by gel electrophoresis using 8% SDS-polyacrylamide gel and transferred to polyvinylidene (PVDF) membranes (Millipore, USA) at 100 V for 1.5 h. The membranes were blocked by overnight exposure to 5% non-fat milk in 1×PBS and 0.1% Tween 20 at 4 °C. Samples were incubated with primary and secondary antibody at room temperature for 2 h and 1 h respectively. After samples had been treated with enhanced chemiluminescence reagent (ECL) (Pierce, USA), they were exposed to photographic films (Kodak).
Primary antibodies used in this study were rabbit anti-β-actin antibody (1:1000) (Cell Signaling Technology, USA), anti-Fibronectin (1:1000) (Sigma- Aldrich, USA) and anti-collagen I (1:200) (Millipore, USA). Secondary antibodies were HRP-conjugated anti-rabbit IgG (1:2000) (Cell Signaling Technology, USA).
2.8 Statistical analysis
All quantitative data were collected from triplicates, or more, and expressed as mean ± standard deviation (s.d.). Statistical comparison between groups was performed using a two-tailed unpaired t-test (two-group comparison). A value of p less than 0.05 was considered to be statistically significant.
3 Results
3.1 Morphology of titanium specimens
The surface morphology of Ti specimens was analyzed by FESEM (Fig. 1). The surface of the titanium plates was smooth as a result of initial polishing (Fig. 1(a)). The surface of AO treated Ti plates exhibited a similar appearance to that of polished Ti plates at low magnification (Fig. 1(b)), but it also showed clearly at high magnification (Fig. 1(c)) that nanotubes of around 50 nm diameter were evenly distributed on its surface.
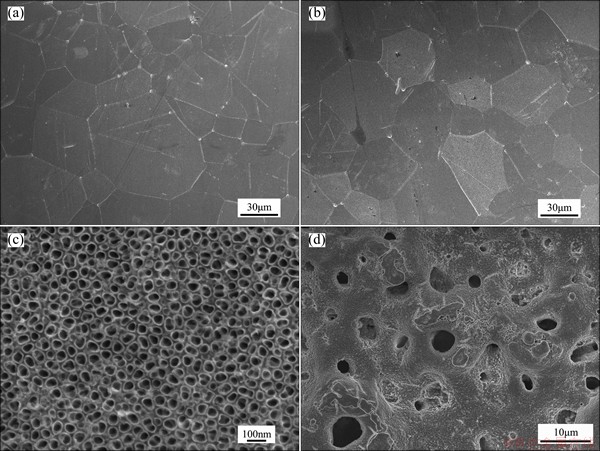
Fig. 1 FESEM morphologies of polished titanium surface (a), AO treated titanium surface (b, c) and MAO treated titanium surface (d)
The surface of MAO treated Ti plates showed micropores of varying size (Fig. 1(d)). Whilst both AO and MAO treatment led to increased surface roughness, and the surface morphologies were quite different.
3.2 Cell morphology on titanium
The morphologies of MG-63 cells incubated on three different treated titanium plates for 0.5 h are shown in Figs. 2(a)-(c). In contrast to MG-63 cells on polished Ti, those seeded on AO treated and MAO treated Ti plates formed filopodia and lamellipodia, consistent with these rougher surfaces stimulating cellular adhesion and ECM formation. At 4 h, cells on the AO and MAO treated surfaces exhibited a regular, polygonal morphology, whereas those on polished Ti remained round, with no indication of stimulated adhesion (Figs. 2(d)-(f)).
3.3 Fibronectin production on titanium by MG-63 cells
The extracellular matrix proteins, FN and COLI, play a key role in cell adhesion, but the surface properties that induce this ECM production are less clear. To help determining biological mechanisms for such stimulated ECM protein production by MG-63 cells, an enhanced adhesion, combined use, was made of Western blotting and RT-PCR (Fig. 3). On this basis, total measured COLI levels were stable across all surfaces.
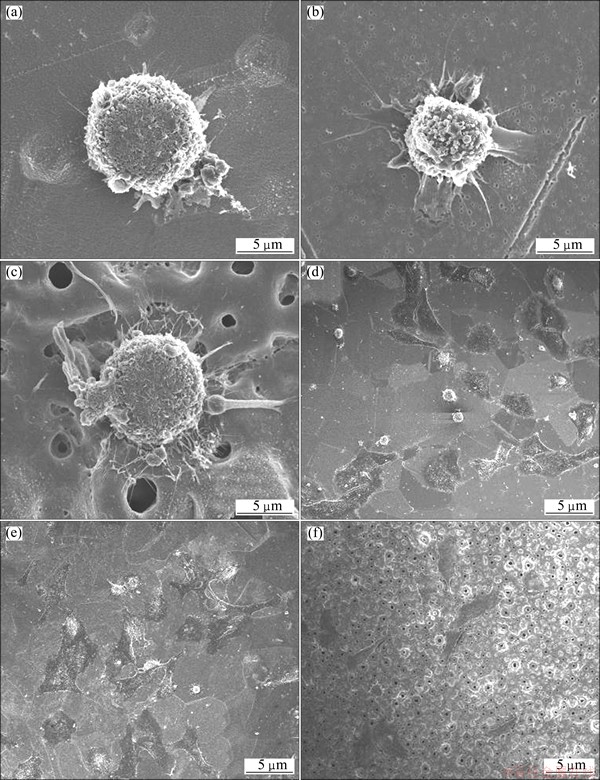
Fig. 2 FESEM morphologies of MG-63 cells cultured for 0.5 h on polished Ti (a), AO treated Ti plate (b), MAO treated Ti plate (c) and cultured for 4 h on polished Ti (d), AO treated Ti plate (e) and MAO treated Ti plate (f)
However, FN levels were actually reduced at MG-63 cells grown on AO and MAO treated Ti plates (Fig. 3(a)) compared with those on polished Ti plates. The results suggest that while MG-63 cells may well secrete increased FN, leading to filopodia and lamellipodia development. This is a distinct feature from total cellular FN production. To test reduced transcription of FN of cells cultured on AO and MAO treated Ti, the transcription of COLI and FN was determined by RT-PCR (Fig. 4(b)). However, the same mRNA levels for FN and COLI were observed for the three types of Ti samples. This indicates not only that the Ti surfaces had no differential effect on FN and COLI transcription, but also that there was no suppression. It appears that cells were not able to vary the transcription pattern of their integrin genes, within the resolution of the assay at this early phase regardless of measured change in FN. It is possible that the relevant variable was FN export rather than synthesis.
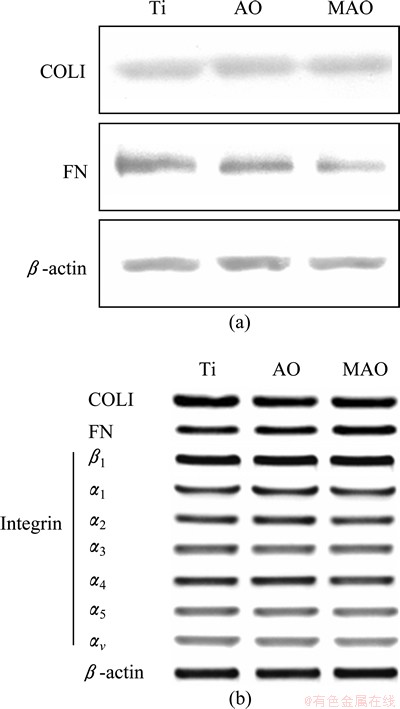
Fig. 3 COLI, FN expression in MG-63 cells cultured with polished, AO and MAO treated Ti plates respectively for 4 h (a), mRNA level of genes listed in MG-63 cells cultured with polished AO and MAO treated Ti plates respectively for 4 h (b)
3.4 Proliferation of MG-63 cells
To determine the proliferation of MG-63 cells on the three surfaces, an AlamarBlue assay was carried out. The AlamarBlue reduction was determined at day 1, 3 and 5 and normalized to day 1 to indicate proliferation rates. Compared with the polished Ti, the proliferation rates on the AO and MAO modified Ti at 3 and 5 d were significantly greater, with the highest value on MAO treated Ti (Fig. 4(a)).
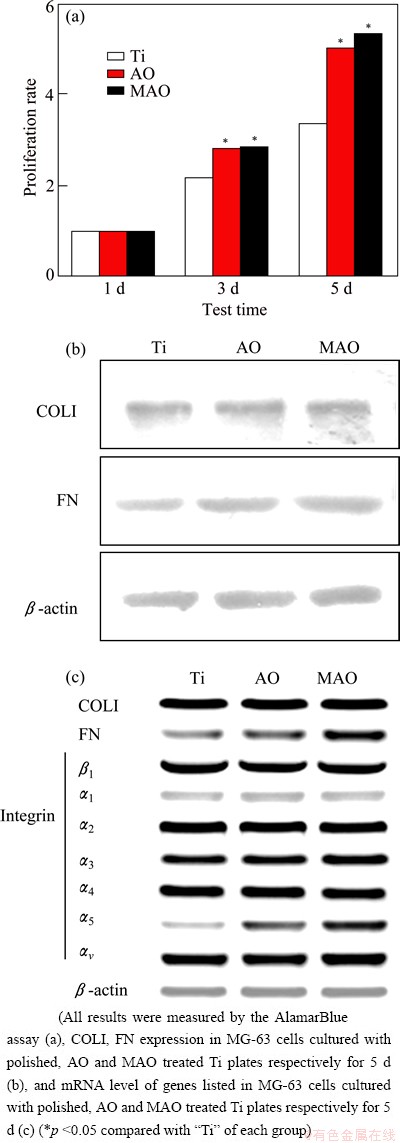
Fig. 4 Proliferation rates of MG-63 cells cultured on three tested samples
3.5 Influence of surface modification on gene transcription at MG-63 cells
As well as conditioning cell adhesion, COLI and FN are also regulatory proteins for cell proliferation [21,22]. To understand the molecular correlates of enhanced cell proliferation on AO and MAO modified surfaces, levels of COLI and FN in MG-63 cells cultured for 5 d with the three samples were measured (Fig. 4(b)). Also, mRNA levels of genes coding integrin β1, α1, α2, α3, α4, α5, and αv that interact with COLI and FN, were examined (Fig. 4(c)).
Figure 4(b) shows similar COLI levels for the three samples, indicating that the expression of COLI was not influenced by surface modification. FN production, however, was raised at day 5 (Fig. 4(b)) and contrasts with a lack of early stage response (Fig. 3(a)). In agreement with this, the transcription of FN by RT-PCR increased in these cells, both on AO and MAO treated Ti plates (Fig. 4(c)).
Extracellular FN interacts with specific integrin heterodimer complexes, which consist of one integrin β1 and an integrin α subunit, notably integrin α3, α4, α5 or αv [23]. As shown in Fig. 4(c), the transcription of FN markedly increased in MG-63 cells cultured on MAO treated Ti plates. According to the quantified data, both AO and MAO modified surfaces significantly enhanced the FN transcription. Figure 4(c) also shows that mRNA levels of integrin β1, α1, α2, α3, α4, α5, and αv, the transcription of integrin β1, α1, α2, α3, α4 and αv are not affected by the different surfaces modifications, with identical mRNA levels found in all samples. Only the transcript of integrin α5 is up-regulated, suggesting this to be the integrin mediating the outside-in signaling.
4 Discussion
The initial cell interaction with a biomaterial, i.e. its adhesion, is regarded as the fundamental event which determines later events, including proliferation [23]. Previous works [9-12] have shown that both topography and chemistry influence cell adhesion on a surface, but how these elements affect the biological process is unclear. Here, the facilitated adhesion on AO and MAO modified Ti plates (Fig. 2), is consistent with the previous reports [7,11]. Moreover, the formation of filopodia and lamellipodia is also stimulated (Figs. 2(a)-(c)). Since faster formation of filopodia and lamellipodia supports earlier cell spreading, the majority of MG-63 cells are seen to be spread over the AO and MAO modified surfaces within 4 h (Figs. 2(d)-(f)). So, the promotion of attachment and spreading, at least of MG-63 cells, is an early process.
Combining Western blotting and RT-PCR assay employed in this study has shed some light on the involvement of COLI and FN. While no early gene transcription effects were seen for either FN or COLI (Fig. 3(b)). The drop in expressed FN (Fig. 3(a)) suggests that a more subtle process of FN regulation and partitioning is in play. The cell morphological changes on the modified surfaces point to higher extracellular FN, and therefore higher secretion, regardless of total measured amount, and the early translation of this into filopodia and lamellipodia formation. The higher proliferation rates of MG-63 cells on AO and MAO modified Ti plates (Fig. 3(a)) are consistent with the known effects of cell adhesion on proliferation enhancement [23].
The COLI level and the transcription of COLI remain stable in MG-63 cells regardless of the chemistry or morphology of the materials on which they are cultured. However, the protein level of FN increases (Fig. 4(b)), with, as expected, significant elevated transcription of FN (Fig. 4(c)), so at a later stage there is a definite transcriptional effect.
Outside-in signaling is the well established route to cell/biomaterial interaction in which integrins are the key cell surface proteins. Integrins can pass information about the extracellular matrix to the cell interior, driving a range of cellular responses [13]. In particular, integrins play a role in cellular proliferation [24,25]. Our data demonstrates clearly that it is specifically integrin α5 that is responsible for stimulated growth on the modified titanium. MILNER et al [26] also found that FN and the α5 integrin subunit are strongly up-regulated in capillary endothelial cells where vigorous cell proliferation is required.
5 Conclusions
1) Compared with the smooth surface of polished Ti plates, the AO and MAO treated Ti surfaces were decorated with nanotubes and micropores, respectively.
2) AO and MAO treated Ti plates significantly promoted cell adhesion and the formation of extracellular matrix by stimulating the secretion of FN from MG-63 cells.
3) AO and MAO treated Ti plates enhanced the cellular proliferation by stimulating the transcription of FN and α5 integrin.
References
[1] LIU X Y, CHU P K, DING C X. Surface modification of titanium, titanium alloys, and related materials for biomedical applications [J]. Materials Science and Engineering R, 2004, 47: 49-121.
[2] LASPRILLA A J R, MARTINEZ G A R, LUNELLI B H, JARDINI A L, MACIEL R. Biomaterials for application in bone tissue engineering [J]. Journal of Biotechnology, 2010, 150: S455.
[3] MINAGAR S, BERNDT C C, WANG J, IVANOVA E, WEN C. A review of the application of anodization for the fabrication of nanotubes on metal implant surfaces [J]. Acta Biomaterialia, 2012, 8(8): 2875-2888.
[4] LI Y, LEE I S, CUI F Z, CHOI S H. The biocompatibility of nanostructured calcium phosphate coated on micro-arc oxidized titanium [J]. Biomaterials, 2008, 29(13): 2025-2032.
[5] NARAYANAN R, LEE H J, KWON T Y, KIM K H. Anodic TiO2 nanotubes from stirred baths: Hydroxyapatite growth and osteoblast responses [J]. Materials Chemistry and Physics, 2011, 125(3): 510-517.
[6] WANG Na, LI Hong-yi, LU Wu-long, LI Jing-hui, WANG Jin-shu, ZHANG Zhen-ting, LIU Yi-ran. Effects of TiO2 nanotubes with different diameters on gene expression and osseointegration of implants in minipigs [J]. Biomaterials, 2011, 32(29): 6900-6911.
[7] DENG Fei-long, ZHANG Wei-zhen, ZHANG Pei-fen, LIU Chen-hai, LING Jun-qi. Improvement in the morphology of micro-arc oxidised titanium surfaces: A new process to increase osteoblast response [J]. Materials Science and Engineering C, 2010, 30(1): 141-147.
[8] LAI M, CAI K Y, HU Y, YANG X F, LIU Q. Regulation of the behaviors of mesenchymal stem cells by surface nanostructured titanium [J]. Colloids and Surfaces B, 2012, 97: 211-220.
[9] DAI Yao, LIU Hai-rong, XIA Lei-lei, ZHOU Zheng. Preparation and characterization of icariin/PHBV drug delivery coatings on anodic oxidized titanium [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2011, 21(11): 2448-2453.
[10] LIU Hai-rong, XIA Lei-lei, DAI Yao, ZHAO Man, ZHOU Zheng, LIU Hong-bo. Fabrication and characterization of novel hydroxyapatite/porous carbon composite scaffolds [J]. Materials Letters, 2012, 66(1): 36-38.
[11] ZHAO L Z, MEI S L, CHU P K, ZHANG Y M, WU Z F. The influence of hierarchical hybrid micro/nano-textured titanium surface with titania nanotubes on osteoblast functions [J]. Biomaterials, 2010, 31(19): 5072-5082.
[12] ZHU X L, CHEN J, SCHEIDELER L, REICHL R, GEIS-GERSTORFER J. Effects of topography and composition of titanium surface oxides on osteoblast responses [J]. Biomaterials, 2004, 25(18): 4087-4103.
[13] SIEBERS M C, TER BRUGGE P J, WALBOOMERS X F, JANSEN J A. Integrins as linker proteins between osteoblasts and bone replacing materials: A critical review [J]. Biomaterials, 2005, 26(2): 137-146.
[14] GARCIA A J. Get a grip: Integrins in cell-biomaterial interactions [J]. Biomaterials, 2005, 26(36): 7525-7529.
[15] GINSBERG M H, PARTRIDGE A, SHATTIL S J. Integrin regulation [J]. Current Opinion in Cell Biology, 2005, 17(5): 509-516.
[16] OHMORI T, KASHIWAKURA Y, ISHIWATA A, MADOIWA S, MIMURO J, HONDA S, MIYATA T, SAKATA Y. Vinculin activates inside-out signaling of integrin alpha IIb beta 3 in Chinese hamster ovary cells [J]. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications, 2010, 400(3): 323-328.
[17] SAMANNA V, WEI H, EGO-OSUALA D, CHELLAIAH M A. Alpha-V-dependent outside-in signaling is required for the regulation of CD44 surface expression, MMP-2 secretion, and cell migration by osteopontin in human melanoma cells [J]. Experimental Cell Research, 2006, 312(12): 2214-2230.
[18] RAJA K S, MISRA M, PARAMGURU K. Formation of self-ordered nano-tubular structure of anodic oxide layer on titanium [J]. Electrochimica Acta, 2005, 51(1): 154-165.
[19] HU Hong-jie, LIU Xuan-yong, DING Chuan-xian. Preparation and cytocompatibility of Si-incorporated nanostructured TiO2 coating [J]. Surface & Coatings Technology, 2010, 204(20): 3265-3271.
[20] HU Hong-jie, QIAO Yu-qin, MENG Fan-hao, LIU Xuan-yong, DING Chuan-xian. Enhanced apatite-forming ability and cytocompatibility of porous and nanostructured TiO2/CaSiO3 coating on titanium [J]. Colloids and Surfaces B, 2013, 101: 83-90.
[21] TSAI S W, CHENG Y H, CHANG Y, LIU H L, TSAI W B. Type I collagen structure modulates the behavior of osteoblast-like cells [J]. Journal of the Taiwan Institute of Chemical Engineers, 2010, 41(3): 247-251.
[22] MAGNUSSON M K, MOSHER D F. Fibronectin: Structure, assembly, and cardiovascular implications [J]. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol, 1998, 18(9): 1363-1370.
[23] ANSELME K. Osteoblast adhesion on biomaterials [J]. Biomaterials, 2000, 21(7): 667-681.
[24] LOBERT V H, BRECH A, PEDERSEN N M, WESCHE J, OPPELT A, MALEROD L, STENMARK H. Ubiquitination of alpha 5 beta 1 lntegrin controls fibroblast migration through lysosomal degradation of fibronectin-lntegrin complexes [J]. Developmental Cell, 2010, 19(1): 148-159.
[25] WANG Yan-song, YAO Meng, ZHOU Ji-hui, ZHENG Wei, ZHOU Chang-wei, DONG Da-ming, LIU Yu-gang, TENG Zhao-wei, JIANG Yong-qing, WEI Guo-jun, CUI Xiao-ying. The promotion of neural progenitor cells proliferation by aligned and randomly oriented collagen nanofibers through beta 1 integrin/MAPK signaling pathway [J]. Biomaterials, 2011, 32(28): 6737-6744.
[26] MILNER R, HUNG S, EROKWU B, DORE-DUFFY P, LAMANNA J C, DEL ZOPPO G J. Increased expression of fibronectin and the alpha 5 beta 1 integrin in angiogenic cerebral blood vessels of mice subject to hypobaric hypoxia [J]. Molecular and Cellular Neuroscience, 2008, 38(1): 43-52.
周 征1,戴 瑶2,刘斌斌2,夏磊磊2,刘洪波2,Pankaj VADGAMA3,刘海蓉2
1. 湖南大学 生物学院,长沙 410082;2. 湖南大学 材料科学与工程学院,长沙 410082;
3. IRC in Biomedical Materials, Queen Mary University, London, UK
摘 要:采用化学抛光处理钛、阳极氧化和微弧氧化处理钛作为生物材料模型,研究成骨细胞MG-63在其表面的黏附和增殖机理。结果表明,阳极氧化和微弧氧化处理的钛表面通过促进MG-63细胞分泌纤维连接蛋白形成细胞外基质从而使其快速附着和伸展。另外,阳极氧化和微弧氧化处理的钛表面通过Outside-in信号传导通路,上调纤维连接蛋白及与其相关的整合素α5的转录水平,促进成骨细胞MG-63在其表面的增殖。
关键词:钛;表面改性;Outside-in信号传导;纤维连接蛋白;整合素
(Edited by Hua YANG)
Foundation item: Project (2010DFA32270) supported by the Ministry of Science and Technology of China (International Science & Technology Cooperation Program of China); Project (51102090) supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China; Project (NCET-12-0170) supported by the Program for New Century Excellent Talents in University of China
Corresponding author: Zheng ZHOU; Tel: +86-731-88822606; E-mail: zhouzheng@hnu.edu.cn
DOI: 10.1016/S1003-6326(14)63163-0

