铋离子在壬基异羟肟酸中金红石-水界面的吸附行为及机制
来源期刊:中国有色金属学报(英文版)2018年第2期
论文作者:肖巍 曹攀 梁倩楠 黄小涛 李开运 张雁生 覃文庆 邱冠周 王军
文章页码:348 - 355
关键词:金红石;浮选;Bi(III)活化;竞争吸附;活性位点
Key words:rutile; flotation; activation of Bi(III) ions; competitive adsorption; activation sites
摘 要:通过单矿物浮选、动电位测试、吸附量测试和X射线光电子能谱研究Bi(III)在金红石-水界面的吸附行为和机制。单矿物浮选结果表明,加入Bi(III)后,金红石的浮选回收率由62%提高到91%。添加Bi(III)可以增加活性位点,降低壬基异羟肟酸阴离子与OH-离子之间的竞争吸附,这是Bi(III)能够活化金红石浮选的本质。Bi(III)吸附在金红石表面,导致Zeta电位正移,有利于壬基异羟肟酸的吸附。XPS结果显示,Bi(III)吸附前后,钛原子周围的化学环境没有发生变化。Bi(III)在金红石-水界面有两种吸附方式:一种是Ca2+、Mg2+和Fe2+溶解后,Bi(III)占据其空位;另一种是Bi(III)以羟基化合物的形式覆盖在金红石表面。
Abstract: The adsorption behavior and mechanism of Bi(III) ions on the rutile-water interface were investigated through micro-flotation, Zeta potential measurement, adsorption amount measurement and X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS). According to the results of micro-flotation, Bi(III) ions could largely improve the rutile flotation recovery (from 62% to 91%), and they could increase the activating sites and reduce the competitive adsorption between nonyl hydroxamic acid negative ions and OH- ions, which determined that Bi(III) ions were capable of activating rutile flotation. The adsorption of Bi(III) ions onto the rutile surface led to the shift of Zeta potential into the positive direction, which was good for the adsorption of nonyl hydroxamic acid anions. In addition, the results of XPS indicated that the chemical environment around Ti atom had not changed before and after the adsorption of Bi(III) ions. Based on the adsorption mechanism of Bi(III) ions, it was deduced that firstly Bi(III) ions occupied the vacancies of the original Ca2+, Mg2+ and Fe2+ ions on the rutile surface; secondly Bi(III) ions covered on the rutile surface in the form of hydroxides.
Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 28(2018) 348-355
Wei XIAO1,2, Pan CAO1,2, Qian-nan LIANG1,2, Xiao-tao HUANG1,2, Kai-yun LI1,2, Yan-sheng ZHANG1,2, Wen-qing QIN1,2, Guan-zhou QIU1,2, Jun WANG1,2
1. Key Laboratory of Biohydrometallurgy of Ministry of Education, Central South University, Changsha 410083, China;
2. School of Minerals Processing and Bioengineering, Central South University, Changsha 410083, China
Received 30 September 2016; accepted 18 July 2017
Abstract: The adsorption behavior and mechanism of Bi(III) ions on the rutile-water interface were investigated through micro-flotation, Zeta potential measurement, adsorption amount measurement and X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS). According to the results of micro-flotation, Bi(III) ions could largely improve the rutile flotation recovery (from 62% to 91%), and they could increase the activating sites and reduce the competitive adsorption between nonyl hydroxamic acid negative ions and OH- ions, which determined that Bi(III) ions were capable of activating rutile flotation. The adsorption of Bi(III) ions onto the rutile surface led to the shift of Zeta potential into the positive direction, which was good for the adsorption of nonyl hydroxamic acid anions. In addition, the results of XPS indicated that the chemical environment around Ti atom had not changed before and after the adsorption of Bi(III) ions. Based on the adsorption mechanism of Bi(III) ions, it was deduced that firstly Bi(III) ions occupied the vacancies of the original Ca2+, Mg2+ and Fe2+ ions on the rutile surface; secondly Bi(III) ions covered on the rutile surface in the form of hydroxides.
Key words: rutile; flotation; activation of Bi(III) ions; competitive adsorption; activation sites
1 Introduction
Rutile is not only one of the raw materials that are necessary for high-grade welding electrodes, but also the most suitable raw material for the production of rutile titanium dioxide [1,2]. However, the majority of rutile ores belong to refractory ores, and thus flotation is one of the most efficient methods of solving the problem related to the fine embedded grain size, the complexity of the mineral and easiness to muddy [3].
With the rapid development of flotation, many effective collectors have been applied to the process of flotation separation of the oxide ores successfully. Many reviews indicated that alkyl hydroxamic collectors have a high selectivity on oxide ores such as cassiterite, cheelite, and rutile [4-7]. Furthermore, their affinity to metal or metal oxide is far stronger than fatty acid, thereby forming more stable metal complexes [8-10]. Unfortunately, the flotation recovery is a little lower when using alkyl hydroxamic collectors in spite of higher concentration. In order to improve the recovery, the consumption of collectors in abundance must be enhanced due to the lack of activating sites for collector adsorption on the mineral surface. And we tried to add surface activating sites with two common surface modification approaches: to change the valence state or structure of present surface elements and to introduce new activating elements to the mineral surface.
A selective control of surface properties is conductive to the design of solid surface, so the anchoring group plays a key role in functional materials and adjusting the interaction between mineral and activating sites of the mineral surface. Pb(II) and Cu(II) ions are effective activators that have already been widely used to modify mineral surface properties. The flotation recovery of sphalerite can be greatly improved in the presence of copper ions. The copper xanthates had lower solubility than zinc xanthates, resulting in a more hydrophobic surface of sphalerite particles to attach air bubbles [11]. Copper ions could also activate the flotation of pyrite, which was suppressed by lime in alkaline condition, because they led to the formation of new metal sulfide phases on pyrite surfaces [12]. FAN and ROWSON [13] found that Pb(NO3)2 could be used as activator to improve ilmenite floatability effectively and selectively. The Pb2+ and Pb(OH)+ species could be attached onto ilmenite surfaces selectively, achieving improvement in the flotation recovery of ilmenite.
In this work, Bi(III) ions (novel activator) were introduced to add the activation sites on the rutile surface, and subsequent flotation reflection to nonyl hydroxamic acid was investigated as well. According to the measurement results of XPS and Zeta potential, the adsorption mechanisms of Bi(III) ions on the rutile surface and subsequent reflection to nonyl hydroxamic acid (collector) were further discussed.
2 Experimental
2.1 Materials
In this work, rutile samples obtained from Zaoyang, Hubei, China were firstly crushed and ground to particles (38-74 μm) and then purified by sieving, and tabling with low/high-intensity magnetic separation methods. The pure rutile samples were washed several times with distilled water and finally dried at room temperature. According to the analysis of particle size (Fig. 1), the average particle size of rutile was 53.98 μm, which was measured through a laser particle-size analyzer (Mastersizer 2000). As a result, all the reagents were analytically pure in this work.
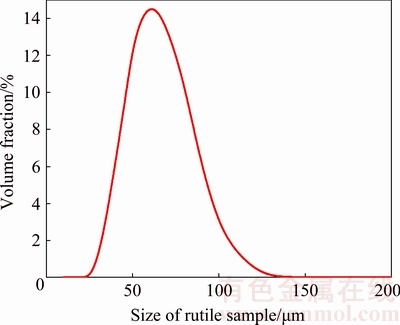
Fig. 1 Size contribution of rutile sample
An analysis of chemical compositions of rutile was carried out by a wavelength dispersive X-ray fluorescence (XRF) spectrometer S4 Pioneer. The results of XRD and XRF are shown in Fig. 2 and Table 1, respectively. The parameter setting and the method of XRD and XRF were previously described in Ref. [14]. From the XRD results in Fig. 2 and the XRF results in Table 1, the purity of rutile samples was calculated to be 93.8%.
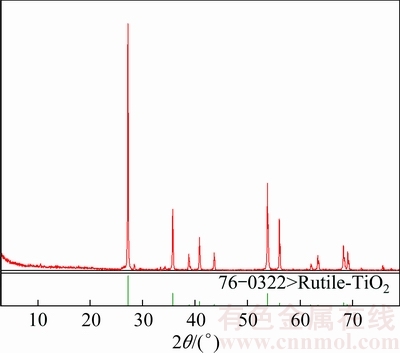
Fig. 2 XRD pattern of rutile
Table 1 Multi-element analysis result of pure rutile mineral (mass fraction, %)

2.2 Experimental methods
2.2.1 Micro-flotation tests
The purified rutile particles (2 g) were placed in a plexiglass cell (40 mL) that was then filled with distilled water so as to adjust the pH value. After 2 min, the bismuth nitrate and the collector were added, respectively. Next, the suspension was agitated for 2 and 3 min, respectively, and then the pH was measured before the flotation (4 min). The concentrates and tailings were weighed after filtration and drying, and finally the flotation recovery was calculated.
2.2.2 Adsorption experiment
The rutile samples (2.0 g) were place in a plexiglass cell (40 mL) that was then filled with distilled water. Then, the pH value was adjusted by 1% hydrochloric acid solution. After constant stirring for 2 min, bismuth nitrate was added. The suspension was agitated for 5 min. Next, the samples were centrifuged and filtered to separate liquid and solid phases after extraction. After washing twice with distilled water, the filter liquor was moved to a 100 mL volumetric flask. Finally, the adsorption amount was calculated by the following equation:
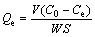 (1)
(1)
where Qe is the amount of nonyl hydroxamic acid adsorbed on the surface of rutile (mol/m2), C0 is the initial concentration of nonyl hydroxamic acid (mol/L), Ce is the residual concentration of nonyl hydroxamic acid in solution (mol/L), V is the volume (L), S is the specific surface area of rutile (m2/g), and W is the mass of rutile (g).
2.2.3 Zeta potential measurement
The Zeta potential of mineral suspension was measured with a Malvern instrument (UK). Then, samples were ground till the size was less than 5 μm. And then, pure rutile (20 mg) was added to deionized water (50 mL) containing 1×10-3 mol/L KCl as the supporting electrolyte before suspension. The suspension was conditioned for 15 min, during which the suspension pH was measured. The pH could be adjusted with either NaOH or H2SO4 over the pH range of 2-12. Zeta potential was measured according to the procedures described in the instrument manual. The reported results were the average of at least three full repeat experiments.
2.2.4 X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy
The chemical compositions on rutile surfaces were determined by XPS on a Thermo Scientific ESCALAB 250Xi through Al Kα X-ray source operated at 200 W with 20 eV pass energy. The vacuum pressure was ranged from 1.33×10-7 to 1.33×10-6 Pa and the takeoff angle was 90°. The data were collected and processed with the help of Thermo Scientific Advantage 4.52.
3 Results and discussion
3.1 Micro-flotation test
The effect of pH value on rutile flotation recovery with nonyl hydroxamic acid as the collector is shown in Fig. 3. According to Fig. 3, it could be found that the optimal pH range of rutile flotation was 3.5-7.0. And the flotation recovery began to decrease when the pH was more than 7.0 or less then 3.5, because the activation sites were dissolved to aqueous solution in the strongly acid (pH<3.5) [15,16]. Along with the increase of acid, more and more activation sites were dissolved, directly resulting in the decrease of adsorption amount of nonyl hydroxamic acid, which included Ti atoms and impurity atoms (such as Ca, Mg and Fe). It had also been reported that the surface hydroxylation of rutile played an important role in adsorption of organics [17-19]. In the strong acid, the surface hydroxylation was more stable, so that it was difficult to show substitution reaction between nonyl hydroxamic acid anions and the surface hydroxylation.
The floatability of rutile was depressed in the alkaline environment, possibly because the competitive adsorption existed between OH- ions and nonyl hydroxamic acid negative ions on the rutile surface [20].
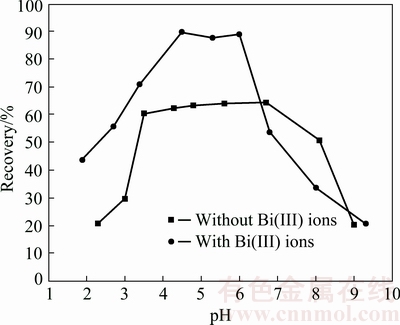
Fig. 3 Recovery of rutile before and after adsorption of Bi(III) ions in presence of nonyl hydroxamic acid (400 mg/L)
With the increase of pH, the competition was more and more fierce, the adsorption of nonyl hydroxamic acid on the rutile surface was more and more difficult, and thus the activating sites were occupied by OH- ions.
Whether pH was greater than 7.0 or less then 3.5, the activating sites were occupied by OH- ions or dissolved, resulting in the decrease of rutile flotation. The artificial increase of new activating sites was feasible for the increase of rutile flotation. After addition of Bi(III) ions, the flotation recovery of rutile was obviously improved and over 91% of rutile particles floated at pH (4.5±0.2), during which the recovery was only 62% without Bi(III) ions. The flotation recovery could increase in the studied pH range.
3.2 Adsorption amount measurement
The adsorption amount of nonyl hydroxamic acid on the rutile surface in the presence/absence of Bi(III) ions as a function of pH is presented in Fig. 4. According to Fig. 4, it could be seen that the pH range of 4.0-7.0 was the optimal for nonyl hydroxamic acid adsorption without Bi(III) ions, which was very consistent with the micro-flotation process. After addition of Bi(III) ions, the adsorption amount of nonyl hydroxamic acid was greatly improved from pH 2.3 to 9.7, which fully suggested that the adsorption amount of nonyl hydroxamic acid was a key factor that can determine the flotation recovery. With the increase of the collector adsorption amount, the hydrophobicity of mineral surface increased, resulting in the improved floatability of mineral [21-23]. The adsorption amount remained stable in the pH range of 4.0-7.0, in which the adsorption equilibrium of nonyl hydroxamic acid negative ions and OH- ions on the rutile surface was rather decisive. The adsorption amount decreased till the pH value was over 8, indicating that OH- ions unlawfully occupied the activating sites.

Fig. 4 Adsorption amount of nonyl hydroxamic acid on rutile surface before and after adsorption of Bi(III) ions as function of pH
3.3 Zeta potential measurement
In Fig. 5, a Malvern instrument was used to investigate the Zeta potentials on the rutile surface in the absence and presence of Bi(III) ions. The results showed that isoelectric point (IEP) of rutile particles appeared at pH (3.7±0.1) approximately almost in accordance with the previous value reported by PARKS [24]. After adsorption of 1×10-4 mol/L Bi(III) ions, Zeta potentials on the rutile surface moved to more positive values and the IEP appeared at pH (4.2±0.1) approximately. According to many reports, the Zeta potential of mineral surface would show a declined tendency after addition of salt solution because the thickness of electric double layer was compressed [25-27], indicating that the existing form of Bi(III) ions in acidic solution (the studied pH range) was not disengaged Bi(III) ions, which was further confirmed by the distribution of Bi(III) ions (Fig. 6). From Fig. 6, it could be shown that hydroxyl compounds (Bi(OH)2+ and 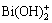 ) were the main existing species at pH 3.5-7.0, so that it could be concluded that hydroxyl compounds were the activating species of Bi(III) ions in rutile flotation. The results of Zeta potentials demonstrated that the adsorption of species containing bismuth with positive charge onto rutile surfaces rendered a positive shift of the Zeta potential. The Zeta potential on the rutile surface shifted to more negative values in the presence of nonyl hydroxamic acid, and thus it could be inferred that the attractive force between nonyl hydroxamic acid and rutile surface was larger than the electrostatic repulsion force (especially at pH 7-11). Therefore, nonyl hydroxamic acid might be adsorbed on the rutile surface by chemical adsorption through covalent bond.
) were the main existing species at pH 3.5-7.0, so that it could be concluded that hydroxyl compounds were the activating species of Bi(III) ions in rutile flotation. The results of Zeta potentials demonstrated that the adsorption of species containing bismuth with positive charge onto rutile surfaces rendered a positive shift of the Zeta potential. The Zeta potential on the rutile surface shifted to more negative values in the presence of nonyl hydroxamic acid, and thus it could be inferred that the attractive force between nonyl hydroxamic acid and rutile surface was larger than the electrostatic repulsion force (especially at pH 7-11). Therefore, nonyl hydroxamic acid might be adsorbed on the rutile surface by chemical adsorption through covalent bond.
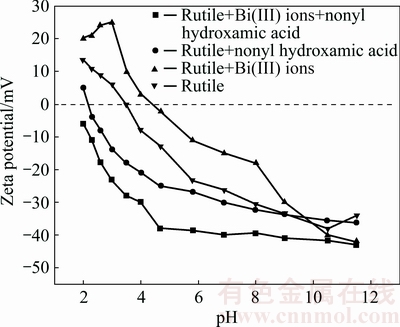
Fig. 5 Zeta potential of rutile surface as function of pH
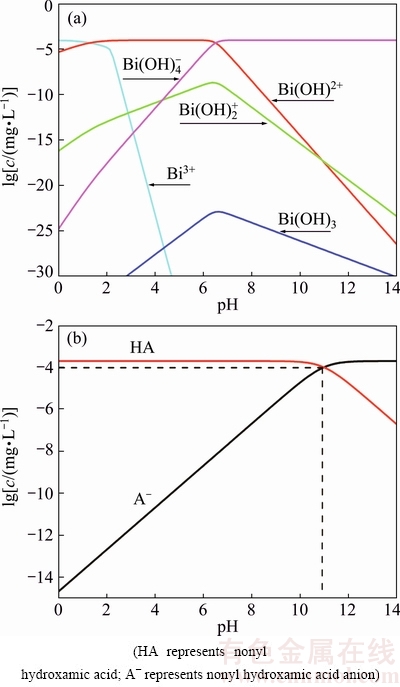
Fig. 6 Distribution of Bi(III) ions (a) and nonyl hydroxamic acid (b) species as function of pH
Figure 6 shows the distribution of Bi(III) ions and nonyl hydroxamic acid species as a function of pH, and the results of Zeta potential experiment were explained. According to Bi(III) ions concentration, the advantages of activation component could be discussed. It was indicated that the best activating pH range to produce hydroxyl compounds (Bi(OH)2+ and 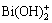 ) was consistent with the pH range of Bi(III) ions. Therefore, it was deduced that hydroxyl compounds (Bi(OH)2+ and
) was consistent with the pH range of Bi(III) ions. Therefore, it was deduced that hydroxyl compounds (Bi(OH)2+ and 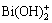 ) were major components of Bi(III) ions to active the rutile flotation. And the chemical reaction was speculated to occur on the rutile surface as follows:
) were major components of Bi(III) ions to active the rutile flotation. And the chemical reaction was speculated to occur on the rutile surface as follows:

The involved hydrolysis equilibria of Bi(III) ions are listed as follows:
Bi3++OH-=Bi(OH)2+,
β1=[Bi(OH)2+]/[Bi3+][OH-]=1012.7 (2)
Bi3++2OH-=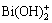 ,
,
β2=[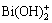 ]/[Bi3+][OH-]2=1015.8 (3)
]/[Bi3+][OH-]2=1015.8 (3)
Bi3++3OH-=Bi(OH)3,
β3=[Bi(OH)3(aq)]/[Bi3+][OH-]3=109.1 (4)
Bi3++4OH-=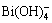 ,
,
β4=[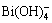 ]/[Bi3+][OH-]4=1035.2 (5)
]/[Bi3+][OH-]4=1035.2 (5)
where β1, β2, β3 and β4 are cumulative stability constants. It was supposed that Bi(III) ions represented the total concentration of components in the solution, and thus the concentration of each component was given as follows (the top concentration of bismuth nitrate was 1×10-4 mol/L):
[Bi]=[Bi3+]+[Bi(OH)2+]+[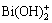 ]+[Bi(OH)3(aq)]+[
]+[Bi(OH)3(aq)]+[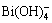 ]=[Bi3+](1+β1[OH-]+β2[OH-]2+β3[OH-]3 +β4[OH-]4) (6)
]=[Bi3+](1+β1[OH-]+β2[OH-]2+β3[OH-]3 +β4[OH-]4) (6)
Define αM for the reaction coefficient:
αM=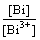 =1+β1[OH-]+β2[OH-]2+β3[OH-]3+β4[OH-]4 (7)
=1+β1[OH-]+β2[OH-]2+β3[OH-]3+β4[OH-]4 (7)
Concentrations of components:
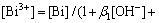
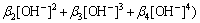 (8)
(8)
lg[Bi3+]=lg [Bi]-lg(1+10pH+β1-14+102pH+β2-2×14+103pH+β3-3×14+104pH+β4-4×14) (9)
lg [Bi(OH)2+]=lg β1+lg [Bi3+]+pH-14 (10)
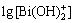 =lg β2+lg [Bi3+]+2(pH-14) (11)
=lg β2+lg [Bi3+]+2(pH-14) (11)
lg [Bi(OH3(aq))]=lg β3+lg [Bi3+]+3(pH-14) (12)
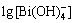 =lg β4+lg [Bi3+]+4(pH-14) (13)
=lg β4+lg [Bi3+]+4(pH-14) (13)
3.4 XPS analysis
Through XPS, the compositions on the rutile surface after adsorption of Bi(III) ions were investigated. Figure 7(a) shows the survey scan XPS spectra of rutile treated with Bi(III) ions over a binding energy range of 100-1300 eV. From Fig. 7(a), it was obviously conscious of the XPS spectra of Ti, O and Bi. The high-resolution XPS spectra of O, Ti and Bi elements are shown in Figs. 7(b), (d) and (c), respectively. From Fig. 7(b), a major part of the oxygen presented on the rutile and/or adsorbed water surface at all potentials included O2- and OH- species. The XPS spectrum of Ti 2p peaks at potentials of 458.1 and 464.0 eV is shown in Fig. 7(c). The characteristic of these peaks were obviously attributed to the XPS spectrum of Ti 2p in TiO2 [28,29]. The XPS spectrum of the Bi 4f peak of rutile obtained after adsorption of Bi(III) ions is presented in Fig. 7(d). After treatment of Bi(III) ions, the Bi 4f5/2 XPS bands appeared on the rutile surface, and thus the adsorption of Bi(III) ions onto the rutile surface was related to Bi(III) ions exchange or Bi(III) hydroxides covering. Compared with the binding energy of Ti 2p, it had no effect on the chemical environment around the Ti atom. There were two ways for adsorption of Bi(III) ions on the rutile surface. Firstly, Bi(III) ions occupied the vacancies after Ca2+, Mg2+ and Fe2+ (the impurity atoms on rutile surface) were dissolved in acidic solution. Secondly, the rutile surface was covered with Bi(III) ions in the form of hydroxides. Bi(III) ions had not formed the chemical bond with Ti or O (in Ti—O) atoms. The XPS spectra of the Bi 4f peak occurred with the theoretical value deviation [30,31], which indicated that Bi(III) ions around chemical environment changed.
Based on above results and discussion, Fig. 8 suggested a potential mechanism of two-step sequential method depicting modification of rutile surfaces with Bi(III) ions.
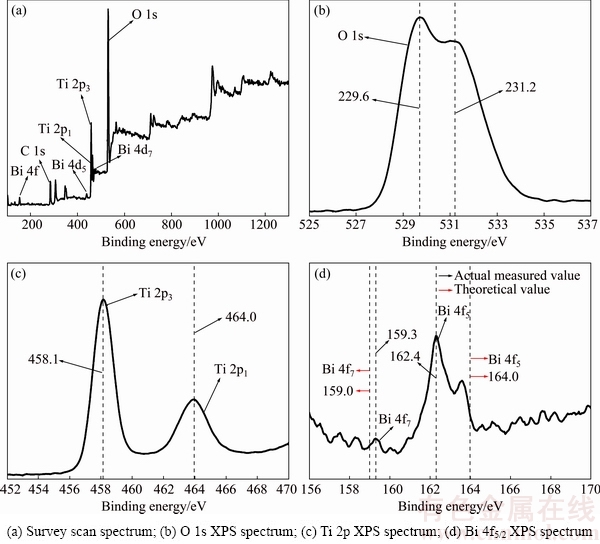
Fig. 7 Survey scan and high-resolution XPS spectra of rutile after Bi(III) adsorption ([Bi3+]=1×10-5 mol/L)
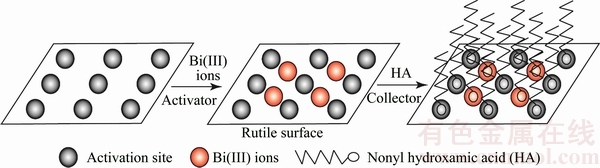
Fig. 8 Active particles of rutile surface before and after adsorption of Bi(Ⅲ) ions
4 Conclusions
1) After the addition of Bi(III) ions, the flotation recovery of rutile achieved an increase from 62% to 91%.
2) There were two ways for adsorption of Bi(III) ions on the rutile surface. Firstly, Bi(III) ions occupied the vacancies after Ca2+, Mg2+ and Fe2+ (the impurity atoms on the rutile surface) were dissolved in the acidic solution. Secondly, the rutile surface was covered with Bi(III) ions in the form of hydroxides.
3) After activation of Bi(III) ions, the nonyl hydroxamic acid was used to modify the rutile surface further. The results showed a great improvement in both the adsorption amount of nonyl hydroxamic acid and the floatability of rutile as expected. In addition, the results of Zeta potential and XPS verified the ability to establish a covalently attached nonyl hydroxamic acid on the rutile surface.
References
[1] LI Ting, WU Yun-long, WANG Qiu-fan, ZHANG Dao-hong, ZHANG Ai-qing, MIAO Meng-he. TiO2 crystalline structure and electrochemical performance in two-ply yarn CNT/TiO2 asymmetric supercapacitors [J]. Journal of Materials Science, 2017, 52(13): 7733-7743.
[2] NAM I, PARK J, Park S, Bae S, Yoo Y G, Han J W, Yi J. Observation of crystalline changes of titanium dioxide during lithium insertion by visible spectrum analysis [J]. Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics, 2017, 19(20): 13140-13146.
[3] Wang Jun, Cheng Hong-wei, Zhao Hong-bo, Qin Wen-qing, Qiu Guan-zhou. Flotation behavior and mechanism of rutile with nonyl hydroxamic acid [J]. Rare Metals, 2016, 35(5): 419-424.
[4] Bulatovic S, Wyslouzil D M. Process development for treatment of complex perovskite, ilmenite and rutile ores [J]. Minerals Engineering, 1999, 12(12): 1407-1417.
[5] Liu Qi, Peng Yong-jun. The development of a composite collector for the flotation of rutile [J]. Minerals Engineering, 1999, 12(12): 1419-1430.
[6] Sun Lei, Hu Yue-hua, Sun Wei. Effect and mechanism of octanol in cassiterite flotation using benzohydroxamic acid as collector [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2016, 26(12): 3253-3257.
[7] Tan Xin, He Fa-yu, Shang Yan-bo, Yin Wan-zhong. Flotation behavior and adsorption mechanism of (1-hydroxy-2-methyl-2- octenyl) phosphonic acid to cassiterite [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2016, 26(9): 2469-2478.
[8] DENG Lan-qing, ZHAO Gang, ZHONG Hong, WANG Shuai, LIU Guang-yi. Investigation on the selectivity of N-((hydroxyamino)- alkyl) alkylamide surfactants for scheelite/calcite flotation separation [J]. Journal of Industrial and Engineering Chemistry, 2016, 33: 131-141.
[9] YU Jun, GE Ying-yong, HOU Jing-tao. Behavior and mechanism of collophane and dolomite separation using alkyl hydroxamic acid as a flotation collector [J]. Physicochemical Problems of Mineral Processing, 2016, 52(1): 155-169.
[10] Marion C, Jordens A, Li R, Rudolph M, Waters K E. An evaluation of hydroxamate collectors for malachite flotation [J]. Separation and Purification Technology, 2017, 183: 258-269.
[11] Albrecht T W J, Addai M J, Fornasiero D. Critical copper concentration in sphalerite flotation: Effect of temperature and collector [J]. International Journal of Mineral Processing, 2016, 146: 15-22.
[12] Chandra A P, Puskar L, Simpson D J, Gerson A R. Copper and xanthate adsorption onto pyrite surfaces: Implications for mineral separation through flotation [J]. International Journal of Mineral Processing, 2012, S114-117(8): s16-s26.
[13] Fan X, Rowson N A. The effect of Pb(NO3)2 on ilmenite flotation [J]. Minerals Engineering, 2000, 13(2): 205-215.
[14] Han Jun-wei, Jiao Fen, Liu Wei, Qin Wen-qing, Xu Tan, Xue Kai, Zhang Tian-fu. Innovative methodology for comprehensive utilization of spent MgO-Cr2O3 bricks: Copper flotation [J]. ACS Suatainable Chemistry & Engineering, 2016, 4(10): 5503-5510.
[15] Liu Wei-jun, Zhang Shi-qiu, Wang Wei-qing, Zhang Jie, Yan Wu, Deng Jie, FENG Qi-ming, HUANG Yang. The effects of Ca(II) and Mg(II) ions on the flotation of spodumene using NaOL [J]. Minerals Engineering, 2015, 79: 40-46.
[16] Fornasiero D, Ralston J. Cu(II) and Ni(II) activation in the flotation of quartz, lizardite and chlorite [J]. International Journal of Mineral Processing, 2005, 76(1-2): 75-81.
[17] Wu C, Chen M, Skelton A A, Cummings P T, Zheng T. Adsorption of RGD tripeptide onto the negatively charged rutile (110) mediated by cations: The effect of surface hydroxylation [J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2013, 5(7): 2567-2579.
[18] Ediati R, Ulfa M, Fansuri H, Ramli Z, NUR H, Prasetyoko D. Influence of TiO2/TS-1 calcination on hydroxylation of phenol [J]. Journal of Mathematical & Fundamental Sciences, 2014, 46(1): 76-90.
[19] Griffiths D M, Rochester C H. Infrared study of the adsorption of acetone on rutile [J]. Journal of the Chemical Society Faraday Transactions, 1978, 74(74): 403-417.
[20] Nuri O S, Mehdilo A, Irannajad M. Influence of microwave irradiation on ilmenite surface properties [J]. Applied Surface Science, 2014, 311(9): 27-32.
[21] Qin Wen-qing, Jiao Fen, Sun Wei, Wang Xing-jie, Liu Bei, Wang Jun, Zeng Ke, Wei Qian, Liu Kai. Effects of sodium salt of N,N-dimethyldi-thiocarbamate on floatability of chalcopyrite, sphalerite, marmatite and its adsorption properties [J]. Colloids & Surfaces A: Physicochemical & Engineering Aspects, 2013, 421(11): 181-192.
[22] Leppinen J O. FTIR and flotation investigation of the adsorption of ethyl xanthate on activated and non-activated sulfide minerals [J]. International Journal of Mineral Processing, 1990, 30(3-4): 245-263.
[23] Jiang Hao, Sun Zhong-cheng, Xu Long-hua, Hu Yue-hua, Huang Kai, Zhu Shu-sheng. A comparison study of the flotation and adsorption behaviors of diaspore and kaolinite with quaternary ammonium collectors [J]. Minerals Engineering, 2014, 65: 124-129.
[24] Parks G A. The isoelectric points of solid oxides, solid hydroxides, and aqueous hydroxo complex systems [J]. Chemical Reviews, 1965, 65(2): 177-198.
[25] Yu Xue-wen, Ruan Dian-bo, Wu Chang-cheng, Jing Wang, Shi Zhi-qiang. Spiro-(1,1′)-bipyrrolidinium tetrafluoroborate salt as high voltage electrolyte for electric double layer capacitors [J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2014, 265: 309-316.
[26] Han T, Park M S, Kim J, Kim J H, Kim K. The smallest quaternary ammonium salts with ether groups for high-performance electrochemical double layer capacitors [J]. Chemical Science, 2016, 7(3): 1791-1796.
[27] de Lara L S, Rigo V A, Michelon M F, Metin C O, Nguyen Q P, Miranda C R. Molecular dynamics studies of aqueous silica nanoparticle dispersions: Salt effects on the double layer formation [J]. Journal of Physics Condensed Matter, 2015, 27(32): 325101.
[28] Hashimoto S, Tanaka A. Alteration of Ti 2p XPS spectrum for titanium oxide by low-energy Ar ion bombardment [J]. Surface & Interface Analysis, 2002, 34(1): 262-265.
[29] Okada K, Uozumi T, Kotani A. Charge-transfer satellites in Ti 2p XAS and XPS of Ti compounds [J]. Carbohydrate Research, 1993, 32(S2): s281-s291.
[30] Suzer S, Ertas N, Ataman O Y. XPS characterization of Bi and Mn collected on atom-trapping silica for AAS [J]. Applied Spectroscopy, 1999, 53(4): 479-482.
[31] Tanaka K, Takaki H, Koyama K, Noguchi S. XPS study on the electronic structure of Bi2Sr2Ca(1-x)Nd(x)Cu2O(y) [J]. Japanese Journal of Applied Physics, 1990, 29(9): 1658-1663.
肖 巍1,2,曹 攀1,2,梁倩楠1,2,黄小涛1,2,李开运1,2,张雁生1,2,覃文庆1,2,邱冠周1,2,王 军1,2
1. 中南大学 生物冶金教育部重点实验室,长沙 410083;
2. 中南大学 资源加工与生物工程学院,长沙 410083
摘 要:通过单矿物浮选、动电位测试、吸附量测试和X射线光电子能谱研究Bi(III)在金红石-水界面的吸附行为和机制。单矿物浮选结果表明,加入Bi(III)后,金红石的浮选回收率由62%提高到91%。添加Bi(III)可以增加活性位点,降低壬基异羟肟酸阴离子与OH-离子之间的竞争吸附,这是Bi(III)能够活化金红石浮选的本质。Bi(III)吸附在金红石表面,导致Zeta电位正移,有利于壬基异羟肟酸的吸附。XPS结果显示,Bi(III)吸附前后,钛原子周围的化学环境没有发生变化。Bi(III)在金红石-水界面有两种吸附方式:一种是Ca2+、Mg2+和Fe2+溶解后,Bi(III)占据其空位;另一种是Bi(III)以羟基化合物的形式覆盖在金红石表面。
关键词:金红石;浮选;Bi(III)活化;竞争吸附;活性位点
(Edited by Bing YANG)
Foundation item: Project (51474254) supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China; Project (2013M531813) supported by the China Postdoctoral Science Foundation; Project (2016zzts111) supported by the Independent Exploration and Innovation Program of Central South University, China; Project (CSUZC201715) supported by Open-End Fund for the Valuable and Precision Instruments of Central South University, China
Corresponding author: Jun WANG; Tel: +86-13975808100; E-mail: wjwq2000@126.com
DOI: 10.1016/S1003-6326(18)64668-0

