文章编号:1004-0609(2012)10-2762-06
热传导系数对TC4钛合金热变形过程摩擦因数测定的影响
陶 欢1,曾卫东1,朱艳春1,邰清安2,李晓光2,李治华2
(1. 西北工业大学 材料学院,西安 710072;
2. 沈阳黎明航空发动机(集团)有限责任公司,沈阳 110043)
摘 要:对TC4钛合金在变形温度为940 ℃、外径、内径和高度之比为20:10:7的圆环进行圆环镦粗实验,并采用有限元软件DEFORM-3D对镦粗过程进行模拟。结果表明:热传导系数对摩擦因数的测定有很大影响,热传导系数增加导致工件与模具的接触面温度下降,摩擦增加;对于不同的润滑介质应采用不同的热传导系数进行模拟,从而建立不同的理论校准曲线。采用不同的热传导系数分别建立玻璃润滑和干摩擦条件下的理论校准曲线,结合圆环镦粗实验,最终得出TC4钛合金940 ℃高温变形时在干摩擦和玻璃润滑条件下的摩擦因数值分别为0.59和0.42。
关键词:圆环镦粗实验;有限元模拟;热传导系数;摩擦因数
中图分类号:TG301 文献标志码:A
Effect of heat transfer coefficient on measurement of
friction factor in hot deformation of Ti-6Al-4V alloy
TAO Huan1, ZENG Wei-dong1, ZHU Yan-chun1, TAI Qing-an2, LI Xiao-guang2, LI Zhi-hua2
(1. School of Materials Science and Engineering, Northwestern Polytechnical University, Xi’an 710072, China;
2. Avic Shenyang Liming Aero-Engine (Group) Co., Ltd., Shenyang 110043, China)
Abstract: The ring-compression test of Ti-6Al-4V alloy was carried out at 940 ℃ and the ratio of outer diameter, inner diameter, height of 20:10:7. And the ring compression process was simulated by means of DEFORM-3D software. The results show that the effect of heat-transfer coefficient on measurement of friction factor is significant. The increase of heat-transfer coefficient results in the decrease of interfacial temperature between the workpiece and dies, and in turn leads to the increase of friction. Therefore, for various lubricant media, different heat-transfer coefficients should be chosen to conduct the FE simulation and establish different calibration curves. Combined with the ring-compression test, different heat-transfer coefficients for glass lubricant and dry friction condition are selected to establish the calibration curves, and finally the friction factors of TC4 titanium alloy under high temperature (940 ℃) deformation for dry friction and glass lubricant condition are determined to be about 0.59 and 0.42, respectively.
Key words: ring-compression test; FE simulation; heat-transfer coefficient; friction factor
基金项目:国家自然科学基金资助项目(51075333);凝固技术国家重点实验室开放课题(35-TP-2009)
收稿日期:2011-11-22;修订日期:2012-03-01
通信作者:曾卫东,教授,博士;电话:029-88494298;E-mail: zengwd@nwpu.edu.cn
金属塑性加工过程中的能量消耗、变形特性与规律、工具磨损、产品质量和生产效率等均与摩擦条件密切相关,并受其严重影响。确定接触面间的摩擦因数对了解金属与模具间的接触、延长模具寿命、提高生产效率等具有重要意义[1-2]。在摩擦因数的众多测定方法中,圆环镦粗法被认为是一种简单有效的方法,而应用圆环镦粗法测定摩擦因数必须先确定理论校准曲线[3]。
对于圆环镦粗理论校准曲线的确定,前人做了大量的研究。AVITZUR等[4]和KUDO[5]奠定了解析法(上限法,滑移线法,下限法)的理论基础;张明如等[6-8]用解析法结合圆环镦粗实验测定了不同材料、不同润滑条件下的摩擦因数。解析法无法考虑变形过程中几何条件与边界条件的变化,限制了该方法的应用;SOFUOGLU等[9]采用物理模拟技术(PMT)结合有限元法(FEM)得出,摩擦因数理论校准曲线会因材料的特性、实验条件的不同而变化;ROBINNSON等[10]也认为,在研究体积成形中的摩擦机制时物理模拟实验结合有限元模拟是一种简单而又高效的方法,但是物理模拟实验所采用的材料与实际情况存在较大的差距。近年来,随着有限元技术的发展和成熟,商用有限元软件的广泛应用,有限元法已成为塑性加工过程分析的有力工具之一。由于有限元法可以正确地处理摩擦边界和传热边界条件,准确地模拟圆环镦粗过程中金属流动和形状尺寸变化规律,因此,圆环镦粗结合有限元法逐渐成为测定摩擦因数的主要手段,由此确定的理论校准曲线更接近实际塑性加工过程中摩擦条件。
与此同时,工件与模具接触面间的热传导条件在金属塑性成形过程中起着重要的作用。在热成型过程中,热传导系数和摩擦因数共同作用于接触面之间,并影响材料流动[11]。而在传统的圆环镦粗有限元模拟过程中,没有考虑到不同界面润滑条件下热传导系数不同的情况,不管何种润滑剂均采用软件默认的热传导系数值,这样所得的结果是不准确的,在国内外相关报道也很少见。本文作者应用大型商用有限元软件DEFORM-3D针对不同热传导系数进行TC4钛合金高温变形的有限元模拟,研究热传导系数在摩擦因数测定中的影响,并结合圆环镦粗实验确定干摩擦和玻璃润滑条件下TC4钛合金高温变形的摩擦因数值。
1 圆环镦粗实验及模拟
1.1 圆环镦粗实验
选用TC4钛合金作为实验材料。圆环镦粗实验在1 000 t电动螺旋压力机上进行。镦粗时,上下模具材料选用工厂常用的4Cr5W2VSi,这是一种空冷硬化的热作模具钢。在中温下具有较高的热强度、硬度、耐磨性、韧性和较好的热疲劳性能。其化学成分如下(GB/T 1299—2000,质量分数,%):C 0.32~0.42,Si 0.80~1.20,Mn≤0.04,Cr 4.50~5.50,W 1.60~2.40,V 0.60~1.00,P≤0.30,S≤0.30。圆环尺寸比例采用20:10:7(外径do 40 mm、内径di 20 mm、高度14 mm)进行实验。钛合金热模锻通常采用玻璃润滑剂,因此实验选用玻璃润滑剂和干摩擦两种条件进行圆环镦粗实验,将玻璃润滑剂均匀涂覆在整个试样表面,随后将试样放入炉温为940 ℃的加热炉,模具预热温度为150~300 ℃,试样由加热炉中取出,直接置于模具上进行变形量为30%和50%的圆环镦粗实验。为了保证实验的可重复性和准确性,每个条件重复做3个试样。实验后用游标卡尺测量圆环的内径和高度,内径在每个试样的上、中、下3个面各测两次,测6个值;高度沿圆周方向每隔120°测一次,测3个值。每个条件下3个圆环的平均值作为实测值。
1.2 有限元模拟
由于有限元模拟能够提供圆环镦粗过程的各种信息,可以与实际圆环压缩实验进行比较,在本模拟中采用有限元模拟软件DEFORM-3D进行计算。模拟所用试样材料为TC4钛合金。圆环的具体尺寸与实验用试样尺寸一致。有限元模拟的初始条件如下:圆环镦粗模拟过程初始温度取940 ℃,上下模设为刚性模具,上模压下量为每子步0.05 mm,下模静止不动,变形量为50%时结束实验。模具初始温度为200 ℃,摩擦因数m取0~1.0。由于圆环呈轴对称,所以选取1/2部分进行模拟,划分网格数约为40 000个。利用有限元软件自带的测量工具记录不同条件和压下量情况下的内径变化量,从而绘制摩擦因数测定的理论校准曲线。
2 结果分析与讨论
2.1 圆环镦粗实验结果
每种条件下每个试样内径的平均值以及3个试样的平均值列于表1中。从表1可以看出,镦粗后试样尺寸具有很好的一致性,说明测量过程控制得很好。图1所示为不同条件下变形后圆环镦粗试样的照片。从图1可以看出,镦粗后的试样表面较为光洁,形状完整,表明实验过程控制得很好,为摩擦因数的准确测定奠定了基础。
表1 20:10:7圆环在不同条件下镦粗后内径尺寸
Table 1 Inner diameters of rings with ratio of 20:10:7 deformed under different deformation conditions
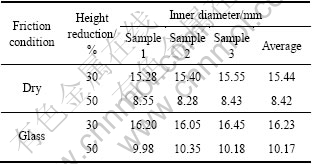

图1 不同条件下圆环镦粗试样照片
Fig. 1 Photos of ring compression test specimens under different conditions: (a) Height reduction of 30%, glass lubrication; (b) Height reduction of 30%, dry friction; (c) Height reduction of 50%, glass lubrication; (d) Height reduction of 50%, dry friction
2.2 热传导系数的影响
热传导系数是传热过程中影响热量传递的一个重要因数,它反映传热过程的强烈程度。金属塑性成型过程总是伴随着热量的产生和传递,它会影响润滑条件、金属的流动性以及产品的最终质量,确定热传导系数对准确测量摩擦因数具有重要意义。研究热传导系数对圆环镦粗实验的影响,国内外几乎全部采用数值模拟的方法。而随着大型商用有限元软件DEFORM-3D的发展,该软件逐渐成为了实现这一模拟的有力工具。为了证明热传导系数对摩擦因数测定的影响,在本实验中,采用TC4钛合金在940 ℃变形的圆环镦粗过程进行研究,选取摩擦因数(m)为0.35,热传导系数(h)分别为1、5[12]、10[13]、15[14]、20[12]和25 kW/(m2·K)进行有限元模拟,以圆环内径变化量为纵坐标,以压下量为横坐标绘制曲线,结果如图2所示。
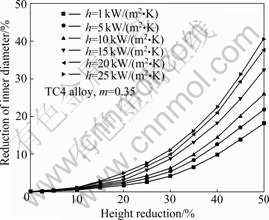
图2 热传导系数对理论校准曲线的影响
Fig. 2 Effect of heat transfer coefficient on calibration curves
由图2可以看出,在相同的摩擦因数条件下,随着热传导系数的逐渐增大,曲线不断上移,内径减小比率增大。这是由于热传导系数的增大,导致坯料与模具之间的热量传递加快,使靠近模具的金属流动性下降,类似于增大了摩擦的效果。而在同一摩擦因数条件下,不同的热传导系数所得的内径变化量相差很大,以变形量为50%为例,当热传导系数分别取10和20 kW/(m2·K)时,内径变化量相差达9.3%。由此可知,在有限元模拟过程中,热传导系数对摩擦因数的测定有很大影响,对于不同的润滑介质,应采用不同的热传导系数分别建立摩擦因数理论校准曲线。
2.3 摩擦因数的测定
在进行圆环镦粗过程有限元模拟时,热传导系数的增加,相当于增大了工件与模具之间的热传导,工件温度迅速降低,这相当于增大了接触面积间的摩擦因数,因此,对于不同的润滑条件,在进行圆环镦粗实验测定理论校准曲线时,应采用不同的热传导系数,建立不同的摩擦因数理论校准曲线。通过查阅相关文献,在本实验中,对玻璃润滑条件选取热传导系数为5 kW/(m2·K)进行模拟,与有限元软件DEFORM-3D所给默认值一致;对于干摩擦条件,选取热传导系数值为10 kW/(m2·K)。利用DEFORM-3D自带的测量工具,测出压下量分别为5%、10%、15%、20%、25%、30%、35%、40%、45%和50%时的内径变化量,然后采用Origin 8.0绘图软件,以压下量为横坐标,内径变化量为纵坐标,绘制理论校准曲线,结果如图3和4所示。
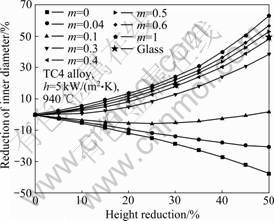
图3 玻璃润滑条件下摩擦因数理论校准曲线
Fig. 3 Friction calibration curves under glass lubrication condition
根据表1所得的实验结果,结合图3和4绘制的摩擦因数理论校准曲线,用线性插值法可以求出实际的摩擦因数。在变形量为30%和50%时,干摩擦条件下的摩擦因数分别为0.60和0.58,玻璃润滑条件下的摩擦因数分别为0.43和0.41,结果非常接近。由此得出,干摩擦条件的摩擦因数为0.59,玻璃润滑摩擦条件为0.42。
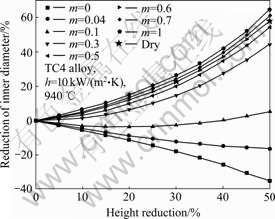
图4 干摩擦条件下摩擦因数理论校准曲线
Fig. 4 Friction calibration curves under dry friction condition
3 验证
为了验证实验结果的准确性,按照干摩擦时m=0.59、玻璃润滑时m=0.42进行模拟计算,模拟参数不变,模拟结果与实验结果的对比如图5所示,将圆环镦粗试样内径与模拟所得进行比较,结果如图6所示。从图5可以看出,模拟结果与实验结果吻合得很好;模拟所得内径值与圆环镦粗试样实测内径值十分接近,实验值分布在模拟曲线的两侧,经计算相对误差不超过3%(见图6),从而验证了本次模拟结果的正确性。
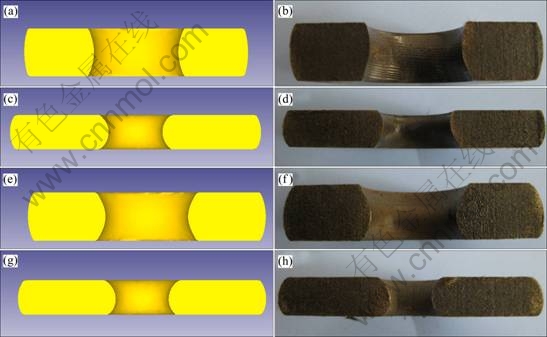
图5 圆环镦粗实验结果与模拟结果对比
Fig. 5 Comparison between ring compression test results and simulation: (a) m=0.42, height reduction of 30%; (b) Glass lubrication, height reduction of 30%; (c) m=0.42, height reduction of 50%; (d) Glass lubrication, height reduction of 50%; (e) m=0.59, height reduction of 30%; (f) Dry friction, height reduction of 30%; (g) m=0.59, height reduction of 50%; (h) Dry friction, height reduction of 50%
DEFORM等商用有限元模拟软件在热模锻情况下默认的摩擦因数为0.3,考虑到钛合金容易粘模,摩擦因数应该比0.3稍高。SHAHRIARI等[15]采用圆环 镦粗实验和有限元模拟相结合的方法测得Ni 115高温合金在玻璃润滑条件下摩擦因数为0.35,在干摩擦条件下摩擦因数为0.69,与本测定的结果较接近。PETERSEN等[16]通过比较两种摩擦模型,即常摩擦模型和广义摩擦模型,并通过补充圆环镦粗实验得出,在干摩擦条件下摩擦因数取0.5较为合适,在本实验条件下,所得干摩擦条件下的值为0.59,数值偏高的原因,是他们采用传统解析法绘制的理论校准曲线会降低摩擦因数值。EBRAHIMI等[17]采用石墨润滑剂进行了圆环镦粗实验,测得摩擦系数为0.24,而干摩擦条件下的摩擦系数为0.58,与本模拟条件的结果吻合。
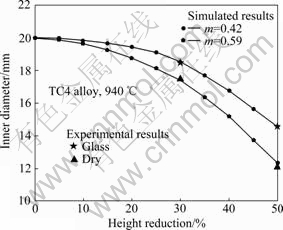
图6 镦粗后试样内径与模拟结果对比
Fig. 6 Comparison of inner diameters between sample results and simulation
4 结论
1) 有限元模拟TC4钛合金热变形过程中,热传导系数对摩擦因数的测定有显著影响,随着热传导系数的增加,圆环内径减小量增大。因此,不同的润滑条件下需采用不同的理论校准曲线进行计算。
2) 建立了TC4钛合金在干摩擦和玻璃润滑条件下940 ℃变形时摩擦因数理论校准曲线,测定其干摩擦条件下的摩擦因数为0.59,玻璃润滑条件下的摩擦因数为0.42,并得到了实验验证。
REFERENCES
[1] 张明如, 钟维淳. 高温摩擦因数的测量与分析[J]. 钢铁, 1998, 33(4): 24-26.
ZHANG Ming-ru, ZHONG Wei-chun. Measurement and analysis of high temperature friction coefficient by ring-compression test[J]. Iron and Steel, 1998, 33(4): 24-26.
[2] 惠媛媛, 唐文亭, 袁中岳. 圆环在平板间镦粗变形规律的数值模拟[J]. 铸造设备研究, 2005(1): 34-36.
HUI Yuan-yuan, TANG Wen-ting, YUAN Zhong-yue. Numerical simulation of the ring upsetting distortion rule between two plates[J]. Research Studies on Foundry Equipment, 2005(1): 34-36.
[3] 俞汉清, 陈金德. 金属塑性成形原理[M]. 北京:机械工业出版社, 1999: 153-155.
YU Han-qing, CHEN Jin-de. Metal forming method[M]. Beijing: China Machine Press, 1999: 153-155.
[4] AVITZUR B, SAUERWINE F R. Limit analysis of hollow disc forging[J]. Journal of Engineering for Industry, 1978, 100(3): 340-355.
[5] KUDO H. Some analytical and experimental studies of axisymmetric cold forging and extrusion[J]. International Journal of Mechanical Sciences, 1961, 3: 91-117.
[6] 张明如, 钟维淳. 用圆环压缩方法测量润滑剂的高温摩擦系数[J]. 马钢技术, 1997(1): 13-16.
ZHANG Ming-ru, ZHONG Wei-chun. Measurement of lubricant friction coefficient by ring-compression[J]. Masteel Technology, 1997(1): 13-16.
[7] SAHI M, RAHOUADJ R, HERBACH R, CHOULIER D. The influence of viscoplasticity in the interpretation of the ring test[J]. Journal of Material Processing Technology, 1996, 58: 286-292.
[8] CHEN C J, TZOU G Y, HUANG M N. Study on the twist compression forming of cylinder based on the upper bound and slab methods[J]. Journal of Materials Processing Technology, 2006, 174: 266-271.
[9] SOFUOGLU H, RASTY J. On the measurement of friction coefficient utilizing the ring compression test[J]. Tribology International, 1999, 32: 327-335.
[10] ROBINNSON T, OU H, ARMSTRONG C G. Study on ring compression test using physical modeling and FE simulation[J]. Journal of Materials Processing Technology, 2004, 153/154: 54-59.
[11] JOOYBARI M B, PILLINGER I, HARTLEY P, DEAN T A. Finite element simulation and experimental study of hot closed-die upsetting[J]. International Journal of Machine Tools and Manufacture, 1996, 36(9): 1021-1032.
[12] WILSON W R D, SCHMID S R, LIU J Y. Advanced simulations for hot forging: Heat transfer model for use with the finite element method[J]. Journal of Materials Processing Technology, 2004, 155/156: 1912-1917.
[13] ANDERSSON K, KIVIVUORI S, KORHONEN A S. Effect of the heat-transfer coefficient in ring-compression tests[J]. Journal of Materials Processing Technology, 1996, 62: 10-13.
[14] 李达人, 刘祖岩, 于 洋, 王尔德. W-40%Cu热加工摩擦因数与换热系数测定[J]. 粉末冶金技术, 2009, 27(3): 178-181.
LI Da-ren, LIU Zu-yan, YU Yang, WANG Er-de. Measurement of the friction-factor and the heat transfer coefficient between W-40wt%Cu and die during hot processing[J]. Powder Metallurgy Technology, 2009, 27(3): 178-181.
[15] SHAHRIARI D, AMIRI A, SADEGHI M H. Study on hot ring compression test of Nimonic 115 super alloy using experimental observations and 3D FEM simulation[J]. Journal of Materials Engineering and Performance, 2010, 19(5): 633-642.
[16] PETERSEN S B, MARTINS P A F, BAY N. Friction in bulk metal forming: A general friction model vs the law of constant friction[J]. Journal of Materials Processing Technology, 1997, 66: 186-194.
[17] EBRAHIMI R, NAJAFIZADEH A. A new method for evaluation of friction in bulk metal forming[J]. Journal of Materials Processing Technology, 2004, 152: 136-143.
(编辑 龙怀中)