DOI: 10.11817/j.issn.1672-7207.2017.05.012
半主动悬架系统刚度动态迭代跟踪控制
李仲兴1,李重重1,刘亚威1,李美2,徐兴3
(1. 江苏大学 汽车与交通工程学院,江苏 镇江,212013;
2. 海南大学 机电工程学院,海南 海口,570228;
3. 江苏大学 汽车工程研究院,江苏 镇江,212013)
摘要:为进一步提高车辆行驶平顺性,结合可变刚度半主动悬架系统的特点,提出动态迭代跟踪控制算法,并应用于可变刚度半主动悬架系统。基于Matlab/Simulink建立七自由度整车仿真模型。选取簧载质量加速度、悬架动行程和轮胎动载荷的均方根为平顺性评价指标,通过层次分析法确定各评价指标的权重系数,利用遗传算法确定典型工况下悬架最优刚度。采用动态迭代跟踪算法控制悬架刚度,根据所得刚度与最优刚度的差异确定控制算法的修正系数,在典型工况下使其控制参数与寻优所得参数吻合,并对其他工况下的控制效果进行验证。仿真结果表明:提出的控制算法在混合工况下能有效地使簧载质量加速度均方根减小6.34%,悬架动行程均方根减小7.35%,从而提高车辆行驶的平顺性。
关键词:半主动悬架;刚度可控;动态迭代跟踪;遗传算法;平顺性
中图分类号:TP272;U463.33+4.2 文献标志码:A 文章编号:1672-7207(2017)05-1204-07
Dynamic and trackable interation controls on stiffness of semi-active suspension system
LI Zhongxing1, LI Chongchong1, LIU Yawei1, LI Mei2, XU Xing3
(1. School of Automotive and Traffic Engineering, Jiangsu University, Zhenjiang 212013, China;
2. Mechanical and Electrical Engineering College, Hainan University, Haikou 570228, China;
3. Automotive Engineering Research Institute, Jiangsu University, Zhenjiang 212013, China)
Abstract: In order to improve the ride comfort of vehicles, a new control method named dynamic and trackable iteration control, which combined the advantages of semi-active suspension system, was proposed to control stiffness for semi-active suspension system. The 7POF simulation model of the vehicle was established by Matlab/Simulink. The root-mean-square values of body acceleration, dynamic suspension travel and tire load were chosen as evaluation indexes, and weight coefficients of the indexes were obtained by analytic hierarchy process method, and genetic algorithm was applied to get the optimal suspension stiffness in the typical condition. By using the dynamic and trackable iteration to control stiffness, and then according to the difference between the stiffness of computational and optimal, the correction coefficient of control algorithm was determined. Under typical conditions, parameters of control and optimization were identical, and control effects were verified under other conditions. The simulation results show that body acceleration and dynamic suspension travel decrease by 6.34% and 7.35% respectively under mixed conditions, and the ride comfort of vehicles is improved by the proposed control method.
Key words: semi-active suspension; controllable stiffness; dynamic and trackable interation; genetic algorithm; ride comfort
车辆行驶平顺性与操纵稳定性是一对矛盾,传统被动悬架当悬架参数确定后,悬架动力学性能也随之确定[1]。然而在不同的行驶工况下,人们对行驶平顺性与操纵稳定性的要求有所不同,为提升车辆对多种工况的适应能力,出现了刚度可调的半主动悬架,并已获得广泛应用[2]。可变刚度的半主动悬架系统能够根据路面状况、车辆载荷的变化调节悬架刚度,具有低频振动、抗道路冲击等优点,在多种工况下均能提高车辆乘坐舒适性[3]。对可变刚度半主动悬架系统实施控制,根据行驶工况调节悬架刚度或阻尼,可提高其对道路、载荷等方面的适应能力,从而改善车辆行驶平顺性。半主动悬架控制理论是车辆工程领域的重要研究热点[4-5],已形成PID控制、模糊控制、鲁棒控制等成熟的控制理论[6-8],这些控制理论均在一定程度上提升了悬架的性能。本文作者提出一种由迭代算法演变而来的动态迭代跟踪控制算法,该控制算法根据簧上质量实时振动情况(外部环境),得出不同的刚度迭代结果,再调节悬架系统刚度为迭代结果,并继续跟踪簧上质量振动,进行下一次刚度迭代,直到迭代结果趋于稳定。该控制算法离散趋近、逐步提升控制效果的特点,可以为半主动悬架控制提供一种新思路。
1 建立系统模型
1.1 刚度可变悬架车辆动力学模型
在刚度可变弹簧系统数学模型的基础上建立7自由度整车半主动空气悬架模型,某款轻型客车相关参数如表1所示。7个自由度分别为簧载质量质心处的垂向位移、车身侧倾、车身俯仰及4个非簧载质量向直位移。
表1 整车相关参数
Table 1 Parameters of vehicle
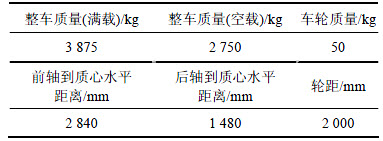
设4个悬架与簧载质量连接位置处的垂直位移为:ZfL0,ZfR0,ZrL0和ZrR0,则有
 (1)
(1)
式中:Zcb为簧载质量质心处垂直位移;θ为簧载质量的侧倾角;φ为簧载质量的俯仰角;lf和lr分别为前后轴簧载质量质心横轴线的水平距离;d为轮距。
4个悬架的悬架力为
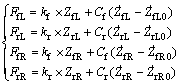 (2)
(2)
式中:FfL,FrL,FfR和FrR为4个悬架和簧载质量连接处的作用力;kf和kr分别为前后悬架的刚度;Cf和Cr分别为前后悬架减振器阻尼系数;ZfL,ZrL,ZfR和ZrR分别为左前轮、右前轮、左后轮、右后轮的垂直位移。根据牛顿第二定律建立7自由度整车半主动空气悬架模型:
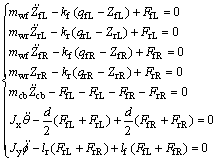 (3)
(3)
式中:qfL,qrL,qfL和qrR分别为左前轮、右前轮、左后轮和右后轮受到的路面垂直位移激励;mwf和mwr分别为前后轮胎质量;mcb为簧载质量;Jx为簧载质量绕其质心纵向轴线的转动惯量;Jy为簧载质量绕其质心横向轴线的转动惯量。
2 系统控制参数优化
2.1 确定目标函数
考虑车辆行驶平顺性,选取簧载质量均方根 (fACC)、轮胎动载荷均方根(fDTL)和悬架动行程均方根 (fSWS)为优化目标参数[9],选择线性加权和法建立多目标优化函数f(x),在赋予相应的加权系数并统一子目标量纲和量级后,建立优化目标函数为
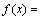
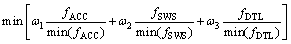 (4)
(4)
式中:ω1为簧载质量加速度均方根的加权系数;ω2 为悬架动行程均方根的加权系数;ω3为轮胎动载荷均方根的加权系数;min(fACC)为簧载质量加速度均方根在刚度可变范围内的最小值;min(fSWS)为悬架动行程均方根在刚度可变范围内的最小值;min(fDTL)为轮胎动载荷均方根在刚度可变范围内的最小值。
2.2 建立约束条件
悬架系统刚度和阻尼等参数优化设计时,为保证系统功能的实现、实用性与安全性等,对其优化变量提出以下约束条件:
1) 轮胎动载荷均方根直接影响车辆的操控稳定性和行驶安全性,当轮胎动载荷与整车质量之比(车轮相对动载荷)大于l时,车轮与地面附着力为0,从而失去驱动力和制动力,因此车轮与路面间的相对动载荷应当控制在合理范围内。当车轮相对动载荷均方根小于1/3时,车轮脱离地面的概率小于0.15%,可近似认为不会脱离地面[10]。
2) 当悬架动行程的均方根与限位行程之比小于1/3时,悬架系统撞击限位块的概率小于0.15%,可视为撞击不会发生[10]。
2.3 确定加权系数
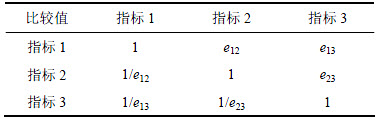
层次分析法(analytic hierarchy process)是一种多目标决策方法[11-13],该方法通过比较各指标之间的重要性确定各评价指标的加权系数。
eij代表指标i与指标j重要性的比较值,该方法规定同等重要为1,很重要为9。根据各评价指标之间重要性的比较可构造如表2所示的判断矩阵。
表2 判断矩阵
Table 2 Judgment matrix
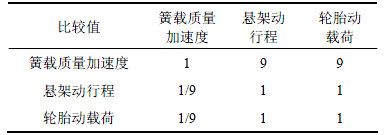
本文选取簧载质量加速度均方根、悬架动行程均方根和轮胎动载荷均方根为车辆行驶平顺性的评价指标。簧载质量加速度均方根是车辆平顺性的主要评价指标,因此相对于其他2个指标,簧载质量加速度均方根具有更高的重要性,而悬架动行程均方根和轮胎动载荷均方根具有相同的重要性。综上所述,得到本文各评价指标的判断矩阵,如表3所示。
表3 评价指标判断矩阵
Table 3 Judgment matrix of evaluation indexes
根据判断矩阵,按下述方法计算各评价指标的加权系数。
1) 计算判断矩阵行元素的乘向量:
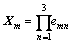 (5)
(5)
计算得Xm=[81, 1/9, 1/9]T。
2) 计算乘向量X的3次方根向量Hm:
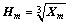 (6)
(6)
计算得Hm=[4.327, 0.4807, 0.4807]TT。
3) 计算向量Hm的正则向量β:
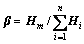 (7)
(7)
计算得β=[0.8,0.1,0.1],向量β即为各评价指标对应的加权系数,即簧载质量加速度均方根的加权系数ω1为0.8,悬架动行程均方根的加权系数ω2为0.1,轮胎动载荷均方根的加权系数ω3为0.1。
4) 检验判断矩阵一致性比率:
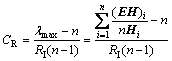 (8)
(8)
式中:当n=3时,经查表得RI=0.58,故经计算得出CR=-2.05<0.1,一致性检验通过。
2.4 基于遗传算法的控制参数优化
基于第1节建立的7自由度可变刚度半主动悬架系统Simulink仿真模型,以式(4)为优化目标函数,在MATLAB中编写遗传算法优化程序,其中遗传算法优化程序控制参数的选取为:群体规模为100,变异概率为0.065,交叉概率为0.73。算法终止条件是进化代数为300。前悬刚度(kf)取值范围为10~50 kN/m,后悬刚度(kr)取值范围为20~100 kN/m。在典型工况下(路面状况选取A,B及C级路面;车速选取80~110 km/h(A级路面),50~80 km/h(B级路面)及30~60 km/h(C级路面),间隔为10 km/h;载荷选取空载及满载)对前后可变半主动悬架刚度(kf,kr)进行寻优。表4和表5所示分别为满载及空载时,A级路面的前后可变刚度半主动悬架刚度(kf,kr)优化结果。
表4 A级路面满载优化结果
Table 4 Optimization results of class A full-load
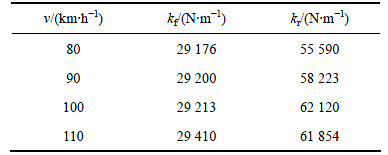
表5 A级路面空载优化结果
Table 5 Optimization results of class A road-load
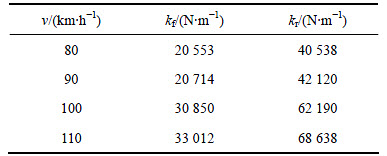
表6和表7所示分别为满载空载时,B级路面可变刚度半主动悬架刚度(kf,kr)优化结果。
表8和表9所示分别为满载及空载时,C级路面可变刚度半主动悬架刚度(kf,kr)优化结果。
根据表4~9的优化结果可以看出:在相同的路面等级和载荷条件下,前后悬架的刚度随着速度的增加而有增加的趋势,但增幅不大;在相同的路面等级和车速下,满载优化所得前后悬架刚度比空载的大。
表6 B级路面满载优化结果
Table 6 Optimization results of class B full load
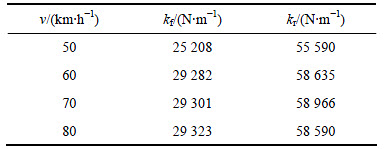
表7 B级路面空载优化结果
Table 7 Optimization results of class B road-load
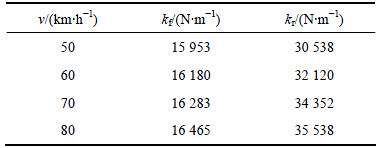
表8 C级路面满载优化结果
Table 8 Optimization results of class C full-load
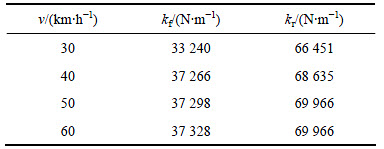
表9 C级路面空载优化结果
Table 9 Optimization results of class C road-load
3 基于动态迭代跟踪算法的系统控制
在传统迭代控制的基础上提出动态迭代跟踪控制,并将其应用于可变刚度半主动悬架系统的控制。该种控制方法实时监测簧载质量的振动信号,并将信号输入到控制器的迭代式中,计算出弹簧的刚度,执行器将弹簧的刚度切换至计算值;继续监测簧载质量的振动情况,重复上述步骤直至计算出的刚度趋于稳定(收敛)。此种控制方法动态监测簧载质量的振动情况,实时改变弹簧刚度,并逐步逼近控制的理想值,从而提高车辆乘坐舒适性。
3.1 确定初始迭代式
以车辆前悬架为例,初始迭代式是基于整车模型和牛顿第二定律,在车辆前悬架处,有
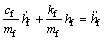 (9)
(9)
式中:cf和cr分别为前后悬架阻尼;kf和kr分别为前后悬架刚度;mf和mr分别为前后悬架位置处对应的簧载质量分量;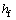 ,
,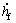 和
和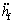 分别为前悬架处簧载质量垂向位移、速度和加速度;
分别为前悬架处簧载质量垂向位移、速度和加速度;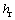 ,
,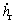 和
和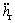 分别为后悬架处簧载质量垂向位移、速度和加速度。
分别为后悬架处簧载质量垂向位移、速度和加速度。
在单位时间内,对式(9)两端同时求均方根,得刚度、阻尼与簧载质量垂向加速度单位时间均方根的关系:
 (10)
(10)
式中: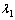 ,
,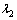 ,
,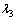 和
和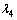 为修正系数;RMS为均方根。
为修正系数;RMS为均方根。
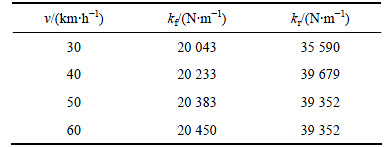
为验证式(10)的敛散性,在B级路面满载车速为60 km/h工况下,设定前悬架阻尼为8 300 N·s/m[14](空载阻尼5 800 N·s/m,后悬架阻尼为前悬架阻尼的2倍[15]),以10 s内监测到的簧载质量振动信号(簧载质量垂向位移h、速度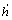 、加速度
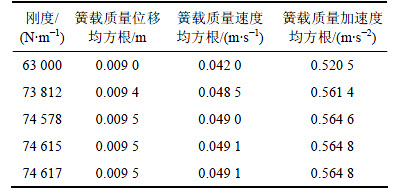
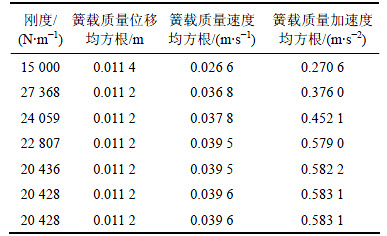
、加速度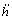 )的均方根代入迭代式。根据上述情况,不同初始刚度的迭代结果如表10和表11所示。式(10)具有比较严格的收敛性且为各评价指标的多项式,且不同的初始刚度(14 300和63 000 N/m)最终的收敛结果基本相同(两者之差为0.007%)。同样,对其他不同路面等级、载荷和车速的迭代结果都表明式(10)具有收敛的特性。
)的均方根代入迭代式。根据上述情况,不同初始刚度的迭代结果如表10和表11所示。式(10)具有比较严格的收敛性且为各评价指标的多项式,且不同的初始刚度(14 300和63 000 N/m)最终的收敛结果基本相同(两者之差为0.007%)。同样,对其他不同路面等级、载荷和车速的迭代结果都表明式(10)具有收敛的特性。
表10 初始刚度为14 300 N/m的迭代结果
Table 10 Iteration result for initial stiffness of 14 300 N/m
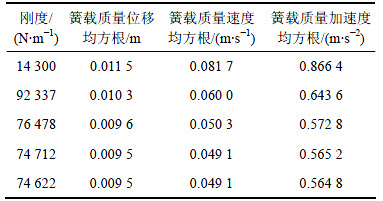
表11 初始刚度为63 000 N/m的迭代结果
Table 11 Iteration result for initial stiffness of 63 000 N/m
3.2 确定迭代式
然而,上述迭代结果与第二部分的参数寻优结果存在很大的差距,因此需要对初始迭代式的系数进行修正,使其结果与寻优结果之差小于5%。为确定刚度项和阻尼项系数改变对最终迭代结果的影响,通过仿真分析比较迭代后刚度的变化可知:在刚度项系数增大后,迭代的结果随之减小;阻尼项的系数增大后,迭代的结果随之增大。
根据上述定性分析,由于未修正的迭代结果大于(74 622 N/m)寻优结果(29 213 N/m),因此,在不改变阻尼项修正系数的同时修改刚度项的修正系数λ2,使其等于或接近寻优结果。本文采用最小二乘曲线拟合法,得到A级路面满载100 km/h和C级路面空载60 km/h的不同修正系数与迭代结果关系,如图2和图3所示。
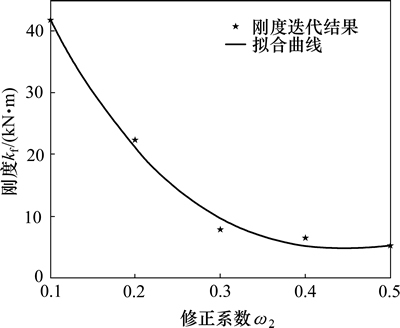
图1 A级路面满载100 km/h修正系数与迭代结果拟合曲线
Fig. 1 Correction coefficient and iterative fitting curve of class A full-load with speed of 100 km/h
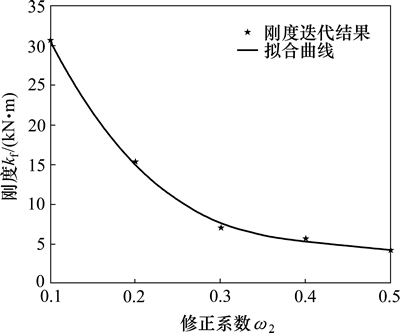
图2 C级路面空载60 km/h修正系数与迭代结果拟合曲线
Fig. 2 Correction coefficient and iterative fitting curve of class C road-load with speed of 60 km/h
根据上述曲线,并比较各自工况下寻优结果,得到最终的迭代式:
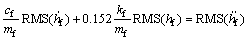 (11)
(11)
在A级路面和C级路面典型工况下,迭代式(11)的迭代结果如表10和表11所示。
对比表12和表13与表4和表9中的刚度寻优结果,相对误差分别为0.16%和1.11%,且其他速度区间和路况等级的迭代结果相对误差均在5%之内,故式(11)可以确定为迭代式。
表12 A级路面满载车速为100 km/h的迭代结果
Table 12 Iteration result of class A full load with speed of 100 km/h
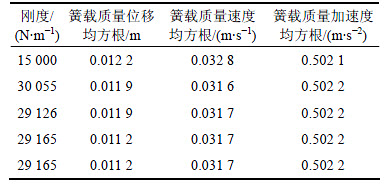
表13 C级路面空载车速为60 km/h的迭代结果
Table 13 Iteration result of class C road-load with speed of 60 km/h
3.3 控制流程
可变刚度半主动悬架动态迭代跟踪控制流程如图3所示。
基于整车模型的可变刚度半主动悬架系统刚度动态迭代跟踪控制,根据整车模型各悬架位置处的簧载质量垂向振动情况,对前后悬架的刚度实施短时跟踪计算,并通过执行器调节悬架刚度;继续跟踪新悬架参数下各悬架位置簧载质量振动情况,再次进行控制计算,层层迭代;当某次控制引起的簧载质量振动情况变化幅度小于某一阀值时(本文选取的阀值为簧载质量加速度均方根与前一次迭代结果之差小于0.000 2 m/s2),控制结束。
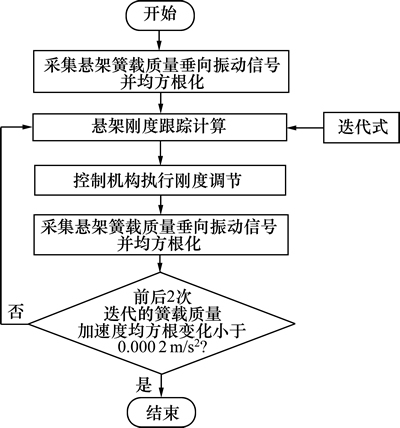
图3 可变刚度半主动悬架动态迭代跟踪控制流程
Fig. 3 Flow of dynamic and trackable interation control of variable stiffness semi-active suspension system
3.4 控制系统仿真分析
为验证动态迭代跟踪控制方案的有效性,在满载A级(80 km/h)—B级(60 km/h)—C级(50 km/h)混合工况下,比较控制前后悬架性能的变化。表14所示为实施动态迭代跟踪控制前后可变刚度半主动悬架性能的对比情况。
表14 控制实施前后悬架性能对比
Table 14 Passive suspension and semi-active suspension performance comparison
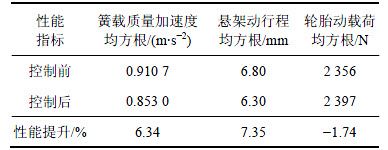
由表14可知:对可变刚度半主动悬架系统实施动态迭代跟踪控制后,车身垂向加速度均方根降低6.34%,悬架动行程均方根、降低7.35%,轮胎动载荷均方根上升1.74%。车身垂向加速度和悬架动行程均方根得到一定改善,悬架抗冲击能力提升尤为明显。轮胎动载荷均方根有小幅上升,但尚在允许范围内,对车辆性能影响不明显,满足国标规定的限值要求。
4 结论
1) 提出控制可变刚度半主动悬架系统的迭代式,并采用最小二乘法拟合修正系数与迭代刚度曲线,确定迭代式的修正系数,修正后的迭代结果与寻优结果之差小于5%,在此基础上,建立动态迭代跟踪控制算法。
2) 在满载混合工况下(A级路面车速80 km/h—B级路面车速级60 km/h—C级路面车速50 km/h),通过仿真验证控制效果,对比控制前后,簧载质量垂向加速度均方根降低6.34%,悬架动行程均方根降低7.35%,车辆行驶平顺性得到提高。
参考文献:
[1] 陈家瑞. 汽车构造[M]. 3版. 北京: 机械工业出版社, 2009: 199-225.
CHEN Jiarui. Automobile structure[M]. 3rd ed. Beijing: China Machine Press, 2009: 199-225.
[2] 姚嘉伶, 蔡伟义, 陈宁. 汽车半主动悬架系统发展状况[J]. 汽车工程, 2006, 28(3): 276-280.
YAO Jialing, CAI Weiyi, CHEN Ning. A review on the development status of automotive semi-active suspension systems[J]. Automotive Engineering, 2006, 28(3): 276-280.
[3] LAUWERYS C, SWEVERS J, SAS P. Model free control design for a semi-active suspension of a passenger car[C]// Proceedings of ISMA. Seattle: Scientific Research Publishing, 2004: 2206-2211.
[4] 琚龙玉, 李仲兴, 江洪, 等. 附加气室容积可调空气悬架多目标参数匹配[J]. 汽车技术, 2014, 1(6): 29-33.
JU Longyu, LI Zhongxing, JIANG Hong, et al. Multi-objective parameters matching of air suspension system with volume adjustable auxiliary chamber[J]. Automobile Technology, 2014, 1(6): 29-33.
[5] 陈龙, 江浩斌, 周孔亢, 等. 半主动悬架系统设计及控制[J]. 机械工程学报, 2005, 41(5): 137-141.
CHEN Long, JIANG Haobin, ZHOU Kongkang, et al. Control and design for semi-active suspension[J]. Journal of Mechanical Engineering, 2005, 41(5): 137-141.
[6] 赵开林. 汽车半主动悬架模糊控制研究[D]. 南昌: 华东交通大学机电与车辆工程学院, 2007: 18-36.
ZHAO Kailin. Research on fuzzy control for vehicle of semi-active suspension[D]. Nanchang: East China Jiaotong University. School of Mechanotronics and Vehicle Engineering, 2007: 18-36.
[7] ARAKI Y. Preview control of active suspension using disturbance information of front wheel[J]. Transactions of the Japan Society of Mechanical Engineers, 1994, 60(578): 3405-3408.
[8] CHOI S B, LEE H K, CHANG E G. Field test results of a semi-active er suspension system associated with skyhook controller[J]. Mechatronics, 2001, 11(3): 345-353.
[9] 高明宏. 基于机电相似理论的带附加气室空气悬架建模与分析[D]. 镇江: 江苏大学机械工程学院, 2013: 18-30.
GAO Minghong. Modeling and analysis of air suspension with auxiliary chamber based on electromechanical similarity theory[D]. Zhenjiang: Jiangsu University. School of Automotive and Traffic Engineering, 2013: 18-30.
[10] 余志生. 汽车理论[M]. 5版. 北京: 机械工业出版社, 2009: 203-251.
YU Zhisheng. Elementary vehicle theory[M]. 5th ed. Beijing, China Machine Press, 2009: 203-251.
[11] HAGAN M T, MENHAJ M B. Training feedforward networks with the Marquardt algorithm[J]. IEEE Trans Neural Netw, 1994, 5(6): 989-993.
[12] 李宁, 王李管, 贾明涛. 基于层次分析法的矿井六大系统模糊综合评价[J]. 中南大学学报(自然科学版), 2015, 46(2): 631-637.
LI Ning, WANG Liguan, JIA Mingtao. An analytic hierarchy process based fuzzy evaluation of underground mine six-system[J]. Journal of Central South University (Science and Technology), 2015, 46(2): 631-637.
[13] 陈士安, 邱峰, 何仁, 等. 一种确定车辆悬架LQG控制加权系数的方法[J]. 振动与冲击, 2008, 2(27): 65-68.
CHEN Shian, QIU Feng, HE Ren, et al. A method for choosing weights in a suspension LQG control[J]. Journal of Vibration and Shock, 2008, 2(27): 65-68.
[14] 黄定师. 基于遗传算法的带附加气室空气悬架参数优化与控制研究[D]. 镇江: 江苏大学机械工程学院, 2013: 20-29.
HUANG Dingshi. Parameter optimization and control based on genetic algorithm of air suspension with auxiliary chamber[D]. Zhenjiang: Jiangsu University. School of Automotive and Traffic Engineering, 2013: 20-29.
[15] 杨启耀. ECAS客车悬架系统的匹配与充放气研究[D]. 镇江: 江苏大学汽车与交通工程学院, 2008: 42-45.
YANG Qiyao. Research on matching and inflating/deflating of suspension system in ECAS-bus[D]. Zhenjiang: Jiangsu University. School of Automotive and Traffic Engineering, 2008: 42-45.
(编辑 陈爱华)
收稿日期:2016-07-21;修回日期:2016-09-13
基金项目(Foundation item):国家自然科学基金资助项目(51575241);江苏省六大人才高峰资助项目(2012-ZBZZ-030);国家青年科学基金资助项目(51305111);江苏省自然科学基金资助项目(BK20131255) (Project(51575241) supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China; Project(2012-ZBZZ-030) supported by the Six Talents Peak Foundation of Jiangsu Province; Project(51305111) supported by the Youth Science Foundation of China; Project(BK20131255) supported by the Natural Science Foundation of Jiangsu Province)
通信作者:李仲兴,教授,博士生导师,从事载运工具运行品质模拟与控制研究;E-mail: la55@163.com