
Microstructure evolution and tensile properties of
friction-stir-welded AM50 magnesium alloy
ZENG Rong-chang (曾荣昌)1, W. DIETZEL2, R. ZETTLER2, CHEN Jun (陈 君) 1, K. U. KAINER2
1. School of Materials Science and Engineering, Chongqing Institute of Technology, Chongqing 400050, China;
2. GKSS-Forschungszentrum Geesthacht GmbH, Geesthacht 21502, Germany
Received 12 June 2008; accepted 5 September 2008
Abstract: Friction stir welding (FSW) technique was utilized to weld cast AM50 magnesium alloy plates. The microstructures in the base metal (BM) and the weld joint were observed by optical microscopy. The mechanical properties were investigated by using hardness measurement and tensile test, and the fractographs were observed by scanning electron microscopy. The results show that the microstructure of the base material was characterized by bulk primary α phase, α-matrix and intermetallic compound β (or Mg17Al12), and the weld nugget exhibiting recrystallized microstructure consists of α-matrix and β phase. The grain size in the weld is smaller than that in the base metal. The hardness of the weld joint is improved but the tensile strength and yield strength, as well as the elongation to failure of the base material decline. The fracture of BM has a rougher surface with more dimples, which is a characteristic of the ductile fracture, whereas the fracture on the nugget reveals a quasi-cleavage feature. The ultimate tensile strength and yield strength of the FSWed AM50 are 86.2% and 94.0% of those of the base metal, respectively.
Key words: AM50 magnesium alloy; friction stir welding; microstructure; mechanical property
1 Introduction
Owing to lower density, high strength-to-mass ratio, good castability and high damping capacity, Mg alloys are potential candidates to replace the steel and aluminum alloys in automobile industry and aeronautic applications[1-2]. The joining of Mg parts, particularly plates, is crucial for these utilities. It is, therefore, desirable that the joining technologies can be developed and made accessible to industrial applications. Friction stir welding (FSW) has been patented[3] and applied in the automotive industry for decades in the manufacture of a variety of components[4]. The major advantage of FSW over conventional fusion welding techniques is that a metallic bond is achieved below the melting point of the base material thus avoiding many of the metallurgical problems associated with the solidification process[4-5]. FSW achieves the weld in solid phase by locally introducing frictional heat and plastic flow by rotation and forward motion of the welding tool resulting in local microstructure changes[6], which have been a major concern in FSW-Mg alloys. Generally, the change in microstructures includes dynamically re-crystallized, equiaxed grains with a high density of dislocations occurred in the weld nugget of the FSWed AZ31 alloy[7-10], and a micro-texture change as well during FSW AZ61 Mg alloys[11] and AZ31B[12-13]. The significant microstructural change in the nuggets thus leads to local variation in the mechanical properties of weld[6-8]. For instance, FSW-AZ31 achieved roughly the same mechanical properties as those of the base material in the weld[7]. For FSW-ZK60, however, it is not the case, the ultimate tensile strength (UTS) merely reached 87% of that of the parent material[14].
In the present, most studies, however, are focused on the FSW of extruded Mg alloys such as AZ31[4-7, 12-13]. And hence the influence of FSW of cast Mg alloys on microstructure and mechanical properties are sparsely reported[15-16]. The purpose of this study is to investigate the microstructure features and mechanical properties of FSW-AM50 and to obtain better under-standing of the FSW of cast Mg alloys.
2 Experimental
The materials used in this study were FSWed Mg alloy AM50 (5.6%-6.4% Al, 0.26%-0.5% Mn, 0.20% Zn, Mg Bal., mass fraction), which was prepared by GKSS Research Center in Germany. The specimens for microstructural observation were cut from the plated base material and FSW zone, and then ground with SiC paper up to 1 200 g, finally polished to a mirror surface. The polished specimens were etched in a solution containing 1.5 g picric acid, 25 mL ethanol, 5 mL acetic acid, and 10 mL water, finally were examined by optical microscopy. The Vickers hardness was measured by using a fully automatic HVS100 hardness scanner at 0.98 N for 20 s on a polished sample. This measurement was conducted from the middle position of the weld nugget across the weld and transverse to the both sides of heat affected zone and base material. The tensile samples parallel to the welding direction (WD) in the base metal and perpendicular to the WD across the weld joint were machined. The width, thickness and gauge length of the tensile specimens were 6, 3 and 25 mm, respectively. Tensile tests were performed on SANS CMT-5105 tensile machine at a strain rate of 2 mm/min at room temperature according to the standard GB/T228—2002. The fractography was discerned through a JSM-6460L type scanning electron microscope (SEM).
3 Results and discussion
3.1 Microstructure observation
The typical macro- and micro-structure of the base material (BM), heat affected zone (HAZ), thermo- mechanically affected zone (TMAZ) and stir zone (SZ) are demonstrated in Fig.1.
The cast microstructure in BM is characterized by bulk primary α-Mg phase with eutectic (mixture of α-Mg matrix and β compounds) at the grain boundaries (GBs) (shown in Fig.1(b)). Note that some pores also exist in the alloy. Adjacent to the weld nugget is the TMAZ, in which the parent metal grains have undergone severe deformation. Fig.1(c) reveals that the deformation in the TMAZ results in severe bending of the grain structure. Most of the β phases are apparently distributing along the plastic flows. Fig.1(c) also demonstrates a distinct boundary between the material which has been dynamically recrystallized, and the material which has been deformed without recrystallization. The SZ (Fig.1(d)) is composed of very fine recrystallized well-homogenized structures. The amount of eutectic on the GBs seems to disappear in the SZ. This region has experienced high temperatures and extensive plastic deformation and contains much smaller grains than the BM. The material on the advancing front side of the weld enters into a rotational zone that rotates and advances with the probe and is very highly deformed. The TMAZ experienced both temperature rising and deformation during FSW, and re-crystallization occurred.
The macrosection of FSWed AM50 is shown in Fig.2(a), which demonstrates the typical macro-structure of BM, HAZ and TMAZ as well as SZ. The nugget shape exhibits an onion ring structure which is frequently seen in aluminum alloys[8]. The weld is found to be devoid of any defects, and a sound weld is apparent, but some surface irregularities are observed. The cross- sectional microstructures of BM and SZ are also shown in Figs.2(b), (c), (d) and (e). It is obvious that the grains on the top and bottom of the weld nugget are highly elongated and pancake shaped, mirroring the deformation imposed during FSW. The grains in the middle thickness of the plate seem to be coarser than those in the upper and low layers. And approximate 200 μm oxide layer on the top and some 60 μm oxide layer on the bottom formed during FSW process. The microstructures with extrusion characteristics within the SN are much smaller and equiaxed for the re-crystallization during FSW due to the friction and squeezing by the stir head, which causes a large plastic deformation of that part metal. No metal melts on the friction stir welding joints. It should be noticed that AlMn particles exist in the AM50 alloy (shown in the middle of Fig.2(c)).

Fig.1 Typical macro- (a) and microstructure of BM((b), in zone A), HAZ-TMAZ((c), zone B), black line in zone B(c) indicating boundary among TMAZ, HAZ and SZ(d) on top surface

Fig.2 Macrosection of FSWed AM50(a), cross-sectional microstructure of BM(b) along line A located at margin of weld and cross-sectional microstructures of SN from top(c) to middle(d) and bottom(e) along line B through center of SN
3.2 Relationship between microstructure and hardness
It is reported that bulky intermetallic compounds (Al2Ca and Mg-Zn-Y phase), broke up and dispersed in the nugget zone, leading to remarkable increase in hardness value during FSW of cast Mg-Al-Ca and Mg-Zn-Y Mg alloys[14]. On the contrary, Refs.[5, 11] described that the hardness values of the wrought or extruded AZ31 and AZ61 were uniformly distributed in the weld. But an increase in the hardness of the weld occurred for AZ61 alloy at the highest weld pitch ratio of rotational speed to transverse speed[5]. It is suggested that the coarse eutectic β-Mg17Al12 phase hardly contributed to the average hardness of the BM (AZ91), thus, the dissolution of β phase in the nugget zone during FSW did not result in the noticeable change in hardness across the weld zone for AZ and AM system Mg alloys[11, 14]. Therefore, PARK et al[11] proposed that the microstructural factors governing hardness in Mg alloy AZ61 would be grain size and dislocation density. Whereas, XIE et al[14] indicated that the hardness of the ZK60 alloy was mainly governed by the MgZn2 precipitates. In this study, the hardness profile of the AM50 weld nugget is shown in Fig.3. These values were measured on the polished top surface of the weld. Obviously, the hardness of the welded area in the middle is higher, and that of the base material (BM) on both sides is relatively lower. Herein, the higher hardness of the welded nugget can be attributed to the relatively smaller grains of FSW zone and the AlMn particles with high melting point dispersed in the GBs and interiors (Fig.2(c)), as well as the high dislocation density in the weld region[11]. Grain refinement plays a crucial role in material strengthening. According to the Hall-Petch equation, hardness increases with decreasing grain size. On the other hand, the small particles of intermetallic compounds are beneficial to hardness enhancement based on the Orowan hardening mechanism. An extra high hardness point in the Fig.3 may be tested precisely on the intermetallic compounds or at a grain boundary (GB).
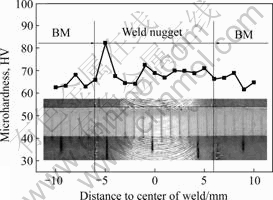
Fig.3 Hardness profile of FSWed AM50 Mg alloy
3.3 Relationship between microstructure and tensile properties
The stress—strain curves of the BMed sample parallel to the WD and the weld sample perpendicular to the WD are demonstrated in Fig.4. Both the BMed and FSWed AM50 have remarkably elastic deformation, and their elastic deformation curves are consistent. The necking points for both the BMed and FSWed sample are located in the middle of the gauge. The ultimate tensile strength (σb), and yield strength at 0.2% proof (σ0.2), of the BM and FSWed samples are 260 MPa, 117 MPa and 224 MPa, 110 MPa, respectively. σb and σ0.2 of the FSWed samples is thus 86.2% and 94.0% of those of the BM samples. The elongation to failure, approximately 10%, which is sometimes sufficient for many practical applications, though the BM exhibits much higher ductility than the joint.

Fig.4 Stress—strain curves of BMed and FSWed samples
The tensile properties of the weld of Mg alloy depend on several microstructural factors such as grain size and dislocation density and crystallographic orientation as well[11]. Though this alloy is predominantly strengthened by solid solution and work hardening, the tensile properties are improved due to reduction in the grain size and increase in dislocation density. However, the crystallographic orientation also strongly influences the plastic deformation during tensile test. It is demonstrated that the (0002) basal planes tended to be arranged parallelly to the plate surface of FSW Mg-Al-Ca alloy[15]. In the cross section of SZ, no obvious texture has evolved and (0002) basal planes show random distribution. The same is the case for AM50 in the weld. Hereby, this basal plane texture probably and easily causes preferential plastic deformation in the fracture region during tensile test. The fracture failed in the nugget zone near the transition region with σb of 86.2% for the parent material are consistent with that of ZK60. and this data of mechanical properties is similar to the result obtained by SKAR on the same alloys[16].
Remarkable different structures are observed on the fractural surfaces, as shown in Fig.5. The fracture of BM has a rougher surface with more dimples, which is a characteristic of the ductile fracture, whereas the flat nugget fracture with fewer dimples, facets and steps reveals a quasi-cleavage feature. The fracture difference further confirms that the weld joint is brittle and hence has lower mechanical properties.
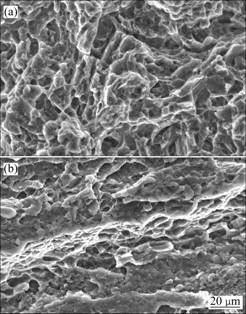
Fig.5 SEM micrographs of BMed(a) and FSWed(b) alloys
4 Conclusions
1) Different microstructures are observed in cast AM50 BM and its FSWed joint. The BMed samples have typical cast microstructures consisting of bulk primary α phase, α-Mg matrix and β phase. While the FSWed AM50 has recrystallized microstructure with smaller equiaxed grains and is characterized by α-Mg matrix and β phase.
2) The hardness of the weld nugget is improved because of the finer grain size and AlMn intermetallic compounds.
3) FSW reduces the tensile strength and yield strength of the BMed samples, as well as the elongation to failure. The fracture on BMed samples has a rougher surface with more dimples, which is a characteristic of the ductile fracture, whereas the flat nugget fracture reveals a quasi-cleavage feature with fewer dimples, facets and cleavage steps.
Acknowledgements
The authors gratefully acknowledge the technical support extended by Mr. U. Burmester, Mr. V. Kree, and Ms. P. Fischer in GKSS Forschungszentrum Geesthacht GmbH during the course of this work.
References
[1] SONG G, ATRENS A. Corrosion mechanisms of magnesium alloys[J]. Adv Eng Mater, 1999, l: 11-33.
[2] ZENG Rong-chang, KE Wei, XU Yong-bo, HAN En-hou, ZHU Zi-yong. Recent development and application of magnesium alloys[J]. Acta Metallurgica Sinica, 2001, 37: 673-685. (in Chinese)
[3] THOMAS W M. Friction welding. US 5460317[P]. 1995.
[4] KANNAN M B, DIETZEL W, ZENG R, ZETTLER R, DOS SANTOS J F. A study of the SCC susceptibility of friction stir welded AZ31 Mg sheet[J]. Mater Sci Eng A, 2007, 460/461: 243-250.
[5] ZETTLER R, BLANCO A C, DOS SANTOS J F, MARYA S. The effect of process parameters and tool geometry on thermal field development and weld formation in friction stir welding of the alloys AZ31 and AZ61[C]// NEELAMEGGHAM N R, DAPLAN H I, POWELL B R. Magnesium Technology 2005. San Francisco: TMS, 2005: 409-423.
[6] ZHANG H, LIN S B, WU L, FENG J C. Microstructural studies of friction stir welded AZ31 magnesium alloy[J]. Acta Metallurgica Sinica, 2004, 17: 747-753.
[7] NAGASAWA T, OTSUKA M, YOKOTA T, UEKI T. Structure and mechanical properties of friction stir weld joints of magnesium alloys AZ31[C]//KAPLAN H K, HRYN J, CLOW B. Magnesium Technology 2000. Nashville: TMS, 2000: 383-387.
[8] KALLEE S W, THOMAS W M, NICHOLAS E D. Friction stir welding of lightweight materials[C]//Kainer K U. Magnesium alloys and their applications. Weiheim: DGM, 2000: 175-190.
[9] COMMIN L, MASSE J E, DUMONT M, BARRALLIER L. Microstructure features of hot rolled AZ31 magnesium alloy for friction stir welding[C]//KAINER K U. Proceedings of the 7th International Conference on Magnesium Alloys and Their Applications. Weiheim: DGM, 2006: 877-882.
[10] ESPARZA J A, DAVIS W C, TRILLO E A, MURR L E. Friction stir welding of magnesium alloy AZ31B[J]. Journal of Materials Science Letters, 2002, 21(12): 917-920.
[11] PARK S H C, SATO Y S, KOKAWA H. Effect of micro-texture on fracture location in friction stir weld of Mg alloy AZ61 during tensile test[J]. Scripta Marerialia, 2003, 49(2): 161-166.
[12] WOO W, CHOO H, BROWN D W, LIAW P K, FENG Z. Texture variation and its influence on the tensile behavior of a friction-stir processed magnesium alloy[J]. Scripta Materialia, 2006, 54(1): 1859-1864
[13] WOO W, CHOO H, PRIME M B, FENG Z, Clausen B. Microstructure, texture and residual stress in a friction-stir-processed AZ31B magnesium alloy[J]. Acta Materialia, 2008, 56(8): 1701-1711.
[14] XIE G M, MA Z Y, GENG L. Effect of microstructural evolution on mechanical properties of friction stir welded ZK60 alloy[J]. Mater Sci Eng A, 2008, 486: 49-55.
[15] ZHANG D T, SUZUKI M, MARUYAMA K. Study on the texture of a friction stir welded Mg-Al-Ca alloy[J]. Acta Metallurgica Sinica, 2006, 19(5): 335-340.
[16] SKAR J I, GJESTLAND H, OOSTERKAMP L D, ALBRIGHT D L. Friction stir welding of magnesium die castings[C]//LAPOVOK R Y, THOMSON P F, LUO A A. Magnesium Technology 2004. North Carolina: TMS, 2004: 25-30.
(Edited by LONG Huai-zhong)
Foundation item: Project(2007AC4073) supported by Chongqing Munciple Science-Tech Tackle Program, China; Project(2008BB0063) supported by the Natural Science Foundation of Chongqing Science and Technology commission, China
Corresponding author: ZENG Rong-chang; Tel: +86-23-68665616; E-mail: rczeng2001@yahoo.com.cn