Q125级ERW用石油套管钢力学性能及CO2腐蚀行为
王立东,唐荻,武会宾,梁金明
(北京科技大学 高效轧制国家工程研究中心,北京,100083)
摘要:设计研发一种低碳的Q125级ERW用石油套管用钢。运用SEM和TEM分析实验钢的强化机制,并采用高温高压反应釜对实验钢的CO2腐蚀行为进行研究。实验结果表明:实验钢的晶粒粒径10~15 μm,晶区的长度约为2 μm,马氏体板条束宽度约150 nm,这些均为实验钢具有较好的强韧性配合提供条件;直径约为50 nm的圆形(Nb,Ti)(C,N)析出物,通过钉扎晶界阻止γ晶粒的粗化过程,可有效阻止奥氏体晶粒的长大;直径约20 nm的椭圆形(Nb,Ti)C以及纳米级圆形NbC析出物,可起到钉扎位错的作用,阻止位错移动,可很大程度地提高强度;实验钢腐蚀速率随着温度的增加先增大后减小,在90 ℃时平均腐蚀速率和点蚀速率均达到最大值;在60℃时,点蚀速率与平均腐蚀速率相差程度最大。
关键词:原始奥氏体晶粒;位错;纳米级析出;CO2腐蚀;点蚀速率
中图分类号:TG172.9 文献标志码:A 文章编号:1672-7207(2012)06-2165-08
Mechanical properties and CO2 corrosion behavior of Q125 grade oil tube steel used for ERW
WANG Li-dong, TANG Di, WU Hui-bin, LIANG Jin-ming
(National Engineering Research Center for Advanced Rolling Technology,
University of Science and Technology Beijing, Beijing 100083, China)
Abstract: A type of Q125 grade high-strength low carbide oil tube steel was designed and researched. The strengthening mechanism of steel was analyzed by SEM and TEM, and the CO2 corrosion behavior of steel was simulated by high-temperature and high-pressure autoclave. The results show that the size of prior austenite grain, packet and block are 10-15 μm, 2 μm and 150 nm, respectively, so that the strength of the steel matched its toughness well. The precipitate of (Nb,Ti)(C,N) whose size is about 50 nm can restrain coarsening of the prior austenite grain through pitting austenite grain boundary. The precipitate of (Nb,Ti)C and nanometer size precipitate of NbC can be an effective barrier for dislocation motion, so that it has great contributions to improve the strength of the steel. The average and pitting corrosion rate increase first and then drop down with the increase of temperature. There is a maximum of average and pitting corrosion rate at 90 ℃. When the temperature is 60 ℃, there is a greatest difference between average corrosion rate and pitting corrosion rate.
Key words: prior austenite grain; dislocation; nanometer sized precipitate; CO2 corrosion; pitting corrosion rate
套管是开采石油天然气必须使用的工程用具。随着西部大开发的深入,采油条件越来越恶劣,深井、超深井的开发量加大,对石油套管的性能提出更高要求[1]。CO2驱油技术大量应用于深井、超深井的开发,CO2腐蚀给石油天然气工业造成巨大损失[2]。这不仅要求石油套管钢具有优良的力学性能,而且还应具备一定的耐腐蚀性。Q125级在API 5L标准中强度级别最高,对Q125钢性能的要求为:屈服强度Rt0.65=862~ 1 034 MPa,抗拉强度Rm≥931 MPa,延伸率A≥14%,横向冲击功Akv(0 ℃)≥20 J,纵向冲击功Akv(0 ℃)≥41 J。为获得最佳的强韧性组合,在API标准中高级别石油套管用钢主要通过调质处理来生产。目前,关于Q125级别石油套管的相关文献研究极少[3],而系统的研究Q125级石油套管钢的组织、力学性能及其耐腐蚀性能方面仍属空白。因此,本文作者设计一种用于高频电阻焊(ERW)的Q125级石油套管用钢。采用低碳设计,既可提高钢的焊接性能,又可增强钢的耐CO2腐蚀能力。运用TMCP和调质处理来实现高级别石油套管用钢的强韧性结合,来满足API 5CT标准中对高强度Q125级别石油套管钢的使用要求。本文系统研究Q125级石油套管钢的显微组织、力学性能和耐CO2腐蚀性能,研究结果对Q125级高强石油套管钢的研发以及其在CO2驱油气田中的腐蚀防护具有重要理论意义和实际参考价值。
1 实验材料和方法
实验材料的化学成分如表1所示。实验用材料在22 kg真空感应电炉中冶炼,将其锻造成长×宽×厚为80 mm×80 mm×90 mm,然后在加热炉中加热至 1 250 ℃并保温2 h,取出在热轧机上经过粗轧和精轧2阶段控轧,轧至到厚度为9 mm。热轧工艺参数:开轧温度1 150 ℃,终轧温度≥850 ℃,轧后的板材经过层流冷却至620 ℃,放入加热炉中模拟卷曲,保温2 h后空冷到室温。调质工艺为:于920 ℃淬火,于450 ℃回火;为满足性能的均匀性,淬火和回火保温时间均为1 h。
从调质处理后的板材上切取金相试样进行打磨抛光,并采用4%的硝酸酒精溶液进行浸蚀,在扫描电镜(SEM)下进行组织观察。切取长×宽×厚为10 mm×10 mm×0.3 mm的透射用试样,用砂纸打磨至50 μm。用酒精清洗后,在打孔器上打取?3的样品,用5%的高氯酸酒精溶液对样品进行电解双喷实验。萃取复型试样是将试样抛光后利用4%硝酸酒精溶液浸蚀后,在真空喷碳仪中喷1层碳膜,用5%高氯酸酒精溶液进行电解剥离。采用透射电镜(JEM-2000FX)对双喷、萃取后的样品进行形貌、析出物的观察。
表1 实验钢的化学成分(质量分数)
Table 1 Chemical constituent of steel %

腐蚀试样规格为曲率直径87 mm、弧长30 mm、面宽12 mm、厚度4 mm的弧形试样,如图1所示。经过800#砂纸打磨后,丙酮除掉试样表面的油污,酒精清洗,然后用精度0.1 mg的电子分析天平称量试样的重量。实验溶液在实验前用CO2除氧10 h,倒入反应釜后再除氧2h后升温,并调整CO2压力和流速。每组实验采用4个平行试样,实验结束后取出试样,经清水酒精冲洗吹干拍照;然后将其中3个试样放入除锈液中,去除腐蚀产物膜后清洗干燥并称质量。点蚀速率的测量方法为:选取面积为1 cm2的腐蚀样品,对其腐蚀面进行打磨,打磨至试样表面没有孔蚀迹象后,用精度为1 μm的螺旋测微器测量并计算损失厚度,将损失的厚度换算成年腐蚀厚度即是孔蚀速率。每种工况保留1个带腐蚀产物膜的试样,用扫描电子显微镜对试样表面形貌进行观察及能谱分析(EDS),运用X线衍射(XRD)分析腐蚀产物的物质构成。
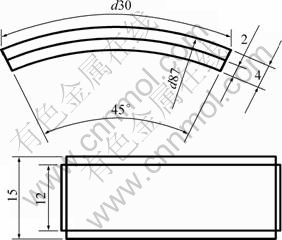
图1 腐蚀实验用试样示意图(单位:mm)
Fig.1 Schematic diagram of specimen for corrosion test
2 实验结果
2.1 力学性能
实验钢是一种低碳的以Nb和Ti为典型合金成分的ERW用石油套管钢,通过TMCP和调质处理来实现其较好的强韧性配合,其力学性能参数如表2所示。API 5L标准中,对Q125级别石油套管钢力学性能要求也列于表2中。由表2可知:实验钢屈服强度、抗拉强度、延伸率、横/纵向冲击功间达到API 5L标准中对Q125钢级的要求,具有较好的综合力学性能。
2.2 显微组织
图2所示为实验钢显微组织的扫描电镜图(SEM),实验钢组织为典型回火马氏体组织。实验钢显微组织中板条特征比较明显,析出的细小碳化物主要在马氏体晶界或原奥氏体晶界聚集。在回火过程中,过饱和的碳原子将从固溶体中不断析出,在马氏体板条内部、板条边缘和奥氏体晶界上大量弥散析出碳化物质点。这些碳化物质点对位错运动阻碍作用非常明显,使钢的强度大幅度提高[4]。
表2 实验钢力学性能
Table 2 Mechanical properties of steel
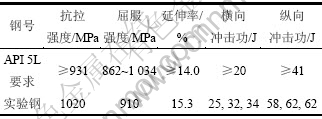

图2 实验钢显微组织SEM图
Fig.2 SEM micrographs of steel
2.3 腐蚀实验结果
抗CO2腐蚀实验在3 L高温高压反应釜中进行,模拟采出液离子浓度见表3。环境参数设置如下:CO2分压为1 MPa,流速为1 m/s,实验周期为7 d,通过失重法测得实验钢的腐蚀速率。实验钢在不同温度下的平均腐蚀速率和点蚀速率见图3。
由图3可见:随着温度的增加,实验钢的平均腐蚀速率和点蚀速率均是先增大后减小;当环境温度为30 ℃时,腐蚀速率最小,平均腐蚀速率和点蚀速率分别为0.458 6 mm/a和0.542 5 mm/a;温度为60 ℃时,平均腐蚀速率与点蚀速率相差程度最大;温度为90 ℃时,平均腐蚀速率和点蚀速率达到最大值;当温度大于90 ℃时腐蚀速率开始降低,实验钢在120 ℃时的平均腐蚀速率和点蚀速率分别为1.844 6 mm/a和2.073 6 mm/a。图4和图5所示为腐蚀产物膜去除前后试样宏观腐蚀形貌。从图4(a)和5(a)可见:30 ℃时实验钢腐蚀产物膜较致密,并且和基体附着性好,局部腐蚀产物膜未发生脱落,从而腐蚀产物膜对基体的保护性较好。从图4(b)和5(b)上观察到腐蚀产物宏观上仍然比较致密,但去除腐蚀产物后发现点蚀坑较明显,且数量较多,排列密集;90 ℃时腐蚀产物膜开始出现大面积脱落,但在去除腐蚀产物膜的试样上并未发现较大的点蚀坑,如图4(c)和5(c)所示,说明在此温度还是以均匀腐蚀为主。与30 ℃时的宏观腐蚀形貌相似,120℃腐蚀产物宏观较致密,没有发生明显的脱落,去除腐蚀产物后,表面也没有明显的点蚀坑,如图4(d)和5(d)所示。
表3 采出液模拟成分质量浓度
Table 3 Mass concentration of ions in simulation environment
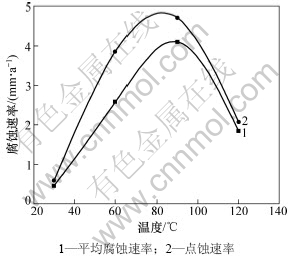
图3 实验钢平均腐蚀速率和点蚀速率与温度的关系
Fig.3 Relationship between average corrosion rate and pitting rate under different temperatures
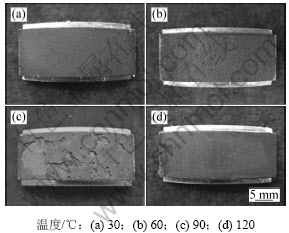
图4 带有腐蚀产物的宏观腐蚀形貌
Fig.4 Morphologies of specimens with scales
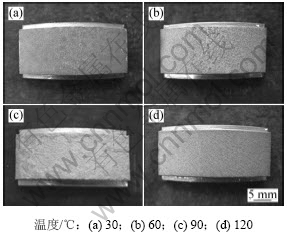
图5 去除腐蚀产物的宏观腐蚀形貌
Fig.5 Morphologies of specimens after descaling
3 讨论
3.1 强化机理分析
细化晶粒是目前唯一一种既能提高强度又能提高韧性的手段,其对于具有中温回火和高温回火组织的高强度钢力学性能影响十分显著。在原奥氏体晶粒中,马氏体亚结构共分为3个层次[5]:晶区、板条束和板条,如图6所示。马氏体亚结构的尺寸由原奥氏体晶粒粒径控制的。奥氏体晶粒越小,则晶区、板条束和板条的尺寸也就越小。马氏体内亚结构的尺寸直接影响钢的性能,晶区和板条束的尺寸是决定马氏体钢的强度和韧性直接因素[6]。相关研究表明[7]:晶区和板条束尺寸对马氏体钢的强度的影响也呈Hall-Petch关系。
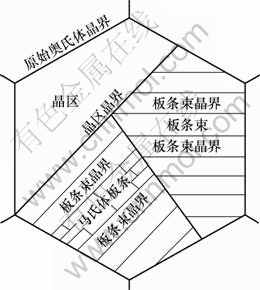
图6 马氏体显微结构
Fig.6 Microstructural hierarchy of lath martensite structure
图7所示为实验钢原始奥氏体晶粒图。由图7可见:实验钢的晶粒粒径为10~15 μm。可见,实验钢的晶粒比较小,这主要得益于合理的控制轧制及淬火和回火工艺的控制。控制轧制在一定程度上细化奥氏体晶粒,淬火及回火时加热温度和时间的合理控制使得大部分细小的奥氏体晶粒尺寸得到保持,从而为后续得到细小的马氏体组织提供条件。图8(a)中完整的展示1个晶区的形貌。晶区的尺寸约为2 μm,晶区中马氏体板条束宽度约150 nm。原奥氏体晶界、晶区晶界以及马氏体板条束的晶界均可以阻碍位错运动。细小的晶粒导致晶界面积增多,位错增多,塑性和韧性加强,使得实验钢具有优异的力学性能。高密度的位错也出现在板条马氏体边界,形成位错塞积。
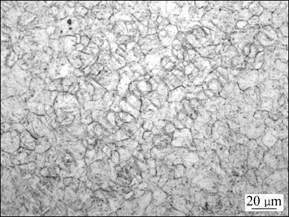
图7 实验钢原始奥氏体晶粒
Fig.7 Prior austenite grain of steel
在图8(a)中可以看到一些细小弥散的析出物,如图中箭头所指。图8(b)是在透射电镜下对实验钢的析出物萃取结果。析出物大体可以分为3种类型:圆形、椭圆形和纳米尺寸级圆形,见图8(b)中(i),(ii)和(iii)。圆形,直径均约50 nm,对该析出物进行能谱分析,如图9(a)所示,确定其为(Nb,Ti)(C,N)。分析认为,这些(Nb,Ti)(C,N)的析出物是在奥氏体中形成的。已有的研究表明[8]:碳氮化物在奥氏体中析出时,与奥氏体之间存在平行位向关系: (001)M(C,N)∥(001)γ,[010]M(C,N)∥[010]γ。在这种平行取向关系下,析出相晶格与奥氏体晶格在3个相互垂直方向上的错配度相等。这说明析出相一旦在奥氏体中形核析出,其长大必然沿着各个方向或3个相互垂直的方向上同时均衡生长。因此,奥氏体中析出的碳氮化物应为球形或近似球形。Ti碳氮化物析出温度较高,在奥氏体中首先析出。而随着温度降低,Nb的碳氮化物也开始形核、长大。Nb的碳氮化物会以先析出的Ti的碳氮化物作为核心并长大,最终形成(Nb,Ti)(C,N)。这些尺寸较大的(Nb,Ti)(C,N)质点通过钉扎晶界的机制而阻止γ晶粒的粗化过程,从而有效阻止奥氏体晶粒的长大。椭圆形,尺寸约20 nm,对该析出物进行能谱分析,结果如图9(b)所示,该析出物析出物也富含Nb和Ti,可以确定为(Nb,Ti)C。分析认为,这种椭圆形的析出物是在奥氏体内形成TiC,而后NbC以其作为核心析出并长大。相关研究表明[9],在α-Fe中,析出物的位向与基体存在的相关性为(001)M(C,N)∥(001)α-Fe,[010]M(C,N)∥[110]α-Fe。在这种取向关系下,析出相晶格与α-Fe晶格在3个相互垂直方向上的错配度不等,因此,析出物应以椭球形、长条形或其他不规则形态出现。这种(Nb,Ti)C的析出物在低于奥氏体区温度范围长大,从而形状表现为椭圆形。纳米级圆形,粒径小于10 nm,对该析出物进行能谱分析(图9(c)),可以确定该析出物为NbC。这些纳米级圆形析出物是在马氏体内形核和长大的,之所以其呈现为圆形,是因为长条形或椭圆形的界面能高于平衡球形的界面能,在高温长时间回火过程中,长条形或椭圆形析出自发的向球形演化。实验钢在淬火时极冷的条件下,较大的相变体积差产生大量的位错;当位错在运动时,这些细小的椭圆形和纳米级圆形析出物可以起到钉扎位错的作用,阻止位错移动,对强度的提高贡献很大。
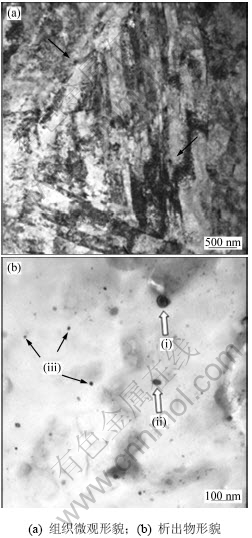
图8 实验钢微观形貌及析出物的TEM图
Fig.8 TEM images of 
 surface morphology and precipitates
surface morphology and precipitates
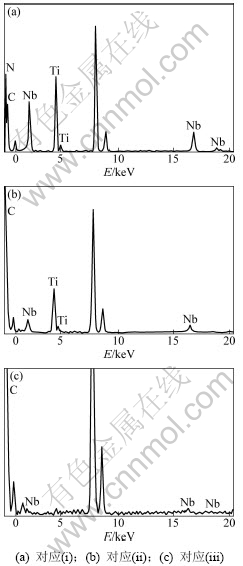
图9 图8中析出物能谱图.
Fig.9 Energy spectra of precipitates in Fig.8
3.2 腐蚀性能分析
CO2水体系的平衡较为复杂,涉及到相平衡、酸碱平衡及水解等形式的平衡[12]。
气液平衡:
CO2(g)=CO2(aq) (1)
酸碱平衡与水解平衡:
CO2(aq)+H2O=H2CO3 (2)
H2CO3=H++HCO3- (3)
HCO3-=H++CO32- (4)
在腐蚀介质中和一定的环境条件下,基体中管线钢的CO2腐蚀过程中存在以下3种阳极反应[10]:
Fe→Fe2++2e (5)
Fe+HCO3-→FeCO3+2e+H+ (6)
Fe+CO32-→FeCO3+2e (7)
酸碱平衡与水解平衡中的HCO3-和CO32-浓度,受温度影响很大。温度的增加直接影响到阳极反应式(6)和(7)生成FeCO3,碳钢在CO2水溶液中的溶解速度随温度的增高而增大;而FeCO3具有负的温度系数,温度升高的同时,腐蚀产物的沉积也会加剧。当碳钢表面形成致密的腐蚀产物膜后,碳钢的溶解速度随温度的升高而降低。温度对腐蚀的双重作用,直接的加速作用与由于温度加速腐蚀而加速沉积的腐蚀产物膜对腐蚀的阻碍作用,使得腐蚀速率随温度升高出现1个最大值。
图10所示为不同温度下,腐蚀产物膜微观SEM图。图11所示为不同温度下,腐蚀产物的XRD图。从图11可见:腐蚀产物膜主要是Fe,FeCO3,Fe3C及少量的Fe2O3。从图10可见:实验钢的微观组织为马氏体板条或板条内存在一些细小的的粒子,实质为过饱和的α-Fe基体上分布着均匀细小的碳化物(Fe3C)。与Fe3C相比,基体Fe具有更负的电位,作为阳极优先溶解,Fe3C是钢基体腐蚀后残留下来的物质,形成网状结构,腐蚀过程中会暴露在钢铁表面充当腐蚀的阴极而加速钢铁的腐蚀[11]。
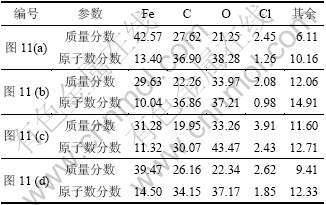
在温度为30 ℃时,由于温度较低,CO2在溶液中的溶解度小,从而生成HCO3-和CO32-的速率变小,即反应物的活性较低,反应速度常数较小,腐蚀产物膜的形成受活化控制,基体金属反应速度降低。在这个阶段,表现为均匀腐蚀,腐蚀速率最小。通过能谱分析结果(见图12和表4)可知:30 ℃时C元素含量较高,这主要是由于腐蚀初期,FeCO3沉淀较少,而钢基体腐蚀后裸露的Fe3C在表面聚集,从而使C元素含量增加。当温度到达60 ℃时,CO2在溶液中的溶解度较高,与Fe的结合速度加快,腐蚀速率加快;同时形成的FeCO3具有负的温度系数[12],在此时在试样表面沉积加剧。从图10(b)可见:腐蚀产物膜存在小孔,证明腐蚀产物与试样表面的结合力较弱,这样的腐蚀产物对腐蚀过程中腐蚀性物质的传输不具有足够的阻挡作用;随温度的升高,电极反应的速度加快,因此,腐蚀速率随温度升高而升高。从EDS分析结果(见表4)也可以看出,60 ℃时腐蚀产物中Cl-的含量最高。多孔的腐蚀产物膜不能有效地阻碍阴离子穿透腐蚀产物膜到达金属表面,在电极反应的作用下,膜与金属界面处的Cl-浓度增加,这样会大大增加Cl-的催化作用导致的点蚀,宏观表现为严重的点蚀坑,与图5(b)所示的相对应。在90 ℃左右时腐蚀速度最大,腐蚀产物膜是一层粗糙的、多裂纹的、厚的碳酸铁膜,如图8(c)所示。HCO3-和CO32-通过这些裂纹穿过腐蚀产物膜直接与基体发生反应,腐蚀速率最大。但在腐蚀过程中,由于腐蚀产物膜脱落严重,以及未脱落腐蚀产物膜存在大量裂纹,从而抑制电偶腐蚀的发生,点蚀速率与平均腐蚀速率相当。在温度为120 ℃时,大量的碳酸铁结晶均匀地在金属表面上形成,与90 ℃相比,腐蚀产物膜比较致密,黏着力好,厚度均匀,且腐蚀产物表面没有出现龟裂现象,这样的腐蚀产物膜可以对介质中腐蚀性物质从溶液本体向金属表面的传输起到阻碍作用,此时产物膜具有明显的保护作用。
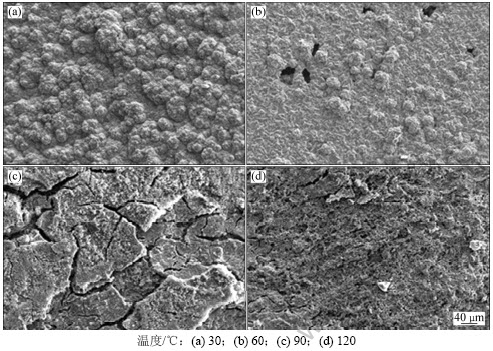
图10 腐蚀产物膜表面SEM图
Fig.10 SEM morphologies of steels with scales
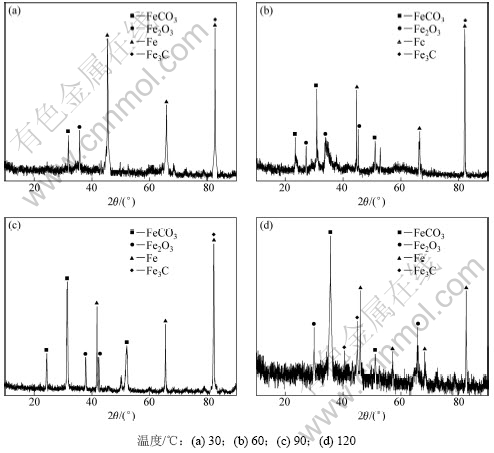
图11 腐蚀产物表面X线衍射分析
Fig.11 XRD pattern of corrosion products formed of tested steels
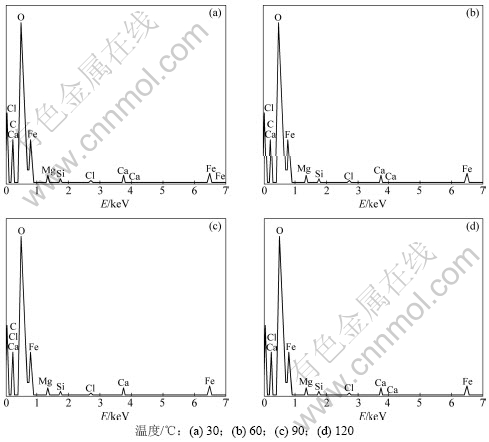
图12 腐蚀产物膜EDS图
Fig.12 Energy spectrum of corrosion product scale
表4 对应图11的EDS分析结果
Table 4 EDS analysis results matching Fig.11 %
4 结论
(1) 合理的控制轧制及淬火和回火工艺的控制,实验钢的晶粒粒径为10~15 μm,晶区的长度约为2 μm,晶区中马氏体板条束宽度约150 nm,这些都为实验钢具有较好的强韧性配合提供了条件。
(2) 在奥氏体中形成的圆形,粒径约50 nm的(Nb,Ti)(C,N)析出物通过钉扎晶界的机制而明显阻止γ晶粒的粗化过程,从而有效阻止奥氏体晶粒的长大;尺寸约20 nm的椭圆形的(Nb,Ti)C、纳米级(尺寸小于10 nm)圆形NbC析出物,可以起到钉扎位错的作用,阻止位错移动,对强度的提高贡献很大。
(3) 在模拟实际工况的条件下,随着温度的升高,实验钢的腐蚀速率先增大后减小。在30 ℃时腐蚀速率最小,在90 ℃时平均腐蚀速率和点蚀速率均达到最大值;在60 ℃时,由于试样与腐蚀产物之间形成微电偶腐蚀,使得点蚀速率与平均腐蚀速率相差程度最大;当温度到达120 ℃时,腐蚀产物表面裂纹减少,且致密度增加,腐蚀速率降低。
参考文献:
[1] 李亚欣, 刘雅政, 赵金锋, 等. P110级25MnV钢石油套管热处理工艺的优化[J]. 特殊钢, 2009, 30(6): 36-38.
LI Ya-xing, LIU Ya-zheng, ZHAO Jin-feng, et al. Optimization of heat treatment process of P110 oil casing tube of steel 25MnV[J]. Special Steel, 2009, 30(6): 36-38.
[2] 李春福, 王斌, 代加林, 等. P110钢高温高压下CO2腐蚀产物组织结构及电化学研究[J]. 材料热处理学报, 2006, 27(5): 73-78.
LI Chun-fu, WANG Bin, DAI Jia-lin, et al. Study on structure and electrochemical properties of CO2 corrosion scales on P110 steel corroded at high temperature and pressure[J]. Transactions of Materials and Heat Treatment, 2006, 27(5): 73-78.
[3] 马爱清, 郭兆成, 贺景春. 30CrMnMo 钢调质Q125 钢级套管的工艺研究[J]. 包钢科技, 2009, 35(1): 25-29.
MA Ai-qing, GUO Zhao-cheng, HE Jing-chun. Study on the heat treatment process for the steel tube of grade Q125 with 30CrMnMo[J]. Science&Technology of Baotou Steel Corporation, 2009, 35(1): 25-29.
[4] Qiu J, Ju X, Xin Y, et al. Effect of direct and reheated quenching on microstructure and mechanical properties of CLAM steel[J]. Journal of Nuclear Materials, 2010, 407(3): 189-194.
[5] Hiromoto Kitahara, Rintaro Ueji, Nobuhiro Tsuji, et al. Crystallographic features of lath martensite in low-carbon steel[J]. Acta Materialia, 2006, 54(5): 1279-1288.
[6] Swarr TE, Krauss G. The effect of structure on the deformation of as-quenched and tempered martensite in a Fe-0.2 pct alloy[J]. Metallurgical Transactions A, 1976, 7(1): 41-48.
[7] 王春芳, 王毛球, 时捷, 等. 低碳马氏体钢的微观组织及其对强度的影响[J]. 钢铁, 2007, 42(11): 57-60.
WANG Chun-fang, Wang Mao-qiu, Shi Jie, et al. Microstructural characterization and its effect on strength of low carbon martensitic steel[J]. Iron and Steel, 2007, 42(11): 57-60.
[8] 雍岐龙. 钢铁材料中的第二相[M]. 北京: 冶金工业出版社, 2006: 225-231.
YONG Qi-long. Secondary phases in steels[M]. Beijing: Metallurgy Industry Press, 2006: 225-231.
[9] 张亮, 李晓刚, 杜翠薇, 等. X70管线钢在含CO2库尔勒土壤模拟溶液中的腐蚀行为[J]. 金属学报, 2008, 44(12): 1439-1444.
ZHANG Liang, LI Xiao-gang, DU Cui-wei,et al. Corrosion behavior of X70 pipeline steel in simulated ku’erle soil solution with CO2[J]. Acta Metallurgica Sinica. 2008, 44(12): 1439-1444.
[10] TAKABE H, UEDA M. The relationship between CO2 corrosion resistance and corrosion products structure on carbon and low Cr bearing steels[J]. Corrosion Engineering, 2007, 56(11): 514-520.
[11] 张国安, 路民旭, 吴荫顺. 碳钢高温高压CO2腐蚀产物膜的形成机制[J]. 北京科技大学学报. 2007, 29(12): 1216-1221.
ZHANG Guo-an, LU Min-xu, WU Yin-shun. Formation mechanism of corrosion scales of carbon steel by CO2 corrosion under high temperature and high pressure[J]. Journal of University of Science and Technology Beijing, 2007, 29(12): 1216-1221.
[12] 梁明华, 苗建, 谢文江, 等. 模拟油田环境中两种P110钢的腐蚀行为研究[J]. 西安工业大学学报, 2010, 30(4): 352-355.
LIANG Ming-hua, MIAO Jian, XIE Wen-jiang, et al. Investigation on corrosion behaviors of two types of P110 tubing steel under simulated condition[J]. Journal of Xi’an Technological University. 2010, 30(4): 352-355.
(编辑 邓履翔)
收稿日期:2011-03-05;修回日期:2011-06-02
基金项目:国家科技重大专项(2011ZX05016-004)
通信作者:武会宾(1774-),男,河北石家庄人,副教授,从事高强超低碳贝氏体钢研究;电话:13910297926;E-mail:huibinwu@163.com