文章编号:1004-0609(2016)-09-1893-06
固态颗粒对TC4合金磨损行为的影响
王 继1,崔向红1,张秋阳1,刘家强2,黄颖斌2,拱建军2,王树奇1
(1. 江苏大学 材料科学与工程学院,镇江 212013;
2. 苏州环球集团科技股份有限公司,苏州 215156)
摘 要:在TC4合金/GCr15钢摩擦界面分别添加MoS2、Fe2O3等固态颗粒,研究两种颗粒对TC4合金磨损行为的影响;采用XRD、SEM、EDS等手段表征TC4合金的磨损特征,并探讨磨损机制。结果表明:TC4合金具有较差的耐磨性,而两种颗粒显著改变其磨损性能。当MoS2或Fe2O3在磨损表面形成连续的固态颗粒层时,TC4合金的磨损质量损失显著下降。Fe2O3颗粒层具有较强的承载能力,可以保护钛合金避免磨损;而MoS2层在高载下容易破碎,TC4合金失去保护作用,磨损增加。无添加及MoS2层破碎时,TC4合金以磨粒和粘着等严重磨损机制为主,当磨损表面连续覆盖固态颗粒层时由严重磨损向轻微磨损转变。
关键词:固态颗粒层;TC4合金;磨损行为;磨损机制
中图分类法:TH 117.1 文献标志码:A
钛合金具有弹性模量小、热导率低、强度高、中温性能好、耐腐蚀及密度小等优点,被广泛应用于航空航天、石油化工、造船、汽车、医疗等领域[1-4]。但由于钛合金较低的塑性变形抗力、较差的加工硬化能力以及形成的摩擦氧化物不具有保护作用等,而被认为具有较差的磨损性能[5-6],从而限制了钛合金在某些领域中的应用。近年来,针对钛合金较差的耐磨性,国内研究人员采用表面渗氮[7]、合金化[8]、微弧氧化[9-10]、激光熔覆[11-12]、等离子喷涂[13]、气相沉积[14-15]等工艺,试图在钛合金表面形成一定厚度的硬质相而改善其摩擦磨损性能。但这些处理工艺都需要进行二次加工,大大增加了工业成本。
近年来,对钛合金摩擦磨损的深入研究发现,钛合金并不总是表现出较差的耐磨性[16]。在高温条件下,钛合金磨损表面容易形成一层致密的且具有保护作用的固态颗粒层(摩擦层),在滑动过程中起到保护基体降低磨损的作用。但这种颗粒层似乎只在较高温度下形成而并未在室温下实现[17-20]。因此,本文作者在室温条件下通过对TC4合金/GCr15钢摩擦界面人工添加MoS2、Fe2O3等固态颗粒,试图加快钛合金磨损表面颗粒层的形成,并探究不同颗粒对TC4合金磨损行为的影响,探讨了磨损机制。
1 实验
选用TC4合金和GCr15轴承钢作为摩擦副材料,其化学成分如表1、2所列。采用线切割将TC4合金和GCr15钢分别加工成d5 mm×23 mm的销试样和d34 mm×10 mm的盘试样。对TC4合金进行固溶时效处理:955 ℃加热2 h,水冷;482 ℃保温4 h,空冷,获得网篮状α+β组织(见图1),硬度为38HRC左右。对GCr15钢进行840 ℃奥氏体化处理,400 ℃回火2 h后硬度达到50HRC。
采用MPX-2000型销盘式摩擦磨损试验机进行磨损实验。为了方便添加固态颗粒,在盘试样表面铣出宽7 mm、深2 mm的环形凹槽,如图2所示。磨损实验在室温下进行,滑动速度为0.5 m/s,滑动距离850 m,实验载荷分别为10、20、30、40和50 N。实验前将销和盘试样分别用38 μm的碳化硅打磨光滑,并用酒精清洗并吹干。将销、盘装到磨损试验机后,分别称取1.3 g的MoS2(0.2~1 μm)或Fe2O3(0.25 μm)颗粒并均匀地添加到环形凹槽内,随后施加载荷,启动机器进行磨损实验。磨损后再用酒精清洗松散的颗粒。采用电子分析天平E180(精度为0.01 mg)称量销试样磨损前后的质量,计算差值作为钛合金的磨损质量损失。
表1 TC4合金的化学成分
Table 1 Chemical composition of TC4 alloy (mass fraction, %)
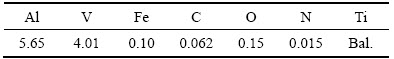
表2 GCr15轴承钢的化学成分
Table 2 Chemical composition of GCr15 steel (mass fraction, %)

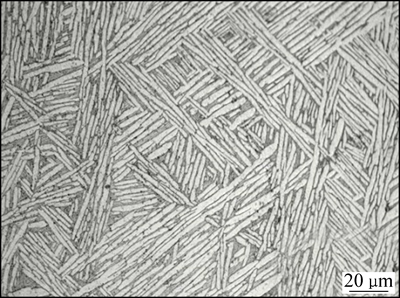
图1 TC4合金固溶时效处理后显微组织
Fig. 1 Microstructure of TC4 alloy after solution and aging
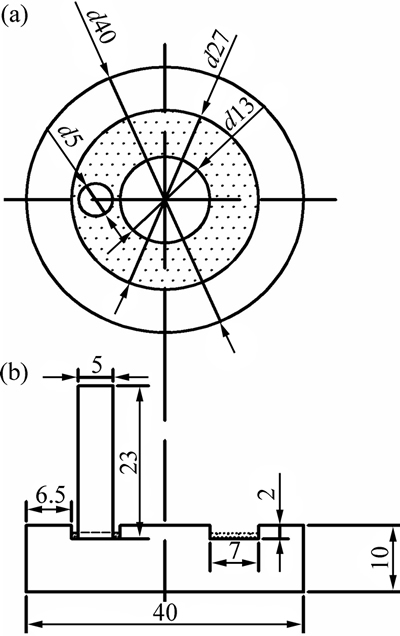
图2 销、盘配合状态示意图
Fig. 2 Schematic diagram for working status of pin (a) and disk (b) (Unit: mm)
保为证实验结果的准确性,每个实验参数重复3次,并取其平均值作为最终结果。
采用D/Max-2500/pc型X射线衍射仪(XRD)、JSM-7001F型扫描电镜(SEM)、Inca Energy 350型能谱仪(EDS)分别检测钛合金磨损后的磨损表面物相、形貌及成分。
2 结果与讨论
2.1 磨损质量损失
图3(a)所示为TC4合金在添加不同颗粒下的磨损质量损失与载荷的关系。当未添加任何颗粒时,TC4合金的磨损质量损失随载荷增加而急剧增加。当添加MoS2时,质量损失在10~20 g范围内,增加极为缓慢,但当载荷超过20 N后磨损质量损失快速增加。尽管如此,其磨损质量损失在整个测试范围内仍然小于未添加颗粒时的。当添加Fe2O3时,TC4合金的磨损质量损失几乎为零,且随着载荷的增加产生略微的波动。
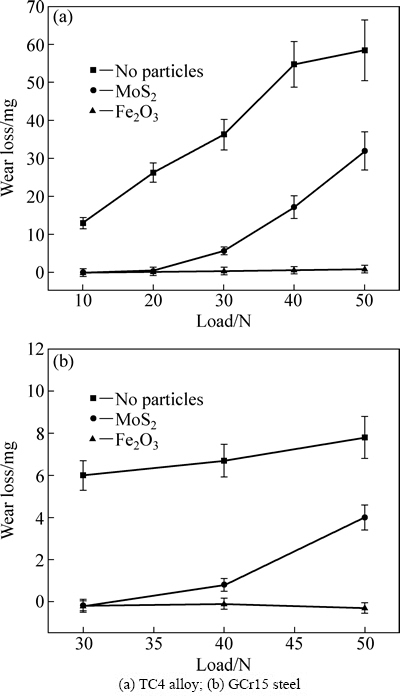
图3 添加不同颗粒时TC合金的磨损质量损失曲线
Fig. 3 Wear loss curves of TC alloy with addition of different particles
显然,干滑动下的钛合金的确具有较差的耐磨性。MoS2、Fe2O3等固态细颗粒的添加显著降低其磨损质量损失,改善了耐磨性。但在高载荷下,MoS2的减磨作用似乎并不明显。当添加颗粒或者无颗粒时,GCr15钢的也存在磨损现在,但磨损质量损失变化趋势似乎与TC4合金的相似(见图3(b))。
2.2 磨损表面物相
图4所示为TC4合金在不同颗粒下的磨损表面XRD谱。未添加任何颗粒时,10~50 N范围内磨损表面仅存在Ti峰。添加MoS2后,10 N时磨损表面除了Ti外开始出现大量的MoS2衍射峰,并在14.34°达到最高值。随着载荷增加,MoS2峰值迅速降低,除了14.34°处的衍射峰外几乎不存在其他MoS2峰。这表面滑动过程中钛合金磨损表面出现大量的MoS2颗粒,但随着载荷增加,MoS2迅速消失。当添加Fe2O3时,磨损表面在10~50 N范围内始终存在Fe2O3峰。
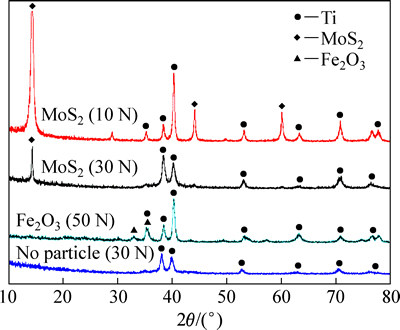
图4 TC4合金磨损表面XRD谱(坐标向内)
Fig. 4 XRD patterns for worn surfaces of TC4 alloy
2.3 磨损表面形貌及成分
图5所示为TC4合金在不同条件下的磨损表面形貌。当未添加颗粒时,磨损表面主要呈现较宽的犁沟、明显的塑形撕裂和粘着痕迹,而且分布较多的金属碎颗粒(见图5(a))。添加MoS2时,低载下的磨损表面覆盖着大面积的黑色光滑区域和少量的浅显犁沟,黑色区域边缘处还存在一定的白色疏松颗粒(见图5(b)放大区域)。EDS分析(见图6(a))表明黑色部分仅包含Mo、S两种元素,因此可以认为该区域为压实的固态颗粒层。随着载荷的增加,黑色区域几乎全部消失,磨损表面出现明显的撕裂痕迹,在撕裂边缘处堆积着疏松的MoS2颗粒(见图5(b)放大区域)。当添加Fe2O3时,几乎观察不到任何钛合金基体,整个磨损表面均被致密的层状结构所覆盖(见图5(d))。在磨损表面的部分区域,压实层似乎更加光滑。结合XRD(见图4)和EDS(见图6(b))可知,磨损表面颗粒层结构完全是由Fe2O3颗粒压实而成。
2.4 讨论
RIGNEY[21]认为干滑动条件下金属材料磨损的基本过程包括:表面微凸体直接接触,表面、亚表面塑性变形,磨屑的形成和材料转移,与环境中的元素(主要是氧)发生反应,并在载荷形作用下压实形成固态颗粒层(摩擦层)。显然,在与GCr15钢干滑动磨损过程中,TC4合金磨损表面几乎没有摩擦氧化物生成。同时,之前的研究发现[17-20],室温下钛合金的磨屑尺寸较大,容易脱离表面而不利于颗粒层的形成。因此,此时的TC4合金没有任何保护,磨损表面呈现大量的犁沟、塑性撕裂以及粘着痕迹,这是典型的磨粒磨损和粘着磨损机制。ARCHARD等[22]认为这种磨损与施加的载荷和滑动距离成正比,而与材料硬度成反比,其公式表述为:W=kLS/H,其中W为磨损体积,k为磨损系数,L为法向载荷,S为滑动距离,H为金属材料硬度。相比于GCr15钢(50HRC)而言,TC4合金的硬度较低,仅为40HRC。在滑动过程中,较软的TC4合金产生更多的磨损。同时,随着载荷的增加,TC4合金的磨损质量损失显著增加。由此看来,TC4合金的确具有极差的耐磨性,这与传统的观点一致[23]。
然而,人工添加固态颗粒后,钛合金的磨损性能得到一定的改善(见图3)。MoS2是一种鳞片状的结晶体,每个晶体具有3层结构,上下的S原子层,中间的Mo原子层,其中,S—Mo之间原子结合力较强,而S—S结合力较弱[24]。当MoS2添加到钛合金表面时,能够快速吸附在较软的金属材料表面,形成连续的颗粒层。在低载下,S—S结合面发生断裂而形成滑移面,原来的金属-金属的直接摩擦转变为MoS2分子层之间的相对滑移,从而显著降低磨损,磨损由严重向轻微转变。连续的MoS2颗粒层具备保护作用,但王兰等[25]采用化学镀的方式将MoS2颗粒添加到Ni-P镀层中,发现干摩擦下的磨损质量损失反而显著增加,镀层硬度的下降是其磨损增加的主要原因。这似乎意味着,MoS2并非具有较强的承载能力。随着载荷的增加(20N以上),TC4合金磨损表面MoS2颗粒层明显减薄、破坏,颗粒层失去其保护作用,金属-金属再次接触,磨损表面产生大量犁沟、塑性撕裂等痕迹,此时磨损表面特征与无添加下的极为相似。磨损机制又变为磨粒和粘着磨损。

图5 TC4合金磨损表面形貌
Fig. 5 Morphologies of worn surfaces of TC4 alloy with additives
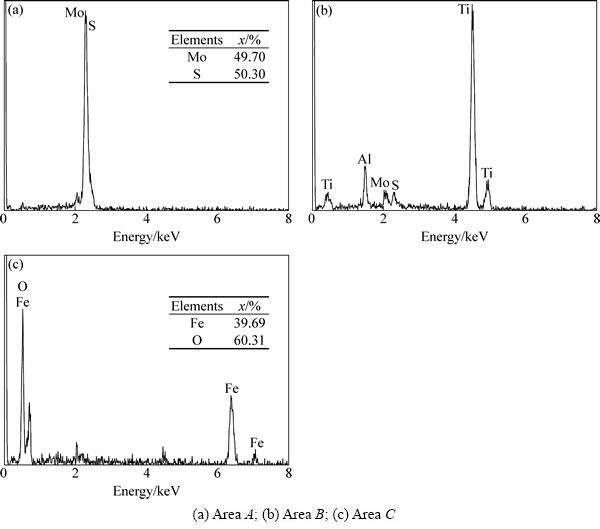
图6 图5中相应EDS区域分析
Fig. 6 Corresponding EDS regional analysis on worn surfaces of TC4 alloy shown in Fig. 5
相比较MoS2而言,Fe2O3形成的颗粒层具有更强的承载能力。ZHANG等[26]研究了45号钢、4Cr5MoSiV1和3Cr3MoV2V 3种钢在不同温度下的磨损行为及机制,发现碳钢在200℃形成的摩擦层致密、均匀、且含大量铁氧化物,显著提高钢材的耐磨性,其承载能力达到200~300 N以上。KATO[27]在碳钢摩擦界面加入一定量的Fe2O3细颗粒,在摩擦过程中快速形成压实颗粒层,显著降低碳钢的磨损质量损失。GODET[28]通过实验并分析证实了这种“第三体”氧化物颗粒层具备足够承载能力。在TC4合金摩擦界面人工添加Fe2O3颗粒时,摩擦热使得Fe2O3细颗粒快速烧结并压实形成颗粒层(见图5)。这种颗粒层连续致密,隔离钛合金和对磨件,避免金属直接接触。同时这种颗粒层具有很强的承载能力,在较大的载荷作用下破坏程度仍然很小。相比于添加MoS2而言,磨损率显著降低。因此,Fe2O3较强的承载能力是较好保护作用的主要原因。此时,磨损机制为氧化物压实颗粒层保护的轻微磨损为主。
3 结论
1) 室温下TC4合金具有较差的耐磨性,MoS2或Fe2O3颗粒的添加显著改变了钛合金的磨损性能。
2) 低载荷下MoS2颗粒层连续致密,但当载荷超过20 N时容易破碎,失去保护作用;而Fe2O3固态颗粒层具有较强的承载能力,在10~50 N范围内显著降低了TC4合金的磨损质量损失。
3) 无添加及MoS2颗粒层破碎时TC4合金以磨粒和粘着等严重磨损机制为主,当磨损表面连续覆盖固态颗粒层时发生严重磨损向轻微磨损的转变。
REFERENCES
[1] REN H S, TIAN X J, LIU J, WANG H M. Microstructural evolution and mechanical properties of laser melting deposited Ti-6.5Al-3.5Mo-1.5Zr-0.3Si titanium alloy[J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2015, 25(6): 1856-1864.
[2] PENG X N, GUO H Z, SHI Z F, QIN C, ZHAO Z L. Microstructure characterization and mechanical properties of TC4-DT titanium alloy after thermomechanical treatment[J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2014, 24(3): 682-689.
[3] 金和喜, 魏克湘, 李建明, 周建宇, 彭文静. 航空用钛合金研究进展[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2015, 25(2): 280-292.
JIN He-xi, WEI Ke-xiang, LI Jian-ming, ZHOU Jian-yu, PENG Wen-jing. Research development of titanium alloy in aerospace industry[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2015, 25(2): 280-292.
[4] 任军学, 刘 博, 姚倡锋, 石 凯, 梁永收, 罗远锋. TC11钛合金插铣工艺切削参数选择方法研究[J]. 机械科学与技术, 2010, 29(5): 634-637.
REN Jun-xue, LIU Bo, YAO Chang-feng, SHI Kai, LIANG Yong-shou, LUO Yuan-feng. On plunge milling process parameters optimization for TC11 titanium alloy[J] Mechanical Science and Technology for Aerospace Engineering, 2010, 29(5): 634-637.
[5] MIGU LEZ M H, SOLDANI X, MOLINARI A. Analysis of adiabatic shear banding in orthogonal cutting of Ti alloy[J]. International Journal of Mechanical Sciences, 2013, 75(11): 212-222.
LEZ M H, SOLDANI X, MOLINARI A. Analysis of adiabatic shear banding in orthogonal cutting of Ti alloy[J]. International Journal of Mechanical Sciences, 2013, 75(11): 212-222.
[6] ALAM M O, HASEEB A S M A. Response of Ti-6Al-4V and Ti-24Al-11Nb alloys to dry sliding wear against hardened steel[J]. Tribology International, 2002, 35(6): 357-362.
[7] DONG H, LI X Y. Oxygen boost diffusion for the deep-case hardening of titanium alloys[J] Materials Science and Engineering A, 2000, 208: 303-310.
[8] LEBEDEVA L, FRESNYAKOVA G N. Adhesion wear mechanisms under dry friction of titanium alloys in vacuum[J]. Wear, 1991, 148(2): 203-210.
[9] SCHRECKENBACH J P, MARX G, SCHLOTTIG F, TEXTOR M, SPENCER N D. Characterization of anodic spark-converted titanium surfaces for biomedical applications[J]. Journal of Material Research, 1999, 10: 453-457.
[10] XUE W B, WANG C, CHEN R Y, DENG Z W. Structure and properties characterization of ceramic coatings produced on Ti-6Al-4V alloy by microarc oxidation in aluminate solution[J]. Materials Letters, 2002, 52(6): 435-441.
[11] 刘仲阳, 廖小东, 王培录, 郑思孝, 孙官清. 氩离子辅助沉积生物玻璃陶瓷膜的结构和特性研究[J]. 功能材料, 2002, 33(2): 200-202.
LIU Zhong-yang, LIAO Xiao-dong, WANG Pei-lu, ZHENG Si-xiao, SUN Guan-qin. Structure and properties of bioglass ceramics film deposited by argon ion beam assistance[J]. Function Materials, 2002, 33(2): 200-202.
[12] 陈赤囡, 苏梅. TC9 激光熔覆 TiN 涂层的组织与耐磨性的研究[J]. 北京航空航天大学学报, 1998, 24(3): 253-255.
CHEN Chi-nan, SU Mei. Study on microstructure and abrasive resistance of laser cladding TiN surface alloyed TC9[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 1998, 24(3): 253-255.
[13] ZHAO L D, LUGSCHEIDER E. Reactive plasma spraying of TiAl6V4 alloy[J]. Wear, 2002; 25(11/12): 1214-1218.
[14] KIN D H, KIN H E, LEE K P, WANG C N, LEE I S. Characterization of diamond-like carbon films deposited on commercially pure Ti and Ti-6Al-4V[J]. Materials Science and Engineering C, 2002, 22: 9-14.
[15] 刘道新, 唐 宾, 陈 华, 何家文. 钛合金表面离子束增强沉积MoS2基膜层及其性能[J]. 中国有色金属报, 2001, 11(3): 454-460.
LIU Dao-xin, TANG Bin, CHEN Hua, HE Jia-wen. MoS2 composite films on Ti alloy prepared by ion-beam-enhanced deposition[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2001, 11(3): 454-460.
[16] 姚小飞, 谢发勤, 韩 勇, 赵国仙, 吴向清. 温度对TC4钛合金磨损性能和摩擦系数的影响[J]. 稀有金属材料与工程, 2012, 41(8): 1463-1466.
YAO Xiao-fei, XIE Fa-qin, HAN Yong, ZHAO Guo-xian, WU Xiang-qin. Effects of temperature on wear properties and friction coefficient of TC4 alloy[J]. Rare Metal Materials and Engineering, 2012, 41(8): 1463-1466.
[17] WANG L, ZHANG Q Y, LI X X, CUI X H, WANG S Q. Dry sliding wear behavior of Ti-6.5Al-3.5Mo-1.5Zr-0.3Si alloy[J]. Metallurgical and Materials Transactions A, 2014, 45: 2284-2296.
[18] WANG L, ZHANG Q Y, LI X X, CUI X H, WANG S Q. Severe-to-mild wear transition of titanium alloys as a function of temperature[J]. Tribology Letters, 2014, 53: 511-520.
[19] MAO Y S, WANG L, CHEN K M, WANG S Q, CUI X H. Tribo-layer and its role in dry sliding wear of Ti-6Al-4V alloy[J]. Wear, 2013, 297: 1032-1039.
[20] CHEN K M, ZHANG Q Y, LI X X, ZHANG Q Y, WANG L, WANG S Q. Investigation on wear characteristics of a titanium alloy/steel tribo-pair[J]. Materials and Design, 2015, 65: 65-73.
[21] RIGNEY D A. Some thoughts on sliding wear[J]. Wear, 1992, 152(1): 187-192.
[22] ARCHARD J F, HIRST W. The wear of metals under unlubricated conditions[J]. Proceeding of the Royal Society of London Series A, 1956, 236: 397-410.
[23] BUDINSKI K G. Tribological properties of titanium alloys[J]. Wear, 1991, 151(2): 203-217.
[24] 林春元. 二硫化钼的润滑机理[J]. 中国钼业, 1993, 45: 40-46.
LIN Chun-yuan. Lubricating mechanism of molybdenum disulfide[J]. China Molybdenum Industry, 1993, 45: 40-46.
[25] 王 兰, 邵红红, 苗润生, 徐文维. Ni-P-MoS2自润滑复合镀层的研究[J]. 润滑与密封, 2006, 12: 60-62.
WANG Lan, SHAO Hong-hong, MIAO Run-sheng, XU Wen-wei. Study on self-lubricant Ni-P-MoS2 composite coating[J]. Lubrication Engineering, 2006, 12: 60-62.
[26] ZHANG Q Y, CHEN K M, WANG L, CUI X H, WANG S Q. Characteristics of oxidative wear and oxidative mild wear[J]. Tribology International, 2013, 61: 214-223.
[27] KATO H. Effects of supply of fine oxide particles onto rubbing steel surfaces on severe-mild wear transition and oxide film formation[J]. Tribology International, 2008, 41(8): 735-742.
[28] GODET M. The third-body approach: A mechanical view of wear[J]. Wear, 1984, 100: 437-452.
Effect of solid particles on wear behavior of TC4 alloy
WANG Ji1, CUI Xiang-hong1, ZHANG Qiu-yang1, LIU Jia-qiang2, HUANG Ying-bin2, GONG Jiang-jun2, WANG Shu-qi1
(1. School of Material Science and Engineering, Jiangsu University, Zhenjiang 212013, China;
2. Suzhou Universal Group Technology Co., Ltd., Suzhou 215156, China)
Abstract: The effect of MoS2, Fe2O3 particles on wear behavior of TC4 alloy was studied by being artificially supplied onto the interface between TC4 alloy/GCr15 steel. The wear characteristics of TC4 alloy were examined by XRD, SEM and EDS; the wear mechanism was also discussed. The results show that TC4 alloy has a poor wear resistance, but two particles significantly change its wear performance. As the continuous solid particle layers of MoS2 or Fe2O3 form, the wear loss of TC4 alloy significantly decreases. Fe2O3 particles layer has a strong load-carrying capacity, and protects titanium alloy against wear. However, MoS2 particles layer is readily broken under high load, resulting in an increase of wear loss of TC4 alloy. As there is no additive, or MoS2 layer is broken, abrasive and adhesion wear prevail during sliding of TC4 alloy. On the contrary, as the continuous particle layer covers worn surface, severe-to-mild wear transition occurs.
Key words: solid particles layer; TC4 alloy; wear behavior; wear mechanism
Foundation item: Project(51071078) supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China; Project (KYLX-1031) supported by the Research Innovation Program for College Graduates of Jiangsu Province, China
Received date: 2015-09-28; Accepted date: 2016-01-20
Corresponding author: CUI Xiang-hong; Tel: +86-511-88797618; E-mail: miracle8980@126.com
(编辑 王 超)
基金项目:国家自然科学基金资助项目(51071078);江苏省普通高校研究生科技创新项目(KYLX-1031)
收稿日期:2015-09-28;修订日期:2016-01-20
通信作者:崔向红,副教授;电话:0511-88797618;E-mail:miracle8980@126.com