DOI: 10.11817/j.ysxb.1004.0609.2021-37628
TC21G钛合金平面应变变形行为及其机理
张欣雨1, 2,贾蔚菊2,毛小南2,尹雁飞2
(1. 东北大学 材料科学与工程学院,沈阳 110006;
2. 西北有色金属研究院 钛合金研究院,西安 710016)
摘 要:利用平面应变压缩实验,研究TC21G钛合金在变形温度为870~940 ℃、应变速率为0.1~1 s-1条件下的变形行为,并分析显微组织的演变过程。同时,研究加工参数对应变硬化指数n值的影响。结果表明:在应变速率一定的条件下,随着变形温度的升高,显微组织中β相的含量增加,合金的流变应力降低;而在变形温度一定的条件下,随着应变速率的增加,可动位错的迁移速率增加,从而使合金的流变应力升高。TC21G钛合金在两相区进行变形,随着变形温度的升高,应变量的增加以及应变速率的降低,片层α相的球化程度增加。基于显微组织的分析可知,应变硬化指数n值与绝热升温效应,β相的动态再结晶(DRX)以及动态回复(DRV)有密切的关系。
关键词:TC21G钛合金;平面应变压缩;动态再结晶;应变硬化指数
文章编号:1004-0609(2021)-01-0049-08 中图分类号:TG146.23 文献标志码:A
引文格式:张欣雨, 贾蔚菊, 毛小南, 等. TC21G钛合金平面应变变形行为及其机理[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2021, 31(1): 49-56. DOI: 10.11817/j.ysxb.1004.0609.2021-37628
ZHANG Xin-yu, JIA Wei-ju, MAO Xiao-nan, et al. Hot deformation behavior in plane strain compression and its mechanism of TC21G titanium alloy[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2021, 31(1): 49-56. DOI: 10.11817/j.ysxb.1004.0609.2021-37628
钛合金因具有比强度高、优异的抗腐蚀性等优点,而被广泛应用于航空、航天、船舶等领域。近年来,随着我国防卫政策由“近海防御”转为“远海防卫”,对舰船、潜艇等海军装备提出了更高的性能要求,促进了钛合金在海军装备上的应用。TC21钛合金作为一种高强高韧的损伤容限型钛合金,是由西北有色金属研究院基于美国的Ti-62222S合金按照损伤容限原则自主研制的新型钛合金[1]。该合金已成功应用于航空结构件的制备,针对舰船用钛合金的工况特点,西北有色金属研究院在TC21钛合金的基础上开展了成分优化研究,设计了改性的TC21G钛合金,使其冲击韧性优于传统的TC21钛合金,该合金的应用目标为船用钛合金板材。常规的圆柱单向压缩常用来模拟材料的挤压和锻造过程,但由于摩擦力的存在,当变形超过一定的变形量时,样品会出现“鼓肚”现象。而平面应变压缩不存在“鼓肚”现象,其对流变应力的测定更加方便且精确。此外,由于平面应变压缩实验的应力、应变及热传导等状态与热轧状态近似[2],因此,利用其可以模拟TC21G钛合金的轧制实验。
控制轧制过程的加工参数对优化钛合金的组织和性能起着至关重要的作用,加工参数主要包括变形温度、变形速率以及变形量等参数。ZHU等[3]研究了TC21合金在热压缩过程中的变形温度和应变速率对组织演变的影响,并建立了热加工图,发现随应变速率增加,失稳区会扩大,最终得到的最优加工参数为1.0×10-2 s-1、1150 ℃。对TC21钛合金的热压缩变形行为进行研究,发现影响合金动态再结晶(DRX)行为的主要因素是应变速率,应变速率较高的条件下不发生DRX,而低应变速率会促进DRX现象的发生[4]。应变硬化指数n值反映了金属材料抵抗均匀塑性变形的能力,是衡量金属材料变形行为的重要参数,因此有众多学者研究应变硬化指数。一些学者的研究表明,应变硬化指数n值对加工参数的变化十分敏感[5-6]。LUO等[7]和WANG等[8]分别以Ti60钛合金和TC8钛合金为研究对象,研究了变形温度对应变硬化指数n的影响,并发现n值会随着变形温度的升高而增大。目前,对TC21钛合金热变形过程的研究较多,而对成分优化后的TC21钛合金的热变形过程研究较少。此外,研究热加工参数对TC21G钛合金应变硬化指数的影响也十分重要,因此,有必要对其进行深入研究。
本研究利用平面应变压缩实验模拟板材轧制变形过程,研究TC21G钛合金的平面应变变形行为,分析其在热变形过程中的组织演变规律,揭示其微观变形机理,为TC21G钛合金的板材制备提供参考。
1 实验
本实验所用的TC21G钛合金铸锭经过3次真空自耗电弧炉熔炼,名义成分如表1所列。合金经β相区开坯,随后在两相区锻造成150 mm×65 mm× 65 mm的板坯。利用淬火金相法测得合金的相变点为930 ℃,原始组织如图1所示,为典型的双态组织,等轴初生α相(αp)的含量约为20%。
表1 TC21G钛合金的名义成分
Table 1 Nominal compositions of TC21G titanium alloy (mass fraction, %)
平面应变压缩实验采用的仪器为Gleeble-1500热模拟实验机,对热压缩试样采用钼丝进行线切割,并对样品表面打磨,以达到所需的精度要求,降低表面粗糙度,保证实验过程中的温度控制更加精确,最终得到的样品尺寸为20 mm×15 mm×10 mm。应变速率为0.1 s-1 和1 s-1;变形温度分别为870 ℃、900 ℃和940 ℃;压缩变形量为30%和50%。试样以10 ℃/s的加热速率加热至变形温度,保温3 min后进行热压缩变形,变形后采取水淬的冷却方式,以保留高温变形后的组织。压缩后的试样沿轴向剖开,经机械打磨和抛光,之后使用Kroll试剂 (10 mL HF+30 mL HNO3+100 mL H2O)进行腐蚀,利用Zeiss Axio Vert. A1光学显微镜和JSM-6700F型扫描电子显微镜进行显微组织观察,并使用图像分析软件(Image Pro Plus 6.0) 测量晶粒尺寸。

图1 TC21G钛合金的原始组织
Fig. 1 Initial microstructure of TC21G titanium alloy
2 结果与分析
2.1 应力-应变曲线特征
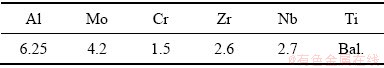
应力-应变曲线反映了材料流动应力与变形条件之间的内在联系,同时它也是材料内部组织变化的宏观表现。图2所示为TC21G钛合金在相同应变速率和不同变形温度下的应力-应变曲线,TC21G钛合金的流变应力对变形温度较为敏感。合金的变形特征可以概括为加工硬化、动态软化和稳态流变。在变形的初始阶段,位错不断增殖和塞积,形成位错缠结和位错胞等障碍,会阻碍位错运动,从而产生加工硬化现象;随着应变的增加,应力迅速增加,在达到应力峰值后,动态再结晶(DRX)、动态回复(DRV)和绝热升温产生的软化效应大于加工硬化的强化效果,流变应力随着应变的增加而逐渐下降,呈现出动态软化的特征;随着变形的继续进行,最终动态软化和加工硬化处于相对平衡的状态,流变应力进入稳态流变阶段。
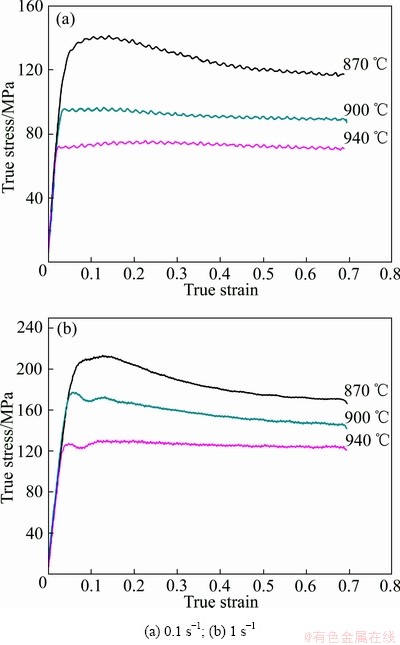
图2 TC21G钛合金在不同应变速率下的真应力-真应变曲线
Fig. 2 Flow true stress-true strain curves of TC21G titanium alloy at different strain rates
由图2可见,当应变速率一定时,随变形温度的升高,TC21G合金的流变应力降低。根据WANG等[8]的研究可知,随变形温度的提高,初生α相(αp)内部的位错数量减少。温度的升高会提高原子的平均动能,降低合金的临界切应力,促进位错运动和热扩散过程的进行,导致TC21G合金变形所需的位错数量减少,从而使流变应力降低[9]。
由图3可以看出,在高温高应变速率的条件下,即变形温度为900 ℃和940 ℃,应变速率为1 s-1时,TC21G合金在0~0.1的应变范围内出现了一个峰值,随后又下降,出现了加工硬化和动态软化,这是应力不连续屈服现象,在Ti26合金[10]、Ti-7333合金[11]中都有过类似的报道,而在低应变速率的条件下,未出现应力不连续屈服现象。一般用两种理论来解释此现象:第一种为动态理论,即不连续屈服现象与晶界可动位错的产生有关系,而变形温度对不连续屈服程度的影响可能与晶界位错的释放有关,如局部位错攀移、晶界迁移或溶质原子的重排等方式都会引起晶界位错的释放[12]。另外一种为静态理论,即初始的屈服是由于溶质原子钉扎的位错开动,对钛合金施加足够大的应力时,位错从钉扎点开动,使可动位错的密度增加,从而导致应力突然下降[13]。然而,根据ANKEM等[14]和WANG等[15]的研究可知,钛合金高温变形过程中出现的应力不连续屈服现象不能用静态理论来解释。位错来源于较高的应变速率[16],因此,TC21G钛合金的应力不连续屈服现象可以用动态理论进行有效的解释。
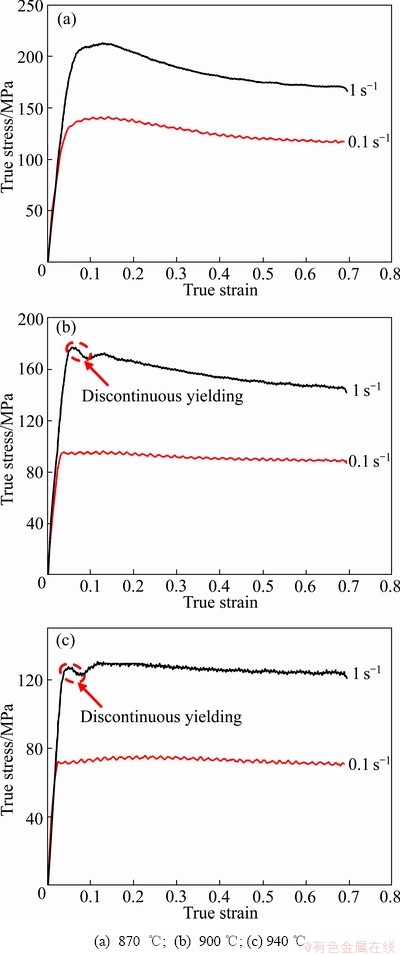
图3 TC21G钛合金在不同变形温度下的真应力-真应变曲线
Fig. 3 Flow true stress-true strain curves of TC21G titanium alloy at different temperatures
由图3(a)和(b)可以看出,在变形温度较低(870 ℃,900 ℃) 的条件下,应变速率越高,TC21G钛合金的峰值应力就越高,变形抗力越大。当应变速率较高(1 s-1) 时,应力-应变曲线表现出流变软化的特征,即流变应力在出现峰值后明显下降。而应变速率较低(0.1 s-1) 时,应力-应变曲线呈现稳态流动的特征,即流变应力达到峰值后趋于稳定。这是由于应变速率低,试样的变形时间较长,有充足的时间发生动态软化来抵消一部分加工硬化的作用。
当变形温度一定时,随应变速率的增加,合金的峰值应力升高。应变速率对流变应力的影响可用位错动力学方程来解释( 和
和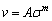 )[11](其中,
)[11](其中,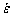 指应变速率,b指位错的Burgers矢量,v指位错的平均迁移速率)。因此,应变速率增大,可动位错的迁移速率增加,从而使合金的流变应力升高。在低温、高应变速率(870 ℃、1 s-1)的条件下,TC21G合金的加工硬化现象十分明显,在应变量为0.14左右才开始软化;而在高温、低应变速率(940 ℃、0.1 s-1)的条件下,应变达到较小值(约0.02)后就发生软化。此现象说明,在高温、低应变速率的条件下,合金更容易发生软化和晶界滑移,且变形抗力更小。特别地,当应变速率为0.1 s-1时,应力-应变曲线呈现锯齿状波动,主要与变形引起的加工硬化和DRX产生的软化交替作用及周期性变化有关。
指应变速率,b指位错的Burgers矢量,v指位错的平均迁移速率)。因此,应变速率增大,可动位错的迁移速率增加,从而使合金的流变应力升高。在低温、高应变速率(870 ℃、1 s-1)的条件下,TC21G合金的加工硬化现象十分明显,在应变量为0.14左右才开始软化;而在高温、低应变速率(940 ℃、0.1 s-1)的条件下,应变达到较小值(约0.02)后就发生软化。此现象说明,在高温、低应变速率的条件下,合金更容易发生软化和晶界滑移,且变形抗力更小。特别地,当应变速率为0.1 s-1时,应力-应变曲线呈现锯齿状波动,主要与变形引起的加工硬化和DRX产生的软化交替作用及周期性变化有关。
2.2 变形组织分析
钛合金的显微组织对热变形参数的变化十分敏感,而显微组织的变化与DRX和DRV等过程密切相关。TC21G钛合金在不同热变形条件下的组织如图4所示。由图4可以看出,变形温度和应变速率对显微组织有显著影响。
应变速率一定时,对比不同变形温度的组织,可以发现随着变形温度的升高,α相的体积分数降低,而β相的体积分数提高。在两相区进行变形,随变形温度的升高,片层α相的球化程度增加。TC21G钛合金在900 ℃进行变形,片层α相发生破碎球化,如图4(b)所示。在β相区(940 ℃)变形时,α相几乎消失且β基体上有针状α相析出,组织由尺寸较大的β晶粒组成且沿着变形方向轻微拉长,说明发生了α→β的相变过程,如图4(c)所示。组织的演变可用来解释应力-应变曲线的变化,即变形温度升高会使流变应力降低,原因是随着变形温度升高,β相含量增加,而具有体心立方结构(BCC)的β相与具有密排六方结构(HCP)的α相相比有更多的滑移系,可以看作“软相”。因此,β相含量增加会使流变应力降低[8]。
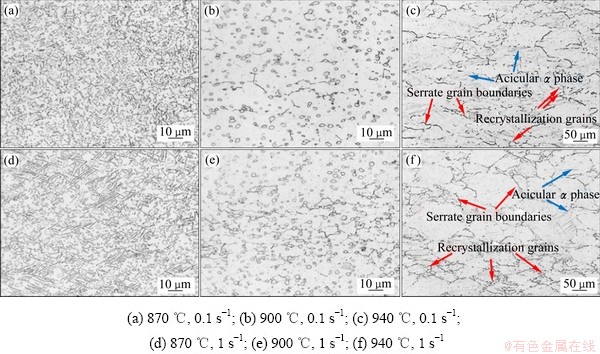
图4 TC21G钛合金在不同应变速率及不同温度变形后的显微组织
Fig. 4 Microstructures of TC21G titanium alloy after deformation at different strain rates and different temperatures
从图4可以看出,在温度一定的条件下,应变速率对组织有显著的影响。当变形温度为870 ℃,应变速率为1 s-1时,与原始组织相比,大量呈小球状或短棒状的α相分布在β基体上,一些片层α相在变形的作用下发生了破碎球化,由图4(d)所示。SESHACHARYULU等[17]指出球化有四个阶段,包括片层切变、位错增殖、位错界面的形成和迁移,如图5所示。当应变速率降低至0.1 s-1时,片层α相破碎球化现象更明显,如图4(a)所示。
当变形温度升至合金的相变点以上(940 ℃),且应变速率为0.1 s-1时,粗大的β晶粒沿变形方向略微拉长,且晶界呈现锯齿状,如图4(c)所示,这是DRV的特征。同时,在锯齿状的晶界存在直径约为15.6 μm的等轴或近等轴的细小晶粒,这是β晶粒在发生变形的过程中,其晶界应变量较大的区域发生选择性再结晶的结果。随着应变速率提高至1 s-1,β晶粒的尺寸增加,且尺寸分布不均匀。同时,β再结晶晶粒的数量增加,但尺寸减小至11.3 μm。
DRX的过程可以分为形核和晶粒长大这两个过程,当应变速率增加时,位错没有充足的时间进行消耗或增殖,因此变形储存能会提高,这会促进β再结晶晶粒的形成,且会导致较强的加工硬化效应,因此与低的应变速率相比,峰值应力较高。然而,由于应变速率高,则变形持续时间较短,原子扩散不充分,因此,再结晶晶粒的长大过程会被抑制。同时,晶界滑移也会被抑制,导致β再结晶晶粒尺寸较小。由于β相与α相相比为“软相”,因此,TC21G钛合金在β相区的加工硬化不太严重,在应变较小的条件下(约为0.03),合金的动态软化就足以抵抗加工硬化,使流动应力在较小值就能达到稳定状态。
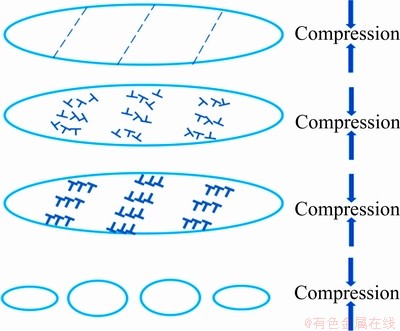
图5 热变形过程中α相的球化过程
Fig. 5 Schematic illustrating globularization process of α phase during hot deformation process
除了变形温度和应变速率对TC21G钛合金的显微组织有影响之外,变形量对其显微组织的影响也不可忽视。图6所示为不同变形量对显微组织的影响。由图6可以看出,在应变速率为1 s-1的条件下,随着变形量的增大,再结晶晶粒的数量增加。在870 ℃进行变形,对比图6(a)和6(d)可知,变形量较小时,片层α相交错排列且无序分布,少量片层α相还发生了扭折,片层α相在变形时会向Taylor因子较低的软取向方向旋转[18]。此外,原始组织的等轴α相变为拉长状。随着变形量增加至50%(真应变为0.7),片层α相通过切变的方式发生了破碎球化,变成短棒状和近等轴状。片层α相的破碎主要由位错滑移控制,与单位应变量有关,为了降低界面能,α/β相界面会进行迁移,从而形成等轴状或近等轴状的α相。当变形温度升至900 ℃,变形量为30%的条件下,片层α相的球化现象非常明显,随着应变量的增加,等轴状α相的含量增加,如图6(e)所示,说明α相的球化程度增加。
在相变点以上(940 ℃) 进行热变形,可以在晶界上观察到再结晶晶粒,这是因为晶界处点阵畸变大且晶界能高,是DRX晶粒的优先形核位置[19]。此外,如图6(c)和(f)所示,一部分β晶粒的晶界弓出,而晶界弓出有利于再结晶晶粒的长大。在变形的初始阶段,位错会迅速增殖,进而形成高密度的位错网,随着应变的增加,高密度的位错网会演变成亚结构,从而转变成DRX晶粒[20]。在变形量较小(变形量为30%、真应变为0.35)的条件下,变形储存能较低,位错没有充足的时间进行重排,因此再结晶程度较小。随着变形量增加至50%(真应变为0.7),变形储存能增加,会促进晶界和位错运动,再结晶晶粒会长大且数量增加。
综合以上分析可知,在本文的试验条件下,TC21G钛合金变形组织中没有出现局部剪切等流变失稳现象,且可热加工范围较宽,其在900 ℃、0.1 s-1的变形条件下可获得更加均匀细小的显微组织。
2.3 应变硬化指数
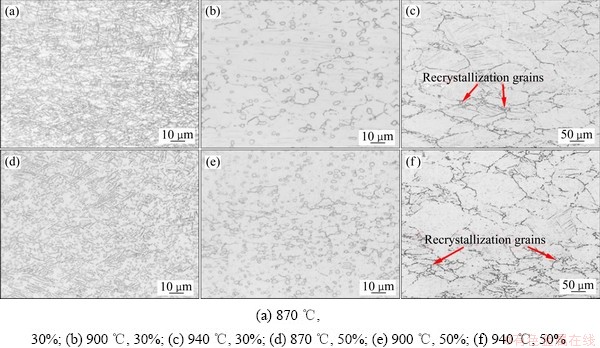
图6 TC21G钛合金在不同变形量及不同变形温度下的显微组织
Fig. 6 Microstructures of TC21G titanium alloy after deformation at different strains and different temperatures
应变硬化指数n值反映了金属材料抵抗均匀塑性变形的能力,是由热效应引起的软化和应变引起的硬化共同作用的参量,应变硬化指数n可以用如下方程式(见式(1))表示[21]。
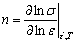 (1)
(1)
式中: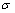 为流变应力(MPa);
为流变应力(MPa); 为应变;
为应变;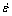 为应变速率(s-1);T为绝对变形温度(K)。在一定的应变速率和变形温度下,利用TC21G钛合金的流变应力即可计算应变硬化指数n的数值。
为应变速率(s-1);T为绝对变形温度(K)。在一定的应变速率和变形温度下,利用TC21G钛合金的流变应力即可计算应变硬化指数n的数值。
图7所示为TC21G合金的应变指数n值随变形温度和应变速率变化的曲线。由图7可看出,在应变速率一定的条件下,n值随变形温度的升高而增加,此规律与WANG等[8]和LUO等[7]的研究结果一致。变形温度低于940 ℃时,n值为负值;升至940 ℃时,n值趋于0。这一实验结果说明软化效应在TC21G钛合金热变形过程中十分重要。应变硬化指数n值是动态软化和加工硬化相互竞争的结果,软化效应的降低会引起n值的增大。因此,TC21G钛合金在两相区进行变形,软化效应大于加工硬化,导致n值为负值。TC21G钛合金在两相区进行变形有明显的软化效应,可能是由于合金在变形过程中产生的绝热升温效应,导致样品的实际温度升高[7, 22]。由图4显微组织演变过程的分析可知,合金在β单相区进行变形,β相仅发生部分DRX和DRV。因此,TC21G合金在β相区进行变形所产生的软化效应明显低于两相区的软化效应。

图7 TC21G合金的应变硬化指数n的曲线
Fig. 7 Curves of strain hardening exponents n of TC21G titanium alloy
由图7可知,当变形温度一定时,应变速率的增加会使应变硬化指数n值略微变小。TC21G钛合金在应变速率较高(1 s-1) 的条件下变形,单位时间内累积的位错密度增加,导致变形储存能提高,从而促进软化机制(DRX、DRV)的开动,造成的软化效应较为明显[8]。此外,应变速率较高,则变形速度快,由于钛合金导热率较低,导致变形热在短时间内无法向周围传递,从而使合金出现流变软化现象[3];而应变速率较低时(0.1 s-1)变形时间更长,形成的位错数目较少且位错运动速度较低,位错之间相互交割的几率也较低,DRX和DRV造成的软化效应也有充足的时间来消耗位错,从而使位错密度降低[8],但与高应变速率相比,造成的软化效应较低。因此,应变速率越高,软化效应越明显。
3 结论
1) 应变速率一定时,TC21G钛合金的流变应力随变形温度的升高而降低,这主要与αp相内部的位错数量和β相含量的减少有关;变形温度一定,随应变速率的增加,合金的峰值应力升高,可以用位错理论来解释;合金在高温高应变速率下变形,应力-应变曲线出现应力不连续屈服现象。
2) TC21G钛合金在两相区进行变形时:随着变形温度的升高,应变量的增加以及应变速率的降低,片层α相的球化程度增加。合金在β单相区进行变形时,随应变速率的增加,β再结晶晶粒的数量增加而尺寸减小;随应变量的增加,变形储存能提高,β晶粒的再结晶程度增加。
3) 应变速率一定时,随变形温度的升高,应变硬化指数n值增加,在β相区变形所产生的软化效应小于两相区的软化效应;变形温度一定时,随应变速率的增加,n值略微变小,合金的软化效应更明显。
REFERENCES
[1] LUO J, GAO J, LI L, et al. The flow behavior and the deformation mechanisms of Ti-6Al-2Zr-2Sn-2Mo-1.5Cr-2Nb alloy during isothermal compression[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2016, 667: 44-52.
[2] 潘红波, 唐 荻, 胡水平, 等. 平面应变压缩技术的研究[J]. 锻压技术, 2008, 33(2): 75-79.
PAN Hong-bo, TANG Di, HU Shui-ping, et al. Study on plane strain physical compression technology[J]. Forging and Stamping Technology, 2008, 33(2): 75-79.
[3] ZHU Y C, ZENG W D, LIU J L, et al. Effect of processing parameters on the hot deformation behavior of as-cast TC21 titanium alloy[J]. Materials and Design, 2012, 33(1): 264-272.
[4] ZHAO Y L, LI B L, ZHU Z S, et al. The high temperature deformation behavior and microstructure of TC21 titanium alloy[J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2010, 527(21): 5360-5367
[5] PICU R C, VINCZE G, QZTURK F, et al. Strain rate sensitivity of the commercial aluminum alloy AA5182-O[J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2005, 390(1): 334-343.
[6] LUO J, LI M Q, YU W X, et al. The variation of strain rate sensitivity exponent and strain hardening exponent in isothermal compression of Ti-6Al-4V alloy[J]. Materials and Design, 2010, 31(2): 741-748.
[7] LUO J, LI M Q. Strain rate sensitivity and strain hardening exponent during the isothermal compression of Ti60 alloy[J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2012, 538: 156-163.
[8] WANG K, LI M Q. Flow behavior and deformation mechanism in the isothermal compression of the TC8 titanium alloy[J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2014, 600(2): 122-128.
[9] ZHAO Q Y, YANG F, TORRENS R, et al. Comparison of hot deformation behaviour and microstructural evolution for Ti-5Al-5V-5Mo-3Cr alloys prepared by powder metallurgy and ingot metallurgy approaches[J]. Materials and Design, 2019, 169(5): 1-6. DOI: 10.1016/j.matdes.2019.107682.
[10] 赵恒章, 奚正平, 郭荻子, 等. Ti26钛合金热变形行为及本构模型[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2013, 23(1): 221-225.
ZHAO Heng-zhang, XI Zheng-ping, GUO Di-zi, et al. Hot deformation behavior and constitutive model of Ti26 alloy[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2013, 23(1): 221-225.
[11] FAN J K, KOU H C, LAI M J, et al. Characterization of hot deformation behavior of a new near beta titanium alloy: Ti-7333[J]. Materials and Design, 2013, 49: 945-952.
[12] PHILIPPART I, RACK H J. High temperature dynamic yielding in metastable Ti-6.8Mo-4.5F-1.5Al[J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 1998, 243(1/2): 196-200.
[13] NING Y Q, LUO X, LIANG H Q, et al. Competition between dynamic recovery and recrystallization during hot deformation for TC18 titanium alloy[J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2015, 635: 77-85.
[14] ANKEM S, SHYUE J G, VIJAYSHANKAR M N, et al. The effect of volume percent of phase on the high temperature tensile deformation of two-phase Ti-Mn alloys[J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 1989, 111: 51-61.
[15] WANG K, LI M Q. Characterization of discontinuous yielding phenomenon in isothermal compression of TC8 titanium alloy[J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2016, 26(6): 1583-1588.
[16] 王哲君, 强洪夫, 王学仁. 发生不连续屈服的钛合金高温变形研究进展[J].中国有色金属学报, 2012, 22(7): 1904-1913.
WANG Zhe-jun, QIANG Hong-fu, WANG Xue-ren. Research and development progress of high temperature deformation of titanium alloy with discontinuous yielding[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2012, 22(7): 1904-1913.
[17] SESHACHARYULU T, MEDEIROS S C, MORGAN J T, et al. Hot deformation mechanisms in ELI grade Ti-6A1-4V[J]. Scripta Materialia, 1999, 41(3): 283-288.
[18] SUN J Z, LI M Q, LI H. Initial flow softening and restoration mechanisms of isothermally compressed Ti-5Al- 2Sn-2Zr-4Mo-4Cr with basket weave microstructure[J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2017, 697(14): 132-140.
[19] LIN Y C, HE D G, CHEN M S, et al. EBSD analysis of evolution of dynamic recrystallization grains and δ phase in a nickel-based superalloy during hot compressive deformation[J]. Materials and Design, 2016, 97: 13-24.
[20] CHEN X M, LIN Y C, CHEN M S, et al. Microstructure evolution of a nickel-based superalloy during hot deformation[J]. Materials and Design, 2015, 77: 41-49.
[21] HOLLOMON J H. Tensile deformation[J]. Metals Technology, 1945, 12: 268-290.
[22] DING R, GUO Z X, WILSON A. Microstructural evolution of a Ti-6Al-4V alloy during thermomechanical processing[J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2002, 327(2): 233-245.
Hot deformation behavior in plane strain compression and its mechanism of TC21G titanium alloy
ZHANG Xin-yu1, 2, JIA Wei-ju2, MAO Xiao-nan2, YIN Yan-fei2
(1. School of Materials Science and Engineering, Northeastern University, Shenyang 110006, China;
2. Titanium Alloy Research Institute, Northwest Institute for Nonferrous Metal Research, Xi’an 710016, China)
Abstract: The hot deformation behavior in plane strain compression of the TC21G titanium alloy was investigated in the deformation temperatures ranging from 870 ℃ to 940 ℃, the strain rates ranging from 0.1 s-1 to 1 s-1. The microstructures evolution was also analyzed. Meanwhile, the effect of processing parameters on the strain hardening exponent n was analyzed. The results show that, under the condition of a certain strain rate, the flow stress of alloy decreases with the increase of the deformation temperature due to the increase of β phase content. However, in the condition of a certain temperature, the flow stress of alloy increases with the increase of the strain rate, because the velocity of mobile dislocations increases. During deforming in the α+β field, with the increase of the deformation temperature or strain, and the decrease of the strain rate, the globularization degree of the lamellar α phase increases. Based on the microstructure examination, the variation of n values is found to depend on the adiabatic heating effect, dynamic recrystallization (DRX) and dynamic recovery (DRV) of β phase.
Key words: TC21G titanium alloy; plane strain compression; dynamic recrystallization; strain hardening exponent
Foundation item: Project(2016YFB0301201) supported by the National Key Research and Development Program of China; Project(51601149) supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China
Received date: 2019-11-07; Accepted date: 2020-12-04
Corresponding author: JIA Wei-ju; Tel: +86-13484674005; E-mail: diana_1025@126.com
(编辑 李艳红)
基金项目:国家重点研发计划项目(2016YFB0301201);国家自然科学基金资助项目(51601149)
收稿日期:2019-11-07;修订日期:2020-12-04
通信作者:贾蔚菊,高级工程师,博士;电话:13484674005;E-mail:diana _1025@126.com