粉末冶金气门座圈裂纹成因分析
朱远志1,尹志民1,曹湘斋2,黄继武1
(1.中南大学 材料科学与工程学院,湖南 长沙,410083;
2 中南大学 粉末冶金研究院,湖南 长沙,410083)
摘要: 采用力学、物理性能测试,金相、扫描电镜、能谱和X衍射分析研究了气门座圈产品失效的主要原因。研究结果表明,失效座圈合金的密度(7.26 g/cm3),洛氏硬度(40.0)和压溃强度(740 MPa)均稍低于正常产品的密度(7.38 g/cm3)、洛氏硬度(46.0)和压溃强度(760 MPa);样品上部平行于表面有细微的分层断面,断面上有大量疏松颗粒、二次裂纹和少量夹杂物;密实工艺不当,造成微观疏松,是座圈失效的直接原因;合金中断口处K和Ca的含量分别达到1.37%,1.61%,导致液态金属脆化,是座圈失效的另一原因。
关键词: 气门座圈; 失效; 粉末冶金; 液态金属脆性
中图分类号: 文献标识码:A 文章编号: 1672-7207(2005)02-0209-04
Failure Analysis of Powder Metallurgy Valve Seat
ZHU Yuan-zhi1,YIN Zhi-min1,CAO Xiang-zai2, HUANG Ji-wu1
(1.School of Materials Science and Engineering, Central South University, Changsha 410083, China;
2.Research Institute of Powder and Metallurgy, Central South University, Changsha 410083, China)
Abstract: The failure of the powder metallurgy valve seat was analyzed by optical microscopy, scanning electronic microscopy, X-ray energy spectrum and X-ray diffraction. The results show that the density(7.26 g/cm3), Rockwell hardness (40.0) and compressing strength(740 MPa) of the failure valve are lower than those of the normal products(7.38 g/cm3, 46.5 and 760 MPa, respectively). There are a lot of incompact particles, secondary microcracks and impurities on the fracture surface that parallels to top surface of valve seat. Unsuitable compaction procedure is a direct reason for the failure of the valve seat. A high content of K(1.37%), Ca (1.61%) in the valve seat causes liquid metal embrittlement, which is another reason for the failure.
Key words: valve seat; failure; powder metallurgy; liquid metal embrittlement
-
气门座是安装在发动机汽缸盖上用于承载气门密封发动机的关键部件,受到高温燃气的冲刷和来自气门的往复冲击磨损[1-3]。因此,对气门座材料的性能要求非常高。粉末冶金气门座是目前各国致力开发的气门座材料[4,5]。如果粉末冶金制造工艺控制不当,往往会使粉末冶金座圈产品存在诸多缺陷,造成产品报废。在此,作者对其缺陷成因进行了分析。
1 实验过程
采用KYKY2800扫描电镜对失效座圈进行能谱分析,确定其化学成分。采用经标准块校正的维氏硬度计测试座圈硬度,用排水法测试座圈的密度,采用CSS-44200电子万能材料试验机测试材料的压溃强度。压溃强度用下式计算:
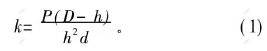
其中:k为压溃强度,MPa;P为外加载荷,N;D为环的外径,cm;d为环的厚度,cm;h为环的高度,cm。测试物理力学性能后,对座圈进行为金相和断口扫描电镜观察。
为了便于对比,还测试了正常产品的物理、力学性能。
2 实验结果与分析
2.1 气门座圈化学成分
在低倍下采用扫描电镜对座圈样品的化学成分进行能谱分析测试。座圈样品成分如表1所示(碳含量未检测)。
表 1 座圈样品成分
Table 1 Chemical compositions of valve w/%

由表1可知,Cr,Mo,Ni和Co的平均含量分别为1.52%,2.55%,1.64%和5.1%。与这类座圈合金的标准成分数据接近。因此,可以认为座圈合金成分符合设计要求。 [] 2.2 座圈的物理、力学性能
材料的密度、硬度等物理、力学性能如表2所示。
表 2 正品和失效产品的性能对比
Table 2 Comparison of properties of normal valve and failure valve

由表2可知,正品的密度、硬度以及压溃强度均比失效产品的略高,由于粉末冶金产品具有一定分散性,可以认为失效产品和正常产品在物理力学性能上无差别。
2.3 X射线衍射物相分析
对失效产品进行X射线衍射物相结构分析,其衍射图谱如图1所示。
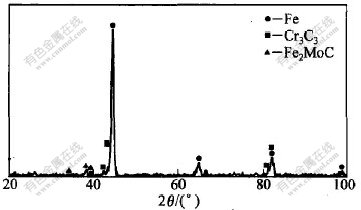
图 1 失效座圈样品的XRD物相分析
Fig. 1 XRD pattern of failure valve
将衍射数据与标准物质的衍射数据进行对比分析可知,样品中的物相为合金铁素体以及Fe2MoC和Cr7C3等化合物,符合设计合金的组织要求。
2.4 金相组织
失效座圈的显微组织如图2所示。

图 2 失效座圈合金的微观组织
Fig. 2 Microstructures of failure valve
由图2可见,失效座圈表面存在大量显微空洞,最大尺寸约为0.4 mm。从背反射电子像以及金相组织可见,该失效座圈的组织为保持马氏体形态的回火屈氏体、粗大的铁素体(亮白块)和碳化物。组织中还可见明显的夹杂物。
2.5 扫描电镜断口分析
失效座圈的断裂是通过座圈径向平面并垂直于其轴线方向的一种崩裂(如图3所示)。与正常座圈产品比较,失效座圈在硬度、密度和压溃强度等都比较低。从其表面形貌(见图2(a))上来看,其最大显微空洞尺寸为0.4 mm,粉末冶金产品上的显微空洞尺寸通常应小于0.2 mm,超出允许尺寸范围。另外,从断口形貌(见图4)来看,可见大量疏松颗粒及氧化物,氧化物周围存在大量的二次裂纹。在断口处(见图4(d)和图4(b))也发现大量的疏松颗粒及沿疏松颗粒界面的二次裂纹。研究结果表明,该失效合金座圈存在微观疏松。在座圈的烧结、淬火和回火过程中,不可能形成这种微观疏松。因此,这种疏松组织应当是在粉末冶金压制成型过程中形成的。可能是在压制成型过程中,压制压力过小或模具等工艺因素造成的压制压力分布不均匀所致。
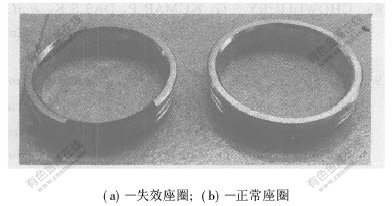
图 3 失效座圈宏观形貌
Fig. 3 Photographs of failure valve seats
从失效座圈的金相组织(见图2(b))中发现有夹杂物。对图4(d)中裂纹处进行能谱分析,结果如图5所示。
可见,该处的化学成分和表1中的化学成分有很大区别。该处Ni和Co的含量已接近0,且含有1.37%的K和1.61%的Ca。K和Ca在该合金中为有害杂质。K,Ca及Fe元素的一些基本物理性能如表3所示[6]。
从表3可见,K是一种低熔点的元素,其硬度和高温强度非常低。无论K以何种形式存在,对合金性能均有不利影响。高温淬火或回火时会导致液态金属出现脆性[7-12]。Ca虽然熔点较高,但其膨胀系数与Fe的相差很大,在热处理过程中温度不断变化时,Ca与周围基体由于膨胀系数不同而形成应力,可能导致裂纹发生。另外,Ca还有可能和Ni等金属形成低熔点的钙基合金。因此,K和Ca等杂质的混入,是造成座圈合金失效的又一原因。

图 4 阀座自然断口边部扫描电镜照片
Fig. 4 Fractographies of failure valve
表 3 K、Ca和Fe的基本物理性能对比
Table 3 Comparison of physical properties of K, Ca and Fe

图 5 断口裂纹处成分
Fig. 5 Compositions of cracks in fractured surface
3 结 论
a. 失效座圈合金的密度(7.26 g/cm3)、洛氏硬度(40.0)和压溃强度(740 MPa)均稍低于正常产品的密度(7.38 g/cm3)、洛氏硬度(46.5)和压溃强度(760 MPa)。
b. 样品上部平行与表面有细微的分层断面,断面上有大量疏松颗粒、二次裂纹和少量夹杂物。密实工艺不当,造成微观疏松,是座圈失效的直接原因;合金中断口处K、Ca的含量分别达到1.37%和1.61%。K和Ca含量过高,导致液态金属脆性,是座圈失效的另一原因。
参考文献:
[1]OOTANI T, YAHATA N, FUJIKI A. Impact Wear Characteristics of Engine Valve and Valve Seat Insert Materials at High Temperature[J]. Wear, 1995,188:175-184. [2]WANG Y S. The Effect of Operating Conditions on Heavy Duty Engine Valve Seat Wear[J]. Wear, 1996, 201: 15-25.
[3]QUINN T F J. Oxidative Wear Modeling Part Ⅲ: The Effects of Speed and Elevated Temperatures[J]. Wear, 1998, 216(2): 262-275.
[4]CHEN W X, TU J P, WANG L Y, et al. Tribological Application of Carbon Nanotubes in a Metal-based Composite Coating and Composites[J]. Carbon, 2003, 41:215-222.
[5]YANG S, GIBSON R F, CROSBIE G M. Vibration Characteristics and Comparisons of Automotive Engine Valves Made from Conventional and Non-conventional Materials[J]. Sound and Vibration, 1996,191(5):986 - 992.
[6]陈冠荣,时钧,朱亚杰,等.化学百科全书[M].北京:化学工业出版社,2001.
CHEN Guan-rong, SHI Jun, ZHU Ya-jie, et al. Chemistry Encyclopedia[M]. Chemical Industry Press, 2001.
[7]MARIANNE C, DAVID R. The Morphology of Thermal Cracks in Brittle Materials[J]. The European Ceramic Society, 2002,22(4):435-445.
[8]CHOWDHURY S G, KUMAR P, DAS S K, et al. Failure Analysis of High Temperature Studs[J]. Engineering Failure Analysis, 2001, 8(6): 521-528.
[9]LEGRIS A, NICAISE G, VOGT J. Liquid Metal Embrittlement of the Martensitic Steel 91: Influence of the Chemical Composition of the Liquid Metal: Experiments and Electronic Structure Calculations[J]. Nuclear Materials, 2002,301(1):70-76.
[10]HILDITCH J P, HURLEY J R, TICE D R. The Liquid Metal Embrittlement of Iron and Ferritic Steels in Sodium[J]. Corrosion Science,1995,37(3):445-454.
[11]CLEGG R E, JONES D R H. Liquid Metal Embrittlement of Tensile Specimens of En19 Steel by Tin[J]. Engineering Failure Analysis,2003,10(1):119-130.
[12]CLEGG R E. A Fluid Flow Based Model to Predict Liquid Metal Induced Embrittlement Crack Propagation Rates[J]. Engineering Fracture Mechanics,2001,68(16):1777-1790.
收稿日期:2004-10-24
作者简介:朱远志(1970-),男,湖南双峰人,博士研究生,从事高温摩擦材料研究
论文联系人: 朱远志,男,博士研究生;电话:0731-8830262(O); E-mail: tuzy21@163.com