
DOI: 10.11817/j.issn.1672-7207.2021.03.019
渤海湾盆地黄骅坳陷潜山中生界火山岩储层特征及成储机制
孟凡超1,周立宏2,魏嘉怡3,崔岩4,楼达2,陈世悦1,鄢继华1
(1. 中国石油大学(华东) 地球科学与技术学院,山东 青岛,266580;
2. 中国石油大港油田公司,天津,300280;
3. 中国石油长庆油田分公司勘探开发研究院,陕西 西安,710018;
4. 山东科技大学 山东省沉积成矿作用与沉积矿产重点实验室,山东 青岛,266590)
摘要:中生界火山岩是渤海湾盆地黄骅坳陷潜山勘探的重要目标之一。受复杂的构造演化影响,潜山火山岩储层的类型与成储机制复杂,限制火山岩油气的勘探开发。通过岩心观察、铸体薄片鉴定、扫描电镜观察、常规孔渗、压汞和流体包裹体均一温度测试,结合录井、测井、地震和试油试采等资料,研究黄骅坳陷潜山中生界火山岩储层特征、控制因素、储层类型、成储机制及模式。研究结果表明:黄骅坳陷潜山中生界火山岩岩性可分为3大类17小类,岩相可分为4类岩相7种亚相。火山岩非均质性强,总体上属于中孔、低渗储层。火山岩储集空间类型可分为原生孔隙、次生孔隙和裂缝3大类。火山岩储层成岩作用可划分为冷凝固结成岩阶段、岩浆期后热液阶段、表生成岩阶段和埋藏成岩阶段,共包含12种成岩作用类型,每种成岩作用对应形成不同的储集空间类型。岩性岩相类型、风化淋滤作用和断裂作用是影响黄骅坳陷中生界火山岩储层储集性能的主要因素。根据火山岩储集空间类型和主控因素,潜山火山岩储层类型可划分为风化淋滤型、埋藏溶蚀型和原生气孔型3种,每种类型储层成岩演化过程与成储机理各有不同。风化淋滤型储层的储集空间以次生裂缝和次生溶蚀孔隙为主,靠近不整合面和断裂分布,是潜山表层的主要储层类型,主要受地表风化淋滤作用形成。埋藏溶蚀型储层以溶蚀形成的次生孔隙为主,靠近断裂分布,烃源岩释放的酸性流体是储层形成的关键因素。原生气孔型储层的储集空间主要为原生气孔和成岩裂缝,是潜山内幕的主要储层类型,储层的形成主要受岩浆冷凝固结成岩作用控制。
关键词:渤海湾盆地;黄骅坳陷;潜山;火山岩储层;储层特征;成储机制
中图分类号:TE132 文献标志码:A 开放科学(资源服务)标识码(OSID):
文章编号:1672-7207(2021)03-0859-17
Characteristics and formation mechanism of Mesozoic volcanic reservoirs from buried hills in Huanghua Depression, Bohai Bay Basin
MENG Fanchao1, ZHOU Lihong2, WEI Jiayi3, CUI Yan4, LOU Da2, CHEN Shiyue1, YAN Jihua1
(1. School of Geosciences, China University of Petroleum(East China), Qingdao 266580, China;
2. Dagang Oilfield Company, PetroChina, Tianjin 300280, China;
3. Exploration and Development Research Institute of PetroChina Changqing Oilfield Company, Xi'an 710018, China;
4. Shandong Provincial Key Laboratory of Depositional Mineralization and Sedimentary Mineral, Shandong University of Science and Technology, Qingdao 266590, China)
Abstract: Mesozoic volcanic rocks are the important targets for exploration of buried hills in Huanghua Depression, Bohai Bay Basin. The types and formation mechanism of volcanic reservoirs from buried hills are quite complicated due to complex tectonic evolution, which restrictes the exploration and development of volcanic oil and gas. Based on logging, drilling, seismic profile, oil testing and production testing data, characteristics, controlling factors and reservoir-forming mechanism, types of Mesozoic volcanic reservoirs from buried hills in Huanghua Depression were studied by means of a series of analytical testing methods such as core observation, casting thin sections scanning identification, conventional porosity and permeability test, mercury injection experiment and fluid inclusions homogenization temperature analysis. The results show that Mesozoic volcanic rocks from buried hills in Huanghua Depression can be divided into 3 major types and 17 sub-types in lithology, and 4 lithofacies and 7 sub-facies in lightfacies. The volcanic reservoirs are highly heterogeneous, belonging to medium porosity and low permeability reservoirs as a whole. The volcanic reservoir space is mainly divided into primary pore, secondary pore and fracture. There are 4 volcanic diagenesis stages, including cooling and consolidation stage, magmatic hydrothermal stage, supergene stage and burial stage, which consists of 12 types of diagenesis. Each type of diagenesis corresponds to different reservoir types. The main controlling factors of Mesozoic volcanic reservoirs in Huanghua Depression include lithology-lithofacies type, weathering-leaching and fracture process. According to volcanic reservoir types and main controlling factors, Mesozoic volcanic reservoirs are classified as primary pore type, weathering-leaching type and buried dissolution type. The diagenetic evolution processes and formation mechanisms of each reservoir type are quite different. As an important reservoir type of surface buried hills, the weathering-leaching reservoir is mainly composed of secondary fractures and dissolution pores, close to unconformities and fractures. It is mainly formed by surface weathering and leaching. Buried dissolution reservoirs contain a large number of dissolution pores, and distribute along the faults. The key factor for this reservoir is the acidic fluid released by source rocks. The primary pore reservoirs retain a large number of primary pores and fractures, which are the important interior reservoirs of buried hills. It is mainly controlled by the magmatism.
Key words: Bohai Bay Basin; Huanghua Depression; buried hills; volcanic reservoir; reservoir characteristics; formation mechanism
火山岩在含油气盆地中广泛发育,对油气成烃、成储及成藏具有重要影响[1]。全球已在100多个国家发现了火山岩油气藏或与火山作用有关的油气显示[1-2]。火山岩作为一种特殊油气储层,在形成过程中受成岩作用[3]、岩性岩相[4-5]、风化淋滤和断裂活动[6]等多种因素共同影响,储层非均质性强[7-8],储层预测难度较大。为了准确预测火山岩有利储层分布,研究火山岩储层的类型以及成储机理尤为重要。根据火山岩储层储集空间类型和控制因素,可以把火山岩储层分为原生型和改造型2种类型。原生型储层主要受旋回期次、火山机构、岩性和岩相等火山作用本身控制[9-12],改造型储层主要受构造、风化淋虑和溶蚀等后期地质作用影响[13-16]。依据盆地内火山岩储层的类型和成储机制差异性进行有利储层的预测,对火山岩油气勘探具有重要意义。
潜山油气藏是渤海湾盆地重要的油气藏类型,已发现的61个潜山油气藏占盆地总储量的10.4%[17]。受印支、燕山和喜马拉雅等多期构造运动的影响,渤海湾盆地内潜山的形成和演化过程复杂。潜山既发育构造裂缝和溶蚀孔隙为主的风化壳储层[18-20],又存在原生气孔和成岩裂缝为主的内幕储层[21-22]。火山岩是渤海湾盆地潜山油气藏重要的储层之一,在辽河坳陷的兴隆台[11, 23]、济阳坳陷的埕岛、桩西[24-25],黄骅坳陷的风化店[26-27]等潜山火山岩中发现了油气藏。然而,目前对潜山火山岩储层的特征、成储机理与发育规律研究仍比较薄弱,常用的原生型和改造型火山岩储层的分类方式很难直接应用到潜山储层预测中,在一定程度上阻碍了潜山火山岩油气藏的勘探。黄骅坳陷在北大港、南大港、扣村―羊三木、风化店、孔店、埕海和王官屯等潜山带钻遇中生界火山岩,其潜山表层和内幕都有火山岩储层发育,是开展潜山火山岩储层成储机制研究的有利场所。本论文以黄骅坳陷潜山中生界火山岩为研究对象,系统研究潜山不同位置火山岩储层特征、类型及成储机制,以便为潜山火山岩优质储层分布预测奠定理论基础。
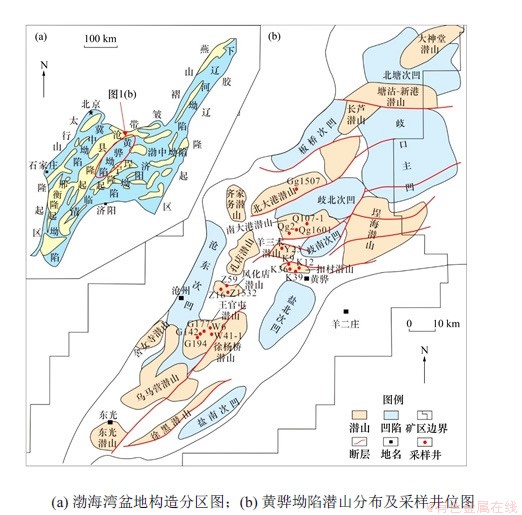
图1 渤海湾盆地构造格局及黄骅坳陷潜山分布简图
Fig. 1 Tectonic framework of Bohai Bay Basin and simplified distribution of buried hills in Huanghua depression
1 区域地质概况
图1所示为渤海湾盆地构造格局及黄骅坳陷潜山分布简图。由图1(a)可见:黄骅坳陷位于渤海湾盆地中北部,沧县隆起以东,埕宁隆起和渤中坳陷以西,北侧结束于燕山褶皱带,南侧以临清坳陷为界,是叠置在华北地台基底上的中―新生代裂谷盆地。黄骅坳陷呈北北东―南南西向延伸,宽度为30~100 km、长度约270 km,整体呈现出北东向展布、凹凸相间的构造格局,总面积约为1.7×104 km2,是渤海湾盆地富油气藏坳陷之一[28-29]。黄骅坳陷基底由太古宇和下元古界变质岩组成,其上覆盖沉积盖层,总厚度最大约14 km。中生代,区域岩石圈减薄,软流圈上涌,岩浆活动频繁[30],坳陷内发育大量火山岩[31-33]。受印支、燕山和喜山运动影响,黄骅坳陷发育了20多个潜山带[34]。火山岩主要分布在潜山中生界白垩系中。由图1(b)可见:本文从北大港、南大港、扣村、羊三木、风化店和王官屯潜山的17口钻井中共采集73块中生界火山岩样品,研究火山岩储层特征和成储机理。
2 储层特征
表1 黄骅坳陷中生界火山岩岩性岩相类型
Table1 Types of Mesozoic volcanic lithology and lithofacies in Huanghua depression

2.1 岩性岩相特征
通过钻井岩心观察和薄片鉴定,将黄骅坳陷中生界火山岩岩性分为火山熔岩、火山碎屑岩和火山碎屑沉积岩3大类17小类。表1所示为黄骅坳陷中生界火山岩岩性岩相类型。图2所示为黄骅坳陷潜山中生界典型火山岩。由表1可见:

图2 黄骅坳陷潜山中生界典型火山岩
Fig. 2 Typical Mesozoic volcanic rocks of buried hills in Huanghua depression
1) 火山熔岩类又分为块状玄武岩、气孔杏仁玄武安山岩、致密安山岩、气孔安山岩、蚀变安山岩和自碎角砾熔岩;
2) 火山碎屑岩类分为熔结角砾岩、熔结凝灰岩、火山集块岩、火山角砾岩、火山凝灰岩、含凝灰火山角砾岩和含角砾火山凝灰岩;
3) 火山碎屑沉积岩类分为沉角砾岩、沉凝灰岩、含火山角砾砂岩和凝灰质砂岩。
17口井182 m取心段火山岩中,以中基性的火山熔岩类(岩心长度占72%)为主,气孔玄武安山岩、气孔安山岩最常见,其次是火山碎屑沉积岩类(岩心长度占21%),火山碎屑岩类最少(岩心长度占7%)。研究区火山熔岩类属于高钾钙碱性系列和橄榄安粗岩系,大多为玄武粗安岩和粗安岩。黄骅坳陷中生界火山岩岩相分为4种岩相7种亚相。4种岩相分别是溢流相、爆发相、火山通道相和火山沉积相。其中,溢流相分为板状熔岩流亚相和自碎熔岩流亚相,爆发相分为热碎屑流亚相和空落亚相,火山沉积相分为沉火山碎屑沉积亚相和含火山碎屑沉积亚相。在火山通道相研究区只发现火山颈亚相。取心段火山岩岩相以溢流相(岩心长度占78%)为主,其次是火山沉积相(岩心长度占12%),爆发相(岩心长度占8%)和火山通道相(岩心长度占2%)最少。详细的火山岩岩性的物质组成、岩石特征和代表性钻井见表1和图2。
2.2 成岩作用与储集空间特征
通过岩心观察和薄片鉴定,研究黄骅坳陷中生界火山岩储层成岩作用和储集空间类型。表2所示为火山岩储层成岩阶段划分及成岩作用特征,图3所示为黄骅坳陷潜山中生界火山岩成岩作用与储集空间类型。由表2和图3可见:黄骅坳陷白垩系火山岩储层储集空间分为原生孔隙、次生孔隙和裂缝3大类,其中,原生孔隙包括原生气孔、杏仁体内孔、角砾间孔,次生孔隙包括杏仁溶蚀残余孔、斑晶溶蚀孔和基质内溶蚀孔,裂缝按照成因分为自碎裂缝、冷凝收缩缝、构造裂缝、风化裂缝、解理溶蚀缝、充填残余构造缝和充填-溶蚀构造缝。
表2 火山岩储层成岩阶段划分及成岩作用特征
Table 2 Diagenetic stages and characteristics of volcanic reservoirs
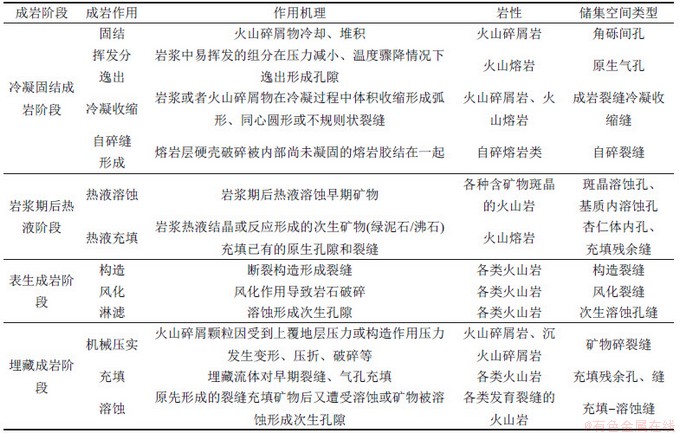
研究区火山岩储层以杏仁体内孔、次生溶蚀孔、构造裂缝和风化裂缝最常见。黄骅坳陷中生界火山岩划分为4个成岩阶段,依次是冷凝固结成岩阶段、岩浆期后热液阶段、表生成岩阶段和埋藏成岩阶段,每种成岩阶段包含了不同的成岩作用类型,如表2所示。火山岩成岩作用控制着储集空间类型。

图3 黄骅坳陷潜山中生界火山岩成岩作用与储集空间类型
Fig. 3 Diagenesis and reservoir space types of Mesozoic volcanic rocks from buried hills in Huanghua depression
1) 冷凝固结成岩阶段主要形成原生气孔、粒间孔、成岩缝和自碎缝等原生孔隙和裂缝。
2) 岩浆期后热液成岩阶段常常对原生孔隙有一定破坏作用,形成杏仁,降低储集空间。
3) 表生成岩阶段形成构造裂缝、风化裂缝和次生溶蚀孔隙,是有效储集空间形成的关键阶段。
4) 埋藏溶蚀成岩阶段,一方面可以形成新的溶蚀孔缝,另一方面也可能导致早期孔缝被充填,对储层改造具有双重作用。
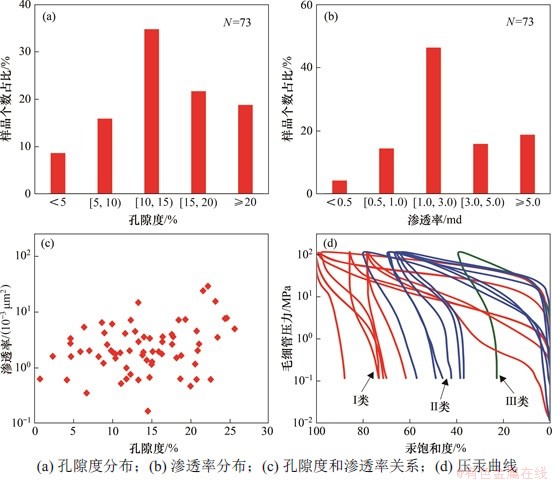
图4 火山岩储层孔渗特征与毛管压力曲线类型
Fig. 4 Characteristics of porosity and permeability and capillary pressure curve types of volcanic reservoirs
2.3 物性特征
图4所示为火山岩储层孔渗特征与毛管压力曲线类型。由图4(a)~(c)可见:孔隙度主要在10%~15%之间,样品数量占样品总数量的34.78%;渗透率主要分布在1~3×10-3 μm2之间,样品数量占样品总数量的46.38%,孔渗相关性差。由图4(d)可见:火山岩储层毛管压力曲线分为Ⅰ,Ⅱ和Ⅲ共3类类型:
Ⅰ类属于平台型,曲线出现1个近似平台,且向图左方凸出,表明以粗孔隙为主,孔喉直径较集中,分选性较好,储层物性好。
Ⅱ类属于长斜坡型,曲线向图右上方靠,无平台发育,表明歪度较小,孔喉分选性较差,储层物性较差。
Ⅲ类属于短斜坡型,曲线向图右上方凸出,无平台发育,表明歪度极小,孔喉分选性很差,储层物性最差或非储层。火山岩储层总体上属于中孔低渗储层,储层非均质性强。
3 火山岩储层的影响因素
黄骅坳陷中生界火山岩具有复杂多样的储集空间类型,表明储层的形成受多种因素的影响,成岩作用复杂。研究表明,研究区火山岩储层的形成主要受岩性岩相类型、风化淋滤作用以及断裂作用的影响。
3.1 岩性岩相
火山岩的岩性岩相类型影响原生孔隙发育类型[35],也制约次生孔隙和裂缝发育程度[13,35-36]。黄骅坳陷中生界火山岩岩相发育近源相和远源相2种组合,如表3所示。岩心和铸体薄片观察结果显示,近源相组合中的火山熔岩类(玄武安山岩和安山岩)和火山角砾岩比远源相组合中的火山凝灰岩、火山碎屑沉积岩类原生孔隙更发育。近源相组合中的安山岩比玄武岩更易遭受溶蚀形成斑晶溶蚀孔隙。远源相组合中的火山凝灰岩比沉火山凝灰岩更容易溶蚀形成溶蚀微孔隙。
选取基本未受构造抬升和风化淋滤影响的取心井段,研究火山岩岩性和岩相与孔隙度关系,发现不同岩性火山岩的平均孔隙度差别较大。总体上,近源相组合比远源相组合的火山岩平均孔隙度大;近源相中安山岩、玄武安山岩和玄武岩储层孔隙度依次降低;远源相中火山凝灰岩、沉火山凝灰岩、含火山碎屑岩储层孔隙度依次变小。近源相组合的渗透率明显比远源相组合的高,近源相中火山角砾岩渗透率最高,其次是自碎角砾熔岩,火山熔岩的渗透率最低。远源相组合中火山碎屑沉积岩渗透率最高,沉火山凝灰岩的渗透率最低,火山凝灰岩的渗透率介于两者之间(图5)。研究区火山岩储层发育的优势岩性是火山熔岩类的安山岩。
表3 黄骅坳陷潜山火山岩岩性岩相与储集空间类型对应关系
Table 3 Correspondence relationship between volcanic lithology-lithofacies and reservoir space types from buried hills in Huanghua depression
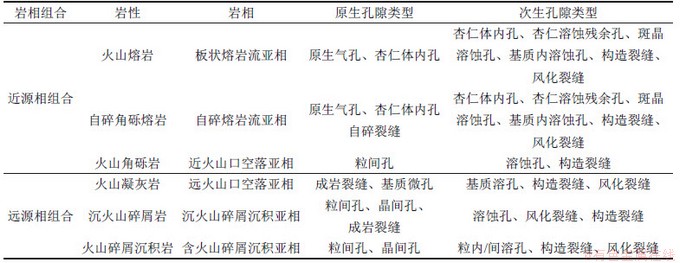

图5 不同岩性岩相火山岩孔隙度的差异
Fig. 5 Discrepancies of porosity and permeability of different volcanic rocks
3.2 风化淋滤
长期暴露于地表的岩石在表生作用影响下,岩石的坚固性变差,易发生破碎和溶蚀,形成裂缝和次生溶孔等储集空间,储集物性得到改善[37]。为了能更好分析风化淋滤对火山岩物性的影响,选取靠近不整合面、没有断裂发育且岩性一致的岩心段进行研究。
以K36井为例,K36井中生界火山岩取心段处于不整合面附近。岩性为玄武安山岩,取心段35块样品孔隙度结果显示,在没有裂缝发育情况下,玄武安山岩孔隙度随距不整合面距离增大而逐渐减小,如图6所示。宏观岩心和微观薄片也显示,距不整合面距离越近,孔隙度较高的岩心段风化程度和溶蚀程度越严重;远离不整合的取心段岩石风化程度、溶蚀程度较弱。由此可见,风化淋滤对火山岩储层物性具有积极影响,研究区储层试油结果与距不整合面距离关系如图7所示,由图7可见:产油层段主要集中在距不整合面顶150 m范围内;随着与中生界不整合面距离增加,产油层段逐渐减少,水层逐渐增多;在距中生界不整合面顶200 m范围外,试油结果几乎全是干层。

图6 K36井火山岩孔隙度变化与距离中生界不整合面的关系
Fig. 6 Porosity variation of volcanic rocks according to the distance away from Mesozoic unconformity in Well K36

图7 火山岩储层试油结果与距离中生界不整合面关系
Fig. 7 Relationship between oil saturation and the distance away from Mesozoic unconformity
3.3 断裂作用
断裂作用产生的裂缝本身就是十分重要的储集空间,而且可以连通孤立的原生储集空间,使其变成有效孔隙,从而改善储层的储集物性[38]。为了更好地研究断裂作用对储层的影响效果,仍然选择岩性一致的取心段进行分析。以W41-1井中生界取心段玄武安山岩为例,100个玄武安山岩孔隙度与距不整合面距离关系显示(如图8(a)所示):随着与不整合面距离增加,绝大部分样品的孔隙度逐渐减小,符合上述风化淋滤作用下物性变化规律;然而,在距不整合面约88 m位置处,火山岩的孔隙度异常升高。由图8(b)可以看出:在中生界不整合面之下,W41-1井处断裂发育,断裂使流体进入火山岩内部,产生大量溶蚀孔隙和裂缝,提高火山岩的孔隙度和渗透率。因此,断裂作用是改善研究区火山岩储层物性的有效途径之一。
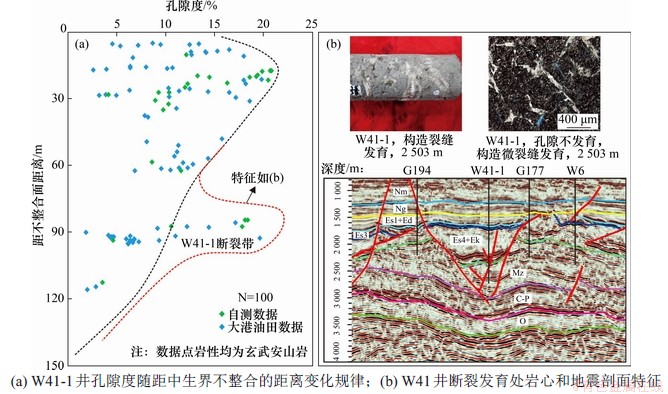
图8 W41-1井孔隙度变化与构造断裂发育的关系
Fig. 8 Relationship betweeen variation of porosity and development of tectonic fracture in Well W41-1
4 潜山火山岩储层成储机理
4.1 潜山火山岩储层类型
根据火山岩储层的储集空间类型和形成的主控因素,将研究区潜山中生界火山岩储层类型分为3种,分别是风化淋滤型、埋藏溶蚀型和原生气孔型,如表4所示。每种类型储集空间组合、储层主控因素、储层发育位置与展布存在较大差异。
1) 风化淋滤型火山岩储层的特征表现为储集空间主要为构造裂缝、风化裂缝和淋滤溶蚀孔组合。储层的形成受断裂作用、风化作用和溶蚀作用控制。
2) 埋藏溶蚀型火山岩储层表现在储集空间主要为溶蚀孔、充填残余构造缝和充填溶蚀构造缝组合。储层的形成主要受深部或者有机流体溶蚀作用控制。
3) 原生气孔型火山岩储层的特征表现在储集空间主要为原生气孔、角砾间孔、杏仁孔和冷凝收缩缝等原生孔缝。储层的形成受岩性岩相、火山机构和旋回期次等火山作用本身控制。
表4 黄骅坳陷潜山中生界火山岩储层类型划分方案
Table 4 Classification scheme of Mesozoic volcanic reservoirs from buried hills in Huanghua depression

4.2 潜山火山岩储层成岩演化与成储机理
图9所示为不同类型火山岩储层储集空间与成储模式图。
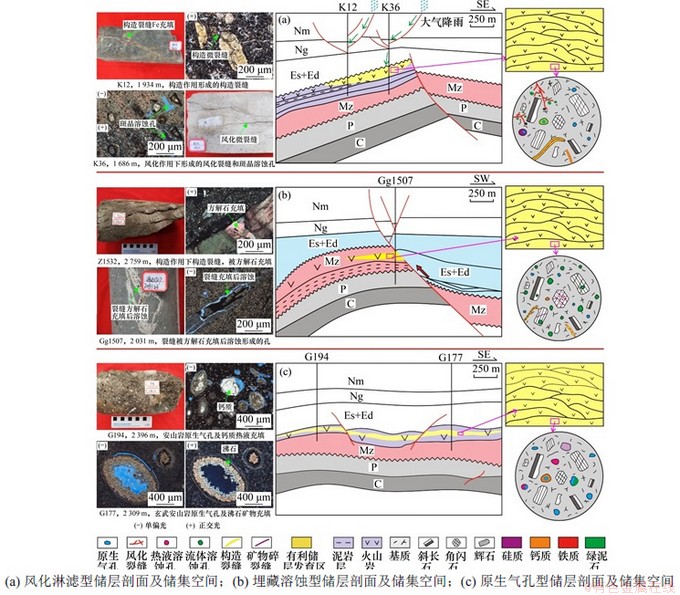
图9 不同类型火山岩储层储集空间与成储模式图
Fig. 9 Reservoir space types of different volcanic reservoirs and their forming models
4.2.1 风化淋滤型火山岩储层
由图9(a)可见:风化淋滤型火山岩储层成岩演化主要经历了冷凝固结→热液充填(绿泥石、沸石和硅质)→构造抬升→风化淋滤作用。中生代火山岩形成以后未埋藏或者受构造抬升作用影响,火山岩地层抬升至地表暴露,受构造和长时间风化作用形成风化裂缝,如图3(i)和图3(m)所示。大气降水和地表水等沿着裂缝或不整合面渗流到火山岩内部,对矿物进行溶蚀改造,在靠近不整合面和裂缝附近处产生淋滤溶蚀孔隙,如图3(j),(k),(n),(o)和(p)所示。由于是开放体系,很少见到溶蚀沉积物。因此,有利储层常靠近不整合面或者断裂发育,在潜山表层最发育,储层厚度变化较大。储层厚度常受古地貌控制,构造高部位剥蚀强烈,风化壳难以保存。在坡度相对平缓和断裂节理发育区,风化壳厚度较大,常形成连片储层。该类储层在扣村潜山、王官屯潜山,北大港潜山和风化店潜山中生界火山岩均有发现。
4.2.2 埋藏溶蚀型火山岩储层
由图9(b)可见:埋藏溶蚀型火山岩储层成岩演化主要经历了5种作用,依次是冷凝固结→热液溶蚀→构造破碎→埋藏充填(钙质)→流体溶蚀钙质。中生代火山岩形成以后,受构造运动影响,沉降埋藏,在此过程中形成大量构造裂缝,如图3(l)和(q)所示。埋藏以后,受地层水或热液作用,在裂缝中形成大量方解石,但显微观察发现,方解石形成以后又发生部分溶蚀,如图3(r)所示。
对北大港潜山Gg1507井裂缝方解石(图10(a))进行岩相学和均一温度测试,发现Gg1507井2 028~2 034 m中生界火山岩裂缝方解石中包裹体可以分为2期。
1) 第1期包裹体发育于方解石脉形成期间,为原生包裹体,包裹体丰度中等(3%,即约3%的方解石脉中发育该期次油气包裹体)。包裹体成群分布于方解石脉中,均为盐水包裹体,如图10(b)所示。
2) 第2期包裹发育于方解石脉形成期后,为次生包裹体,发育丰度极高(5%)。包裹体主要为方解石脉中成群或呈带状分布。
包裹体中的液烃呈淡黄色、淡褐色和黄褐色,显示黄绿色、黄色和黄褐色荧光,如图10(c)所示。134个方解石脉中流体包裹体均一温度显示,包裹体均一温度为85~95 ℃和105~115 ℃这2个区间,如图10(d)所示。早期原生流体包裹体的温度85~95 ℃与构造演化史古近纪―新近纪时期火山岩埋藏后的地温相吻合[39],代表了方解石形成温度,方解石的形成与埋藏阶段的地层水沉淀有关,并非风化淋滤阶段在地表水环境下形成。晚期次生含烃流体包裹体均一温度105~115 ℃代表了有机酸溶蚀作用的环境温度,受构造断裂控制,Gg1507井中生界潜山内火山岩通过断裂与古近纪烃源岩连通,新生界成熟的烃源岩产生油气前会产生大分子的干酪根,而干酪根在热演化过程中脱氢产生大量有机酸,这些有机酸性流体沿着大断裂进入火山岩中,对易溶矿物和裂缝钙质充填物进行溶解,形成大量基质内溶蚀孔和充填―溶蚀构造缝,如图9(b)和图10(a)所示。有利储层通常靠近深大断裂,沿断裂展布,如图9(b)所示,这类储层在北大港潜山最为发育。
4.2.3 原生气孔型储层
由图9(c)可见:原生气孔型储层成岩演化过程比较简单,主要经历了冷凝固结→热液充填(绿泥石/沸石/重晶石)。中生代火山爆发后,形成的爆发相火山碎屑岩和溢流相火山熔岩未经过明显的风化淋滤和有机酸溶蚀,火山碎屑岩仍保留着部分角砾间/晶间孔隙,火山熔岩保留着部分原生气孔和成岩微裂缝,如图3(a)~(d)所示。火山岩的原生气孔部分被岩浆后期热液形成的热液矿物充填,如绿泥石、沸石和方解石等(如图3(e)~(g)所示),还会对早期形成矿物进行熔融(如图3(h)所示)。
官177井玄武安山岩岩石致密,裂缝发育少,气孔中充填沸石和方解石等矿物,气孔中沸石中流体包裹体均一温度为115~125 ℃(如图10(d)和(f)所示),为岩浆期后热液充填或蚀变产物,而非地层水沉淀,在一定程度上降低了火山岩储层物性。原生气孔型火山岩有利储层的分布主要受控于岩相类型,储层展布稳定,沿层分布,如图9(c)所示。王官屯潜山最为典型,其他潜山内幕也多有发育。
4.3 潜山火山岩储层的发育规律
潜山的形成和发育受控于多期构造运动,渤海湾盆地黄骅坳陷古潜山的形成分为4个演化阶段。

图10 港古1507和官177井流体包裹体岩相特征与均一温度
Fig. 10 Petrography characteristics and homogenization temperature of fluid inclusions in Well Gg1507 and G177
1) 中元古代至古生代为潜山内幕地层建造阶段;
2) 中生代为潜山内幕构造发育阶段;
3) 古近纪为潜山宏观面貌定型阶段;
4) 新近纪为潜山深埋阶段[34]。
火山岩是黄骅坳陷白垩系的重要充填物质[26, 33],火山岩形成以后,伴随着潜山发育,经历复杂的成岩演化作用,处于潜山不同位置的火山岩经历的成岩作用各不相同,从而形成不同类型火山岩储层和油气藏[40]。风化淋滤型储层分布广泛,全区潜山基本可见,在扣村、王官屯、南大港和风化店潜山尤为发育。埋藏溶蚀型储层要求潜山内部断裂发育且与周围烃源岩地层连通,在南大港、北大港和风化店潜山都有发育。原生气孔型储层常发育在潜山带内部,作为潜山内幕的重要储层类型,主要分布在王官屯和南大港潜山。
5 结论
1) 黄骅坳陷潜山中生界火山岩岩性复杂(3大类17小类),岩相多样(4类岩相7种亚相)。岩性以中基性的火山熔岩类为主,安山岩、玄武安山岩和玄武岩最常见。岩相以溢流相的板状熔岩流亚相为主。火山岩储层储集空间类型可分为原生孔隙、次生孔隙和裂缝3种类型,以杏仁体内孔、次生溶蚀孔、构造裂缝和风化裂缝最常见。火山岩储层总体上属于中孔低渗储层,储层非均质性强。
2) 岩性岩相类型、风化淋滤作用和断裂作用是影响黄骅坳陷中生界火山岩储层储集性能的主要因素。依据储集空间类型和控制因素,火山岩储层可分为风化淋滤型、埋藏溶蚀型和原生气孔型3种,每种类型储层成岩演化过程与成储机理各不相同。
3) 风化淋滤型储层分布广泛,全区潜山基本可见,在扣村、王官屯、南大港、风化店潜山尤为发育;埋藏溶蚀型储层与断裂和烃源岩关系密切,在南大港、北大港、风化店潜山都有发现。原生气孔型储层受岩性岩相本身控制,常发育在潜山带内部,主要分布在王官屯、南大港潜山。
参考文献:
[1] 刘嘉麒, 孟凡超, 崔岩, 等. 试论火山岩油气藏成藏机理[J]. 岩石学报, 2010, 26(1): 1-13.
LIU Jiaqi, MENG Fanchao, CUI Yan, et al. Discussion on the formation mechanism of volcanic oil and gas reservoirs[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2010, 26(1): 1-13.
[2] SCHUTTER S R. Occurrences of hydrocarbons in and around igneous rocks[J]. Geological Society, London, Special Publications, 2003, 214(1): 35-68.
[3] SRUOGA P, RUBINSTEIN N. Processes controlling porosity and permeability in volcanic reservoirs from the Austral and Neuquén basins, Argentina[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 2007, 91(1): 115-129.
[4] YI Jian, SUN Fengyue, WANG Pujun, et al. Vesicle distribution in acidic lava flow units in the rift basins of NE China: implications for petroleum reservoir exploration[J]. Geological Journal, 2017, 52(4): 609-623.
[5] YI Jian, WANG Pujun, GAO Youfeng, et al. Vesicle distribution in basalt lava flow units in the Mesozoic rift basins of northeast China and its application in gas reservoir prediction[J]. Canadian Journal of Earth Sciences, 2016, 53(1): 59-70.
[6] WANG Yong, YANG Renchao, SONG Mingshui, et al. Characteristics, controls and geological models of hydrocarbon accumulation in the Carboniferous volcanic reservoirs of the Chunfeng Oilfield, Junggar Basin, northwestern China[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2018, 94: 65-79.
[7] 邹才能, 赵文智, 贾承造, 等. 中国沉积盆地火山岩油气藏形成与分布[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2008, 35(3): 257-271.
ZOU Caineng, ZHAO Wenzhi, JIA Chengzao, et al. Formation and distribution of volcanic hydrocarbon reservoirs in sedimentary basins of China[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2008, 35(3): 257-271.
[8] WANG Pujun, CHEN Shumin. Cretaceous volcanic reservoirs and their exploration in the Songliao Basin, northeast China[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 2015, 99(3): 499-523.
[9] FENG Zhiqiang. Volcanic rocks as prolific gas reservoir: a case study from the Qingshen gas field in the Songliao Basin, NE China[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2008, 25(4/5): 416-432.
[10] 衣健, 唐华风, 王璞珺, 等. 基性熔岩火山地层单元类型、特征及其储层意义[J]. 中南大学学报(自然科学版), 2016, 47(1): 149-158.
YI Jian, TANG Huafeng, WANG Pujun, et al. Types, characteristics and reservoir significance of basic lava flow units[J]. Journal of Central South University(Science and Technology), 2016, 47(1): 149-158.
[11] CHEN Zhenyan, YAN Huo, LI Junsheng, et al. Relationship between Tertiary volcanic rocks and hydrocarbons in the Liaohe basin, People's Republic of China[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 1999, 83(6): 1004-1014.
[12] DUTKIEWICZ A, VOLK H, RIDLEY J, et al. Geochemistry of oil in fluid inclusions in a middle Proterozoic igneous intrusion: implications for the source of hydrocarbons in crystalline rocks[J]. Organic Geochemistry, 2004, 35(8): 937-957.
[13] 侯连华, 邹才能, 刘磊, 等. 新疆北部石炭系火山岩风化壳油气地质条件[J]. 石油学报, 2012, 33(4): 533-540.
HOU Lianhua, ZOU Caineng, LIU Lei, et al. Geologic essential elements for hydrocarbon accumulation within Carboniferous volcanic weathered crusts in northern Xinjiang, China[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2012, 33(4): 533-540.
[14] 匡立春, 薛新克, 邹才能, 等. 火山岩岩性地层油藏成藏条件与富集规律: 以准噶尔盆地克—百断裂带上盘石炭系为例[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2007, 34(3): 285-290.
KUANG Lichun, XUE Xinke, ZOU Caineng, et al. Oil accumulation and concentration regularity of volcanic lithostratigraphic oil reservoir: a case from upper-plate Carboniferous of KA-BAI fracture zone, Junggar Basin[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2007, 34(3): 285-290.
[15] 李军, 刘丽峰, 赵玉合, 等. 古潜山油气藏研究综述[J]. 地球物理学进展, 2006, 21(3): 879-887.
LI Jun, LIU Lifeng, ZHAO Yuhe, et al. A review of study on ancient buried hill reservoir[J]. Progress in Geophysics, 2006, 21(3): 879-887.
[16] 宋明水, 赵乐强, 吴春文, 等. 准噶尔盆地车排子地区石炭系顶部风化壳结构及其控藏作用[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2016, 37(3): 313-321.
SONG Mingshui, ZHAO Leqiang, WU Chunwen, et al. Structure and reservoir-controlling of top Carboniferous weathering crust in Chepaizi area, Junggar Basin[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2016, 37(3): 313-321.
[17] 宋明水, 王惠勇, 张云银. 济阳坳陷潜山“挤-拉-滑”成山机制及油气藏类型划分[J]. 油气地质与采收率, 2019, 26(4): 1-8.
SONG Mingshui, WANG Huiyong, ZHANG Yunyin. “Extrusion, tension and strike-slip” mountain forming mechanism and reservoir type of buried hills in Jiyang Depression[J]. Petroleum Geology and Recovery Efficiency, 2019, 26(4): 1-8.
[18] 袁静. 埕北30潜山带太古界储层特征及其影响因素[J]. 石油学报, 2004, 25(1): 48-51.
YUAN Jing. Characters and influence factors on Archeozoic reservoir in the Chengbei 30 buried hills[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2004, 25(1): 48-51.
[19] 胡志伟, 徐长贵, 杨波, 等. 渤海海域蓬莱9-1油田花岗岩潜山储层成因机制及石油地质意义[J]. 石油学报, 2017, 38(3): 274-285.
HU Zhiwei, XU Changgui, YANG Bo, et al. Reservoir forming mechanism of Penglai 9-1 granite buried-hills and its oil geology significance in Bohai Sea[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2017, 38(3): 274-285.
[20] 王德英, 王清斌, 刘晓健, 等. 渤海湾盆地海域片麻岩潜山风化壳型储层特征及发育模式[J]. 岩石学报, 2019, 35(4): 1181-1193.
WANG Deying, WANG Qingbin, LIU Xiaojian, et al. Characteristics and developing patterns of gneiss buried hill weathering crust reservoir in the sea area of the Bohai Bay basin[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2019, 35(4): 1181-1193.
[21] 田世峰, 高长海, 查明. 渤海湾盆地冀中坳陷潜山内幕油气成藏特征[J]. 石油实验地质, 2012, 34(3): 272-276.
TIAN Shifeng, GAO Changhai, ZHA Ming. Reservoir-forming characteristics of inner buried hills in Jizhong Depression, Bohai Bay Basin[J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 2012, 34(3): 272-276.
[22] 金凤鸣, 王鑫, 李宏军, 等. 渤海湾盆地黄骅坳陷乌马营潜山内幕原生油气藏形成特征[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2019, 46(3): 521-529.
JIN Fengming, WANG Xin, LI Hongjun, et al. Formation of the primary petroleum reservoir in Wumaying inner buried-hill of Huanghua Depression, Bohai Bay Basin, China[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2019, 46(3): 521-529.
[23] LUO Jinglan, MORAD S, LIANG Zhigang, et al. Controls on the quality of Archean metamorphic and Jurassic volcanic reservoir rocks from the Xinglongtai buried hill, western depression of Liaohe basin, China[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 2005, 89(10): 1319-1346.
[24] 武群虎. 埕岛—桩海地区中生界火成岩油气成藏特征[J]. 特种油气藏, 2014, 21(3): 32-36.
WU Qunhu. Characteristics of volcanic reservoir accumulation in Mesozoic group of Chengdao-Zhuanghai area[J]. Special Oil & Gas Reservoirs, 2014, 21(3): 32-36.
[25] 孙耀庭, 孙超, 李辉, 等. 济阳拗陷桩西地区中生界火成岩储层控制因素[J]. 成都理工大学学报(自然科学版), 2016, 43(3): 257-265.
SUN Yaoting, SUN Chao, LI Hui, et al. Controlling factors of Mesozoic igneous rock reservoirs in Zhuangxi area, Jiyang depression, Shandong, China[J]. Journal of Chengdu University of Technology(Science & Technology Edition), 2016, 43(3): 257-265.
[26] LUO Jinglan, ZHANG Chengli, QU Zhihao. Volcanic reservoir rocks: a case study of the Cretaceous Fenghuadian suite, Huanghua basin, Eastern China[J]. Journal of Petroleum Geology, 1999, 22(4): 397-416.
[27] 罗静兰, 张成立. 风化店中生界火山岩油藏特征及油源[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2002, 23(4): 357-360.
LUO Jinglan, ZHANG Chengli. Characteristics and oil source for Mesozoic volcanic pools in Fenghuadian region[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2002, 23(4): 357-360.
[28] 渠芳, 陈清华, 连承波, 等. 黄骅坳陷南区油气分布规律及其成藏机制[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2008, 35(3): 294-300.
QU Fang, CHEN Qinghua, LIAN Chengbo, et al. Distribution and accumulation of the oil and gas in southern Huanghua Depression[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2008, 35(3): 294-300.
[29] 赵贤正, 蒲秀刚, 姜文亚, 等. 黄骅坳陷古生界含油气系统勘探突破及其意义[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2019, 46(4): 621-632.
ZHAO Xianzheng, PU Xiugang, JIANG Wenya, et al. An exploration breakthrough in Paleozoic petroleum system of Huanghua Depression in Dagang Oilfield and its significance[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2019, 46(4): 621-632.
[30] SUN Jing, LIU Zheng, ZHANG Shuai, et al. Large-scale removal of lithosphere underneath the North China Craton in the Early Cretaceous: Geochemical constraints from volcanic lavas in the Bohai Bay Basin[J]. Lithos, 2017, 292/293: 69-80.
[31] 杜旭东, 张一伟, 漆家福. 黄骅坳陷中生代隐伏火山岩系的特征及其形成的构造环境[J]. 地球学报, 1999, 20(1): 30-38
DU Xudong, ZHANG Yiwei, QI Jiafu. Characteristics and tectonic setting of the Mesozoic volcanic sequence in the Huanghua depression[J]. Acta Geoscientia Sinica, 1999, 20(1): 30-38.
[32] 罗静兰, 高知云. 河北风化店中生代火山岩的地球化学特征及其成因探讨[J]. 岩石学报, 1998, 14(1): 108-116.
LUO Jinglan, GAO Zhiyun. Discussion on the origin and geochemical characteristics of the Mesozoic volcanic sequences in Fenghuadian area, Hebei Province[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 1998, 14(1): 108-116.
[33] 金春爽, 乔德武, 淡伟宁. 渤海湾盆地中、新生代火山岩分布及油气藏特征[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2012, 33(1): 19-29.
JIN Chunshuang, QIAO Dewu, DAN Weining . Meso-Cenozoic volcanic rock distribution and reservoir characteristics in the Bohai Bay Basin[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2012, 33(1): 19-29.
[34] 张津宁, 付立新, 周建生, 等. 渤海湾盆地黄骅坳陷古潜山的宏观展布特征与演化过程[J]. 地质学报, 2019, 93(3): 585-596.
ZHANG Jinning, FU Lixin, ZHOU Jiansheng, et al. Macroscopic distribution characteristics and evolution process of buried hill in the Huanghua depression, Bohai Bay basin[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2019, 93(3): 585-596.
[35] 黄玉龙, 王璞珺, 舒萍, 等. 松辽盆地营城组中基性火山岩储层特征及成储机理[J]. 岩石学报, 2010, 26(1): 82-92.
HUANG Yulong, WANG Pujun, SHU Ping, et al. Characteristics and formation mechanism of the Cretaceous intermediate and mafic volcanic reservoirs in Songliao Basin, NE China[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2010, 26(1): 82-92.
[36] 孟凡超, 操应长, 崔岩, 等. 准噶尔盆地西缘车排子凸起石炭系火山岩储层成因[J]. 中国石油大学学报(自然科学版), 2016, 40(5): 22-31.
MENG Fanchao, CAO Yingchang, CUI Yan, et al. Genesis of Carboniferous volcanic reservoirs in Chepaizi salient in western margin of Junggar Basin[J]. Journal of China University of Petroleum(Natural Science Edition), 2016, 40(5): 22-31.
[37] 邹才能, 侯连华, 杨帆, 等. 碎屑岩风化壳结构及油气地质意义[J]. 中国科学(地球科学), 2014, 44(12): 2652-2664.
ZOU Caineng, HOU Lianhua, YANG Fan, et al. Structure of weathered clastic crust and its petroleum potential[J]. Scientia Sinica (Terrae), 2014, 44(12): 2652-2664.
[38] 王京红, 邹才能, 靳久强, 等. 火成岩储集层裂缝特征及成缝控制因素[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2011, 38(6): 708-715.
WANG Jinghong, ZOU Caineng, JIN Jiuqiang, et al. Characteristics and controlling factors of fractures in igneous rock reservoirs[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2011, 38(6): 708-715.
[39] 吴智平, 张飞鹏, 李伟, 等. 黄骅坳陷中生代构造演化的磷灰石裂变径迹证据[J]. 中国矿业大学学报, 2020, 49(1): 123-136.
WU Zhiping, ZHANG Feipeng, LI Wei, et al. Apatite fission track evidence of Mesozoic tectonic evolution in the Huanghua depression[J]. Journal of China University of Mining & Technology, 2020, 49(1): 123-136.
[40] 周立宏, 李洪香, 杨朋, 等. 沧东中生界火山岩特征与油气成藏模式[J]. 特种油气藏, 2017, 24(3): 9-14.
ZHOU Lihong, LI Hongxiang, YANG Peng, et al. Geologic characteristics and hydrocarbon accumulation model of Mesozoic volcanic rocks in Cangdong area[J]. Special Oil & Gas Reservoirs, 2017, 24(3): 9-14.
(编辑 秦明阳)
收稿日期: 2020 -05 -20; 修回日期: 2020 -07 -25
基金项目(Foundation item):国家科技重大专项(2016ZX05006-007) (Project(2016ZX05006-007) supported by the National Science and Technology Major Program)
通信作者:孟凡超,博士,副教授,从事岩石学及火山岩储层研究;E-mail: mengfc@upc.edu.cn
引用格式: 孟凡超, 周立宏, 魏嘉怡, 等. 渤海湾盆地黄骅坳陷潜山中生界火山岩储层特征及成储机制[J]. 中南大学学报(自然科学版), 2021, 52(3): 859-875.
Citation: MENG Fanchao, ZHOU Lihong, WEI Jiayi, et al. Characteristics and formation mechanism of Mesozoic volcanic reservoirs from buried hills in Huanghua Depression, Bohai Bay Basin[J]. Journal of Central South University(Science and Technology), 2021, 52(3): 859-875.