DOI: 10.11817/j.issn.1672-7207.2015.05.021
渤海湾盆地板桥凹陷内部新生代断裂活动性与油气成藏
宋璠1,苏妮娜1,侯加根2,程远忠3,姚瑞香3
(1. 中国石油大学(华东) 地球科学与技术学院,山东 青岛,266580;
2. 中国石油大学(北京) 地球科学学院,北京,102249;
3. 大港油田 第四采油厂,天津,300280)
摘要:为了揭示渤海湾盆地板桥凹陷内部新生代断裂构造与油气关系,利用油区构造解析理论对板桥凹陷新生代断裂构造发育及演化特征进行研究。综合生储盖组合、断裂构造以及油气分布特征,总结断裂活动对油气成藏各要素的控制作用。研究结果表明:板桥凹陷可划分为北部复杂断裂褶皱带、中部大型断鼻构造带以及南部雁列式走滑变形带3个具有明显不同的新生代构造变形组合特征的区段,新生代断裂活动主要发生在沙一下—沙一中亚段以及东营组沉积时期,构造演化具有明显的继承性。板桥凹陷在不同区段的构造变形特征造成了油气成藏模式的差异性。
关键词:板桥凹陷;新生代;断裂活动;构造演化;油气成藏
中图分类号:TE111.2 文献标志码:A 文章编号:1672-7207(2015)05-1723-09
Cenozoic fault activity and hydrocarbon accumulation within Banqiao Sag of Bohai Bay Basin
SONG Fan1, SU Nina1, HOU Jiagen2, CHENG Yuanzhong3, YAO Ruixiang3
(1. College of Geo-science and Technology, China University of Petroleum, Qingdao 266580, China;
2. College of Geo-science, China University of Petroleum, Beijing 102249, China;
3. No.4 Oil Production Plant, Dagang Oilfield Company, Tianjin 300280, China)
Abstract: In order to reveal the relationship between the Cenozonic fault structure and hydrocarbon distribution of Banqiao sag of Bohai Bay Basin, the development and evolution of the fault structure were researched by using the oilfield structural analysis method. Based on comprehensive research of source-reservoir-caprock combination, fault structure and the hydrocarbon distribution, the control of fault activity on hydrocarbon accumulation was summarized. The results show that the sag can be divided into three different segments based on their Cenozoic deformed structure assemblages, i.e. the complex faulted fold in the north, the large faulted nose belt in the central and en-echelon strike-slip deformation belt in the south. The evolution of Cenozonic fault structure mainly developed in the period of lower Es1-middle Es1 and Dongying formation has obvious inheritance. The structure deformations in different segments of the Banqiao Sag result in the difference of various hydrocarbon accumulations.
Key words: Banqiao sag; Cenozoic; fault activity; structure evolution; hydrocarbon accumulation
大型断裂带的发育及活动史在区域构造演化与油气成藏过程中具有重要作用[1],断裂的多期活动从宏观上控制着生储盖组合及圈闭的形成,纵横交错的断层网络决定了油气运聚方式,形成了具有区域特色的油气成藏模式[2-3]。板桥凹陷作为渤海湾盆地黄骅坳陷内重要的新生代含油气凹陷,已有学者对其构造特征开展了研究,例如邬光辉等[4]认为盆地基底结构及伸展活动强弱的差异形成了该区古构造格局;梁峰等[5]认为凹陷内构造变换带对油气分布具有一定影响。尽管前人从不同角度对板桥凹陷的构造性质与油气富集等方面进行了讨论,但大多是围绕基底沧东断裂开展研究工作,对于凹陷内部的断裂构造活动解剖不够细致。本文作者综合2009年新处理的三维高品质地震数据以及650余口钻测井资料,对板桥凹陷内部新生代断裂构造发育及演化特征进行系统分析,并深入总结断裂活动对油气成藏各要素的控制作用。
1 地质概况
板桥凹陷位于渤海湾盆地内黄骅坳陷中北部,西以沧东断裂为界、北以海河断裂与北塘凹陷相接,东南以北大港潜山构造带与歧口凹陷相隔,西南止于沈青庄构造带,整体呈北东向展布,面积约540 km2。边界断层沧东断裂呈北东方向延伸,是发育于上地壳的上陡下缓的铲式断层,并在深部发生滑脱[6]。位于沧东断裂下降盘的板桥凹陷内断层也基本呈北东、北北东向展布(图1),受区内长芦断层、板桥断层、大张坨断层以及白水头断层等Ⅱ级断裂的影响,凹陷内整体呈由北向南逐级抬升的阶梯式构造格局,各次级构造单元特征差异明显。
通过钻井、地震以及古生物等资料研究表明,板桥凹陷地层主要由前新生界基底与新生代沉积盖层组成,南部与岐口凹陷相接的地区发育奥陶纪碳酸盐岩古潜山[7]。凹陷内巨厚的沉积层主要包括古近系沙河街组—东营组、新近系馆陶组—明化镇组,各层组均为砂泥岩互层沉积,具有丰富的原油及凝析气资源。与邻区相比,凹陷内缺失沙四段及孔店组地层。
2 断裂构造特征
根据新生代断裂发育分布特点以及构造样式的差异性,将板桥凹陷由北至南划分为3个次级构造单元,依次为北部复杂断裂褶皱带、中部大型断鼻构造带以及南部雁列式走滑变形带。
2.1 北部复杂断裂褶皱带
位于板桥断层以北,西北临近沧东断裂带,东部以驴驹河断块群与长芦断裂带相邻。受沧东断裂影响,该构造带主要继承发育一系列北东、北东东走向的断裂,整体呈斜列式展布;此外,受沧东断裂深部走滑活动的影响,板桥凹陷北部还存在多支近于正北方向的较大规模断裂,这些断层平面上止于板桥断层,并在新生代早期发生滑脱,形成了大量调节断层,将北区分割成众多大小不等的断块,形成了棋盘式的构造格局(图2)。

图1 板桥凹陷区域构造位置及构造单元划分(据大港油田资料编绘)
Fig. 1 Structural division and its location in Banqiao Sag
整体上,板桥凹陷北部表现为受沧东断裂控制形成的强制褶皱,地层倾向为北西方向,但受到了新生代早期形成的滑脱断层和晚期形成的张扭性断层进一步复杂化。
2.2 中部大型断鼻构造带
板桥凹陷中部位于板桥断层与大张坨断层所夹持的区域,沧东断裂主要影响深部基底,新生代断裂活动变得相对简单。西侧仅在2条主断层根部派生几条次级断裂,在剖面上与主断层组成“Y”字型结构;东侧发育一组北东走向的断层截止于高沙岭断层,属于大张坨断层下降盘的调节断层,剖面上整体形态表现为负花状结构(图3),是走滑断层派生的在张扭性应力场中形成的典型构造。
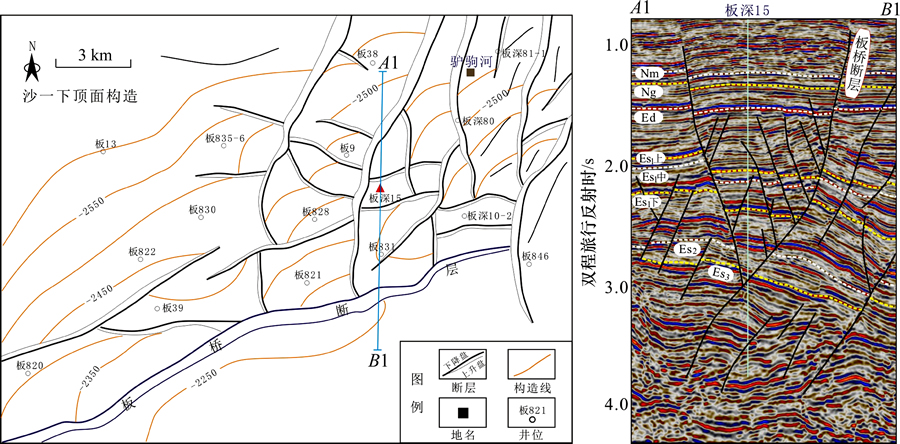
图2 板桥凹陷北部复杂断裂褶皱带构造样式
Fig. 2 Complex faulted fold at the north of Banqiao Sag

图3 板桥凹陷中部大型断鼻带构造样式
Fig. 3 Large faulted nose belt at the central of Banqiao Sag
板桥与大张坨断层在新生代持续强烈活动,在凹陷中区沿断裂并排发育断鼻构造群,是板桥凹陷滚动勘探的重点区带。
2.3 南部雁列式走滑变形带
板桥凹陷南部紧邻北大港潜山构造带,是新生代大张坨断层、白水头断层持续活动形成的地垒区。大张坨断层平面上呈弧形,整体为北东走向,局部发生转向并派生出大量次级断裂(见图4中板南断层)。区内Ⅲ级断裂港8井断层发育较早,它与一系列次级断层呈雁列式依附于大张坨断层南侧,倾向与大张坨断层截然相反,明显是受南部北大港潜山隐伏基底断裂的右旋走滑运动所影响。
在地震剖面上,由于深、浅层岩石能干性的差异,导致新生代地层中的断层样式与基底断裂具有明显差异。基底中可见典型的负花状构造,形成诸多复杂的小断块;新生代地层中断层近平行排列,倾向东南,与大张坨断层组合呈反“Y”型特征(图4),其间发育受扭动构造形成的小背斜。
3 新生代断裂活动
喜山运动时期,黄骅坳陷中部在张性应力下产生新的断裂,不同沉积时期断层的活动强度存在一定差异[8]。板桥凹陷新生代构造活动主要表现为各级断层在不同位置、不同阶段的活动性,各断裂系统受控于各自的主干断层。
3.1 断裂活动时期
针对板桥凹陷各级断裂发育特征,采用定量求取Ⅱ级同生断层活动速率与盆地伸展变形强度,进而明确断裂主要活动时期。
同生断层活动速率是反映断裂活动时期与活动强度的一项重要指标。根据板桥凹陷内控凹同生断层的垂直断距,计算了断层平均活动速率参数,结果见图5。从图5可知:该区存在2个大的断裂活动期,其中,沙一下—沙一中沉积时期断层活动速率最大,平均为167.8 m/Ma,东营组沉积时期断层活动速率次之,约为85.2 m/Ma,均属于板桥凹陷的主要断陷时期;其他沉积时期断层的活动速率相对较低,不是断裂主要活动时期,或为断裂相对静止期。
不同时期盆地伸展率参数也能够反映断裂主要活动时期与活动强度,通常利用垂直主干构造走向的地质剖面来分析构造变形过程(图1中AA′~CC′)。各剖面伸展率分布特征表明,在沙一下—沙一中以及东营组沉积时期,板桥凹陷的伸展率相对较大(图6),为主要的断裂构造变形时期,馆陶组、明化镇组—第四系沉积时期伸展率较小,基本处于稳定期,计算结果与同生断层活动速率相吻合。
3.2 断裂活动过程
上述断裂活动时间分析表明,板桥凹陷新生代主要有2期大规模断层活动。通过构造平衡剖面方法,也能清晰反映断裂的主要活动时期,同时可以再现构造演化过程[9]。由断裂形成演化过程(图7)可以看出:Ⅱ级同生断层发育具有一定连续性,受其影响凹陷整体构造特征由深向浅也具有明显继承性。板桥凹陷新生代构造格局的形成继承了沙三段沉积末期的古构造,贯穿于整个沙二段、沙一段、东营组及新近系沉积史之中。
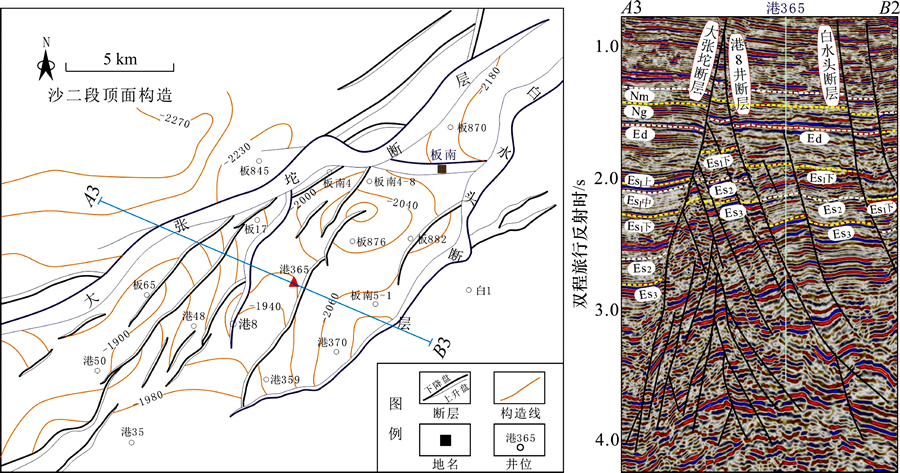
图4 板桥凹陷南部雁列式走滑变形带构造样式
Fig. 4 En-echelon strike-slip deformation belt at the south of Banqiao Sag

图5 板桥凹陷主干断裂平均活动速率分布
Fig. 5 Average active rate of main faults in Banqiao Sag

图6 板桥凹陷典型地质剖面各时期伸展率
Fig. 6 Extension rate of typical geological section in Banqiao Sag
沙二段沉积初期,大张坨、白水头等Ⅱ级断层开始活动,然而活动速率较低,对地层发育影响较小。板桥断层发育明显较晚,在沙一段沉积时期才开始活动。凹陷北部受沧东断裂深部走滑活动表现为大型褶皱,并开始出现多支南北向派生断层,向南距离沧县隆起越远,受深部断层活动影响越小;大张坨断层以南在北大港潜山隐伏基底断裂的右旋走滑运动影响下,形成了雁列式断层组合样式。
沙一下、沙一中亚段沉积时期是凹陷的主要断陷期,断裂活动总体表现为伸展加走滑的双重运动形式,同生断层活动强烈,且平面上不同区域活动特点有所不同。凹陷北区由于沧东断裂的派生断层发生滑脱,形成了大量调节断层使得构造进一步复杂化(图3);该时期Ⅱ级断层活动性最强,大张坨断层下降盘地层出现强烈“回倾”,形成滚动背斜构造,板桥断层上升盘地层产生掀斜,沿其上升盘形成反向断鼻构造;大张坨断层向东延伸应力释放并逐渐消亡,形成了一系列翘倾断块圈闭,其上升盘断裂分布样式变化不大,但地层厚度显著减小。
沙一上亚段断层活动性明显减弱,地层沉积时期构造面貌变化不大。古近纪末东营组沉积时期,板桥断层与大张坨断层再次强烈活动,断层两盘沉积厚度相差较大,南北向剖面显示地层常呈楔状发育,表明同生断层对上盘地层具有明显控制作用,断裂运动形式以伸展运动为主。新近纪馆陶组、明化镇组沉积时期,区域构造演化进入坳陷阶段,断裂活动明显减弱,直至构造定型。
4 断裂活动对油气成藏的控制作用
断陷盆地中断裂的形成与演化直接控制着沉积充填和油气成藏过程,断裂作为沟通烃源岩与圈闭的桥梁和枢纽,对油气成藏各方面要素都具有一定的控制作用[10-11]。
4.1 断裂活动控制了烃源岩的发育和演化
断裂活动控制盆地沉降以及沉积充填,从而控制了烃源岩的分布特征。板桥凹陷发育沙一段、沙二段以及沙三段等多套烃源岩,岩性均为暗色泥岩,富含松柏类高等植物中的树脂体和山地蜡等有机组分,易于生成凝析气,勘探实践表明板桥凹陷具有丰富的原油及凝析气资源[12]。
沙三段沉积晚期至沙二段早期为湖盆初始裂陷时期,受沧东断裂影响凹陷内发育大量北东向基底正断层,形成了多个生烃中心,烃源岩主要沿基底断裂呈北东向分布。沙二段沉积时期区内大张坨断层、白水头断层开始强烈活动,在下降盘形成了烃源岩沉积中心,但由于该时期全区广泛发育滩坝砂体,因此烃源岩厚度不大,生烃潜力中等。沙一段沉积时期,北部板桥断层也开始强烈活动,区内3个构造带均发育优质烃源岩,其中沙一中亚段的暗色泥岩厚度达100~300 m,是凹陷内生烃能力最强的烃源岩。干酪根元素组成、烃源岩热解以及显微组分实验表明,该区烃源岩母质类型主要为Ⅱ2型,其中沙一段、沙二段为Ⅱ1~Ⅱ2型,沙三段为Ⅱ2~Ⅲ型。
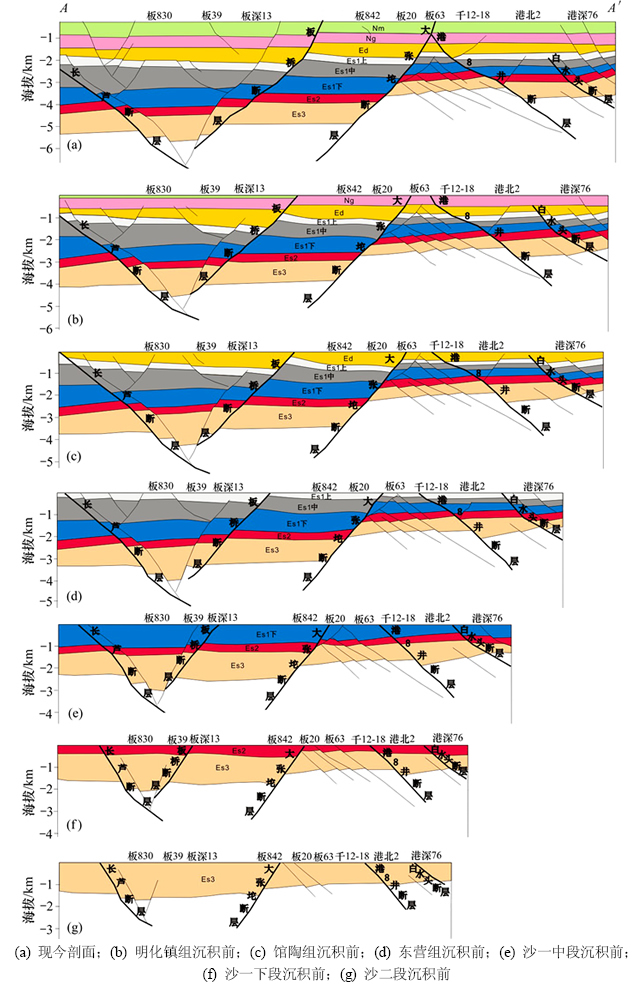
图7 板桥凹陷典型地质剖面构造发育史(A-A′剖面)
Fig. 7 Structural history of typical geological section in Banqiao sag
断裂活动是形成断陷区热活动的重要因素,从而影响烃源岩的成熟及热演化过程。烃源岩热解与黏土矿物演化等实验结果表明,板桥凹陷新生代地层纵向上在2 200~2 800 m和3 200~4 200 m处存在2个生烃高峰,分别对应于沙一中亚段与沙三段,表明断层的强烈活动使沿其走向分布的厚层烃源岩迅速埋藏,从而加速了有机质向油气转化。
4.2 断裂活动控制了储集体的宏观展布
断层的多期活动性以及古构造格局对沉积砂体的展布有着重要影响。板桥凹陷沉积物主要来自北部的沧县隆起带以及燕山褶皱带,受古构造格局的影响,北部、中部构造带在沙三段形成了一套扇三角洲-浊积扇-深湖相沉积体系[13],沙二段由于湖盆扩张主要发育滩坝沉积,沙一段物源欠充足,形成了以鲍马序列和滑塌变形构造为主的重力流水道沉积[14-15];南部构造带由于地处大张坨断层上升盘,古地形较高,整个沙河街组均以滩坝沉积为主[16]。古近纪末东营组至新近纪,断裂活动减弱,沉积相由扇三角洲逐渐过渡为准平原化的河流相类型。
板桥凹陷Ⅰ级、Ⅱ级断裂以及少数Ⅲ级断裂均属于同沉积断层,前人对Ⅰ级沧东断裂的活动及其构造坡折带对沉积相的控制进行研究,认为断裂活动控制了扇三角洲及湖底扇的发育和分布,储集砂体主要呈平行断层走向展布[17-18]。通过对Ⅱ级同生断层附近的砂体进行标定与追踪发现:凹陷内板桥断层、大张坨断层对砂体展布同样起重要的控制作用[15]。
板桥断层、大张坨断层为2条走向北东方向近于平行的同生断层,断面倾向约为310°,倾角约为43°,其中大张坨断层活动性较强,平均垂直断距可达280 m,而板桥断层平均断距为95 m。断裂活动不仅能为沉积物提供可容空间,更重要的是当可容空间不足时则会对其起到阻挡作用。由于新生代沉积物主要来自北西、北东2个方向,当沉积体向凹陷中部推进时,2条同生断层活动形成的古地貌形成了大规模屏障,使得下降盘的重力流水道砂、滩坝砂体发生转向沿断层呈北东向展布。其中,大张坨断层下降盘砂体规模明显较大,沿其走向分布的滩坝砂已成为板桥凹陷沙二段最主要的原油储量富集区。
4.3 断裂活动控制了油气的运移与聚集
断陷盆地的断裂活动对油气运聚成藏有着至关重要的影响。板桥凹陷新生代油气藏分布主要受断层控制(图8),然而凹陷内部不同区段的断裂构造变形特点,造成了油气成藏特征的差异性。凹陷北部在沧东断裂的控制下,表现为大型的强制褶皱,并受重力影响发生滑脱形成了大量调节断层,活动稍晚的板桥同生断层有效开启了包括沙三段在内的各套烃源岩,它与下降盘的调节断层组合形成了复杂的断裂网络,造成北区油气分布零星而杂乱。凹陷中部夹持于板桥、大张坨2条Ⅱ级同生断层之间,断裂持续活动形成了大型断鼻构造,是油气富集的最佳场所。凹陷南部由于受大张坨同生断层强烈活动影响了沉积物源有效供给[18],造成该区砂体规模较小且分布不连续,主要发育断层-岩性油气藏。依附于大张坨断层呈雁列式分布的Ⅲ级和Ⅳ级断层除港8井断层持续强烈活动外,其余断层输导能力均较差,对油气分布控制作用较小。
板桥凹陷具有丰富的凝析气资源,且以带油环的凝析气藏为主。勘探实践表明,沙一下亚段顶部凝析气最为富集,占整个凹陷凝析气储量的80%以上,气源主要为深部沙三段富含腐殖型有机质的暗色泥岩。从凝析气平面分布特征可看出,同生断层附近的鼻状构造或小断块为凝析气藏的主要富集区(图8),表明深大断裂是沙三段高势烃源岩与浅部低势聚油区的有利通道,凝析气沿断裂带向上快速运移,直至沙一中亚段的区域性厚层泥岩将其封隔。沿板桥、大张坨断层两侧的构造高部位聚集凝析气,低部位常聚集轻质油,形成了该区下生上储型带油环的凝析气藏,与普通气藏相比天然气常具有高重烃含量(平均质量分数为12.6%)、低甲烷含量(平均质量分数为84.3%)的特点。
强烈的断裂活动还能够引起沉积体滑塌,在本区形成小规模以滑塌浊积体为主的岩性隐蔽油气藏。如图8所示,凹陷中区板深25井区油砂体位于南北两侧断鼻带中间的低洼部位,勘探证实该油藏为细粒浊积岩岩性油藏,整体厚度较大。此类浊积岩能够形成砂泥互层,并且常伴有异常高压存在。异常高压不仅能使浊积砂体保留一定原生孔隙,还能通过影响成岩作用来溶蚀长石产生次生孔隙[19],形成良好的油气储层。此类位于相对低洼部位、由断裂活动引起沉积物滑塌而形成的细粒浊积岩岩性油藏,应作为该地区值得重视的一个勘探方向。

图8 板桥凹陷新生代断裂与油气藏分布关系图(沙一下亚段)
Fig. 8 Relationship of Cenozoic fault and reservoir in Banqiao sag
5 结论
1) 板桥凹陷在不同部位表现出不同的构造特征:北部受沧东断裂控制形成了大型强制褶皱,新生代早期形成的滑脱断层和晚期形成的张扭性断层又将其进一步复杂化;中部地区断裂变形样式较简单,其西侧的大型断鼻带是本区滚动勘探的重点区带;南部受北大港潜山隐伏基底断裂走滑运动影响,于大张坨上升盘形成了雁列式走滑变形带。
2) 板桥凹陷新生代断层活动主要发生在沙一下—沙一中以及东营组沉积时期,其中沙一下—沙一中沉积期断裂活动总体表现为伸展加走滑的双重运动形式,而东营组沉积期断裂运动形式以伸展运动为主,新生代构造样式总体具有明显的继承性。
3) 新生代断裂多期活动性及断层产状控制了烃源岩的纵、横向分布,促进了有机质热演化;Ⅱ级断裂活动形成的古地形对沉积物分配有重要影响,进而控制了断裂带附近储集体的展布;板桥凹陷不同区段构造变形差异较大,也造成了不同区段油气分布的差异性,Ⅱ级断裂附近的构造油藏、沙一下顶部的凝析气藏以及断裂活动形成的滑塌浊积体岩性油藏,都是具有重要意义的勘探目标。
参考文献:
[1] 何登发, 贾承造, 周新源, 等. 多旋回叠合盆地构造控油原理[J]. 石油学报, 2005, 26(3): 1-9.
HE Dengfa, JIA Chengzao, ZHOU Xinyuan, et al. Control principles of structures and tectonics over hydrocarbon accumulation and distribution in multistage superimposed basins[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2005, 26(3): 1-9.
[2] 宁飞, 汤良杰, 张钰, 等. 塔中Ⅱ号断裂带构造特征及油气勘探前景[J]. 石油学报, 2010, 31(3): 368-372.
NING Fei, TANG Liangjie, ZHANG Yu, et al. Structural characteristics and exploration prospect of No.Ⅱ fault zone in Tazhong area[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2010, 31(3): 368-372.
[3] 肖冬升, 杨占龙. 吐哈盆地台北凹陷西缘油气成藏过程主控因素及成藏模式[J], 中南大学学报(自然科学版), 2013, 44(2): 679-686.
XIAO Dongsheng, YANG Zhanlong. Controlling factors and accumulation model of hydrocarbon accumulation in western Taibei Sag, Turpan-Hami Basin[J]. Journal of Central South University (Science and Technology), 2013, 44(2): 679-686.
[4] 邬光辉, 漆家福. 黄骅盆地一级构造变换带的特征与成因[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 1999, 20(2): 125-128.
WU Guanghui, QI Jiafu. Characteristics and origin of first order transfer zones in Huanghua Basin[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 1999, 20(2): 125-128.
[5] 梁锋, 范军侠, 李宏伟, 等. 大港油田板桥凹陷构造变换带与油气富集[J]. 古地理学报, 2008, 10(1): 73-76.
LIANG Feng, FAN Junxia, LI Hongwei, et al. Relationship between tectonic transfer zones and petroleum accumulation in Banqiao Sag, Dagang Oilfield[J]. Journal of Palaeogeography, 2008, 10(1): 73-76.
[6] 祁鹏, 任建业, 史双双, 等. 歧口凹陷沿岸带新生代构造特征及其形成机制[J]. 石油学报, 2010, 31(6): 900-905.
QI Peng, REN Jianye, SHI Shuangshuang, et al. Features of the Cenozoic structure of the coastal zone in Qikou sag and its formation mechanism[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinaca, 2010, 31(6): 900-905.
[7] 陈纯芳, 赵澄林, 李会军. 板桥和歧北凹陷沙河街组深层碎屑岩储层物性特征及其影响因素[J]. 中国石油大学学报(自然科学版), 2002, 26(1): 4-7.
CHEN Chunfang, ZHAO Chenglin, LI Huijun. Physical properties of reservior and influencing factors of deep burial clastic rocks in Banqiao-Qibei Sag[J]. Journal of the University of Petroleum, China (Edition of Natural Science), 2002, 26(1): 4-7.
[8] 何书, 杨桥, 漆家福, 等. 黄骅坳陷中区新生代断裂系统及其成因分析[J]. 地质科学, 2008, 43(3): 533-545.
HE Shu, YANG Qiao, QI Jiafu, et al. Cenozoic fault systems and their genetic analysis in central area of the Huanghua Depression[J]. Chinese Journal of Geology, 2008, 43(3): 533-545.
[9] 李明刚, 漆家福, 童亨茂, 等. 辽河西部凹陷新生代断裂构造特征与油气成藏[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2010, 37(3): 281-288.
LI Minggang, QI Jiafu, TONG Hengmao, et al. Cenozoic fault structure and hydrocarbon accumulation in Western Sag, Liaohe Depression[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2010, 37(3): 281-288.
[10] 付晓飞, 尚小钰, 孟令东. 低孔隙岩石中断裂带内部结构及与油气成藏[J]. 中南大学学报(自然科学版), 2013, 44(6): 2428-2438.
FU Xiaofei, SHANG Xiaoyu, MENG Lingdong. Internal structure of fault zone and oil/gas reservior in low-porosity rock[J]. Journal of Central South University (Science and Technology), 2013, 44(6): 2428-2438.
[11] 李春荣, 张功成, 梁建设, 等. 北部湾盆地断裂构造特征及其对油气的控制作用[J]. 石油学报, 2012, 33(2): 195-203.
LI Chunrong, ZHANG Gongcheng, LIANG Jianshe, et al. Characteristics of fault structure and its control on hydrocarbons in the Beibuwan basin[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2012, 33(2): 195-203.
[12] 杨池银. 板桥凹陷深层天然气气源对比与成因分析[J]. 天然气地球科学, 2003, 14(1): 47-52.
YANG Chiyin. Nature gas source correlation and its genesis analysis for the deep gas pool in Banqiao Sag[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 2003, 14(1): 47-52.
[13] 陈纯芳, 郑浚茂, 王德发. 板桥凹陷沙三段沉积体系与物源分析[J]. 古地理学报, 2001, 3(1): 55-62.
CHEN Chunfang, ZHENG Junmao, WANG Defa. Depositional systems and source provenance of the third member of Shahejie Formation in Banqiao Sag[J]. Journal of Palaeogeography, 2001, 3(1): 55-62.
[14] 高祥成, 宋璠, 王俊友, 等. 板桥油田重力流水道沉积特征及其对开发效果的影响[J]. 沉积与特提斯地质, 2012, 32(4): 23-28.
GAO Xiangcheng, SONG Fan, WANG Junyou, et al. Characteristics and effects of the gravity flow channel deposits on the development of the Banqiao Oil Field[J]. Sedimentary Geology and Tethyan Geology, 2012, 32(4): 23-28.
[15] 宋璠, 苏妮娜, 侯加根, 等. 黄骅坳陷板桥油田板桥油层沉积特征及演化[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2012, 33(6): 914-922.
SONG Fan, SU Nina, HOU Jiagen, et al. Sedimentary characteristics and evolution of the Banqiao reservoir in Banqiao oilfield, Huanghua Depression[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2012, 33(6): 914-922.
[16] 宋璠. 板桥凝析油气藏井震综合储层表征研究[D]. 北京: 中国石油大学地球科学学院, 2010: 39-54.
SONG Fan. Reservoir characterization in Banqiao condensate oil and gas reservoir with integrating seismic and well logs[D]. Beijing: China University of Petroleum. College of Geoscience, 2010: 39-54.
[17] 黄传炎, 王华, 肖敦清, 等. 板桥凹陷断裂陡坡带沙一段层序样式和沉积体系特征及其成藏模式研究[J]. 沉积学报, 2007, 25(3): 386-391.
HUANG Chuanyan, WANG Hua, XIAO Dunqing, et al. Sequence patterns, characteristics of depositional systems and model of reserviors of fault steep slope belt of First Member of Shahejie formation in Banqiao Sag[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2007, 25(3): 386-391.
[18] 侯宇光, 何生, 王冰洁, 等. 板桥凹陷构造坡折带对层序和沉积体系的控制[J]. 石油学报, 2010, 31(5): 754-761.
HOU Yuguang, HE Sheng, WANG Bingjie, et al. Constraints by tectonic slope-break zones on sequences and depositional systems in the Banqiao Sag[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2010, 31(5): 754-761.
[19] 吴娟, 叶加仁, 施和生, 等. 恩平凹陷中央断裂构造带超压发育及成藏意义[J]. 中南大学学报(自然科学版), 2013, 44(7): 2801-2811.
WU Juan, YE Jiaren, SHI Hesheng, et al. Overpressure forming and its effect on petroleum accumulation in central faulted structural belt of Enping depression, China[J]. Journal of Central South University (Science and Technology), 2013, 44(7): 2801-2811.
(编辑 赵俊)
收稿日期:2014-04-18;修回日期:2014-07-29
基金项目(Foundation item):高等学校博士学科点专项科研基金资助项目(20120133120013);国家科技重大专项(2011ZX05009-002);中央高校基本科研业务费专项资金资助项目(12CX04009A) (Project(20120133120013) supported by the Specialized Research Fund for the Doctoral Program of Higher Education; Project(2011ZX05009-002) supported by the National Science and Technology Major Program of China; Project(12CX04009A) supported by the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities)
通信作者:苏妮娜,博士,讲师,从事沉积学与储层地质学研究;E-mail: sunina1981@163.com