钛合金中α相对富氧层演化的影响
来源期刊:中国有色金属学报(英文版)2019年第3期
论文作者:农智升 雷雨浓 朱景川
文章页码:534 - 545
关键词:富氧层;钛合金;氧扩散
Key words:oxygen-rich layer; titanium alloys; oxygen diffusion
摘 要:为了探索钛合金中富氧层的演化过程,在850 °C空气气氛下热暴露近α型TA15和α+β型TC4钛合金,研究α相的含量对富氧层的形成和演化的影响,并通过第一性原理计算近似揭示氧在钛合金α和β相的迁移行为。结果表明,含有更多α相的TA15钛合金相对于TC4有着更大的富氧层扩散系数。第一性原理计算表明,间隙氧原子最稳定的位置是α钛的八面体间隙位置,并且氧原子在α钛中沿着平行于c轴[0001]方向上的最近邻八面体间隙之间的扩散需要最小的激活能,是氧原子在α和β钛中最有利的扩散机制。
Abstract: In order to understand the evolution of oxygen-rich layer (ORL) on titanium alloys, the near α titanium alloy TA15 and α+β type titanium alloy TC4 were thermally exposed in air at 850 °C to evaluate the effect of α phase content on formation and evolution of ORL, and the stability and diffusion of oxygen in α- and β-Ti were investigated by first principles calculations to reveal the oxygen diffusion rate. TA15 with more α phases has a higher diffusion coefficient of ORL evolution than TC4, resulting in forming thicker ORL on TA15 under the same thermal exposure condition. The first principles calculations indicate that octahedral interstice of α-Ti is the most stable site for oxygen atom. The nearest neighbor diffusion between octahedral interstices along the [0001] direction in α-Ti presenting the lowest activation energy is the most favorable oxygen diffusion mechanism in α- and β-Ti.
Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 29(2019) 534-545
Zhi-sheng NONG1, Yu-nong LEI1, Jing-chuan ZHU2
1. School of Materials Science and Engineering, Shenyang Aerospace University, Shenyang 110136, China;
2. School of Materials Science and Engineering, Harbin Institute of Technology, Harbin 150001, China
Received 10 March 2018; accepted 11 October 2018
Abstract: In order to understand the evolution of oxygen-rich layer (ORL) on titanium alloys, the near α titanium alloy TA15 and α+β type titanium alloy TC4 were thermally exposed in air at 850 °C to evaluate the effect of α phase content on formation and evolution of ORL, and the stability and diffusion of oxygen in α- and β-Ti were investigated by first principles calculations to reveal the oxygen diffusion rate. TA15 with more α phases has a higher diffusion coefficient of ORL evolution than TC4, resulting in forming thicker ORL on TA15 under the same thermal exposure condition. The first principles calculations indicate that octahedral interstice of α-Ti is the most stable site for oxygen atom. The nearest neighbor diffusion between octahedral interstices along the [0001] direction in α-Ti presenting the lowest activation energy is the most favorable oxygen diffusion mechanism in α- and β-Ti.
Key words: oxygen-rich layer; titanium alloys; oxygen diffusion
1 Introduction
Titanium alloys which are considered as ideal structural materials for critical jet-engine components have been rapidly developed in the aerospace field. Because of the outstanding chemical activity of titanium and its alloys, oxygen would be absorbed rapidly by the exposed surfaces of titanium alloys at temperatures above 600 °C, resulting in the formation of oxygen-rich layer (ORL) on the sub-surface of alloys [1]. It is reported that the maximum value of oxygen solubility in α and β phases of titanium alloys is about 33.9 and 3.8 at.%, respectively [2]. However, there is still deleterious effect on the crack growth behavior when 0.06-0.18 wt.% oxygen is absorbed into titanium alloys studied by MAHONEY and PATON [3]. Hence, in order to improve the service efficiency of titanium alloys, it is necessary to understand the evolution mechanism of oxygen-rich layer. The common methods of estimating ORL thickness are optical microscopy and hardness measurements which were standardized by SATKO et al [4]. The thickness of ORL can also be evaluated by distinguishing hardness of the hardened regions and base metal. The obtained data of ORL thickness by these two methods are used to compare between each other, and then for subsequent analysis on the ORL evolution [5,6]. Due to the small thickness of ORL compared to the bulk of alloys, the Fick’s second law of diffusion is widely applied to estimating the oxygen-containing layer and ORL thickness at different temperature and exposure time [7]. Actually, a number of efforts have revealed that the evolution of ORL depends mainly on the oxygen diffusion in titanium alloys, and there is also an important effect of microstructures on the diffusion coefficient of oxygen in the same titanium alloys [4,8-10]. The titanium alloy with more α phase has been considered to have thicker ORL and higher oxygen diffusivity summarized by LIU and WELSCH [11] according to various titanium alloys. Therefore, the stability and diffusion of oxygen atom in the crystal structure of α and β phases become a key point of the investigation on the evolution mechanism of ORL in titanium alloys.
Due to the limitation of measurement methods, it is difficult to estimate the diffusion coefficient directly. The scarce results reported by BROCKMAN et al [12] indicated that the oxygen diffusion coefficient in Ti-6242S alloy is about 2.0×10-4 μm2/s by using the method of two-dimensional finite element method simulations based on electron backscatter diffraction data. This obtained diffusion coefficient is close to the value studied by SHAMBLEN and REDDEN [13] at 639 °C. Fortunately, the first principles method has been employed to investigate the micro-mechanism of interstitial atom diffusion successfully in recent years [14,15]. The hydrogen diffusion in α-Ti is widely studied, and it is reported by BAKULIN et al [16] that the indirect hydrogen diffusion between two next nearest neighbor octahedral sites through a tetrahedral interstitial is the most favored mechanism in the basal plane. However, there is rather scarce investigation on atomic mechanism of oxygen diffusion in α- and β-Ti.
In this work, in order to investigate the evolution of oxygen-rich layer on titanium alloys, the following works were executed. Firstly, two titanium alloy samples with different α phase contents were used to estimate the ORL thickness at various exposure time, and then the relationship between diffusion coefficient of ORL evolution and α phase content was discussed. Next, the first principles method was introduced to calculate the stability and diffusion of oxygen atom in the crystal structure of α- and β-Ti. Finally, based on the results of the first principles calculations, the impact of α and β phases in titanium alloys on evolution of oxygen-rich layer was explained approximately.
2 Experimental and computational details
2.1 Materials and experimental procedures
The near α titanium alloy TA15 and α+β type titanium alloy TC4 were chosen to discuss the effect of α phase content on the thickness of ORL after thermal exposure. The chemical compositions of TA15 and TC4 alloys are Ti-6.23Al-1.42Mo-2.32V-1.86Zr and Ti-6.23Al-2.32V in wt.%, respectively. The as-received materials of TA15 and TC4 were all in mill-annealed conditions, and Fig. 1 shows the microstructures consisting of strip alpha for TA15 and typical bimodal structures for TC4 in corresponding as-received states.
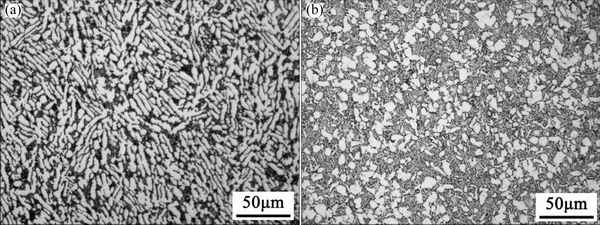
Fig. 1 Optical microscopy images of TA15 (a) and TC4 (b) in mill-annealed conditions
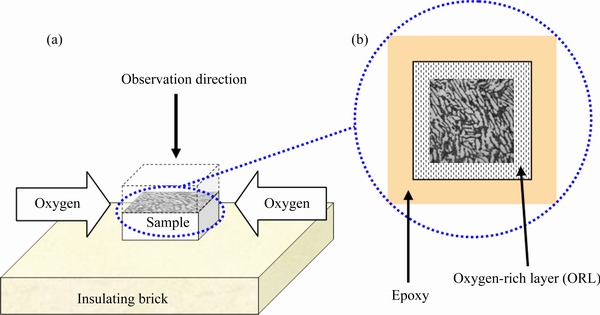
Fig. 2 Experimental processes of thermal exposure (a) and optical microscopy (b)
Figure 2 shows the experimental processes of thermal exposure and optical microscopy observation. Thermal exposure in this work was performed in air at 850 °C for 5, 10, 15, 30, 45, 60, 90, 120, 150 and 180 min via isothermal oxidation method in a laboratory box furnace. Before thermal exposure, samples were mechanically ground to remove any oxidation layer. Then, cube samples with dimensions of 10 mm ×10 mm × 10 mm were positioned on an insulating brick, making sure that all faces are uniformly exposed to furnace atmosphere except the bottom face. Samples were sectioned along the direction perpendicular to the observation plane to obtain the cross-section of ORL. In order to prevent the damage of ORL during the process of mechanical grinding and polishing, the samples were mounted in epoxy. The thickness of ORL was estimated by measuring the bright layer when observed surfaces were processed by the etchant consisting of 2 mL HF, 3 mL HNO3 and 95 mL H2O for 10 s. It is the method of optical measurement. In addition, Vickers microhardness profile measurement was also introduced to further verify the thickness of ORL measured by optical method for these two alloys. A series of hardness test from surface to base metal (about 120 μm with additional indents) were performed at 1 N load for 15 s to establish the relationship between hardness change and oxygen ingress depth, and the transition point on the curve corresponds to the boundary between ORL and base metal.
2.2 First principles approach
The aim of this work is to reveal the effect of α phase on evolution of ORL in titanium alloys from the view of comparing different oxygen diffusion diffusivities in α and β phases. Because α and β phases in TA15 (or TC4) titanium alloy are complex substitution solid solutions with hexagonal and cubic structures, respectively, the crystal structures of these two phases are hard to be built under current conditions. However, oxygen diffusion in α- and β-Ti would be calculated by the first principles method and be considerer as an approach to explain the difference of oxygen diffusion diffusivities in α and β phases. Hence, the first principle calculations based on the density functional theory (DFT) were introduced in this work to investigate the stability and diffusion of oxygen in α- and β-Ti instead of α- and β-Ti based solid solutions. In these calculations, ultra-soft pseudo-potentials [17] were adopt to obtain the core-valence interaction, and exchange and correlation terms were described by the generalized gradient approximation (GGA) of Perdew-Burke-Ernzerhof (PBE) parameters [18,19]. The following converged conditions were utilized for these calculations: Maximum force on the atom <0.01 eV/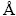 , maximum displacement between cycles <5.0×10-4
, maximum displacement between cycles <5.0×10-4 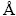 , maximum stress <0.02 GPa and energy change <5.0×10-6 eV/atom. Monkhorst-Pack scheme [20,21] of special k-points was used to perform the Brillouin zone sampling referring to calculations of energy and density of states. The plane-wave cutoff energy of 350 eV was set to ensure the precision of calculations. All calculations in this work were performed in the Cambridge Sequential Total Energy Package (CASTEP) code.
, maximum stress <0.02 GPa and energy change <5.0×10-6 eV/atom. Monkhorst-Pack scheme [20,21] of special k-points was used to perform the Brillouin zone sampling referring to calculations of energy and density of states. The plane-wave cutoff energy of 350 eV was set to ensure the precision of calculations. All calculations in this work were performed in the Cambridge Sequential Total Energy Package (CASTEP) code.
3 Results and discussion
3.1 Evolution of oxygen-rich layer on TA15 and TC4
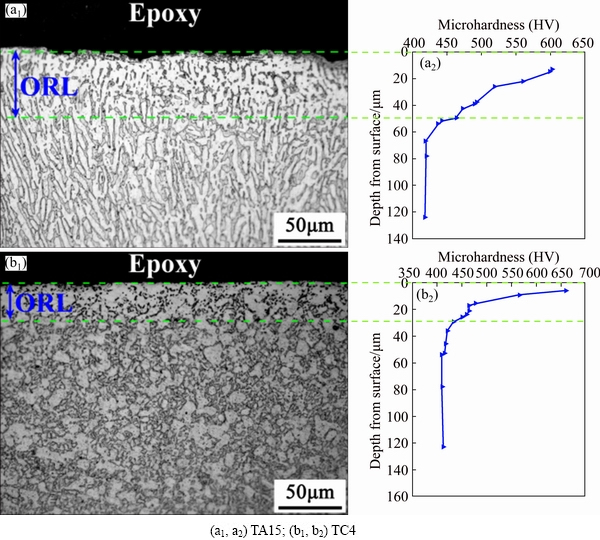
Fig. 3 Optical metallographic microstructures (a1, b1) of alloys exposed at 850 °C for 90 min and corresponding microhardness change (a2, b2) from surface to base metal
Figure 3 shows the optical metallographic microstructures of TA15 and TC4 alloys exposed at 850 °C for 90 min and corresponding microhardnesschange from surface to base metal. By comparing with alloys in mill-annealed states (Fig. 1), microstructures of base alloys after thermal exposure coarsen slightly, and there are layers which are brighter than base metal on the surface of alloys (green dashed lines area in Fig. 3). These bright layers are considered as the oxygen-rich layer (ORL) on titanium alloys, and the thickness of layers is defined as the depth of oxygen ingress. It can also be seen that there is no clear boundary between ORL and base metal but the brightness, and morphologies are continuous, which indicates that the formation of ORL is associated with oxygen solution into the crystal of Ti, instead of phase transition. As seen in Fig. 3, microstructures coarsen obviously with oxygen added into the crystal of Ti to form oxygen-containing solid solutions, which is another characteristic of ORL. Based on the results of optical measurement, the thickness of ORL for TA15 and TC4 are estimated to be about 50 and 30 μm, respectively. In addition, microhardness test is usually taken as a supplementary to further verify the correctness of ORL thickness measured by optical method. Obvious transition points of hardness curves at about 60 and 32 μm for TA15 and TC4 are obtained, suggesting there is a good consistency between these two methods. The higher hardness of ORL is attributed to the lattice distortion introduced by oxygen solution into the crystal of Ti, and the higher the oxygen concentration in alloys is, the larger the hardness of ORL is. Hence, there is a downward trend for hardness from surface to base metal.
Referring to optical method, the thicknesses of ORL for TA15 and TC4 exposed at 850 °C for different holding time are shown in Fig. 4. In particular, the estimated ORL thickness by optical and microhardness methods show a good consistency, and thus, the thickness data obtained from optical measurement would be used for subsequent analysis on oxygen diffusion in TA15 and TC4. As seen in Fig. 4, the ORL thicknesses of TA15 are all larger than those of TC4 at different thermal exposure time, which seems to imply that ORL evolution (or oxygen diffusion) on near α titanium alloy TA15 is more easily, and more α phase content in titanium alloy is beneficial for oxygen diffusion and formation of ORL.
Due to the small ORL thickness (maximum is only ~60 μm) compared to the specimen dimensions (10000 μm), specimens would be considered as the semi-infinite thickness. Hence, the Fick’s second law of diffusion can be applied to investigating the relationship between ORL thickness and thermal exposure time approximately. The corresponding equation is usually expressed as
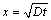 (1)
(1)
where x refers to ORL thickness at exposure time t, and D is the diffusion coefficient of ORL evolution. Figure 5 shows the fitting curves of ORL thickness versus exposure time for TA15 and TC4 alloys. The excellent correlation coefficients R of above 0.98 and best-fitting exponents which are close to 0.5 reveal that there is a better applicability of Fick’s second law of diffusion for this work. Based on the results of fitting curves, diffusion coefficients of ORL evolution for TA15 and TC4 alloys exposed at 850 °C would be estimated to be 3.95×10-1 and 2.42×10-2 μm2/s, respectively. In particular, analysis on the Arrhenius plots by CHAN et al [22] revealed that the diffusion coefficient of ORL evolution for TC4 alloys at 850 °C is 1.33×10-2 μm2/s, which indicates that the experimental results and ORL thickness measurement of this work are reliable. In addition, obvious higher diffusion coefficient for TA15 implies that oxygen diffusion in near-α TA15 alloy is easier than that in α+β type TC4 alloy, and it can be surmised that oxygen absorption and diffusion mainly proceed in α phases with hexagonal close packed structure, and more α phase content in titanium alloy corresponds to thicker ORL under thermal exposure.
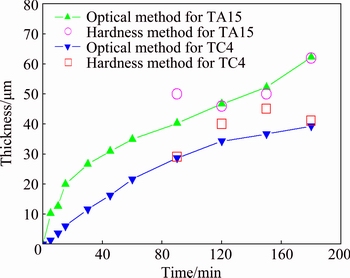
Fig. 4 Measured ORL thickness of TA15 and TC4 exposed at 850 °C for different holding time
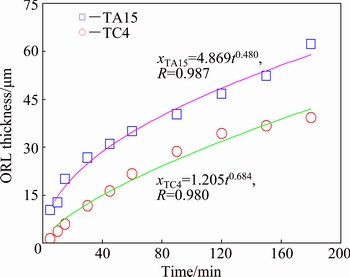
Fig. 5 Variation of ORL thickness as function of time used for determination of diffusion coefficients
3.2 First principles approach
3.2.1 Crystal structure
The α- and β-Ti correspond to space group P63/mmc (No. 194) with lattice parameters of a=b=2.950 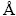 , c=4.686
, c=4.686 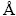 [23] and
[23] and 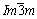 (No. 229) with lattice parameters of a=b=c=3.294
(No. 229) with lattice parameters of a=b=c=3.294 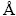 [24], respectively. Referring to the hydrogen-containing α- and β-Ti, there are two common high symmetry interstitial sites including octahedral (O) and tetrahedral (T) sites available for the temporary alloying element oxygen in the crystal structures of α- and β-Ti. Meanwhile, hexahedral (H) interstice in the crystal structure of α-Ti has also been considered in this work [25]. As shown in Fig. 6 drawn by VESTA [26], taking oxygen solubility of 5.88 at.% for example, periodic supercells constructed from 2×2×2 conventional unit cells of α- and β-Ti structures were adopted, and oxygen atom was severally set at the central site of octahedral, hexahedral and tetrahedral interstices. For investigating the effect of oxygen solubility on stability and elastic properties of α- and β-Ti, 2×2×2, 2×2×1, 1×1×3 and 1×1×2 supercells of corresponding Ti unit cell were built, and oxygen atom was added in the octahedral, hexahedral and tetrahedral interstices of crystal structures, respectively.
[24], respectively. Referring to the hydrogen-containing α- and β-Ti, there are two common high symmetry interstitial sites including octahedral (O) and tetrahedral (T) sites available for the temporary alloying element oxygen in the crystal structures of α- and β-Ti. Meanwhile, hexahedral (H) interstice in the crystal structure of α-Ti has also been considered in this work [25]. As shown in Fig. 6 drawn by VESTA [26], taking oxygen solubility of 5.88 at.% for example, periodic supercells constructed from 2×2×2 conventional unit cells of α- and β-Ti structures were adopted, and oxygen atom was severally set at the central site of octahedral, hexahedral and tetrahedral interstices. For investigating the effect of oxygen solubility on stability and elastic properties of α- and β-Ti, 2×2×2, 2×2×1, 1×1×3 and 1×1×2 supercells of corresponding Ti unit cell were built, and oxygen atom was added in the octahedral, hexahedral and tetrahedral interstices of crystal structures, respectively.
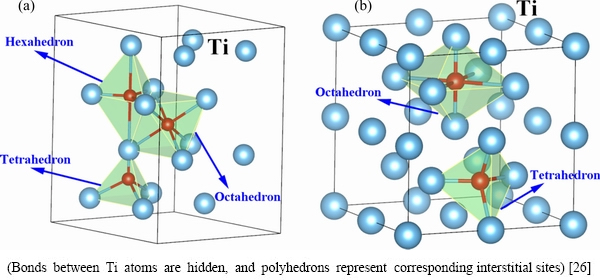
Fig. 6 Oxygen positions in tetrahedron, hexahedron and octahedron sites of crystal structures for hexagonal α-Ti (a), and tetrahedron and octahedron sites of crystal structures for cubic β-Ti (b)
Table 1 Calculated equilibrium lattice constants and oxygen absorption energy for α- and β-Ti with 5.88 at.% oxygen solubility
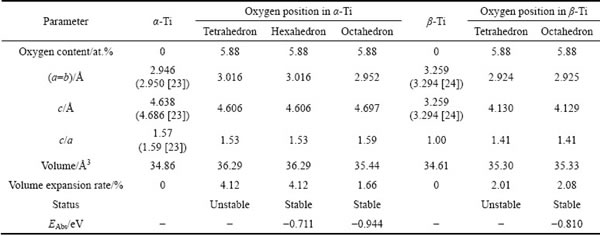
The crystal structures of oxygen-containing α- and β-Ti were optimized by using the method of Broyden- Fletcher-Goldfarb-Shanno (BFGS) algorithm [27] to obtain the equilibrium structures, and corresponding equilibrium structural properties for α- and β-Ti with oxygen solubility of 5.88 at.% are listed in Table 1. Compared with the available experimental data about α- and β-Ti, the calculated lattice constants are overestimated with deviations no more than 2%, which implies the reliability of present calculations. In addition, there are slight changes for lattice constants and volume expansion with oxygen ingress into the tetrahedral, hexahedral or octahedral interstices of α-Ti, while crystal structure transformation from cubic to tetragonal structure appears when oxygen is absorbed by β-Ti. This transformation is derived from atoms which constitute interstices being excluded at <100> direction after structure optimization, leading to the decrease in lattice constants of a- and b-axis and increase of c-axis. In particular, during the process of structure optimization, it was found that oxygen atom spontaneously shifted from tetrahedral to neighboring hexahedral interstice along <0001> direction in crystal structure of α-Ti, resulting in almost the same results of structural parameters for α-Ti with oxygen in tetrahedral and hexahedral sites, which indicates that tetrahedral interstice is only a semi-stable or even unstable site for oxygen atom in α-Ti, and oxygen is more likely to enter into the hexahedral (or octahedral) interstice. Similarly, regarding β-Ti, tetrahedral interstice is also an unstable site for oxygen, and oxygen atom would move from tetrahedral site into neighboring octahedral one along <010> direction after complete relaxation. This indicates that the tetrahedral interstices in α- and β-Ti are all unstable for oxygen atom, attributed to the smaller size of tetrahedral interstice which is hard to absorb oxygen atom with larger atomic radius.
In addition, taking the oxygen content into consideration, the absorption energy per 1 at.% oxygen, EAbs, which is a direct characterization on the stability of interstitial oxygen atoms in alloy, was introduced to describe the most optimal interstice position for oxygen atoms in α- and β-Ti. In this work, the absorption energy EAbs was defined by [28]
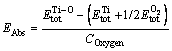 (2)
(2)
where  and
and 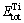 are total energies of oxygen-containing Ti and pure Ti with equilibrium structures, respectively.
are total energies of oxygen-containing Ti and pure Ti with equilibrium structures, respectively. 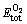 is the total energy of spin-polarized O2 molecule in a large box. COxygen (in at.%) is the atomic percentage of oxygen atom in corresponding crystal structures. The negative oxygen absorption energy EAbs for α- and β-Ti with oxygen solubility of 5.88 at.% listed in Table 1 implies that there is an exothermic process that oxygen atoms are absorbed into the tetrahedral or octahedral interstices of α- and β-Ti. It is worth noting that the lowest value of -0.944 eV for EAbs is obtained when oxygen atom enters into octahedral interstice of α-Ti, which indicates that the most stable interstice position for oxygen atom in α- and β-Ti is the octahedral site (seen in Fig. 6(a)) of α-Ti. The smallest volume expansion rate in this case implying the minimum lattice distortion is also favorable for the stability of interstitial oxygen atoms in octahedral site of α-Ti. This shows a very good consistency with hydrogen atom ingress into the crystal structures of α- and β-Ti [14-16]. Consequently, the crystal structure of oxygen-containing α-Ti, in which oxygen atom is in the octahedral site, was chosen for following investigation on electronic and elastic properties.
is the total energy of spin-polarized O2 molecule in a large box. COxygen (in at.%) is the atomic percentage of oxygen atom in corresponding crystal structures. The negative oxygen absorption energy EAbs for α- and β-Ti with oxygen solubility of 5.88 at.% listed in Table 1 implies that there is an exothermic process that oxygen atoms are absorbed into the tetrahedral or octahedral interstices of α- and β-Ti. It is worth noting that the lowest value of -0.944 eV for EAbs is obtained when oxygen atom enters into octahedral interstice of α-Ti, which indicates that the most stable interstice position for oxygen atom in α- and β-Ti is the octahedral site (seen in Fig. 6(a)) of α-Ti. The smallest volume expansion rate in this case implying the minimum lattice distortion is also favorable for the stability of interstitial oxygen atoms in octahedral site of α-Ti. This shows a very good consistency with hydrogen atom ingress into the crystal structures of α- and β-Ti [14-16]. Consequently, the crystal structure of oxygen-containing α-Ti, in which oxygen atom is in the octahedral site, was chosen for following investigation on electronic and elastic properties.
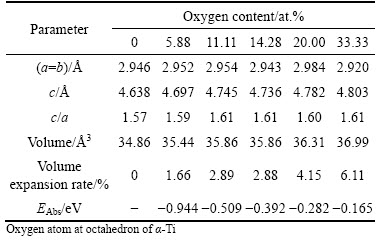
The equilibrium structural parameters and corresponding oxygen absorption energy EAbs for α-Ti with different oxygen contents were obtained, as listed in Table 2. It can be easily seen that the axes ratios c/a of these oxygen-containing α-Ti show values of around 1.59, while there is an obvious increase of volume expansion rate. This implies that α-Ti would still keep original hexagonal crystal structure when the oxygen solubility is high up to 33.33 at.%, which is consistent with the reported maximum value of oxygen solubility in α-Ti [2]. Meanwhile, the lattice distortion increases with the rise of oxygen content in these solid solutions, and the value of oxygen absorption energy EAbs also presents an upward trend, which results in worsening of oxygen solubility in the crystal structure of α-Ti. This indicates that the stability of interstitial oxygen atoms reduces when more oxygen atoms are absorbed into octahedral sites of the crystal structure of α-Ti. It can also be speculated that interstitial oxygen atoms would be unstable and the absorption of oxygen into octahedral interstice would be prevented when oxygen content is high up to a certain degree (above 33.33 at.%), because the oxygen absorption energy should be a higher or even positive value and cannot alleviate the added lattice distortion coming from increase of oxygen solubility in α-Ti at this time. It is the main reason that there is a maximum value of oxygen solubility in α-Ti.
Table 2 Calculated equilibrium structural parameters and oxygen absorption energy for α-Ti with different oxygen contents
3.2.2 Bonding behavior
Taking α-Ti with oxygen solubility of 5.88 at.% for example, total and partial densities of states (DOS) were calculated, as plotted in Fig. 7. This oxygen-containing solid solution still presents obvious metallic feature due to the positive value of total DOS at Fermi level. At lower energy regions which are far away from the Fermi level (from -60 to -20 eV), two peaks locating at about -57 and -33 eV in total DOS are dominated by Ti-s and Ti-p, respectively, while the peak at -21 eV is contributed by s states of O element. Regarding energy regions of near Fermi level (from -10 to 5 eV), total DOS are mainly dominated by s, p and d states of Ti element in the energy range from -6 to 3 eV, and absorbed oxygen element introduces p state at the lower energy level between -9 and 6 eV. In particular, these introduced O-p states bring out new hybridizations with s, p and d states of base Ti in this region. The appearance of hybridizations implies that there is formation of bonding with covalent feature in this solid solution, which is an important source of structure stability.
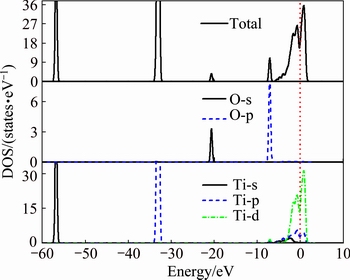
Fig. 7 Calculated total and partial densities of states for α-Ti with oxygen solubility of 5.88 at.% (The Fermi level was set at 0 on the x-axis)
Figure 8 shows the calculated electron density difference map on  plane, in which positive density difference means that electron density is greater than that obtained from overlap of original atomic densities while negative density difference indicates the opposite [29]. It is significant that electron densities of absorbed oxygen atom increase, while increasing and decreasing electron densities of Ti atoms accord to a certain direction distribution. It is reasonable evidence for oxygen atom gaining electrons after oxygen entering into the octahedral interstice of α-Ti to form oxygen-containing solid solution; meanwhile, there is bonding with covalent feature between the nearest neighbors of Ti atoms. In contrast to Ti—Ti bonding with covalent feature, the bonding between oxygen and the nearest neighbors of Ti (O—Ti4 and O—Ti5 in Fig. 8) are inferred to be of mainly ionic feature. In particular, Ti4 and Ti5 are exactly these two kinds of atoms that constitute a top and bottom of octahedral interstice configuration of α-Ti (seen in Fig. 6(a)). The bonding lengths for O—Ti4 and O—Ti5 are all 2.107
plane, in which positive density difference means that electron density is greater than that obtained from overlap of original atomic densities while negative density difference indicates the opposite [29]. It is significant that electron densities of absorbed oxygen atom increase, while increasing and decreasing electron densities of Ti atoms accord to a certain direction distribution. It is reasonable evidence for oxygen atom gaining electrons after oxygen entering into the octahedral interstice of α-Ti to form oxygen-containing solid solution; meanwhile, there is bonding with covalent feature between the nearest neighbors of Ti atoms. In contrast to Ti—Ti bonding with covalent feature, the bonding between oxygen and the nearest neighbors of Ti (O—Ti4 and O—Ti5 in Fig. 8) are inferred to be of mainly ionic feature. In particular, Ti4 and Ti5 are exactly these two kinds of atoms that constitute a top and bottom of octahedral interstice configuration of α-Ti (seen in Fig. 6(a)). The bonding lengths for O—Ti4 and O—Ti5 are all 2.107 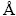 , higher than theoretical value obtained from half of the length between top and bottom of octahedral interstice of original α-Ti (
, higher than theoretical value obtained from half of the length between top and bottom of octahedral interstice of original α-Ti (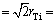 2.067
2.067 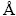 ), which indicates that octahedral interstice is mainly extended perpendicular to the direction of quadrilateral after oxygen being absorbed into α-Ti, resulting in corresponding changes for lattice constants.
), which indicates that octahedral interstice is mainly extended perpendicular to the direction of quadrilateral after oxygen being absorbed into α-Ti, resulting in corresponding changes for lattice constants.
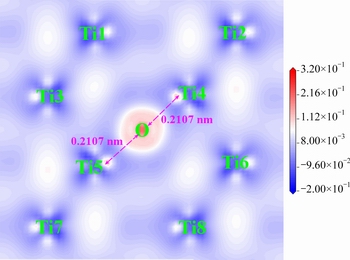
Fig. 8 Calculated electron density difference map on 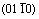 plane for α-Ti with oxygen solubility of 5.88 at.%
plane for α-Ti with oxygen solubility of 5.88 at.%
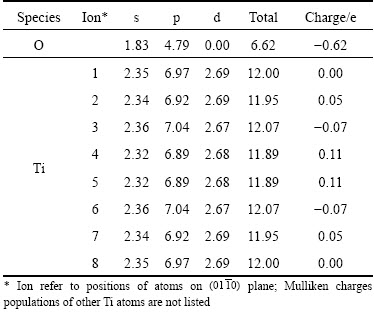
Table 3 gives is the corresponding atomic Mulliken charges populations of Ti and O atoms on 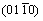 plane (as shown in Fig. 8) in crystal structure of α-Ti with oxygen solubility of 5.88 at.%. In this calculation, initial valence states of Ti and O were described as 3s23p63d24s2 and 2s22p4, respectively. It is noted that majority of charge transfer comes from O, Ti4 and Ti5 atoms, and charge transfer for other Ti atoms in Table 3 can be ignored due to the tiny charge change after bonding. Ti4 and Ti5 are exactly these two kinds of atoms that constitute top and bottom of octahedral interstice configuration of α-Ti, and there are still four Ti atoms which constitute the octahedral interstice configuration having the same atomic distance of Ti—O with that of Ti4 and Ti5. Hence, it is inferred that these four Ti atoms which are not on
plane (as shown in Fig. 8) in crystal structure of α-Ti with oxygen solubility of 5.88 at.%. In this calculation, initial valence states of Ti and O were described as 3s23p63d24s2 and 2s22p4, respectively. It is noted that majority of charge transfer comes from O, Ti4 and Ti5 atoms, and charge transfer for other Ti atoms in Table 3 can be ignored due to the tiny charge change after bonding. Ti4 and Ti5 are exactly these two kinds of atoms that constitute top and bottom of octahedral interstice configuration of α-Ti, and there are still four Ti atoms which constitute the octahedral interstice configuration having the same atomic distance of Ti—O with that of Ti4 and Ti5. Hence, it is inferred that these four Ti atoms which are not on 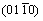 plane also have the same change of charge distribution with Ti4 and Ti5, and present the charge of 0.11 e after bonding. Therefore, the sum of charge for α-Ti with oxygen solubility of 5.88 at.% is zero. It can be summarized that there would be charge transferring from six Ti atoms which constitute the octahedral interstice configuration to a O atom when oxygen enters into the crystal structure of α-Ti to form the 5.88 at.% oxygen-containing solid solution, and only parts (about 0.11 e) of the lost valence electrons on the 4s states (1.68 e) of Ti atom are transferred to O atom while majority contributes to the incremental free-electron states of the Ti-p and Ti-d. It is worth noting that p-electrons of Ti atoms in Table 3 all show values of more than 6, higher than the value of initial state (3s23p63d24s2). The reason for this phenomenon is mainly that there is appearance of hybridizations between p and d states of Ti and O atoms with oxygen being absorbed into α-Ti to form oxygen-containing solid solution (and also p-d hybridizations between Ti atoms). Hence, transferred valence electrons would enter not only 3d but also 4p orbits of Ti without full filling of Ti-3d states, resulting in Ti atoms all showing p-electrons more than 6. The results of atomic Mulliken charges populations further confirm the formation of bonding with ionic feature between O and the nearest neighbors of Ti atoms in this compound, which agrees with the previous discussion about electron density difference map.
plane also have the same change of charge distribution with Ti4 and Ti5, and present the charge of 0.11 e after bonding. Therefore, the sum of charge for α-Ti with oxygen solubility of 5.88 at.% is zero. It can be summarized that there would be charge transferring from six Ti atoms which constitute the octahedral interstice configuration to a O atom when oxygen enters into the crystal structure of α-Ti to form the 5.88 at.% oxygen-containing solid solution, and only parts (about 0.11 e) of the lost valence electrons on the 4s states (1.68 e) of Ti atom are transferred to O atom while majority contributes to the incremental free-electron states of the Ti-p and Ti-d. It is worth noting that p-electrons of Ti atoms in Table 3 all show values of more than 6, higher than the value of initial state (3s23p63d24s2). The reason for this phenomenon is mainly that there is appearance of hybridizations between p and d states of Ti and O atoms with oxygen being absorbed into α-Ti to form oxygen-containing solid solution (and also p-d hybridizations between Ti atoms). Hence, transferred valence electrons would enter not only 3d but also 4p orbits of Ti without full filling of Ti-3d states, resulting in Ti atoms all showing p-electrons more than 6. The results of atomic Mulliken charges populations further confirm the formation of bonding with ionic feature between O and the nearest neighbors of Ti atoms in this compound, which agrees with the previous discussion about electron density difference map.
Table 3 Atomic Mulliken charges populations of Ti and O atoms on 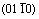 plane (as shown in Fig. 8) in crystal structure of α-Ti with oxygen solubility of 5.88 at.%
plane (as shown in Fig. 8) in crystal structure of α-Ti with oxygen solubility of 5.88 at.%
3.2.3 Elastic properties
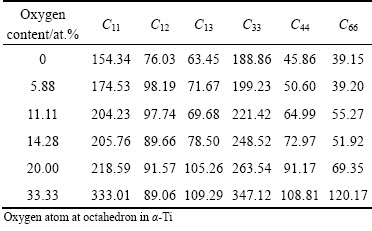
Because ORL are mainly constituted of α phases, the mechanism of hardness for ORL would be approximately explained by the effect of oxygen concentration on elastic properties of α-Ti in this section. Single crystal elastic constants Cij can be obtained by calculating corresponding variations of the total energy when small strains were applied to the equilibrium unit cell [30]. The calculated single crystal elastic constants Cij for α-Ti with different oxygen contents are listed in Table 4. The value of C11 and C33 can give some evidence on the stiffer compound, and it is usually accepted that compound with higher C11 and C33 is hard to be compressed under the x(ε11) and z(ε33) uniaxial stress, respectively. It is easily seen that there is a rising trend for C11 and C33 with the increase of oxygen content, implying that the oxygen-containing α-Ti solid solution would be stiffer with the rising oxygen content.
Table 4 Calculated single crystal elastic constants Cij for α-Ti with different oxygen contents (GPa)
Single crystal elastic constants Cij are also considered as the important criteria for mechanical stability, and a stable hexagonal crystal should satisfy the following Born criteria [31] at zero pressure:
C12>0, C44>0, C11-C12>0, (3)
(3)
According to obtained single crystal elastic constants Cij listed in Table 4, these oxygen-containing α-Ti solid solutions all obey the Born criteria well, revealing that these compounds all present mechanical stability at zero pressure.
The polycrystalline structural properties, which are more intuitive parameters of the elastic properties for materials, are usually calculated by using the Voigt-Reuss-Hill (V-R-H) approximations [32,33] from obtained single crystal elastic constants:

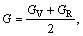
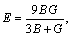
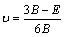 (4)
(4)
where B, G, E and ν represent the polycrystalline bulk modulus, shear modulus, elastic modulus and Poisson ratio, respectively. Subscripts “V” and “R” are Voigt and Reuss bounds for corresponding modulus, respectively:
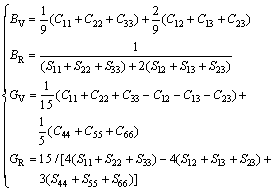 (5)
(5)
where Cij and Sij refer to elastic constants and compliances, and Sij is the inverse of Cij. Based on Eq. (4), Eq. (5) and calculated single crystal elastic constants Cij listed in Table 4, elastic properties for polycrystalline oxygen-containing α-Ti solid solutions were estimated and the results are shown in Table 5. Regarding bulk modulus B, shear modulus G and elastic modulus E, there is an obvious upward trend with the increase of oxygen content, which indicates that the abilities of resistance to volume change, resistance to reversible deformations and resistance against uniaxial tensions are all improved when oxygen is absorbed into the crystal structure of α-Ti, and more oxygen content in α-Ti is favorable for enhancing these abilities. In addition, the plasticity of materials can be evaluated by using values of Poisson ratio ν and ratio of bulk to shear modulus B/G. A material with larger value of Poisson ratio is usually considered to have a better plasticity. It is easily seen that the structural plasticity of oxygen- containing α-Ti solid solutions reduces obviously with the increase of oxygen content while less oxygen ingress (about 5.88 at.%) would enhance the plasticity of α-Ti slightly. As an important parameter for predicting the elastic behavior, the boundary between brittleness and plasticity for B/G is 1.75, and higher B/G corresponds to better plasticity. Similar with the results of Poisson ratio, the result coming from B/G implies that larger oxygen content is harmful for the plasticity of α-Ti, and oxygen-containing α-Ti solid solution presents obvious brittleness when oxygen content is high up to 33.33 at.%.
Table 5 Calculated elastic modulus, Poisson ratio and hardness for α-Ti with different oxygen contents by using Voigt-Reuss-Hill approximation
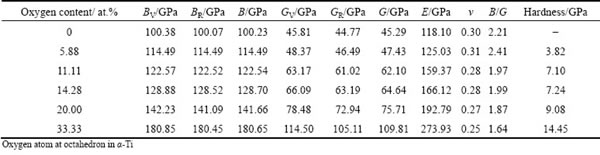
Based on the calculated polycrystalline elastic properties, the hardness of solid solutions can be estimated by following empirical equation [34]:
 (6)
(6)
It can be easily seen from Table 5 that there is an upward trend of hardness with the increase of oxygen content (predicted hardness for α-Ti is not given because Eq. (6) is unfit for pure metals), and the hardness of α-Ti with 33.33 at.% oxygen content is 14.45 GPa, higher than that of polycrystalline Si (12 GPa) [35]. The hardness shows the minimum value (3.82 GPa) when the oxygen content is 5.88 at.%, which approaches to the hardness of InAs (3.8 GPa) [36]. These predicted results are consistent well with the experimental ones. There is an oxygen content gradient from surface to base metal; meanwhile, corresponding hardness change has also been confirmed by experiments. The lattice distortion increases with more oxygen entering into the crystal structure of α- and β-Ti, resulting in the higher hardness. Although the case for β-Ti is not yet investigated, similar conclusion is easy to be speculated.
3.2.4 Oxygen diffusion mechanism
Generally speaking, the available diffusion pathway for interstitial atoms should satisfy the high symmetry criteria [14-16]. Because the stability site for oxygen atom in α- and β-Ti is octahedral interstice, referring to hydrogen diffusion mechanism [16], there are four common available pathways between octahedral interstices considered in this work for α-Ti with hexagonal close-packed structure: (1) from an octahedral interstice to a nearest neighbor one along the 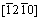 direction perpendicular to the c-axis; (2) from an octahedral interstice to a nearest neighbor one along the [0001] direction parallel to the c-axis; (3) from an octahedral interstice to a nearest tetrahedral interstice firstly and then to another nearest octahedral interstice (O-T-O mechanism); (4) from an octahedral interstice to a nearest hexahedral interstice firstly and then to another nearest octahedral interstice (O-H-O mechanism). Regarding β-Ti with body-centered cubic structure, oxygen atom can migrate linearly from an octahedral site to its neighbor octahedral site along the [010] or
direction perpendicular to the c-axis; (2) from an octahedral interstice to a nearest neighbor one along the [0001] direction parallel to the c-axis; (3) from an octahedral interstice to a nearest tetrahedral interstice firstly and then to another nearest octahedral interstice (O-T-O mechanism); (4) from an octahedral interstice to a nearest hexahedral interstice firstly and then to another nearest octahedral interstice (O-H-O mechanism). Regarding β-Ti with body-centered cubic structure, oxygen atom can migrate linearly from an octahedral site to its neighbor octahedral site along the [010] or  directions. In order to investigate the oxygen diffusion mechanism in α- and β-Ti, the process of above six neighbor diffusion pathways between octahedral interstices were calculated, and the corresponding energy difference (total energy difference of oxygen-containing α- and β-Ti between oxygen atoms at current migration and original octahedral sites) with displacement curves were obtained, as shown in Fig. 9. Except O-T-O and O-H-O mechanisms in α-Ti, it is worth noting that saddle points for other four oxygen diffusion mechanisms are explicitly located at the midpoint of the migration paths, which fits a common diffusion feature in many high symmetry structures [15]. In terms of O-T-O (or O-H-O) mechanism in α-Ti, the midpoint of diffusion curves corresponding to the nearest tetrahedral (or hexahedral) interstice site is a local minimum saddle point while the maximum saddle points lie near midpoints of local O-T (or O-H) and T-O (or H-O) diffusion paths. Hence, the activation energy for oxygen diffusion QO, which is identified as the energy barrier in diffusion pathways, can be calculated as QO=Esad-E0=Esad. The lower the activation energy is, the more the favorable diffusion mechanism for oxygen is. It is easily seen from Fig. 9 that the nearest neighbor diffusion for oxygen between octahedral interstices along the [0001] direction parallel to the c-axis requiring the lowest activation energy of 4.71 eV is the most favorable diffusion mechanism for oxygen in α-Ti. In particular, the activation energy for direct diffusion between octahedral interstices along c-axis in α-Ti obtained by WU [37] is 3.25 eV, lower than that in this work. Considering there is obvious difference of oxygen solubility between this work (5.88 at.%) and WU’s work (2.04 at.%), calculated results of activation energy in this work are still reasonable and credible.
directions. In order to investigate the oxygen diffusion mechanism in α- and β-Ti, the process of above six neighbor diffusion pathways between octahedral interstices were calculated, and the corresponding energy difference (total energy difference of oxygen-containing α- and β-Ti between oxygen atoms at current migration and original octahedral sites) with displacement curves were obtained, as shown in Fig. 9. Except O-T-O and O-H-O mechanisms in α-Ti, it is worth noting that saddle points for other four oxygen diffusion mechanisms are explicitly located at the midpoint of the migration paths, which fits a common diffusion feature in many high symmetry structures [15]. In terms of O-T-O (or O-H-O) mechanism in α-Ti, the midpoint of diffusion curves corresponding to the nearest tetrahedral (or hexahedral) interstice site is a local minimum saddle point while the maximum saddle points lie near midpoints of local O-T (or O-H) and T-O (or H-O) diffusion paths. Hence, the activation energy for oxygen diffusion QO, which is identified as the energy barrier in diffusion pathways, can be calculated as QO=Esad-E0=Esad. The lower the activation energy is, the more the favorable diffusion mechanism for oxygen is. It is easily seen from Fig. 9 that the nearest neighbor diffusion for oxygen between octahedral interstices along the [0001] direction parallel to the c-axis requiring the lowest activation energy of 4.71 eV is the most favorable diffusion mechanism for oxygen in α-Ti. In particular, the activation energy for direct diffusion between octahedral interstices along c-axis in α-Ti obtained by WU [37] is 3.25 eV, lower than that in this work. Considering there is obvious difference of oxygen solubility between this work (5.88 at.%) and WU’s work (2.04 at.%), calculated results of activation energy in this work are still reasonable and credible.
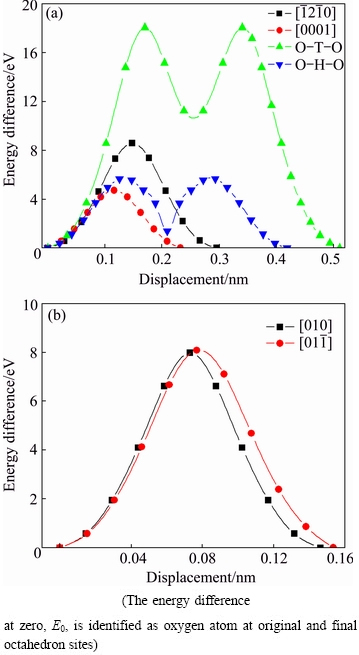
Fig. 9 Variation of energy difference with displacement for oxygen diffusion in α- (a) and β-Ti (b)
In addition, it is noteworthy that there is a huge energy difference between oxygen entering into tetrahedral and octahedral interstice (about 10.5 eV) on the middle of O-T-O diffusion path (as shown in Fig. 9(a)). From the results about stable interstice for oxygen atom in α-Ti, tetrahedral site for oxygen atom is unstable and oxygen atom would spontaneously move from tetrahedral site into hexahedral one after relaxation. Hence, the energy of oxygen entering into tetrahedron of α-Ti is not the final value at a steady state, and this energy difference between O and T sites in α-Ti can be approximatively composed of two parts: one is energy difference between O and H sites, and the other is energy difference between H and T sites. Accordingly, this energy difference shows a huge value. This instability of tetrahedral interstice for oxygen atom in α-Ti is also confirmed by the energy difference between O-T-O and O-H-O mechanisms in the midpoint of diffusion curves. Regarding β-Ti, values of activation energy for these two diffusion mechanisms are very close (about 8.00 eV), implying that these two oxygen diffusion mechanisms would happen in β-Ti. Compared with the results of hydrogen diffusion in α-Ti preferentially adopting indirect O-T-O (or O-H-O) mechanism [16], direct octahedral to octahedral interstices along c-axis mechanism for oxygen with the lowest activation energy is most favored in α-Ti instead of O-T-O (or O-H-O) mechanism due to the larger atomic radius of O atom than that of H atom, and this activation energy for oxygen diffusion in α-Ti is approximately 10 times higher than that of hydrogen diffusion. In addition, combined with obtained activation energies in Fig. 9, it can be inferred that oxygen diffusion in α-Ti is more easily to take place than in β-Ti, and more α-Ti contents are favorable for oxygen diffusing from surface into base metal resulting in thicker ORL. This approximately explains the reason that the ORL of near-α TA15 titanium alloy is thicker than that of α+β type TC4 titanium alloy in the same thermal exposure situation.
4 Conclusions
(1) The ORL thicknesses measured by optical and microhardness methods have a good consistency, and ORL thickness of near-α titanium alloy TA15 is larger than that of α+β type titanium alloy TC4 on thermal exposure at 850 °C.
(2) The curves of ORL thickness versus exposure time for TA15 and TC4 alloys show a good applicability of Fick’s second law of diffusion, and the fitted diffusion coefficient of ORL evolution at 850 °C for TA15 is 3.95×10-1 μm2/s, higher than that of TC4.
(3) Oxygen atom is more likely to enter into the octahedral interstice of α-Ti to form the stable oxygen-containing solid solution, and the rising oxygen absorption energy with the increase of oxygen content results in worsening of oxygen solubility in the crystal structure of α-Ti.
(4) The most favorable oxygen diffusion mechanism in α- and β-Ti is the nearest neighbor diffusion between octahedral interstices along the [0001] direction parallel to the c-axis in α-Ti.
References
[1] PILCHAK A L, PORTER W J, JOHN R. Room temperature fracture processes of a near-α titanium alloy following elevated temperature exposure [J]. Journal of Materials Science, 2012, 47: 7235-7253.
[2] ROSA C J. Oxygen diffusion in alpha and beta titanium in the temperature range of 932 to 1142 °C [J]. Metallurgical Transactions, 1970, 1: 2517-2522.
[3] MAHONEY M W, PATON N E. Fatigue and fracture characteristics of silicon bearing titanium alloys [J]. Metallurgical Transactions A, 1978, 9: 1497-1501.
[4] SATKO D P, SHAFFER J B, TILEY J S, SEMIATIN S L, PILCHAK A L, KALIDINDI S R, KOSAKA Y, GLAVICIC M G, SALEM A A. Effect of microstructure on oxygen rich layer evolution and its impact on fatigue life during high-temperature application of α/β titanium [J]. Acta Materialia, 2016, 107: 377-389.
[5] GADDAM R, SEFER B, PEDERSON R, ANTTI M L. Oxidation and alpha-case formation in Ti-6Al-2Sn-4Zr-2Mo alloy [J]. Materials Characterization, 2015, 99: 166-174.
[6] MCREYNOLDS K, TAMIRISAKANDALA S. A study on alpha- case depth in Ti-6Al-2Sn-4Zr-2Mo [J]. Metallurgical and Materials Transactions A, 2011, 42: 1732-1736.
[7] SHEWMON P G. Diffusion in solids [M]. 2nd ed. Warrendale: PA TMS, 1989.
[8] PARTHASARATHY T A, PORTER W J, BOONE S, JOHN R, MARTIN P. Life prediction under tension of titanium alloys that develop an oxygenated brittle case during use [J]. Scripta Materialia, 2011, 65: 420-423.
[9] JIN O, MALL S. Effects of microstructure on short crack growth behavior of Ti-6Al-2Sn-4Zr-2Mo-0.1Si alloy [J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2003, 359: 356-367.
[10] ZHU Yan-yan, CHEN Bo, TANG Hai-bo, CHENG Xu, WANG Hua-ming, LI Jia. Influence of heat treatments on microstructure and mechanical properties of laser additive manufacturing Ti-5Al- 2Sn-2Zr-4Mo-4Cr titanium alloy [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2018, 28: 36-46.
[11] LIU Z, WELSCH G. Literature survey on diffusivities of oxygen, aluminum, and vanadium in alpha titanium, beta titanium, and in rutile [J]. Metallurgical Transactions A, 1988, 19: 1121-1125.
[12] BROCHMAN R A, PILCHAK A L, III W J P, JOHN R. Estimation of grain boundary diffusivity in near-α titanium polycrystals [J]. Scripta Materialia, 2011, 65: 513-515.
[13] SHAMBLEN C E, REDDEN T K. Air contamination and embrittlement of titanium alloys [M]//The Science Technology & Application of Titanium. Pergamon Press, 1970: 199-208.
[14] CONNETABLE D, HUEZ J, ANDRIEU E, MIJOULE C. First- principles study of diffusion and interactions of vacancies and hydrogen in hcp-titanium [J]. Journal of Physics-Condensed Matter, 2011, 23: 405401-1-14.
[15] HAN X L, WANG Q, SUN D L, SUN T, GUO Q. First-principles study of hydrogen diffusion in alpha Ti [J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2009, 34: 3983-3987.
[16] BAKULIN A V, SPIRIDONOVA T I, KULKOVA S E, HOCKERD S, SCHMAUDER S. Hydrogen diffusion in doped and undoped α-Ti: An ab-initio investigation [J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2016, 41: 9108-9166.
[17] VANDERBILT D. Soft self-consistent pseudopotentials in a generalized eigenvalue formalism [J]. Physical Review B, 1990, 41: 7892-7895.
[18] MARLO M, MILMAN V. Density-functional study of bulk and surface properties of titanium nitride using different exchange- correlation functionals [J]. Physical Review B, 2000, 62: 2899-2907.
[19] WHITE J A, BIRD D M. Implementation of gradient-corrected exchange-correlation potentials in Car-Parrinello total-energy calculations [J]. Physical Review B, 1994, 50: 4954-4957.
[20] PACK J D, MONKHORST H J. Special points for Brillouin-zone integrations—A reply [J]. Physical Review B, 1977, 16: 1748-1749.
[21] MONKHORST H J, PACK J D. Special points for Brillouin-zone integrations [J]. Physical Review B, 1976, 13: 5188-5192.
[22] CHAN K S, KOIKE M, JOHNSON B W, OKABE T. Modeling of alpha-case formation and its effects on the mechanical properties of titanium alloy castings [J]. Metallurgical and Materials Transactions A, 2008, 39: 171-180.
[23] SWANSON H E, FUYAT R K, UGRINIC G M. Standard X-ray diffraction powder patterns III [J]. National Bureau of Standards, 1954, 359: 1-73.
[24] TOMASZEWSKI P E. Structural phase transitions in crystals. I. Database [J]. Phase Transitions, 1992, 38: 127-220.
[25] HENNIG R G, TRINKLE D R, BOUCHET J, SRINIVASAN S G, ALBERS R C, WILKINS J W. Impurities block the α to ω martensitic transformation in titanium [J]. Nature Materials, 2005, 4: 129-133.
[26] MOMMA K, IZUMI F. VESTA: A three-dimensional visualization system for electronic and structural analysis [J]. Journal of Applied Crystallography, 2008, 41: 653-658.
[27] BROYDEN C G, DENNIS J E, MOREF J J. On the local and superlinear convergence of quasi-Newton methods [J]. Journal of the Institute of Mathematics & Its Applications, 1973, 12: 223-246.
[28] HONG S, FU C L. Hydrogen in Laves phase ZrX2 (X=V, Cr, Mn, Fe, Co, Ni) compounds: Binding energies and electronic and magnetic structure [J]. Physical Review B, 2002, 66: 094109.
[29] LI Run-yue, DUAN Yong-hua. Electronic structures and thermodynamic properties of HfAl3 in L12, D022 and D023 structures [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2016, 26: 2404-2412.
[30] WU M M, WEN L, TANG B Y, PENG L M, DING W J. First-principles study of elastic and electronic properties of MgZn2 and ScZn2 phases in Mg-Sc-Zn alloy [J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2010, 506: 412-417.
[31] BORN M, HUANG K. Dynamical theory of crystal lattices [M]. Oxford: Oxford University Press, 1954.
[32] WANG Feng, SUN Shi-jie, YU Bo, ZHANG Feng, MAO Ping-li, LIU Zheng. First principles investigation of binary intermetallics in Mg-Al-Ca-Sn alloy: Stability, electronic structures, elastic properties and thermodynamic properties [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2016, 26: 203-212.
[33] CAO Y, ZHU P X, ZHU J C, LIU Y. First-principles study of NiAl alloyed with Co [J]. Computational Materials Science, 2016, 111: 34-40.
[34] CHEN X Q, NIU H Y, LI D Z, LI Y Y. Modeling hardness of polycrystalline materials and bulk metallic glasses [J]. Intermetallics, 2011, 19: 1275-1281.
[35] MINISINI B, ROETTING J, TSOBNANG F. Elastic and thermodynamic properties of OsSi, OsSi2 and Os2Si3 [J]. Computational Materials Science, 2008, 43: 812-817.
[36] AZUHATA T, SOTA T, SUZUKI K. Elastic constants of III-V compound semiconductors: Modification of Keyes’ relation [J]. Journal of Physics-Condensed Matter, 1996, 8: 3111-3119.
[37] WU H. Oxygen diffusion through titanium and other HCP metals [D]. Urbana: University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign, 2013: 52-57.
农智升1,雷雨浓1,朱景川2
1. 沈阳航空航天大学 材料科学与工程学院,沈阳 110136;
2. 哈尔滨工业大学 材料科学与工程学院,哈尔滨 150001
摘 要:为了探索钛合金中富氧层的演化过程,在850 °C空气气氛下热暴露近α型TA15和α+β型TC4钛合金,研究α相的含量对富氧层的形成和演化的影响,并通过第一性原理计算近似揭示氧在钛合金α和β相的迁移行为。结果表明,含有更多α相的TA15钛合金相对于TC4有着更大的富氧层扩散系数。第一性原理计算表明,间隙氧原子最稳定的位置是α钛的八面体间隙位置,并且氧原子在α钛中沿着平行于c轴[0001]方向上的最近邻八面体间隙之间的扩散需要最小的激活能,是氧原子在α和β钛中最有利的扩散机制。
关键词:富氧层;钛合金;氧扩散
(Edited by Bing YANG)
Foundation item: Project (51701128) supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China
Corresponding author: Zhi-sheng NONG; Tel: +86-24-89724198; E-mail: nzsfir@163.com
DOI: 10.1016/S1003-6326(19)64962-9

