DOI: 10.11817/j.issn.1672-7207.2021.04.008
生物酶改良膨胀土的动骨干曲线模型
文畅平1, 2,任睆遐1, 2
(1. 中南林业科技大学 土木工程学院,湖南 长沙,410018;
2. 中南林业科技大学 现代木结构工程材制造及应用技术湖南省工程实验室,湖南 长沙,410018)
摘要:基于Hardin-Drnevich双曲线本构模型,研究生物酶改良膨胀土的动应力-应变关系。首先通过一系列不同生物酶掺量下的动三轴不固结不排水剪切试验,得到生物酶改良膨胀土的动骨干曲线;然后,根据三轴试验结果,分别拟合最大动弹性模量Edmax、最大动应力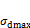 、动骨干曲线切线变形模量Edt与生物酶掺量z、围压
、动骨干曲线切线变形模量Edt与生物酶掺量z、围压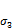 的回归方程;最后,基于Hardin-Drnevich模型,建立考虑生物酶掺量影响的动骨干曲线模型以及动骨干曲线应力-应变归一化方程。研究结果表明:Hardin-Drnevich模型能很好地描述生物酶改良膨胀土的动骨干曲线双曲线特性,最大动弹性模量Edmax、最大动应力
的回归方程;最后,基于Hardin-Drnevich模型,建立考虑生物酶掺量影响的动骨干曲线模型以及动骨干曲线应力-应变归一化方程。研究结果表明:Hardin-Drnevich模型能很好地描述生物酶改良膨胀土的动骨干曲线双曲线特性,最大动弹性模量Edmax、最大动应力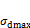 、动骨干曲线切线变形模量Edt等的回归方程能较好地描述其随生物酶掺量z、围压
、动骨干曲线切线变形模量Edt等的回归方程能较好地描述其随生物酶掺量z、围压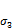 的变化规律;最大动弹性模量Edmax、最大动应力
的变化规律;最大动弹性模量Edmax、最大动应力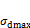 、动骨干曲线切线变形模量Edt随生物酶掺量z的增加、围压
、动骨干曲线切线变形模量Edt随生物酶掺量z的增加、围压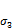 的增大而呈非线性增大;最大动应力
的增大而呈非线性增大;最大动应力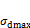 可作为生物酶改良膨胀土的动骨干曲线应力-应变关系归一化因子,使动骨干曲线的线性化程度较高;引入的生物酶掺量影响因子
可作为生物酶改良膨胀土的动骨干曲线应力-应变关系归一化因子,使动骨干曲线的线性化程度较高;引入的生物酶掺量影响因子 和
和 可定量反映生物酶掺量z对Edmax,
可定量反映生物酶掺量z对Edmax,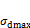 和Edt等的影响;生物酶掺量影响因子
和Edt等的影响;生物酶掺量影响因子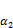 可定量反映生物酶掺量z对动应力
可定量反映生物酶掺量z对动应力 的影响。
的影响。
关键词:生物酶改良膨胀土;动骨干曲线模型;动应力-应变关系;动三轴试验
中图分类号:U416.1 文献标志码:A
文章编号:1672-7207(2021)04-1109-09
Dynamic backbone curve model of bioenzyme-treated expansive soil under cyclic loading
WEN Changping1, 2, REN Huanxia1, 2
(1. School of Civil Engineering, Central South University of Forestry and Technology, Changsha 410018, China;
2. Hunan Engineering Laboratory for Manufacturing and Application Technology of Modern Timber Structural Engineering Materials, Central South University of Forestry and Technology, Changsha 410018, China)
Abstract: The dynamic stress-strain properties of bioenzyme-treated expansive soil were studied based on Hardin-Drnevich hyperbola constitutive model. Firstly, a series of the dynamic triaxial unconsolidated undrained shear tests of bioenzyme-treated expansive soil at different ratios of bioenzyme-based soil stabilizer were conducted, and a series of dynamic backbone curves were obtained. Secondly, the regression expressions between the parameters such as the maximum dynamic modulus of elasticity Edmax, the maximum dynamic stress  ,the tangent deformation modulus of dynamic backbone curve Edt, and the ratio of bioenzyme-based soil stabilizer z, confining pressure
,the tangent deformation modulus of dynamic backbone curve Edt, and the ratio of bioenzyme-based soil stabilizer z, confining pressure  , were fitted based on the triaxial test results respectively. Finally, a dynamic backbone curve constitutive model based on Hardin-Drnevich model, which can reflect the effect of the ratio of bioenzyme-based soil stabilizer z on the dynamic stress-strain property of bioenzyme-treated expansive soil, was proposed. The results show that Hardin-Drnevich model can better describe the hyperbola characteristics of dynamic backbone curves of bioenzyme-treated expansive soil, and the regression equations can better reflect the influences of the ratio of bioenzyme-based soil stabilizer z and confining pressure
, were fitted based on the triaxial test results respectively. Finally, a dynamic backbone curve constitutive model based on Hardin-Drnevich model, which can reflect the effect of the ratio of bioenzyme-based soil stabilizer z on the dynamic stress-strain property of bioenzyme-treated expansive soil, was proposed. The results show that Hardin-Drnevich model can better describe the hyperbola characteristics of dynamic backbone curves of bioenzyme-treated expansive soil, and the regression equations can better reflect the influences of the ratio of bioenzyme-based soil stabilizer z and confining pressure  on Edmax,
on Edmax,  , and Edt. The maximum dynamic modulus of elasticity Edmax, the maximum dynamic stress
, and Edt. The maximum dynamic modulus of elasticity Edmax, the maximum dynamic stress  , and the tangent deformation modulus of dynamic backbone curve Edt increase nonlinearly with the increase of the ratio of bioenzyme-based soil stabilizer z and confining pressure
, and the tangent deformation modulus of dynamic backbone curve Edt increase nonlinearly with the increase of the ratio of bioenzyme-based soil stabilizer z and confining pressure  . The maximum dynamic stress
. The maximum dynamic stress  can be adopted as the normalized factor in the normalization analysis of dynamic stress-strain relation of bioenzyme-treated expansive soil, and it can normalize the dynamic stress-strain relationship of dynamic backbone curves much better. The introduced factor
can be adopted as the normalized factor in the normalization analysis of dynamic stress-strain relation of bioenzyme-treated expansive soil, and it can normalize the dynamic stress-strain relationship of dynamic backbone curves much better. The introduced factor 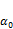 and
and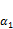 can quantitatively reflect the influences of the ratio of bioenzyme-based soil stabilizer z on Edmax,
can quantitatively reflect the influences of the ratio of bioenzyme-based soil stabilizer z on Edmax,  and Edt, respectively, and the introduced factor
and Edt, respectively, and the introduced factor 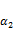 can quantitatively reflect the influences of the ratio of bioenzyme-based soil stabilizer z on dynamic stress
can quantitatively reflect the influences of the ratio of bioenzyme-based soil stabilizer z on dynamic stress 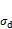 .
.
Key words: bioenzyme-treated expansive soil; dynamic backbone curve model; dynamic stress-strain relation; dynamic triaxial test
大量研究和工程实践结果表明,掺石灰、水泥等无机钙基材料是改良膨胀土最有效的方法[1]。但这种化学改良方法的不足也很突出,体现在:1) 生产石灰、水泥需要消耗矿产资源和能源,并且伴随有大量的碳排放,因此,被认为是一种成本较高、对环境不友好的膨胀土改良方法[2];2) 干湿循环或土体中含水量的变化对改良膨胀土的耐久性产生较大影响[3]。随着干湿循环次数增加,钙基无机材料将产生钙矾石之类的膨胀矿物,使得改良膨胀土的膨胀潜势增大[4],并且强度逐渐丧失[5],因此,必须进行能够满足可持续发展需要、环境友好型的膨胀土非传统改良材料的研究[6]。土体改良材料一般可分为传统型材料和非传统型材料[7]。传统型改良材料包括石灰、水泥等无机钙基材料,而生物酶之类的土体改良材料属于非传统型材料[8]。目前大多将传统型与非传统型材料结合使用对土体进行改良。生物酶是一种通过植物发酵而提取的无毒、无腐蚀性的液体酶制剂[8]。有研究表明,生物酶是一种低成本、环保型的土壤改良材料[9]。对于膨胀土,其膨胀机制一般认为是其亲水矿物晶格的膨胀以及黏土颗粒间的膨胀[10]。当膨胀土中的亲水矿物蒙脱石吸水后矿物晶格膨胀,使得土体产生膨胀。又由于土体吸收水分后,引起黏土颗粒间的毛细管张力松弛,黏土颗粒间距增大,土体也发生膨胀。生物酶是一种生物表面活性剂,其分子结构具有亲水键和疏水键[9],亲水键可紧紧包裹在黏土颗粒表面,而疏水键则阻滞水分进入土体,从而保持土体含水量稳定。此外,生物酶中含有乙醇影响土体的介电常数,减小吸附水的厚度。有研究发现,生物酶易于与土体均匀拌和[8],能显著降低膨胀土的膨胀潜势[11],提高膨胀土的无侧限抗压强度(UCS)、加州承载比(CBR)、弹性模量等力学指标以及改善其工程特性[12],并且在干湿循环下的耐久性[10]、动力特性[9]等方面性能优良。现有研究表明,生物酶作为膨胀土改良材料的研究仍然停留在试验室研究阶段,较少应用于工程实践,研究成果主要集中在膨胀土改良后的物理特性、工程特性以及静力学特性等方面,较少涉及动力学特性。膨胀土改良后作为路基填料,路基本体承受各类车辆荷载的循环作用,因而,研究生物酶改良膨胀土的动力特性,是该方面研究成果应用于工程实践前的重要环节,但目前人们对生物酶改良膨胀土的动力特性研究不多。在土体动力特性研究中,动骨干曲线及其模型是主要研究内容。动骨干曲线反映了土体的动应力-应变关系,构建动骨干曲线模型是分析土体动应力-应变关系特性的前提和基础性工作,国内外学者在该方面开展了大量研究。目前,主要是基于Masing法则、通过相应的动力试验得到动骨干曲线,然后构建相应的动骨干曲线模型。基于Masing法则的动骨干曲线模型实际上是经验类模型,一般可分为以下几类:1) 双直线模型;2) 基于Kondner双曲线假设的Hardin-Drnevich两参数模型、Martin-Davidenkov三参数模型;3) Ramberg-Osgood三参数模型等。上述模型各具特色和适用范围。周文权等[13]通过研究发现,基于双直线模型建立的饱和粗粒土动骨干曲线模型能够反映土体的刚度变化规律。张勇等[14]发现基于Hardin-Drnevich模型所建立的动骨干曲线模型能够反映土体的刚度软化特性。Hardin-Drnevich模型实际上是Martin-Davidenkov模型的特例。KRAVCHENKO等[15]基于Martin-Davidenkov模型建立了聚丙烯纤维改良黏土的动骨干曲线模型,认为该模型能够很好地描述冻融循环下的动应力-应变关系。迟世春等[16]认为变参数Ramberg-Osgood模型能够较好地描述筑坝土石料的动力特性。Hardin-Drnevich模型[17]的动骨干曲线采用了KONDNER[18]的双曲线假设,即动剪应力与动剪应变为双曲线关系。该模型数学表达式简洁,参数只有2个并且物理意义明确,易于通过试验拟合,广泛应用于土体动骨干曲线模型的研究。ZHAO等[19]认为Hardin-Drnevich双曲线模型可以很好地描述冻结粉土在动荷载作用下的动应力-应变响应关系。WU等[20]以含水量、冻结压力等参数为变量,得到了青藏高原冻结粉质黏土最大动剪切模量与Hardin-Drnevich模型两参数之间的关系。庄妍等[21]基于Hardin-Drnevich模型,提出了考虑超固结比、孔隙比影响的饱和粉质黏土动骨干曲线模型。SHANG等[22]基于Hardin-Drnevich模型研究了重载铁路路基水泥改良膨胀土的动骨干曲线模型。ZHANG等[23]通过研究天水黄土动应力应变关系认为Hardin-Drnevich模型能够很好地描述其动骨干曲线的应力-应变关系特性。LING等[24]在研究冻融循环作用下冻土的动力特性时,提出了基于动荷载循环作用次数、温度、初始含水量、动荷载频率、围压的修正Hardin-Drnevich模型,由该修正模型所得动骨干曲线与试验得到的动骨干曲线有较好的一致性。WANG等[25]基于Hardin-Drnevich模型研究了石灰改良膨胀土的动骨干曲线模型。这些研究只有少数针对改良膨胀土的动力特性,但没有分析动骨干曲线的归一化特性。为此,本文作者基于现有研究成果,以生物酶改良膨胀土的动应力-应变关系为研究对象,通过一系列动三轴固结不排水剪切试验,基于Hardin-Drnevich模型分析生物酶掺量对模型参数的影响规律,建立考虑生物酶掺量影响的生物酶改良膨胀土的动骨干曲线模型以及动骨干曲线应力-应变归一化方程。
1 试验材料与方法
1.1 试验材料
试验所用材料为膨胀土、生物酶。其中,膨胀土试验土样取自湖南省益阳—娄底高速公路K28+980处,取土深度为1.7 m左右。该膨胀土样为中膨胀土,呈黄褐色,夹灰白色土,见图1,其主要物理力学指标见表1。所采用的生物酶试剂为Terra-Zyme。
表1 膨胀土试样的主要物理力学指标
Table 1 Physical and mechanical behavior of expansive soil samples

图1 膨胀土试样
Fig. 1 Expansive soil sample
1.2 试验方法
1.2.1 试验设备
试验采用GDS动三轴试验系统,其轴向最大负荷为10 kN;最大围压为2 MPa,精度为1 kPa;最大频率为5 Hz,轴向位移最大量程为100 mm。
1.2.2 土样试件制备
1) 动三轴试验采用直径为39.1 mm、高度为80.0 mm的圆柱形试件。
2) 生物酶掺量(设为z)为膨胀土干质量分数,设定为0,1%,2%,3%,4%,据此分别制作5类土样的试件。制作土样试件时均统一采用干密度 1.48 g/cm3(即压实度为90%),含水量为17.0%。土样试件标准养护28 d。
1.48 g/cm3(即压实度为90%),含水量为17.0%。土样试件标准养护28 d。
3) 土样试件制备方法为:首先将膨胀土试样烘干碾散,过孔径为2 mm的土工筛,加入配置好的生物酶溶液并拌合均匀,静置风干,再掺加规定的含水量。将配置好的土料分4层依次装入成型筒,各层接触面刨毛,分层静压成型。
1.2.3 试验方案
本文研究生物酶掺量z、围压 对生物酶改良膨胀土动力特性的影响。不同生物酶掺量z下,围压分别为100,200和300 kPa。每一组土样试件分别在设定的围压下进行不排水动三轴试验。
对生物酶改良膨胀土动力特性的影响。不同生物酶掺量z下,围压分别为100,200和300 kPa。每一组土样试件分别在设定的围压下进行不排水动三轴试验。
循环动荷载为等幅值正弦波荷载,循环荷载分级加载方式示意图如图2所示,动荷载振动频率f为1 Hz。
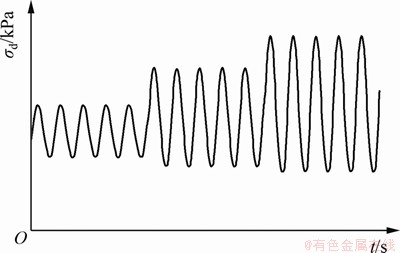
图2 循环荷载分级加载方式示意图
Fig. 2 Sketch of multi-stage cyclic loading
动三轴试验采用应力控制加载方式。试验前,将土样试件进行抽气饱和,再装入压力室进行反压饱和。根据设定的围压 ,首先对土样试件进行等向加载,30 min后对土样试件分级施加轴向循环荷载。在不排水条件下逐级加大荷载幅值实现对土样分级加载,初始动荷载幅值为25 kPa,以每级25 kPa递增,每级循环振动20次。为消除上一级循环荷载动孔压的影响,在每级循环加载完成后快速开关排水阀门1次,再继续下一级荷载的循环加载,直至土试件被破坏为止。
,首先对土样试件进行等向加载,30 min后对土样试件分级施加轴向循环荷载。在不排水条件下逐级加大荷载幅值实现对土样分级加载,初始动荷载幅值为25 kPa,以每级25 kPa递增,每级循环振动20次。为消除上一级循环荷载动孔压的影响,在每级循环加载完成后快速开关排水阀门1次,再继续下一级荷载的循环加载,直至土试件被破坏为止。
2 试验结果与分析
生物酶掺量z=3%的土样试件在 kPa时的动三轴试验的滞回曲线如图3所示。根据动三轴试验结果,将每级动荷载作用下第10圈滞回曲线的顶点相连,从而得到生物酶改良膨胀土的动应力-应变关系的骨干曲线。不同围压
kPa时的动三轴试验的滞回曲线如图3所示。根据动三轴试验结果,将每级动荷载作用下第10圈滞回曲线的顶点相连,从而得到生物酶改良膨胀土的动应力-应变关系的骨干曲线。不同围压 下的动骨干曲线如图4所示。从图4可见:
下的动骨干曲线如图4所示。从图4可见:
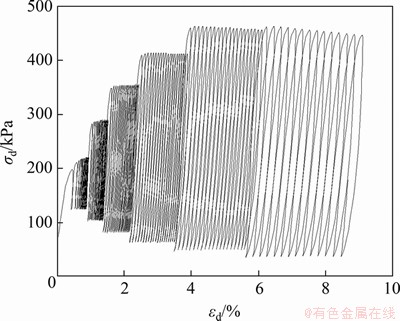
图3 滞回曲线
Fig. 3 Hysteretic curve
1) 生物酶改良膨胀土的动应力(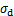 )-应变(
)-应变(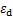 )关系呈现出明显的非线性特性。通过分析
)关系呈现出明显的非线性特性。通过分析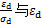 之间的近似线性关系,可得到
之间的近似线性关系,可得到 的关系曲线为近似双曲线。
的关系曲线为近似双曲线。
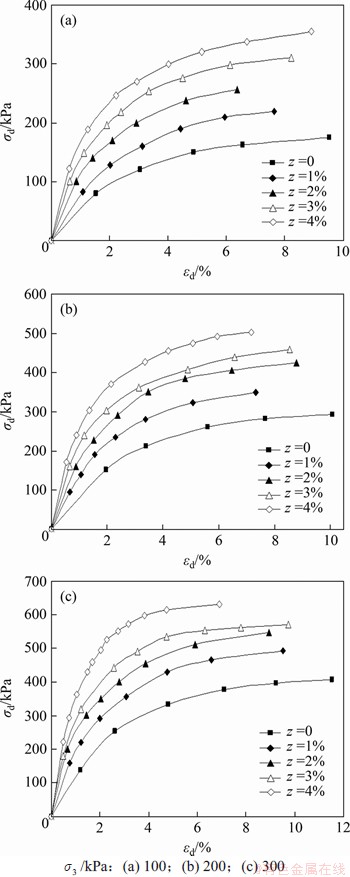
图4 不同围压下的动骨干曲线
Fig. 4 Dynamic backbone curves under different confining pressures
2) 随着围压 增大,同一生物酶掺量下土体的动应力
增大,同一生物酶掺量下土体的动应力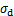 呈近似线性增大;在一定围压
呈近似线性增大;在一定围压 下,随着生物酶掺量增加,土体的动应力
下,随着生物酶掺量增加,土体的动应力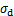 显著增大;当生物酶掺量大于3%时,这种增大趋势减缓。
显著增大;当生物酶掺量大于3%时,这种增大趋势减缓。
根据Hardin-Drnevich模型,循环动荷载作用下土体的动应力-应变关系的骨干曲线采用双曲线表达,即
 (1)
(1)
式中: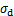 和
和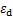 分别为动应力幅值、动弹性应变;
分别为动应力幅值、动弹性应变;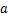 和
和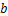 为试验常数。根据动弹性模量的定义
为试验常数。根据动弹性模量的定义 可得:
可得: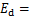
 。当
。当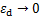 时,动弹性模量Ed为最大动弹性模量Edmax,
时,动弹性模量Ed为最大动弹性模量Edmax,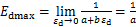 ,即参数a的物理意义为最大动弹性模量Edmax的倒数。当
,即参数a的物理意义为最大动弹性模量Edmax的倒数。当 时,
时,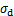 为最大动应力
为最大动应力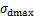 ,根据式(1)可得
,根据式(1)可得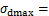
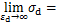
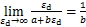 ,即参数
,即参数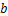 的物理意义为最大动应力
的物理意义为最大动应力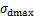 的倒数。
的倒数。
将式(1)改写为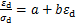 ,该式表明
,该式表明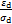 与
与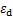 的关系为直线关系,该直线的截距、斜率分别为a和b。因此,采用
的关系为直线关系,该直线的截距、斜率分别为a和b。因此,采用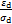 与
与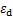 之间的直线关系对图4所示的动骨干曲线进行近似拟合,可得到参数
之间的直线关系对图4所示的动骨干曲线进行近似拟合,可得到参数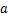 ,
,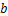 ,Edmax和
,Edmax和 。有关参数拟合结果见表2。
。有关参数拟合结果见表2。
表2 动骨干曲线参数拟合结果
Table 2 Parameters fitting results of dynamic backbone curves
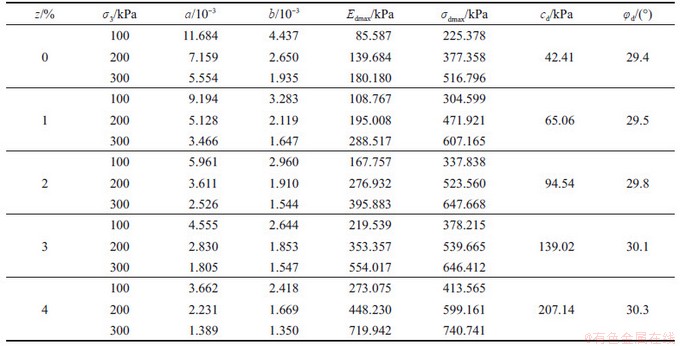
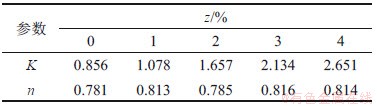
2.1 最大动弹性模量Edmax
根据表2,考虑生物酶掺量z、围压 的影响,按照
的影响,按照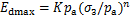 建立最大动弹性模量Edmax的回归方程(式中,K和n为试验拟合参数,
建立最大动弹性模量Edmax的回归方程(式中,K和n为试验拟合参数,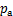 为大气压,一般取
为大气压,一般取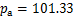 kPa)。根据表2可得到参数K和n的拟合结果,见表3。
kPa)。根据表2可得到参数K和n的拟合结果,见表3。
根据表3中的K和n拟合结果,取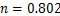 。设
。设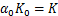 ,其中,K0为生物酶掺量z为0时的K,即K0=0.856,可得到
,其中,K0为生物酶掺量z为0时的K,即K0=0.856,可得到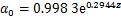 。此处引入的参数
。此处引入的参数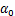 反映了生物酶掺量z对拟合参数K的影响即对最大动弹性模量Edmax的影响。因此,Edmax与生物酶掺量z围压
反映了生物酶掺量z对拟合参数K的影响即对最大动弹性模量Edmax的影响。因此,Edmax与生物酶掺量z围压 的回归方程可表示为
的回归方程可表示为
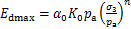 (2)
(2)
式中: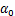 为生物酶掺量z对Edmax的影响因子,为材料试验常数。
为生物酶掺量z对Edmax的影响因子,为材料试验常数。
式(2)表明,随着围压 和
和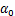 的增大(即生物酶掺量z的增加),膨胀土体被生物酶固化稳定后,土体密度增大孔隙比减小,弹性波在土体中的传播速度更快。也就是说,在一定的动应力幅值
的增大(即生物酶掺量z的增加),膨胀土体被生物酶固化稳定后,土体密度增大孔隙比减小,弹性波在土体中的传播速度更快。也就是说,在一定的动应力幅值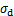 下,土体的动应变
下,土体的动应变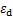 减小,而土体的动弹性模量Ed增大。拟合结果表明,式(2)能较好地定量描述
减小,而土体的动弹性模量Ed增大。拟合结果表明,式(2)能较好地定量描述 随生物酶掺量z、围压
随生物酶掺量z、围压 的变化规律。
的变化规律。
表3 参数K和n的拟合结果
Table 3 Fitting results of K and n
2.2 最大动应力
根据表2,按照 建立生物酶掺量z、围压
建立生物酶掺量z、围压 的回归方程,其中,参数K1和n1根据表2进行拟合,结果见表4。
的回归方程,其中,参数K1和n1根据表2进行拟合,结果见表4。
表4 参数K1和n1拟合结果
Table 4 Fitting results of K1 and n1
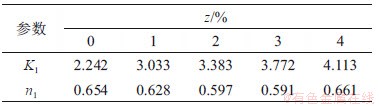
根据表4中K1和n1的拟合结果,取n1=0.626。设 ,其中,K01为生物酶掺量z=0时的K1,即K01=2.242,可得
,其中,K01为生物酶掺量z=0时的K1,即K01=2.242,可得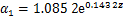 。此处引入的参数
。此处引入的参数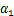 反映了生物酶掺量z对拟合参数K1的影响,即对最大动应力
反映了生物酶掺量z对拟合参数K1的影响,即对最大动应力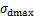 的影响。因此,
的影响。因此,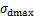 与生物酶掺量z、围压
与生物酶掺量z、围压 的回归方程可表示为
的回归方程可表示为
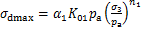 (3)
(3)
式中: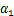 为生物酶掺量z对
为生物酶掺量z对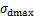 的影响因子。
的影响因子。
式(3)表明,随着围压 和
和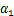 增大(即生物酶掺量z增加),膨胀土体被生物酶固化稳定后,在一定的动应变
增大(即生物酶掺量z增加),膨胀土体被生物酶固化稳定后,在一定的动应变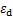 下,土体能承受的最大动应力
下,土体能承受的最大动应力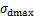 越大。该式能定量描述
越大。该式能定量描述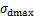 随生物酶掺量z、围压
随生物酶掺量z、围压 的变化规律。
的变化规律。
2.3 动切线变形模量Edt
参照KARG等[26]利用Duncan-Chang模型拟合动骨干曲线的方法,建立动骨干曲线切线变形模量Edt的回归方程。
对于双曲线关系的动骨干曲线,根据式(1)可得到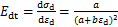 。定义动破坏比
。定义动破坏比 ,其中,
,其中,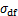 为破坏时的动应力。根据
为破坏时的动应力。根据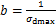 可得
可得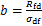 。再根据
。再根据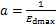 可得
可得
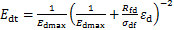 (4)
(4)
根据式(1),动应变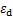 可表示为:
可表示为: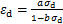
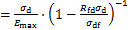 。将该式代入式(4)可得:
。将该式代入式(4)可得: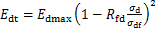 。根据Mohr-Coulomb准则,土的动破坏强度
。根据Mohr-Coulomb准则,土的动破坏强度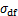 与围压
与围压 之间的关系可表示为:
之间的关系可表示为: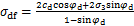 。结合式(2),将式(4)改写为
。结合式(2),将式(4)改写为
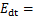
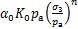
 (5)
(5)
式中: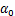 ,
, ,
,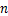 ,
, ,
,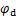 和
和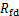 为材料试验常数。式(5)表明,参数
为材料试验常数。式(5)表明,参数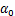 同样能反映生物酶掺量z对动切线变形模量Edt的影响。
同样能反映生物酶掺量z对动切线变形模量Edt的影响。
式(5)为反映生物酶掺量z、围压 变化规律的动骨干曲线切线变形模量Edt的回归方程。该式不包含动应变
变化规律的动骨干曲线切线变形模量Edt的回归方程。该式不包含动应变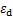 项,只是动应力
项,只是动应力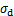 的函数。由于式(4)包含了动应力
的函数。由于式(4)包含了动应力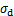 项和动应变
项和动应变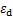 项,因此,式(4)比式(5)使用难度较大。
项,因此,式(4)比式(5)使用难度较大。
根据表2,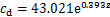 ,
,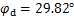 ,取
,取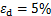 所对应的
所对应的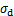 为
为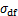 ,得到动破坏比的平均值Rfd=0.783。
,得到动破坏比的平均值Rfd=0.783。
3 动骨干曲线归一化特性
有研究表明,土的应力-应变本构关系具有归一化性状[27]。土的应力-应变关系归一化就是采用统一的本构方程表达其应力-应变关系。选取合适的归一化因子是研究土的应力-应变关系归一化特性的关键。
根据式(1),动骨干曲线归一化的应力-应变关系可表示为
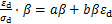 (6)
(6)
式中: 为归一化因子。本文采用最大动应力
为归一化因子。本文采用最大动应力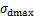 作为归一化因子,即
作为归一化因子,即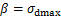 。令
。令 ,由于
,由于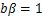 ,故可得归一化条件为
,故可得归一化条件为
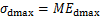 (7)
(7)
该式表明,作为归一化因子的 需满足2个条件,即:M为常数;最大动应力
需满足2个条件,即:M为常数;最大动应力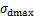 与最大动弹性模量
与最大动弹性模量 呈线性关系。根据表2所示拟合结果,各生物酶掺量下的
呈线性关系。根据表2所示拟合结果,各生物酶掺量下的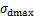 与
与 都近似呈线性关系,因此,满足式(7)的归一化条件。
都近似呈线性关系,因此,满足式(7)的归一化条件。
根据不同生物酶掺量z、不同围压 条件下的动骨干曲线应力-应变试验结果,对
条件下的动骨干曲线应力-应变试验结果,对 与
与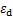 之间的关系进行线性拟合,可得到相关关系表达式为
之间的关系进行线性拟合,可得到相关关系表达式为
 (8)
(8)
该回归方程的相关系数为R2=0.959 4,也就是说,采用最大动应力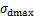 作为归一化因子,能够使得
作为归一化因子,能够使得 与
与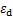 之间具有较高的线性相关性,即动骨干曲线的归一化程度较高。
之间具有较高的线性相关性,即动骨干曲线的归一化程度较高。
结合式(3)和式(8)可得

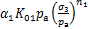 (9)
(9)
该式即为生物酶改良膨胀土的动骨干曲线应力-应变关系归一化方程。
令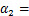
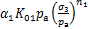 ,则式(9)可简写为
,则式(9)可简写为

 (10)
(10)
式中: 为生物酶掺量z、围压
为生物酶掺量z、围压 的函数。在一定围压
的函数。在一定围压 下,引入的参数
下,引入的参数 反映了生物酶掺量z对动应力
反映了生物酶掺量z对动应力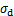 的影响,因此,可称其为生物酶掺量z对动应力
的影响,因此,可称其为生物酶掺量z对动应力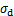 的影响因子。实际上,影响因子
的影响因子。实际上,影响因子 为最大动应力
为最大动应力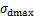 。
。
4 结论
1) Hardin-Drnevich双曲线模型能较好地描述生物酶改良膨胀土的动骨干曲线特性。建立的最大动弹性模量Edmax、最大动应力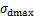 、动骨干曲线切线变形模量Edt等回归方程能较好地描述其随生物酶掺量z、围压
、动骨干曲线切线变形模量Edt等回归方程能较好地描述其随生物酶掺量z、围压 的变化规律。
的变化规律。
2) 生物酶掺量z以及围压 对生物酶改良膨胀土体的动力特性影响显著。随着生物酶掺量z以及围压
对生物酶改良膨胀土体的动力特性影响显著。随着生物酶掺量z以及围压 的增大,Edmax,
的增大,Edmax,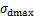 和Edt等呈非线性增大。引入的生物酶掺量影响因子
和Edt等呈非线性增大。引入的生物酶掺量影响因子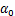 和
和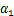 可定量反映生物酶掺量z对Edmax,
可定量反映生物酶掺量z对Edmax,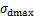 和Edt等的影响。
和Edt等的影响。
3) 采用最大动应力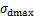 作为归一化因子,满足生物酶改良膨胀土的动骨干曲线应力-应变关系归一化分析条件,且动骨干曲线的应力-应变关系线性归一化程度较高。引入的生物酶掺量影响因子
作为归一化因子,满足生物酶改良膨胀土的动骨干曲线应力-应变关系归一化分析条件,且动骨干曲线的应力-应变关系线性归一化程度较高。引入的生物酶掺量影响因子 可定量反映生物酶掺量z对动应力
可定量反映生物酶掺量z对动应力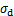 的影响。
的影响。
参考文献:
[1] IKEAGWUANI C C, NWONU D C. Emerging trends in expansive soil stabilization:a review[J]. Journal of Rock Mechanics and Geotechnical Engineering, 2019, 11(2): 423-440.
[2] BEHNOOD A. Soil and clay stabilization with calcium- and non-calcium-based additives: a state-of-the-art review of challenges, approaches and techniques[J]. Transportation Geotechnics, 2018, 17: 14-32.
[3] YONG R N, OUHADI V R. Experimental study on instability of bases on natural and lime/cement-stabilized clayey soils[J]. Applied Clay Science, 2007, 35(3/4): 238-249.
[4] CELIK E, NALBANTOGLU Z. Effects of ground granulated blastfurnace slag (GGBS) on the swelling properties of lime-stabilized sulfate-bearing soils[J]. Engineering Geology, 2013, 163: 20-25.
[5] STOLTZ G, CUISINIER O, MASROURI F. Weathering of a lime-treated clayey soil by drying and wetting cycles[J]. Engineering Geology, 2014, 181: 281-289.
[6] TINGLE J S, NEWMAN J K, LARSON S L, et al. Stabilization mechanisms of nontraditional additives[J]. Transportation Research Record: Journal of the Transportation Research Board, 2007 (1): 59-67.
[7] LATIFI N, MEEHAN C L, MAJID M Z A, et al. Strengthening montmorillonitic and kaolinitic clays using a calcium-based non-traditional additive: a micro-level study[J]. Applied Clay Science, 2016, 132/133: 182-193.
[8] KANNIYAPPAN S P, DHILIP K R G, FAIZUNEESA A, et al. Experimental investigation on black cotton soil using bio-enzyme as a soil stabilizer in road construction[J]. CIKITUSI Journal for Multidisciplinary Research, 2019, 6(5): 234-250.
[9] THOMAS A, TRIPATHI R K, YADU L. Application of Taguchi method for optimization of various factors in improving the shear modulus of enzyme treated soil[J]. National Academy Science Letters, 2020, 43(2): 171-175.
[10] POONI J, GIUSTOZZI F, ROBERT D, et al. Durability of enzyme stabilized expansive soil in road pavements subjected to moisture degradation[J]. Transportation Geotechnics, 2019, 21: 100255.
[11] NAAGESH S, GANGADHARA S. Swelling behaviour of bio-enzyme treated expansive soil[J]. International Journal of Earth Sciences and Engineering, 2011, 4(3): 555-560.
[12] SURESH K, KUMAR P S. Efficacy of Terrazyme-a bioenzyme on strength characteristics of expansive soil[J]. Global Journal of Engineering Science and Researches, 2018,5(2): 89-96.
[13] 周文权, 冷伍明, 刘文劼, 等. 低围压循环荷载作用下饱和粗粒土的动力特性与骨干曲线模型研究[J]. 岩土力学, 2016, 37(2): 415-423.
ZHOU Wenquan, LENG Wuming, LIU Wenjie, et al. Dynamic behavior and backbone curve model of saturated coarse-grained soil under cyclic loading and low confining pressure[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2016, 37(2): 415-423.
[14] 张勇, 孔令伟, 李雄威. 循环荷载下饱和软黏土的动骨干曲线模型研究[J]. 岩土力学, 2010, 31(6): 1699-1704.
ZHANG Yong, KONG Lingwei, LI Xiongwei. Dynamic backbone curve model of saturated soft clay under cyclic loading[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2010, 31(6): 1699-1704.
[15] KRAVCHENKO E, LIU Jiankun, KRAINIUKOV A, et al. Dynamic behavior of clay modified with polypropylene fiber under freeze-thaw cycles[J]. Transportation Geotechnics, 2019, 21: 100282.
[16] 迟世春, 陈崇茂, 贾宇峰. 筑坝土石料的变参数Ramberg-Osgood模型及其适应性研究[J]. 岩土力学, 2013, 34(1): 1-5.
CHI Shichun, CHEN Chongmao, JIA Yufeng. Ramberg-Osgood model with variable parameters of earth-rock materials for earth-rock dam and its adaptability[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2013, 34(1): 1-5.
[17] HARDIN B O, DRNEVICH V P. Shear modulus and damping in soils:design equations and curves[J]. Journal of the Soil Mechanics and Foundations Division, 1972, 98(SM7): 667-692.
[18] KONDNER R L. Hyperbolic stress-strain response: cohesive soil[J]. Journal of the Soil Mechanics and Foundations Division, 1963, 89(SM1): 115-143.
[19] ZHAO Futang, CHANG Lijun, ZHANG Wuyu. Experimental investigation of dynamic shear modulus and damping ratio of Qinghai―Tibet frozen silt under multi-stage cyclic loading[J]. Cold Regions Science and Technology, 2020, 170: 102938.
[20] WU Zhijian, ZHANG Dan, ZHAO Tao, et al. An experimental research on damping ratio and dynamic shear modulus ratio of frozen silty clay of the Qinghai―Tibet engineering corridor[J]. Transportation Geotechnics, 2019, 21: 100269.
[21] 庄妍, 朱伟, 张飞. 饱和粉质黏土动弹性模量影响因素分析及骨干曲线模型研究[J]. 中南大学学报(自然科学版), 2019, 50(2): 445-451.
ZHUANG Yan, ZHU Wei, ZHANG Fei. Analysis of factors affecting dynamic modulus of elasticity of saturated silty clay and research on backbone curve model[J]. Journal of Central South University(Science and Technology), 2019, 50(2): 445-451.
[22] SHANG Yonghui, XU Linrong, ZHAO Y, et al. Experimental study on the dynamic features of cement-stabilized expansive soil as subgrade filling of heavy haul railway[J]. Journal of Engineering Science and Technology Review, 2017, 10(6): 136-145.
[23] ZHANG Zelin, WANG Tao, WU Shuren, et al. Dynamics stress-strain behavior of Tianshui soils[J]. Landslides, 2017, 14(1): 323-335.
[24] LING X Z, ZHANG F, LI Q L, et al. Dynamic shear modulus and damping ratio of frozen compacted sand subjected to freeze-thaw cycle under multi-stage cyclic loading[J]. Soil Dynamics and Earthquake Engineering, 2015, 76: 111-121.
[25] WANG Min, KONG Lingwei, ZHAO Chong, et al. Dynamic characteristics of lime-treated expansive soil under cyclic loading[J]. Journal of Rock Mechanics and Geotechnical Engineering, 2012, 4(4): 352-359.
[26] KARG C, HAEGEMAN W. Elasto-plastic long-term behavior of granular soils: Experimental investigation[J]. Soil Dynamics and Earthquake Engineering, 2009, 29(1): 155-172.
[27] VARDANEGA P J, BOLTON M D. Stiffness of clays and silts: normalizing shear modulus and shear strain[J]. Journal of Geotechnical and Geoenvironmental Engineering, 2013, 139(9): 1575-1589.
(编辑 陈灿华)
收稿日期: 2020 -05 -24; 修回日期: 2020 -07 -24
基金项目(Foundation item):国家国际科技合作专项(2014DFA53120);现代木结构工程材制造及应用技术湖南省工程实验室开放基金资助项目(HELFMTS1707);湖南省重点学科建设项目(2013ZDXK006) (Project(2014DFA53120) supported by the National Special Program for International Scientific and Technology Cooperation; Project(HELFMTS1707) supported by the Open Fund of Hunan Engineering Laboratory for Manufacturing and Application Technology of Modern Timber Structural Engineering Materials; Project(2013ZDXK006) supported by the Key Discipline Construction Program of Hunan Province)
通信作者:文畅平,博士,教授,从事岩土工程研究;E-mail:wenchangping@163.com
引用格式: 文畅平, 任睆遐. 生物酶改良膨胀土的动骨干曲线模型[J]. 中南大学学报(自然科学版), 2021, 52(4): 1109-1117.
Citation: WEN Changping, REN Huanxia. Dynamic backbone curve model of bioenzyme-treated expansive soil under cyclic loading[J]. Journal of Central South University(Science and Technology), 2021, 52(4): 1109-1117.