组织工程用Mg-Ca-Zn-Co合金泡沫的制备及氟化处理
来源期刊:中国有色金属学报(英文版)2018年第1期
论文作者:Ilven MUTLU
文章页码:114 - 124
关键词:Mg-Ca-Zn-Co合金;支架;氟化处理;金属泡沫;腐蚀
Key words:Mg-Ca-Zn-Co alloy; scaffold; fluoride treatment; metal foam; corrosion
摘 要:以尿素为造孔剂,利用基于粉末冶金法的“造孔剂-水浸出”法制备可用于骨组织工程的多孔 Mg-Ca-Zn-Co合金支架。并研究合金浸泡在氟化氢(HF)溶液中进行表面氟化处理对合金耐腐蚀性能的影响。结果表明,随着Zn含量的增加,合金的弹性模量提高。Ca 的添加可以阻止烧结过程中样品的氧化。合金在模拟体液中的电化学腐蚀行为的研究表明,当Zn含量从1.0%增加到 3.0%时,合金的腐蚀率和质量损失都先减小,随着Zn 含量的进一步增加,合金的腐蚀率和质量损失而后增大。氟化处理后合金表面形成了氟化物涂层,提高了合金的耐腐蚀性。
Abstract: Highly porous Mg-Ca-Zn-Co alloy scaffolds for tissue engineering applications were produced by powder metallurgy based space holder-water leaching method. Mg-Ca-Zn-Co alloy foam can be used as a scaffold material in tissue engineering. Carbamide was used as a space holder material. Fluoride conversion coating was synthesized on the alloy by immersion treatment in hydrofluoric acid (HF). Increasing Zn content of the alloy increased the elastic modulus. Ca addition prevented the oxidation of the specimens during sintering. Electrochemical corrosion behaviour of the specimens was examined in simulated body fluid. Corrosion rate decreased with Zn addition from 1.0% up to 3.0% (mass fraction) and then increased. Mass loss of the specimens initially decreased with Zn addition up to about 3% and then increased. Fluoride conversion coating increased the corrosion resistance of the specimens.
Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 28(2018) 114-124
Ilven MUTLU
Metallurgical and Materials Engineering Department, Istanbul University, Istanbul 34320, Turkey
Received 5 November 2016; accepted 20 July 2017
Abstract: Highly porous Mg-Ca-Zn-Co alloy scaffolds for tissue engineering applications were produced by powder metallurgy based space holder-water leaching method. Mg-Ca-Zn-Co alloy foam can be used as a scaffold material in tissue engineering. Carbamide was used as a space holder material. Fluoride conversion coating was synthesized on the alloy by immersion treatment in hydrofluoric acid (HF). Increasing Zn content of the alloy increased the elastic modulus. Ca addition prevented the oxidation of the specimens during sintering. Electrochemical corrosion behaviour of the specimens was examined in simulated body fluid. Corrosion rate decreased with Zn addition from 1.0% up to 3.0% (mass fraction) and then increased. Mass loss of the specimens initially decreased with Zn addition up to about 3% and then increased. Fluoride conversion coating increased the corrosion resistance of the specimens.
Key words: Mg-Ca-Zn-Co alloy; scaffold; fluoride treatment; metal foam; corrosion
1 Introduction
Scaffold provides support for cells, and its architecture determines the shape of new tissue. In general, bone substitute material should be osteoconductive, biodegradable and strong enough [1,2]. Several scaffold materials, including hydroxyapatite and polymers, have been investigated for tissue engineering. Brittle nature of ceramics and low strength of polymers have limited applicability of these materials. Stainless steels, Co alloys and Ti alloys have been studied in orthopaedic implants. However, they cannot degrade and a surgical operation is needed after tissues have healed [1,2].
Porous Mg has potential to use as a biodegradable scaffold for bone substitute applications [1,2]. Mg exhibits low corrosion resistance in physiologic environments [3-5]. Non-toxic oxides or hydroxides which formed during the degradation enhance activity of osteoblast and decrease amount of osteoclast during regeneration. These properties have attracted attention to the development of biodegradable Mg implants [1-3]. Mg alloys have closer elastic modulus to the bone compared with Ti alloys, better ductility and toughness than hydroxyapatite and higher strength than polymers. Another performance for degradable biomaterial is the degradation rate. It influences not only the healing period but also the loss of mechanical properties during degradation [2].
Studies on the Mg alloys are focused on corrosion and biocompatibility. Most Mg alloys contain Al and rare earth (RE) elements, whereas Al is neurotoxicant, and hepatotoxicity is detected after administration of rare earth. The main issue to limit application of Mg is its low strength and poor corrosion resistance. Commercial Mg alloys are well researched. Some Mg alloys, such as AZ31, AM60B and WE43 are attempted as biomaterials. Al, Mn, Zr and RE elements are employed to improve the mechanical and corrosion properties. However, these products result in negative effects on the human [3-6].
Zn is a grain refiner and enhances strength of the Mg. Mg-Zn alloys reveal the improved corrosion properties, which is attributed to the ability of Zn to form precipitates. Low volume fractions of MgZn decrease the corrosion rate, whereas larger volume fractions promote microgalvanic corrosion. Zn contents up to 5.6% (mass fraction) improve the corrosion properties. Since the maximum solubility of Zn in Mg is 8.4%, a high amount of Zn can be retained in the solid solution [3-5]. New Mg-Zn alloy exhibits moderate mechanical properties and cytocompatibility. Mg-Zn alloys offer constant degradation rate owing to homogeneous microstructure. Zn improves corrosion resistance and mechanical properties of the Mg. Mg-Zn alloys possess the highest capacity for aging [1-6].
Ca refines the microstructure of the Mg alloys, and enhances the strength and corrosion resistance. Formation of a calcium-phosphate layer is observed during immersion in simulated body fluid, which points to a beneficial influence on cell adhesion and corrosion protection. In the Mg-Ca system, up to 0.5%-0.7% Ca produces superior mechanical and corrosion properties [3-5]. Wrought Mg alloys have low strength and low workability. Powder metallurgy overcomes these problems. Powder metallurgy is known to strengthen the material by its microstructure. Powder metallurgy is suitable for manufacturing Mg foam because of its high activity. In addition, space holder method is suitable for manufacturing open cell foams [7,8]. Mg-Zn alloy is a precipitation hardenable system, in which solubility of Zn decreases with the increase of temperature. Atomic radius of Zn is smaller than that of Mg. Another feature is that mixing enthalpy between solute elements is negative. During aging, decomposition of super-saturated solid solution results in formation of precipitates [9,10].
The addition of Co to the Mg-Zn alloy raises the eutectic temperature and induces response to aging. The microstructure of Mg-Zn-Co is finer than that of Mg-Zn. Intermetallics are refined by Co addition. Co permits use of higher temperature for solution, which leads to larger supersaturation of Zn atoms and higher concentration of vacancies in Mg grains after quenching. The increase in eutectic temperature permits use of higher solution temperature, ensuring supersaturation of Zn, which leads to larger fraction of precipitates [9-11]. Kinetics of aging is accelerated in Co-containing alloy. Co segregates into the intermetallics [9-11].
Mg alloys suffer from a high corrosion rate in body fluids. To improve the corrosion resistance, one of the ways might be coatings. There are several surface treatments for improving the corrosion resistance, but they are mainly developed for Mg alloys in industrial applications. The surface treatment methods include conversion coatings, carbonate treatment, alkali-heat- treatment, anodizing, polymeric coatings and electro- deposition. Surface treatment of Mg can be classified into conversion and deposition coatings. Conversion treatment via hydrofluoric acid is promising due to its simplicity and low cost. Mg alloys are resistant to hydrofluoric acid (HF) due to the formation of a protective layer of MgF2. Corrosion resistance of Mg could be improved by fluoride treatment, since the fluoride ion is a corrosion inhibitor for Mg. By this method, corrosion rate decreases by providing MgF2 protective layer. Moreover, one of the components of bone and teeth is fluorine. Fluoride coating has good bonding strength and can be performed on complex shaped parts [12-18].
SEYEDRAOUFIN and MIRDAMADI [1] prepared Mg-Zn scaffolds. According to their results, Mg-Zn alloy could be considered as scaffold materials. Porous Mg has potential to serve as a degradable scaffold for bone substitution. The dissolved Mg ions may promote bone cell attachment and tissue growth. BOBE et al [19] fabricated a biodegradable, open-porous, mechanically adaptable scaffold from Mg alloy by sintering. The in vitro environment influenced the corrosion rates compared with the in vivo environment. Culture media composition influences the ionic composition of the extract by selectively dissolving ions. AGHION et al [20] produced Mg foams by space holder method as a scaffold for drug delivery. The amount and delivery time of the released drug were controlled by space holder. WEN et al [21] produced Mg foams for scaffold applications. They investigated the mechanical properties of Mg with the porosity of 35%-55% and the pore size of 70-400 μm. Results indicate that the elastic modulus increases with decreasing porosity. The mechanical properties were close to those of human bone.
The purpose of this work is to study the novel Mg-Ca-Zn-Co alloy, with greater aging response. There has been no study on open-cell porous Mg-Ca-Zn-Co scaffolds produced by powder metallurgy. In this study, Mg-Ca-Zn-Co alloy foams were produced by powder metallurgy based on space holder method. Fluoride treatment was carried out by immersion treatment in HF. Although cast Mg-Ca-Zn/Mg-Ca-Zn-Co alloys were studied [3-5], studies on Mg-Ca-Zn-Co foams produced by powder metallurgy were limited. Since the corrosion rates in the literature are not as low as those required for implant applications, further investigations regarding an improved alloy composition design are required. In the range of the low alloyed Mg systems, the effect of alloying elements on the degradation behaviour has not been fully investigated.
2 Experimental
2.1 Foam production
Foams were produced by powder metallurgy based on space holder-water leaching method using Mg, Ca, Zn and Co powders (Alfa Aesar, USA). The purity of the powders was >99.5%. The mean particle size of the powders was about 34 μm. In the alloy preparation stage, 0.7% Ca, 1% Zn, 3% Zn, 5% Zn, 8% Zn and 0.3% Co, 0.6% Co powders were added to the Mg powder. The powder mixtures were ball-milled to prepare the alloys, using a ball-milling machine. The mixture was loaded in a hardened steel vial with ZrO2 balls (3 mm in diameter) to give a ball-to-powder mass ratio of 10:1. Powders were mechanically alloyed (MA) for 4 h with a rotational speed of 400 r/min without addition of any process control agent to avoid contamination of the powder. As a space holder, carbamide (Merck, Germany), in the fraction of 710-1000 μm was used. Binder for green strength was polyvinylalcohol (PVA). Metal powders were mixed with 1.5% PVA. Mixtures were compacted at 200 MPa into cylindrical specimens with diameters of 20 mm and 12 mm and heights of 15-17 mm. Specimens were immersed in water for 10 h and then carbamide was leached out. Sintering cycle consisted of heating at a rate of 5 °C/min to 400 °C (debinding) with dwell time of 40 min, followed by heating at a rate of 11 °C/min to sintering temperatures. Specimens were sintered at 560 °C for 60 min in argon atmosphere.
Some sintering studies were carried out in order to determine the optimum sintering temperature and time of the alloy. In addition, sintering temperature of the alloy was also determined in the light of experimental studies in Refs.[7,8]. There was insufficient sintering at sintering temperatures below 530-540 °C. Lower sintering temperature resulted in insufficient bonding between the Mg particles. On the other hand, geometrical shape of the specimens was deformed at sintering temperatures above 590-600 °C due to high temperature and excessive liquid phase formation. Higher sintering temperature can lead to partial melting. Moreover, the increase in the sintering temperature can lead to the decrease in the grain size. As a result, optimum sintering temperature was determined as 560-580 °C. Excessive grain growth resulted in degradation of the mechanical properties.
For surface treatment, the polished specimens were washed with distilled water, rinsed and degreased with ethanol and dried. Then, the specimens were immersed in 250 g/L sodium hydroxide solution (NaOH) for 2 h. Subsequently, specimens were cleaned in water and dried. The specimens were immersed vertically in a plastic bottle containing hydrofluoric acid (40% HF) at room temperature for 24 h. The treatment specimens were washed with water, dried and weighed.
2.2 Microstructure and mechanical properties
The microstructure and pore morphology of the specimens were examined by field emission gun-scanning electron microscopy (FEG-SEM), FEI Quanta FEG 450. X-ray diffraction (XRD) analysis (Rigaku D/Max-2200/PC) was used to characterize the alloys. Total porosity content was determined from measurements of masses and dimensions of the specimens. Archimedes method was also used to measure the density (total porosity). Open porosity contents of the specimens were measured by using Hg intrusion porosimeter (Quantachrome Poremaster). Digital scanning electron microscopy (SEM) images of the specimens were used to determine the mean pore size. The area of each pore on the SEM image was calculated, and mean equivalent spherical diameter as pore size was determined by using image analyser.
Mechanical properties of the specimens were studied by compression tests (Devotrans, Turkey). In addition, nondestructive ultrasonic tests (ultrasonic velocity measurements) were carried out in order to determine the elastic modulus. Ultrasonic velocity is related to the elastic modulus and density of material. Ultrasonic velocities were measured by using pulse-echo method. A pulse-receiver type ultrasonic instrument (General Electric, USMGo), with 4 MHz normal beam wave transducer was used for ultrasonic velocity measurements. Elastic modulus (E) was calculated by Eq. (1) [22] using density (ρ), ultrasonic longitudinal velocity (vL), and ultrasonic transverse velocity (vT). Densities of the specimens were determined by mass over volume method.
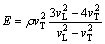 (1)
(1)
2.3 Simulated body fluid preparation
Simulated body fluid (SBF) solution was prepared from chemicals (Merck, Germany) according to Refs. [22-28]. Amounts of the chemical reagents were 8.03 g/L NaCl, 0.29 g/L CaCl2, 0.22 g/L KCl, 0.31 g/L MgCl2·6H2O, 0.23 g/L K2HPO4·3H2O, 0.35 g/L NaHCO3, 0.07 g/L Na2SO4, 39 mL 1.0 mol/L HCl, 6.11 g/L tris (hydroxymethyl) aminomethane, and appropriate amount of 1.0 mol/L HCl. The pH of the SBF solution was adjusted to 7.40.
2.4 Electrochemical corrosion
Electrochemical corrosion studies were carried out using a potentiostat (Interface 1000 Potentiostat/ Galvanostat/ZRA, Gamry, USA) controlled by a personal computer. Volume of glass corrosion test cell was 1000 mL. A conventional three-electrode system with high-density graphite rod as a counter electrode, a saturated calomel electrode (SCE) as reference electrode, and specimen as a working electrode was used. Data acquisition was carried out through a computer software (Framework, Gamry, USA), while data analysis was carried out by Echem Analyst Software, Gamry, USA. Specimens were prepared by cutting and then mounted into epoxy resin. So, only circular cross section with diameter of 10 mm of the specimens was exposed to the solution. All corrosion experiments were carried out at room temperature. Open circuit potential (OCP) of the specimens was measured before carrying out the electrochemical corrosion experiments. OCP level was measured for durations of 2 to 3 h, until the OCP was stabilized. Tafel curves were obtained by polarizing the specimens from -250 to 250 mV (vs SCE), with respect to the OCP, at a scan rate of 1.0 mV/s. Corrosion rate was calculated by the software (DC105, Gamry). Calculations were based on numerical curve fit to the Butler-Volmer equation. Corrosion rate (mm/year, i.e., mm/a), corrosion potential (φcorr), corrosion current density (Jcorr), the anodic beta Tafel constant (βanode), the cathodic beta Tafel constant (βcathode) values were calculated. Beta coefficients (β) give kinetic information about anodic and cathodic reactions. In linear polarization resistance (LPR) test, the specimens were polarized from -20 to 20 mV (vs SCE), at a scanning rate of 0.125 mV/s, in order to measure polarization resistance and corrosion rate of the specimens.
Cyclic polarization tests were carried out from -500 mV (vs SCE) to apex potential and to final potential, which was 0 mV (vs SCE). Forward and reverse polarization scan rates were 5 and 2.5 mV/s, respectively. Cyclic (forward and reverse) polarization technique was used to evaluate tendency to localized corrosion (pitting) in corrosive environment. Hysteresis between the forward and reverse polarization sweeps is an indication of the pit formation.
2.5 Static immersion test
Specimens were immersed vertically to SBF solution at room temperature for soaking time up to 120 h. Samples were immersed in a 500 mL solution. Porosity values and surface areas of specimens were equal. Solution volume to surface area ratio was constant in all tests. The inductively coupled plasma-mass spectrometer, ICP-MS (Thermo Scientific Elemental X Series 2) was employed to measure the Mg ions. Mass loss/gain values of the specimens were determined by gravimetric method. After different soaking periods, the specimens were removed from the SBF solutions. Then, the specimens were rinsed with distilled water and then dried. The dried specimens were weighed and mass gain was determined. The immersed samples were cleaned using a solution of 180 g/L chromic acid to remove the surface corrosion product, and then rinsed with ethanol, dried in air and finally weighed to calculate the mass loss [29-31].
3 Results and discussion
3.1 Microstructure
Highly porous Mg-Ca-Zn-Co alloy foams were produced by powder metallurgy based space holder-sintering method for scaffold applications. Pore size and pore morphology of the sintered foams replicated the initial size and morphology of the carbamide particles. Figure 1 shows the SEM images of the Mg, Ca, Zn, Co and irregular shaped carbamide (space holder) powders.
Figure 2 shows the SEM image from the crack surface of the sintered foam with a porosity of about 74%, SEM image from cell-wall of the foam, photograph of the sintered foam, and microstructure of the sintered foam. As shown in Fig. 2(b), sintering temperature was suitable. Lower sintering temperature results in insufficient bonding and requires long time for bonding. Higher sintering temperature can lead to partial melting of the Mg particles. The increase in the sintering temperature can lead to the increase in grain size. 560 °C should be considered the optimum sintering temperature because the grain growth results in degradation of the mechanical properties of the specimens. Figure 2(d) shows the microstructure of the sintered foam. Microstructure of the sintered Mg-Ca-Zn-Co alloy mainly consists of Mg phase matrix (bright regions). Some Co phase (MgCo), Zn phase (MgZn) and oxide (MgO) are also observed (dark regions at grain boundaries). Table 1 shows the actual chemical compositions of the sintered Mg alloys. As Mg is a highly active metal, 2.0%-5.0% oxygen (MgO) was detected in the actual chemical composition of the sintered specimens.
Major problems of the implant materials are related to high elastic modulus of metals and low mechanical properties of porous ceramics and polymers. These problems can be solved by selecting Mg alloy scaffold with appropriate porosity. Although strength and elastic modulus decrease as porosity increases, mechanical properties of the alloy are closer to those of the bone. Therefore, porous Mg alloy is a promising scaffold material for hard tissue regeneration [1-5, 29-33].
Table 2 shows the mean sizes of the carbamide (space holder) particles and mean pore size of the sintered foams. As seen in Table 2, the final pore size value is related to the mean carbamide particle size. Meanwhile, pore shape is also similar to initial carbamide particle shape. Mean diameter (pore size) of specimens, which was produced using irregular carbamide in the range of 1000-710 μm, is 570 μm. Meanwhile, mean equivalent spherical diameter of the carbamide particles was determined to be 860 μm. The decrease in the size was attributed to crushing of the carbamide particles during pressing and moistening before mixing. Porosity and pore size both play an important role in bone growth. Minimum requirement for pore size is considered to be about 100 μm due to cell migration and transport. Higher porosity and larger pore size result in greater bone growth. For the pores with size less than 100 μm, cells did not grow into the pores because of spanning of pores by cells.
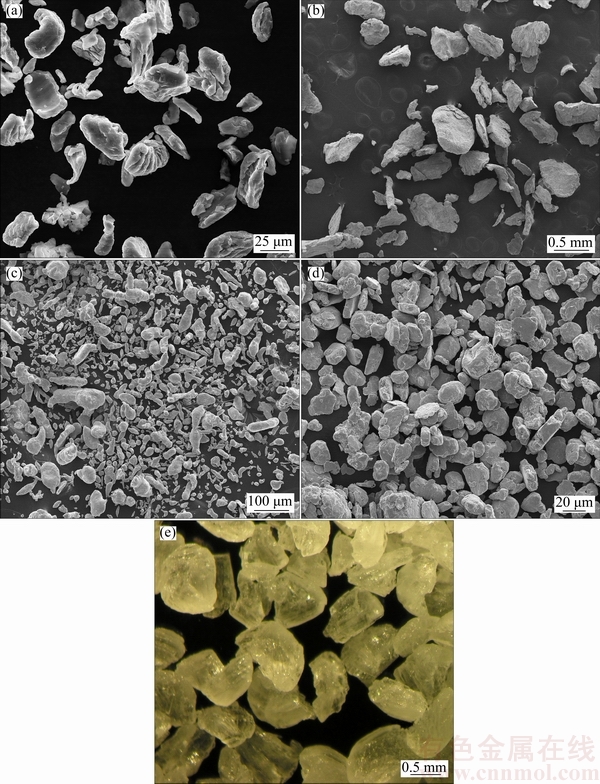
Fig. 1 SEM images of Mg (a), Ca (b), Zn (c), Co (d) and carbamide (e) powders
Figure 3 shows the XRD patterns of the Mg, Ca, Zn, Co powders and sintered specimen. The as-received Mg powder consists of Mg phase. Sintered Mg-Ca-Zn-Co alloy specimen mainly consists of Mg phase. Some Ca phase, Co phase (MgCo), Zn phase (MgZn) and oxide (MgO) were also formed on the surfaces of the sintered Mg-Ca-Zn-Co alloy specimens. For Mg alloys, which were immersed in NaOH solution, a Mg(OH)2 layer formed and then by immersing the specimen into the hydrofluoric acid, the Mg(OH)2 film transformed into protective MgF2 [1,15,18,33,34].
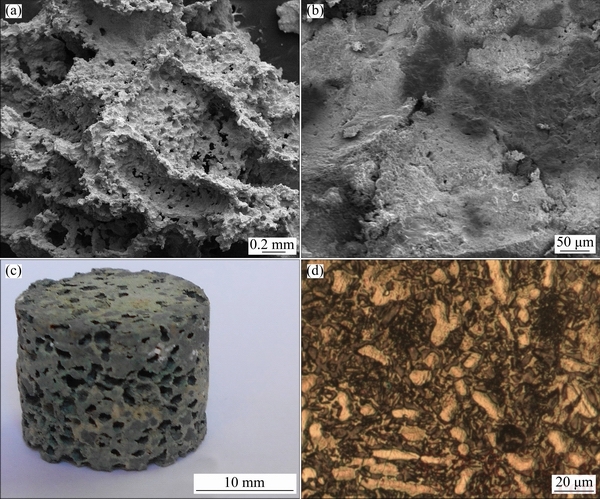
Fig. 2 SEM images from crack surface (a) and cell-wall (b), photograph of sintered foam (c) and microstructure of sintered foam (d)
Table 1 Actual chemical compositions of studied alloys (mass fraction, %)
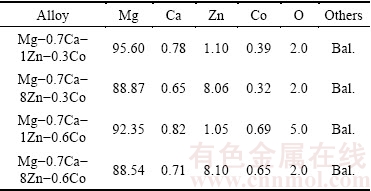
Table 2 Mean size of carbamide particles and mean pore size of sintered foams

Improved strength is attributed to the fine grain size and homogeneous precipitates. Zn can be added to the Mg alloy as a grain refiner. Increasing the Zn content can produce a decrease in the grain size and improve mechanical properties. Figure 4 shows the effect of Zn content of the alloy on the elastic modulus of the sintered specimens and grain size of the sintered specimens. As seen from Fig. 4(a), Zn addition to the alloy increased the elastic modulus of the sintered specimens.
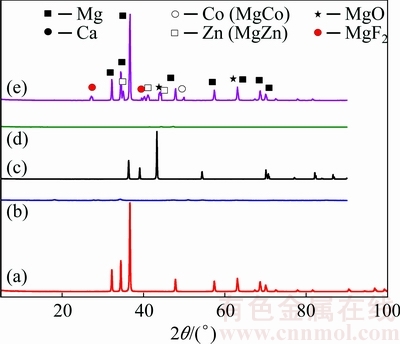
Fig. 3 XRD patterns of Mg (a), Ca (b), Zn (c), Co (d) powders and sintered Mg-Ca-Zn-Co alloy specimen (e)
Figure 4(b) shows the effect of Zn content of the alloy on the grain size of the sintered specimen. As seen from Fig. 4(b), Zn addition to the alloy decreases the grain size of the sintered specimens. Grain size decreases with increasing Zn content. Zn resolves in the Mg when Zn content is 1%-2%, which can improve strength by solid-solution strengthening. When Zn content is 4% or 6%, MgZn phases precipitate from the matrix. This effect enhances the strength by dispersion strengthening. Zn can act as constituent to refine the microstructure of the matrix and to improve the strength [1-3,9,10].
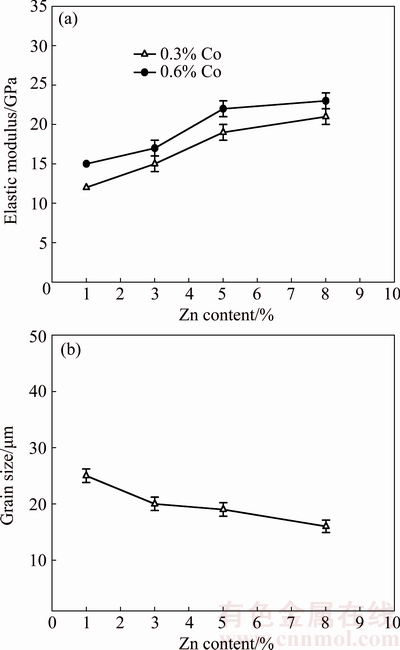
Fig. 4 Effect of Zn content on elastic modulus (a) and grain size (b) of specimens
The addition of Co to Mg alloy can increase the elastic modulus and allow the use of higher solution treatment temperatures that can lead to higher concentrations of Zn atoms and vacancies in the Mg grains, which can increase the age-hardening response. Age-hardening involves dislocation particle interaction, load transfer from matrix to particles, and generation of dislocation due to the difference between thermal expansions of matrix and particles. These phases become sites to pin movement of dislocations. Strength can be improved due to the fine precipitates [1-3,9,10].
3.2 Electrochemical corrosion tests
3.2.1 Open circuit potential
Open-circuit potential (OCP) is a potential at which an alloy is in equilibrium with environment [35]. High OCP means that material is stable in a certain corrosive environment. Figure 5 shows the variation of the OCP level with the alloying element addition in the specimens with about 74% porosity. As shown in Fig. 5, increasing Co and Zn contents of Mg-Ca-Zn-Co alloy decreases the OCP value.

Fig. 5 Variation of OCP level with Co and Zn contents of alloy
3.2.2 Tafel tests
Tafel curves were used to examine electrochemical corrosion behaviour of the specimens. Figure 6 shows the effect of chemical composition (alloying element addition) on the Tafel curves of the specimens with about 74% porosity. As shown in Fig. 6, increasing Co and Zn contents of the alloy decreased the electrochemical corrosion potential and increased the corrosion current density of the specimens. In general, with addition of more than 1% Zn at a constant Ca content of 0.5% or 1% a reduction of corrosion rates of the alloy was achieved. However, larger amount of the Zn above 2%-3% leads to an increase in the corrosion rates [1-3,9,10].
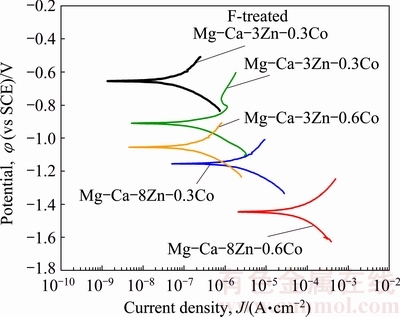
Fig. 6 Effect of Co and Zn contents of alloy on Tafel curves
Table 3 shows the corrosion parameters obtained from the Tafel curves. In Table 3, corrosion rate (mm/a), corrosion potential (φcorr), corrosion current density (Jcorr), the anodic beta Tafel constant (βanode), and the cathodic beta Tafel constant (βcathode) values are given.
Table 3 Corrosion parameters obtained from Tafel curves

3.2.3 Linear polarization tests
Figure 7 shows the effect of Zn and Co contents of the Mg-Ca-Zn-Co alloy on the polarization resistance, while Fig. 8 shows the effect of Zn and Co contents of the alloy on the corrosion rate of the specimens with about 74% porosity. Polarization resistance is connected with kinetic phenomena at the metal-solution interface. In general, polarization resistance and corrosion rate values characterize the protection degree of the passive surface oxide. As seen from Fig. 7, polarization resistance initially increased with Zn addition up to 3% and then decreased. Increasing Co content from 0.3% to 0.6% decreased the polarization resistance of the specimens. As seen from Fig. 8, corrosion rate decreased with Zn addition up to 3% and then increased. Increasing Co content from 0.3% to 0.6% increased the corrosion rate.
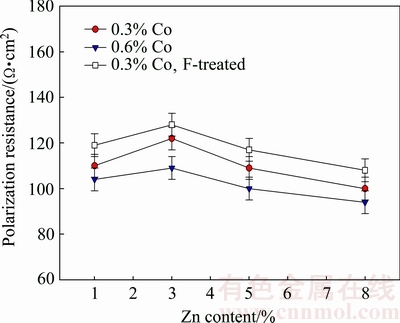
Fig. 7 Effect of Co and Zn contents of alloy on polarization resistance

Fig. 8 Effect of Co and Zn contents of alloy on corrosion rate
The microstructure of the sintered Mg-Ca-Zn-Co alloy mainly consists of Mg phase matrix. Some Co phase (MgCo), Zn phase (MgZn) and oxide (MgO) were also observed at grain boundaries. Zn addition improves corrosion properties of the Mg phase, which is attributed to the ability of the Zn to form precipitates. Zn contents up to 5%-6% improve the corrosion resistance of the alloy, while larger volume fractions promote micro- galvanic corrosion. Ca refines the microstructure in the Mg alloys and enhances the corrosion resistance. Co addition also refines the microstructure. Co segregates into the intermetallics.
Meanwhile, increasing porosity content decreases the corrosion resistance and increases the corrosion rate of the foams. Porosity affects the corrosion resistance by providing preferential paths for corrosive species to penetrate through the open porous (interconnected pores) material. In addition, corrosion rate increases with increasing porosity due to a defective surface passive oxide film.
3.2.4 Cyclic polarization test
Figure 9 shows the effect of fluoride treatment on the cyclic polarization curves of the alloy. As seen from Fig. 9, fluoride treatment of the alloy increases the localized corrosion resistance. Cyclic polarization is used to qualitatively evaluate tendency to localized corrosion (pitting or crevice). Hysteresis between forward and reverse sweeps during cyclic polarization is an indication of localized corrosion (pit formation). Hysteresis (loop) decreases with fluoride treatment.

Fig. 9 Effect of fluoride treatment on cyclic polarization curves of alloy
Cyclic polarisation curves were also analyzed in terms of breakdown potential (φbd) and repassivation potential (φrp). Breakdown potential (pitting potential) corresponds to potential for new pit formation and stable pit growth. The increase in the resistance to pitting is associated with the increase in the φbd. Pits are initiated above the φbd, but if pits are once initiated they propagate at all potentials above the φrp. Thus, φrp is used in the design as protection potential. A metal will resist to pitting if its potential is kept below φrp. Below φrp all the pits can repassivate. The difference between these potentials (φbd-φrp) can be used instead of the values themselves. Fluoride treatment increased the breakdown potential (φbd) and repassivation potential (φrp). Based on the φrp and φbd values, tendency of the localized corrosion increases with fluoride treatment.
3.2.5 Static immersion test
Determination of the chemical interaction of biomaterials with body fluids is important. Figure 10 shows the effect of immersion time on the mass gain and mass loss of the alloy with about 74% porosity in SBF environment. The mass loss/gain values of fluoride- treated specimens were also provided. As seen from Fig. 10(a), mass gain increases with increasing immersion time. As seen from Fig. 10(b), mass loss also increases with increasing immersion time. Meanwhile, mass loss/gain values of the specimen initially decrease with Zn addition up to 3% and then increase. So, mass loss/gain levels of the Mg alloy can be adjusted by alloying.
Mass loss was observed in the specimens, which were cleaned using chromic acid. Mass loss in the SBF environment happened as a result of dissolving of Mg by the reaction between Mg and SBF solution. Mass gain was observed in the specimens which were not cleaned using chromic acid. Mass gain of the Mg alloys happened as a result of formation of insoluble corrosion (precipitation) products on the surface [29-33].
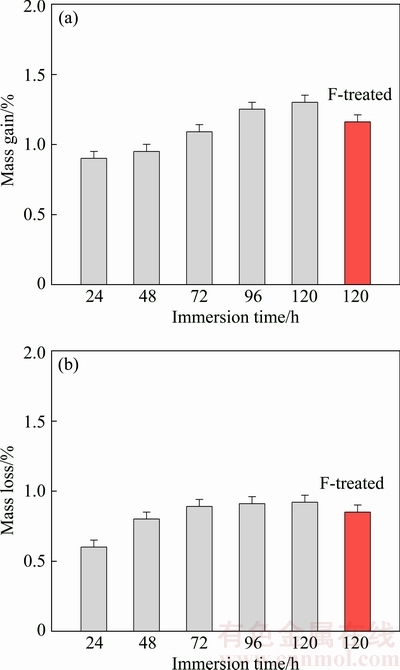
Fig. 10 Effect of immersion time on mass gain (a) and mass loss (b) of alloy in SBF environment
Figure 11 shows the effect of immersion time and Zn content of the alloy on the Mg ion release in the SBF solution. The Mg ion release values of the fluoride-treated specimens were also provided. It can be seen from Fig. 11(a) that, increasing immersion time increased the quantities of released metal (Mg) ions. The mass loss/gain values and Mg ion release values of the fluoride-treated specimens were lower than those of the untreated specimen. This was due to the formation of MgF2 protective layer on the surface of the specimens which acted as inhibitor to prevent from further corrosion in SBF environment.
In general, Mg is osteoconductive and osteoinductive, and promotes bone formation [30]. Porous Mg has potential to serve as a degradable scaffold for bone substitute applications. Dissolved Mg ions promote cell attachment and tissue growth [1]. Mg may improve the formation of new bones, and its alloys show improved osteoconductive bioactivity.
SEYEDRAOUFIN and MIRDAMADI [1] prepared Mg-Zn scaffolds. Porous Mg-Zn alloy could be considered as degradable scaffold materials for hard tissue regeneration. Dissolved Mg ions may promote cell attachment and tissue growth on the implants. Althoughelastic modulus decreases with increasing porosity, mechanical properties of the alloy are closer to those of bone. GUO et al [29] highlighted the potential of Mg-REE alloys for uses in bone regeneration. As Mg alloys were degraded, corrosion occurred and a rough surface formed. This rough surface helps cell attachment. MOUSAA et al [30] prepared apatite-like coatings on Mg surface. Ceramic coating supported corrosion protection and bioactivity to the Mg alloys, which could be applied as a bioactive layer for bone regeneration. JOHNSON et al [32] investigated the effect of the oxidized and polished surfaces of Mg-Y alloy on the degradation. The initial surfaces not only influenced the degradation, but also determined cell attachment, which is critical for tissue integration.
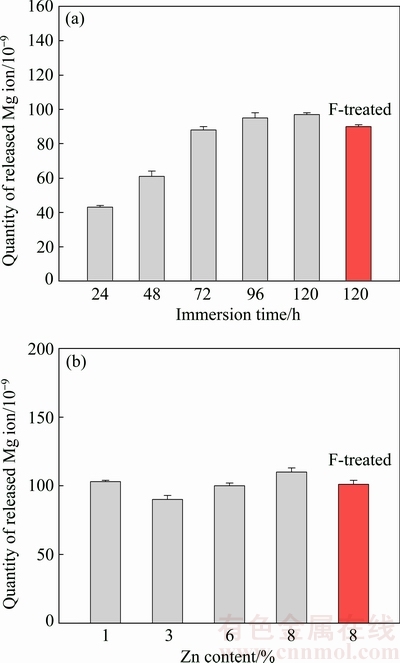
Fig. 11 Effect of immersion time (a) and Zn content (b) of alloy on Mg ion release in SBF
4 Conclusions
Mg-Ca-Zn-Co alloy scaffolds were produced by powder metallurgy based space holder method. Highly porous Mg-Ca-Zn-Co alloy could be a scaffold material in tissue engineering. As Mg is highly active metal, Ca addition to the Mg alloy prevented the oxidation of the specimens during sintering. Zn addition to the alloy increased the elastic modulus. Electrochemical corrosion behaviour of the specimens was examined in the simulated body fluid. Polarization resistance of the specimen initially increased with Zn addition up to 3% and then decreased. Corrosion rate decreased with Zn addition up to 3% and then increased. In addition, increasing Co content increased the corrosion rate and decreased the polarization resistance. Mass loss of the specimens increased with increasing immersion time. Increasing immersion time also increased the quantities of released Mg ions. Mass loss decreased with Zn addition and then increased. So, mass loss of the Mg alloy can be adjusted by Zn addition. Corrosion resistance of the fluoride-treated specimens is higher than that of the untreated specimens. Although corrosion behaviour of the Mg alloy slightly decreased with alloying, mechanical properties of the alloys can be improved to the desired levels for biomedical applications. As a result, Mg-Ca-Zn-Co alloy can be used as a scaffold material.
References
[1] SEYEDRAOUFIN Z S, MIRDAMADI S. Synthesis, microstructure and mechanical properties of porous Mg-Zn scaffolds [J]. Journal of the Mechanical Behaviour of Biomedical Materials, 2013, 21: 1-8.
[2] GU X N, ZHENG Y F. A review on magnesium alloys as biodegradable materials [J]. Front Mater Sci China, 2010, 4(2): 111-115.
[3] ZANDER D, ZUMDICK N A. Influence of Ca and Zn on the microstructure and corrosion of biodegradable Mg-Ca-Zn alloys [J]. Corrosion Science, 2015, 93: 222-233.
[4] PARK W W, YOU B S, LEE H R. Precipitation hardening and microstructures of rapidly solidified Mg-Zn-Ca-X alloys [J]. Metals and Materials International, 2002, 8(2): 135-138.
[5] OSORIO-HERNANDEZ J O, SUAREZ M A, GOODALL R, LARA-RODRIGUEZ G A, ALFONSO I, FIGUEROA I A. Manufacturing of open-cell Mg foams by replication process and mechanical properties [J]. Materials and Design, 2014, 64: 136-141.
[6] LI H, PENG Q, LI X, LI K, HAN Z, FANG D. Microstructures, mechanical and cytocompatibility of degradable Mg-Zn based orthopedic biomaterials [J]. Materials and Design, 2014, 58: 43-51.
[7] HAO G L, HAN F S, LI W D. Processing and mechanical properties of magnesium foams [J]. Porous Mater, 2009, 16: 251-256.
[8] GIBSON L J, ASHBY M F. Cellular solids-structures and properties [M]. 2nd ed. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 1997.
[9] GENG J, GAO X, FANG X Y, NIE J F. Enhanced age-hardening response of Mg–Zn alloys via Co additions [J]. Scripta Materialia, 2011, 64: 506-509.
[10] JAYARAJ J, MENDIS C L, OHKUBO T, OH-ISHI K, HONO K. Enhanced precipitation hardening of Mg-Ca alloy by Al addition [J]. Scripta Materialia, 2010, 63: 831-834.
[11] HONO K, MENDIS C L, SASAKI T T, OH-ISHI K. Towards the development of heat-treatable high-strength wrought Mg alloys [J]. Scripta Materialia, 2010, 63: 710-715.
[12] PEREDA M D, ALONSO C, BURGOS-ASPERILLA L, del VALLE J A, RUANO O A, PEREZ P, MELE M F L. Corrosion inhibition of powder metallurgy Mg by fluoride treatments [J]. Acta Biomaterialia, 2010, 6: 1772-1782.
[13] PEREDA M D, ALONSO C, GAMERO M, VALLE J A, MELE M F L. Comparative study of fluoride conversion coatings formed on biodegradable powder metallurgy Mg: The effect of chlorides at physiological level [J]. Materials Science and Engineering C, 2011, 31: 858-865.
[14] BAKHSHESHI-RAD H R, IDRIS M H, KADIR M R A, DAROONPARVAR M. Effect of fluoride treatment on corrosion behaviour of Mg-Ca binary alloy for implant application [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2013, 23: 699-710.
[15] CHIU K Y, WONG M H, CHENG F T, MAN H C. Characterization and corrosion studies of fluoride conversion coating on degradable Mg implants [J]. Surface & Coatings Technology, 2007, 202: 590-598.
[16] MAO L, YUAN G, NIU J, ZONG Y A, DING W. In vitro degradation behaviour and biocompatibility of Mg-Nd-Zn-Zr alloy by hydrofluoric acid treatment [J]. Materials Science and Engineering C, 2013, 33: 242-250.
[17] ZHANG J, KONG N, NIU J, SHI Y, LI H, ZHOU Y, YUAN G. Influence of fluoride treatment on surface properties, biodegradation and cytocompatibility of Mg-Nd-Zn-Zr alloy [J]. J Mater Sci: Mater Med, 2014, 25: 791-799.
[18] YAN T, TAN L, XIONG D, LIU X, ZHANG B, YANG K. Fluoride treatment and in vitro corrosion behaviour of an AZ31B magnesium alloy [J]. Materials Science and Engineering C, 2010, 30: 740-748.
[19] BOBE K, WILLBOLD E, MORGENTHAL I, ANDERSEN O, STUDNITZKY T, NELLESEN J, TILLMANN W, VOGT C, VANO K, WITTE F. In vitro and in vivo evaluation of biodegradable, open-porous scaffolds made of sintered magnesium W4 short fibres [J]. Acta Biomaterialia, 2013, 9: 8611-8623.
[20] AGHION E, YERED T, PEREZ Y, GUETA Y. The prospects of carrying and releasing drugs via biodegradable magnesium foam [J]. Adv Bio Mater, 2012, 12(8): 374-379.
[21] WEN C E, YAMADA Y,  Y, HOSOKAWA Y H, MABUCHI M. Compressibility of porous magnesium foam: Dependency on porosity and pore size [J]. Mater Lett, 2004, 58: 357-360.
Y, HOSOKAWA Y H, MABUCHI M. Compressibility of porous magnesium foam: Dependency on porosity and pore size [J]. Mater Lett, 2004, 58: 357-360.
[22] MUTLU I. Electrochemical corrosion behavior of TiN-coated biomedical Ti-Cu alloy foam in fluoride containing artificial saliva [J]. Metallurgical and Materials Transactions A, 2014, 45: 3640-3649.
[23] KOKUBO T, TAKADAMA H. How useful is SBF in predicting in vivo bone bioactivity? [J]. Biomaterials, 2007, 27: 2907-2915.
[24] ZHECHEVA A, SHA W, MALINOV S, LONG A. Enhancing the microstructure and properties of titanium alloys through nitriding and other surface engineering methods [J]. Surf Coat Technol, 2005, 200: 2192-2220.
[25] GURAPPA I. Characterization of different materials for corrosion resistance under simulated body fluid conditions [J]. Mater Charact, 2002, 49: 73-79.
[26] OKAZAKI Y, GOTOH E. Comparison of metal release from various metallic biomaterials in vitro [J]. Biomaterials, 2005, 26: 11-21.
[27] LIN F H, HSU Y S, LIN S H, SUN J S. The effect of Ca/P concentration and temperature of simulated body fluid on the growth of hydroxyapatite coating on alkali-treated 316L stainless steel [J]. Biomaterials, 2002, 23: 4029-4038.
[28] MUTLU I. Sinter-coating method for the production of TiN-coated titanium foam for biomedical implant applications [J]. Surface & Coatings Technology, 2013, 232: 396-402.
[29] GUO Y, LIU W, MA S, WANG J, ZOU J, LIU Z, ZHAO J, ZHOU Y. A preliminary study for novel use of two Mg alloys (WE43 and Mg3Gd) [J]. J Mater Sci: Mater Med, 2016, 27, 82: 1-14.
[30] MOUSAA H M, LEEA D H, PARKA C H, KIMA C S. A novel simple strategy for in situ deposition of apatite layer on AZ31B magnesium alloy for bone tissue regeneration [J]. Applied Surface Science, 2015, 351: 55-65.
[31] XU L, ZHANG E, YIN D, ZENG S, YANG K. In vitro corrosion behaviour of Mg alloys in a phosphate buffered solution for bone implant applications [J]. J Mater Sci: Mater Med, 2008, 19: 1017-1025.
[32] JOHNSON I, PERCHY D, LIU H. In vitro evaluation of the surface effects on magnesium-yttrium alloy degradation and mesenchymal stem cell adhesion [J]. Journal of Biomedical Materials Research A, 2012, 100(2): 477-485.
[33] PAN H, PAN F, WANG X, PENG J, SHE J, ZHAO C, HUANG Q, SONG K, GAO Z. High conductivity and high strength Mg-Zn-Cu alloy [J]. Materials Science and Technology, 2014, 30(7): 759-764.
[34] LI Z, GU X, LOU S, ZHENG Y. The development of binary Mg-Ca alloys for use as biodegradable materials within bone [J]. Biomaterials, 2008, 29: 1329-1344.
[35] MUTLU I. Synthesis and characterization of Ti-Co alloy foam for biomedical applications [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2016, 26: 126-137.
Ilven MUTLU
Metallurgical and Materials Engineering Department, Istanbul University, Istanbul 34320, Turkey
摘 要:以尿素为造孔剂,利用基于粉末冶金法的“造孔剂-水浸出”法制备可用于骨组织工程的多孔 Mg-Ca-Zn-Co合金支架。并研究合金浸泡在氟化氢(HF)溶液中进行表面氟化处理对合金耐腐蚀性能的影响。结果表明,随着Zn含量的增加,合金的弹性模量提高。Ca 的添加可以阻止烧结过程中样品的氧化。合金在模拟体液中的电化学腐蚀行为的研究表明,当Zn含量从1.0%增加到 3.0%时,合金的腐蚀率和质量损失都先减小,随着Zn 含量的进一步增加,合金的腐蚀率和质量损失而后增大。氟化处理后合金表面形成了氟化物涂层,提高了合金的耐腐蚀性。
关键词:Mg-Ca-Zn-Co合金;支架;氟化处理;金属泡沫;腐蚀
(Edited by Wei-ping CHEN)
Foundation item: Project (214M438) supported by the Scientific and Technological Research Council of Turkey (TUBITAK); Projects (20795, 42796) supported partially by Scientific Research Projects Coordination Unit of Istanbul University, Turkey
Corresponding author: Ilven MUTLU; Tel: +90-5365718461; E-mail: imutlu@istanbul.edu.tr
DOI: 10.1016/S1003-6326(18)64644-8

