生物医学用泡沫Ti-Co合金的制备与表征
来源期刊:中国有色金属学报(英文版)2016年第1期
论文作者:Ilven MUTLU
文章页码:126 - 137
关键词:Ti-Co合金;金属泡沫;粉末冶金;电化学腐蚀;生物医学植入物
Key words:Ti-Co alloy; metal foam; powder metallurgy; electrochemical corrosion; biomedical implant
摘 要:采用粉末冶金技术添加造孔剂制备生物医学用高孔隙度Ti-Co合金。Ti合金因具有高的熔点和氧亲和力。而难以进行直接加工。添加Co能降低其熔点,因而Ti-Co合金能在更低的温度进行烧结。在人工唾液中考察制备的Ti-Co合金样品的电化学腐蚀行为。研究合金的Co含量、人工唾液的pH值和氟离子浓度升高对样品的电化学腐蚀性能的影响对样品的显微组织和力学性能进行测试。电化学阻抗谱分析结果表明,样品的耐蚀性随氟离子浓度升高和pH值降低而降低。根据Mott-Schottky分析,缺陷密度随氟离子浓度的增加和人工唾液pH值的降低而增加。
Abstract: Highly porous Ti-Co alloy specimens for biomedical applications were synthesized by powder metallurgy based space holder technique. Ti alloys have high melting temperature and affinity for oxygen, which makes Ti alloys difficult to be processed. The Co addition reduces the melting temperature and Ti-Co alloy was sintered at lower temperatures. The electrochemical corrosion behaviour of the specimens was examined in the artificial saliva solution. The effects of Co content of the alloy, the pH value and fluoride concentration of the artificial saliva solution on the electrochemical corrosion properties of the specimens were investigated. The microstructure and mechanical properties of the specimens were examined. The electrochemical impedance spectroscopy results indicate that the corrosion resistance of the specimens decreases at high fluoride concentrations and low pH value. The defect density increases with increasing the fluoride concentration and decreasing the pH value of artificial saliva according to Mott-Schottky analysis.
Ilven MUTLU
Metallurgical and Materials Engineering Department, Istanbul University, Istanbul, Turkey
Received 23 December 2014; accepted 29 May 2015
Abstract: Highly porous Ti-Co alloy specimens for biomedical applications were synthesized by powder metallurgy based space holder technique. Ti alloys have high melting temperature and affinity for oxygen, which makes Ti alloys difficult to be processed. The Co addition reduces the melting temperature and Ti-Co alloy was sintered at lower temperatures. The electrochemical corrosion behaviour of the specimens was examined in the artificial saliva solution. The effects of Co content of the alloy, the pH value and fluoride concentration of the artificial saliva solution on the electrochemical corrosion properties of the specimens were investigated. The microstructure and mechanical properties of the specimens were examined. The electrochemical impedance spectroscopy results indicate that the corrosion resistance of the specimens decreases at high fluoride concentrations and low pH value. The defect density increases with increasing the fluoride concentration and decreasing the pH value of artificial saliva according to Mott-Schottky analysis.
Key words: Ti-Co alloy; metal foam; powder metallurgy; electrochemical corrosion; biomedical implant
1 Introduction
Metal foams are used as energy absorbers, heat exchangers, filters and biomedical implants. Highly porous metal foams exhibit a structure similar to cancellous bone. The advantage of metal foams for implant applications is their ability to provide anchorage for the surrounding bone tissue via the ingrowth of tissue into the pores [1-5]. Biomedical implants suffer from mismatch of elastic modulus with surrounding bone. By adjusting the porosity content, the stiffness of implant can be controlled in order to reduce the stress-shielding effect between the implant and surrounding bony tissue due to the mismatch of the elastic modulus [1-5].
Ti alloys are used as biomedical implant because of their high specific strength, high biocompatibility and electrochemical corrosion resistance. However, there are disadvantages such as high elastic modulus, low wear resistance, high melting temperature and high affinity for oxygen [3-7]. High melting ranges and affinity for oxygen make the Ti alloys difficult to be processed. Ti alloy with Co addition has lower melting temperature, especially at eutectic composition. Co addition enhances the sinterability of Ti particles, and the compacts were sintered at lower temperatures than the traditional Ti alloys [7].
The applications of Co include wear, corrosion, and heat resistant Co-based alloys, Ni-based superalloys, Fe-based superalloys, cemented carbides and magnetic materials. Some Co alloys are biocompatible, which are used as biomedical implant. CoCrMo alloy is widely used in total hip and knee replacements and dental devices. They are preferred for particular applications with metal-on-metal contact for tribological properties [8-10]. The biocompatibility of Co alloys is based on the formation of a passive oxide film. Co is protected from the oxidation by this passive film [10]. The heating of Co in the oxygen produces Co3O4 which transforms to CoO at 900 °C. CoO is oxidized with water and oxygen to Co(OH)3. The corrosion behaviour of Co in aqueous solutions depends on the composition and pH value. In neutral and alkaline solutions, the surface oxide film is stable. In the presence of chloride in the solution, pitting corrosion takes place [9].
In this study, highly porous Ti-Co alloy foams were produced for biomedical implant (hard tissue) applications. The Co addition reduced the sintering temperature of the Ti alloy. Ti-Co alloys were prepared with different Co contents in order to determine the optimum Co addition. Although there are some studies on the Ti-Co alloys, there is no study on the electrochemical corrosion properties of Ti-Co alloy and no study on highly porous Ti-Co alloy foams. The electrochemical corrosion studies on the metal foams are also scarce. The electrochemical corrosion behaviour of the specimens was examined by DC corrosion tests, electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS) tests and Mott-Schottky analysis in the artificial saliva environment. The effects of Co content of alloy, pH value and fluoride concentration of the artificial saliva solution on the electrochemical corrosion behaviour of the specimens were evaluated. The microstructure and mechanical properties of the specimens were also examined.
2 Experimental
2.1 Foam production
Foams were produced by powder metallurgy based space holder-water leaching method using Ti and Co powders (Alfa Aesar, USA). The chemical composition of Ti powder was 99.61% Ti, 0.23% O, 0.018% N, 0.03% Fe, 0.01% Mn, 0.01% Mg, 0.009% C, <0.01% Al, 0.01% Cl, <0.01% Na and 237×10-6 H (mass fraction). The chemical composition of Co powder was 99.7% Co and 0.15% O (mass fraction). The mean particle size of the irregular shaped Ti and Co powders were 44 and 34 μm, respectively. In the alloy preparation stage, 3%, 5%, 7% and 10% Co (mass fraction) powder were added to the Ti powder. As a space holder, carbamide (Merck, Germany) in the fraction of 710-1000 μm was used. The binder for green strength was polyvinylalcohol (PVA). The metal powders were mixed with 1.5% PVA (mass fraction). The mixtures were compacted at 200 MPa into cylindrical specimens with diameter of 12 mm. The specimens were immersed in water and then carbamide was leached out. The sintering cycle consisted of heating at a rate of 5 °C/min to 400 °C (debinding) with dwell time of 40 min, followed by heating at a rate of 11 °C/min to the sintering temperatures. The specimens were sintered at temperatures between 1000 and 1100 °C for 45 min. The sintering was performed in high purity argon gas atmosphere in a horizontal tube furnace (Lenton, UK). The dimensions of the cylindrical sintered specimens were about 11.9 mm in diameter and 16-18 mm in height.
2.2 Characterization of microstructure and mechanical properties
The microstructure of specimens was examined by a field emission gun-scanning electron microscope (FEG-SEM, FEI Quanta FEG 450). Energy dispersive spectroscopy (EDS) analysis was carried out to study the chemical composition of the surface. In the metallographic examinations, the sintered specimens were ground, polished and etched. The etchant was Kroll’s reagent, which was composed of 3 mL HF, 6 mL HNO3 and 91 mL H2O. The SEM images of the sintered specimens were used to determine the mean pore size, pore size distribution and pore shape of the foams using image analyzer software (Clemex Vision, PE). The density and total porosity content were determined from the measurements of mass and dimensions of the cylindrical specimens. The mechanical properties of the sintered specimens were studied by compression tests performed on a Schimadzu AG-X materials testing machine.
2.3 Artificial saliva preparation
Artificial saliva solution was prepared from chemicals supplied by Merck, Germany [4,11-14]. The compositions of reagents are 0.40 g/L NaCl, 0.79 g/L CaCl2·H2O, 0.40 g/L KCl, 0.005 g/L Na2S·9H2O, 0.78 g/L NaH2PO4·H2O, 0.35 g/L carbamide. In oral environment, in which the pH value ranges from 2 to 11, the fluoride concentration has effect on the implants. There is increased use of gels containing fluoride to prevent plaque and caries [25-31]. In order to determine the effect of fluoride on the implant, artificial saliva solutions with 0.25%, 0.50%, 0.75% and 1.00% F- were prepared using NaF addition. The pH value was adjusted to 2.50, 5.00 and 7.40 by adding lactic acid. The pH value of the artificial saliva solution was measured and monitored using a pH meter (WTW, inoLab 720, Germany). The metal ion release was investigated by static immersion tests. Inductively coupled plasma-mass spectrometer (ICP-MS) (Thermo Scientific Elemental X Series 2) was used to determine the metal (Ti and Co) ion release. 70% porous specimens were cut along longer axes and semi-cylindrical specimens were obtained. Then, the specimens were polished and washed. The porosity and surface area values of each specimen were equal in the immersion tests. The specimens were then exposed to artificial saliva solution (50 mL) in closed polyethylene bottles. The foams with equal porosity (70%) were immersed in the artificial saliva solution. The ratio of solution volume to specimen surface area was constant in all immersion tests. An artificial saliva solution without a specimen was used for blank test in ICP measurements. The area of the pores was subtracted from total surface area of the foams to find actual solid surface area.
2.4 Electrochemical corrosion study
Electrochemical corrosion studies were carried out in the artificial saliva solution using a potentiostat (Interface 1000 Potentiostat/Galvanostat/ZRA, Gamry Instruments Inc., USA) controlled by a personal computer. The volume of glass corrosion test cell was 1000 mL. A conventional three-electrode system with high-density graphite rod as a counter electrode, saturated calomel electrode (SCE) as a reference electrode, and the specimen as a working electrode was used. Data acquisition was carried out through a computer software (Framework, Version 6.04, Gamry Instruments, USA), while data analysis was carried out by Echem Analyst Software, Version 6.04, Gamry Instruments, USA. The specimens were cut from the sintered foam and then mounted into epoxy resin. So, only circular cross section with diameter of about 11.91 mm of the specimens was exposed to the artificial saliva solution. The specimens were connected to a copper wire. All experiments were carried out at room temperature. The open circuit potential (OCP) of specimens was measured before carrying out the electrochemical corrosion experiments. The OCP level was measured for durations of 2 to 3 h, until the OCP was stabilized. Tafel curves were obtained by polarizing the specimens from -250 to 250 mV (vs SCE), with respect to the OCP, at a scan rate of 1.0 mV/s. Current density, Tafel slopes, corrosion rate and corrosion potentials were obtained from Tafel extrapolation analyses. In linear polarization resistance (LPR) test, the specimens were polarized from -20 to 20 mV (vs SCE) at a scan rate of 0.125 mV/s in order to measure the polarization resistance and corrosion rate of specimens. Cyclic polarization tests were carried out from -500 mV (vs SCE) to the apex potential and then to the final potential which was 0 mV (vs SCE). The forward and reverse polarization scan rates were 5 and 2.5 mV/s, respectively. Cyclic (forward and reverse) polarization technique was used to evaluate tendency to localized corrosion (pitting) in corrosive environment. Considerable hysteresis between the forward and reverse polarization sweeps is an indication of the formation of pit. Cyclic polarization curves were analyzed in terms of breakdown potential (φbd) and repassivation potential (φrp) values.
Electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS) measurements were started after each specimen reaching a steady-state condition. Electrochemical impedance spectroscopy measurements were carried out in potentiostatic mode, at OCP with a constant potential perturbation AC sine wave. The potential amplitude of signal was 5 mV. EIS studies were conducted at a frequency range of 100 kHz to 1 mHz, with 5 points per frequency decade. The impedance spectra were fitted by an electrical equivalent circuit model using Gamry, EIS100 software, by a complex non-linear-least-square method. The quality of fit was described by the average error of regression. Nyquist and Bode spectra were recorded.
Mott-Schottky plots were used for electrochemistry studies on semiconductor electrodes. A fixed frequency, small signal AC potential excitation was applied to the electrochemical cell. The impedance of working electrode interface was measured as a function of DC voltage. Mott-Schottky plot is a graph of capacitive and resistive components of impedance versus voltage. The resistance and capacitance were calculated assuming a parallel resistor-capacitor (RC) circuit. Mott-Schottky tests were performed at 100 Hz. The specimens were polarized in voltage steps of 100 mV (vs SCE) at the potential range of -1.50 to 1.00 V (vs SCE). AC voltage was 10 mV (root-mean-square). The defect densities were determined from the slopes of straight lines in the plots.
3 Results and discussion
3.1 Microstructure and mechanical properties
The Ti-Co alloy foams with 70% porosity were produced by powder metallurgy based space holder- sintering method. The mean pore size and pore shape (morphology) of the sintered foams replicated the initial size and morphology of the carbamide (space holder) particles. The mean pore sizes of the foams were 400-550 μm, which is a suitable range for biomedical implant (hard tissue) applications [3-5]. The pore shape (morphology) of the foams was irregular.
Figure 1(a) shows the photograph of the sintered foam. Figure 1(b) shows the SEM image of the cracked surface of the sintered Ti-Co alloy with 70% porosity content. Figure 1(c) shows the microstructure from the cell wall of the sintered Ti-10%Co specimen. As shown in Fig. 1(c), the microstructure of the Ti-Co alloy specimens consists of the solid solution Ti-Co matrix phase (region A) and some Ti2Co intermetallic compound at the grain boundaries (region B). Some pure alpha-Ti phase is also observed (region C). The chemical composition of the sintered specimens consists of mainly Ti, Co and some O according to the EDS spot analysis. According to the EDS results, the surface chemical composition of sintered Ti-10% Co specimens consists of 89%-92% Ti and 8%-10% Co. According to the EDS analysis of the specimens in Fig. 1(c), the composition of region A (Ti-Co matrix) consists of about 9.6% Co and 90.1% Ti, while the chemical composition of region B (Ti2Co intermetallic compound) consists of 40%-45% Co and 60%-65% Ti. The composition of region C (alpha-Ti phase) in Fig. 1(c) consists of pure Ti.
Liquid phase formation occurred during sintering at higher sintering temperatures (over 1100 °C). The Co addition to the Ti alloy enhanced the sinterability and the compacts were sintered at lower temperatures than traditional Ti alloys. Excessive liquid phase formation was observed when sintering above 1100 °C. The optimum sintering temperature, for 10% Co addition, was determined as 1000 °C for 45 min. The Co addition increases the compressive yield strength and elastic modulus of the specimens. Increasing the Co content from 3% to 10% in the alloys increases the compressive yield strength from 67 to about 92 MPa, while increasing the Co content from 3% to 10% increases the elastic modulus of the specimens from 1.49 to 2.09 GPa, which are suitable (close to cancellous bone) values for the biomedical hard tissue implant applications [3-5].

Fig. 1 Photograph of sintered foam (a), SEM image from crack surface of sintered foam (b), and microstructure from cell wall of specimen (c)
3.2 DC corrosion tests
3.2.1 Open circuit potential
Open circuit potential (OCP) is the potential at which an alloy is in equilibrium with environment. High OCP value (φOCP) means that the material is stable in a certain corrosive environment. Figure 2 shows the variation of OCP with the Co content of the alloy (at pH value of 2.50 and 0.5% fluoride concentration), and the pH value and F- concentration of the artificial saliva solution (10% Co). As shown in Fig. 2(a), increasing the Co content of alloy decreases the OCP. Increasing the F- concentration and decreasing the pH value of the artificial saliva solution decrease the OCP (Fig. 2(b)).
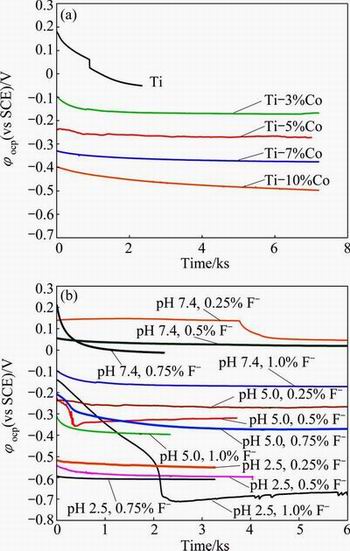
Fig. 2 Variation of OCP with Co content of alloy (at pH value of 2.50 and 0.5% fluoride) (a) and pH value and F- concentration of artificial soaliva solution (10% Co) (b)
3.2.2 Tafel tests
Tafel curves were used to examine the electrochemical corrosion behaviour of the specimens. Figures 3(a) and (b) show the effect of Co content of the alloy, and F- concentration and pH value of artificial saliva solution on the Tafel curves of the specimens, respectively. Increasing the Co content of the alloy decreases the corrosion potential and increases the corrosion current density of the specimens. Decreasing the pH value and increasing the fluoride concentration decrease the corrosion potential and increase the current density. For a certain pH value, the current density increases and the corrosion potential decreases with increasing the fluoride concentration. Low pH value also leads to the increase of current density and the decrease of corrosion potential.
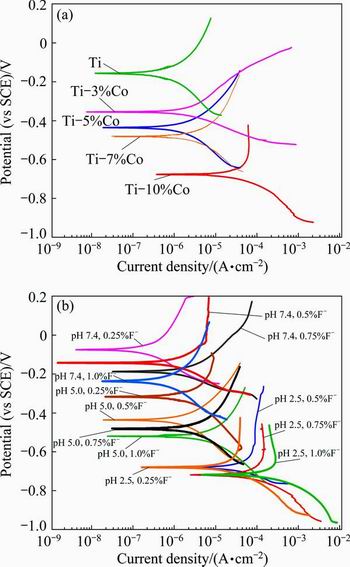
Fig. 3 Effect of Co content of alloy (at pH value of 2.50) (a), and F- concentration and pH value of artificial saliva solution (10% Co) (b) on Tafel curves of specimens
Figure 4 shows the effect of Co addition on the polarisation resistance and corrosion rate. Figure 5 shows the effect of pH value and fluoride concentration of the artificial saliva solution on the polarisation resistance and corrosion rate. The polarization resistance is connected with the kinetic phenomena at the metal-solution interface. Polarization resistance characterizes the protection degree of the oxide layer. As seen from Fig. 4, the polarization resistance decreases with increasing the Co content, while the corrosion rate increases with increasing the Co content of the alloy. As seen from Fig. 5, the polarization resistance decreases with increasing the fluoride concentration and decreasing the pH value, while the corrosion rate increases with increasing the fluoride concentration and decreasing the pH value of the artificial saliva solution.
Corrosion resistance (low metal ion release) is a requirement for biomedical implants. Metal ions from implants are released by various mechanisms, including corrosion, wear and electrochemical processes. In general, two features determine the corrosion behaviour of metals. One is the thermodynamic driving force and the other is the kinetic barrier. Thermodynamic driving forces correspond to energy required during a chemical reaction. Kinetic barriers prevent corrosion by physical limitation of reaction rate. The films on the metal surfaces are the forms of kinetic barriers.
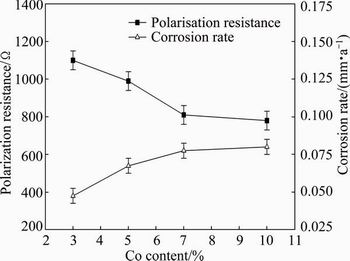
Fig. 4 Effect of Co content on polarisation resistance and corrosion rate at pH value of 2.50 and with 0.5% fluoride
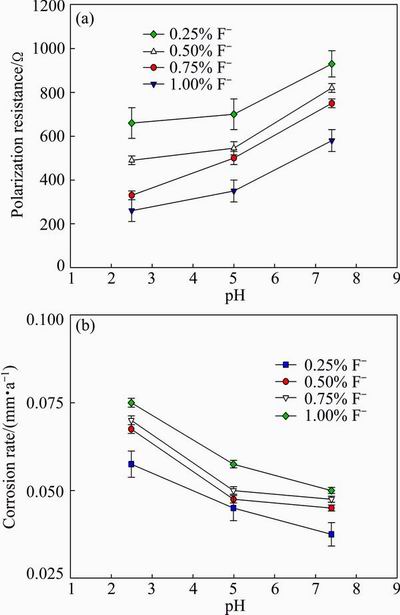
Fig. 5 Effect of pH value and fluoride concentration of artificial saliva solution on polarisation resistance (a) and corrosion rate (b) with 10% Co
3.2.3 Cyclic polarization test
Figures 6(a)-(c) show the effects of Co content of the alloy (pH 2.5, 1.0% F-), pH value (10% Co, 1.0% F-) and F- concentration of artificial saliva solution (pH 2.5, 10%Co) on the cyclic polarization curves of the specimens, respectively. Increasing the Co content of the alloy decreases the corrosion potential and increases the current density. Increasing the F- concentration and decreasing the pH value of the artificial saliva decreases the corrosion properties of the specimens. Cyclic polarization is used to qualitatively evaluate tendency to pitting in a corrosive environment. Hysteresis between forward and reverse sweeps during cyclic polarization is an indication of pit formation. As shown in Fig. 6, hysteresis (loop), which is an indication of pitting, is enlarged with increasing the Co content of the alloy, increasing the F- concentration and decreasing the pH value of the artificial saliva solution.
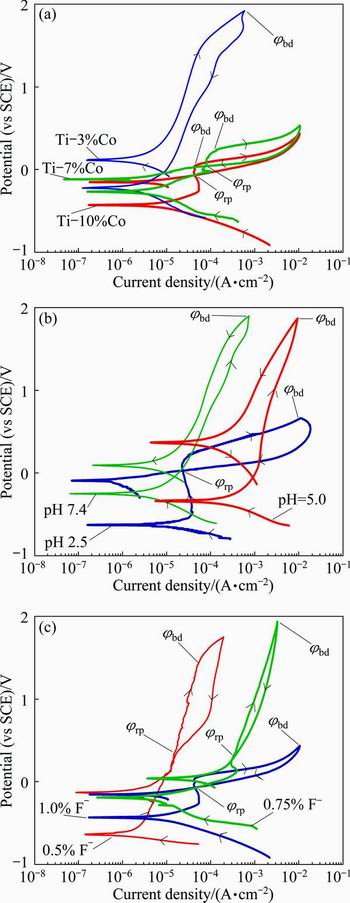
Fig. 6 Effects of Co content of alloy (pH 2.5, 1.0% F-) (a), pH value of artificial saliva (10% Co, 1.0% F-) (b) and F- concentration of artificial saliva (pH 2.5, 10% Co) (c) on cyclic polarization curves of specimens
The cyclic polarization curves were also analysed in terms of breakdown potential (φbd) and repassivation potential (φrp). Breakdown potential (critical pitting potential) corresponds to the potential for new pit formation and stable pit growth. In general, the increase of resistance to pitting is associated with the increase of φbd. Pits are initiated above φbd, but if pits are initiated, they propagate at all potentials above φrp. Thus, φrp is used as the protection potential. The metal will resist to pitting if its potential keeps below φrp. Below φrp, all pits are repassivated. In general, the difference between these potentials (φbd-φrp) can be used instead of the values themselves.
As shown in Fig. 6(a), the φbd value decreases from 1.90 to 0.40 V (vs SCE), while the φrp value decreases from 1.50 to 0.05 V (vs SCE) with increasing the Co content from 3% to 10%. In the alloy with 10% Co content, a hysteresis is observed, while in the alloy with 3% Co content, a hysteresis is not observed. As shown in Fig. 6(b), the φbd value decreases from 1.80 to 0.70 V (vs SCE), while the φrp value decreases -0.1 V (vs SCE) with decreasing the pH value of the artificial saliva solution from 7.4 to 2.5. As shown in Fig. 6(c), the φbd value decreases from 1.80 to 0.40 V (vs SCE), while the φrp value decreases from 0.30 to -0.1 V (vs SCE) with increasing the fluoride concentration of the artificial saliva solution from 0.5% to 1.0%. Based on the φrp and φbd values, the tendency of the localised corrosion slightly increases with increasing the Co content of the alloy, decreasing the pH value and increasing the fluoride concentration of the artificial saliva.
3.3 Electrochemical impedance spectroscopy
Equivalent electric circuit with two time constants is used to analyze the electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS) data and to interpret the behaviour of alloy. Figure 7 shows the equivalent electric circuit, Rsol(Cpore(Rpore(CbarrRbarr))), to fit the EIS data. The model assumes that the passive oxide layer consists of a barrier-like inner layer and a porous outer layer. Rsol represents the electrolyte resistance, and the constant phase element (C) representing shift from ideal capacitor is used instead of capacitance. Rpore and Rbarr are the resistances of the porous and barrier layers, respectively, which are associated with the charge transfer resistance through porous layer and participation of adsorbed intermediates. Cpore and Cbarr correspond to the capacitances of porous and barrier layers, respectively, which are related to the formation of double layer. The fitting quality of EIS data is judged by chi-squared (χ2) values of about 10-6, indicating good fitting to the electric circuit. The n value close to one indicates near capacitive behaviour of the oxide film. The n and m values are associated with non-uniform distribution of current as a result of surface roughness and surface defects.
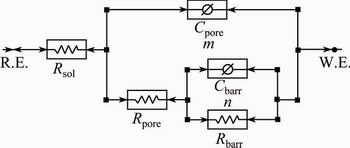
Fig. 7 Equivalent electric circuit to fit EIS data
3.3.1 Effect of fluoride concentration and pH value of artificial saliva solution
The experimental and simulated impedance spectra of the specimens are presented as Nyquist and Bode plots. Figures 8(a) and (b) show the effect of pH value of the artificial saliva solution on the Nyquist plots, and the Bode magnitude and Bode phase angle plots of specimens, respectively. As shown in Fig. 8(a), the capacitive semicircles are observed in the Nyquist plots. The size of the semicircles decreases as the pH value of the artificial saliva solution decreases. The Nyquist plot is composed of two semicircles. The Bode magnitude plots are characterized by two regions. As shown in Fig. 8(b), in high frequency, the Bode magnitude plots exhibit constant Zmod, associated with phase angle near zero degree, indicating that the impedance is dominated by electrolyte resistance. In low frequency, the Bode magnitude plots display linear slope, due to capacitive behaviour [15,16]. The Bode phase plots show different behaviours. There are three regions in the Bode phase plots. In high frequency, the phase angle drops due to electrolyte resistance. In middle frequency, the phase angle remains about -50° indicating capacitive response. The phase angle approaching -90° indicates passive film and capacitive response. In low frequency, the phase angle decreases because of film resistance. The magnitudes and phase angles decrease with decreasing the pH value. The constant phase angle maximum over a wide frequency range suggests the formation of stable passive film and difficulty in the charge transfer. Two phase angel peaks are indicative of two relaxation time constants and the formation of a two-layer oxide.
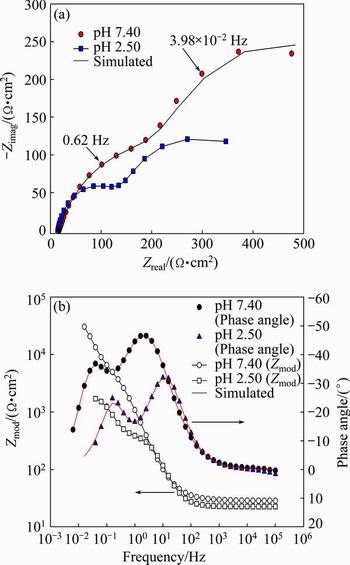
Fig. 8 Effect of pH value of artificial saliva solution on Nyquist plots (a), and Bode magnitude and Bode phase angle plots (b) of specimens with 10% Co
Table 1 shows the effect of pH value of artificial saliva on the electrochemical impedance spectroscopy parameters of the alloy obtained by fitting with the equivalent electrical circuit model (10% Co, 1.0% F-). As shown in Table 1, at lower pH value levels of the artificial saliva solution, the specimens show lower R values, which can be confirmed by smaller and deformed semicircles. The resistances of inner barrier layer (Rbarr) are higher than those of outer porous layer (Rpore), demonstrating that the inner layer dominates the corrosion protection. The capacitances decrease and the resistances increase with increasing the pH value of the artificial saliva. The passive oxide film becomes more resistive with increasing the pH value.
Figures 9(a) and (b) show the effect of fluoride concentration of artificial saliva solution on the Nyquist plots, and the Bode magnitude and Bode phase angle plots of the specimens, respectively. As shown in Fig. 9(a), the capacitive semicircles are observed in the Nyquist plots. The size of the semicircles decreases as the fluoride concentration of the artificial saliva increases. As seen from Fig. 9(b), the Bode magnitude values decrease with increasing the F- concentration of the artificial saliva solution. The phase angle values decrease with increasing the F- concentration of the artificial saliva. The dissolution of Ti is due to the formation of Ti-F complex. The incorporation of F- in surface oxide results in the formation of a porous layer. Depending on the concentration of F- and pH value, titanium fluoride, titanium oxyfluoride and sodium titanium fluoride may form. HF is responsible for destroying the oxide. Once the oxide film is destroyed, the regeneration of passive layer is a function of dissolved oxygen. The electrochemical behaviour of titanium in fluoride added acidic solutions is determined by the presence of HF. Under low pH value conditions, HF leads to the destruction of the oxide. There are two kinds of fluoride in solutions, HF and fluoride, both can affect the corrosion resistance of the Ti. The porosity of the film is increased by F- and low pH value [15-19].
Table 1 Effect of pH value of artificial saliva solution on electrochemical impedance spectroscopy parameters of alloy obtained by fitting with equivalent electrical circuit model (10% Co, 1.0% F-)
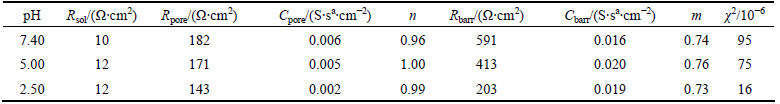
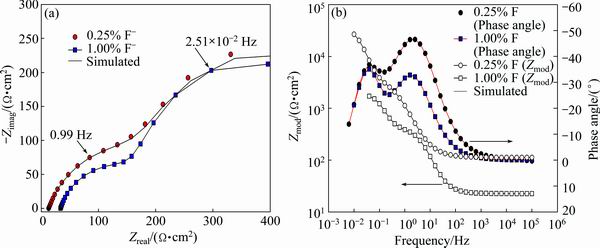
Fig. 9 Effect of F- concentration of artificial saliva solution on Nyquist plots (a) and Bode magnitude and Bode phase angle plots (b) of specimens with 10% Co
Table 2 shows the effect of F- concentration of artificial saliva solution on the electrochemical impedance spectroscopy parameters of the alloy (pH 2.50, 10% Co). As shown in Table 2, at higher F- concentrations of artificial saliva solution, the specimens show lower R values. The Rbarr values are higher than Rpore values, demonstrating that the inner layer dominates the corrosion protection. The capacitances decrease and the resistances increase with decreasing the F- concentration of artificial saliva solution. The passive oxide film becomes more resistive with decreasing the F- concentration of the solution.
3.3.2 Effect of Co content of alloy
Figures 10(a) and (b) illustrate the effect of Co content of the alloy on the Nyquist plots, and the Bode magnitude and Bode phase angle plots of the specimens, respectively. The Nyquist plot is characterized by a semicircle, indicating the capacitive response of the passive oxide film. The semicircle diameter decreases with increasing the Co content of the alloy. The electrochemical corrosion resistance of the alloys decreases with increasing the Co content. Higher Co contents lead to the formation of Ti2Co. The increase of Co content of the alloy induces higher corrosion rate. As seen from Fig. 10(b), the magnitude values decrease with increasing the Co content of the alloy. In addition, the phase angle values decrease with increasing the Co content of the alloy.
The specimens show lower R values in low pH values and high fluoride contentrations, which can be confirmed by smaller semicircles. The resistances of the inner barrier layer (Rbarr) are higher than those of the outer porous layer (Rpore), demonstrating that the inner layer dominates the corrosion protection. The capacitances decrease and the resistances increase with increasing the pH value and decreasing the F- concentration of the artificial saliva. Higher impedance, lower capacitances and larger phase angle are attributed to nobler corrosion behaviour. The specimen with high Co content shows lower R value (smaller semicircle). The capacitances decrease and the resistances increase with decreasing the Co content. The porous layer is helpful for osseointegration [4,20,21].
Table 3 illustrates the effect of Co content of the alloy on the electrochemical impedance spectroscopy parameters (pH 2.50, 1.0 % F-). As shown in Table 3, the Ti-Co alloy specimens with high Co contents show lower R values. The resistances of the barrier layer (Rbarr) are higher than those of the outer porous layer (Rpore). The capacitances decrease and the resistances increase with decreasing the Co content of the alloy. The passive oxide film becomes more resistive with decreasing the Co content of the alloy.
3.4 Mott-Schottky analysis
3.4.1 Effect of pH value and fluoride concentration of artificial saliva
The semiconducting properties of the passive oxide film on the specimens was investigated by Mott- Schottky analysis. Figure 11 shows the effect of F- concentration and pH value of artificial saliva solution on the Mott-Schottky plots. Decreasing the pH value of artificial saliva increases the acceptor concentration (inverse slope of the curves), which indicates disordered nature and low electrochemical corrosion behaviour of the oxide film. Increasing the F- concentration of artificial saliva solution also increases the acceptor concentration. The slopes of linear regions of the Mott-Schottky plots are inversely proportional to the defect density in the oxide. The specimens show negative slopes which represents the p-type semiconductor behaviour of the oxide. If the slope decreases, the defect density increases, and the oxide becomes more defective. Figure 12 shows the effect of pH value and fluoride concentration of the artificial saliva solution on the defect (donor/acceptor) density. As seen from Fig. 12, the defect density increases with decreasing the pH value and increasing the fluoride concentration of artificial saliva solution. In general, the corrosion behaviour of the oxide is related to the transport of matter and charge through the films. The positive slope is the n-type semiconductor behaviour associated with the outer porous layer. The negative slope below flat band potential (φfb) is p-type semiconductor behaviour that is related to the inner oxide layer. The donors in the outer layer are correlated with the oxygen vacancies while the acceptors in the inner layer are correlated with the metal vacancies.
Table 2 Effect of F- concentration of artificial saliva on electrochemical impedance spectroscopy parameters of alloy obtained by fitting with equivalent electrical circuit model (pH 2.50, 10 %Co)
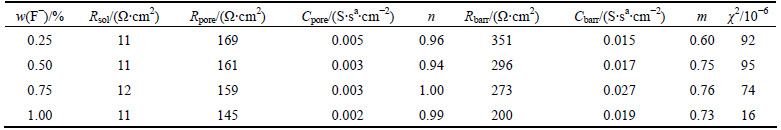
Table 3 Effect of Co content of alloy on electrochemical impedance spectroscopy parameters obtained by fitting with equivalent electrical circuit model (pH 2.50, 1.0% F-)
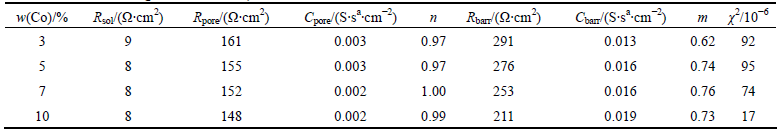
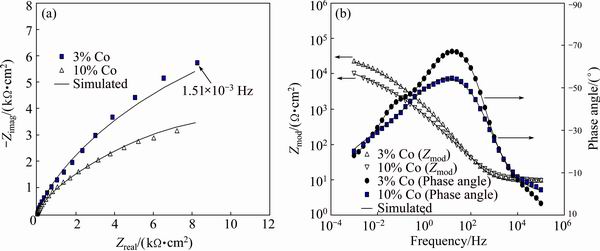
Fig. 10 Effect of Co content of alloy on Nyquist plots (a), and Bode magnitude and Bode phase angle plots (b) of specimens (pH 2.50 and 1.0% fluoride)
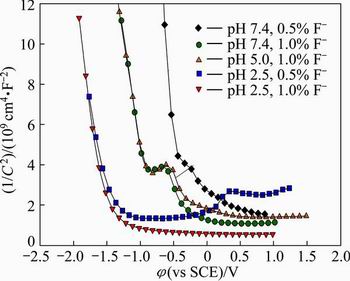
Fig. 11 Effect of F- concentration and pH value of artificial saliva solution on Mott-Schottky plots of passive oxides on specimens with 10% Co
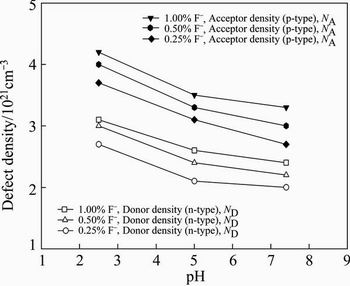
Fig. 12 Effect of pH value and fluoride concentration of artificial saliva solution on defect (donor/acceptor) density
3.4.2 Effect of Co content of alloy
Figure 13 shows the Mott-Schottky plots of the pasive oxides film (TiO2) on the alloys with different Co contents. Increasing the Co content of the alloy increases the defect (donor/acceptor) concentration in the oxide, which indicates low corrosion behaviour of the oxide film. The slopes of the linear regions of the plots are inversely proportional to the defect density in the oxide. The flat band potential and defect density are obtained from the intercepts and slopes of linear regions, using measured dielectric constants. The addition of Co to Ti modifies the structure of the oxide layer. The outer layer is thicker and its corrosion resistance is lower. The barrier properties of the oxide films are related to the inner layer. The resistance of the oxide is lower for alloy with higher Co content. Above -0.50 V (vs SCE), the slope is positive, whilst below -1.00 V (vs SCE) the slope is negative. The positive slope indicates the n-type behaviour associated with the outer porous layer, while the negative slope indicates p-type behaviour of the oxide that is related to the inner oxide layer. In general, the n-type semiconductor oxides are beneficial for blood compatibility in implants. Meanwhile, the n-type oxide films can be more susceptible to pitting due to the existence of oxygen vacancies. Figure 14 shows the effect of Co content of the alloy on the defect (donor/acceptor) density. As seen from Fig. 14, the defect density increases with increasing the Co content of the alloy. High defect density indicates disordered nature of the oxide. The donor density (ND) in the n-type semiconductor and the acceptor density (NA) in the p-type semiconductor were calculated using the dielectric constant of the TiO2 and from the slope of plot. The stability of the oxide decreases with increasing the Co content of the alloy. The decrease of stability of the oxide film is due to the Co dissolution from the film, which increases the defect density and decreases its stability.
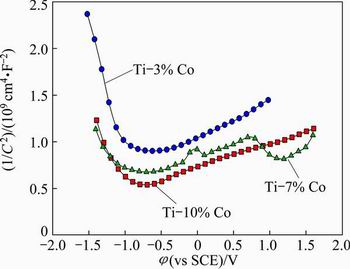
Fig. 13 Mott-Schottky plots of passive oxides on specimens with different Co contents at pH value of 7.40 and with 1.0% F- concentration of artificial saliva
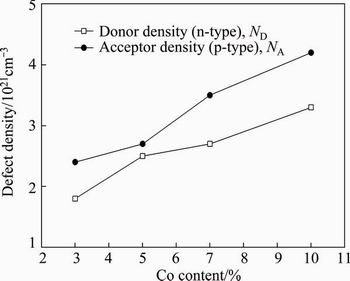
Fig. 14 Effect of Co content of alloy on defect (donor/acceptor) density
3.5 Metal ion release behaviour
Low metal ion release in the body fluids is requirement for the biomedical implant materials. According to the static immersion tests in the artificial saliva environment for 14 d, decreasing the pH value of the artificial saliva solution increases the metal (Ti and Co) ion release level, due to the increase of acidity. Decreasing the pH value of artificial saliva solution from 7.40 to 2.50 increases the Ti ion release from 54×10-9 to 103×10-9, while the Co release increases from about 35×10-9 to 62×10-9. Meanwhile, the metal (Ti and Co) ion release values of the specimens are not higher than the reference levels of both Ti and Co ions in the human body fluids [4,22-24].
4 Conclusions
1) Ti-Co alloy foams for biomedical implant applications were produced by powder metallurgy technique. The Co addition enhanced the sinterability and Co added compacts were sintered at lower temperatures compared with traditional Ti alloys. The electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS) results indicate that the passive oxide film formed on the specimens consists of an outer porous layer and an inner barrier layer.
2) Increased fluoride concentration of the artificial saliva solution reduces its corrosion protection behaviour. Fluoride ions attack the alloys, and the severity of this attack depends on its concentration and pH value of the artificial saliva. The electrochemical corrosion resistance of the specimens decreases at high fluoride concentrations and low pH levels. The electrochemical corrosion resistance of the alloys decreases with increasing the Co content.
3) The diameters of the capacitive semiarcs in Nyquist plots decrease with increasing the Co content of the alloy. Decreasing the pH value and increasing the fluoride concentration of artificial saliva solution decrease the corrosion potential and increase the current density of the specimens according to the DC corrosion tests. Increasing the Co content of the alloy slightly increases the current density and decreases the corrosion potential of the specimens.
4) The Mott-Schottky analysis confirms that the passive oxide film has duplex character. High defect density is an indication of nonstiochiometric oxide film. The defect density increases with increasing the fluoride concentration and decreasing the pH value of the artificial saliva. The defect density of the oxide also increases with increasing the Co content of the alloy. The stability of the oxide decreases with increasing the Co content of the alloy, suggesting that the oxide is less stable. The decrease of stability is due to the Co dissolution from the oxide, which increases the defect density of the film and decreases its stability.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported partially by Scientific Research Projects Coordination Unit of Istanbul University, Project numbers 42796 and 42922.
References
[1] ASHBY M F, EVANS A G, FLECK N A, GIBSON L J, HUTCHINSON J W, WADLEY H N G. Metal foams: A design guide [M]. Boston, MA: Elsevier Science, 2000.
[2] GIBSON L J, ASHBY M F. Cellular solids-structures and properties [M]. 2nd ed. US: Cambridge University Press, 1997.
[3] NIU Wen-juan, BAI Chen-guang, QIU Gui-bao, WANG Qiang. Processing and properties of porous titanium using space holder technique [J]. Mater Sci Eng A, 2009, 506(1-2): 148-151.
[4] MUTLU I, OKTAY E. Characterization of 17-4 PH stainless steel foam for biomedical applications in simulated body fluid and artificial saliva [J]. Mater Sci Eng C, 2013, 33: 1125-1131.
[5] GIBSON L J. Biomechanics of cellular solids [J]. J Biomech, 2005: 38: 377-399.
[6] LIN J G, LI Y C, WONG C S, HODGSON P D, WEN C E. Degradation of the strength of porous titanium after alkali and heat treatment [J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2009, 485: 316-319.
[7] WANG R, WELSCH G. Evaluation of an experimental Ti-Co alloy for dental restorations [J]. Journal of Biomedical Materials Research B: Applied Biomaterials, 2013, 101(8): 1419-1427.
[8] DAVIS J R. ASM specialty handbook: Nickel, cobalt, and their alloys [M]. Materials Park, OH, US: ASM International, 2000.
[9] HUKOVIC M M, BABIC R. Passivation and corrosion behaviours of cobalt and cobalt-chromium–molybdenum alloy [J]. Corrosion Science, 2007, 49: 3570-3579.
[10] RODRIGUES W C, BROILO L R, SCHAEFFER L, KNORNSCHILD G, ESPINOZA F R M. Powder metallurgical processing of Co-28%Cr-6%Mo for dental implants: Physical, mechanical and electrochemical properties [J]. Powder Technology, 2011, 206: 233-238.
[11] MARECI D, CHELARIU R, DAN I, GORDIN D M, GLORIANT T. Corrosion behaviour of Ti20Mo alloy in artificial saliva [J]. J Mater Sci Mater Med, 2010, 21: 2907-2913.
[12] SHARMA M, KUMAR A V R, SINGH N, ADYA N, SALUJA B. Electrochemical corrosion behavior of dental/implant alloys in artificial saliva [J]. J Mater Eng Perform, 2008, 17: 695-701.
[13] HO W F, WU S C, LIN C W, HSU S K H C. Electrochemical behavior of Ti-20Cr-X alloys in artificial saliva containing fluoride [J]. J Appl Electrochem, 2011, 41: 337-343.
[14] OSHIDA Y, SELLERS C B, MIRZA K, FARZIN-NIA F. Corrosion of dental materials by dental traetment agents [J]. Mater Sci Eng C, 2005, 25: 343-348.
[15] LIN F H, HSU Y S, LIN S H, SUN J S. The effect of Ca/P concentration and temperature of simulated body fluid on the growth of hydroxyapatite coating on alkali-treated 316L stainless steel [J]. Biomaterials, 2002, 23: 4029-4038.
[16] LIN F H, HSU Y S, LIN S H, CHEN T M. The growth of hydroxyapatite on alkaline treated Ti-6Al-4V soaking in higher temperature with concentrated Ca2+/HPO42- simulated body fluid [J]. Materials Chemistry and Physics, 2004, 87: 24-30.
[17] OSORIO W R, CREMASCO A, ANDRADE P N, GARCIA A, CARAM R. Electrochemical behavior of centrifuged cast and heat treated Ti-Cu alloys for medical applications [J]. Electrochimica Acta, 2010, 55: 759-770.
[18] ROBIN A, MEIRELIS J P. Influence of fluoride concentration and pH on corrosion behavior of titanium in artificial saliva [J]. J Appl Electrochem, 2007, 37: 511-517.
[19] FOJT J, JOSKA L, MALEK J. Corrosion behaviour of porous Ti-39Nb alloy for biomedical applications [J]. Corrosion Science, 2013, 71: 78-83.
[20] CARDOSO F F, CREMASCO A, CONTIERI R J, LOPES E S N, AFONSO C R M, CARAM R. Hexagonal martensite decomposition and phase precipitation in Ti-Cu alloys [J]. Materials and Design, 2011, 32: 4608-4613.
[21] KUMAR S, NARAYANAN T S N S, KUMAR S S. Influence of fluoride ion on the electrochemical behaviour of β-Ti alloy for dental implant application [J]. Corrosion Science, 2010, 52: 1721-1727.
[22]
[23] GURAPPA I. Characterisation of different materials for corrosion resistance under simulated body fluid conditions [J]. Mater Charact, 2002, 49: 73-79.
[24] OKAZAKI Y, GOTOH E. Comparison of metal release from various metallic biomaterials in vitro [J]. Biomaterials, 2005, 26: 11-21.
Ilven MUTLU
Metallurgical and Materials Engineering Department, Istanbul University, Istanbul, Turkey
摘 要:采用粉末冶金技术添加造孔剂制备生物医学用高孔隙度Ti-Co合金。Ti合金因具有高的熔点和氧亲和力。而难以进行直接加工。添加Co能降低其熔点,因而Ti-Co合金能在更低的温度进行烧结。在人工唾液中考察制备的Ti-Co合金样品的电化学腐蚀行为。研究合金的Co含量、人工唾液的pH值和氟离子浓度升高对样品的电化学腐蚀性能的影响对样品的显微组织和力学性能进行测试。电化学阻抗谱分析结果表明,样品的耐蚀性随氟离子浓度升高和pH值降低而降低。根据Mott-Schottky分析,缺陷密度随氟离子浓度的增加和人工唾液pH值的降低而增加。
关键词:Ti-Co合金;金属泡沫;粉末冶金;电化学腐蚀;生物医学植入物
(Edited by Mu-lan QIN)
Corresponding author: Ilven MUTLU; Tel: +90-5365718461; E-mail: imutlu@istanbul.edu.tr
DOI: 10.1016/S1003-6326(15)64028-6

