Hydration phase and pore structure evolution of hardened cement paste at elevated temperature
来源期刊:中南大学学报(英文版)2021年第6期
论文作者:龙广成 何富强 向宇 谢友均
文章页码:1665 - 1678
Key words:cement paste; high-temperature curing; pore structure; AC impedance; nuclear magnetic resonance
Abstract: To understand the effect of steam curing temperature on the hydrate and microstructure of hardened cement paste, several measuring methods including X-ray diffraction (XRD), atomic absorption spectroscopy (ASS), ion chromatography, conductivity meter, alternating-current impedance spectroscopy and nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) are employed to investigate the hydration characteristics, pore solution composition and conductivity, resistivity and pore structure during the steam curing process. Experimental results show that steam curing promotes the hydration process, greatly raises the resistivity, and decreases the porosity of specimen at early age. Compared with being treated at 45 °C, higher temperature leads to a fast decomposition of ettringite at initial stage of the constant temperature treatment period, which improves the relative content and ionic activity of the conductive ions in pore solution. Furthermore, the number of pores larger than 200 nm increases significantly, which reduces the resistivity of the hardened cement paste. Cement paste treated at 45 °C has a more stable and denser microstructure with less damages.
Cite this article as: XIANG Yu, XIE You-jun, LONG Guang-cheng, HE Fu-qiang. Hydration phase and pore structure evolution of hardened cement paste at elevated temperature [J]. Journal of Central South University, 2021, 28(6): 1665-1678. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11771-021-4725-7.

J. Cent. South Univ. (2021) 28: 1665-1678
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11771-021-4725-7
XIANG Yu(向宇)1, XIE You-jun(谢友均)1, LONG Guang-cheng(龙广成)1, HE Fu-qiang(何富强)2, 3
1. School of Civil Engineering, Central South University, Changsha 410075, China;
2. School of Civil Engineering and Architecture, Xiamen University of Technology, Xiamen 361024, China;
3. Key Laboratory of Green Building Materials (Xiamen University of Technology),Fujian Province University, Xiamen 361024, China
 Central South University Press and Springer-Verlag GmbH Germany, part of Springer Nature 2021
Central South University Press and Springer-Verlag GmbH Germany, part of Springer Nature 2021
Abstract: To understand the effect of steam curing temperature on the hydrate and microstructure of hardened cement paste, several measuring methods including X-ray diffraction (XRD), atomic absorption spectroscopy (ASS), ion chromatography, conductivity meter, alternating-current impedance spectroscopy and nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) are employed to investigate the hydration characteristics, pore solution composition and conductivity, resistivity and pore structure during the steam curing process. Experimental results show that steam curing promotes the hydration process, greatly raises the resistivity, and decreases the porosity of specimen at early age. Compared with being treated at 45 °C, higher temperature leads to a fast decomposition of ettringite at initial stage of the constant temperature treatment period, which improves the relative content and ionic activity of the conductive ions in pore solution. Furthermore, the number of pores larger than 200 nm increases significantly, which reduces the resistivity of the hardened cement paste. Cement paste treated at 45 °C has a more stable and denser microstructure with less damages.
Key words: cement paste; high-temperature curing; pore structure; AC impedance; nuclear magnetic resonance
Cite this article as: XIANG Yu, XIE You-jun, LONG Guang-cheng, HE Fu-qiang. Hydration phase and pore structure evolution of hardened cement paste at elevated temperature [J]. Journal of Central South University, 2021, 28(6): 1665-1678. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11771-021-4725-7.
1 Introduction
High-temperature steam curing is an effective way to accelerate the early growth of strength of fresh concrete mixture. In China, the growing demand for the rapid construction of high-speed railways positively promotes the development of steam-cured concrete prefabricated components industry (components such as rail sleepers, track slabs, as well as simply supported box girders), which then raises the production scale of above components. Because high temperature steam curing accelerates the hydration reaction of concrete in very early stage, the rapid development of the internal structure offers the concrete a relatively high early strength. Therefore, the production mould turnover efficiency is greatly improved and the project schedule is shortened. At present, steam-cured concrete prefabricated components have been successfully applied to thousands of kilometers of Chinese high-speed railway track structures. However, compared with the standard-cured concrete, steam-cured concrete often shows high brittleness and poor durability. Obviously, there is a serious adverse impact on concrete components and track structures [1-4]. At the meantime, scholars and railway project managers are monitoring and evaluating the quality and durability of those concrete components during the long-term service.
Optimizing the steam curing regime is the commonly used method to improve the quality of steam-cured concrete prefabricated components. In the past, the conventional treatment temperature in the production of steam-cured concrete prefabricated components was 60 °C. However, sometimes prefabrication plants choose 80 °C as the treatment temperature and then maintain or shorten the constant-temperature treatment time to prepare the concrete components with higher strength. It is true that the higher the treatment temperature is, the faster the cement hydration will be, which will increase the early strength of the concrete. However, the adoption of high temperature steam curing also produces the “thermal damage” problems such as the volume expansion, the coarsened pore structure, and the increased brittleness [5-8]. Today, engineers usually control the core temperature of concrete at approximately 60 °C, so the maximum treatment temperature is no more than 45 °C from experience. But reasonable explanation is lacking for choosing the above treatment temperature.
Research has shown that the mechanical properties and durability of steam-cured concrete are lower than those of standard-cured concrete with the same mix proportioning, component materials as well as the age. Steam-cured concrete always shows some quality problems such as cracks and peeling, honeycombed surfaces, poor impermeability, exposed and corroded reinforcement, and the inadequate bearing capacity. On the one hand, with the increase of the treatment temperature, the calcium silicate hydrate (C—S—H) gel gradually turns into crystallization formation, and the microstructure of hardened cement paste begins to bring out the thermal damages. For example, the microhardness declines and a greater strain rate sensitivity is presented, which raise the brittleness of steam-cured concrete [2, 9-12]. On the other hand, the relative content of the coarsened pore of steam-cured concrete significantly increases and the width of the interface transition zone (ITZ) becomes larger. At the end of steam curing, the number of pores larger than 200 nm in the surface layer of hardened cement paste is 10.3 times than that of pores in the interior. Besides, the above proportion of pores is still 1.6 times than that in the standard-cured specimens when all specimens were treated at 28 d [13-16]. Above conclusions are primarily based on the experimental research on the full-age steam-cured concrete (at least 28 d), standard-cured concrete, and the investigation of existing railway concrete structures. Although some methods to deal with the thermal damages of steam-cured concrete have been proposed, there are few explanations for the causes of that damages and few studies on the microstructure evolution of the hardened cement paste in the process of steam curing.
In this study, three high temperature conditions (80, 60 and 45 °C) for treating cement paste specimens are compared horizontally. In addition, pure ordinary Portland cement (PC) is used to prepare the test specimens, and the microstructure evolution characteristics of fresh cement paste under above treating temperature condition are studied. The hydrate phase composition of hardened cement paste and the main ionic concentration and the conductivity of pore solution are analyzed by X-ray diffraction (XRD), atomic absorption spectroscopy (AAS), ion absorption spectroscopy (ICS) and conductivity meter. Alternating-current (AC) impedance spectroscopy and nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) are employed to study the evolution of the pore structure of hardened cement paste to evaluate the impact of high temperature on its internal microstructure. The purpose of this study is to examine whether the high temperature steam curing has an adverse effect on the microstructure of hardened cement paste specimens, and to determine an appropriate treating temperature.
2 Experimental methodology
2.1 Raw materials
P·I 42.5 type Portland cement produced by the China Building Materials Academy is used in this experiment. The primary chemical composition of PC is listed in Table 1. Besides, newly prepared high purity deionised water (W) with a resistivity greater than 18 MΩ (at 20 °C), is used in the applicable experimental steps such as specimen preparing, soaking, rinsing, and the dilution.
Table 1 Main oxide compositions of PC (wt%)

2.2 Sample mix proportioning, preparation and curing method
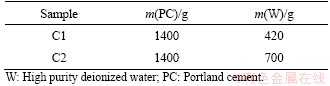
The mix proportioning of samples is shown in Table 2. In this experiment, the water-to-cement ratio for preparing the cement paste is 0.3 (C1), which is typically used for steam-cured concrete in high-speed railway. However, under the condition of steam curing, cement paste with a low water-to-cement ratio always has a higher hydration speed and consumes more free water to generate more hydration products, which leads to gain a limited pore solution extraction. Though the increase of water-to-cement ratio has a significant effect on the hydration and microstructure of hardened cement paste, but it does not change the types of hydration products as well as the conductive ions in pore solution. Therefore, a water-to-cement ratio of 0.5 is also used (C2) in order to obtain enough pore solution by the extraction method.
Table 2 Mixing proportioning of samples
The main processes for preparing samples C1 and C2 are as follows. The mixture of cement and water is firstly mixed slowly for 2 min in a mixer and then quickly mixed for another 2 min. After the mixing process, fresh mixed cement paste samples C1 and C2 can be obtained. Then, a steam curing method is employed to treat all specimens. All specimens are sealed with plastic film to prevent the exchange of water between the ambient steam and the specimen, and the specimens are only influenced by temperature. By controlling the temperature and time and adjusting the heating rate, the steam curing environment for treating the specimen can reach different high-temperature states. The steam curing regime for the cement paste specimens is presented in Figure 1, including 3 h precuring time at 20 °C,2 h heating time to reach the designed temperature, 8 h treatment at a constant temperature and cooling process to 20 °C within 2 h.
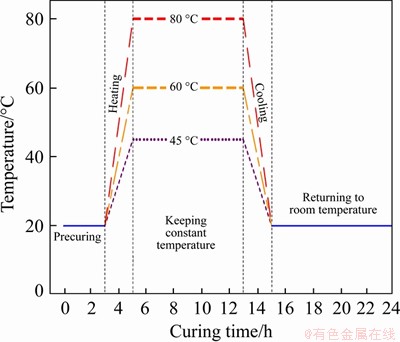
Figure 1 Steam curing scheme for cement paste specimens
2.3 Test methods
2.3.1 XRD
XRD test is used to analyze the hydration products of the hardened cement paste. In this test, a Bruker D2 Phaser XRD analyzer equipped with a Cu Kα (1.54184 A) X-ray source is used to determine the phase composition. Operating conditions are 30 kV and 10 mA. A continuous PSD fast scan mode is selected, and during the data collection process, the step-length is 0.02°; the scanning rate is 0.3 s/step; and 2θ ranges from 5° to 65°. Two time nodes, namely, the end of the temperature increase and the end of the constant-temperature treatment period, are selected for XRD tests to analyze the phase compositions. Above time nodes are chosen because the hardened cement paste has an initial structural strength and then hydration products might change after a long period of high-temperature treating.
2.3.2 Pore solution extraction
The pore solution in the hardened cement paste is collected by the pore solution extraction method (see Figure 2) [17], and the ionic concentration and other properties of this solution are then tested and analyzed. In this experiment, samples with five treating time are selected for extracting the pore solution.
The pore solution extraction procedures are as follows. C2 sample is poured into a 120 mL cylindrical sample cup; then the sample cup is sealed with a plastic film and placed on bracket of a handmade steam curing box; and then the water of box is heated according to the steam curing regime. When the temperature treating time reaches the required time for extraction, the device is placed on the center of test chamber in a 100 t press machine and the specimen is placed into the sample chamber. The machine starts loading to 600 kN at a loading rate of 2 kN/s and then this status is remained for 5 min. When the extraction is completed, the liquid sample cup is taken out, and the pore solution is extracted by a syringe. A 0.45-μm filter screen is then installed in the front of the syringe to filter the impurities in the pore solution, and the rest of the solution is squeezed into a new 30 mL sample cup.
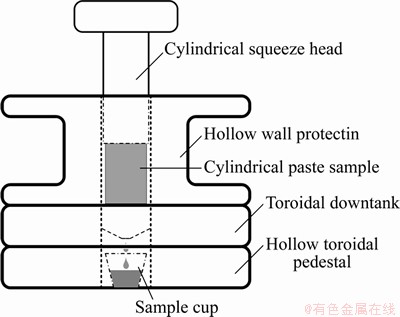
Figure 2 Pore solution extraction device
2.3.3 Atomic absorption spectroscopy
The main purpose of AAS test is to analyze the changing trend in the relative content of Ca2+ in the original pore solution using an INESA 4530F flame atomic absorption spectrophotometer. The main settings of this test are as follows. The combustion gas is acetylene with an output pressure of 0.08-0.1 MPa, while oxygen is the auxiliary gas. The wavelength of Ca element is 422.7 nm. Only when the calibration curve reaches 85%-100% fitting degree of the Ca wavelength, the position of the Ca element hollow-cathode lamp is calibrated and fixed. A standard curve method is adopted, and standard curve is drawn after testing the particular dilution ratios of the Ca2+ standard solution samples, and then the original pore solution is tested. The final test result is the average of three test results.
2.3.4 Ion absorption spectroscopy
The main purpose of this test is to quantitatively test the concentration of SO2-4at different treating stages and to further explain the changes in cement hydrate phase by analyzing its changing trend. A Thermo Scientific DIONEX ICS-600 with AS-DV is used as the testing instrument, and the test object is the pore solution diluted 1000 times with deionised water.
The main settings of this test are as follows. The eluate is prepared by dissolving 0.477 g Na2CO3 and 0.067 g NaHCO3 in 1 L high purity deionised water. The total injection volume of the sample is 1350 μL; the injection rate is 4 mL/min; the pump flow is 1.0 mL/min; and the pump pressure is limited within 200–3000 Psi. The temperature of the experimental environment is kept at 20 °C. When the baseline is stable, the curve is first calibrated, and then the specimens can be tested. The final test result is the average of three test results.
2.3.5 Conductivity
The pore solution is diluted 20 times and then tested by an INESA DDS-307A conductivity meter equipped with a DJS-1C-type conductivity electrode. The changing trend of the conductivity of the diluted pore solution under different constant treating temperatures is analyzed. In this experiment, to simulate the ambient temperature of the pore solution, the sample cup is placed in a small water-bath box (see Figure 3). The water level in the box is below the sample cup, and the temperature sensor of the conductivity meter is inserted into the sample cup. When the temperature of the sample solution is stable at the required constant temperature of the test, the conductivity test is carried out. The conductivity electrode constant is set at 1.023, and the instrument electrode constant is set at 1 cm-1. The final test result is the average of three test results.
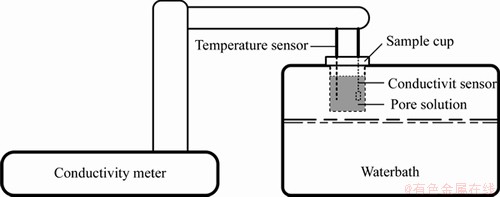
Figure 3 Conductivity test diagram
2.3.6 AC impedance spectroscopy
The properties of the solid phase (hydrates and unhydrated particles), the liquid phase (pore solution), and the solid-liquid interface during the cement hydration can be obtained by the AC impedance spectroscopy. It can well reflect the comprehensive development of the internal structure under different high temperature conditions [17-20]. In this experiment, a Solartron SI 1260 impedance/gain-phase analyzer is used.
The specimen treatment procedures and main settings are as follows. Six stainless steel electrode pieces (40 mm×40 mm×1 mm) are firmly pasted on the both ends of a 40 mm×40 mm×160 mm plastic triple mould. Then 1.5 mm2 insulated copper wire with a length of 15 cm is welded on a small stainless steel piece (10 mm×10 mm×1 mm) stretched out in the middle of the top edge of the electrode piece, and then the weld is covered with hot melt adhesive. C1 sample is poured into the triple mould. Then, a scraper is used to grind the specimens to flush with the electrode piece and a wet towel is used to wipe off the superfluous paste on the top surface of the mould, so that the test specimens are not in contact with each other. Then seal and wrap the entire triple mould with plastic film for multiple layers, just leaving the insulated copper wire exposed. The triple mould is placed on the bracket of the steam curing box, and the box lid covers the extended insulated copper wire and the water is heated according to the steam curing regime. The ZPlot program is used to control the equipment to conduct the test. The applied E mode is selected; the monitor is turned off; the DC potential is set to 0 V; and the AC amplitude is set to 100 mV in the polarisation setting. Then, the logarithmic mode is selected; the initial and final frequencies are set to 3×107 and 10 Hz, respectively; and the step interval is set to 15.
The effective high frequency section of the test data is analyzed by the ZSimpWin program. The equivalent circuit of SONG is adopted [21], where Rccp is the connected hole resistance; Rcp is the non-connected hole resistance; Cdp is the non-connected hole capacitance; Cmat is the base material capacitance; and Rmat is the base material resistance. As Rmat is generally much larger than Rccp, Rmat is usually ignored. The handmade steam curing box, the test diagram, as well as the equivalent circuit are shown in Figure 4. In this study, only Rccp in the fitting results is analyzed, and the fitting accuracy is within 10%. Then, the development of resistivity (ρ) of the hardened cement paste is calculated, and the calculation of ρ (Ω·m) is carried out according to Eq. (1):
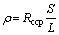 (1)
(1)
where S is the area of the electrode piece; L is the actual length of the specimen. The internal structure of hardened cement paste has not been formed in the precuring and heating stages; at the same time, the cement is in the rapid hydration stage. Because the resistance of the specimen is constantly changing at this time, it is meaningless and difficult to measure the AC impedance. Therefore, the test is conducted once an hour after the completion of the temperature increase because the basic structure of hardened cement paste has formed. Each specimen is tested twice, and the average value of six tests is used to calculate ρ.
2.3.7 Low-field NMR
In this experiment, a Suzhou Niumag 2 MHz NMR (MicroMR02-050V, Limecho) is employed. Samples with different treating conditions and times are selected for the experiment.
The specimen treatment procedures and main settings are as follows. C1 sample is poured into a 30 mL sample cup to a height of 15 mm. Then the sample cup is sealed with a plastic film and placed on the bracket of the steam curing box and the water of box is heated according to the steam curing regime. When the treating time reaches the required time for the test, the specimen can be taken out. The specimen should be immediately immersed in a new sample cup filled with 100 mL absolute ethanol (AE) and soaked for 7 d with new AE. Then it needs to be vacuum dried for at least 7 d. The magnet temperature is maintained at 35 °C, and T2 spectrum sequence is adopted. The echo time is 100 μs; the reply time is 1 s; the echo count is 5000; and scan time is 128.
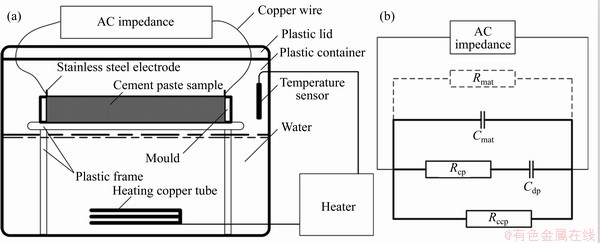
Figure 4 AC impedance test diagram and equivalent circuit
The basic principle for NMR method is as follows [22, 23]. With the saturated water state, the transverse relaxation rate 1/T2 of the fluid in the pores is the sum of the free relaxation T2B, the surface relaxation T2S, and the diffusion relaxation T2D. T2B is the transverse relaxation time of the fluid in a large volume container which can be negligible. T2S is the transverse relaxation time caused by the surface relaxation. T2D is the transverse relaxation time caused by diffusion under the magnetic field gradient which can be also negligible. Therefore, the transverse relaxation rate 1/T2 can be shown as Eq. (2):
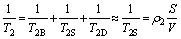 (2)
(2)
where T2 is the observed transverse relaxation time; ρ2 is the surface relaxation rate of T2; and S/V is the specific surface area of the pores. According to Ref. [23], if the micro-pores are assumed as cylindrical, then an equivalent radius r is straightforward yielded:
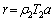 (3)
(3)
where a is the shape coefficient (2 for cylinder model, and 3 for sphere model). It can be seen that the pore radius r of porous materials is directly proportional to T2. Therefore, the T2 spectrum reflects the pore size distribution of the specimen. In this experiment, ρ2 is taken as 0.05 μm/ms, and a is taken as 2. The volume of the saturated specimen is calculated using the method of drainage with deionised water. In addition, the specimen’s water saturation process mainly includes placing it in a vacuum water saturator and vacuumising for 3 h, then injecting deionised water into the saturator and soaking the specimen for 3 h, and finally soaking it for another 3 h under a normal atmosphere pressure.
3 Results and discussion
3.1 Hydration product and phase components
The XRD patterns in 2θ of 5°–25° for different samples are presented in Figure 5, and Table 3 lists the changes in phase composition during the entire constant temperature treating period. It can be seen that for the pure cement paste specimen, there is no difference in the types of hydration products under different treating temperatures, and the difference is mainly in the relative content of hydration phases. The main cement hydration products are C—S—H gel, calcium hydroxide (CH), ettringite (AFt), and monosulide calcium sulphoaluminate hydrate (AFm). AFm results from the decomposition of AFt at a high temperature.
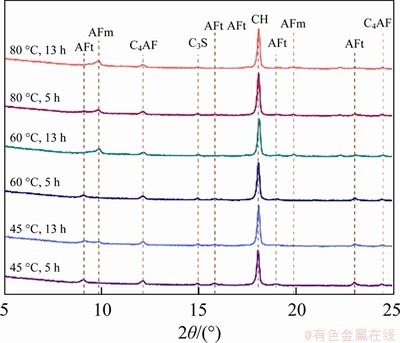
Figure 5 XRD patterns of constant temperature maintaining stage
Table 3 XRD test result
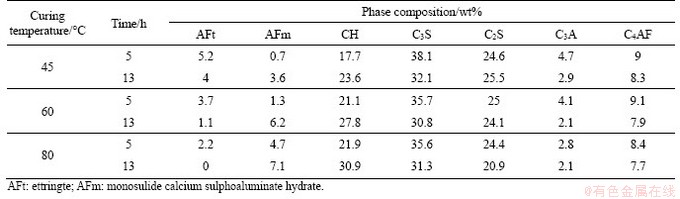
It can also be seen from Figure 5 that with the constant temperature treating, the peak strengths of cement clinker such as C3S and C4AF in each cement paste specimen declines, while the CH peak rises significantly, which indicates that the high temperature promotes cement hydration and generates a large amount of hydration products. The higher the treating temperature is, the faster the cement hydration is, and the higher the CH peak value is with the same treating time. At the beginning of the constant temperature treating period, the peak of AFt can be seen clearly in all cement paste specimens and the highest peak is under 45 °C treating. The lowest peak of AFt is under 80 °C treating; however, the peak of AFm is much higher. Then, at the end of the constant temperature treating period, the AFt peak decreases, and the AFm peak increases gradually in each cement paste specimen. At this moment, the highest peak of AFm is under 80 °C treating.
Table 3 shows the detailed transformation results of the cement hydration product composition and clinker in the entire constant temperature treating period. AFt of hardened cement paste specimens gradually changes into AFm under each treating temperature. At 45 °C, AFt of the cement paste is the highest at the early treating stage, and it partially converts into AFm. However, a large amount of unconverted AFt still stably exists in the specimen. When the external treating temperature rises to 60 °C and 80 °C, AFt declines gradually. And with the extension of the treating time, it finally converts into AFm. In addition, with the increase in treating temperature, the CH content increases significantly in the hardened cement paste. It increases by 41.1% during 5-13 h at 80 °C and is 7.8% higher than that at 45 °C.
According to the XRD results, high temperature has a great influence on the phase composition of the cement hydrates [10]. The amount of AFt, CH, and other hydration products (C—S—H gel) increases rapidly in the hardened cement paste, which cuts off the flow path of pore solution and rapidly reduces the electrical conductivity of the hardened cement paste in the early stage. With the constant temperature treating, the amount of the hydration products further increases, and the resistance of the hardened cement paste continues to increase. However, with the conversion of AFt to AFm, the internal structure of hardened cement paste becomes loose, and the original closed pore solution path can be reconnected again. At the same time, a large number of conductive ions such as Ca2+, Al3+, and SO2- 4 are released. Therefore, in a higher temperature treating environment, although the matrix resistance continues to increase, the conductivity is enhanced.
3.2 Pore solution ion characteristics
The concentration changes of Ca2+ and SO2- 4 at the constant temperature treating period and after cooling are shown in Figure 6. On one hand, the changing trend of Ca2+ concentration can well reflect the consumption of Ca2+ in the process of cement hydration and the formation of hydration products. While the SO2- 4concentration changing trend mainly reflects the influence of the AFt decomposition in pore solution under the conditions of high temperature treating.
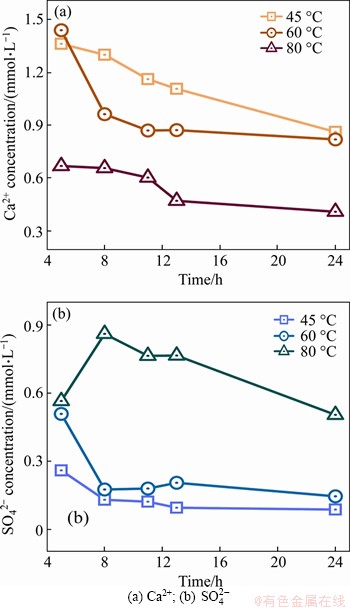
Figure 6 Changing trend of main ion concentration:
It can be seen from Figure 6 that the Ca2+ concentration at every treating temperature continues to decrease during the constant temperature treating and cooling periods, which indicates that the microstructure of hardened cement paste is continuously developed. C—S—H gel, CH, and other hydrated products (such as AFt) are generated in large quantities and continuously to fill the internal pores of hardened cement pastes. Therefore, the porosity of the entire specimen decreases; the connectivity path of the pore solution is cut off; and the conductivity of the cement paste specimen is greatly reduced. With the same treating time, the concentration of Ca2+ in the pore solution of hardened cement paste treated at 45 °C is the highest, followed by that treated at 60 °C and 80 °C, which means that increasing the temperature can further accelerate the hydration and promote the rapid formation of internal microstructure of hardened cement paste. However, the potentiality of internal cracking caused by temperature stress and shrinkage stress still cannot be ignored.
Furthermore, the concentration of SO2- 4 in pore solution at 45 °C and 60 °C continually decreases, which indicates that the internal structure becomes denser. Under the condition of 80 °C treating, the concentration of SO2- 4in pore solution increases rapidly at first and then slowly decreases, which shows that AFt is decomposing at the beginning of the constant temperature treating period. This greatly improves the conductivity of pore solution under the joint action of other decomposed conductive ions. While the decreasing trend of SO2- 4 concentration in cooling stage can be considered the process of AFm adsorbing SO2- 4 for regenerating AFt [24].
On the other hand, the conductivity of the pore solution directly influences the AC impedance spectroscopy test and the resistivity calculation of hardened cement paste. Figure 7 presents the changing trend of the conductivity of pore solution under different high temperatures.
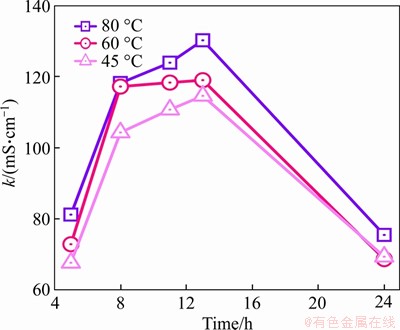
Figure 7 Conductivity of diluted pore solution
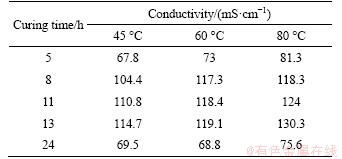
As seen in Figure 7, the conductivity of pore solution is very sensitive to temperature. With the increase in treating temperature, the conductivity of pore solution increases obviously in each treating period. At the same time, the conductivity of pore solution increases rapidly first and then slowly and finally decreases sharply during cooling. In the early constant temperature treating period, a large number of ions are consumed and the ionic concentration drops faster, which improves the ionic activity of pore solution and then raises the conductivity. Furthermore, in the middle and late stages of the constant temperature treating period, the hydration rate slows down and the concentration of the various ions in the pore solution continues to decrease as well as the corresponding consumption rate. However, under the condition of 80 °C treating, the conductivity of the pore solution increases greatly, which indicates that the decomposed conductive ions in the pore solution play an important role. When the concentration of each conductive ion is relatively low due to the formation of hydration products, and other decomposed conductive ions provide more charge transfer paths, which enhances the conductivity of the pore solution. Table 4 lists the specific conductivity of the diluted pore solution of hardened cement paste at different treating temperatures and treating times.
and other decomposed conductive ions provide more charge transfer paths, which enhances the conductivity of the pore solution. Table 4 lists the specific conductivity of the diluted pore solution of hardened cement paste at different treating temperatures and treating times.
Table 4 Conductivity of hardened cement paste diluted pore solution
To summarize, raising the treating temperature can accelerate the hydration rate of cement, build a denser microstructure, and improve the resistivity of hardened cement paste. However, increasing the treating temperature to very high like 80 °C would improve the conductivity of pore solution, which means that more defects are newly formed inside the hardened cement paste. Obviously, the denser microstructure of hardened cement paste with fewer internal defects can be obtained by treating at 45 °C.
3.3 AC impedance and resistivity characteristics
The changes in AC impedance spectroscopy of hardened cement paste under different temperature treating conditions are shown in Figure 8. AC impedance spectroscopy of the hardened cement paste is a typical Nyquist diagram, which is composed of a high frequency semicircle and an oblique line 45° from the real axis. The intersection of the high-frequency semicircle and oblique line in the real axis is called the high-frequency resistance (R), which can be generally considered Rccp, and is inversely proportional to the porosity of the test specimen. The increase of R is related to the development of pore structure and ionic concentration in the pore solution. With continuously treating, the diameter of the high frequency semicircle continues to grow, which means that R gradually increases and the internal structure of the hardened cement paste becomes denser [18, 19].
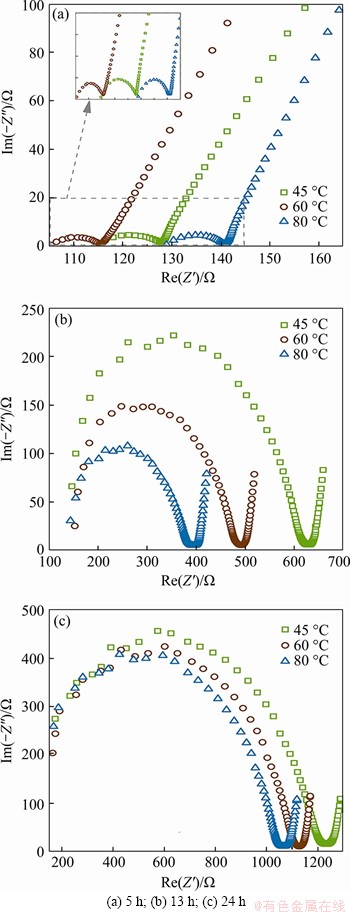
Figure 8 AC impedance test result at different curing stage:
At the end of temperature rising, R of the hardened cement paste is the highest and more than 140 Ω at 80 °C; while it is relatively low at other treating temperatures, which means that the early hydration of cement under the action of a high temperature is accelerated. Large amounts of hydration products are produced in the heating stage to fill the internal pores, which reduces the conductivity of the pore solution and raises the resistance. At the end of the constant temperature treating period, R of the hardened cement paste increases at each treating temperature, and at the meantime, the diameter of the high-frequency semicircle increases gradually. The resistance of hardened cement paste treated at 45 °C is the largest, with an increase of 386.3% compared with that at the end of temperature rising. While the resistance of hardened cement paste treated at 80 °C is the lowest, with an increase of 180.5% compared with that at the end of the temperature rising. The possible explanation is that high temperature although accelerates the hydration, it often causes high self-shrinkage and chemical shrinkage in the hardened cement paste. Therefore, it is possible to release the shrinkage stress through the cracking of the internal structure of hardened cement paste. This kind of potential internal cracking behavior of the hardened cement paste would lead to an increase in connected pores. With the decrease in the number of ions consumed in hydration, the ionic concentration decreases but the ionic activity rises, which finally raises the conductivity of the pore solution.
When temperature declines to room temperature (20 °C), R of the hardened cement paste at each treating temperature still increases further and is greater than 1000 Ω. Besides, the diameter of the high frequency semicircle continues to grow. In this stage, the hydration rate significantly decreases and the internal cracking caused by self-shrinkage and chemical shrinkage is relatively less. However, due to the rapid cooling of the specimen, in addition to the recovery of some temperature deformation, the internal temperature stress of hardened cement paste can be released by cracking of the microstructure [25]. This is why the R of the cement paste with a higher treating temperature is much lower. At the same time, the continuous evaporation of free water decreases the continuity of pore solution and cuts off the current path, which causes R of hardened cement paste to increase.
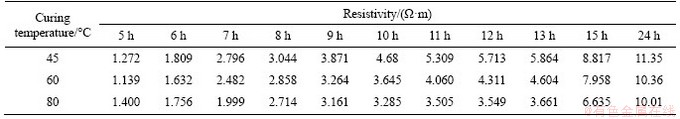
In addition, the resistivity can also reflect the changing process of the microstructure of the hardened cement paste, and the changing trend of the resistivity is shown in Figure 9. The main factors that affect the resistivity of the hardened cement paste are still the internal pore structure and pore solution. The cement paste with a low water-to-cement ratio can produce more hydration products under high temperature treating. Because its internal pore structure develops rapidly, the pore solution channel would be interrupted to raise the resistivity. The main conductive ions in the pore solution, such as Ca2+, Na+, OH-, and SO2- 4, are different in concentration, activity, and conductivity in different stages of hydration [26]. Table 5 shows the resistivity of the hardened cement paste at various treating temperatures and treating times.
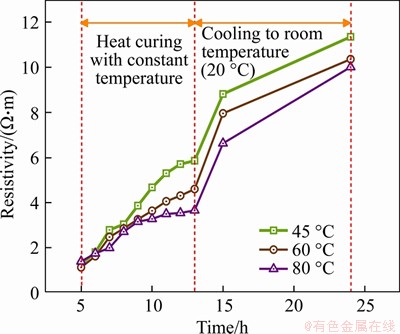
Figure 9 Resistivity growing trend of hardened cement pastes
According to Figure 9 and Table 5, the resistivity of hardened cement paste increases with treating time and the cooling stage. The resistivity of the hardened cement paste treated at 45 °C is basically the largest during the whole treating process, while that of the hardened cement paste treated at 80 °C is the lowest.
In the first 5-8 h of the constant temperature treating period, the resistivity of hardened cement paste rises rapidly. At this time, the hydration products are generated rapidly, which has a blocking effect on the pore solution path. The microstructure of hardened cement paste develops faster and becomes denser. Therefore, the increase in the resistivity is obvious. However, the increasing trend of resistivity under different treating temperatures begins to show significant differences in the later 8-13 h of the constant temperature treating period. The resistivity of hardened cement paste treated at 60 °C and 80 °C increases slowly and the specimen treated at 80 °C has the lowest resistivity. A possible explanation is that new pore solution connection channels are established by cracks produced by the action of shrinkage stress and the decomposition of hydration products under the higher temperature treating conditions. Furthermore, high temperature also raises the ionic activity. Therefore, the increase in the resistivity is relatively slow at 60 °C and 80 °C. Because the hydration products are still being continuously generated, the resistivity of each specimen increases correspondingly. The resistivity of hardened cement paste treated at 45 °C begins to slow down at later 11 h, which indicates that treating at a lower temperature has a less adverse effect on the development of the microstructure of hardened cement paste.
Lastly, during the cooling period of 13-24 h, the resistivity of each hardened cement paste increases significantly, which is mainly affected by the water evaporation and temperature decrease. The evaporation of water has a great influence on the connectivity of the pore solution. Besides, the higher the treating temperature is, the greater the temperature difference to room temperature is, which obviously shows that the release of the temperature stress has a certain adverse effect.
Table 5 Resistivity of hardened cement paste specimen
3.4 Pore structure evolution
The T2 relaxation time reflects the chemical environment of H protons in saturated porous media, which is related to the binding effect of H protons in the specimen and their degree of freedom. Above binding effect is closely related to the internal pore structure of the specimen. A larger pore diameter indicates a longer T2 relaxation time of pore water, while a smaller pore diameter indicates greater pore water binding as well as a shorter T2 relaxation time. That is, the position of the peak corresponds to the pore size of the specimen, while the area of the peak corresponds to the distribution of the pore diameters in the T2 spectrum [27]. The T2 spectra of hardened cement paste at different temperature treating conditions are shown in Figure 10.
It can be seen from the T2 spectra that there are relaxation time distributions of 0.01-10 ms, 10-100 ms, and 100-10000 ms in the hardened cement paste under various treating times. The short relaxation time of 0.01-10 ms is the main part, which indicates that the hardened cement paste is primarily composed of small pores. With the constant temperature treating, it can be seen that the signal strength of the peak declines. Furthermore, some small pores gradually develop into larger pores, and the signal strength of 10-100 ms is enhanced. During the cooling period, the signal strength of 10-100 ms further increases, while the strength of the short relaxation time section is slightly reduced. This is because the hydration continues to take place and generates more hydrates. However, under the effect of temperature stress, cracks with larger pore diameters are produced in the hardened cement paste.
The development of pore structure (including pore size) in the hardened cement paste under different treating temperatures is obtained. According to Ref. [28], the internal pores of the hardened cement paste are divided into the harmless pores of less than 20 nm, the less harmful pores of 20-50 nm, the harmful pores of 50-200 nm, and the more harmful pores greater than 200 nm. The porosity of different apertures is converted to the porosity per unit volume, which is related to the total porosity and the volume of the test specimen, and is presented in Figure 11.
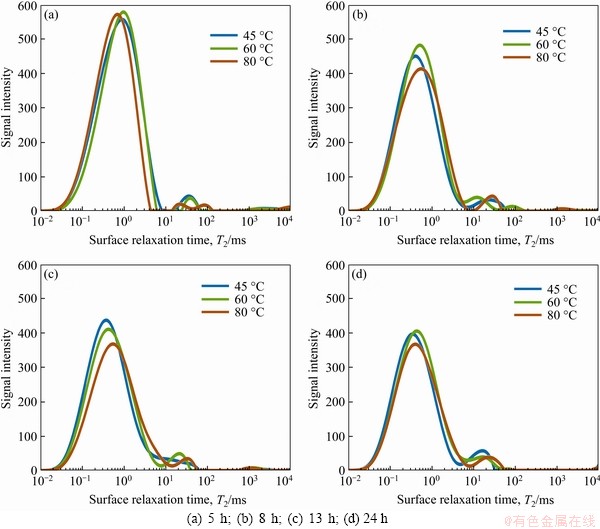
Figure 10 T2 distribution spectra of hardened cement paste under different curing stage:
Figure 11 further clarifies the changes of pore diameter of the different hardened cement pastes with treating time after the conversion to unit volume. With the extension of treating time, all pores in the hardened cement paste shows a continuous decline, which indicates that the total porosity of the sample is decreasing and consistent with the development trend of the conventional cement hydration microstructure. The harmless pores content of the hardened cement paste treated at 45 °C and 60 °C increases first and then decreases slowly, while the content of the hardened cement paste treated at 80 °C is the highest at first and then decreases constantly. Furthermore, all kinds of harmful pores contents in the hardened cement paste treated at 45 °C are relatively low, which implies that there is less defects produced by lower treating temperature and the microstructure is better. However, when the treating temperature increases, the number of harmful pores increases, which eventually helps to create new pore solution connectivity paths.
The above results show that under different treating temperatures, the total porosity of the hardened cement paste decreases, the internal structure becomes denser. With the consumption of pore solution, the resistance of the cement specimen significantly increases. However, the higher the treating temperature is, the more obvious the development of internal defects in the hardened cement paste is. This kind of defect can weaken the resistivity of the cement specimen.
4 Conclusions
1) Elevated temperature at the initial stage of constant temperature treating period is conducive to the rapid formation of hydration products and the development of the microstructure. Although the total porosity of the hardened cement paste continues to decline, the relative content of harmful pores rises. With the increase in treating temperature (such as 80 °C treating), the number of harmful pores greater than 200 nm increases as well as the relative content of the conductive ions in the pore solution. Besides, new conductive paths are generated, which reduces the resistivity of the hardened cement paste.
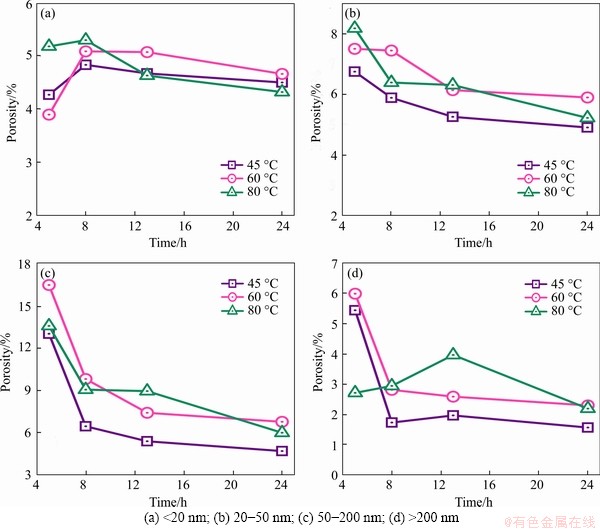
Figure 11 Development of diameter pore with curing time:
2) The electric resistance of the hardened cement paste gradually increases with continually treating, which indicates that the internal pore structure tends to be dense and the conductive path of pore solution decreases. The higher the treating temperature is, the higher the high frequency resistance is in the early stage. However, with the extension of the treating time until cooling to room temperature, the specimen treated at 45 °C shows greater high-frequency resistance and the highest resistivity compared to 60 °C and 80 °C conditions, which indicates that reasonable high temperature (such as 45 °C) will be benefit well to the internal dense microstructure of the hardened cement paste. Although higher temperature promotes the rapid hydration of cement, it also leads to formations of the big pores, new cracks and conductive paths. In this study, it is recommended that the maximum temperature for steam curing cement-based materials should not exceed 45 °C.
Contributors
XIE You-jun and LONG Guang-cheng provided the concept and edited the draft of manuscript. XIANG Yu implemented the experiment and wrote the first draft of the manuscript. HE Fu-qiang provided the experiment instrument and advised on the analysis of the experiment result.
Conflict of interest
XIANG Yu, XIE You-jun, LONG Guang-cheng, and HE Fu-qiang declare that they have no conflict of interest.
References
[1] JIN Qin-hua, DENG Min, HAN Su-fen. Investigation of deteriorated concrete railway ties [J]. Cement and Concrete Research, 1996, 26(7): 999-1006. DOI: 10.1016/0008-8846(96)00086-5.
[2] LOTHENBACH B, WINNEFELD F, ALDER C, WIELAND E, LUNK P. Effect of temperature on the pore solution, microstructure and hydration products of Portland cement pastes [J]. Cement and Concrete Research, 2007, 37(4): 483-491. DOI: 10.1016/j.cemconres.2006.11.016.
[3] BA Ming-fang, QIAN Chun-xiang, GUO Xin-jun, HAN Xiang-yang. Effects of steam curing on strength and porous structure of concrete with low water/binder ratio [J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2011, 25(1): 123-128. DOI: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2010.06.049.
[4] MA Kun-lin, LONG Guang-cheng, XIE You-jun. A real case of steam-cured concrete track slab premature deterioration due to ASR and DEF [J]. Case Studies in Construction Materials, 2017, 6: 63-71. DOI: 10.1016/j.cscm.2016.12.001.
[5] XIANG Yu, XIE You-jun, LONG Guang-cheng. Volume deformation characteristics of concrete mixture during thermal curing process [C]// International Conference on Materials Science and Manufacturing Engineering. EDP Sciences Press, 2018: 01008. DOI: 10.1051/matecconf/ 201925301008.
[6] LONG Guang-cheng, HE Zhi-min, OMRAN A. Heat damage of steam curing on the surface layer of concrete [J]. Magazine of Concrete Research, 2012, 64(11): 995-1004. DOI: 10.1680/macr.11.00164.
[7] SHI Jin-yan, LIU Bao-ju, WU Xiang, TAN Jin-xia, DAI Jing-dan, JI Rou-jia. Effect of steam curing on surface permeability of concrete: Multiple transmission media [J]. Journal of Building Engineering, 2020, 32: 101475. DOI: 10.1016/ j.jobe.2020.101475.
[8] SHI Jin-yan, LIU Bao-ju, ZHOU Feng, SHEN Shuai, DAI Jing-dan, JI Rou-jia, TAN Jin-xia. Heat damage of concrete surfaces under steam curing and improvement measures [J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2020, 252: 119104. DOI: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2020.119104.
[9] PATEL H H, BLAND C H, POOLE A B. The microstructure of concrete cured at elevated temperatures [J]. Cement and Concrete Research, 1995, 25(3): 485-490. DOI: 10.1016/ 0008-8846(95)00036-C.
[10] MEI Jun-peng, MA Bao-guo, TAN Hong-bo, LI Hai-nan, LIU Xiao-hai, JIANG Wen-bin, ZHANG Ting, GUO Yu-lin. Influence of steam curing and nano silica on hydration and microstructure characteristics of high volume fly ash cement system [J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2018, 171: 83-95. DOI: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2018.03.056.
[11] WANG Meng, XIE You-jun, LONG Guang-cheng, MA Cong, ZENG Xiao-hui. Microhardness characteristics of high-strength cement paste and interfacial transition zone at different curing regimes [J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2019, 221: 151-162. DOI: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat. 2019.06.084.
[12] WANG Meng, XIE You-jun, LONG Guang-cheng, MA Cong, ZENG Xiao-hui, QIANG Fu. The impact mechanical characteristics of steam-cured concrete under different curing temperature conditions [J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2020, 241: 118042. DOI: 10.1016/ j.conbuildmat.2020.118042.
[13] DETWILER R, KJELLSEN K, GJORV O. Resistance to chloride intrusion of concrete cured at different temperatures [J]. ACI Materials Journal, 1991, 88(1): 19-24. DOI: 10.14359/2326.
[14] GESOGLU M, GUNEYISI E, ALI B, MERMERDAS K. Strength and transport properties of steam cured and water cured lightweight aggregate concretes [J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2013, 49: 417-424. DOI: 10.1016/ j.conbuildmat.2013.08.042.
[15] MA Kun-lin, HE Jiong-huang, LONG Guang-cheng, DANG Han-fei, XIE You-jun. Steam-curing temperature effect and its influence on heat damage of cement-based material [J]. Materials Report, 2017, 31(12): 171-176. DOI: 10.11896/ j.issn.1005-023X.2017.023.025. (in Chinese)
[16] SHI Jin-yan, LIU Bao-ju, HE Zhi-hai, WU Xiang, TAN Jin-xia, CHEN Jia-zhuo, JIANG Jun-yi. Properties evolution of high-early-strength cement paste and interfacial transition zone during steam curing process [J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2020, 252: 119095. DOI: 10.1016/ j.conbuildmat.2020.119095.
[17] HOU Wei, LIU Zan-qun, HE Fu-qiang, HUANG Ju, ZHOU Jin. Sulfate diffusion in calcium sulphoaluminate mortar [J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2020, 234: 117312. DOI: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2019.117312.
[18] ZHANG Yan-rong, KONG Xiang-ming. Influences of superplasticizer, polymer latexes and asphalt emulsions on the pore structure and impermeability of hardened cementitious materials [J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2014, 53: 392-402. DOI: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2013.11.104.
[19] DONG Bi-qin, LI Gui, ZHANG Jian-chao, LIU Yu-qing, XING Feng, HONG Shu-xian. Non-destructive tracing on hydration feature of slag blended cement with electrochemical method [J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2017, 149: 467-473. DOI: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2017.05.042.
[20] WANG Hui, ZHANG Ai-lian, ZHANG Lin-chun, WANG Qian, HAN Yan, LIU Jun-zhe, GAO Xiao-jian, SHI Fei-ting, LIN Xue-yan, FENG Li-yu. Hydration process of rice husk ash cement paste and its corrosion resistance of embedded steel bar [J]. Journal of Central South University, 2020, 27(11): 3464-3476. DOI: 10.1007/s11771-020-4559-8.
[21] SONG Guang-ling. Equivalent circuit model for AC electrochemical impedance spectroscopy of concrete [J]. Cement and Concrete Research, 2000, 30(11): 1723-1730. DOI: 10.1016/S0008-8846(00)00400-2.
[22] ZHOU Chun-sheng, REN Fang-zhou, WANG Zhen-di, CHEN Wei, WANG Wei. Why permeability to water is anomalously lower than that to many other fluids for cement-based material? [J]. Cement and Concrete Research, 2017, 100: 373-384. DOI: 10.1016/j.cemconres.2017.08.002.
[23] ZHOU Chun-sheng, REN Fang-zhou, ZENG Qiang, XIAO Li-zhi, WANG Wei. Pore-size resolved water vapor adsorption kinetics of white cement mortars as viewed from proton NMR relaxation [J]. Cement and Concrete Research, 2018, 105: 31-43. DOI: 10.1016/j.cemconres.2017.12.002.
[24] SAHU S, THAULOW N. Delayed ettringite formation in Swedish concrete railroad ties [J]. Cement and Concrete Research, 2004, 34(9): 1675-1681. DOI: 10.1016/ j.cemconres.2004.01.027.
[25] HE Zhi-min, LONG Guang-cheng, XIE You-jun, LIU Jun-zhe. Surface layer degradation effect of steam-cured concrete [J]. Journal of Building Materials, 2014, 17(6): 994-1001. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-9629.2014.06.010. (in Chinese)
[26] QIAN Ru-sheng, ZHANG Yun-sheng, ZHANG Yu, YANG Yong-gan. Relationships between liquid ion concentration and electrical conductivity during the early hydration of cement-fly ash system [J]. Materials Review, 2018, 32(12): 2066-2071. (in Chinese)
[27] WANG Yong, YUAN Qiang, DENG De-hua, YE Tao, FANG Lei. Measuring the pore structure of cement asphalt mortar by nuclear magnetic resonance [J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2017, 137: 450-458. DOI: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat. 2017.01.109.
[28] ZHANG Mao-hua, LI Hui. Pore structure and chloride permeability of concrete containing nano-particles for pavement [J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2011, 25(2): 608-616. DOI: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2010.07.032.
(Edited by ZHENG Yu-tong)
中文导读
高温下硬化水泥浆体水化物相及孔隙结构的演化
摘要:为了解蒸汽养护温度对硬化水泥浆体水化物相及孔隙结构的影响,采用X射线衍射、原子吸收光谱、离子色谱、电导率仪、核磁共振、交流阻抗等方法研究了在蒸汽养护过程中水泥浆体的水化特征、孔溶液组成与导电特性、基体电阻率以及孔隙结构。试验结果表明,蒸汽养护促进了水化过程,大幅度提高了基体早期电阻率并降低了孔隙率。与在45 °C养护温度下相比,在恒温养护阶段初期,更高的养护温度导致钙矾石快速分解,从而提高了孔溶液中导电离子的相对含量和离子活度。此外,大于200 nm的孔数量显著增加,降低了硬化水泥浆体的电阻率。45 °C养护温度下的水泥浆体微观结构较稳定且致密,产生的内部损伤较小。
关键词:水泥浆体水化;高温硬化;孔隙结构;交流阻抗;核磁共振
Foundation item: Projects(U1534207, 11790283, 51878583) supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China
Received date: 2020-09-02; Accepted date: 2020-12-25
Corresponding author: LONG Guang-cheng, PhD, Professor; Tel: +86-13873137563; E-mail: longguangcheng@csu.edu.cn; ORCID: https://orcid.org/0000-0003-2210-2115; HE Fu-qiang, PhD, Professor; Tel: +86-13235929023; E-mail: 77163594@qq.com; ORCID: https://orcid.org/0000-0003-3360-7143

