Q345c连铸坯在热装热送中表面裂纹成因分析
王生朝1, 2,赵刚1,鲍思前1
(1. 武汉科技大学 材料与冶金学院,湖北 武汉,430081;
2. 湖南工业大学 冶金工程学院,湖南 株洲,412007)
摘要:应用有限元软件(ABAQUS) 对Q345c连铸板坯单坯冷却过程温度场和应力场进行模拟,通过Gleeble 2000热模拟试验机研究Q345c钢连铸坯的高温热塑性,测得材料的高温热塑性曲线和高温抗拉极限曲线。研究结果表明:材料的脆性区在600~850 ℃之间,高温断裂强度随温度升高而降低,最大不超过160 MPa;板坯单独冷却在850~750 ℃之间,正处在材料的脆性区,模拟所得其表面拉应力,最大达到164 MPa,超过材料的高温抗拉强度;为避免过高的表面热应力产生热裂纹缺陷,连铸火焰切机至板坯加热炉之间,除应安装保温加热装置外,尽量缩短板坯的输送时间,必要时堆垛缓冷。
关键词:连铸坯;温度场;应力分析;导热系数;裂纹;高温热塑性
中图分类号:TG335.11 文献标志码:A 文章编号:1672-7207(2013)09-3634-06
Surface cracks analysis on continuous casting slab Q345c during hot delivery and hot charging
WANG Shengzhao1, 2, ZHAO Gang1, BAO Siqian1
(1. College of Material and Metallurgical Engineering, Wuhan University of Science and Technology, Wuhan 430081, China;
2. College of Metallurgical Engineering, Hunan University of Technology, Zhuzhou 412007, China)
Abstract: The temperature field and stress field were simulated using the finite element software (ABAQUS) for Q345c continuous casting slab during cooling process. The hot ductility of continuous casting Q345c slabs was tested by Gleeble 2000 thermal/strain simulation machine. The hot ductility curve and high temperature tensile strength curve were obtained according to thermal simulation experiments. The results show that the temperature of brittleness zone is in 600-850 ℃, high temperature tensile strength decreases with increasing temperature and the maximum does not exceed 160 MPa. The simulation value of surface stress is up to 164 MPa and larger than the high temperature tensile strength in the cooling process of the single slab. At the same time temperature between 750-850 ℃ is in the brittle zone of the material. In order to avoid hot crack defects caused by excessive thermal stress on the surface in the process of hot slab delivery, the insulation heating device should be installed between the flame cutting machine and the heating furnace, and the delivery time of slab should be shorter. Furthermore, if necessary, slabs need to be stacked up to slow down the cooling speed.
Key words: continuous casting slab; temperature fields; stress analysis; thermal conductivity; cracks; hot ductility
连铸坯热装热送工艺是将切割后的连铸坯立即通过铁路或辊道运送至加热炉,经过缓冲装置如连铸坯库、保温罩,以较高温度连铸坯装入加热炉的工艺方法。近年来,热装热送技术在国内外迅速发展,许多研究机构与钢铁企业对此进行深入研究。热装热送技术代表着钢铁企业的生产水平,它引起了钢铁生产企业全面的技术革新与生产技术的跨越式发展,给钢铁企业带来了巨大的经济效益[1]。连铸坯热装热送及热送直轧技术的应用程度已成为衡量钢铁生产技术水平的新指标,连铸坯热送热装具有提高生产率、降低能耗和减少铸坯氧化烧损的作用,工艺控制对成品质量具有重要影响[2]。生产中连铸坯受到的应力与很多因素如钢的化学成分、钢水的浇注温度与速度,钢液的冷却与凝固以及热装热送工艺等有关。连铸坯无论是在冷却还是在加热过程中,都存在温度、相变、内应力三者耦合的关系,它们之间相互影响、相互作用[3-4]。一般来说,连铸坯在热装热送过程中,受到的应力主要由热应力和组织应力2个部分组成。前者是由于在冷却或加热过程中,连铸坯温度分布不均,表面与心部之间存在温差,各处膨胀变形或收缩变形不一致,相互约束而产生内应力;后者是板坯在传送辊道上或保温车中冷却过程中低于相变点,发生奥氏体向铁素体和珠光体的转变,此过程会产生组织应力。本文作者针对某厂生产含Nb微合金钢Q345c连铸坯,在热装热送过程中产生热裂纹质量缺陷的情况,模拟连铸坯从火焰切割到进加热炉这个过程的温度场和应力场,并根据材料在这个温度区间的高温热塑性和高温断裂强度,探讨热送生产中裂纹产生的机理,以便为实现连铸直接轧制工艺提供理论依据。
1 试验材料及模拟数学模型
1.1 试验材料
取连铸坯试样Q345c,在铸坯的中部切割试样,位置靠近铸坯上表面,在1/4和3/4铸坯宽度处切取。试验所用试样直径×长度为10 mm×120 mm,其他参数如图1所示,化学成分如表1所示。
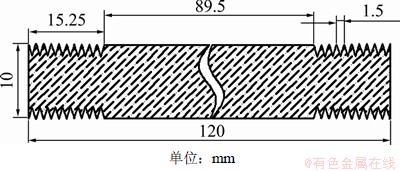
图1 试样参数
Fig.1 Parameters of sample
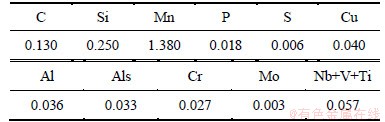
表1 试验用钢的化学成分(质量分数)
Table 1 Chemical composition of experimental steel %
在有限元仿真中采用的板坯模拟厚度×宽度×长度为250 mm×1 500 mm×10 000 mm。板坯的长度远大于厚度和宽度,忽略板坯长度方向的温度变化,板坯上下2面和左右2面(近似认为对称冷却)冷却条件相同,以板坯断面建立描述钢坯冷却过程二维瞬态传热过程数学模型。
1.2 试验材料物性参数
在有限元方程中应用ABAQUS进行温度场模拟,主要涉及的热物理参数有材料密度、比容、导热系数、弹性模量、泊松比、对流换热系数、辐射换热系数、热膨胀系数等。这些参数均与温度相关,为温度的函数[5-7]。它们与温度的关系曲线如图2所示。用顺序耦合的方法先计算出板坯的温度场,进而得到应力场。
1.3 数学模型
1.3.1 板坯传热数学模型
由Fourier传热定律和能量守恒定律,对板坯空冷过程进行热分析时,对于所研究的微元体,其长度分别为dx,dy和dz,在时间间隔dt内,由该微元体内的能量平衡可得到各向同性体热传导瞬态温度场 T(x,y,z,t)满足以下方程:
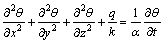 (1)
(1)
其中: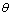 为温度,℃;t为时间,s;x为板坯宽度坐标值,m;y为板坯厚度坐标,m;
为温度,℃;t为时间,s;x为板坯宽度坐标值,m;y为板坯厚度坐标,m;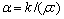 为材料导温系数;ρ为材料密度,kg·m-3;c为材料比热容,J/(kg·K);k为材料热导率,W/(m·K);q为凝固发生相变释放的潜热[8-10]。
为材料导温系数;ρ为材料密度,kg·m-3;c为材料比热容,J/(kg·K);k为材料热导率,W/(m·K);q为凝固发生相变释放的潜热[8-10]。
1.3.2 应力场模型
板坯在辊道输送过程中不存在外载荷,引起热应力和热变形的原因是温度分布不均匀引起膨胀量的不同。因此,板坯板冷却过程的应力/应变属于热弹性或热弹塑性问题。若材料的弹性模量E,泊松比μ和热膨胀系数α都是温度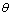 的函数,则在塑性区,全应变增量由弹性应变增量、塑性应变增量和温度应变增量组成,即
的函数,则在塑性区,全应变增量由弹性应变增量、塑性应变增量和温度应变增量组成,即
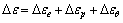 (2)
(2)
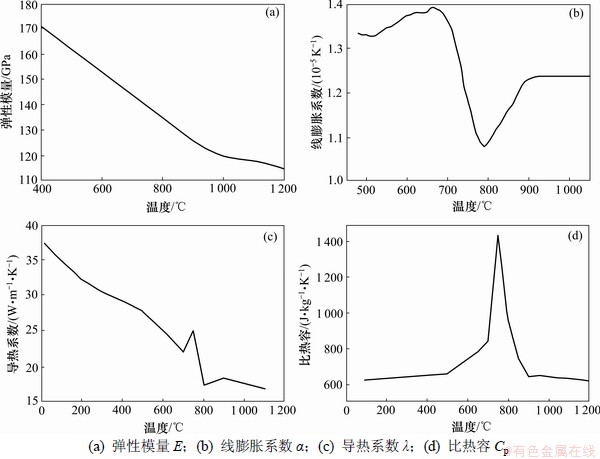
图2 各种参数随温度变化的曲线
Fig.2 Curves of E, α, λ and Cp variation with temperature
根据温度场的模拟结果,求解应力场。根据相关资料[5-7],求解应力在有限元模型中设置参数时,考虑相变对线胀系数等热物理性质的影响[11]。
1.4 初始和边界条件
空冷状态下板坯冷却主要有热辐射和热对流2种传热方式。初始条件为板坯切割机出口的温度为1 000 ℃;边界条件为板坯和空气的对流换热方程和对环境的热辐射方程。初始边界条件在t=0时刻用以下函数方程描述:
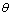 (x,y,z,0)=
(x,y,z,0)=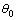 (3)
(3)
考虑到辐射和对流的综合影响,板坯在空气中的综合散热系数可表示成[12-13]:
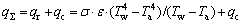 (4)
(4)
其中: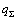 为板坯综合换热系数,W/(m2·K);qr为辐射换热系数,W/(m2·K);qc为对流换热系数,W/(m2·K);σ为Stefan-Boltzmann常数,σ=5.768×10-8,W/(m2·K4);ε为材料表面的辐射率,由试验测定;Tw和Ta分别为板坯表面温度和环境温度,K。
为板坯综合换热系数,W/(m2·K);qr为辐射换热系数,W/(m2·K);qc为对流换热系数,W/(m2·K);σ为Stefan-Boltzmann常数,σ=5.768×10-8,W/(m2·K4);ε为材料表面的辐射率,由试验测定;Tw和Ta分别为板坯表面温度和环境温度,K。
由于热物性参数随温度的变化,综合换热系数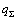 的确定需经多次拟合修正。
的确定需经多次拟合修正。
2 试验过程
2.1 高温热塑性试验
试验设备采用Gleeble-2000试验机,热模拟过程在真空条件下完成。试验工艺曲线按图3所示。以10 ℃/s升温到达1 320 ℃后保温5 min,然后以3 ℃/s的速率分别降温到1 300~600 ℃,每隔 50 ℃取1个预定的变形温度,保持 2 min 后在该温度下以1×10-3/s的应变速率进行拉伸试验。试样拉断后立即对断裂部位大量喷水冷却,冷却后测量断裂部位截面积,计算其断面收缩率RA,并测定高温断裂强度。
2.2 数值模拟
应用ABAQUS/standard分析模块,采用顺序耦合进行热应力分析。
(1) 先进行热分析。模型网格划分选择quad- structured的DC2D4单元网格,设置分析步时都采用“heat transfer”,建立材料的温度场。
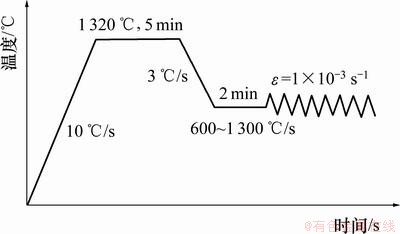
图3 试验工艺曲线
Fig.3 Experimental process curve
(2) 对同一个集合模型在建立应力分析,划分网格时用3D Stress,设置分析步时用Static和Geneal,导入前面热分析温度场的结果,进行应力分析。
3 试验结果与讨论
3.1 Q345c钢热塑性试验结果分析
通过在Gleeble-1500进行热模拟实验,得出Q345c试样的变形温度与断面收缩率(RA)的关系如图4所示。试验表明Q345c钢的高温热塑性区可分为:第Ⅰ脆性区在1 300~1 200 ℃温度区间,试样的RA低于60%;第Ⅱ高塑性区在区间1 200~875 ℃,试样的塑性远高于60%,在1 050 ℃最高塑性RA可达85.8%;第Ⅲ脆性区在600~875 ℃温度区间,RA分布在40%上下,试样表现出较低的塑性。
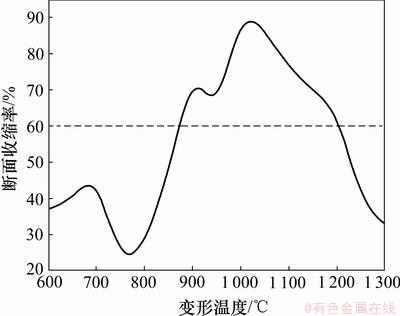
图4 Q345c钢断面收缩率RA与变形温度曲线
Fig.4 RA-deformation temperature curve of Q345c
3.2 温度场计算结果分析
板坯断面表层沿宽度各点在240,600,960和1 200 s时温度如图5所示。由图5可见:距板坯边沿200 mm温降较快,除去边部宽度表层各点温度与中点温度基本一致。板坯表层沿宽度中点温度、板坯正中心温度如图6所示,温度差随时间变化曲线如图7所示。
由图7可见:表面在开始的1 000 s内温度降低很快,这是由于前期连铸坯的温度很高,辐射散失的热量较大。在单独空冷的条件下,铸坯内外存在着比较大的温度差,在1 200 s内,铸坯表面的温度下降大约230 ℃(在1 200 s时,表层温度为769 ℃),空冷的速率约为0.23 ℃/s。在前一阶段的温降速率较快,在后一阶段的温降速率较慢。这主要是受辐射换热系数减小的影响。1 200 s以后温度差趋于平稳,连铸坯上表面中心与板坯中心的温差保持在120 ℃左右。
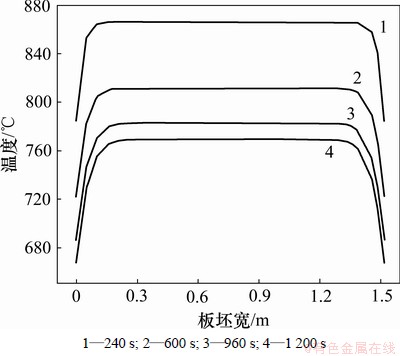
图5 板坯表层沿宽度随时间温度分布
Fig.5 Slab surface temperature along width at different cooling time
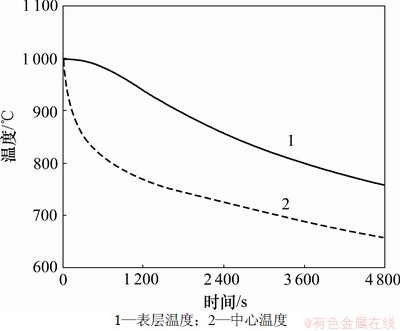
图6 板坯表层沿宽度中点、板坯中心温度
Fig.6 Temperature at middle point of slab surface and central section of slab
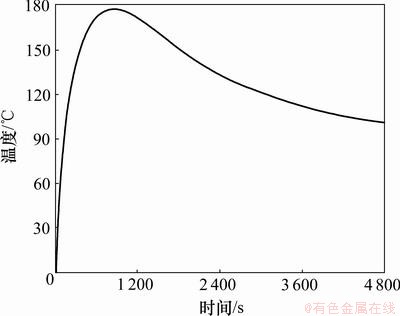
图7 板坯表层与中心温度差随时间变化关系
Fig.7 Temperature difference between slab surface and center over time
表2 上表面中心点温度模拟值与实测值的对比
Table 2 Contrast of simulated and measured temperatures of center on surface ℃
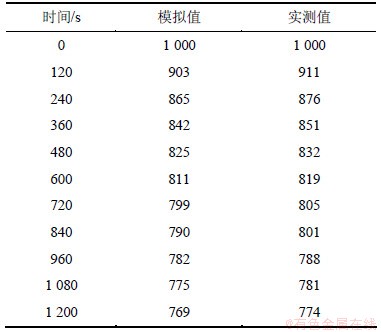
表2所示为铸坯的模拟值和在热送现场用红外感应测温仪测得的温度,温差基本都控制在15 ℃内。厚度为250 mm板坯,在冷却600和960 s断面温度场,如图8所示。
3.3 应力计算结果分析
板坯在冷却过程中表面温度低而受拉应力,心部温度高则受压应力。随表面和心部的温度梯度增大,表面的拉应力和心部的压应力也随之增加;随后温差减小,表面和心部的应力相应减小。通过热模拟试验测出Q345c的断裂应力及模拟出的板坯表层、角部热应力随温度变化关系如图9所示。从图9可见:板坯角部冷却速度虽大,但温度梯度小,热应力不大于35 MPa。板坯表层的应力768 ℃达到最大值164 MPa,由于冷却到Ar3-Ar1之间开始产生相变应力(压应力),以及温度梯度变小,所以,等效应力逐渐降低。
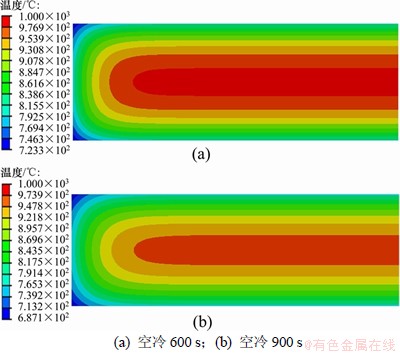
图8 厚度为250 mm板坯在冷却600和960 s断面温度场
Fig.8 Temperature field of cross section of 250 mm thick slab after cooled for 600 and 960 s
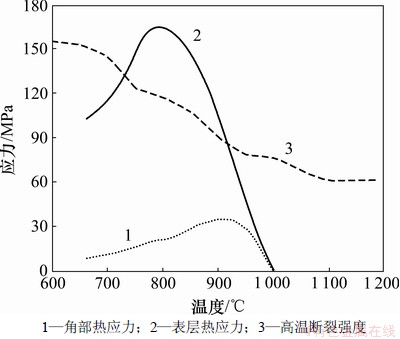
图9 板坯表层热应力和高温强度随温度变化曲线
Fig.9 Curves of thermal stress in slab surface and high temperature tensile strength with temperature
比较铸坯的高温抗拉强度与铸坯热送过程中的应力值,及连铸坯的高温热塑性,可衡量连铸坯产生裂纹的可能性。对于Q345c钢连铸坯,在1 300~1 200 ℃区间与875~600 ℃区间是脆性区,材料不容易发生塑性变形,其消化应力的能力很小。在塑性区材料所受拉应力超过高温强度,材料也能通过塑性变形来消化拉应力,而不产生热装热送裂纹[14-16]。
板坯单纯空冷时,在875~720 ℃冷却时间内,表层的等效应力(拉应力)已经超过材料的高温强度,且材料正处在低塑性区,这正是产生热送裂纹的原因。模拟证明,冷却速度继续增加,其拉应力值更大。所以,板坯从火焰切割机到进加热炉热装,应该采用堆冷的方式或保温辊道输送,降低冷速,减小连铸坯内外温差,从而降低热应力,使拉应力峰值在高温强度以下,减少表层产生裂纹的可能性。
4 结论
(1) 建立了单个板坯自然空冷时温度场和应力场的分析模型。有限元模拟值具有较高的精度。越靠近板坯中部,具有相同的温降速率。
(2) 铸坯在单独空冷过程中,在宽度和厚度方向温度分布不均,会带来热应力和相变应力分布不均。角部冷却速率虽大,热应力并不大。在低应变速率下, Q345c钢第Ⅲ脆性区出现在600~875 ℃。
(3) 根据热模拟实验测得的热塑性曲线和材料的抗拉极限值曲线以及模拟出的表层应力,板坯单独冷却时,在875~720 ℃,其表面应力超过了高温抗拉强度。
参考文献:
[1] 周娜, 于明, 王丙兴, 等. 中厚板控冷过程热-应力-组织藕合模拟分析[J]. 中国冶金, 2008, 18(4): 28.
ZHOU Na, YU Ming, WANG Bingxing, et al. Coupling of thermo, mechanical and microstructure FEM simulation and analysis of plate control cooling[J]. China Metallurgy, 2008, 18(4): 28.
[2] 蔡正, 王国栋, 刘相华, 等. 热轧带钢在冷却中温度与相变的耦合解析[J]. 塑性工程学报, 2000, 7(2): 16-19.
CAI Zheng, WANG Guodong, LIU Xianghua, et al. Acoupling analysis of temperature and phase transformation during cooling of hot-rolled strip[J]. Journal of Plasticity Engineering, 2000, 7(2): 16-19.
[3] 李长生, 何晓明, 刘相华, 等. 固相板坯空冷过程温度场有限元分析[J]. 东北大学学报: 自然科学版, 2000, 21(4): 427-428.
LI Changsheng, HE Xiaoming, LIU Xianghua, et al. Finite element analysis for temperature field of the solid slab during air-cooling[J]. Journal of Northeastern University: Natural Science, 2000, 21(4): 427-428.
[4] 余万华, 张中平. 热轧钢板在加速冷却时的温度模型[J]. 北京科技大学学报, 2005, 27(5): 567-570.
YU Wanhua, ZHANG Zhongping. Temperature model of hot rolled strips in accelerate cooling process[J]. Journal of University of Science and Technology Beijing, 2005, 27(5): 567-570.
[5] Hamouda A M, Sulaiman S, Lau C K. Finite element analysis on the effect of workpiece geometry on the quenching of ST50 steel[J]. Journal of Materials Processing Technology, 2001, 119(1): 354.
[6] 彭良贵, 刘相华, 王国栋. 超快冷却条件下温度场数值模拟[J]. 东北大学学报: 自然科学版, 2004, 25(4): 360-362.
PENG Lianggui, LIU Xianghua, WANG Guodong. Simulation on temperature field ultra fast cooling[J]. Journal of Northeastern University: Natural Science, 2004, 25(4): 360-362.
[7] 王海儒, 万爱霞, 王颖旺, 等. 高线穿水冷却过程温度场的数值模拟[J]. 燕山大学学报, 2004, 29(6): 476-479.
WANG Hairu, WAN Aixia, WANG Yingwang, et al. Numerical simulation on temperature field of water cooling process of high speed wire[J]. Journal of Yanshan University, 2004, 29(6): 476-479.
[8] 俞昌铭. 热传导及其数值分析[M]. 北京: 中国工业出版社, 1981: 51-58.
YU Changming. Heat conduction and numerical analysis[M]. Beijing: Chinese Industry Publishing Company, 1981: 51-58.
[9] 王宝同, 王邦文, 贾爱红, 等. 中厚板控冷过程三维温度场的数值模拟[J]. 冶金设备, 2005(6): 14-17.
WANG Baotong, WANG Bangwen, JIA Aihong, et al. Numerical simulation to the three-dimension temperature field of medium steel plate during control-cooling with water[J]. Metallurgical Equipment, 2005(6): 14-17.
[10] Lin H T, Huang S F. Flow and heat transfer of plane surface moving in parallel and reversely to the free stream[J]. Int J Heat Mass Transfer, 1994, 37(2): 333-336.
[11] 马交成. 连铸坯凝固过程传热模型与热应力场模型的研究及应用[D]. 沈阳: 东北大学信息科学与工程学院, 2009: 13-23.
MA Jiaocheng. Research and application of heat transfer model and thermal stress model in solidification process of billet continuous casting[D]. Shenyang: Northeastern University. College of Information Science and Engineering, 2009: 13-23.
[12] Kemp I P. Model of deformatoin and heat transfer in hot rolling of bars and sections[J]. Iron and Steel Making, 1990, 17(2): 139.
[13] Thomas B G, Samarasekera I V, Brimacombe I K. Investigation of panel crack formation steel ingot: PartⅡ off Corner panel crack[J]. Metallurgical Transactions B, 1988, 19B(4): 289.
[14] YU Hailiang, LIU Xianghua, LI Changsheng. Behavior of transversal crack on slab corner during VH rolling processes[J]. Journal of Iron and Steel Research International, 2006, 13(6): 31.
[15] Yu C H, Suzuki M, Shibata H, et al. Simulation of crack formation on solidifying steel shell in continuous casting mold[J]. ISIJ International, 1996, 36(Suppl): S159-170.
[16] Toru K A T O, Yoshiki I T O. Prevention of slab surface transverse cracking by microstructure control[J]. ISIJ International, 2003, 43(11): 1742-1750.
(编辑 邓履翔)
收稿日期:2012-06-06;修回日期:2012-09-04
基金项目:湖南省科学技术厅科技计划项目(2011GK3147)
通信作者:王生朝(1970-),男,河南南阳人,博士研究生,副教授,从事材料加工等研究;电话:0731-22183831;E-mail: super_wsz @163.com