Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 23(2013) 3816-3821
Corrosion of NiFe2O4-10NiO-based cermet inert anodes for aluminium electrolysis
Han-bing HE, Yuan WANG, Jia-ju LONG, Zhao-hui CHEN
School of Metallurgy and Environment, Central South University, Changsha 410083, China
Received 30 December 2012; accepted 28 April 2013
Abstract: NiFe2O4-10NiO-based cermet inert anodes for aluminium electrolysis were prepared and their properties were investigated in a lab-scale electrolysis cell. The results show that the inert anodes exhibit good performance during electrolysis in molten salt cryolite at 960 °C, but according to the analyses of phase compositions and microstructures through XRD, SEM/EDX and metallographic analysis, the metal in the anodes is preferentially corroded and many pores are produced on the anode surface after electrolysis. The preferential dissolution of Fe in the NiFe2O4 phase may lead to the non-uniform corrosion of NiFe2O4 grains. Moreover, a dense protective layer of NiFe2O4-NiAl2O4-FeAl2O4 is formed on the anode surface, which originates from the reaction of Al2O3 dissolved in the electrolyte with NiO or FeO, the annexation of NiFe2O4-NiAl2O4-FeAl2O4 to NiO and volume expansion. Thus, the dense NiFe2O4-NiAl2O4-FeAl2O4layer inhibits the metal loss and ceramic-phase corrosion on the surface of the cermet inert anodes.
Key words: NiFe2O4-10NiO; aluminium electrolysis; inert anode; cermet; corrosion
1 Introduction
At present, much research has been conducted to find an appropriate material as an inert anode [1-4] NiFe2O4-10NiO-based cermets, which have desirable properties of both metals and ceramics, good resistivity against corrosion in molten cryolite and a relatively high electrical conductivity. NiFe2O4-10NiO-based cermets are thus promising materials in inert anodes for aluminium electrolysis [5-7].
The corrosion mechanisms of copper, nickel and nickel ferrite have been examined in recent years. CHIN et al [8] found that the electrolyte is close to saturation with respect to these impurities, and the rate-determining step of anode corrosion process is the alloying of the species into aluminium, where the stability of elements is in the order of Ni>Fe>Cu.
LUO et al [9] observed the electrical conduction mechanism of nickel ferrite that Fe3+ is much more easily corroded by the electrolyte during electrolysis. The corrosion mechanism is as follows:
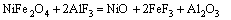 (1)
(1)
LIU et al [10] examined the nickel ferrite spinel as an inert cermet anode for aluminium electrolysis, and found that the chemical corrosion is 0.18% solubility of NiO in Na3AlF6 melt containing 5% Al2O3 (mass fraction) and 0.003% Fe2O3. The electrochemical corrosion reaction is as follows:
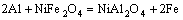 (2)
(2)
LORENTSEN and THONSTAD [11] and OLSEN and THONSTAD [12] reported the formation of a dense layer with about 50 μm in thickness after 50 h of electrolysis, and suggested that it resulted mainly from the formation of aluminates such as FeAl2O4. LIU et al [13] reported the dense layer of about 100 μm in thickness after 24 h electrolysis, and LIU et al [14] reported the dense layer of about 150 μm in thickness after 40 h electrolysis. However, the preferential dissolution of Fe and the formation mechanism of a dense protective layer should be investigated.
In this work, a NiFe2O4-10NiO-based cermet was examined, and the operational performance of a cup-shaped cermet inert anode was evaluated in a lab- scale electrolysis cell that consisted of metal Ni, Cu or Ni/Cu and ceramic NiFe2O4-10NiO. The corrosion behaviour and mechanism in Na3A1F6-Al2O3 melts were also investigated.
2 Experimental
2.1 Preparation of samples
Nickel powder (99.9%, Tianjin, China), copper powder (99.9%, Tianjin, China), NiO (99%, Jinchuan, China) and Fe2O3 (99%, Qidong, China) were of all reagent grade. NiFe2O4-10NiO-based cermet samples were prepared by an isostatic pressing-sintering process [15-17]. Fe2O3 and NiO were employed as raw materials, which were ball-milled in distilled water for 2 h. The mixture was dried at 90 °C for 12 h and then calcined at 1200 °C for 4 h in air. The calcined samples were cooled. The X-ray diffraction patterns showed that the calcined powders consisted of NiFe2O4 and NiO phases. Metal nickel powders or Ni-Cu powders were added to the calcined powder and the mixture was again ball-milled. Finally, the mixture was uniaxially pressed into cylindrical blocks (about 20 mm in diameter and 40 mm in thickness) at 200 MPa and sintered at 1300 °C for 4 h in a nitrogen atmosphere with an original oxygen partial pressure of 100×10-6 to obtain the desired cermet samples.
2.2 Electrolysis
The electrolyte was composed of Na3AlF6 (99%, Shanghai, China), AlF3 (98%, Shanghai, China), CaF2 (98.5%, Tianjin, China) and Al2O3 (98%, Tianjin, China). The exact composition was 5% CaF2, 7.43% A12O3 and balanced cryolite (CR=2.3). All of the components were dried at 120 °C for 48 h to remove any water before using. 60 g of metal aluminium was placed in the bottom of a cell as the cathode. The cell was then heated to the required temperature of 960 °C and stored for 2 h before the anode was immersed in it at a depth of 20 mm. A distance of 3 cm was maintained between the anode and the cathode, and the current density of 1.0 A/cm2 was adjusted based on the bottom area of the anode. Al2O3 was added at 15 min intervals based on the electrolytic consumption rate at 80% cathode current efficiency.
After electrolysis, the anode was raised out of the melt to prevent the reduction of anode material by the dissolved metal. The cell was cooled with the anode laid above the electrolyte. Some of the electrolyte samples taken during electrolysis were dissolved in HClO4 solution, and the anode was sectioned, polished and analyzed with XRD and SEM/EDX. The phase compositions of electrolyte and cermet were identified by X-ray diffraction analysis using a Philips PW1390 X-ray diffractometer with Cu Kα radiation. The microstructure was analyzed with a JSM25600LV scanning electron microscope and an XJP26A metallographic microscope.
3 Results and discussion
3.1 Corrosion of inert cermet anodes
Figure 1 shows the metallographic images of 17Ni/(NiFe2O4-10NiO) anode after electrolysis. The anode shown in Fig. 1(a) is an intrinsic layer. The white part is metal Ni and the grey part is ceramic NiFe2O4-10NiO. Figure 1(b) shows the presence of many holes and pores, indicating that the metal in the cermet was preferentially corroded, thus decreasing the density of the anode. It is thus clear that the metal phase Ni was preferentially leached [18].
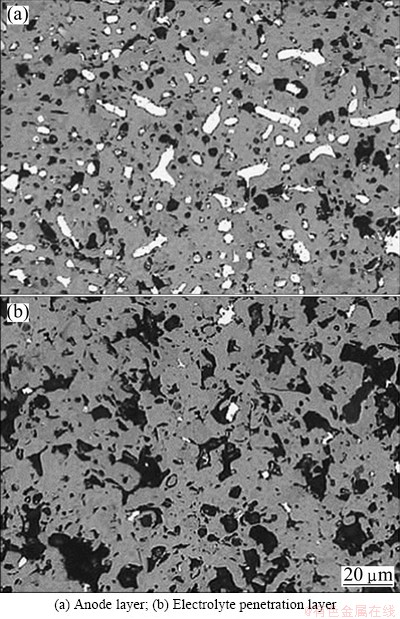
Fig. 1 Metallographic images of anode after electrolysis
The 17Ni/(NiFe2O4-10NiO) inert cermet anode was sectioned and a corroded layer was revealed on the anode surface. The X-ray diffraction patterns of corroded layer are shown in Fig. 2. According to Figs. 1 and 2, the corroded layer that formed on the anode surface contained much more NiO and less Ni than the non-corroded anode layer, probably due to the preferential oxidation and dissolution of Ni. This resulted in the formation of many pores and allowed the electrolyte to penetrate into the interior of the anode.
The pores occurred during the electrochemical dissolution of metal phase when the anode was polarized or when the metal phase was oxidized, allowing the electrolyte to penetrate into the pores by capillary effect. The relative density of anode was low (only 93.52%) and the metal Ni content was high (17%). To restrain or eliminate the aforementioned factors that diminish the inert anode’s resistance to corrosion, the relative density should be improved and the metal content decreased.
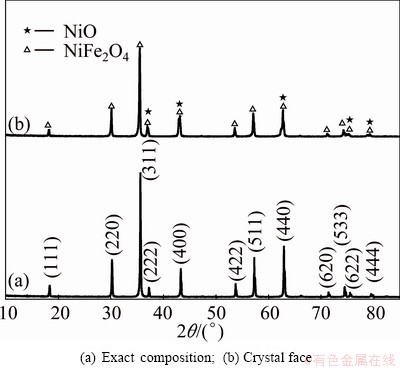
Fig. 2 XRD patterns of corroded anode layer on surface of anode cermet 17Ni/(NiFe2O4-10NiO)
The post-testing SEM images of 10Cu/(NiFe2O4- 10NiO) and 10(Ni-Cu)/(NiFe2O4-10NiO) anodes are presented in Fig. 3. The loss of Cu in the 10Cu/(10NiO- NiFe2O4) cermet anode was severe, with about 300 μm in thickness of metal being lost from the surface layer.
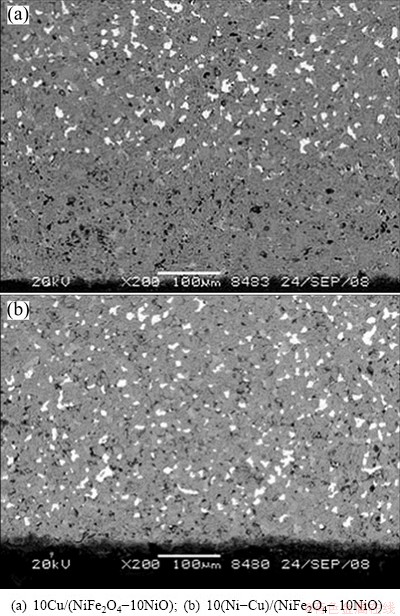
Fig. 3 Backscattered SEM images on bottom of cermet inert anode
In contrast, only 50 μm in thickness of Cu disappeared from the surface layer of 10(Ni-Cu)/(NiFe2O4-10NiO). According to the SEM images, the metal in the inert anode was preferentially corroded during electrolysis and many pores were produced, but the process had a smaller effect on the 10(Ni-Cu)/(NiFe2O4-10NiO) anode, implying that the corrosion resistance of cermet inert anode doped with a Ni-Cu alloy was better than that of the anode doped with Cu.
3.2 Preferential corrosion of Fe
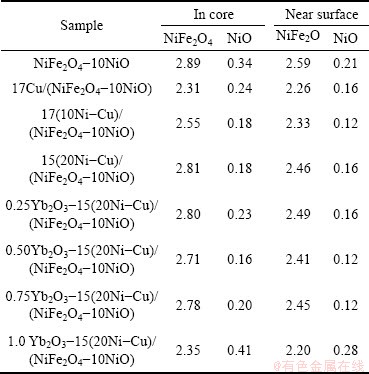
Table 1 shows the results of energy dispersive X-ray spectroscopy in the core and on the surface of the anode after anodic electrolysis at 960 °C for 10 h. The average mole ratio of Fe to Ni was obtained by scanning five points in the region. The mole ratio of Fe to Ni of surface layer was lower than that of the core region, and the mole ratio of Fe to Ni in the NiFe2O4 phase was much higher than 2. These phenomena suggest that the preferential corrosion of Fe in the NiFe2O4 and NiO phases during electrolysis may be an interaction result of chemical corrosion and electrochemical corrosion.
Table 1 Fe to Ni mole ratios of NiFe2O4 and NiO phases distributed in core and near surface after anodic electrolysis at 960 °C for 10 h
The selective electrochemical dissolution of Fe2+, Fe3+ and Ni2+ in the NiFe2O4 phase is shown in Eqs. (3)-(5). The electrochemical corrosion also enhanced the vacancy concentration of crystal structure and provided Al3+ for the cathodic reaction.
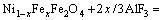
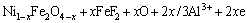 (3)
(3)
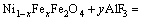
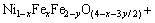
 (4)
(4)
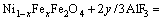
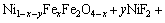
 (5)
(5)
In the chemical corrosion, because of the higher saturated concentration of FeO relative to Fe2O3 in the electrolyte [19], the Fe2+ in the NiFe2O4 phase may dissolve more easily than the Fe3+. The dissolution reactions of two substances are given in Eqs. (6) and (7), respectively.
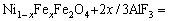
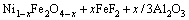 (6)
(6)
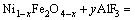
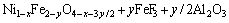 (7)
(7)
3.3 Formation mechanism of dense NiFe2O4- NiAl2O4-FeAl2O4 layer on surface of cermet inert anodes
Figure 4(a) indicates that although NiFe2O4 was precipitated on the surface of the NiO phase, the NiFe2O4-NiO phase interface was very clear. Figure 4(b) shows that after 10 h of electrolysis the NiO phase was gradually dismembered and engulfed by the NiFe2O4 phase, and the NiFe2O4-NiO phase interface became indistinct. To further understand why this occurred, the microstructure of anode after 40 h of electrolysis was investigated. Figure 5 shows that a 80 μm-thick dense layer without NiO or a metal phase appeared on the surface of anode. An energy dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (EDX) of anode surface demonstrated that this dense layer contained Al but not Na and F, which suggested that the disappearance of NiO was related to the interaction of NiFe2O4 phase and Al2O3 dissolved in the electrolyte. Figure 6 shows the XRD pattern of the dense layer on the surface of the 15(20Ni-Cu)/ (NiFe2O4-10NiO) cermet after electrolysis for 40 h. As diffraction peaks of NiAl2O4 and FeAl2O4 were overlapped, components corresponding to diffraction peaks were NiAl2O4 and FeAl2O4.
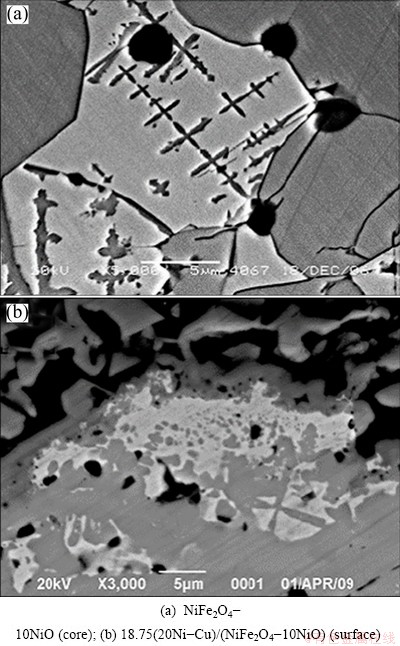
Fig. 4 SEM images of core and surface of NiFe2O4-based cermet after electrolysis at 960 °C for 10 h
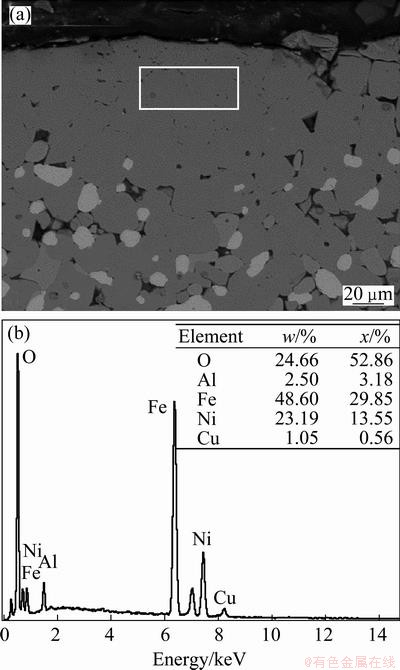
Fig. 5 SEM image (a) and EDX result (b) of 15(20Ni-Cu)/ (NiFe2O4-10NiO) cermet after electrolysis at 960 °C for 40 h
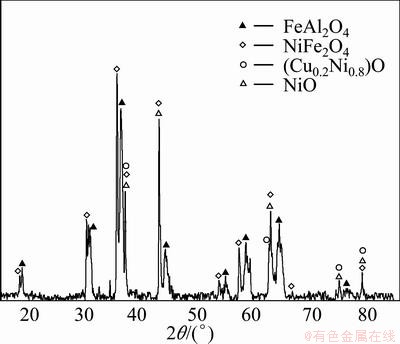
Fig. 6 XRD pattern of dense layer on surface of 15(20Ni-Cu)/ (NiFe2O4-10NiO) cermet after electrolysis for 40 h
Clearly, electrochemical factors caused the formation of dense NiFe2O4-NiAl2O4-FeAl2O4 layer on the surface of inert cermet anodes. In cryolite electrolyte that contained a relatively high concentration of Al2O3, the NiAl2O4 and FeAl2O4 spinel phases formed through the anodic discharge reaction of a complex anion [20] that included oxygen in the NiO-electrolyte and FeO-electrolyte interface (see Eqs. (8) and (9)). At the same time, the Fe2+ in the NiO phase was oxidized by the oxygen generated during electrolysis process and then precipitated on the surface of original NiFe2O4 (see Eq. (10)). Solid-state homogeneous diffusion occurred among NiAl2O4, FeAl2O4 and NiFe2O4. Sequentially, the NiFe2O4 in the NiO phase gradually extended and then connected with the original NiFe2O4 grains, finally the Fe content in the NiO phase decreased.
The density of NiO phase (6.81 g/cm3) was greater than that of NiAl2O4 (4.58 g/cm3), NiFe2O4 (5.37 g/cm3) or FeAl2O4 (4.39 g/cm3) phase. Thus, reactions (8)-(10) transformed materials with a relatively high density into materials with a relatively low density, which suggested that the solid materials expanded in volume. This expansion overcame the porosity caused by the dissolution of metal phase, resulting in the production of dense NiFe2O4-NiAl2O4-FeAl2O4 layer on the anode surface.
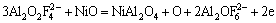 (8)
(8)
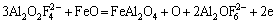 (9)
(9)
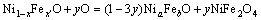 (10)
(10)
where a=(1-x-y)/(1-3y) and b=(x′-2y)/ (1-3y).
4 Conclusions
1) SEM analysis shows that the metal in the inert cermet anodes is preferentially corroded during electrolysis and many pores on the surface are produced. The corrosion resistance of cermet inert anode doped with Ni-Cu alloy is better than that of the anode doped with Cu.
2) In the process of electrolysis, the mole ratio of Fe to Ni in the NiFe2O4 and NiO phases decreases to some extent, and the corrosion dissolution of Fe occurs due to the chemical corrosion and electrochemical corrosion.
3) The gradual disappearance of NiO phase and the formation of a dense NiFe2O4 phase containing Al originated from the NiO phase reaction with Al2O3 in the electrolyte, which produces NiAl2O4 and FeAl2O4 phase. New oxidation of Fe2+ in the NiO phase results in the formation of NiFe2O4 phase. Finally, a dense NiAl2O4-FeAl2O4-NiFe2O4 layer is produced by solid-state homogeneous diffusion and volume expansion.
References
[1] OLSEN E, THONSTAD J. Nickel ferrite as inert anodes in aluminum electrolysis, Part I: Material fabrication and preliminary testing [J]. Journal of Applied Electrochemistry, 1999, 29: 293-299.
[2] TAO Yu-qiang, LIU Jian-yuan, LI Zhi-you, ZHOU Ke-chao, TAN Zhan-qiu. Conductivity and corrosion resistance of 10Cu-(NiFe2O4-10NiO) inert anode doped Yb2O3 or Y2O3 [J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2011, 21(5): 1137-1144. (in Chinese)
[3] ZHOU Ke-chao, TAO Yu-qiang, LIU Bao-gang, LI Zhi-you. Enhanced sintering and molten salt corrosion behavior of nickel ferrite based cermets [J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2011, 21(6): 1348-1358. (in Chinese)
[4] PETERSON R D, RICHARDS N E, TABEREAUX A T. Results of 100 hour electrolysis test of a cermet anode: Operational results and industry perspective [C]//CHRISTIAN M B. Light Metals. Warrendale, PA, UAS: TMS, 1990: 385-393.
[5] RAY S P. Inert anodes for hall cells [C]//MILLER R T. Light Metals. Warrendale, PA: TMS, 1986: 287-298.
[6] OLSEN E, THONSTAD J. The behaviour of nickel ferrite cermet materials as inert anodes [C]//HALE W. Light Metals. Warrendale, PA, USA: TMS, 1996: 249-257.
[7] SADOWAY D R. Inert anodes for the Hall-Heroult cell: The ultimate materials challenge [J]. Journal of the Minerals, Metals and Materials Society, 2001, 53: 34-35.
[8] CHIN P C, SIDES P J, KELLER R. The transfer of nickel, iron, and copper from Hall cell melts to molten aluminum [J]. Canadian Metallurgical Quarterly, 1996, 35: 61-67.
[9] LUO T, WANG Z, YU X. Solubilities of oxides for inert anodes in cryolite–based melts [C]// M. Light Metals. Warrendale, PA, USA: TMS, 2007: 941-943.
M. Light Metals. Warrendale, PA, USA: TMS, 2007: 941-943.
[10] LIU Y, YAO G, LUO H, ZHANG X. Study on the nickel ferrite spinel inert anode for aluminum electrolysis [C]//TRAVIS J G. Light Metals. Warrendale, PA, USA: TMS, 2006: 415-420.
[11] LORENTSEN O A, THONSTAD J. Electrolysis and post-testing of inert cermet anodes [C]//WOLFGANG S. Light Metals. Warrendale PA, USA: TMS, 2002: 443-449.
[12] OLSEN E, THONSTAD J. Nickel ferrite as inert anodes in aluminum electrolysis, Part II: Material performance and long-term testing [J]. Journal of Applied Electrochemistry, 1999, 29: 301-311.
[13] LIU Jian-yuan, LI Zhi-you, TAO Yu-qiang, ZHANG Dou, ZHOU Ke-chao. Phase evolution of 17(Cu-10Ni)-(NiFe2O4-10NiO) cermet inert anode during aluminum electrolysis [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2011, 21(3): 566-572.
[14] LIU Bao-gang, ZHANG Lei, ZHOU Ke-chao, LI Zhi-you, WANG Hao. Electrical conductivity and molten salt corrosion behavior of spinel nickel ferrite [J]. Solid State Sciences, 2011, 13: 1483-1487.
[15] HE Han-bing, ZHOU Ke-chao, LI Zhi-you, HUANG Bai-yun. Effect of BaO addition on electric conductivity of xCu/NiFe2O4-10NiO cermets [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2008, 18(5): 1134-1138.
[16] HE Han-bing, XIAO Han-ning, ZHOU Ke-chao. Effect of additive BaO on corrosion resistance of xCu/10NiO-NiFe2O4 cermet inert anodes for aluminum electrolysis [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2011, 21(1): 102-108.
[17] LI Jie, ZHANG Gang, LAI Yan-qing, ZHANG Yong, TIAN Zhong-liang. Densification and sintering dynamics of 10NiO- NiFe2O4 composites doped with CaO [J]. Journal of Central South University of Technology, 2007, 14(5): 629-632.
[18] STRACHAN D M, KOSKI O, MORGAN L G. Results from a 100-hour electrolysis test of a cermet anode: Material aspects [C]//CHRISTIAN M B. Light Metals. Warrendale, PA, USA: TMS, 1990: 395-401.
[19] DENEK V, GUSTAVSEN O T, OSTVOLD T. Structure of the MF-AlF3-Al2O3 (M=Li, Na, K) melts [J]. Canadian Metallurgical Quarterly, 2000, 39: 153-162.
[20] DEYOUNG D H. Solubilities of oxides for inert anode in cryolite-based melts [C]// MILLER R E. Light Metals. Warrendale, PA, USA: TMS, 1986: 299-307.
铝电解用NiFe2O4-10NiO基金属陶瓷惰性阳极的耐腐蚀性能
何汉兵,王 原,龙佳驹,陈照辉
中南大学 冶金与环境学院,长沙 410083
摘 要:制备铝电解用NiFe2O4-10NiO基金属陶瓷惰性阳极,并在实验室电解槽中考察其电解腐蚀性能。结果表明,电解过程中虽然惰性阳极在960 °C熔盐电解质中表现出优异的耐腐蚀性能,但采用XRD、SEM/EDX和金相分析其物相组成和微观结构后发现,电解后阳极中的金属相发生了优先腐蚀,在阳极表面产生大量孔洞。NiFe2O4相中的Fe元素的优先溶解可能导致NiFe2O4晶粒的不均匀腐蚀。溶解在电解液中的Al2O3与阳极中的NiO 或FeO发生反应生成的NiFe2O4-NiAl2O4-FeAl2O4 相对 NiO相的吞并以及体积膨胀,阳极表面形成致密的NiFe2O4-NiAl2O4-FeAl2O4保护层。因此,致密的NiFe2O4-NiAl2O4-FeAl2O4保护层可以阻挡阳极表面金属相的损失和陶瓷相的腐蚀。
关键词:NiFe2O4-10NiO;铝电解;惰性阳极;金属陶瓷;腐蚀
(Edited by Xiang-qun LI)
Foundation item: Project (2012FJ6123) supported by the Project of Science and Technology of Hunan Province, China; Project supported by Post-Doctoral Foundation of Central South University, China; Project (CL12100) supported the Undergraduate Innovative Training of Central South University, China; Project (2282013bkso13) supported by Free Exploration Plan of Central South University, China
Corresponding author: Han-bing HE; Tel: 86-731-88830216; Fax: 86-731-88710171; E-mail: hehanbinghhb@163.com
DOI: 10.1016/S1003-6326(13)62934-9