
Microstructure evolution of Cu-Pb monotectic alloys during directional solidification
CUI Hong-bao(崔红保), GUO Jing-jie(郭景杰), SU Yan-qing(苏彦庆),
DING Hong-sheng(丁宏生), WU Shi-ping(吴士平), BI Wei-sheng(毕维生),
XU Da-ming(徐达鸣), FU Heng-zhi(傅恒志)
School of Materials Science and Engineering, Harbin Institute of Technology, Harbin 150001, China
Received 30 September 2005; accepted 23 January 2006
Abstract: Planar, cellular and dendrite morphologies were observed at different concentrations in the directional solidification of Cu-Pb monotectic alloys. In Cu-Pb hypomonotectic alloys, the directional solidification microstructure changes from columnar dendrite to the irregular rod composite structure with increasing lead content and growth rate. In Cu-Pb hypermonotectic alloys, the structure changes from the band structure and elongated droplets to irregular rod composite structure with increasing growth rate. The range of composition of forming the rod composite structure around the monotectic points increases with the increasing growth rate. The transient morphology of Cu-Pb alloys in the directional solidification was obtained. The solid/liquid interface of Cu-Pb alloys presents planar and the second liquid droplets are pushed by growing front under the high temperature gradient. With increasing growth rate or decreasing temperature gradient the planar interface becomes unstable and the cellular structures with L2 phase at the cell boundaries are developed.
Key words: copper-lead monotectic alloy; directional solidification; transient morphology; microstructure evolution
1 Introduction
Monotectic alloy is an important class of alloy whose binary phase diagram has a miscibility gap, in which the original single liquid will decompose into two distinct immiscible liquids within a few seconds. In the normal gravity field, a serious gravity segregation will happen due to the sedimentation of the heavier phase. This kind of structure has no any valuable application. But many immiscible alloys having an aluminum or copper matrix with homogeneous structure or fibrous arrangement of the second phases, lead, bismuth and indium are regarded as useful materials for light and soft in situ superconductors[1], wear-resistant[2-6], electrical contact materials[7] and so on.
However, some good physical, chemical and mechanical properties are present with the microstructure of the fibrous or dispersion of L2 phase in the matrix. Directional solidification is one of the most widely used methods for production of high quality components, as it permits a precise control of the temperature gradient and growth rate to obtain a desirable structure with the fibrous or dispersion of L2 phase.
Directional solidification of monotectic alloys can be grouped into two families, one gives a regular array of uniform parallel fibrous in the matrix, for example, Al-Bi[8], Al-In[9-11], the other shows an irregular morphology of branching fibre of variable radius. Cu-Pb alloys belong to the latter[12]. The formation mechanism of the monotectic composite structure has been discussed from the viewpoint of energy balance between the three phases involved, solid S phase, liquid phases L1 and L2. CHADWICK[13] and LIVINGSTONE and CLINE[14] proposed that a monotectic composite structure, similar to the eutectic structure, can be achieved if the liquid phase L2 separated at the monotectic reaction can wet the solid phase formed in the monotectic reaction, i.e. 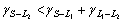 (where
(where 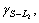
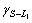 and
and 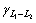 are the interfacial energies between S and L2, S and L1, L1 and L2 respectively). CAHN[15] pointed out that, however, even if the energy balance is
are the interfacial energies between S and L2, S and L1, L1 and L2 respectively). CAHN[15] pointed out that, however, even if the energy balance is 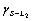 >
>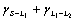 and L2 phase can not wet the solid S, composite growth accompanied by the incorporation of the L2 into growing S is possible at higher growth rates. DERBY and FAVIER[16] argued that there is no difference in the interfacial energy balances between Al-In regular monotectic alloys and Cu-Pb irregular nomotectic alloys. Therefore, the mechanism of the directional monotectic solidification is still not clear.
and L2 phase can not wet the solid S, composite growth accompanied by the incorporation of the L2 into growing S is possible at higher growth rates. DERBY and FAVIER[16] argued that there is no difference in the interfacial energy balances between Al-In regular monotectic alloys and Cu-Pb irregular nomotectic alloys. Therefore, the mechanism of the directional monotectic solidification is still not clear.
The microstructure of directional solidification of monotectic alloys is influenced by microsegregation and thermal profiles ahead of the solid-liquid interface. These structures influence the mechanical properties of the final product. Hence, the instabilities of a planar interface and its development into a periodic array of cells or dendrites have received particular attention from the metallurgists. In the present work, Cu-Pb monotectic alloy was directionally solidified over a wide range of composi- tions and the evolution of transient morphology under the high temperature gradient was observed.
2 Experimental
2.1 Alloy preparation
Alloys were prepared by melting 99.5%Cu(mass fraction, the same below if not mentioned) and 99.9%Pb in the high-purity Al2O3 crucible with an induction furnace which was evacuated, and backfilled with 5×104 Pa argon. According to the phase diagram of copper-lead shown in Fig.1, the alloys were heated to the single liquid phase and held more than 5 min to be homogenized. Then the molten alloy was directionally solidified at a growth rate of 10 mm/s so that the no macrosegregations appears in the master billets. Samples with 5 mm in diameter and 105 mm in length were machined from the ingots. Alloy compositions studied ranged from Cu-25%Pb to Cu-50%Pb.
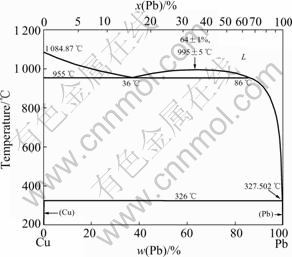
Fig.1 Phase diagram of copper-lead[17]
2.2 Directional solidification of experimental alloys
The samples were placed in the graphite crucible under an argon atmosphere and the entire sample was remelted in the hot zone of the furnace, as shown in Fig.2. The directional solidification was performed by moving the crucible, which was screw-driven, with a wide range of withdrawal velocities available. A liquid-metal coolant of Ga-In-Sn alloy with a melting point of 5 ℃ was used to enhance the heat transfer within the graphite crucible containing the specimen and the chill. A baffle was used as an insulator between the heating and the cooling zone. A thermocouple was positioned in the center hole of the specimen to determine the temperature gradient during the directional solidification. The temperature gradient measured was 15 K/mm and 40 K/mm at the steady directional solidification and the initial growth stage, respectively. The samples were sectioned both longitudinally and transversely after the directional solidification and polished. The optical micrograph was viewed after removing some copper matrix with nitric acid.
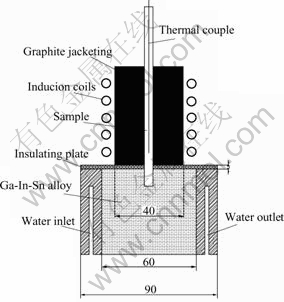
Fig.2 Schematic diagram of directional solidification apparatus
3 Results and discussion
3.1 Hypomonotectic alloys
The solidification structures of Cu-25%Pb hypomo- notectic alloy at different growth rates are shown in Fig.3. The dendrite structures are formed from the melt during the solidification process. The L2 phase precipitates at monotectic reaction, and disperses between the dendrites because of the limited solubility of Pb in the copper matrix. At low growth rate, there is enough time to coarsen the dendrite, and the lead-rich liquid L2 phase droplets can not wet the solid matrix, (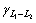 = 0.02 J/m2,
= 0.02 J/m2,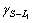 =0.26 J/m2 and
=0.26 J/m2 and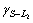 =0.35 J/m2, hence,
=0.35 J/m2, hence, 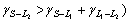 and aggregate between the dendrites. Some coarsening liquid droplets are elongated along the primary of the cellular or dendrite which grows directionally, as shown in Fig.3(b). The microstructure of hypomonotectic alloys depends on the morphology of the growing solid phase which shapes the L2 liquid during the growth at a constant rate. In this interpretation, the solid dominates in the formation of the structure and the L2 phase just fills the remaining volume. At higher growth rates, where the columnar crystal is fully developed, as shown in Fig.3(c), the L2 liquid becomes interconnected through the whole structure, as observed in Fig.3(d). It is also shown that the secondary dendrite arms and the pronounced crystallographic directions become evident with further increases in growth rates. With the increasing lead content, the monotectic growth front shows more irregular cells, the lead-rich liquid L2 separated through the monotectic reaction is incorporated into the cell boundaries, forming the irregular shape rod-like L2 composite, as shown in Fig.4. With the increasing growth rate, the rod composite becomes finer, as shown in Fig.5.
and aggregate between the dendrites. Some coarsening liquid droplets are elongated along the primary of the cellular or dendrite which grows directionally, as shown in Fig.3(b). The microstructure of hypomonotectic alloys depends on the morphology of the growing solid phase which shapes the L2 liquid during the growth at a constant rate. In this interpretation, the solid dominates in the formation of the structure and the L2 phase just fills the remaining volume. At higher growth rates, where the columnar crystal is fully developed, as shown in Fig.3(c), the L2 liquid becomes interconnected through the whole structure, as observed in Fig.3(d). It is also shown that the secondary dendrite arms and the pronounced crystallographic directions become evident with further increases in growth rates. With the increasing lead content, the monotectic growth front shows more irregular cells, the lead-rich liquid L2 separated through the monotectic reaction is incorporated into the cell boundaries, forming the irregular shape rod-like L2 composite, as shown in Fig.4. With the increasing growth rate, the rod composite becomes finer, as shown in Fig.5.
3.2 Hypermonotectic alloys
The liquid L2 is the first precipitated phase from the solidification of hypermonotectic alloys whose lead content is beyond 36%. Generally, once the second phase droplets separate from the immiscible gap, a spherical shape presents, and then they will collide and coagulate rapidly and become much coarser. They will settle and pile up successively because of the density difference between the second phase and the parent liquid. As solidification proceeds, the coalesced L2 phase finally covers the solid/liquid interface if the growth front maintains flat at a slow growth rate. After L2 phase completely covers the interface, the monotectic reaction that requires the coexistence of all the three phases is prohibited by the lead-rich L2 phase layer. This situation leads to a decrease and poverty of lead content of L1 liquid above the lead-rich L2 phase layer, with the withdrawal proceeding, copper solid will nucleate in the interface, the repetition mentioned above will result in the banded structure found in the directional solidification, as shown in Fig.6. Even though the growth rate is increased , the elongated droplets form instead of rod because of high lead concentration, as shown in Fig.7.
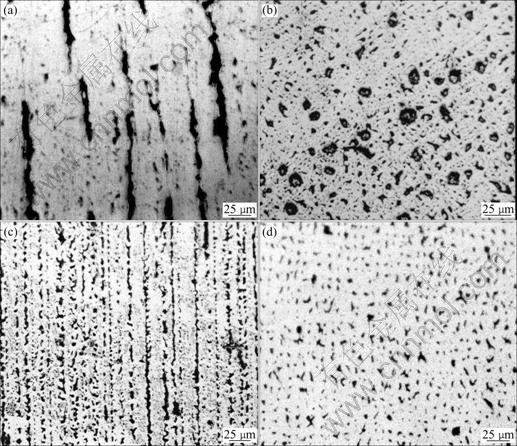
Fig.3 Directional solidification structures of Cu-25%Pb at different growth rates: (a) Longitudinal section of sample at growth rate of 200 μm/s; (b) Transverse section of sample at growth rate of 200 μm/s; (c) Longitudinal section of sample at growth rate of 400 μm/s; (d) Transverse section of sample at growth rate of 400 μm/s
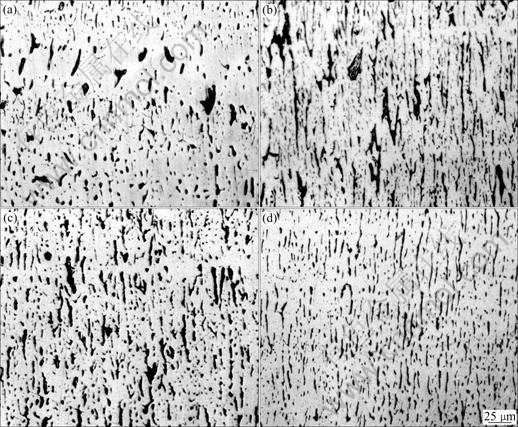

Fig.4 Directional solidification structures of Cu-34%Pb at various growth rates: (a)100 μm/s; (b) 200 μm/s; (c) 300 μm/s; (d) 400 μm/s
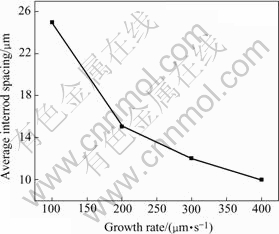
Fig.5 Relationship between average interrod spacing and growth rate of hypomonotectic alloy
So it is necessary to decrease the concentration and

Fig.6 Band structure of Cu-50%Pb directionally solidified at growth rate of 33 μm/s
increase the growth rate in front of solid/liquid interface to avoid occurrence of the band structure and elongated droplets. With the increasing growth rate, the monotectic growth front shows irregular cells which pass by the lead-rich L2 separated from L1, and these liquid droplets are too late to coarsen and incorporated into cell boundaries, forming the irregular shape rod-like L2 composite, as shown in Fig.8. With the increasing growth rate, the average interrod spacing will decrease, as shown in Fig.9.
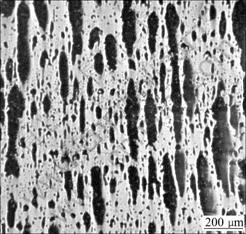
Fig.7 Elongate droplets structure of Cu-50%Pb at growth rate of 500 μm/s
3.3 Transient morphology of solid/liquid interface
Generally speaking, the irregular type of monotectic structure has a similar mechanism of formation as faceted/non-faceted eutectics except one product phase at the monotectic reaction is a liquid which brings about many interesting microstructures. This liquid L2 phase,
precipitating at the solidification front can not maintain the final morphology during the precipitation process because of the strong tendency of the growing solid phase to shape the L2 phase, not only at the moment of quenching but also during the growth at a constant growth rate, therefore, when considering the morphology evolution of the solid/liquid interface, primary interest should be focused on the growth of solid phase, not liquid L2 phase. Experiments were carried out to examine the shape of the solidification front.
At the initial growth stage, the bottom of the sample is just contacted with the liquid melt Ga-In-Sn alloy, the transient temperature gradient is the highest for the whole directional solidification process, as shown in Fig.10, where Tm is the monotectic temperature and TL is the liquid melt temperature. Therefore the growth front maintains a flat interface, and lead-rich L2 phase separated through the monotectic reaction is pushed by the solid/liquid interface and collected in nodes, as shown in Fig.11. Meantime, Marangoni convection caused by the interfacial tension gradient is also contributed to the liquid droplets away from the solid/liquid interface. The droplets pushing will not continue until the temperature gradient decreases and Marangoni convection can not overcome the Stokes motion resulted from the gravity. At the moment, the planar interface becomes unstable and the cellular structures of L2 phase at the cell boundaries are developed, as shown in Fig.12(a). However, when the growth rate increases, the ratio of temperature gradient to growth rate value decreases and irregular finer rod composite forms even though the temperature gradient is high, as shown in Fig.12(b).
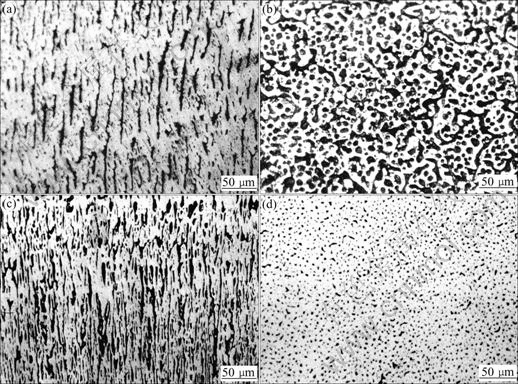
Fig.8 Directional solidification structures of Cu-43%Pb at different growth rates: (a) Longitudinal section of sample at growth rate of 200 μm/s; (b) Transverse section of sample at growth rate of 200 μm/s; (c) Longitudinal section of sample at growth rate of 400 μm/s; (d) Transverse section of sample at growth rate of 400 μm/s
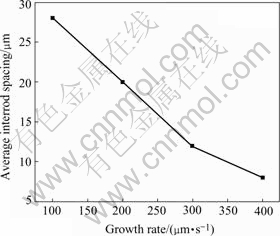
Fig.9 Relationship between average interrod spacing and growth rate of hypermonotectic alloy
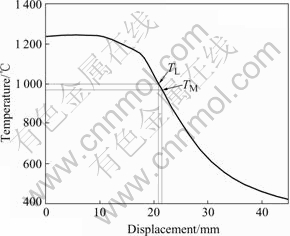
Fig.10 Determination for temperature gradient of Cu-30%Pb at growth rate of 200 μm/s
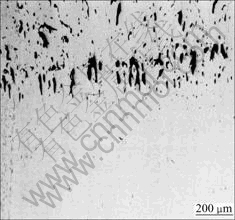
Fig.11 Planar solidification structure of Cu-30%Pb at growth rate of 200 μm/s under 40 K/mm temperature gradient
3.4 Microstructure evolution of Cu-Pb monotectic alloys during directional solidification
The microstructure evolution of Cu-Pb monotectic alloys during directional solidification mainly depends on the composition and the growth rate and is summarized, as shown in Fig.13. The major aspects of these experimental results that call for discussion are the range of compositions over which composite structures are observed. The results clearly demonstrate that the range of compositions of forming the rod composite structure around the monotectic points increases with the increasing growth rate.
The microstructure of hypomonotectic alloys presents the dendrite structure. With the increasing growth rate, the dendrite becomes finer and the content of lead required to form rod composite decreases. For the hypermonotectic alloys, the lead droplets and band structure form at low growth rate. With the increasing growth rate, competitive growth between the composite structure and liquid lead drops occurs, the results of this competitive growth can be seen clearly in Fig.7, where an increase in growth velocity results in the composite interface overtaking the large droplets. The band structures change to the elongated lead droplets at the relative high concentration and the lead droplets become the finer rod composite at the relative low concentration. The existence of a large composition range of composite structure at high growth rate is significant. High growth rates are attractive because they lead to very fine structures which usually improve the properties. Meantime, the short processing time can be obtained at high growth rates. It can be concluded from our experimental results that the fine rod composite structure will be obtained if the specimens with compositions ranging from 34% to 43% are drawn at a speed above 400 μm/s.
4 Conclusions
1) Directional solidification microstructure of Cu-Pb hypomonotectic alloys changes from columnar dendrite to the irregular rod composite structure with the increasing lead content and the growth rate.
2) The transition of Cu-Pb hypermonotectic alloys from the band structure and elongated droplets to the irregular rod composite structure is observed with the increasing growth rate. The range of compositions of forming the rod composite structure around the monotectic points increases with increase of the growth rate.
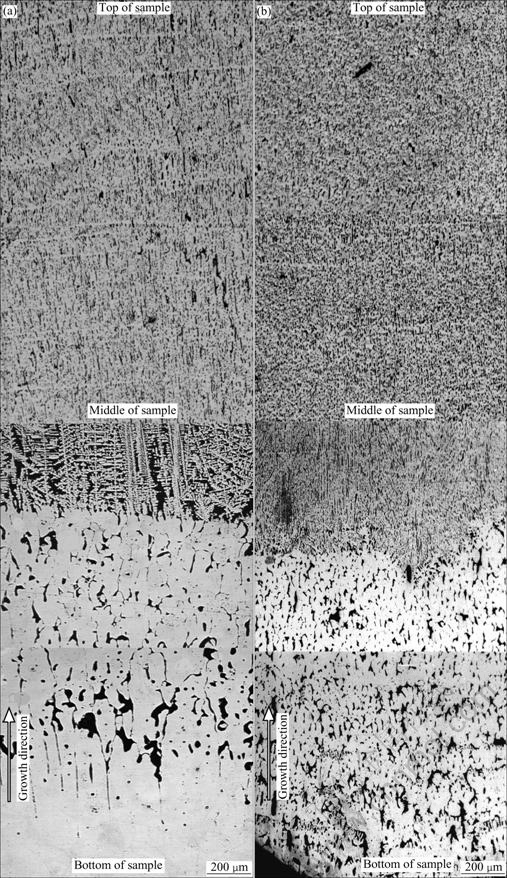
Fig.12 Directional solidification structures of Cu-36%Pb at different growth rates: (a) 200 μm/s; (b) 400 μm/s
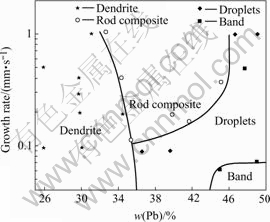
Fig.13 Microstructure evolution of Cu-Pb during directional solidification (arrow marks monotectic composition)
3) The transient morphology of directional solidification microstructure of Cu-Pb alloys is obtained. The solid/liquid interface of Cu-Pb alloys presents planar and the second liquid droplets are pushed by the growth front under a high temperature gradient. With the increasing growth rate or the decreasing temperature gradient the planar interface becomes unstable and the cellular structures of L2 at the cell boundaries are developed.
References
[1] FUJII H, KIMURA T, KITAGUCHI H, KUMAKURA H, TOGANO K, MOHRI M. Fabrication of uniform Al-Pb-Bi monotectic alloys under microgravity utilizing the space shuttle: microstructure and superconducting properties [J]. Journal of Materials Science, 1995, 30(13): 3429-3434.
[2] WANG Cui-ping, LIU Xing-jun, OHNUMA I, KAINUMA R, ISHIDA K. Thermodynamic assessment of the Cu-Ni-Pb system [J]. CALPHAD, 2000, 24(2): 149-167.
[3] BUCHANAN V E, MOLIAN P A, SUDARSHAN T S, AKERS A. Frictional behavior of non-equilibrium Cu-Pb alloys [J]. Wear, 1991, 146(2): 241-256.
[4] ZHU Min, ZENG Mei-Qin, ZHANG Yao, OUYANG Liu-zhang, LI Bai-lin. Microstructure and wear properties of Al-Pb-Cu alloys prepared by mechanical alloying [J]. Wear, 2002, 253(7-8): 832-838.
[5] KIM H M, KIM T S, SURYANARAYANA C, CHUN B S. Microstructure and wear characteristics of rapidly solidified Al-Pb-Cu alloys [J]. Materials Science & Engineering A (Structural Materials: Properties, Microstructure and Processing), 2000, A287(1): 59-65.
[6] SUN Da-ren, CAO Zhan-yi, LIU Yong-bing. Effect of plastic deformation on microstructure and properties of stir cast Al-Pb bearing alloy [J]. Materials Science and Technology, 2003, 19(1): 43-47.
[7] STOBRAWA J, CIURA L, RDZAWSKI Z. Rapidly solidified strips of Cu-Cr alloys [J]. Scripta Materialia, 1995, 34(11): 1759-1763.
[8] GRUGEL R N, HELLAWELL A. The occurrence of aligned microstructures in directionally solidified aluminum-bismuth alloys [J]. Metall Trans A, 1982, 13(3): 493-495.
[9] KAMIO A, KUMAI S, TEZUKA H. Solidification structure of monotectic alloys [J]. Materials Science & Engineering A, 1991,146(1-2): 105-121.
[10] HAYES L J, ANDREWS J B. Effect of convective instability in directionally solidified hypermonotectic Al-In alloys [J]. Materials Science Forum, 2000, 329-330: 209-218.
[11] ST?KER C, RATKE L. A new‘Jackson-Hunt’model for monotectic composite growth [J]. Journal of Crystal Growth, 1999, 203: 582-593.
[12] AOIA I, ISHINOA M, YOSHIDA M, FUKUNAGAB H, NAKAEA H. Influence of growth direction on the microstructure of unidirectionally solidified Cu-Pb monotectic alloy using zone-melt technique [J]. Journal of Crystal Growth, 2001, 222(4): 806-815.
[13] CHADWICK G A. Monotectic solidification [J]. Br J Appl Phys, 1965, 16: 1095-1097.
[14] LIVINGSTONE J D, CLINE H E. Monotectic solidification of Cu-Pb alloys [J]. Trans Metall Soc AIME, 1969, 245(2): 351-357.
[15] CAHN J W. Monotectic composite growth [J]. Metall Trans A, 1979, 10(1): 119-121.
[16] DERBY B, FAVIER J J. A criterion for the determination of monotectic [J]. Structure Acta Metall, 1983, 31(7): 1123-1130.
[17] YU Jue-qi. Phase Diagram of Binary alloys [M]. Shanghai: Shanghai Science and Technology Press, 1987. 341.(in Chinese)
(Edited by LI Xiang-qun)
Corresponding author: CUI Hong-bao; Tel: +86-451-86418815; E-mail: cuihongbao@hit.edu.cn