文章编号:1004-0609(2013)S1-s0472-05
焊后热处理对Ti2AlNb合金焊接接头显微组织及力学性能的影响
韩晓东1,宋 涛2,胡 明2,杨秀娟1,任 萍1,卢 斌2
(1. 中航工业沈阳黎明航空发动机(集团)有限责任公司,沈阳 110043;
2. 中国科学院 金属研究所,沈阳 110016)
摘 要:研究不同时效温度对Ti2AlNb基合金电子束焊接显微组织及力学性能的影响,利用金相显微镜和扫描电镜观察和分析焊接接头显微组织,并分析断口形貌。结果表明:在时效过程中,熔合区B2晶粒内析出大量的O相板条,时效温度越高,析出的板条尺寸越粗大;同时,从近热影响区到远热影响区的焊后热处理组织为网篮组织向双态组织过渡。时效处理后拉伸试样的断裂位置均为接头部位,且因时效温度升高造成细小O相板条含量减少,因而焊接接头强度下降、塑性升高。当时效温度为830 ℃时,焊件接头的室温抗拉强度σb达1 041 MPa,伸长率达到6.5%;650 ℃下σb为810 MPa,伸长率为6.5%,达到强度和塑性的最佳匹配。
关键词:Ti2AlNb基合金;电子束焊接;时效温度;焊接接头;拉伸性能
中图分类号:TG146.2 文献标志码:A
Effect of post-weld heat treatment on microstructure and mechanical properties of electron beam welded joint of Ti2AlNb based alloy
HAN Xiao-dong1, SONG Tao2, HU Ming2, YANG Xiu-juan1, REN Ping1, LU Bin2
(1. AVIC Shenyang Liming Aero-engine (Group) Co., Ltd., Shenyang 110043, China;
2. Institute of Metal Research, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Shenyang 110016, China)
Abstract: The effects of post-weld heat treatment on the microstructure and mechanical properties of electron beam welded joints of Ti2AlNb based alloy were studied. The microstructure and fractographs were analyzed by OM and SEM. The results show that during the aging process, the laths of O phase precipitate in B2 grains in fusion zone, while the microstructure is transient microstructure from the basket-weave microstructure of near-HAZ to duplex microstructure of far-HAZ. All ruptures take place at the weld joints during tensile test after aging treatment, and with the increase of aging temperature, the strength decreases and ductility increases. When aged at 830 ℃, the tensile strengths are 1 041 and 810 MPa, respectively, and the elongations are 6.5% both at room temperature and 650 ℃, the welded joint has the best combinations of the strength and ductility.
Key words: Ti2AlNb based alloy; electron beam weld; aging temperature; welded joint; tensile properties
现代航空、航天等发动机性能的不断提高对高温结构材料的性能提出了新的要求,因此,发展综合性能良好的轻质高温结构材料显得尤为必要。Ti2AlNb基合金由于具有较高的比强度、室温塑性、断裂韧性和蠕变抗力,以及较好的抗氧化性、无磁性等优点,使其成为在600~750 ℃使用的最具潜力的航空发动机材料之一[1-4]。
由于宇航部件多为钣金件、环形件等组合而成的复杂结构件,因而在制造过程中,焊接是不可缺少的。即使在高温条件下暴露较短的时间,焊接接头组织也会发生改变,进而影响其力学性能,因此对Ti2AlNb基合金焊接接头的力学性能研究是非常必要的。
目前对Ti2AlNb基合金焊接接头的显微组织和力学性能进行了报道[5-6],本文作者在已有的研究基础上研究了焊后时效温度对焊接接头显微组织和力学性能的影响。
1 实验
本实验所用材料的名义成分为Ti-22Al-24Nb- 0.5Mo, 其实测化学成分如表1所列。合金经真空自耗炉多次熔炼后,在B2单相区锻造开坯,最终在(α2+B2+O)三相区锻造成尺寸为410 mm×470 mm×60 mm的锻件。采用电火花线切割切取规格为170 mm×105 mm×7 mm的板材。图1所示为原始锻件的显微组织,由图1可知,合金的显微组织在蠕变前后均为三相复合组织,即白色的B2基体上分布着黑色的α2相和灰色的O相,且α2相与部分O相形成镶嵌组织。
表1 Ti-22Al-24Nb-0.5Mo合金的化学成分
Table 1 Chemical composition of Ti-22Al-24Nb-0.5Mo alloy (mass fraction, %)
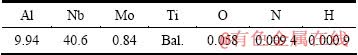
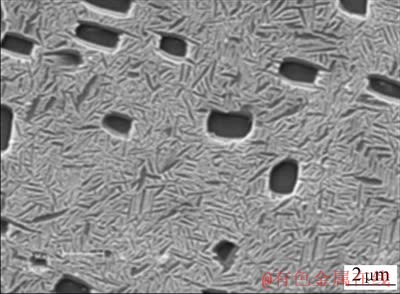
图1 Ti-22Al-24Nb-0.5Mo合金的显微组织
Fig. 1 OM microstructure of Ti-22Al-24Nb-0.5Mo alloy
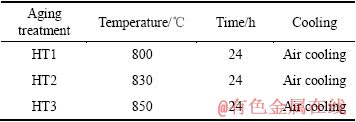
采用型号为ZD150-15A真空电子束焊接机进行堆焊。焊前先对样品进行固溶处理,试板表面用丙酮清洗以去除油污。焊接工艺参数为:加速电压120 kV,电子束电流3 mA,焊接速度1.2 m/min。焊后进行热处理,方案如表2所列。
采用线切割沿垂直于焊接方向切取拉伸与持久试样,通过岛津SSX-55扫描电镜观察焊接接头显微组织和断口形貌。利用AG-100KN电子万能试验机进 行室温和650 ℃高温拉伸。
表2 Ti-22Al-24Nb-0.5Mo合金热处理工艺
Table 2 Heat treatment processes of Ti-22Al-24Nb-0.5Mo alloy
2 结果与分析
2.1 焊接接头显微组织
图2所示为焊接接头显微组织照片。图2(a)为焊后焊接接头的整体形貌,在熔合区上部可观察到明显的分层现象,这是由结晶过程中放出的结晶潜热和热能输入周期性变化以及化学成分分布不均匀造成的[5]。
由于焊接过程中焊缝熔合区的温度最高,高温的B2相快冷抑制B2→O或B2→α2相转变,熔合区最终形成单一粗大的B2相。根据温度—时间转变关系 (TTT)得出[6],800~850 ℃位于(O+B2)两相区,因此当焊接接头在该温度区间时效处理时,B2晶粒内有大量的O相板条析出而形成网篮组织,且时效温度越高,O相板条越粗大。
按照加热过程中热影响区(HAZ)达到的最高温度可将热影响区分为近热影响区和远热影响区[7]。在近热影响区,焊接过程中的温度高于β相变点,使O相完全转变为B2相而仅保留了少量的α2相;而在远热影响区由于温度低于β相变点,O相逐渐转变为B2相和α2相,因此从近热影响区到远热影响区的焊后热处理组织为网篮组织向双态组织过渡,即自熔合区至母材,且热影响区中的α2/O相的数量逐渐增多。
2.2 拉伸性能
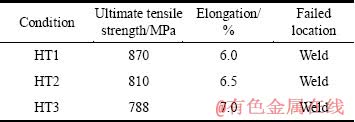
表3和4所列是热处理态焊接接头在室温和650 ℃的拉伸性能数据(焊接试样只给出抗拉强度)。可以看出,热处理后焊接接头具有良好的拉伸性能,而且每个试样的断裂位置均为接头部位,表明热处理后接头部位的强度低于母材。随着时效温度的升高,焊接接头强度逐渐降低,而室温塑性逐渐升高。高温下的拉伸性能与室温下的相近,但塑性有所提高,而强度下降。
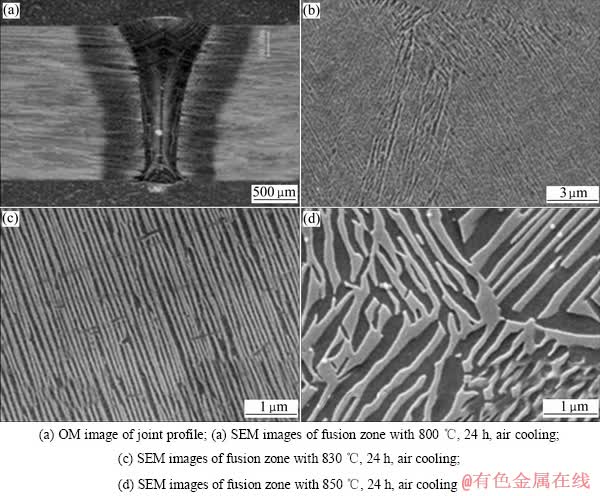
图2 焊接接头的显微组织
Fig. 2 Microstructures of weld joint

图3 热影响区的显微组织
Fig. 3 Microstructures of HAZ at 830 ℃
表3 Ti-22Al-24Nb-0.5Mo合金焊接接头在室温下的拉伸性能
Table 3 Tensile properties of weld joints in Ti-22Al-24Nb- 0.5Mo alloy at room temperature
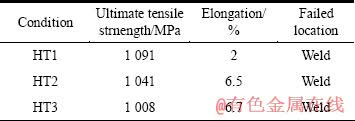
表4 Ti-22Al-24Nb-0.5Mo合金焊接接头在650 ℃的拉伸性能
Table 4 Tensile properties of weld joints in Ti-22Al-24Nb-0.5Mo alloy at 650 ℃
不同的热处理工艺所获得的微观组织有所差异,这直接影响合金的力学性能。时效温度越低,O相析出的动力越大,形核率就越高,所以析出的O相较为细小。因此在时效处理完成后,B2晶粒内析出的O相板条的体积分数增大将导致合金的强度上升,塑性下降。KUMPFERT和KEYENCE[8]在研究Ti2AlNb基合金的显微硬度的也发现B2晶粒内析出的细小O相会产生显著硬化。
2.3 断口形貌
热处理后试样的显微组织存在差异,这是影响材料性能的主要因素,这种差异更加直观的表现在拉伸断裂后的断口形貌上。经800 ℃时效处理后的合金,其室温塑性仅为2%,断裂方式为以沿晶断裂与穿晶断裂为主的混合断裂形式,断口面上存在大而平的解理断面(见图4(b))。当时效温度为830 ℃时,其室温塑性上升至6.5%,断裂方式为穿晶断裂(见图4(c)),断口面上有大量的解理面。经850 ℃时效后的拉伸断口具有明显的分层现象和韧性脊,在韧性脊中存在大量的细小韧窝(见图4(f))。
3 结论
1) 经过焊后热处理,在焊接接头熔合区中的B2晶粒内析出大量的O相板条而形成网篮组织,时效温度越高,B2晶粒内析出的O相板条越粗大。
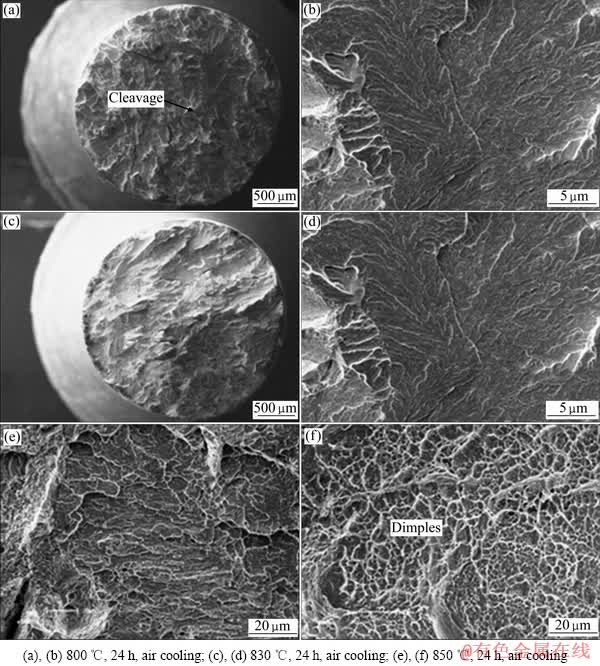
图4 焊后热处理Ti-22Al-24Nb-0.5Mo合金的室温拉伸断口形貌
Fig. 4 SEM fractographs of tensile samples at room temprature for post-weld heat treated Ti-22Al-24Nb-0.5Mo alloy
2) 焊后热处理后的试样断裂位置均为焊接接头部位,表明热处理后接头的强度低于母材的。
3) 时效温度越高,接头强度越低,塑性越高。在830 ℃时效处理后的焊接接头具有强度和塑性的最佳匹配。
REFERENCES
[1] BANEJEE D, GOFIA A K, NANDI T K, JOSHI V A. A new ordered orthorhombic phase in Ti3Al-Nb alloy [J]. Acta Metall, 1988, 36: 871-882.
[2] GOFIA A K, NANDI T K, BANEJEE D. Microstructure and mechanical properties of orthorhombic alloys in the Ti-Al-Nb system [J]. Intermetallics, 1998, 6(7/8): 741-748.
[3] CHU F, MITCHELL T E, MAJUMDAR B, MIRACLE D, NANDI T K, BANEJEE D. Elastic properties of O phase in Ti-Al-Nb alloys [J]. Intermetallics, 1997, 5(2):147-156.
[4] 司玉峰, 孟丽华, 陈玉勇. Ti2AlNb基合金的研究进展[J]. 宇航材料工艺, 2006, 3:10-13.
SI Yu-feng, MENG Li-hua, CHEN Yu-yong. Research development of Ti2AlNb-based alloy [J]. Aerospace Materials and Technology, 2006, 3: 10-13.
[5] 尹建明, 卢 斌, 李玉兰, 杨 锐. Ti2AlNb合金板材电子束焊接[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2010, 20(1): 325-330.
YIN Jian-ming, LU Bin, LI Yu-lan, YANG Rui. Electron beam welding of Ti2AlNb based alloy sheet [J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2010, 20(1): 325-330.
[6] LEI Zheng-long, DONG Zhi-jun, CHEN Yan-bin, ZHANG Jian, ZHU Rui-can. Microstructure and tensile properties of laser beam welded Ti-22Al-27Nb alloys [J]. Materials and Design, 2013(46): 151-156.
[7] 吴会强, 冯吉才, 何景山, 张秉刚. 焊接工艺对高铌Ti3Al合金电子束焊接接头显微组织和显微硬度的影响[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2004, 14(8): 1313-1317.
WU Hui-qiang, FENG Ji-cai, HE Jing-shan, ZHANG Bing-gang. Microstructure evolution of high Nb containing Ti3Al based alloy electron beam welding joints [J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2004, 14(8): 1313-1317.
[8] KUMPFERT J, LEYENCE C. Microstructure evolution, phase transformation and oxidation of an orthorhombic titanium aluminide alloy [J]. On Structural Intermetallic, 1997, 1997: 895-904.
[9] BAESLACK Ⅲ W A, PHILLIPS D, SCARR G K. Characterization of the weld heat-affected zone in an alpha-two titanium aluminide [J]. 1992, 28(1): 61-73.
[10] KUMPFERT J, KAYSSER W A. Orthormbic titanium aluminides: Phase, phase transformation and microstructure evolution [J]. Z Metallkd, 2001, 92(2): 128-134.
(编辑 方京华)
收稿日期:2013-07-28;修订日期:2013-10-10
通信作者:卢 斌,副教授,博士;电话:024-23971961;E-mail: blu@imr.ac.cn