文章编号:1004-0609(2010)S1-s0342-06
600 ℃时钛合金高温低循环疲劳行为及其微观机理
蔡建明1,张 华2,黄 旭1,曹春晓1
(1. 北京航空材料研究院,北京 100095;2. 贵州安大航空锻造有限责任公司,贵州561005)
摘 要:研究近α型TG6钛合金盘锻件双态组织在600 ℃不同应变幅条件下的低循环疲劳行为,总应变幅?εt/2控制在±0.6%~±1.5%,应变比R=-1,采用三角波方式加载。结果表明:600 ℃低循环疲劳条件下,随着总应变幅的增加,循环峰值应力smax提高,而疲劳寿命Nf下降;对于TG6钛合金盘锻件双态组织,存在一个循环软化/硬化的总应变幅临界值(?εt/2)c,约为±1.0%,当总应变幅高于此值,表现为循环硬化行为,而低于此值时,则表现为循环软化行为;在所有应变幅条件下,疲劳裂纹均为多源萌生模式,600 ℃低循环疲劳变形行为主要受α晶粒内位错的平面滑移所控制,位错平面滑移集中的结果是最早在α晶粒内萌生疲劳裂纹;随着疲劳测试温度的提高,不同滑移系上位错滑移的临界分切应力的差别缩小,促进位错交滑移的进行。
关键词:钛合金;低循环疲劳;平面滑移
中图分类号:TF 804.3 文献标志码:A
High temperature low cycle fatigue behavior and
its micro-mechanism of titanium alloy at 600 ℃
CAI Jian-ming1, ZHANG Hua2, HUANG Xu1, CAO Chun-xiao1
(1. Beijing Institute of Aeronautical Materials, Beijing 100095, China;
2. Guizhou Anda Aviation Forging Co., Ltd, Guizhou 561005, China)
Abstract: High temperature low cycle fatigue behavior and its micro-mechanism of near a TG6 titanium alloy disc forging with duplex microstructure in different strain amplitude at 600 ℃ were studied. The total strain amplitudes (?εt/2) and strain ratio R were controlled at ±0.6%-±1.5% and -1, and tested with triangular waveform loading. The results show that the maximum tensile stress (smax) increases and the low cycle fatigue life (Nf) decreases with increasing ?εt/2 under low cycle fatigue at 600 ℃. The critical total strain amplitude ((?εt/2)c) of cyclic hardening and softening is about ±1.0% for TG6 titanium alloy disc forging with α+β microstructure, the cyclic hardening behavior dominates while the strain amplitude is above (?εt/2)c, and the cyclic softening behavior dominates while the strain amplitude is below the (?εt/2)c. The fatigue crack initiates at several origins under cyclic deformation at all strain amplitude. The LCF fatigue behavior is controlled by planar slip of dislocation and which may result in fatigue crack in the α grain. The difference of critical resolved shear stress (CRSS) at each slip plane is gradually reduced, and which may promote the cross slip of dislocations.
Key words: titanium alloy; low cycle fatigue; planar slip
TG6是我国自行研制的能在600 ℃下长期使用的Ti-Al-Sn-Zr-Nb-Ta-Si-C系高温钛合金,通过多元复杂合金化的固溶强化作用和适当利用α2和硅化物的沉淀强化作用,合金具有优异的热强性,兼有良好的热稳定性。随着航空发动机推重比的不断提高,压气机的工作条件更为复杂和苛刻,在依靠整体叶盘、整体叶环等新颖结构的同时,还要越来越多地依赖于比强高、密度低和耐高温能力强的先进材料[1],对具有轻质、高强、高韧、耐高温、抗氧化、耐腐蚀等特点的高性能材料提出了更高的性能要求[2],TG6钛合金恰恰符合这一要求,可代替钢或镍基高温合金用于制造航空发动机压气机轮盘、叶片等,可以减轻结构质量40%左右,从而显著提高发动机的推重比和使用性能。
在航空工业应用中,疲劳断裂是最常见的一种失效模式,航空发动机的关键部件如压气机的轮盘,服役期间同时承受着高温、高压和低循环应力的复杂共同作用,其失效模式主要表现为低循环疲劳破坏,因此,研究钛合金在高温下的低循环疲劳行为具有重要意义。本文作者研究TG6钛合金盘锻件在600 ℃和不同应变幅条件作用下的应力响应和疲劳行为,以及相应的低循环疲劳断裂机制。
1 实验
本研究所用的试验材料为采用a+b区近等温模锻工艺制造的某型发动机压气机TG6钛合金盘模锻件,盘锻件采用两相区固溶和时效热处理,得到如图1所示的双态组织,在b转变组织的基体上分布着等轴的初生a晶粒,初生a相呈球状,其含量在10%左右。
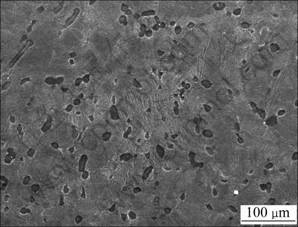
图1 TG6钛合金a+b区模锻盘锻件固溶时效状态下的显微组织
Fig.1 Microstructures of TG6 titanium alloy a+b processed disc forging in solution treatment and aging state
高温轴向应变控制低循环疲劳(LCF)试验是在MTS-809伺服液压控制的疲劳试验机上按GB/T—15248在空气环境下进行试验的。总应变幅控制在±0.6%~±1.5%,应变比R=-1,试验频率为0.067~0.167 Hz,恒应变速率 =4?10-3 s-1,为了保持
=4?10-3 s-1,为了保持 在整个循环拉伸过程和压缩过程中处于恒定状态,采用了三角波加载方式。
在整个循环拉伸过程和压缩过程中处于恒定状态,采用了三角波加载方式。
2 实验结果
表1所列为TG6钛合金在600 ℃不同应变幅测试条件下的低循环疲劳性能。由表1可看出,随着应变幅的增加,循环加载的峰值应力随之提高,而低循环疲劳寿命却随之下降。图2所示为在600 ℃不同应变幅条件下最大拉伸应力与断裂前循环次数的关系,在低应变幅(±0.6%)条件下,随着循环次数的增加,最大应力下降很慢,局部变形不足以造成有效的滑移变形,因此表现为近似的循环稳态行为。当总应变幅为±0.8%~±1.0%时,循环最大应力随着循环次数的增加而略微降低,特别是在循环开始的10周次内,最大应力下降相对较快,显示出较弱的循环软化特征;在以后的循环过程中,循环软化趋于平缓直至断裂。当总应变幅为±1.5%时,表现为循环硬化特征,即随着循环次数的增加,循环最大应力不断提高;当循环达到60次时循环最大应力达到饱和,并快速降低直至断裂。TG6钛合金在600 ℃下循环软化/硬化对应的临界总应变幅约为±1.0%,高于此值,表现为循环硬化行值,则表现为循环软化行为。
表1 600 ℃时钛合金的低循环疲劳性能
Table 1 LCF properties of Ti alloy at 600 ℃
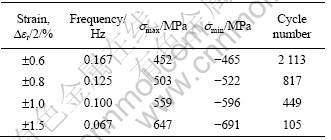
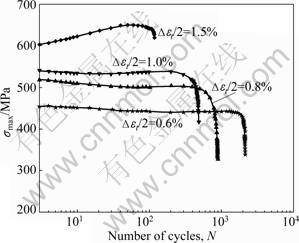
图2 600 ℃时不同应变幅下的循环最大应力响应
Fig.2 Cyclic stress response at 600 ℃ and different strain amplitudes
3 分析和讨论
对于单纯应变控制的循环载荷作用,低循环疲劳(LCF)寿命主要取决于两个因素,即裂纹萌生和微裂纹扩展阻力,裂纹形核和小裂纹的扩展行为对于LCF疲劳寿命均非常重要,L?TJERING等[3]认为,钛合金的LCF大约一半寿命为裂纹形核,另一半寿命为小裂纹的扩展,而长裂纹扩展的贡献几乎可以忽略不计。对于在室温下的光滑试样,90%的疲劳寿命在于裂纹的萌生,只有10%的疲劳寿命消耗在小裂纹的扩展阶段;而在高温下,对于给定总应变幅条件,在循环应力作用下,因变形均匀性程度的提高使得裂纹扩展阶段的循环次数占总寿命的比例提高[4]。如果认为循环应力达到最大值是小裂纹扩展的开始,从图2可以看出,在600 ℃不同应变幅下低循环疲劳小裂纹扩展至断裂对应的循环次数占总寿命的50%以上,但不超过70%,如当?εt/2=±0.8%,该值为67%。在较低的应变幅作用下,TG6钛合金呈现循环软化行为,在前10个循环周次内,有一个快速软化,在后面的循环软化相对较小,大部分的疲劳寿命保持稳定的循环应力。随着应变幅的增加,循环软化程度降低,这与IMI834的研究结果相同[5]。当总应变幅?εt/2约大于1.0%时,转为循环硬化。
图3~6所示分别为TG6钛合金在600 ℃不同应变幅下疲劳的断口形貌。由图3~6可看出,在所有应变幅条件的应力作用下,均为表面多源疲劳裂纹萌生,且为穿晶断裂模式,裂纹沿着组织中合适取向的密排面发生扩展。在断口表面的裂纹扩展区域,能看到清晰的疲劳条带,且存在大量的二次裂纹,应为集束间的界面或者是解理面。普遍认为,对于在a+b区加工的钛合金,低循环疲劳裂纹在初生a晶粒中发生形 核[6]。通过EBSD方法分析IMI834钛合金断口表面可知,这些断裂面是近基面取向的[7],在循环应力作用下,裂纹萌生于一些“弱”的区域,而与应力方向垂直的基面是特别“强”的区域,这种方向不利于滑移。因此,基面往往成为断裂面[8],随着裂纹的扩展,应力会发生重新分布,这是由于滑移系和显微组织不均匀造成的。比较不同总应变幅下的疲劳断口可知,随着总应变幅的提高,疲劳裂纹扩展区域减少,瞬断区增加。这意味着,在较大的总应变幅应力作用下,裂纹萌生和小裂纹扩展所需要的循环次数在减少,使得总的疲劳寿命下降。
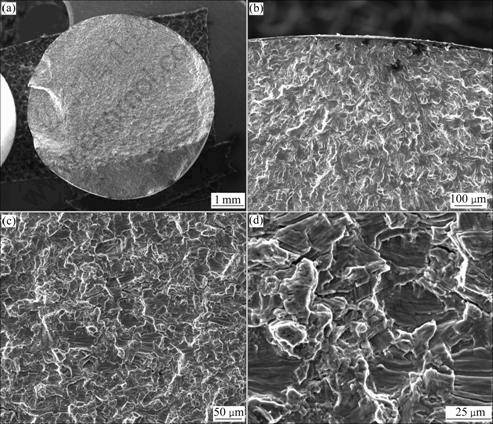
图3 应变幅为?εt/2=±0.6%,600 ℃时低循环疲劳断裂断口形貌
Fig.3 Fractographs of LCF specimen tested at ?εt/2=±0.6% and 600 ℃: (a) Macro-fractograph; (b) Fatigue crack origin zone; (c), (d) Fatigue crack propagation zone
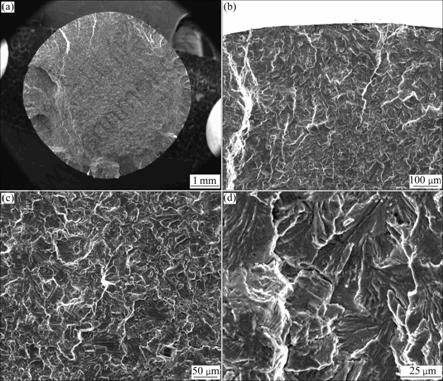
图4 应变幅?εt/2=±0.8%、600 ℃时低循环疲劳断裂断口形貌
Fig.4 Fractographs of LCF specimen tested at ?εt/2=±0.8% and 600 ℃: (a) Macro-fractograph; (b) Fatigue crack origin zone; (c), (d) Fatigue crack propagation zone
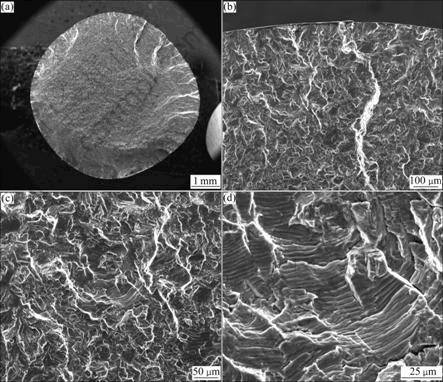
图5 应变幅为?εt/2=±1.0%、600 ℃时低循环疲劳断裂断口形貌
Fig.5 Fractographs of LCF specimen tested at ?εt/2=±1.0% and 600 ℃: (a) Macro-fractograph; (b) Fatigue crack origin zone; (c), (d) Fatigue crack propagation zone
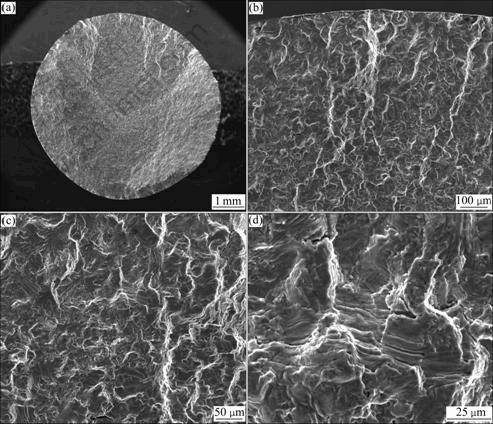
图6 应变幅为?εt/2=±1.5%、600 ℃时低循环疲劳断裂断口形貌
Fig.6 Fractographs of LCF specimen tested at ?εt/2=±1.5% and 600 ℃: (a) Macro-fractograph; (b) Fatigue crack origin zone; (c), (d) Fatigue crack propagation zone
图7所示为TG6钛合金在应变幅?εt/2=±1.5%, 600 ℃时低循环疲劳变形位错结构。由图7可看出,在疲劳变形过程中,出现最多的位错结构为位错缠结、平行位错列和滑移带组织。在变形过程中,位错明显增殖,位错之间的交互作用产生严重的缠结。从图7(b)中可以看到成对的位错列出现,这说明位错的平面滑移特征。TG6钛合金中析出的a2相会促进位错的平面滑移,打头的位错剪切a2相时会破坏其有序结构,随后的位错再次经过时可以消除上一位错切割时形成的反相畴,因此,位错易于以成对形式运动。其结果是,下一个位错在同一滑移面内运动所需的应力变小,使得位错更容易集中在已活动的滑移面上运动,而在其它滑移面上滑移更为困难[9]。
在高应变幅(±1.5%)条件下,位错滑移活性明显增加,因残留b相基本分解完毕,a片层间的界面不会提供阻碍位错滑移的抗力。很明显,在a晶粒内只有一组滑移系被激活了,本质上是平面化的,LCF疲劳的变形模式主要还是平面滑移[10]。
TEM像结果揭示,高温低循环疲劳均为平面位错滑移控制变形行为,在a晶粒内均观察到了平面位错滑移,这个效应随着剪切a2颗粒而加强。作为平面滑移带应变集中的结果是,疲劳裂纹最早在a晶粒内产生。当在600 ℃下测试时,不同滑移系之间的临界分切应力(CRSS)值差别在缩小,有可能促进位错交滑移的进行[11]。
4 结论
1) 对于TG6钛合金a+b区模锻盘锻件的双态组织,在600 ℃低循环疲劳载荷作用下,随着总应变幅的增加,循环峰值应力提高,而低循环疲劳寿命下降。
2) TG6钛合金在600 ℃低循环疲劳时的循环软化/硬化临界总应变幅约为±1.0%;高于此值,表现为循环硬化行为;而低于此值,则表现为循环软化行为。
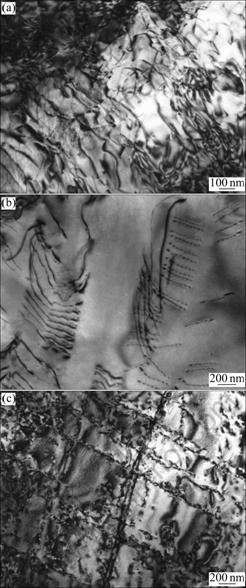
图7 在应变幅?εt/2=±1.5%、600 ℃时低循环疲劳变形位错结构
Fig.7 Dislocation structures in LCF specimen tested at 600 ℃ and ?εt/2=±1.5%: (a) High density tangled dislocations; (b) Dislocation array showing pairing style; (c) Widely slip traces and intersection of slip traces
3) 在所有应变幅条件的应力作用下,TG6钛合金低循环疲劳变形均为多源疲劳裂纹萌生模式,且受平面位错滑移变形行为所控制,在a晶粒内位错运动以平面滑移为主,位错平面滑移集中的结果是疲劳裂纹最早在a晶粒内产生。600 ℃时,位错在不同滑移系上滑移的临界分切应力(CRSS)的差别在缩小,可以促进位错交滑移的进行。
REFERENCES
[1] HICKS M A, THOMAS M C. Advances in aeroengine materials [C]// Proceedings of the 6th International Charles Parsons Turbine Conference. Ireland: Trinity College Dublin, 2003: 43- 56.
[2] LEYENS C, KOCIAN F, HAUSMANN J, KAYSSER W A. Materials and design concepts for high performance compressor components [J]. Aerospace Science and Technology, 2003, 7: 201-210.
[3] L?TJERING G, GYSLER A, ALBRECHT J. Influence of microstructure on fatigue resistance [C]// Fatigue 96. Pergamon: Pergamon Press, 1996: 893-904.
[4] SATYANARAYANA D V V, VARMA V K, NAGALAKSHMI G, RAO M K S. Creep and fatigue behaviour of a near a IMI 834 titanium alloy [J]. Metals Materials and Processes, 2007, 19: 101-110.
[5] GOUTHAMA N S, SINGH V. Low cycle fatigue behavior of Ti alloy Ti metal 834 at 873 K [J]. International Journal of Fatigue, 2007, 29: 843-851.
[6] WANG X, VO P, JAHAZI M, YUE S. Dwell fatigue microstructure in a near-a titanium alloy [J]. Metallurgical and Materials Transaction, 2007, 38A: 831-839.
[7] BACHE M R, EVANS W J, DAVIES H M. Electron back scattered diffraction (EBSD) analysis of quasi-cleavage and hydrogen induced fractures under cyclic and dwell loading in titanium alloys [J]. Journal of Materials Science, 1997, 32: 3435-3442.
[8] EVANS W J. Optimizing mechanical properties in alpha + beta titanium alloys [J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 1998, 243: 89-96.
[9] WOODFIELD A P, POSTANS P J, LORETTO M H, SMALLMAN R E. The effect of long-term high temperature exposure on the structure and properties of the titanium alloy Ti 5331S [J]. Acta Metall, 1988, 36: 507-515.
[10] WANG X, JAHAZI M, YUE S. Substructure of high temperature compressed titanium alloy IMI 834 [J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2006, 434: 188-193.
[11] MAIER H J, TETERUK R G, CHRIST H J. Modeling thermomechanical fatigue life of high-temperature titanium alloy IMI 834 [J]. Metallurgical and Materials Transaction A, 2000, 31: 431-444.
(编辑 李艳红)
基金项目:国家重点基础研究发展计划资助项目(2007CB613803)
通信作者:蔡建明; 电话: 010-62496624; E-mail: caijianming1975@126.com