分子动力学模拟铜纳米团簇的结构稳定性
齐卫宏1, 2, 汪明朴1, 李 周1, 谢 丹1
(1. 中南大学 材料科学与工程学院, 长沙 410083;
2. 江苏大学 材料科学与工程学院, 镇江 212013)
摘 要: 利用分子动力学研究了原子数为13~1055的铜纳米团簇。 结果表明: 随着尺寸的减小, 铜纳米团簇的结构发生晶体→非晶→晶体→非晶→晶体→非晶的转变。 团簇平均原子结合能随着尺寸的减小而减小, 且只依赖于短程有序, 这说明了团簇平均原子结合能一般不能够作为非晶与密堆结构晶体转变的判据。 平均原子间距不但依赖于团簇的尺寸, 且对团簇结构的变化敏感, 可以作为非晶与密堆结构晶体转变的一个判据。 对偶分布函数的研究表明, 大尺寸团簇的内部和表层原子结构都表现出晶格收缩效应, 且不同于相应块体晶格, 这表明了目前文献中关于团簇的块体加表面模型与壳核模型都有待改进。
关键词: 分子动力学; 铜团簇; 结合能; 平均原子间距 中图分类号: O482.2; TG111.5
文献标识码: A
Molecular dynamics simulating of structural stability of copper nanoclusters
QI Wei-hong1, 2, WANG Ming-pu1, LI Zhou1, XIE Dan1
(1. School of Materials Science and Engineering,Central South University, Changsha 410083, China;
2. School of Materials Science and Engineering,Jiangsu University, Zhenjiang 212013, China)
Abstract: The Cu nanoclusters with atom number of 13-1055 have been studied by molecular dynamics simulation method. The results show that the structure of Cu nanoclusters follows the sequence of crystalline→amorphous→crystalline→amorphous→crystalline→amorphous with the decrease of the cluster size. The average atom cohesive energy decreases with the decrease of the cluster size, and only depends on the short-range order, which shows that the mean atom cohesive energy can not be regarded as the criterion of determining the structure of amorphous and close packed crystallines. However, the mean atom distance depends on not only the cluster size, but also the cluster structure, which can be regarded as the criterion of determining the structure transformation. Furthermore, the study on pair correlation function shows that both the interior and outer shells of the larger clusters contract a little, and are different from those of the corresponding bulk crystal, which suggests that the present bulk-surface and core-shell models of clusters should be improved.
Key words: molecular dynamics; Cu nanoclusters; cohesive energy; mean atom distance
金属纳米团簇的研究是近几年的一个热点, 主要是由于团簇被看作是分子和宏观材料的过渡态[1,2], 其很多特性既不同于单个分子, 也不同于块体材料所致。 金属纳米团簇在催化以及纳米技术领域有着非常广泛的用途[3-6]。 材料的性能取决于结构, 纳米团簇的特性也来自于其特殊的结构。 本研究主要讨论铜纳米团簇的结构特性。
Taylor等[7]利用光电谱法研究了气相铜纳米团簇, Knickelbein[8]测定了中性铜团簇的离化能并发现了电子壳层结构。 在理论研究方面, Massobrio等[9]利用密度泛函方法计算了原子数n为2, 4, 6, 8及10的铜团簇结构以及相关能量, Kabir等[10, 11]利用FP-LMTO方法研究了原子数小于9的铜团簇, 并利用分子动力学研究了n为10~55的铜团簇结构特性。 本文作者利用分子动力学结构驰豫方法研究了原子数为13~1055铜纳米团簇的稳定结构, 通过计算铜团簇结合能和平均原子间距给出晶态与非晶态的一个判据, 并评价已有的金属团簇的模型。
1 模拟方法
利用Materials Explorer 分子动力学软件包模拟, 采用紧束缚势, 利用结构驰豫的方法来获得团簇最稳定结构。 采用正则系综(NTV)模拟。 团簇的初始形态可以通过软件包建立为从理想的面心立方铜晶体中取出球形的铜团簇, 任选一个中心原子, 从第1近邻一直取到第29近邻, 团簇的原子数分别为13、 19、 43、 55、 79、 87、 135、 141、 177、 201、 225、 249、 321、 369、 381、 429、 459、 531、 555、 603、 627、 675、 683、 767、 791、 887、 935、 959和1055。 让每个团簇分别在800K运行5000步达到平衡, 然后将温度从800K逐渐降到0K, 共运行45000步, 步长为2fs, 采用自由边界条件。
2 结果与讨论
图1所示为铜团簇的对偶分布函数。 由图1可见, 虽然n=249时铜团簇的初始结构为理想晶体, 但通过分子动力学演化, 很多峰消失, 最后的稳定结构为非晶态。 对于n=321的铜团簇, 从对偶分布函数来看, 初始结构是晶体, 通过分子动力学驰豫后, 峰位更尖锐, 说明其结构保持长程有序, 仍然是晶态。 通过对其它团簇的对偶分布函数研究表明, 原子数为19, 43, 55, 79, 87, 135, 141, 249及459的团簇为非晶态, 而原子数为177, 201, 225, 321, 369, 381, 429以及n≥531的团簇为晶态。 原子数为13的团簇只有一层原子, 可以认为是晶态, 也可以认为是非晶态。 分子动力学驰豫是为了找出团簇的最低能量。 因此, 团簇结构呈非晶态, 说明非晶态的自由能更低, 结构更稳定。 而团簇结构经驰豫后成晶态团簇, 说明结构为晶态, 且其能量更低。 这种结构的择优选择主要是由于纳米团簇有较大的比表面积, 较大的比表面积可以直接影响团簇结构性能。 但比表面积如何影响纳米团簇的结构则需进一步的研究。
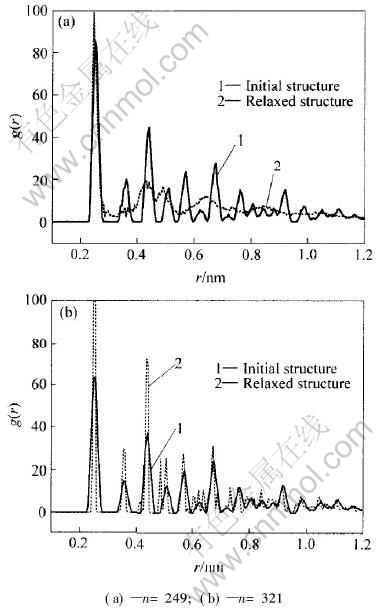
图1 铜团簇的对偶分布函数
Fig.1 Pair correlation function of Cu clusters
图2所示为铜纳米团簇平均原子结合能与原子数的关系。 由图2可看出, 纳米团簇的平均原子结合能随着团簇尺寸的减小而降低。 虽然铜团簇的稳定结构有晶态和非晶态, 但其平均原子结合能没有发生突变, 而是随着尺寸的变化平滑地变化。 这说明团簇的结合能不依赖于团簇的长程有序性, 而是依赖于短程有序性, 晶态和非晶态的差别在于长程有序, 长程有序不能从结合能的差异上表现出来; 平均原子结合能不能作为晶态与非晶态的判据。
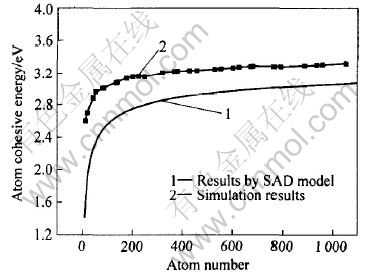
图2 铜团簇的结合能与原子数的关系[12, 13]
Fig.2 Relationship between cohesive energy and atom number of Cu nanoclusters[12, 13]
为了比较, 图2中也给出了表面积差异模型(surface area difference, SAD)对于铜团簇原子结合能的计算结果[12, 13]。 由图2可看出, SAD模型预测结果和本研究模拟结果的变化趋势一致。 SAD模型的核心内容为: 结合能是将材料分成孤立原子所需要的能量, 如将孤立原子也看作一个具有表面的球形实体, 那么, 所有孤立原子的表面积和将大于原材料的表面积, 也就是说结合能的直接结果相当于产生了新的表面, 从这个意义上讲, 结合能就应该等于所有孤立原子的表面能与材料表面能之差。 SAD模型的计算公式为 Ep=Eb(1-αn-1/3), 式中Ep和Eb分别是团簇和块体材料的结合能。 对于铜, Eb=3.49eV[14], α为形状因子; 对于多面体形纳米团簇, α=1.245[15]。 由此可看出, SAD模型没有考虑晶格驰豫。 本研究中的分子动力学模拟采用的是表面充分驰豫后的结合能, 而结构驰豫可以使自由能降低, 结构更稳定, 当然结合能也就更大。 因此, 结构驰豫后的分子动力学模拟的结合能比未驰豫的SAD模型给出的结合能要大, 这与图2所示的结果一致。
图3所示为铜团簇平均原子间距与原子数的关系。 由图3可看出, 平均原子间距也依赖于团簇原子数, 团簇的平均原子间距都小于相应块体铜的平均原子间距。 但与结合能不同的是, 平均原子间距依赖于团簇结构。 对于具有晶态结构n为13, 177, 201, 225, 321, 369, 381, 429以及n≥531(这里n=13的结构也看成晶态)的团簇, 其平均原子间距随着团簇尺寸的增大而平滑地增大, 逐渐趋向于块体铜晶体的平均原子间距。 但对于具有非晶态结构的n为19, 43, 55, 79, 87, 135, 141, 249及459的团簇, 其平均原子间距则表现处幻数效应, 时大时小, 但总的来说, 非晶团簇的平均原子间距要大于相应晶态的平均原子间距。 如果将晶态平均原子间距的平滑变化拟合成一条曲线, 那么就可以判断纳米团簇是否具有晶态结构。 如果得到的平均原子间距落在曲线上, 则团簇具有理想的晶态结构。 但如果偏离曲线, 则其结构也就相应地偏离晶态, 离曲线愈远, 偏离的程度愈大。 从这个角度来说, 团簇平均原子间距可以作为判定团簇结构的一个判据。
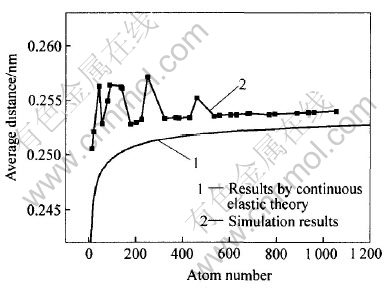
图3 铜团簇的平均原子间距与原子数的关系
Fig.3 Relationship between average distance and atom number of Cu nanoclusters
为了比较, 图3也给出了连续介质弹性模型(continuous elastic mediums, CEM)理论的计算结果[16]。 CEM模型的基本假设为:从块状晶体中取出一个纳米尺度的球形晶体, 相当于增加了表面能, 使体系能量升高, 为了降低能量, 晶体收缩, 但在晶体中又贮存了一定的弹性能, 阻碍晶体收缩。 当增加的表面能和弹性能达到平衡时, 一个稳定的纳米微粒就产生了。 CEM模型的计算公式为d=db[1-1/(1+(G/γ)·db·α-1/2·n1/3)], 式中d和db分别为团簇和块体材料的平均原子间距; G为切变模量; γ为0K时的单位面积表面能; α为形状因子。 对于铜, db=0.2553nm[17], G=4.83GPa[18], γ=1.592mJ/m2[19], α=1.245[15]。 由此可以看出, CEM模型考虑了晶体的驰豫, 其计算结果和本研究模拟值基本一致。 CEM是基于理想晶体的模型, 因此, 不能够预测非晶团簇平均原子间距的变化。 但由于CEM模型将晶体看作一个连续介质, 且没有考虑晶体各向异性, 因此计算结果和团簇晶体的模拟值还存在一定的差距。
对于较大尺寸团簇, 一般有两种模型: 1) 块体-表面模型, 也就是说, 团簇的内部结构与块体没有什么分别, 而是只要考虑表面影响而已[19]; 2) 壳-核模型, 即团簇的结构可以看作表面部分的壳与内部的核两部分构成, 内部的核与块体材料相同, 而表面的壳则不同于块体材料[20]。 两种模型的准确性可通过对对偶分布函数的研究来说明。 图4所示为n=1055时的对偶分布函数。 由图4可看出, 驰豫后几乎所有的峰都向右移, 在图1中也有这种现象。 这说明了驰豫后的晶格与驰豫前的晶格有所不同, 并不是只有最外层的晶格发生收缩, 而几乎所有壳层的晶格都发生收缩。 而这一现象正好与Gilbert等[21]关于ZnS结构的实验结果相一致。 因此, 纳米团簇的结构既不是块体加表面结构, 也不是壳核结构。 若要精确研究纳米团簇的性能, 则必须仔细考虑团簇结构的特殊性。
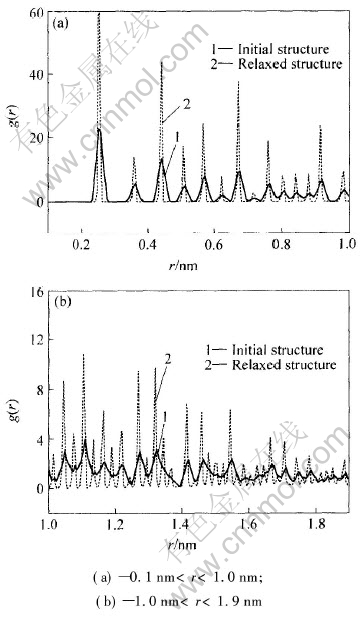
图4 n=1055时的铜团簇的对偶分布函数
Fig.4 Pair correlation function of Cu clusters with n of 1055
3 结论
1) 随着尺寸的减小, 铜纳米团簇的结构发生晶体→非晶→晶体→非晶→晶体→非晶的转变(n=13的结构可以看作晶体也可以看作非晶)。
2) 团簇平均原子结合能随着尺寸的减小而平滑地减小, 且只依赖于短程有序, 因此不能作为非晶团簇与晶态团簇结构变化的判据。
3) 平均原子间距则对团簇结构的变化敏感, 依赖于长程有序, 可以作为结构变化的一个判据。
4) 大尺寸团簇的内部和表层都与块体材料的不同。
REFERENCES
[1]Heer W A D. The physics of simple metal clusters: experimental aspects and simple models [J]. Reviews of Modern Physics, 1993, 65(3): 611-676.
[2]Brack M. The physics of simple metal clusters: self-consistent jellium model and semiclassical approaches [J]. Reviews of Modern Physics, 1993, 65(3): 677-732.
[3]Valden M, Lai X, Goodman D W. Onset of catalytic activity of gold clusters on titania with the appearance of nonmetallic properties [J]. Science, 1998, 281(5383): 1647-1650.
[4]Hansen P L, Wagner J B, Helveg S, et al. Atom-resolved imaging of dynamic shape changes in supported copper nanocrystals[J]. Science, 2002, 295(5562): 2053-2055.
[5]Binns C. Nanoclusters deposited on surfaces [J]. Surface Science Reports, 2001, 44(1-2): 1-49.
[6]Park S J, Taton T A, Mirkin C A. Array-based electrical detection of DNA with nanoparticle probes[J]. Science, 2002, 295(5559): 1503-1506.
[7]Taylor K J, Pettiette-Hall C L, Cheshnovsky O, et al. Ultraviolet photoelectron-spectra of coinage metal clusters[J]. Journal of Chemical Physics, 1992, 96(4): 3319-3329.
[8]Knickelbein M B. Electronic shell structure in the ionization potentials of copper clusters [J]. Chemical Physics Letters, 1992, 192(1): 129-134.
[9]Massobrio C, Pasquarello A, Car R. Structural and electronic-properties of small copper clusters—a first principles study[J]. Chemical Physics Letters, 1995, 238(4-6): 215-221.
[10]Kabir M, Mookerjee A, Datta R P, et al. Study of small metallic nanoparticles: an ab-initio full-potential muffin-tin orbitals based molecular dynamics study of small Cu clusters[J]. International Journal of Modern Physics B, 2003, 17(10): 2061-2075.
[11]Kabir M, Mookerjee A, Bhattacharya A K. Structure and stability of copper clusters: A tight-binding molecular dynamics study[J]. Physical Review A, 2004, 69(4): 043203.
[12]Qi W H, Wang M P. Size effect on the cohesive energy of nanoparticle[J]. Journal of Materials Science Letters, 2002, 21(22): 1743-1745.
[13]Qi W H, Wang M P, Zhou M, et al. Surface-area-difference model for thermodynamic properties of metallic nanocrystals[J]. Journal of Physics D: Applied Physics, 2005, 38(9): 1429-1436.
[14]Kittel C. Introduction to Solid State Physics[M]. New York: John & Sons Inc, 1996.
[15]Qi W H, Wang M P, Liu Q H. Shape factor of non-spherical nanoparticles[J]. Journal of Materials Science, 2005, 40(9-10): 2737-2739.
[16]Qi W H, Wang M P. Size and shape dependent lattice parameters of metallic nanoparticles[J]. Journal of Nanoparticle Research, 2005, 7(1): 51-57.
[17]Barrett C S, Massalski T B. Structure of Metals[M]. New York: Pergamon Press, 1980.
[18]Brandes E A. Smithells Metals Reference Book[M]. Boston: Butterworths, 1983.
[19]Nanda K K, Sahu S N, Behera S N. Liquid-drop model for the size-dependent melting of low-dimensional systems[J]. Physical Review A, 2002, 66(1): 013208.
[20]Palosz B, Stelmakh S, Grzanka E, et al. High pressure X-ray diffraction studies on nanocrystalline materials[J] Journal of Physics Condensed Matter, 2004, 16(5): S353-377.
[21]Gilbert B, Huang F, Zhang H, et al. Measurement of internal strain and lattice stiffening in ZnS nano-particles[J]. Science, 2004, 305(5684): 651-654.
(编辑李艳红)
基金项目: 国家自然科学基金资助项目(50401010)
收稿日期: 2005-07-15; 修订日期: 2005-08-20
作者简介: 齐卫宏(1975-), 博士研究生
通讯作者: 齐卫宏, 电话: 0511-5856821; E-mail: weihong.qi@gmail.com