DOI:10.19476/j.ysxb.1004.0609.2018.09.05
Al2Cu拉伸变形的分子动力学模拟
刘晓波,熊 震,方 洲,李 艳
(南昌航空大学 航空制造工程学院,南昌 330063)
摘 要:采用分子动力学方法研究Al2Cu的拉伸变形行为。建立Al2Cu分子动力学模拟模型,采用嵌入原子法模拟Al2Cu模型在常温、恒定工程应变速率的拉伸环境下对Al2Cu力学性能的影响,探讨温度和应变率对体系拉伸变形行为的影响。结果表明:发现Al2Cu非常脆,应变ε=0.086时应力达到峰值6.4 GPa,在拉伸初期不易产生位错,从而弹性变形阶段较长。Al2Cu对温度十分敏感,温度上升使Al2Cu的原子动能成倍增加,导致塑性变强但抗拉强度明显下降;Al2Cu在应变率为 为0.005~0.006 ps-1之间存在一个值,当Al2Cu的应变率超过这个值时,一些拉伸产生的空位来不及发生大幅移位,只能聚集在发射处附近,使体系内各处均出现大量孔洞。
为0.005~0.006 ps-1之间存在一个值,当Al2Cu的应变率超过这个值时,一些拉伸产生的空位来不及发生大幅移位,只能聚集在发射处附近,使体系内各处均出现大量孔洞。
关键词:Al2Cu;拉伸;分子动力学模拟;温度;应变率
文章编号:1004-0609(2018)-09-1746-09 中图分类号:TG146.2 文献标志码:A
7XXX系铝合金是Al-Zn-Mg-Cu系超硬铝合金,合金具有密度小、屈服极限高、加工性能好等优点,被广泛应用于航空航天工业和交通工具等[1-2]。但是7XXX系铝合金在生产时,受原材料、加工工艺、热处理工艺等因素的影响,存在着难以忽略的各种缺陷如结疤、非金属夹杂、异金属夹杂物、白点等,合金基体中还存在大量的共格和不共格的第二相粒子[3-4]。这些第二相粒子对材料的再结晶行为、力学性能、断裂韧性、耐腐蚀性能等均产生重要影响[1, 5]。铝合金中根据颗粒大小分成3种第二相粒子,其中对材料性能影响最显著是直径在0.1 μm以上的粗大椭球第二 相[6]。Al2Cu作为7XXX系中主要的粗大椭圆第二相之一,是在合金铸造凝固和均匀化过程中形成的。Al2Cu的塑性很差,在较低的应力下即可发生微裂纹,萌生孔洞,Al2Cu的变化对合金的性能有十分重要的影响[7],因此,必须掌握这种微观缺陷对合金性能的影响规律。
分子动力学模拟作为计算机模拟中非常重要的一种方法,在金属材料领域起着至关重要的作用,尤其在描述微观层次的细节方面[8-9]。目前,国内外学者在金属材料拉伸的分子动力学模拟方面做了大量的研究工作,LYNDEN-BELL等[10]用分子动力学模拟单晶铑的单向拉伸过程,研究了不同条件下的拉伸变形行为。DOYAMA[11]采用分子动力学模拟单晶Cu和Fe的拉伸过程,结果表明凹槽是位错和裂纹的来源。文玉华等[12]在模拟纳米晶Cu的拉伸变形时,发现强度随晶粒尺寸减小而降低。DIAO等[13]通过分子动力学模拟研究单晶金纳米丝的屈服机制,认为金纳米丝的塑性变形主要是通过不全位错的运动进行。CAO等[14]用分子动力学模拟了纳米孪晶铜在受单向均匀拉伸载荷下的变形机制,发现孪晶对位错滑移具有阻挡作用,使得孪晶纳米线得到强化。KIM等[15]通过模拟纳米多晶Mg的拉伸过程,认为应力条件的变化会引发滑移、孪晶和晶界迁移等不同的变形机制。陈明等[16]通过分子动力方法,分别对无孔洞和有孔洞的纳米单晶铜杆,运用EAM(Embedded atom model)势函数研究了其拉伸特性。CHEN等[17]研究了单轴拉伸载荷加载下,铜(001)/镍(001)旋转晶界所形成的不同晶格失配网络对其力学性能的影响。ZHANG等[18]对含孪晶的铜纳米线的分子动力学模拟结果表明,在拉伸载荷作用下,孪晶界间距越小,纳米线在塑性变形区域内的应力越低。WANG等[19]基于EAM势,采用分子动力学方法对超细镍纳米线在(100)晶向的拉伸性能进行研究,并对其温度相关性和拉伸应变率相关性进行探讨。张晓泳等[20]利用分子动力学模拟研究Ti-Al纳米杆的单向拉伸变形过程,比较分析不同拉伸速率、拉伸温度以及Al含量对Ti-Al应力-应变关系及其塑性变形行为的影响。袁林等[21]用分子动力学方法模拟了不同晶粒尺寸下多晶银纳米线的拉伸变形行为,分析了晶粒尺寸对多晶银纳米线弹性模量、屈服强度、塑性变形机理的影响。梁力等[22]利用分子动力学模拟方法分别研究了空位、自间隙杂质原子、杂质He原子等缺陷对金属Ti样品的力学性能的影响,对完整晶格的金属Ti在不同拉伸应变速率下的应力-应变曲线进行计算。樊倩等[23]采用分子动力学模拟方法,研究了层厚度和应变率对铜-金多层复合纳米线在均匀拉伸载荷下力学性能的影响, 并分析了铜-金位错成核机理。结果表明,分子动力学是研究金属材料拉伸微观缺陷演变的有效方法。
然而,目前在Al2Cu拉伸变形模拟很少,因此,本文作者使用EAM势在LAMMPS中对Al2Cu进行了拉伸变形模拟,并分析其对Al2Cu力学性能的影响,采用可视化软件OVITO得到的原子特殊时刻体系变形轨迹图,以便能清楚地观察Al2Cu在拉伸载荷作用下的变形情况。
1 Al2Cu模型的建立
建立10a0×10a0×10b0的模拟初始模型,此模型体系中共计12000个原子,模型实际大小为6.07 nm×6.07 nm×4.88 nm,a0、b0为一定温度下Al2Cu的晶格常数[24]。模型中x、y和z方向分别对应的是[100]、[010]、[001]晶向。
由于模型是按照理想晶格排列来建立的,在实际的模拟中这个模型并不稳定,存在较大的预应力,若直接进行模拟,系统应力及能量会发生明显的波动。为使系统预应力降低,必须对模型弛豫(Relaxation),弛豫时原子会在原有位置上轻微移动以降低整体系统的能量。为进行分子动力学弛豫,将生成的初始模型在NPT的条件下保持300 K的热浴运行50000步,时间步设为0.001 ps。
2 模拟的势函数和算法
嵌入原子法的基本思想是将体系里单个原子看作成不同于其它原子的“杂质”,对所有原子的能量求和即为体系的总能量。采用嵌入原子势(EAM)[19, 25] 作为各原子相互作用的势函数,每个原子的能量Ei可由式(1)表示:
 (1)
(1)
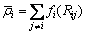 (2)
(2)
式中:Fi是在其他原子组成的基体中再嵌入第i个原子所需要的能量,即嵌入能,它是一个关于所有电子分布密度 的函数,
的函数, 的求法如式(2)所示。Rij是第i和第j原子间的距离;
的求法如式(2)所示。Rij是第i和第j原子间的距离;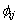 是第i和第j原子间相互作用势;fi(Rij)是第i个原子的核外电子在第j个原子处贡献的电荷密度。
是第i和第j原子间相互作用势;fi(Rij)是第i个原子的核外电子在第j个原子处贡献的电荷密度。
所以系统的总势能为
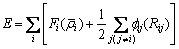 (3)
(3)
采用Velocity-Verlet速度算法,该算法能同时得出位置、速度和加速度,而且计算时只需要一个时刻的变量。
Velocity-Verlet速度算法基本形式如下:
 (4)
(4)
 (5)
(5)
式中:R(t+Δt)是原子在t+Δt时刻的位置;R(t)是原子在t时刻的位置;v(t)是t时刻的速度;a(t)是加速度。
3 结果与讨论
3.1 Al2Cu常温拉伸变形行为分析
将所得模型在300 K恒温条件下沿x轴匀速拉伸,为保证计算精度,整个体系每运行一个时间步变形一次,工程应变速率为0.001 ps-1,模拟体系使用正则系综(NVT),拉伸过程持续200000步,期间每200步输出原子的坐标信息、应变、温度和应力。
将运算获得的数据绘制成如图1所示的应力-应变曲线,并将原子轨迹信息通过可视化软件OVITO处理,得到的原子特殊时刻体系裂纹扩展轨迹图2,两者对应进行分析。
从图1可以看出,理想Al2Cu在充分弛豫后初始应力为零,应变在0.025之前有一段很短的弹性变形阶段,应力应变关系近似直线。应力随应变呈线性增大,在此范围内胡克定律所反映的线性关系依然成立,可以据此计算材料的弹性模量。从图2(a)和(b)可以看出,在0.08以下时,模拟体系近似均匀扩大,原子位置存在微小的扰动,微裂缝没有明显发展,整体没有出现孔洞。应变在0.05之后由于塑性变形量的增加,应力增加速率略有减少。

图1 Al2Cu模型的应力-应变曲线
Fig. 1 Stress-strain curve of Al2Cu model
Al2Cu非常脆,应变ε=0.086左右应力达到峰值6.4 GPa后骤然下降。在y方向截取距离边部为3  ,厚度为6
,厚度为6 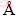 的原子进行观察。可以发现模型在很短的时间步内从一个如图2(c)所示的微小孔洞发展成如图2(d)所示的巨大孔洞。随着拉伸的继续,当晶格中积累的应变能过高时,会在裂纹尖端处发射出位错释放应变能,形成无序区域。在由图2(c)发展至图2(d)的过程中,孔洞周围原子扰动十分剧烈,出现了较大的混乱排列,空位大量产生,孔洞吸收周围的空位而不断长大。
的原子进行观察。可以发现模型在很短的时间步内从一个如图2(c)所示的微小孔洞发展成如图2(d)所示的巨大孔洞。随着拉伸的继续,当晶格中积累的应变能过高时,会在裂纹尖端处发射出位错释放应变能,形成无序区域。在由图2(c)发展至图2(d)的过程中,孔洞周围原子扰动十分剧烈,出现了较大的混乱排列,空位大量产生,孔洞吸收周围的空位而不断长大。
由于模型3个方向均是采用周期性边界,相当于模拟的是一个无限大的体系,不存在宏观上的拉断现象,所以应变ε=0.11之后仍然有相当的应力存在。由图2(e)和(f)可以看出,这个阶段孔洞增长缓慢,在各个方向均匀的发展、长大。
模拟得出的Al2Cu抗拉强度为6.44 GPa,数值较大,造成这种巨大差异的原因是由于宏观材料内部存在较多位错、空隙及杂质等缺陷,这些缺陷进一步的成长和演变使材料的强度降低。边界条件的不同对抗拉强度和变形过程也有很大影响,即自由表面越少,结构越稳固,强度也越高。与使用一个方向是周期边界,另两个方向是自由边界的纳米丝和两个方向是周期边界,另一个方向是自由边界纳米薄膜不同,3个方向都是周期边界的Al2Cu块体没有自由表面,原子运动自由度小、在拉伸初期不易产生位错,从而弹性变形阶段较长。 在拉伸过程中Al2Cu块体的应变能不断积累,最终使晶体内部突然出现孔洞,孔洞的逐渐成长导致材料的破坏。
3.2 温度对Al2Cu拉伸变形影响与分析
为了研究体系温度对Al2Cu拉伸变形力学性能的影响,方便与初始模型所设定的300 K相比较,设置5个温度进行模拟,分别是200 K、300 K、400 K、500 K、600 K,其他模拟参数设置保持不变。模拟体系使用正则系综(NVT),拉伸过程运行200000步,期间每200步输出原子的坐标信息、应变、温度和应力。图3所示为不同温度所对应的应力-应变曲线图。
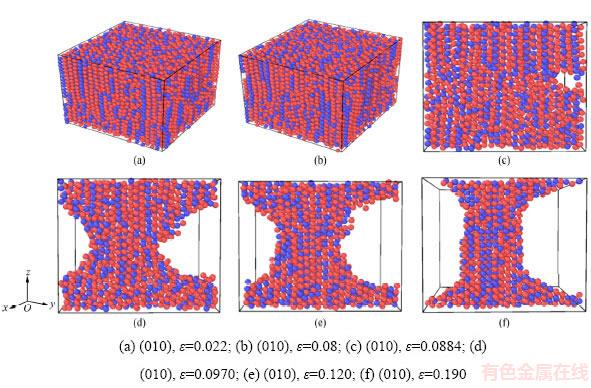
图2 图1中不同应变时Al2Cu模型的原子轨迹图
Fig. 2 Atomic trajectories of Al2Cu model at different strains in Fig. 1
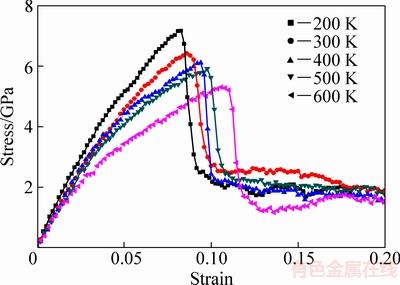
图3 不同温度的Al2Cu模型应力-应变曲线图
Fig. 3 Stress-strain curves of Al2Cu model at different temperatures
图3中观察到,在5个不同的温度下Al2Cu均存在很短的弹性变形阶段,应力应变关系近似直线,但是随着温度的升高,这段距离也逐渐变短,对应的弹性模量也略有减小。而且对比观察可以发现,在上升阶段时,200 K的应力-应变曲线其整体更为平滑,在应变ε=0~0.082的上升阶段几乎没有波动,300 K、400 K、500 K、600 K的应力-应变曲线均表现出比200 K时更明显的波动。这是由于原子处于低温时,原子具有动能也较小,需要更大的外力作用才能引起Al2Cu块体的塑性变形。温度提高以后,原子的动能成倍增加,热振动加剧,原子间距离增大,导致弹性模量的减小。同时原子拥有了更多的动能,更容易偏离其平衡位置并克服某些障碍继续运动即高温下出现新的滑移系,从而使塑性变形能力得到提高。
随着应变的加剧,200 K时,Al2Cu在应变为0.082时便到达抗拉强度7.21 GPa;300 K时,Al2Cu在应变为0.0862时到达抗拉强度6.44 GPa;400 K时,Al2Cu在应变为0.0928时到达抗拉强度6.14 GPa;500 K时,Al2Cu在应变为0.0978时到达抗拉强度5.91 GPa;而在600 K时,Al2Cu在应变为0.108时才达到抗拉强度5.29 GPa。做出不同温度对应的抗拉强度曲线图如图4所示。可以发现抗拉强度表现出与模拟热浴条件相反的变化趋势,即温度越高,Al2Cu的抗拉强度越小。温度升高还使Al2Cu的塑性增加,从200 K时的应变ε=0.082,增加到600 K时ε=0.108。这是由于随着温度的升高,给原子和空位提供了足够的动能,使得位错可以继续进行,从而使塑性变形能力得到提高。温度的升高让原子动能成倍的增加,在外载荷作用下产生大量的细小空位,并且不断的迁移汇合,使得孔洞的萌生更容易发生。孔洞迅速吸收周围的空位而不断长大,也更容易达到其断裂所需要的极限应力。

图4 不同温度的抗拉强度曲线图
Fig. 4 Tensile strength curve at different temperatures
由于是无限大的块体,不存在拉断的现象,所以在到达抗拉强度后应力迅速下降后稳定在一个应力值附近小幅波动。不同温度下的这个稳定值没有明显规律。
通过对不同温度下的模型进行模拟表明,Al2Cu对温度十分敏感,温度上升抗拉强度下降明显,弹性变形阶段也随着温度的升高相应变短。高温对孔洞形成的过程也具有很大影响,温度升高成倍地增加了原子的动能,在较低的应力状态下即位错发射产生的空位汇集起来形成孔洞。
3.3 应变率对Al2Cu拉伸变形影响与分析
为了研究应变率对Al2Cu拉伸变形结果的影响,分析Al2Cu的力学性能对加载应变率变化的响应,该部分设置了5个不同拉伸模拟程序并分别对应5个不同的工程应变速率:0.0005 ps-1、0.001 ps-1、0.005 ps-1、0.01 ps-1、0.015 ps-1。为使每个模型最终的应变值为0.20,不同拉伸率的程序需要设定不同的时间步,在300 K的环境下它们的应力应变曲线图如图5所示。
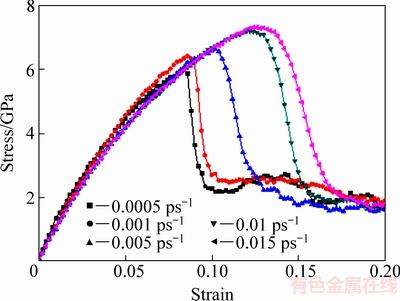
图5 300 K下不同应变率加载下的应力-应变曲线
Fig. 5 Stress-strain curves of different strain rates at 300 K
由图5中可发现,在Al2Cu的弹性变形阶段以及弹塑性混合阶段,各个应变速率下的应力-应变曲线近似重合且斜率基本相同,这表明应变速率变化对弹性变形阶段影响微乎其微。在模拟的应变率变动范围内,Al2Cu的抗拉强度和塑性都随着应变率的增加而稳步上升,应变率对Al2Cu的强化效应显著。随着外载荷的加载,应变率为0.0005 ps-1的曲线首先出现波峰后应力迅速下降,随后0.001 ps-1、0.005 ps-1、0.01 ps-1和0.015 ps-1对应的应力应变曲线依次抵达波峰并迅速下降,其中应变率为0.015 ps-1的峰值即抗拉强度达到了7.32 GPa。在模拟的应变率范围内,Al2Cu的抗拉强度表现出了与工程应变率正相关的规律。从图5还可以看出,应变率为0.0005 ps-1时曲线下降的十分迅猛,而随着应变速率的增加,各曲线的下降趋势有减缓之势,这可能是由于应变率增大导致模型内在同一时间内产生了大量的空位,空位的增多变相减慢了空位汇聚的过程。
各个应变速率的原子轨迹图如图6所示,截面厚度均为6  。可以看出,应变率为
。可以看出,应变率为 =0.0005 ps-1时,模型首先在应变为ε=0.0824如图所示的(100)面处萌生了孔洞。在随后的ε=0.0908时体系处于应力急速下降的阶段中,从(100)面观察到孔洞已经迅速长大,而且孔洞边缘呈现出大范围的混乱排列,晶格产生畸变,产生的空位逐步向孔洞汇集。应变ε=0.155时,孔洞的成长趋于平缓,边缘的无序化大幅减弱,最初的孔洞位置近似处于此时孔洞的中心。
=0.0005 ps-1时,模型首先在应变为ε=0.0824如图所示的(100)面处萌生了孔洞。在随后的ε=0.0908时体系处于应力急速下降的阶段中,从(100)面观察到孔洞已经迅速长大,而且孔洞边缘呈现出大范围的混乱排列,晶格产生畸变,产生的空位逐步向孔洞汇集。应变ε=0.155时,孔洞的成长趋于平缓,边缘的无序化大幅减弱,最初的孔洞位置近似处于此时孔洞的中心。
应变率 =0.001 ps-1时,模型首先在应变ε=0.0884 如图所示的(010)面萌生了孔洞,孔洞周围原子存在一定扰动。ε=0.0970时,此时体系处于应力急速下降的阶段中,从(010)面观察到孔洞在很短的时间内吸收空位长大,孔洞边缘原子排列十分混乱,不停有原子晶格断裂、重组并发射位错。在0.086到0.100孔洞迅速成长的这个阶段,孔洞边缘呈现出大范围的混乱排列。应变ε=0.190时,孔洞的成长早已趋于平缓,边缘的无序化大幅减弱,最初的孔洞位置近似处于此时孔洞的中心。
=0.001 ps-1时,模型首先在应变ε=0.0884 如图所示的(010)面萌生了孔洞,孔洞周围原子存在一定扰动。ε=0.0970时,此时体系处于应力急速下降的阶段中,从(010)面观察到孔洞在很短的时间内吸收空位长大,孔洞边缘原子排列十分混乱,不停有原子晶格断裂、重组并发射位错。在0.086到0.100孔洞迅速成长的这个阶段,孔洞边缘呈现出大范围的混乱排列。应变ε=0.190时,孔洞的成长早已趋于平缓,边缘的无序化大幅减弱,最初的孔洞位置近似处于此时孔洞的中心。
应变率 =0.005 ps-1时,模型首先在应变ε=0.095 如图所示的(100)面萌生了孔洞,孔洞周围原子存在一定扰动。与较低应变率的
=0.005 ps-1时,模型首先在应变ε=0.095 如图所示的(100)面萌生了孔洞,孔洞周围原子存在一定扰动。与较低应变率的 =0.001 ps-1和
=0.001 ps-1和 =0.0005 ps-1孔洞长大的过程不同,应变率为
=0.0005 ps-1孔洞长大的过程不同,应变率为 =0.005 ps-1的体系在应变ε=0.105时,孔洞下侧产生了一条向外延伸的裂纹。在随后的时间里,裂纹尖端出现了钝化促使裂纹张开,裂纹变得越来越宽,最后和孔洞汇合成应变为ε=0.156时的大孔洞,此时孔洞的成长趋于平缓,边缘的无序化大幅减弱。
=0.005 ps-1的体系在应变ε=0.105时,孔洞下侧产生了一条向外延伸的裂纹。在随后的时间里,裂纹尖端出现了钝化促使裂纹张开,裂纹变得越来越宽,最后和孔洞汇合成应变为ε=0.156时的大孔洞,此时孔洞的成长趋于平缓,边缘的无序化大幅减弱。
应变率 =0.01 ps-1时,模型首先在应变ε=0.116如图所示的(120)面萌生了孔洞,孔洞周围原子扰动较为剧烈,无序现象明显。紧接着在应变为ε=0.125体系处于应力急速下降阶段时,整个体系内部各处均萌生了大量孔洞,如图示(110)面就同时萌生了4个孔洞。继续观察 (110)面的孔洞,发现随着拉伸的继续,上方两个较大的孔洞成长迅速而下方两个较小的孔洞则成长缓慢。在应变为ε=0.140时,上方两个较大的孔洞已经相互汇合且有吸收下方孔洞的趋势。
=0.01 ps-1时,模型首先在应变ε=0.116如图所示的(120)面萌生了孔洞,孔洞周围原子扰动较为剧烈,无序现象明显。紧接着在应变为ε=0.125体系处于应力急速下降阶段时,整个体系内部各处均萌生了大量孔洞,如图示(110)面就同时萌生了4个孔洞。继续观察 (110)面的孔洞,发现随着拉伸的继续,上方两个较大的孔洞成长迅速而下方两个较小的孔洞则成长缓慢。在应变为ε=0.140时,上方两个较大的孔洞已经相互汇合且有吸收下方孔洞的趋势。
应变率 =0.015 ps-1时,模型首先在应变ε=0.120 如图所示的(010)面萌生了孔洞,孔洞周围原子扰动较为剧烈,无序现象明显。紧接着在整个体系内部各处均萌生了孔洞,在如图应变为ε=0.142时(
=0.015 ps-1时,模型首先在应变ε=0.120 如图所示的(010)面萌生了孔洞,孔洞周围原子扰动较为剧烈,无序现象明显。紧接着在整个体系内部各处均萌生了孔洞,在如图应变为ε=0.142时( 01)面所示,此时体系上方已经发展出了一个较大孔洞,而体系下方仍然不断有新的孔洞生成。当拉伸进行到应变为ε=0.183时,(
01)面所示,此时体系上方已经发展出了一个较大孔洞,而体系下方仍然不断有新的孔洞生成。当拉伸进行到应变为ε=0.183时,( 01)面上方那个较大的孔洞成长迅速而且孔洞边缘无序化仍然十分严重,下方两个较小的孔洞则成长缓慢。
01)面上方那个较大的孔洞成长迅速而且孔洞边缘无序化仍然十分严重,下方两个较小的孔洞则成长缓慢。
总的来说,在模拟的应变率变动范围内,Al2Cu的抗拉强度和塑性都随着应变率的增加而稳步上升。当应变率在 =0.005 ps-1以下时,随着外载荷加载,晶格产生畸变,产生的空位有足够的时间逐步向某一个处汇集,从而只产生一个孔洞并逐渐长大。当Al2Cu的应变率超过这个值时,如本次模拟当应变率在
=0.005 ps-1以下时,随着外载荷加载,晶格产生畸变,产生的空位有足够的时间逐步向某一个处汇集,从而只产生一个孔洞并逐渐长大。当Al2Cu的应变率超过这个值时,如本次模拟当应变率在 =0.01 ps-1以上时,拉伸时体系内会产生多个孔洞并同时成长。进一步计算应变率为
=0.01 ps-1以上时,拉伸时体系内会产生多个孔洞并同时成长。进一步计算应变率为 =0.006 ps-1时的原子轨迹图如图7所示,截面厚度均为6
=0.006 ps-1时的原子轨迹图如图7所示,截面厚度均为6  。
。
从图7知道,当应变率 =0.006 ps-1时,拉伸过程中整个体系内部各处均萌生了孔洞,如图ε=0.136(
=0.006 ps-1时,拉伸过程中整个体系内部各处均萌生了孔洞,如图ε=0.136( 23)面所示。可以得出在应变率为0.005至0.006 ps-1之间存在一个值,当Al2Cu的应变率超过这个值时,一些拉伸产生的空位来不及发生大幅移位,使其只能聚集在发射处附近,从而使体系内各处均出现大量孔洞。从后面孔洞成长的规律发现较大的孔洞由于有更大的接触面积使其更容易吸收周围的空位进行成长,从而压制周围较小孔洞的成长。
23)面所示。可以得出在应变率为0.005至0.006 ps-1之间存在一个值,当Al2Cu的应变率超过这个值时,一些拉伸产生的空位来不及发生大幅移位,使其只能聚集在发射处附近,从而使体系内各处均出现大量孔洞。从后面孔洞成长的规律发现较大的孔洞由于有更大的接触面积使其更容易吸收周围的空位进行成长,从而压制周围较小孔洞的成长。
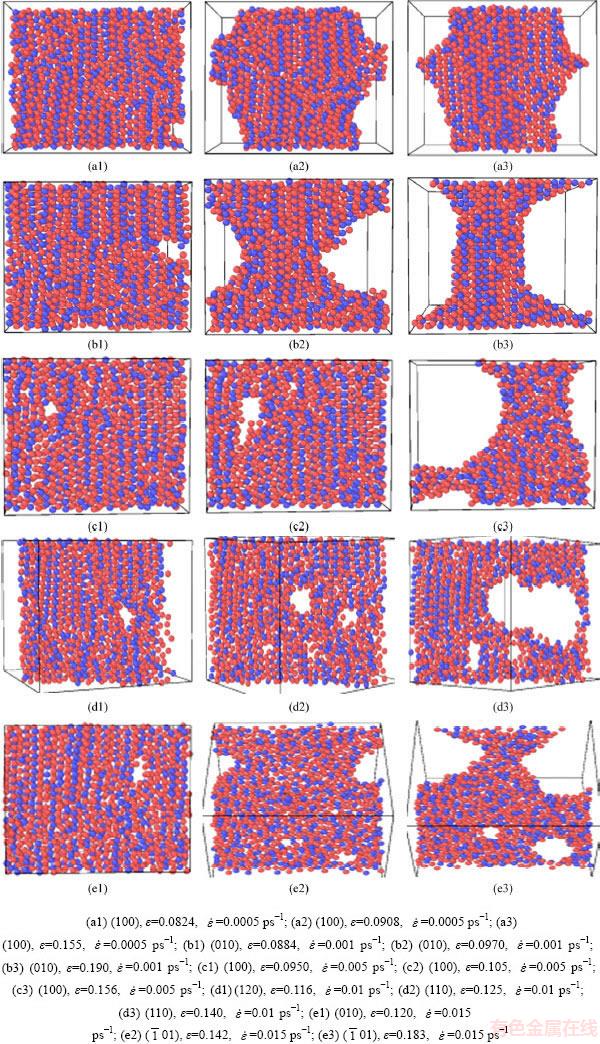
图6 不同应变率下原子轨迹图
Fig. 6 Atomic trajectories at different strain rates

图7 应变率 =0.006 ps-1时的原子轨迹图
=0.006 ps-1时的原子轨迹图
Fig. 7 Atomic trajectories at  =0.006 ps-1
=0.006 ps-1
4 结论
1) 通过300K常温时的Al2Cu沿x轴拉伸模拟发现Al2Cu非常脆,应变ε=0.086应力达到峰值6.4 GPa。而且3个方向都是周期边界的Al2Cu块体没有自由表面,原子运动自由度小、在拉伸初期不易产生位错,从而弹性变形阶段较长。
2) 通过不同温度的Al2Cu沿x轴拉伸模拟发现,Al2Cu对温度十分敏感,温度上升使Al2Cu的原子动能成倍增加,导致塑性变强但抗拉强度明显下降。
3) 通过不同应变率的Al2Cu沿x轴拉伸模拟发现,Al2Cu在应变率为0.005 ps-1至0.006 ps-1之间存在一个值,当Al2Cu的应变率超过这个值时,一些拉伸产生的空位就来不及发生大幅移位,从而只能聚集在发射处附近,使体系内各处均出现大量孔洞。而且较大的孔洞有更大的接触面积使其更容易吸收周围的空位进行成长,从而压制周围较小孔洞的成长。
REFERENCES
[1] LUKASAK D A, HART R M. Aluminum alloy development efforts for compression dominated structure of aircraft[J]. Light Metal Age, 1991, 49(9): 11-15.
[2] 刘俊涛, 张永安, 李锡武, 李志辉, 熊柏青, 张济山. 新型7056铝合金双级时效的显微组织和性能[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2016, 26(9): 1850-1857.
LIU Jun-tao, ZHANG Yong-an, LI Xi-wu, LI Zhi-hui, XIONG Bai-qing, ZHANG Ji-shan. Microstructure and properties of two-step aged novel 7056 aluminum alloy[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2016, 26(9): 1805-1857.
[3] 曾 渝, 尹志民, 潘青林, 郑子樵, 刘志义. 超高强铝合金的研究现状及发展趋势[J]. 中南工业大学学报(自然科学版), 2002, 33(6): 592-596.
ZENG Yu, YIN Zhi-min, PAN Qin-lin, ZHENG Zi-qiao, LIU Zhi-yi. Present research and developing trends of ultra high strength aluminum alloys[J]. Journal of Central South University of Technology (Science and Technology), 2002, 33(6): 592-596.
[4] ZIELINSKI A, CHRZANOWSKI J, WARMUZEK M, GAZDA A, JEZIERSKA E. Influence of retrogression and reaging on microstructure, mechanical properties and susceptibility to stress corrosion cracking of an Al-Zn-Mg alloy[J]. Materials and Corrosion, 2004, 55(2): 77-87.
[5] 赵中魁, 周铁涛, 刘培英, 陈昌麒. 含Li的Al-Zn-Mg-Cu合金的研究进展[J]. 材料导报, 2006, 20(7): 69-70, 75.
ZHAO Zhong-kui, ZHOU Tie-tao, LIU Pei-ying, CHEN Chang-qi. Research and development of Al-Zn-Mg-Cu alloys containing Li[J]. Materials Review, 2006, 20(7): 69-70, 75.
[6] HAHN G T, ROSENFIELD A R. Metallurgical factors affecting fracture toughness of aluminum alloys[J]. Metallurgical Transactions A, 1975, 6: 653-668.
[7] DUMONT D, DESCHAMPS A, BRECHET Y. On the relationship between microstructure, strength and toughness in AA7050 aluminum alloy[J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2003, 356: 326-336.
[8] MAKI-JASKARI M, KASKI K, KURONEN A. Simulations of crack initiation in silicon[J]. Computational Materials Science, 2000, 17: 336-342.
[9] 张明亮, 杨 亮, 魏承炀, 李赛毅, 张新明. 基于修正球形双晶模型的金属Al晶界能分子动力学计算[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2015, 25(11): 3060-3066.
ZHANG Ming-liang, YANG Liang, WEI Cheng-yang, LI Sai-yi, ZHANG Xin-ming. Molecular dynamics calculation of Al grain boundary energy based on modified spherical bicrystal model[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2015, 25(11): 3060-3066.
[10] LYNDEN-BELL R M. Computer simulations of fracture at the atomic level[J]. Science, 1994, 263(5154): 1704-1705.
[11] DOYAMA M. Simulation of plastic deformation of small iron and copper single crystals[J]. Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research, 1995, 102(1): 107-112.
[12] 文玉华, 周富信, 刘曰武, 周承恩. 纳米晶铜单向拉伸变形的分子动力学模拟[J]. 力学学报, 2002, 34(1): 29-36.
WEN Yu-hua, ZHOU Fu-xin, LIU Yue-wu, ZHOU Cheng-en. Molecular dynamics simulation of the unlaxlal tensile deformation of nanocrystalline copper[J]. Acta Mechanica Sinica, 2002, 34(1): 29-36.
[13] DIAO J, GALL K, DUNN M L. Yield strength asymmetry in metal nanowires[J]. Nano Letters, 2004, 4(10): 1863-1867.
[14] CAO A J,WEI Y G. Atomistic simulations of the mechanical behavior of fivefold twinned nanowires[J]. Physical Review B, 2006, 74(21): 214108.
[15] KIM D H, MANUEL M V, EBRAHIMI F , TULENKO J S, PHILLPOT S R. Deformation processes in [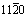 ]-textured nanocrystalline Mg by molecular dynamics simulation[J]. Acta Materialia, 2010, 58: 6217-6229.
]-textured nanocrystalline Mg by molecular dynamics simulation[J]. Acta Materialia, 2010, 58: 6217-6229.
[16] 陈 明, 李 革, 张文飞. 纳米尺度孔洞周围应力集中现象分析[J]. 材料导报 B, 2011, 25(3): 131-134.
CHEN Ming, LI Ge, ZHANG Wen -fei. Discussion on the phenomenon of stress concentration around hole in nano -scale[J]. Materials Review B, 2011, 25(3): 131-134.
[17] CHEN S D, ZHOU Y K, SOH A K. Molecular dynamics simulations of mechanical properties for Cu(001)/Ni(001) twist boundaries[J]. Computational Materials Science, 2012, 61: 239-242.
[18] ZHANG Jun-jie, XU Fang-da, YAN Yong-da, SUN Tao. Detwinning-induced reduction in ductility of twinned copper nanowires[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2013, 58(6): 684-688.
[19] WANG Wei-dong, YI Cheng-Long, FAN Kang-qi. Molecular dynamics study on temperature and strain rate dependences of mechanical tensile properties of ultrathin nickel nanowires[J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2013, 23(11): 3353-3361.
[20] 张晓泳, 张 斌, 李 超, 周科朝. 低Al含量Ti-Al 纳米杆拉伸变形的分子动力学模拟[J]. 稀有金属材料与工程, 2013, 42(10): 2057-2062.
ZHANG Xiao-yong, ZHANG Bin, LI Chao, ZHOU Ke-chao. Molecular dynamics simulation of tensile deformation of Ti-Al nano-rod with low Al content[J]. Rare Metal Materials and Engineering, 2013, 42(10): 2057-2062.
[21] 袁 林, 敬 鹏, 刘艳华, 徐振海, 单德彬, 郭 斌. 多晶银纳米线拉伸变形的分子动力学模拟研究[J]. 物理学报, 2014: 63(1): 276-281.
YUAN Lin, JING Peng, LIU Yan-hua, XU Zhen-hai, SHAN De-bin, GUO Bin. Molecular dynamics simulation of polycrystal silver nanowires under tensile deformation[J]. Acta Physica Sinica, 2014, 63(1): 276-281.
[22] 梁 力, 马明旺, 谈效华, 向 伟, 王 远, 程焰林. 含缺陷金属Ti力学性能的模拟研究[J]. 金属学报, 2015, 51(1): 107-113.
LIANG Li, MA Ming-wang, TAN Xiao-hua, XIANG Wei, WANG Yuan, CHENG Yan-lin. A simulation study of mechanical properties of metal Ti sample with defects[J]. Acta Metallurgica Sinica, 2015, 51(1): 107-113.
[23] 樊 倩, 徐建刚, 宋海洋, 张云光. 层厚度和应变率对铜-金复合纳米线力学性能影响的模拟研究[J]. 物理学报, 2015, 64(1): 225-231.
FAN Qian, XU Jian-gang, SONG Hai-yang, ZHANG Yun-guang. Effects of layer thickness and strain rate on mechanical properties of copper-gold multilayer nanowires[J]. Acta Physica Sinica, 2015, 64(1): 225-231.
[24] MEETSMA A, de BOER J L, van SMAALEN S. Refinement of the crystal structure of tetragonal Al2Cu[J]. Journal of Solid State Chemistry, 1989, 83: 370-372.
[25] DAW M S, BASKES M I. Semiempirical, quantum mechanical calculation of hydrogen embrittlement in metals[J]. Physical Review Letters, 1983, 50(17): 1285-1288.
Molecular dynamics simulation of tensile deformation of Al2Cu
LIU Xiao-bo, XIONG Zhen, FANG Zhou, LI Yan
(School of Aeronautical Manufacturing Engineering, Nanchang Hangkong University, Nanchang 330063, China)
Abstract: The tension deformation behavior of Al2Cu was studied by molecular dynamics method. The molecular dynamics simulation model of Al2Cu was established, and the influence of Al2Cu model on mechanical properties of Al2Cu under constant engineering strain rate tension at constant temperature was simulated by using the embedded atom method. The influences of temperature and strain rate on the tension deformation were discussed. The results show that Al2Cu is very brittle under that condition, when the strain is 0.086, the stress reaches the peak value of 6.4 GPa, and it is difficult to produce dislocations at the initial stage of tension, thus the elastic deformation stage is relatively long. Al2Cu is very sensitive to temperature. The kinetic energy of Al2Cu increases exponentially with the temperature rising, resulting in a stronger plasticity, but the tensile strength decreases obviously. The analysis also reveals a value between the strain rate of 0.005 to 0.006 ps-1, when the tensile strain rate of Al2Cu exceeds this value, some of the vacancies produced by stretching are too late to take place in the system, can only gather near the launch site, which leads to the formation of voids in the system.
Key words: Al2Cu; tension; molecular dynamics simulation; temperature; strain rate
Foundation item: Project(11362017) supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China; Project (2010GQC0803) supported by the Natural Science Foundation of Jiangxi Province, China; Project(KJLD12073) supported by the Science and Technology Project of Jiangxi Province Education Department, China
Received date: 2017-07-24; Accepted date: 2018-03-23
Corresponding author: LIU Xiao-bo; Tel: +86-791-83953108; E-mail: liuxb2000@sina.com
(编辑 王 超)
基金项目:国家自然科学基金资助项目(11362017);江西省自然科学基金资助项目(2010GQC0803);江西省教育厅科技落地计划科学前沿项目(KJLD12073)
收稿日期:2017-07-24;修订日期:2018-03-23
通信作者:刘晓波,教授,博士;电话:0791-83953108;E-mail:liuxb2000@sina.com