DOI:10.19476/j.ysxb.1004.0609.2017.07.03
AA2024-H18铝合金同步冷却热成形后的强化机制
陈国亮1, 2,陈明和1,王 宁1,孙佳伟1
(1. 南京航空航天大学 机电学院,南京 210016;
2. 常州机电职业技术学院 模具技术系,常州 213164)
摘 要:为了研究同步冷却热成形工艺对可热处理铝合金的显微组织演变规律以及强化机制的影响,选用H18态AA2024铝合金板料进行同步冷却热成形及自然时效试验,并进行力学性能测试、光学显微组织观察及TEM分析。结果表明:同步冷却热成形工艺对AA2024铝合金的显微组织影响明显;H18态AA2024铝合金板料经过同步冷却热成形及96 h自然时效后,试样变形区的位错密度增加,并出现细针状的Al2CuMg(S′)相,使得变形区的屈服强度及抗拉强度分别较冷冲压工艺试样提高4%、12%;此时,AA2024铝合金的强化机制主要是弥散相Al20Cu2Mn3(T相)和沉淀相Al2CuMg(S′相)对位错的钉扎作用,以及位错间的相互作用。
关键词:同步冷却热成形;AA2024铝合金;显微组织;强化机制;力学性能
文章编号:1004-0609(2017)-07-1337-07 中图分类号:TG146.1 文献标志码:A
可热处理铝合金具有质轻、耐腐蚀、比强度和比刚度高,良好的损伤容限等特性,广泛应用于航空航天及交通运输业中[1-4]。但相对于低碳钢而言,常温下该铝合金塑性变形范围窄、弹性模量小,采用常规冷冲压工艺加工时易开裂、回弹严重,很难生产出形状复杂的零件[5]。采用传统的温[6-7]/热[8]成形工艺虽然能改善可热处理铝合金的成形性能,但也带来诸如晶粒长大、能耗高以及生产效率低等新问题。此外,成形后的可热处理铝合金零件还需进行固溶处理和时效处理才能获取所需的力学性能,但成形零件往往壁厚较薄,在固溶处理过程中容易发生翘曲变形,从而影响尺寸精度。同步冷却热成形工艺[9]可以很好地解决可热处理铝合金传统的室温及温/热成形工艺存在的急需解决的问题,该工艺借鉴高强钢的热冲压[10-13]方法,即利用热成形改善成形性及淬火(固溶)强化机理相结合,演化而来的一种对可热处理铝合金同时进行固溶处理和冲压成形的新工艺。其工艺过程是先将可热处理铝合金板料加热到固溶处理温度,并保温一段时间,待其组织均匀化后移入模具进行冲压成形及快速冷却(同时完成成形及固溶处理),之后再进行相应的时效处理,从而获得零件所需的力学性能。采用同步冷却热成形工艺并辅以相应的时效处理,能在改善可热处理铝合金成形性能的基础上,提高成形精度,缩短生产周期,降低生产成本,并且不会降低零件的力学性能。
目前,对于同步冷却热成形工艺的研究主要集中在该工艺的可行性以及对可热处理铝合金成形性能和力学性能的影响:GARRETT等[14]对AA6082铝合金的同步冷却热成形工艺进行了可行性研究;英国帝国理工学院的研究人员研究了同步冷却热成形条件下的AA6082[15]、AA2024[16]铝合金的成形性能和断裂机理;国内南京航空航天大学的研究人员利用热成形模拟机上进行了同步冷却热成形工艺下AA6016、AA6181铝合金的成形性能及力学性能研究[13, 17-19],证实该工艺可大幅度提高AA6016高强铝合金的成形性能,并可以使成形后的AA6016强度较原始状态提高16%。但现有研究并未涉及可热处理铝合金在同步冷却热成形过程中显微组织演化以及最终制品的强化机制。另外,同步冷却热成形工艺与传统的“冷冲压成形+固溶处理”生产工艺存在一定的差异:首先,同步冷却热成形时,板料在温度急剧下降时成形,而冷冲压成形时板料温度基本不会变化;其次,同步冷却热成形的传热机理和冷却速度与传统可热处理铝合金零件在水或其他介质中进行热交换的情况不同。因此,传统工艺下可热处理铝合金显微组织演化及强化机 制[20-22],不适用于同步冷却热成形工艺。本文作者选用AA2024-H18铝合金进行同步冷却热成形、自然时效试验,对成形试样进行光学及TEM显微组织观察,分析同步冷却热成形工艺对AA2024铝合金微观组织演化及强化机制的影响。
1 实验
1.1 试验材料及装置
选用西南铝业公司生产的H18态AA2024铝合金轧制板料,规格为2400 mm×1200 mm×0.8 mm(L×W×H),其主要成分如表1所列。试验前利用剪板机加工出184 mm×80 mm×0.8 mm的毛坯,毛坯的宽度沿轧制方向,保证成形时板料的轧制方向与弯曲方向一致。成形试验在安装于高速液压机上的同步冷却热成形模具中进行,如图1所示,模具中设有冷却管路,保证模具在试验过程中一直处于室温状态。
表1 AA2024-H18铝合金成分
Table 1 Chemical compositions of AA2024-H18 (mass fraction, %)

1.2 成形试验方法及流程
首先将AA2024-H18毛坯加热到495 ℃并保温5 min,再将毛坯快速移动到同步冷却热成形模具上进行冲压并保压1 min,然后开模取出试样,最后对试样进行96 h的自然时效处理,试验流程如图2(a)所示。为了对比研究,按传统生产工艺进行冷冲压成形、固溶处理及时效试验,其流程如图2(b)所示:将室温下的AA2024-H18板料放入如图1所示的同步冷却热成形模具上进行冲压,再将成形试样加热到495 ℃并保温5 min,然后放入室温的水中淬冷,最后对试样进行96 h的自然时效处理。
1.3 显微组织观察
自然时效完成后,对两种成形工艺获得的AA2024铝合金试样的变形区和非变形区进行显微组织观察。使用PME OLYMPUS TOKYO光学显微镜观察试样不同部位的显微组织分布及晶粒尺寸情况;利用JEM-2100透射电镜观察试样不同部位的位错密度及分布情况,合金相的尺寸、成分及分布情况,并分析合金相与位错之间的相互作用。

图1 同步冷却热成形模具
Fig. 1 Hot forming die with synchronous cooling (Unit: mm)

图2 试验流程图
Fig. 2 Flow-sheet of forming experiment

图3 单拉试样的示意图
Fig. 3 Schematic diagram of specimens for uniaxial tensile test (Unit: mm)
1.4 力学性能测量
利用线切割机床在AA2024铝合金试样的相应部位切割出如图3所示的拉伸试样,在RG2000-20试验机上进行拉伸试验,测量其力学性能(制品上圆角区域处按图3所示的拉伸试样投影进行加工,并使用特制的夹具在万能材料试验机上测试力学性能)。试验过程中试验机横梁移动速度由程序控制,保证试样的应变速率为2.5×10-4 s-1,误差小于2%。
2 结果及分析
2.1 成形精度
图4所示为两种不同成形工艺获得的AA2024铝合金试样。由图4可以看出,室温下H18态AA2024铝合金成形性能相对较差,冷冲压成形试样在R5的弯曲圆角处发生了破裂,只成形出了R10的圆角;而由于是在高温下成形,H18态AA2024铝合金毛坯在同步冷却热成形时能顺利成形出R5的弯曲圆角。此外,由于同步冷却热成形工艺是在模具闭合的状态下对试样进行冷却的,没有空间进行翘曲变形,所以试样外形平整没有翘曲;而传统的固溶处理是将试样直接放在水中进行冷却,导致了冷冲压成形试样发生翘曲变形,如图4所示。两种不同工艺获得的AA2024铝合金试样外观及尺寸精度上的差异验证了同步冷却热成形工艺可以提高AA2024铝合金的成形性能以及零件成形精度的论断。
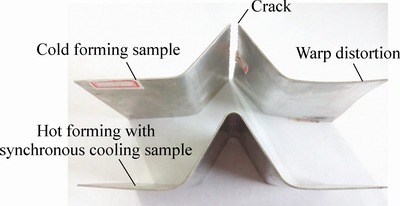
图4 AA2024铝合金试样
Fig. 4 AA2024 aluminum alloy samples formed under different conditions
2.2 显微组织及强化机制
图5所示为96h自然时效后同步冷却成形AA2024铝合金试样变形区域(R5)的光学显微组织。由图5可以看出,试样弯曲截面上各个部位的晶粒尺寸存在一定差别:试样弯曲截面内侧,晶粒因压缩变形显得相对较短,存在大量直径为10 μm左右的细小晶粒;而弯曲截面外侧,晶粒因拉伸变形呈长度50 μm宽度10 μm的细长条状,并沿同一方向排布。图5(b)所示的区域位于弯曲截面的中心,由于在成形过程中基本没有变形,晶粒呈等轴状。由此可见,在同步冷却热成形过程中AA2024铝合金的晶粒尺寸的变化效果直接保留在最终试样上。
经96 h自然时效后两种不同成形工艺获得的AA2024铝合金试样变形区域的位错分布情况如图6所示,其中同步冷却热成形试样的取样部位位于R5弯曲圆角处,冷冲压成形试样由于R5弯曲圆角处发生断裂,所以取样部位在R10弯曲圆角处。从图6中可以看出,在变形区域内,同步冷热成形试样的位错密度明显高于冷冲压试样的。这是由于在冷冲压试样中,冷冲压产生的位错由于后续固溶处理的加热和保温过程中因静态回复和静态再结晶的作用而消除;而在同步冷却热成形过程中,AA2024铝合金毛坯是先进行固溶处理的加热和保温,然后在降温过程中进行冲压成形,虽然会发生动态回复,但是由于时间较短并不能消除成形过程中增加的所有位错,从而提高了试样的位错密度。

图5 同步冷却热成形试样弯曲截面的光学显微组织
Fig. 5 Microstructures of cross section in formed region of hot forming with synchronous cooling sample
经过同步冷却热成形及96h自然时效后的AA2024铝合金试样中含有3种不同的合金相:含Fe元素的组分相Al7Cu2Fe、含Mn和Cu元素的弥散相Al20Cu2Mn3(T相)及含Mg和Cu元素的沉淀相Al2CuMg(S′相),如图7所示,但在冷冲压成形试样中只有组分相Al7Cu2Fe和弥散相Al20Cu2Mn3。沉淀相Al2CuMg通常只出现在经过人工时效后的AA2024铝合金中[23],而经96 h自然时效后的同步冷却热成形AA2024铝合金试样的变形区域内出现细针状沉淀相Al2CuMg,这是温度变化和外力相互作用下合金原子聚集析出而成的结果。由于尺寸上的差异,同步冷却热成形后3种合金相对AA2024铝合金强度的影响也不同:组分相Al7Cu2Fe因为尺寸较大(1~100 μm),无法起到对位错的钉扎及增值作用,因而会降低AA2024铝合金制品的强度[24];弥散相Al20Cu2Mn3尺寸介于0.02到 0.2 μm之间,能有效钉扎位错及亚晶界,提高AA2024铝合金的强度,是主要强化相,如图8所示;细针状的沉淀相Al2CuMg尺寸更小,具有很强的沉淀强化效应[25]。由此可见,同步冷却热成形并经96 h自然时效以后,AA2024铝合金中主要的强化机制为弥散相Al20Cu2Mn3(T相)和沉淀相Al2CuMg(S′相)对位错和亚晶界的钉扎作用,以及位错之间的相互作用。

图6 试样变形区域位错分布
Fig. 6 Dislocation distribution of sample

图7 同步冷却热成形后试样中合金相的形貌、衍射谱及能谱图
Fig. 7 Micromorphologies ((a1), (b1), (c1)), diffraction patterns ((a2), (b2), (c2)) and energy spectra ((c3), (b3), (c3)) of alloy phase in formed region of hot forming with synchronous cooling sample
2.3 力学性能
图9所示为两种不同成形方法并经96 h自然时效后获得的AA2024铝合金试样各个区域的强度。由图9可以看出,由于沉淀相Al2CuMg对位错和亚晶界具有钉扎作用,强化了基体(α相)增加了变形抗力[25],使得同步冷却热成形AA2024铝合金的屈服强度和抗拉强度较冷冲压成形后AA2024铝合金分别提高了4%、12%。另外,虽然同步冷却热成形试样各个部位的抗拉强度基本相等,但变形区的屈服强度要高于非变形区,如图9(b)所示。这是由于变形区的AA2024铝合金在同步冷却热成形过程中发生了加工硬化,成形后,变形区位错密度高于非变形区的,需要较大的外力才能克服位错之间以及位错与合金相之间的相互作用力使位错产生滑移,增加发生塑性变形所需的临界剪切应力,从而提高了AA2024铝合金的屈服强度。由此可见,在自然时效条件下,采用同步冷却热成形工艺可以提高AA2024铝合金的强度。

图8 弥散相与位错之间的形貌
Fig. 8 Morphologies of dispersion phase pin dislocations and subgrain boundaries (In unformed region of hot forming with synchronous cooling sample)

图9 最终AA2024试样强度
Fig. 9 Final strength of AA2024 aluminum alloy sample (Region 4 in cold forming sample was crack, so strength of where did not be tested)
3 结论
1) 与传统冷冲压成形工艺相比,同步冷却热成形工艺可以提高AA2024铝合金的成形性能。
2) 经过同步冷却成形后,AA2024铝合金的位错密度显著增加,发生了明显的加工硬化。
3) 在自然时效条件下,采用同步冷却热成形工艺获得到的AA2024铝合金变形区出现了沉淀相Al2CuMg(S′相),提高了AA2024铝合金的强度。
4) 经过同步冷却热成形及96 h自然时效以后,AA2024铝合金中主要的强化机制为弥散相Al20Cu2Mn3(T相)和沉淀相Al2CuMg(S′相)对位错和亚晶界的钉扎,以及位错之间的相互作用。
REFERENCES
[1] HIRSCH J. Recent development in aluminium for automotive applications[J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2014, 24(7): 1995-2002.
[2] 曹景竹, 王祝堂. 铝合金在航空航天器中的应用(2)[J]. 轻合金加工技术, 2013, 41(3): 1-12.
CAO Jing-zhu, WANG Zhu-tang. Application of aluminum alloy in aeronautics and aerospace vehicle (2)[J]. Light Alloy Fabrication Technology, 2013, 41(3): 1-12.
[3] 刘 兵, 彭超群, 王日初, 王小锋, 李婷婷. 大飞机用铝合金的研究现状及展望[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2010, 20(9): 1705-1715.
LIU Bing, PENG Chao-qun, WANG Ri-chu, WANG Xiao-feng, LI Ting-ting. Recent development and prospects for giant plane aluminum alloys[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2010, 20(9): 1705-1715.
[4] STARKE E A, STALEY J T. Application of modern aluminum alloys to aircraft[J]. Progress in Aerospace Sciences, 1996, 32(2): 131-172.
[5] 潘复生, 张丁非. 铝合金及应用[M]. 北京: 化学工业出版社, 2007.
PAN Fu-sheng, ZHANG Ding-fei. Aluminum alloy and its application[M]. Beijing: Chemical Industry Press, 2007.
[6] 李 翔, 唐建国, 张新明, 凌利月, 刘文辉, 廖志宇, 杨 涛, 邓运来. 温变形对汽车车身用6061铝合金自然时效及力学性能的影响[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2016, 26(1): 1-6.
LI Xiang, TANG Jian-guo, ZHANG Xin-ming, LING Li-yue, LIU Wen-hui, LIAO Zhi-yu, YANG Tao, DENG Yun-lai. Effect of warm deformation on natural ageing and mechanical property of aluminum alloy 6061 sheets for automotive body[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2016, 26(1): 1-6.
[7] TOROS S, OZTURK F, KACAR I. Review of warm forming of aluminum-magnesium alloys[J]. Journal of Materials Processing Technology, 2008, 207(1/3): 1-12.
[8] PYE A M. Superplastic forming of aluminium alloys[J]. Materials & Design, 1981, 2(6): 304-309.
[9] CHEN Ming-he, CAO Yuan-yuan, CHEN Wei, CHEN Guo-liang. Research on synchronized cooling hot forming process of 6016 aluminum alloy[J]. Advanced Materials Research, 2012, 452/453: 81-85.
[10] KARBASIAN H, TEKKAYA A E. A review on hot stamping[J]. Journal of Materials Processing Technology, 2010, 210(15): 2103-2118.
[11] MORI K I. Smart hot stamping of ultra-high strength steel parts[J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2012, 22(2): 496-503.
[12] 李辉平, 赵国群, 张 雷, 贺连芳. 超高强度钢板热冲压及模内淬火工艺的发展现状[J]. 山东大学学报(工学版), 2010, 40(3): 69-74.
LI Hui-ping, ZHAO Guo-qun, ZHANG Lei, HE Lian-fang. The development status of hot stamping and quenching of ultra high-strength steel[J]. Journal of Shandong University (Engineering Science), 2010, 40(3): 69-74.
[13] 马 宁, 胡 平, 闫康康, 郭 威, 孟祥兵, 翟述基. 高强度硼钢热成形技术研究及其应用[J]. 机械工程学报, 2010, 46(14): 68-72.
MA Ning, HU Ping, YAN Kang-kang, GUO Wei, MENG Xiang-bing, ZHAI Shu-ji. Research on boron steel for hot forming and its application[J]. Journal of Mechanical Engineering, 2010, 46(14): 68-72.
[14] GARRETT R P, LIN J, DEAN T A. Solution heat treatment and cold die quenching in forming AA 6xxx sheet components: Feasibility study[J]. Advanced Materials Research, 2005, 6/8: 673-680.
[15] MOHAMED M S, FOSTER A D, LIN Jian-guo, BALINT D S, DEAN T A. Investigation of deformation and failure features of AA6082: Experimentation and modelling[J]. International Journal of Machine Tools & Manufacture, 2012, 53(1): 27-38.
[16] WANG L, STRANGWOOD M, BALINT D, LIN J, DEAN T A. Formability and failure mechanisms of AA2024 under hot forming conditions[J]. Materials Science & Engineering A, 2011, 528(6): 2648-2656.
[17] WANG Ning, CHEN Guo-liang, CHEN Ming-he. Constitutive relationship and parameters optimization of 6181 H18 aluminum alloy hot forming process with synchronous cooling[J]. Materials Science Forum, 2014, 770: 324-328.
[18] 曹园园, 陈明和, 王小芳, 李琳琳, 陈 伟. 6181H18铝合金同步冷却热成形工艺研究[J]. 航空制造技术, 2012(5): 81-84.
CAO Yuan-yuan, CHEN Ming-he, WANG Xiao-fang, LI Lin-lin, CHEN Wei. Research on synchronized cooling hot forming process of 6181H18 aluminum alloy[J]. Aeronautical Manufacturing Technology, 2012(5): 81-84.
[19] 李琳琳. 6000系铝合金同步冷却热成形及烘烤时效工艺研究[D]. 南京: 南京航空航天大学, 2012.
LI Lin-lin. Research on paint baking process after synchronization cooling hot forming of 6000 series aluminum alloys[D]. Nanjing: Nanjing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2012.
[20] WANG S C, STARINK M J. Precipitates and intermetallic phases in precipitation hardening Al-Cu-Mg-(Li) based alloys[J]. International Materials Reviews, 2005, 50(4): 193-215.
[21] 桂奇文. 热处理工艺对2024铝合金析出相及性能的影响[D]. 长沙: 湖南大学, 2008.
GUI Qi-wen. The influence of heat treatment process on the precipitates and properties of 2024 aluminum alloy[D]. Changsha: Hunan University, 2008.
[22] 陈康华, 刘允中, 刘红卫. 7075和2024铝合金的固溶组织与力学性能[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2000, 10(6): 819-822.
CHEN Kang-hua, LIU Yun-zhong, LIU Hong-wei. Microstructure and mechanical properties of enhanced solution treated 7075 and 2024 aluminum alloys[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2000, 10(6): 819-822.
[23] 贺双喜, 刘向阳, 谢广辉, 刘西刚, 尚 坤, 张新军. 时效制度对2A12 铝合金组织与性能的影响[J]. 金属热处理, 2014, 39(6): 94-96.
HE Shuang-xi, LIU Xiang-yang, XIE Guang-hui, LIU Xi-gang, SHANG Kun, ZHANG Xin-jun. Effects of aging on microstructure and mechanical properties of 2A12 aluminum alloy[J]. Heat Treatment of Metals, 2014, 39(6): 94-96.
[24] WILLIAMS J C, STARKE E A. Progress in structural materials for aerospace systems[J]. Acta Mater, 2003, 51(19): 5775-5799.
[25] 王祝堂. 2024型铝合金的热处理[J]. 金属世界, 2009(2): 43-48.
WANG Zhu-tang. Heat treatment for 2024 aluminum alloy[J]. Metal World, 2009(2): 43-48.
Strengthening mechanism of hot forming with synchronous cooling of AA2024-H18 aluminum alloy
CHEN Guo-liang1, 2, CHEN Ming-he1, WANG Ning1, SUN Jia-wei1
(1. College of Mechanical and Electrical Engineering, Nanjing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, Nanjing 210016, China
2. Department of Mould Technology, Changzhou Institute of Mechatronic Technology, Changzhou 213164, China)
Abstract: Hot forming test with synchronous cooling, metallographic and TEM observation and tensile test were performed to investigate the influence of hot forming with synchronous cooling operations on the microstructure evolution and strengthening mechanism of AA2024-H18 aluminum alloy. The results show that, the yield strength of hot formed AA2024 sheet with 96 h natural aging is 4%, which is superior to that of traditionally formed sheet, and meanwhile, the tensile strength is increased by 12%. Based on the microstructure observation and analysis, the strengthening is generated by the increase of the dislocation density and precipitation of some fine acicular particles in form of Al2CuMg (S′). The main strengthening mechanism of AA2024 aluminum alloy underwent hot forming with synchronous cooling is the pinning effect of dispersoid phase Al20Cu2Mn3 (T) and precipitated phase Al2CuMg (S′) on dislocation as well as the interaction of dislocation.
Key words: hot forming with synchronous cooling; AA2024 aluminum alloy; microstructure; strengthening mechanism; mechanical behavior
Foundation item: Projects(51175252) supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China
Received date: 2016-05-17; Accepted date: 2016-11-11
Corresponding author: CHEN Ming-he; Tel: +86-13951809276; E-mail: meemhchen@nuaa.edu.cn
(编辑 李艳红)
基金项目:国家自然科学基金资助项目(51175252)
收稿日期:2016-05-17;修订日期:2016-11-11
通信作者:陈明和,教授,博士;电话:13951809276;E-mail:meemhchen@nuaa.edu.cn