Influence diversity of extracellular DNA on bioleaching chalcopyrite and pyrite by Sulfobacillus thermosulfidooxidans ST
来源期刊:中南大学学报(英文版)2020年第5期
论文作者:申丽 曾伟民 蔡宇鑫 侯春伟 刘阿娟 彭堂见 陈淼 邱冠周
文章页码:1466 - 1476
Key words:extracellular DNA; Sulfobacillus thermosulfidooxidans ST; chalcopyrite; pyrite; confocal laser scanning; bioleaching
Abstract: In this paper, Sulfobacillus thermosulfidooxidans ST was selected for use in bioleaching of pyrite and chalcopyrite. The adsorption experiments revealed that more cells were adsorbed on the surface of pyrite than on the surface of chalcopyrite. The role of extracellular DNA (eDNA) in the bioleaching process was investigated by depletion of eDNA using DNase I. The number of cells attached on the chalcopyrite and pyrite surfaces decreased on a large scale, and the lag phase of cell growth increased, causing the leaching percentages of pyrite and chalcopyrite to decrease by approximately 11.6% and 20.5%, respectively. The formation and distribution of eDNA secreted during bioleaching was assessed by a fluorescent dye-based method and visualized by confocal laser scanning microscopy (CLSM). The content of eDNA increased with bioleaching time. Furthermore, ST showed a stronger capacity to produce eDNA on the surface of pyrite than on the surface of chalcopyrite. These results showed that the removal of eDNA has a more significant effect on the bioleaching of chalcopyrite than on pyrite.
Cite this article as: ZENG Wei-min, CAI Yu-xin, HOU Chun-wei, LIU A-juan, PENG Tang-jian, CHEN Miao, QIU Guan-zhou, SHEN Li. Influence diversity of extracellular DNA on bioleaching chalcopyrite and pyrite by Sulfobacillus thermosulfidooxidans ST [J]. Journal of Central South University, 2020, 27(5): 1466-1476. DOI: https://doi.org/ 10.1007/s11771-020-4382-2.

J. Cent. South Univ. (2020) 27: 1466-1476
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11771-020-4382-2
ZENG Wei-min(曾伟民)1, 2, 3, CAI Yu-xin(蔡宇鑫)1, HOU Chun-wei(侯春伟)1, LIU A-juan(刘阿娟)1,
PENG Tang-jian(彭堂见)1, CHEN Miao(陈淼)3, QIU Guan-zhou(邱冠周)1, 2, SHEN Li(申丽)1, 2
1. School of Minerals Processing and Bioengineering, Central South University, Changsha 410083, China;
2. Key Laboratory of Biohydrometallurgy of Ministry of Education, Central South University,Changsha 410083, China;
3. CSIRO Mineral Resources, Clayton, Victoria, Australia
 Central South University Press and Springer-Verlag GmbH Germany, part of Springer Nature 2020
Central South University Press and Springer-Verlag GmbH Germany, part of Springer Nature 2020
Abstract: In this paper, Sulfobacillus thermosulfidooxidans ST was selected for use in bioleaching of pyrite and chalcopyrite. The adsorption experiments revealed that more cells were adsorbed on the surface of pyrite than on the surface of chalcopyrite. The role of extracellular DNA (eDNA) in the bioleaching process was investigated by depletion of eDNA using DNase I. The number of cells attached on the chalcopyrite and pyrite surfaces decreased on a large scale, and the lag phase of cell growth increased, causing the leaching percentages of pyrite and chalcopyrite to decrease by approximately 11.6% and 20.5%, respectively. The formation and distribution of eDNA secreted during bioleaching was assessed by a fluorescent dye-based method and visualized by confocal laser scanning microscopy (CLSM). The content of eDNA increased with bioleaching time. Furthermore, ST showed a stronger capacity to produce eDNA on the surface of pyrite than on the surface of chalcopyrite. These results showed that the removal of eDNA has a more significant effect on the bioleaching of chalcopyrite than on pyrite.
Key words: extracellular DNA; Sulfobacillus thermosulfidooxidans ST; chalcopyrite; pyrite; confocal laser scanning; bioleaching
Cite this article as: ZENG Wei-min, CAI Yu-xin, HOU Chun-wei, LIU A-juan, PENG Tang-jian, CHEN Miao, QIU Guan-zhou, SHEN Li. Influence diversity of extracellular DNA on bioleaching chalcopyrite and pyrite by Sulfobacillus thermosulfidooxidans ST [J]. Journal of Central South University, 2020, 27(5): 1466-1476. DOI: https://doi.org/ 10.1007/s11771-020-4382-2.
1 Introduction
Retrieving metals from pyrite and chalcopyrite using acidophiles is known as biomining and has been widely used in industry for many years. Typical microorganisms used in biomining include Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans, Acidithiobacillus thiooxidans, Leptospirillum ferrooxidans and Sulfobacillus thermosulfidooxidans. There have been many studies on the bioleaching mechanisms of sulfide minerals with a focus on reaction kinetics, electrochemistry, microorganism ecology and mineralogy [1-3]. It has been reported that extraction of metal ions mainly occurs in the microenvironment of the interface between the mineral and the microorganism [4, 5]. During bioleaching of sulfide minerals, bacteria such as S.thermosulfidooxidans prefer to attach to mineral surface [6]. After inoculation, this attachment happens rapidly, and the process takes only a few hours [7]. The bacteria that have adsorbed on the mineral surface are encapsulated by self-produced extracellular polymeric substances (EPSs). EPSs mediate contact between the bacteria/archaea and minerals and play an important role in biofilm formation and interfacial biochemical reactions [8, 9].
EPSs are one of the main components of biofilms. EPSs are composed of carbohydrates, proteins, lipids, DNA, vesicles, and cellular fragments, whose composition and concentration vary as a function of the organism and environmental conditions [10, 11]. Most studies have focused on the function of extracellular proteins and extracellular polysaccharides but ignored another important substance, extracellular DNA (eDNA). In fact, some studies have shown that eDNA can enhance the initial adhesion and aggregation of bacteria and that it is also an important structural component of the biofilm [12-14]. To date, the formation mechanism and function of eDNA is still under debate [15, 16]. CRUZ et al [17] reports that eDNA could provide the ability to adhere to carrier surfaces and maintain the stability of biofilm by attaching to other extracellular substances as a skeleton component of EPS.
Several methods, such as high-speed centrifugation, membrane filtration and some chemical methods, have been used to extract and isolate eDNA from biofilm samples. However, the extracted amount of eDNA was different due to the different extraction methods, bacterial strains, incubation time and experimental conditions [18]. In recent years, with the development of visualization technologies such as confocal laser scanning microscopy (CLSM), atomic force microscopy, genomics and proteomics, an increasing number of studies have been conducted on eDNA. OKSHEVSKY et al [19] found that eDNA in Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilms showed fine tendrils by CLSM. SENAVELEZ et al [20] found that eDNA of Xanthomonas citri subsp. citri strains showed a fibrous structure. The composition difference between extracellular and intracellular DNA observed by using fingerprint analysis has been investigated in many studies. Furthermore, some studies have illustrated that bacterial eDNA could be removed by DNase I addition, which has an effect on the formation and stability of biofilms as well as the adsorption of bacteria [21, 22].
In the field of biometallurgy, the interface between bacteria and minerals involves electrochemical, biochemical, and surface chemical processes, and eDNA is involved in the contact of bacteria with the minerals [23, 24]. ZHANG et al [25] performed a visualization of the eDNA of the thermophilic archaea Sulfolobus metalus and YU et al [26] revealed that eDNA can promote the adsorption of bacteria on the surface of chalcopyrite and improve the efficiency of bioleaching during the chalcopyrite bioleaching by Sulfobacillus thermosulfidooxidans ST.
Sulfobacillus thermosulfidooxidans ST is a typical acidophile and moderate thermophile (40-60 °C), and it is considered to be an effective strain for sulfide mineral bioleaching [27]. However, the adsorption and eDNA secretion of Sulfobacillus thermosulfidooxidans ST on different mineral surfaces are less poorly understood. In this paper, the efficiencies of bioleaching of pyrite and of chalcopyrite by S. thermosulfidooxidans ST were studied and compared, along with additional bioleaching parameters. Additionally, the amount of eDNA as a function of time and the effect of removing eDNA on bioleaching were studied, and the interactions between the minerals and microorganisms were also analyzed. This investigation aimed to explore the relationships among eDNA production, mineral extraction and microorganism growth during bioleaching, and to provide more theoretical basis for future industrial production.
2 Materials and methods
2.1 Bacterial strain and culture conditions
The Sulfobacillus thermosulfidooxidans ST used throughout this study was isolated from the Key Laboratory of Biometallurgy of Central South University, China. Sulfobacillus thermosulfidooxidans ST was obtained from an acidic hot spring in the Tengchong region of China [28]. The constituents of the culture medium were 3.0 g/L (NH4)2SO4, 0.5 g/L MgSO4·7H2O, 0.5 g/L K2HPO4, 0.1 g/L KCl, and 0.01 g/L Ca(NO3)2 supplemented with 0.02% yeast extract. The initial pH of the medium was set to 1.6 using H2SO4 (5 mol/L), and cells were grown on pyrite (5%) or chalcopyrite (5%). Flasks (250 mL) containing 100 mL of medium were used for both seed culture and EPS production at 45 °C.
2.2 Mineral components
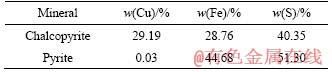
The mineral samples were originated from the Daye Mine in Hubei Province, China. The chalcopyrite concentrate was mainly composed of CuFeS2 (88.1%), FeS2 (3.7%), CuS2 (4.19%) and other minerals (2.7%). The pyrite mainly consisted of FeS2 (90.0%), FeSO4 (4.4%) and other minerals (5.6%). The main elements contained in the samples are shown in Table 1. The distribution size of mineral powders used in the experiments was less than 74 μm (95% of grains). Prior to use, the chalcopyrite and pyrite concentrates were dried in a vacuum drying chamber at room temperature for 24 h. Finally, the minerals were sterilized by UV irradiation for 24 h in an aseptic room.
Table 1 Chemical composition of mineral samples
2.3 Microorganism culture and enumeration
5 g mineral powder was placed in a 250-mL shaker flask containing 100 mL of medium with an initial pH of 1.6. Cells were harvested by centrifugation at 8000g for 10 min to obtain the pellets. Then, the cell pellets were washed twice using sterilized acidified water (pH 2.0), resuspended in the culture medium and adjusted to obtain an initial density of 6×106 cell/mL. The culture was incubated in temperature incubator at 170 r/min and 45 °C. Deionized water was routinely added to compensate for the water loss caused by evaporation. All experiments were performed in triplicate.
The planktonic cells density was measured with a blood cell counting chamber under an optical microscope. Previously reported methods were adopted to analyze the amount of attached cells [29]. The pH, redox potential and concentrations of copper, ferrous ions, total iron and sulfate ions in the bioleaching solutions were analyzed each day. The bis(cyclohexanone)oxaldihydrazone (BCO) light-intensity method was used to quantify the concentration of copper in solution [30]. Ferrous and total irons in solution were determined by the phenanthroline spectrophotometric method [31]. The concentration of sulfate ions was determined by the colorimetric method using barium chromate [32]. The pH value was measured with a pHS-3C acid meter (LEICI, Shanghai, China), and the ORP (vs. Ag/AgCl) value was measured against a Ag/AgCl reference electrode.
DNase I treatment was performed to further elucidate the role of eDNA in the bacterial adsorption and bioleaching process. DNase I was diluted using DNase- and protease-free water and was added to the bacterial culture at a final concentration of 50 μg/mL. DNase I supplementation was performed every 2 d to guarantee that no residual eDNA remained in the bioleaching system. Three parallel groups were set up for each experiment.
2.4 Extraction of eDNA
The eDNA of bacterial cells was analyzed on the 5th, 10th, 15th, 20th, and 25th day after incubation. The extraction of EPS from free and attached cells was reported previously [10, 33]. The leaching solution was settled for 2 h, and the supernatant was discarded. Then, the homogenate was centrifuged at 2000g for 4 min at 4 °C, and the resulting supernatant was centrifuged at 12000g for 10 min at 4 °C in order to obtain planktonic cells.
The residual ore was used to harvest EPS-attached cells. The process has been described previously [11]. Briefly, the residual ore was centrifuged at 2000g, and the supernatant was discarded to eliminate planktonic cells. Then, the obtained sludge was resuspended and shaken on a vortexer in the presence of glass beads. This mixture was centrifuged at 3000 r/min, and the supernatant was collected. The above steps were repeated to maximally remove EPS from the attached cells. Finally, all of the supernatants were combined and centrifuged at 12000 r/min. The soluble fraction contained the EPS extract of the sessile cells. The vortex method was also adopted to extract EPS from planktonic cells. The cell debris was sterilized by filtration through a 0.22-μm millipore filter, and then the EPSs were stored at -20 °C until use.
Potential impurities from non-EPS constituents of cells were checked by measuring the activity of glucose 6-phosphate dehydrogenase (G6PDH). One million bacteria or cells in the reaction system will produce 1 nmol of NADPH per minute, defined as one enzymatic unit. In addition, the protein content in the EPS differed from the content of polysaccharides by no more than 5-fold, and eDNA accounted for less than 15% of the total EPS, demonstrating that the cells were not destroyed [34, 35]. High-quality eDNA was obtained from EPSs by the cetyltrimethylammonium bromide- DNA precipitation method [36, 37]. A NanoDrop ND-1000 spectrophotometer was used to quantify the eDNA samples.
ND-1000 spectrophotometer was used to quantify the eDNA samples.
2.5 CLSM analysis of eDNA on mineral surfaces during bioleaching
The in-situ observation of eDNA was analyzed on the 5th, 10th, 15th, 20th and 25th day by CLSM during the bioleaching of chalcopyrite and pyrite. The ore residue was cleaned with sterile distilled water (SDW) to remove free cells from the surface of mineral. The eDNA and attached cells on the surface of the ore residue were stained by specific fluorescent dyes, acridine orange (AO)/ propidium iodide (PI). Mix the working solution (66.7 μg/mL AO and 33.4 μg/mL PI) with bacteria and incubate for 30 min at room temperature and keep in dark place. Take single layer image of ore residue with CLSM after incubation. PI (excitation wavelength 488 nm, emission wavelength 630 nm) specifically stains eDNA [19, 38] and cannot penetrate living cell membranes [39, 40], thus characterizing the distribution of eDNA. AO (excitation wavelength 488 nm/emission wavelength 515 nm) can penetrate living cell membranes and bind to intracellular DNA [41], so its fluorescence intensity was related to the amount of attached cells.
3 Results and discussion
3.1 Planktonic cells density and attached cell amount during bioleaching
Figure 1 shows the planktonic and attached biomass during bioleaching of chalcopyrite and pyrite. The amount of attached biomass peaked (8.5×109 cells/per gram of ore residue) on the 9th day during chalcopyrite bioleaching (Figure 1(a)). Afterward, the quantity of attached biomass steadily fell until the 18th day and then dropped slightly. By contrast, the planktonic biomass in the leach liquor increased slowly after a prolonged lag period, reached a peak on the 14th day (12.6×108 cell/mL) and began to decrease on the 20th day. The trend of microorganism growth during pyrite bioleaching was similar to that during chalcopyrite bioleaching, as shown in Figure 1(b). The attached biomass amount reached its maximum on the 11th day (13.19×109 cells per gram of ore residue) and began to decrease on the 23rd day. The planktonic biomass reached its maximum on the 16th day (16.8×108 cell/mL) and began to decrease on the 23rd day.
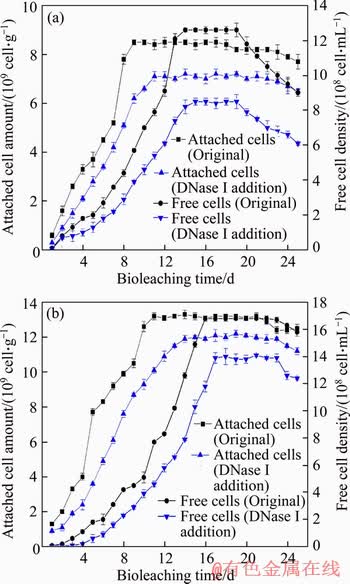
Figure 1 Variations in planktonic and attached biomass during bioleaching of chalcopyrite (a) and pyrite (b) by S. thermosulfidooxidans ST at 5% pulp density and an initial pH of 1.6
During bioleaching, microorganisms prefer to attach onto the surface of minerals [7] because energy substances such as ferrous iron, which is needed for bacterial growth, are released from minerals after the liberation of ferric iron and protons. Thus, the attached cells reach the logarithmic phase first. It can also be seen that only after the attached cell amounts reached their maximum, the increase in planktonic cells density could begin to accelerate. However, the kinds and origins of minerals can also affect bioleaching microorganism adsorption and growth [42]. Some authors have published that the electrostatic force between mineral surfaces and bacteria is the main factor in initial bacterial attachment. They found that at low pH, electrostatic forces can promote the adsorption of bacteria to the pyrite surface, but the electrostatic force between chalcopyrite and bacteria is very weak [43, 44]. RODRIGUEZ et al [45] and HUANG et al [46] found that pyrite is easier than chalcopyrite to biooxidiz. Therefore, pyrite would release more ferrous iron to support cell growth at the beginning of bioleaching. Finally, the maximum planktonic cells density and attached cell amount during pyrite bioleaching were obviously higher than those during chalcopyrite bioleaching.
The addition of DNase I affected bacterial growth during the bioleaching of both chalcopyrite and pyrite. During the bioleaching of chalcopyrite, the amount of attached cells and planktonic cells density decreased by 15.3% and 32.7%, respectively, and the time to reach the maximum adsorption amount was delayed by 5 d. In the bioleaching of pyrite, the amount of attached cells and the planktonic cells density decreased by 7.5% and 16.7%, respectively, and the time to reach the maximum adsorption amount was delayed by 2 d. After removing the eDNA, the main component of the EPS, the number of adsorbed cells on the surface of chalcopyrite was reduced more than that on the surface of pyrite. These data indicate that DNase I eliminated eDNA, which inhibited the attachment of cells, leading to a decrease in energy sources (ferrous ion or inorganic sulfur compounds) in the bioleaching environment and thereby reducing the planktonic cells density. Furthermore, the deficiency of eDNA showed more influence on cell growth during chalcopyrite bioleaching than during pyrite bioleaching.
3.2 Comparison between chalcopyrite and pyrite bioleaching by S. thermosulfidooxidans ST
The variation in pH value with time is shown in Figure 2(a). The pH value during pyrite bioleaching showed a decreasing trend; however, the pH value during chalcopyrite bioleaching first increased and then decreased until the end. Obviously, in the chalcopyrite and pyrite bioleaching processes, the addition of DNase I will inhibit the generation of hydrogen ions. The decrease in pH is mainly because sulfur in the mineral was oxidized into sulfuric acid, liberating hydrogen ions [1].
The variation in redox potential with time is shown in Figure 2(b). The redox potential during pyrite bioleaching continued to increase until the 17th day and reached a maximum of 570 mV (vs. Ag/AgCl). After that, its redox potential decreased slightly. In the DNase I-treated experimental group, the redox potential reached a maximum of 551 mV on the 20th day. However, the redox potential of chalcopyrite bioleaching increased gradually during the bioleaching time and finally remained at a high level of 618 mV (vs. Ag/AgCl). In the DNase I-treated experimental group, the final value decreased slightly at 573 mV. During the bioleaching of chalcopyrite and pyrite, the group that was treated by DNase I resulted in a reduced redox potential, and DNase I had more influence on the redox potential change in the bioleaching of chalcopyrite than in the bioleaching of pyrite. The redox potential is mainly related to the ratios of Fe3+/Fe2 + in the leachate.
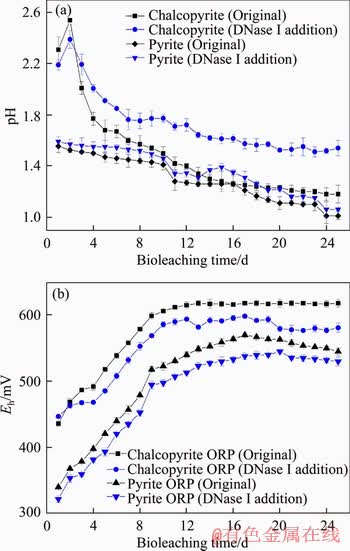
Figure 2 Variations in pH value (a) and redox potential (b) of leach liquor during bioleaching of chalcopyrite and pyrite by S. thermosulfidooxidans ST at 5% pulp density and an initial pH of 1.6
Over the whole chalcopyrite bioleaching process (Figure 3(a)), the copper ion concentration continued to increase and was basically constant after the 21st day. However, the concentration of Fe2+ in chalcopyrite leachate was relatively low. The total iron concentration first increased continuously and then decreased slightly after the 18th day, and the redox potential value increased persistently throughout the process (Figure 2(b)). It has been found that a high concentration of total irons can significantly promote copper extraction. Iron ions play a key role in the bioleaching of chalcopyrite. Ferrous iron as the energy source for bioleaching microorganisms is oxidized to regenerate ferric iron, which is the main oxidizing agent during bioleaching. In the case in which eDNA was removed during the whole chalcopyrite bioleaching process, the content of ferrous ions was still very low, and the concentration of total iron and copper ions decreased significantly. On the 21st day, the total leaching percentage decreased from 10.1 g/L in the presence of eDNA to 7.6 g/L in the absence of eDNA.
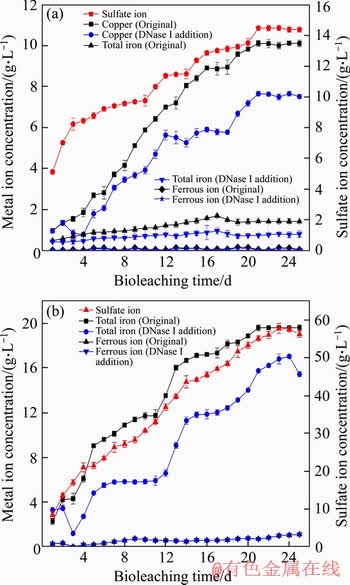
Figure 3 Variations in metal ion and sulfate ion concentrations in leach liquor as a function of time during bioleaching of chalcopyrite (a) and pyrite (b) by S. thermosulfidooxidans ST at 5% pulp density and an initial pH of 1.6
During bioleaching of pyrite, it can be seen from Figure 3(b) that the concentration of ferrous ion presented a continued upward trend, and the final leaching percentage of total iron reached 19.6 g/L. The maximum total iron content that can be achieved was reduced to 17 g/L during bioleaching with DNase I addition. An increase in the sulfate ion concentration and a decrease in the pH value indicated that oxidation of sulfur was a continuous process in this experiment. X-ray diffraction (XRD) analysis of both chalcopyrite and pyrite leaching residues showed that the final copper extraction of chalcopyrite and total iron extraction of pyrite were 79.9% and 87.8%, respectively. However, only 59.4% copper and 76.2% total iron were extracted in chalcopyrite and pyrite in the DNase I treated group.
3.3 Extraction and analysis of eDNA from free and attached cells during bioleaching
Later analyses of the EPS extracts of planktonic cells (0.0665) and adsorbent cells (0.0718) did not detect significant differences in G6PDH activity compared with the untreated control group (0.0611). Storage at -20 °C for more than 70 d is known to completely impair the activity of other intracellular enzymes, but in this study, samples were analyzed only at 48 h after extraction. According to the results for the extraction of EPS from the adsorbent cells on the mineral surface, the protein content in the EPS differed from the polysaccharide content by no more than 5-fold. In addition, eDNA accounted for less than 15% of the total EPS. Thus, the low ratio of proteins/ polysaccharides and the low content of eDNA indicates that the method for extraction of EPS in section 2.4 did not cause obvious cell rupture, and this implied negligible contamination from intracellular substances in the collected eDNA [35, 36, 47].
Figure 4 shows the content of eDNA on the 5th, 10th, 15th, 20th and 25th day during bioleaching of chalcopyrite and pyrite. As shown in Figure 4(a), as the chalcopyrite leaching time increased, the eDNA content of planktonic cells and the number of attached cells increased. The eDNA content of planktonic cells reached 68 μg/1010 cell on the 25th day. However, the eDNA content of the attached cells was much higher than that of planktonic cells, which was 637 μg/1010 cell on the 25th day. After that, eDNA content of the attached cells still increased slightly. Additionally,Figure 4(b) shows that when pyrite was used as the energy source, free and attached cells both secreted more eDNA. The eDNA content of planktonic cells was 135 μg/1010 cell, and the eDNA content of attached cells was 1750 μg/1010 cell on the 25th day during bioleaching of pyrite.
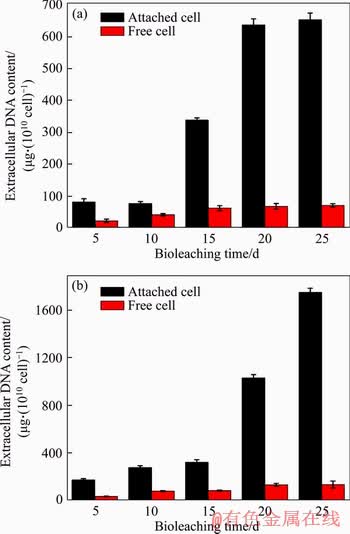
Figure 4 Variations in eDNA content during bioleaching of chalcopyrite (a) and pyrite (b)
In the beginning of bioleaching of both chalcopyrite and pyrite, the eDNA secretion was very slow, mainly because the bacterial cells were still in the adaptive phase (Figure 1). Subsequently, as the energy source was released from minerals, cell growth accelerated, resulting in increased eDNA production. This variation trend for eDNA content was in agreement with the research reported by YING et al [48]. Although the number of bacteria decreased in the late stage, the eDNA content did not decline. This result may be because some of the bacterial cells began to break down and release some eDNA. Some studies have reported that eDNA release mainly occurred during cell lysis, at which point the eDNA turned into a key component of the macromolecular scaffold in biofilms [34, 49].
It can also be seen from Figure 4 that the eDNA produced by the attached cells was much more abundant than that produced by the planktonic cells, similar to other EPS production [50, 51]. The mineral surface was the main location where energy sources, such as ferrous iron and sulfur, were produced. Therefore, the attached cells could more easily obtain an energy source to yield EPS. In our previous research, we found that the attached cells would yield a large amount of EPS quickly and form biofilms covering the mineral surface [52]. Furthermore, the results also showed that bacteria produced more eDNA on the pyrite surface than on the chalcopyrite surface. This finding may be because the different main components and states of the sulfides of chalcopyrite and pyrite, the differences in the crystal structure of the two ores, and the high iron content during the pyrite bioleaching [53, 54].
3.4 CLSM analysis of eDNA in ore residue during bioleaching
On the 5th, 10th, 15th, 20th, 25th day of bioleaching, combined with AO/PI staining, the attached cell and eDNA amount on the mineral surface was detected by CLSM. It can be seen from Figure 5 that whether chalcopyrite or pyrite was used as an energy source, the green fluorescence intensity increased with increasing leaching time. This result indicated that the abundance of bacteria adsorbed on the surface of the minerals increased, which was consistent with Figure 1. Additionally, the red fluorescence intensity also increased over the leaching time, suggesting that the amount of eDNA increased, which was consistent with Figure 4. In general, the fluorescence intensity of eDNA on pyrite was stronger than that on the chalcopyrite surface. This finding further suggests that using pyrite as the energy source would produce more eDNA.
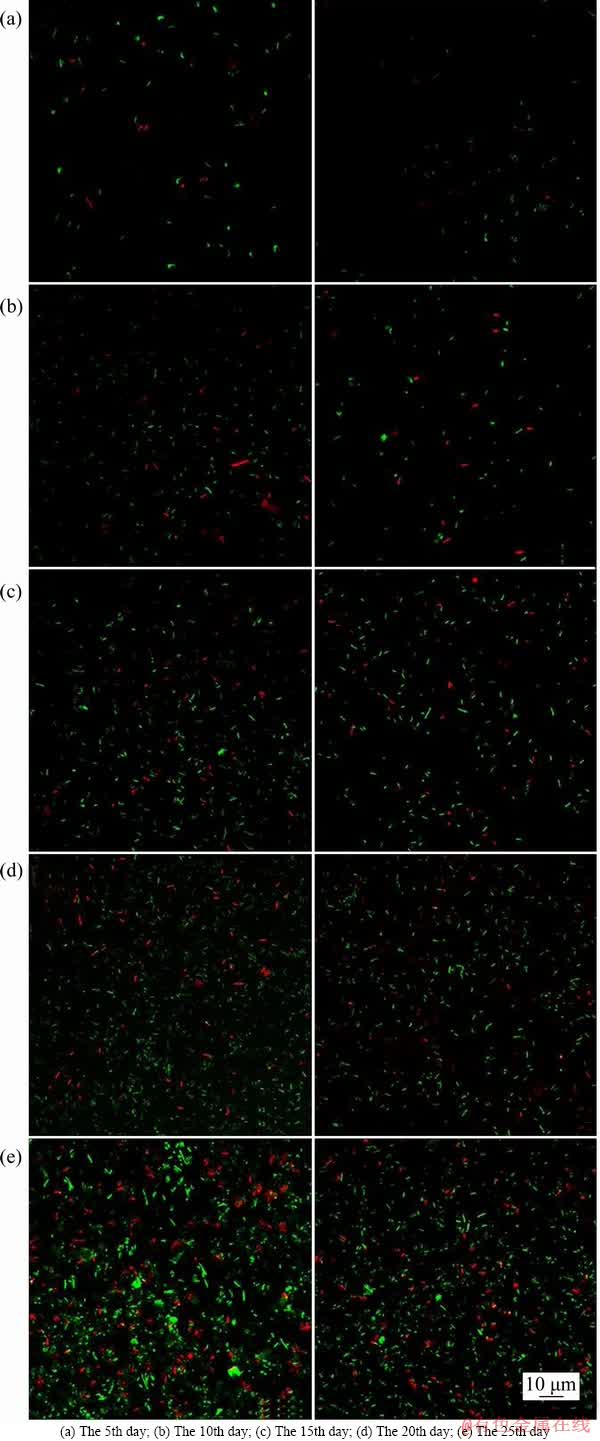
Figure 5 CLSM image of surface of chalcopyrite and pyrite (DNA was stained with propidium iodide for eDNA (red) and acridine orange for intracellular DNA (green). The left column shows bacteria using pyrite for energy and the right column shows bacteria using chalcopyrite for energy):
4 Conclusions
In situ detection in conjunction with conventional extraction and analytical methods is a better way to study the production of eDNA in various periods of bioleaching. The results indicated that bacteria were more likely to adsorb and produce more eDNA on the surface of pyrite than on the surface of chalcopyrite. Compared with the bioleaching of pyrite, the deletion of eDNA was more detrimental to chalcopyrite bioleaching in reducing the number of attached cells and the final bioleaching efficiency. In all, eDNA could significantly promote the bioleaching process of the bacteria ST cultured with chalcopyrite and pyrite. In the future bioleaching industry, attempts can be made to modify the bioleaching system to promote the production of eDNA to improve the bioleaching efficiency. We will further investigate the formation pathway and structure of eDNA to obtain greater theoretical proof to explain the effect of eDNA during bioleaching.
References
[1] PENG Tang-jian, ZHOU Dan, LIU Ya-nan, YU Run-lan, QIU Guan-zhou, ZENG Wei-ming. Effects of pH value on the expression of key iron/sulfur oxidation genes during bioleaching of chalcopyrite on thermophilic condition [J]. Annals of Microbiology, 2019, 69(6): 627-635. DOI: 10.1007/s13213-019-01453-y.
[2] ZHAO Hong-bo, ZHANG Yi-shen, ZHANG Xian, QIAN Lu, SUN Meng-lin, YANG Yu, ZHANG Yan-sheng, WANG Jun, KIM H, QIU Guan-zhou. The dissolution and passivation mechanism of chalcopyrite in bioleaching: An overview [J]. Mineral Engineering, 2019, 136: 140-154. DOI: 10.1016/ j.mineng.2019.03.014.
[3] ZENG Wei-min, QIU Guan-zhou, ZHOU Hong-bo, LIU Xue-dong, CHEN Miao, CHAO Wei-liang, ZHANG Cheng- gui, PENG Juan-hua. Characterization of extracellular polymeric substances extracted during the bioleaching of chalcopyrite concentrate [J]. Hydrometallurgy, 2010, 96(3): 77-80. DOI: 10.1016/j.hydromet.2009.11.002.
[4] MITSUNOBU S, ZHU Ming, TAKEICHI Y, OHIGASHI T, TAKAHASHI Y. Direct detection of Fe(II) in extracellular polymeric substances (EPS) at the mineral-microbe interface in bacterial pyrite leaching [J]. Microbes and Environments, 2016, 31(1): 63-69. DOI: 10.1264/jsme2.ME15137.
[5] GIESE E C. Evidences ofEPS-iron (III) ions interactions onbioleachingprocess mini-review: The key to improve performance [J]. Orbital the Electronic Journal of Chemistry, 2019, 11(3): 200-204. DOI: 10.17807/orbital.v11i3.1389.
[6] VERA M, SCHIPPERS A, SAND W. Progress in bioleaching: Fundamentals and mechanisms of bacterial metal sulfide oxidation-part A [J]. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 2013, 97(17): 7529-7541. DOI: 10.1007/ s00253-013-4954-2.
[7] GHAURI M A, OKIBE N, JOHNSON D B. Attachment of acidophilic bacteria to solid surfaces: The significance of species and strain variations [J]. Hydrometallurgy, 2007, 85(2): 72-80. DOI: 10.1016/j.hydromet.2006.03.016.
[8] VELMOUROUGANE K, PRASANNA R, SINGH S B, KUMAR R, SAHA S. Sequence of inoculation influences the nature of exopolymeric substances (EPS) and biofilm formation in Azotobacter chroococcum and Trichoderma viride [J]. FEMS Microbiology Ecology, 2017, 93(7): 1-13. DOI: 10.1093/femsec/fix066.
[9] AI Chen-bing, YAN Zhang, ZHOU Han, HOU Shan-shan, CHAI Li-yuan, QIU Guang-zhou, ZENG Wei-min. Metagenomic insights into the effects of seasonal temperature variation on functional potentials of activated sludge [J]. Microorganisms, 2019, 713(7): 1-18. DOI: 10.3390/ microorganisms7120713.
[10] DAS T, KROM B P, VAN D M H C, BUSSCHER H J, SHARMA P K. DNA-mediated bacterial aggregation is dictated by acid-base interactions [J]. Soft Matter, 2011, 7(6): 2927-2935. DOI: 10.1039/c0sm01142h.
[11] YU Run-lan, LIU A-juan, LIU Ya-nan, YU Zhao-Jing, PENG Tang-jian, WU Xue-ling, SHEN Li, LIU Yuan-dong, LI Jiao-kun, LIU Xue-duan, QIU Guan-zhou, CHEN Miao, ZENG Wei-min. Evolution of Sulfobacillus thermosulfidooxidans secreting alginate during bioleaching of chalcopyrite concentrate [J]. Journal of Applied Microbiology, 2017, 122(6): 1586-1594. DOI: 10.1111/jam. 13467.
[12] DAS T, SHARMA P K, BUSSCHER H J, MEI H C V D, KROM B P. Role of extracellular DNA in initial bacterial adhesion and surface aggregation [J]. Applied & Environmental Microbiology, 2010, 76: 3405-3408. DOI: 10.1128/aem.03119-09.
[13] BOCKELMANN U, JANKE A, KUHN R, NEU T R, WECKE J, LAWRENCE J R, SZEWZYK U. Bacterial extracellular DNA forming a defined network-like structure [J]. FEMS Microbiology Letters, 2006, 262(1): 31-38. DOI: 10.1111/ j.1574-6968.2006.00361.x.
[14] WHITCHURCH C B, TOLKER-NIELSEN T, RAGAS P C, MATTICK J S. Extracellular DNA required for bacterial biofilm formation [J]. Science, 2002, 295(5559): 1487. DOI: 10.1111/j.1574-6968.2006.00361.x.
[15] STEINBERGER R E, HOLDEN P A. Extracellular DNA in single- and multiple-species unsaturated biofilms [J]. Applied & Environmental Microbiology, 2005, 71(9): 5404- 5410. DOI: 10.1128/aem.71.9.5404-5410.2005.
[16] VORKAPIC D, PRESSLER K, SCHILD S. Multifaceted roles of extracellular DNA in bacterial physiology [J]. Current Genetics, 2016, 62(1): 71-79. DOI: 10.1007/ s00294-015-0514-x.
[17] CRUZ L F, COBINE P A, FUENTE L D L. Calcium increases Xylella fastidiosa surface attachment, biofilm formation, and twitching motility [J]. Applied & Environmental Microbiology, 2012, 78(5): 1321. DOI: 10.1128/AEM.06501-11.
[18] GEYIK A G, CECEN F. Variations in extracellular polymeric substances (EPS) during adaptation of activated sludges to new feeding conditions [J]. International Biodeterioration & Biodegradation, 2015, 105: 137-145. DOI: 10.1016/j.ibiod. 2015.08.021.
[19] OKSHEVSKY M, MEYER R L. Evaluation of fluorescent stains for visualizing extracellular DNA in biofilms [J]. Journal of Microbiological Methods, 2014, 105: 102- 104. DOI: 10.1016/j.mimet.2014.07.010.
[20] SENAVELEZ M, REDONDO C, GRAHAM J H, CUBERO J. Presence of extracellular DNA during biofilm formation by Xanthomonas citri subsp. citri strains with different host range [J]. Plos One, 2016, 11(6): e156695. DOI: 10.1371/ journal.pone.0156695.
[21] PATEL K K, SUREKHA D B, TRIPATHI M, ANJUM M M, MUTHU M S, TILAK R, AGRAWAL A K, SINGH S. Antibiofilm potential of silver sulfadiazine-loaded Nanoparticle formulations: A study on the effect ofDNase-I on microbial biofilm and wound healing activity [J]. Molecular Pharmaceutics, 2019, 16(9): 3916-3925. DOI: 10.1021/acs.molpharmaceut.9b00527.
[22] OZDEMIR C, AKCELUK M, AKCELIK N. The role of extracellular DNA in salmonella biofilms [J]. Molecular Genetics Microbiology and Virology, 2018, 33(1): 60-71. DOI: 10.3103/S089141681801010X.
[23] RONG Xin-min, HUANG Qiao-yun, CHEN Wen-li, CAI Peng, LIANG Wei. Surface thermodynamical analysis of adsorption of bacteria on two soil clay minerals [J]. Acta Pedologica Sinica, 2010, 48(2): 331-337. DOI: 10.11766/ trxb201003160095.
[24] HUFTON J, HARDING J H, ROMERO-GONZALEZ M E. The role of extracellular DNA in uranium precipitation and biomineralization [J]. Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics, 2016, 18(42): 29101-29112. DOI:10.1039/c6cp03239g.
[25] ZHANG Rui-yong, NEU T R, ZHANG Yu-tong, BELLENT S, KUHLICHE U, LI Qian, SAND W, VERA M. Visualization and analysis of EPS glycoconjugates of the thermoacidophilic archaeonSulfolobus metallicus [J]. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 2015, 99(17): 7343-7356. DOI: 10.1007/s00253-015-6775-y.
[26] YU Run-lan, HOU Chun-wei, LIU A-juan, PENG Tang-jian, XIA Ming-chen, WU Xue-ling, SHEN Li, LIU Yuan-dong, LI Jiao-kun, YANG Fei, QIU Guan-zhou, CHEN Miao, ZENG Wei-min. Extracellular DNA enhances the adsorption of Sulfobacillus thermosulfidooxidans, strain ST on chalcopyrite surface [J]. Hydrometallurgy, 2018, 176: 97-103. DOI: 10.1016/j.hydromet.2018.01.018.
[27] DING Jian-nan, GAO Jian, WU Xue-ling, ZHANG Cheng-gui, WANG Dian-zuo, QIU Guan-zhou. Jarosite-type precipitates mediated by YN22, Sulfobacillus thermosulfidooxidans, and their influences on strain [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2007, 17(5): 1038-1044. DOI: 10.1016/s1003-6326(07)60222-2.
[28] GUO Xue, YIN Hua-qun, LIANG Yi-li, HU Qi, ZHOU Xi-shu, XIAO Yun-hua, MA Li-yuan, ZHANG Xian, QIU Guan-zhou, LIU Xue-dong. Comparative genome analysis reveals metabolic versatility and environmental adaptations of Sulfobacillus thermosulfidooxidans Strain ST [J]. Plos One, 2014, 9(6): e99417. DOI: 10.1371/journal. pone.0099417.
[29] ZENG Wei-ming, QIU Guan-zhou, ZHOU Hong-bo, PENG Juan-hua, CHEN Miao, TAN Su-ne, CHAO Wei-liang, LIU Xue-dong, ZHANG Yan-sheng. Community structure and dynamics of the free and attached microorganisms during moderately thermophilic bioleaching of chalcopyrite concentrate [J]. Bioresource Technol, 2010, 101(18): 7079-7086. DOI: 10.1016/j.biortech.2010.04.003.
[30] JIANG Bi-xian. The Mensuration of the copper contents in the Stannum based alloy with BCO light-intensity method [J]. Heavy Castings & Forgings, 2006, 12(1): 38-39. (in Chinese)
[31] YE Ai-ying, ZUO Yin-hu. Determination of iron in ion exchange resin by-phenanthroline [J]. Industrial Water Treatment, 2013, 33(3): 74-76. (in Chinese)
[32] SUN Cheng-zhi, MAI Jin-hua, WEI Yan. Discussion on the Improment of the determination of SO42- in water [J]. Trace Elements Science, 2001, 8(3): 55-56. (in Chinese)
[33] YU Run-lan, LIU Zhen-hua, YU Zhao-jing, WU Xue-ling, SHEN Li, LIU Yuan-dong, LI Jiao-kun, QIN Wen-qing, QIU Guan-zhou, ZENG Wei-min. Relationship among the secretion of extracellular polymeric substances, heat resistance, andbioleachingability of Metallosphaera sedula [J]. International Journal of Minerals Metallurgy & Materials, 2019, 26(12): 1504-1511. DOI: 10.1007/s12613-019- 1851-4.
[34] WU Jian-feng, XI Chuan-wu. Evaluation of different methods for extracting extracellular DNA from the biofilm matrix [J]. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 2009, 75(16): 5390-5395. DOI: 10.1128/AEM.00400-09.
[35] CORINALDESI C, DANOVARO R, DELLANNO A. Simultaneous recovery of extracellular and intracellular DNA suitable for molecular studies from marine sediments [J]. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 2005, 71(1): 46-50. DOI: 10.1128/AEM.71.1.46-50.2005.
[36] BO F, PALMGREN R, KEIDING K, NIELSEN P H. Extraction of extracellular polymers from activated sludge using a cation exchange resin [J]. Water Research, 1996, 30(8): 1749-1958. DOI: 10.1016/0043-1354(95)00323-1.
[37] LIAO Bao-qian, ALLEN D G, DROPPO I G, LEPPARD G G, LISS S N. Surface properties of sludge and their role in bioflocculation and settleability [J]. Water Research, 2001, 35(2): 339-350. DOI: 10.1016/s0043-1354(00)00277-3.
[38] QIN Zhi-qiang, OU Yuan-zhu, YANG Liang, ZHU Yu-li, TOLKER-NIELSEN T, MOLIN S, QU Di. Role of autolysin-mediated DNA release in biofilm formation of Staphylococcus epidermidis [J]. Microbiology, 2007, 153(7): 2083. DOI: 10.1099/mic.0.2007/006031-0.
[39] FUXMAN BASS J I, RUSSO D M, GABELLONI M L, GEFFNER J R, GIORDANO M, CATALANO M, ZORREGUIETA A, TREVANI A S. Extracellular DNA: A major proinflammatory component of Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilms [J]. Journal of Immunology, 2010, 184(11): 6386-6395. DOI: 10.4049/jimmunol.0901640.
[40] ZRELLI K, GALY O, LATOURLAMBERT P, KIRWAN L, GHIGO J M, BELOIN C, HENRY N. Bacterial biofilm mechanical properties persist upon antibiotic treatment and survive cell death [J]. New Journal of Physics, 2013, 15(12): 5026. DOI: 10.1088/1367-2630/15/12/125026.
[41] RANJITHA V R, MUDDEGOWDA U, RAVISHANKAR R V. Potent activity of bioconjugated peptide and selenium nanoparticles against colorectal adenocarcinoma cells [J]. Drug Development and Industrial Pharmacy, 2019, 45(9): 1-21. DOI: 10.1080/03639045.2019.1634090.
[42] JIA Chun-yun, WEI De-zhou, LIU Wen-gang, HAN Chong, GAO Shu-ling, WANG Yu-juan. Selective adsorption of bacteria on sulfide minerals surface [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2008, 18(5): 1247-1252. DOI: 10.1016/s1003-6326(08)60211-3.
[43] LOOSDRECHT M C V, LYKLEMA J, NORDE W, SCHRAA G, ZEHNDER A J. Electrophoretic mobility and hydrophobicity as a measured to predict the initial steps of bacterial adhesion [J]. Applied & Environmental Microbiology, 1987, 53(8): 1898-1901. DOI: 10.1002/bit. 260300227.
[44] GEHRKE T, HALLMANN R, KINZLER K, SAND W. The EPS of Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans-a model for structure- function relationships of attached bacteria and their physiology [J]. Water Science and Technology, 2001, 43(6): 159-167. DOI: 10.2166/wst.2001.0365.
[45] RODRIGUEZ Y, BALLESTER A, BLAZQUEZ M L, GONZALEZ F, MUNOZ J A. Study of bacterial attachment during the bioleaching of pyrite, chalcopyrite, and sphalerite [J]. Geomicrobiology Journal, 2003, 20(2): 131-141. DOI: 10.1080/01490450303880.
[46] HUANG Tao, LI Dong-wei. Presentation on mechanisms and applications of chalcopyrite and pyrite bioleaching in biohydrometallurgy―A presentation [J]. Biotechnology Reports, 2014, 4(1): 107-119. DOI: 10.1016/j.btre.2014.09. 003.
[47] HE Zhi-gao, YANG Yan-ping, ZHOU Shou, HU Yue-hua, ZHONG Hui. Effect of pyrite, elemental sulfur and ferrous ions on EPS production by metal sulfide bioleaching microbes [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2014, 24(4): 1171-1178. DOI: 10.1016/S1003-6326 (14)63176-9.
[48] YING Xu, LIU Yan-an, ZHAO Liang. Study on the function of the extracellular DNA in the candida albicans biofilm formation in the root canal [J]. Journal of Modern Stomatology, 2009, 84: 1-17. DOI: 10.1016/j.na.2013.02. 005.
[49] DESAI S, SANGHRAJKA K, GAJJAR D. High adhesion and increased cell death contribute to strong biofilm formation in Klebsiellapneumoniae [J]. Pathogens (Basel, Switzerland), 2019, 8(4): 1504-1511. DOI: 10.3390/pathogens8040277.
[50] HARNEIT K, SAND W. Influence of growth substrate and attachment substratum on EPS and biofilm formation by Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans [J]. Advanced Materials Research, 2007, 20-21: 385. DOI: 10.4028/www. scientific.net/AMR.20-21.385.
[51] YU Run-lan, LIU Jian, TAN Jian-xi, ZENG Wei-min, SHI Li-juan, GU Guo-hua, QIN Wen-qing, QIU Guan-zhou. Effect of pH values on the extracellular polysaccharide secreted by Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans during chalcopyrite bioleaching [J]. International Journal of Minerals Metallurgy and Materials, 2014, 21(4): 311-316. DOI: 10.1007/s12613-014-0910-0.
[52] ZENG Wei-min, TAN Su-ne, CHEN Miao, QIU Guan-zhou. Detection and analysis of attached microorganisms on the mineral surface during bioleaching of pure chalcopyrite with moderate thermophiles [J]. Hydrometallurgy, 2011, 106(1): 46-50. DOI: 10.1016/j.hydromet.2010.11.014.
[53] SCHIPPERS A, SAND W. Bacterial leaching of metal sulfides proceeds by two indirect mechanisms via Thiosulfate or via Polysulfides and sulfur [J]. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 1999, 65(1): 319-321. DOI: 10.1002/abio.370190413.
[54] AI Chen-bing, YAN Zhang, CHAI Hong-sheng, GU Tian-yuan, WANG Jun-jun, CHAI Li-yuan, QIU Guan-zhou, ZENG Wei-min. Increased chalcopyrite bioleaching capabilities of extremely thermoacidophilic Metallosphaera sedula inocula by mixotrophic propagation [J]. Journal of Industrial Microbiology & Biotechnology, 2019, 46(8): 1113-1127. DOI: 10.1007/s10295-019-02193-3.
(Edited by YANG Hua)
中文导读
黄铜矿与黄铁矿的生物浸出过程中Sulfobacillus thermosulfidooxidans ST胞外DNA的差异性研究
摘要:选取Sulfobacillus thermosulfidooxidans ST用于黄铁矿和黄铜矿的生物浸出实验。吸附实验表明,相较于黄铜矿,细菌更多地吸附在黄铁矿的表面。实验使用DNase I特异性去除胞外DNA(eDNA)来研究eDNA在生物浸出过程中的作用,eDNA的缺失使吸附在黄铜矿和黄铁矿表面的细菌数量大量减少,菌种生长周期延长,并且黄铁矿和黄铜矿的最终浸出率分别降低了11.6%和20.5%。同时,基于荧光染料的方法评估生物浸出过程中分泌的eDNA的形成和分布,并选择共聚焦激光扫描显微镜(CLSM)可视化了矿物表面的吸附菌和eDNA。eDNA的产量随着生物浸出时间的延长而增加。此外,吸附在黄铁矿表面的ST菌比吸附在黄铜矿表面的Sulfobacillus thermosulfidooxidans ST菌有更高的eDNA产量。综上结果表明,eDNA的去除对黄铜矿的生物浸出比对黄铁矿的生物浸出具有更大的影响。
关键词:胞外DNA;Sulfobacillus thermosulfidooxidans ST;黄铜矿与黄铁矿;激光共聚焦;生物浸出
Foundation item: Projects(31470230, 51320105006, 51604308) supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China; Project(2017RS3003) supported by the Youth Talent Foundation of Hunan Province of China; Project(2018JJ2486) supported by the Natural Science Foundation of Hunan Province of China; Project(2018WK2012) supported by the Key Research and Development Projects in Hunan Province, China
Received date: 2019-06-25; Accepted date: 2020-04-07
Corresponding author: SHEN Li, PhD, Associate Professor; Tel: +86-731-88879815; E-mail: lishen@csu.edu.cn; ORCID: 0000-0001- 9204-1114

