
DOI: 10.11817/j.issn.1672-7207.2021.03.010
基于混凝土损伤模型的卸载作用下盾构隧道损伤机理
刘建文1,施成华1,雷明锋1, 2,彭立敏1,王祖贤1
(1. 中南大学 土木工程学院,湖南 长沙,410075;
2. 重载铁路工程结构教育部重点实验室 (中南大学),湖南 长沙,410075)
摘要:在密集的地铁交通网附近区域进行工程活动会引起下卧盾构隧道产生较大纵向差异变形,对隧道结构服役性能及行车安全造成不利影响。既有研究大多基于弹性、弹塑性理论框架,忽视盾构隧道纵向变形带来的结构损伤的影响。考虑混凝土材料非线性损伤力学特性,首先引入一种基于能量的拉应力和压应力分解,考虑混凝土拉/压力学特性的差异;其次,建立双标量混凝土弹塑性损伤本构模型;最后,基于三维非连续接触模型及多尺度建模技术构建盾构隧道-围岩精细化模型,探究差异变形下盾构隧道损伤劣化机理。研究结果表明:卸载作用下,管片混凝土以局部拉损伤为主而压损伤较小,在管环拱顶和拱底内缘、拱腰外缘以及螺栓连接处拉损伤最严重;卸载作用会引起盾构隧道隆起变形,横截面椭圆度也随纵向发生变化,拐点附近管环椭圆度最大;卸载引起的盾构隧道纵向附加剪力和弯矩最大值分别出现在拐点附近和模型中心处;混凝土材料损伤劣化会降低盾构隧道承载能力、纵向刚度和环向刚度,基于弹性本构的计算模型会高估整体结构的刚度;当前分析工况下,管片钢筋较难屈服,而中间部位管段上半侧纵向连接螺栓较易屈服;加载曲线拐点附近管环受损最严重,且承受较大的附加剪力和弯矩,应特别予以关注。
关键词:卸载作用;盾构隧道;混凝土弹塑性损伤本构;三维非连续接触模型;多尺度建模技术
中图分类号:U25 文献标志码:A 开放科学(资源服务)标识码(OSID):
文章编号:1672-7207(2021)03-0758-12
Damage mechanism of shield tunnel under unloading based on elastoplastic damage model of concrete
LIU Jianwen1, SHI Chenghua1, LEI Mingfeng1, 2, PENG Limin1, WANG Zuxian1
(1. School of Civil Engineering, Central South University, Changsha 410075, China;
2. MOE Key Laboratory of Engineering Structure of Heavy Haul Railway (Central South University),Changsha 410075, China)
Abstract: Engineering activities in the vicinity of dense metro traffic network caused large longitudinal differential deformation of the underlying shield tunnel, which adversely affected the service performance and traffic safety of the metro system. Previous relevant studies were mostly carried out within the framework of elastic or elastoplastic theory, despite the influence of structural damage caused by longitudinal deformation of shield tunnel. The nonlinear damage characteristics of concrete material were considered, and a novel positive/negative decomposition of stress tensor in energy norm was introduced to consider the asymmetric tensile/compressive material behavior of concrete. Secondly, a bi-scalar damage constitutive model of concrete was further developed. Finally, to investigate the damage and degradation mechanisms of shield tunnel under unloading, 3D discontinuous contact model in conjunction with multiscale mixed modelling technology was employed to develop tunnel-soil numerical model. The results show that when shield tunnel suffers unloading stress, localized tension damage dominates while compression damage is minor. The severest tension damage is observed at the inner sides of tunnel crown and bottom, outer sides of tunnel waist, and bolt connections. Tunnel heave is induced by unloading process, ellipticity of tunnel cross section varies along the longitudinal direction, and the maximum convergence deformation is observed at the segmental ring near the inflection point. The unloading-induced maximum additional shear force appears near the inflection point, while the peak bending moment is observed at the model center. The damage and degradation of concrete materials will reduce the tunnel bearing capacity, longitudinal and circumferential stiffness, whilst the elastic-based model will overestimate the integral structural stiffness. According to the investigated cases herein, the segmental rebar is hard to yield, while the longitudinal coupling bolts on the tunnel upper half are easier to yield. It should be noted that the segmental rings near the inflection point are most seriously damaged, and bear large shear forces and bending moments.
Key words: unloading stress; shield tunnel; elastoplastic damage model of concrete; 3D discontinuous contact model; multiscale mixed modelling technology
城市地下轨道交通系统为缓解城市交通压力起到关键作用,而盾构隧道技术因其施工速度快、机械化程度高和对环境扰动小等优势,被国内外普遍采用[1-3]。为最大化利用有限土地资源,在密集的地下交通网邻近区域进行新建工程活动不可避免。基坑开挖会引起邻近地铁线路产生纵向变形,造成盾构隧道管片开裂、螺栓屈服和渗漏水等病害,严重降低其服役性能,甚至威胁列车行车安全。CHANG等[4]报道了台北某区间盾构隧道在邻近基坑开挖作用下导致隧道结构裂损破坏的案例。
当前,针对基坑开挖卸荷作用下邻近盾构隧道力学行为的研究可归结为4大类,包括现场实测[5-6]、模型试验[7-8]、数值计算[9-10]及理论解析方法[11-12]。其中,现场实测和模型试验存在周期长且耗资较大的缺点;理论解析法有助于研究开挖-围岩-隧道之间的相互作用机理;比较经典的是采用“两阶段法”研究基坑开挖对邻近盾构隧道的影响[11-14],作用于盾构隧道上的基坑开挖卸荷效应可基于Mindlin解计算,而后将盾构隧道视为弹性地基中的梁以考虑隧道-围岩相互作用,由此求解卸荷作用下盾构隧道的力学响应。需要指出的是,盾构隧道不同于连续均质管道,通常由一系列预制管片和螺栓拼装而成,存在接头是其最显著的特征。经典的梁-弹簧模型将盾构隧道等效为Euler-Bernoulli梁,忽略剪力对其变形的影响,认为弯矩导致梁发生挠曲。
随着对盾构隧道纵向力学行为研究的深入,尤其是对软土地区发生较大不均匀沉降的地铁线路观测中发现,管片接缝的张开与错台同时存在。由此,许多学者认为盾构隧道纵向变形由弯曲和剪切2种基本变形组成[15-17]。基于此,WU等[17]将盾构隧道视为非连续梁,考虑纵向接头对隧道整体抗弯刚度和剪切刚度的影响,采用Timoshenko梁理论同时考虑盾构隧道发生纵向变形时的弯曲和剪切效应,并给出了盾构隧道等效抗弯刚度和剪切刚度的计算方法。而后该模型被应用于超载和卸载作用(邻近工程活动)下盾构隧道力学行为研究中[3, 12, 18-19]。另一方面,将地基对盾构隧道的作用简单地视为连续分布的离散弹簧(Winkler模型),忽略了邻近土弹簧的相互剪切作用,不能合理反映隧道-围岩相互作用关系。为此,LIANG等[12]和ZHANG等[18]在研究邻近工程活动对盾构隧道的影响时分别采用Pasternak模型和Kerr模型考虑土体的受压和剪切作用,并分别建立了Timoshenko-Pasternak模型和Timoshenko-Kerr模型模拟隧道-围岩纵向力学行为。
解析法虽具有计算快捷和理论清晰等优点,但往往需要基于一定假设和简化,且多用于一维或二维问题的分析,适用性受限。相对而言,在处理更复杂问题时,数值计算是普遍采用的分析手段之一。盾构隧道接头会削弱其整体刚度,为考虑这种影响,数值计算中较简便做法是将盾构隧道简化为等效均质管道,采用刚度折减系数进行刚度折减。HUANG等[20]采用该模型研究深基坑开挖对下卧盾构隧道影响,分析隧道-基坑相对位置关系、隧道直径和开挖尺寸等参数对下卧盾构隧道的影响;LIU等[21]以南京某明挖法新建隧道工程为例,研究了上部土方开挖对下卧盾构隧道的影响。然而,等效均质模型过于简化,虽计算效率较高,但无法合理模拟细部结构(螺栓、接头等)的力学行为,因而仅适用于研究盾构隧道宏观力学行为。随着计算机性能的提升,更精细和复杂的盾构隧道模型得到了发展。如三维非连续接触模型[10, 22-24],基于非线性接触理论模拟接头管片与管片之间、衬砌与围岩之间的相互作用关系,最后建立三维精细化盾构隧道拼装模型,但其主要问题在于计算资源和精细化模拟之间的矛盾。为此,SHI等[10]在研究邻近基坑开挖(侧向卸载)对盾构隧道的影响时,基于多尺度建模技术,盾构隧道关键部位采用三维非连续接触模型模拟,非关键部位则简化为等效均质管,建立的模型既能得到关键部位细部结构的力学特性(如管片张开与错台、接头接触应力等),还能大幅提高计算效率;YAN等[23]基于类似建模技术,研究列车振动荷载作用下重叠盾构隧道管片衬砌的动力响应。
然而,既有研究大多是在弹性、弹塑性理论框架,且以等效均质模型居多,而混凝土作为一种多相复合材料,弹塑性理论无法合理解释其性能劣化和刚度退化等非线性特性,因此,无法得到盾构隧道发生较大纵向变形时细部结构的损伤力学行为。经过多年发展,损伤力学理论已成为混凝土本构关系建模及结构非线性分析中最为常用的手段之一。基坑开挖卸载作用下盾构隧道发生较大变形,局部可能发生螺栓屈服和混凝土裂损,而基于混凝土损伤模型和精细化三维非连续接触模型的盾构隧道致损机理的研究很少。
为此,本文作者在既有研究基础上,引入一种基于能量的拉应力和压应力分解考虑混凝土受拉和压力学特性的差异(单边效应),建立双标量弹塑性损伤本构模型描述混凝土材料的损伤劣化行为,而后基于三维非连续接触模型及多尺度建模技术构建盾构隧道-围岩精细化模型,探究卸载作用下盾构隧道损伤劣化机理。
1 混凝土弹塑性损伤本构模型
1.1 基于能量的拉应力和压应力分解
一般认为混凝土为一种准脆性材料,具有典型单边效应,受拉时表现为脆性而受压时具有一定塑性,且抗压强度显著高于抗拉强度[25-26]。为此,许多学者引入拉损伤变量和压损伤变量描述混凝土的非线性力学行为,而在连续介质力学的理论框架内,确定拉损伤变量和压损伤变量取决于其对应的拉应力和压应力/应变状态,这就自然转入了另一个问题——三维应力/应变状态的拉(正)、压(负)分解。经典的正/负应力分解[27-28]认为正/负有效应力张量的内积为0,即:
 (1)
(1)
式中: 为有效应力张量,为混凝土无损部分的应力状态;
为有效应力张量,为混凝土无损部分的应力状态;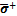 和
和 分别为正(拉)和负(压)有效应力张量;
分别为正(拉)和负(压)有效应力张量;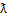 表示二阶对称张量空间。该应力分解策略最主要的缺陷在于无法保证刚度张量的主对称性以及在单轴拉时会产生不合理的侧向变形,如图1所示,并非最优的分解策略。为克服经典正/负应力分解的缺陷,WU等[26]提出了一种基于能量的分解策略:
表示二阶对称张量空间。该应力分解策略最主要的缺陷在于无法保证刚度张量的主对称性以及在单轴拉时会产生不合理的侧向变形,如图1所示,并非最优的分解策略。为克服经典正/负应力分解的缺陷,WU等[26]提出了一种基于能量的分解策略:
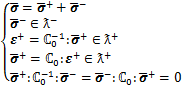 (2)
(2)
式中: 为四阶刚度张量;
为四阶刚度张量;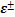 为正/负应变张量。
为正/负应变张量。
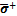 和
和 的显式解答可由式(2)推导得出:
的显式解答可由式(2)推导得出:
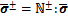 ;
; (3)
(3)
式中: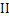 为四阶对称单位张量;
为四阶对称单位张量; 为正/负四阶投影张量,可由下式计算:
为正/负四阶投影张量,可由下式计算:
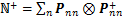 ;
;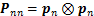 (4)
(4)
式中: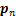 为有效应力张量
为有效应力张量 第n个(n=1,2,3)主应力
第n个(n=1,2,3)主应力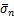 对应的主方向;
对应的主方向;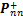 与3个主应力有关:
与3个主应力有关:
1) 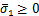 ,
,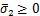 ,
,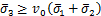 :
:
 ,
,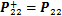 ,
,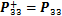 (5)
(5)
2) 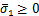 ,
,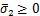 ,
,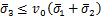 :
:
 ,
,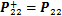 ,
,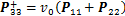 (6)
(6)
3) 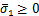 ,
, :
:
 ,
,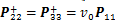 (7)
(7)
4) 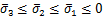 :
:
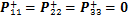 (8)
(8)
式中: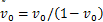 ,
,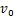 为泊松比。
为泊松比。
图1所示为单轴拉条件下采用2种应力分解策略模拟出的应力-应变关系曲线。由图1可知:2种应力分解策略模拟出的轴向应力-应变关系(σxx-εxx)基本一致,表现为脆性,混凝土轴向应力在达到其抗拉极限强度后呈指数衰减。而侧向应力-应变曲线(σxx-εyy)存在明显差异,经典应力分解将导致出现过大的侧向变形;而基于能量的应力分解模拟出的侧向变形始终处于弹性加/卸载状态,不会产生不合理的侧向变形,比较符合实际。
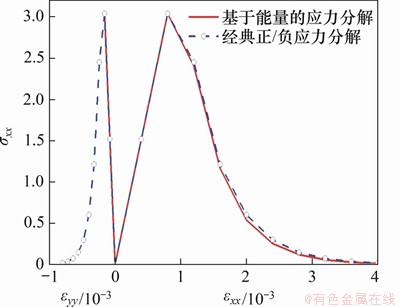
图1 混凝土单轴拉应力-应变曲线
Fig. 1 Uniaxial tensile stress-strain curve of concrete
1.2 弹塑性损伤本构
引入拉/压损伤变量d +/ ,混凝土双标量损伤模型的名义应力
,混凝土双标量损伤模型的名义应力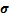 与拉/压有效应力张量的关系可表示为:
与拉/压有效应力张量的关系可表示为:
 (9)
(9)
基于应变等效假定,有效应力可由应变得到:
 (10)
(10)
式中: 为应变张量,且
为应变张量,且 ;
;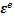 和
和 分别为弹性应变张量和塑性应变张量。
分别为弹性应变张量和塑性应变张量。
损伤演化法则可参考文献[29]给出的单轴条件下混凝土损伤本构模型,其损伤变量定义为应变的函数。而在更复杂的多轴受力状态下,损伤由在热力学框架内基于Helmholtz自由能势导出的损伤能释放率 驱动[27],其表达式为
驱动[27],其表达式为
 ;
;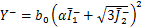 (11)
(11)
式中: 为
为 的第一不变量;
的第一不变量;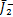 为有效应力偏量
为有效应力偏量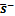 的第二不变量;α和b0为模型参数。由式(11)可知:损伤能释放率与受力状态有关,为应力张量的函数。从能量等效的角度,多轴应力状态下的等效应变可写为
的第二不变量;α和b0为模型参数。由式(11)可知:损伤能释放率与受力状态有关,为应力张量的函数。从能量等效的角度,多轴应力状态下的等效应变可写为
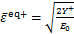 ,
, 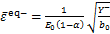 (12)
(12)
式中: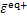 和
和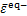 分别为拉等效应变和压等效应变;E0为混凝土初始弹性模量。
分别为拉等效应变和压等效应变;E0为混凝土初始弹性模量。
至此,混凝土损伤演化法则可表达为:
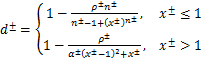 (13)
(13)
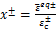 ,
, 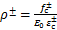 ,
,  (14)
(14)
式中: 为混凝土拉/压强度;
为混凝土拉/压强度; 为与
为与 为对应的应变;
为对应的应变; 为控制混凝土拉/压应力-应变曲线下降段的参数。
为控制混凝土拉/压应力-应变曲线下降段的参数。
另一个问题是塑性应变的确定。为提高模型计算效率,塑性应变可定义在有效应力空间,其经验表达为[30]
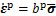 ,
, 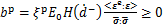 (15)
(15)
式中: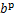 为与塑性应变率相关的系数;
为与塑性应变率相关的系数; 为模型参数;
为模型参数; 为McCauley括号,其运算法则为
为McCauley括号,其运算法则为 ;H(·)为Heaviside函数,其表达式为
;H(·)为Heaviside函数,其表达式为
 (16)
(16)
2 模型建立
2.1 三维非连续接触模型
盾构隧道接头的存在,对整体结构的纵向刚度和环向刚度影响较大。为合理考虑接头的作用,兼顾精细化建模计算效率低的问题,本文基于三维非线性接触理论,建立多尺度精细化三维盾构隧道-围岩数值计算模型。文献[10,22,24]中详细介绍了该模型,并成功应用于研究邻近基坑开挖对盾构隧道的影响和列车动载作用下管片结构静动力响应特性。
在本研究中,主要关注卸载作用引起盾构隧道发生纵向差异变形时的损伤力学行为,因此模型纵向尺寸较大,长为120 m,在核心部位(中间34环)采用三维非连续接触模型,两侧采用等效均质模型(见图2(a)),以提高计算效率。基于ABAQUS有限元平台建立的三维非连续接触模型(以错缝拼装为例)局部结构示意图如图2所示。管环内径为5.4 m,外径为6.0 m,环宽为1.2 m,由1个封顶块(16°),2个邻接块(64°)和2个标准块(72°)组成,接头采用12个环向螺栓(M27)和16个纵向螺栓(M27)连接。各管片外侧钢筋主筋直径为16 mm,内侧主筋由管片两端直径为22 mm和中间直径为20 mm的钢筋组成,箍筋直径为10 mm(见图2(b))。
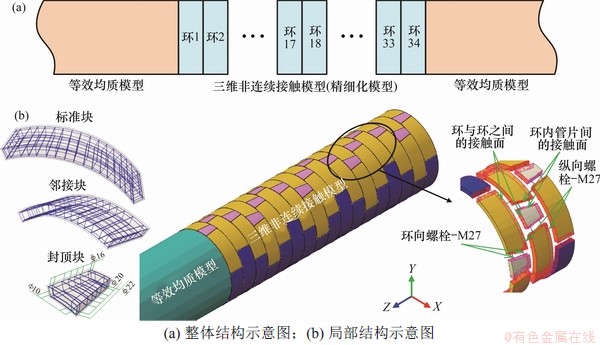
图2 盾构隧道错缝拼装三维非连续接触模型
Fig. 2 3D discontinuous contact model of shield tunnel with staggered joints
模型中混凝土管片采用C3D8R实体单元模拟,钢筋和螺栓简化为梁单元B31,并将梁单元嵌入到管片混凝土中模拟钢筋与混凝土无黏结滑动情况下的钢筋混凝土结构。管片与管片之间的接触面法向行为均采用“硬接触”,即接触面之间能够传递的接触压力不受限制,当接触压力为零或负值时,2个接触面分离,并且去掉相应节点上的接触约束。接触面切向行为采用Cloumb摩擦模拟,若接触面闭合,接触面则可传递摩擦力[10, 22]。由于模型尺寸较大(纵向长为120 m),若采用实体单元模拟围岩则会产生数十万个单元,超出一般计算机的计算能力且十分耗时。此外,本文的研究重点为盾构隧道发生纵向变形时的损伤力学行为而忽视围岩的力学响应。因此,围岩对隧道的约束作用采用非线性弹簧单元模拟(弹簧只受压而不承受拉力),包括径向弹簧、纵向弹簧和切向弹簧,地层抗力系数为5 000 kN/m3,如图3所示。
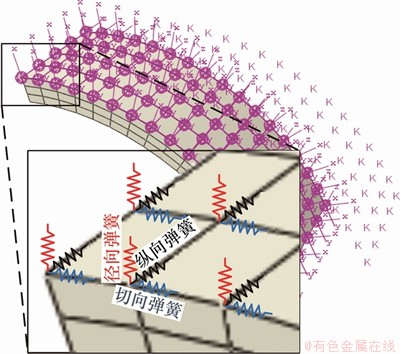
图3 地基弹簧接触模型
Fig. 3 Contact model of ground springs
核心部位混凝土管片采用上述基于能量分解的弹塑性损伤本构模型,需编制用户材料UMAT子程序,两侧等效均质管则为线弹性本构。管片混凝土等级为C50,弹性模量E0为34.5 GPa,泊松比为0.2,塑性模型参数 为0.1,抗拉/压强度
为0.1,抗拉/压强度 和
和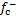 分别为3.0 MPa和23.1 MPa,对应的应变
分别为3.0 MPa和23.1 MPa,对应的应变 和
和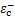 分别为1.18×10-4和1.525 8×10-3,损伤参数
分别为1.18×10-4和1.525 8×10-3,损伤参数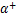 和
和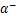 分别取2.810 0和0.938 4。钢筋为HPB300和HRB400级钢筋,螺栓为5.8级高强螺栓,屈服强度为400 MPa,极限强度为500 MPa,模型中采用有屈服点弹塑性本构。
分别取2.810 0和0.938 4。钢筋为HPB300和HRB400级钢筋,螺栓为5.8级高强螺栓,屈服强度为400 MPa,极限强度为500 MPa,模型中采用有屈服点弹塑性本构。
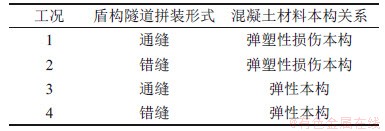
此外,为对比研究盾构隧道不同拼装形式以及混凝土非线性损伤特性对结构纵向力学行为的影响,本文设置了4种计算工况,具体如表1所示。
表1 计算工况
Table 1 Cases for analysis
2.2 卸载作用下盾构隧道受荷
图4所示为盾构隧道“荷载-结构”计算模式。隧道上覆土层厚H为15 m,重度γ为19 kN/m3,侧压力系数λ为0.6,则可计算盾构隧道承受的水土压力:p1=285 kPa,p2=313.3 kPa,p3=171 kPa, p4=239.4 kPa,p5=28.3 kPa。文献[10-14]表明,基坑开挖会造成隧道周围应力场改变,进而导致其产生纵向差异变形,卸载应力场可采用高斯函数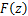 描述:
描述:
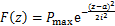 (17)
(17)
式中:Pmax为附加应力场的峰值;z为纵向坐标;a为峰值应力对应的纵向坐标;i为曲线拐点与峰值应力之间纵向距离。
在本文研究中,Pmax取200 kPa,表现为卸载,方向与P1相反;a取60,即峰值应力作用于模型纵向中心位置;i取3。作用于隧道横截面的卸载应力场如图4(b)中F1(z)和F2(z)所示。模型加载过程分2步进行:1) 施加原始状态下的土压力;2) 施加卸载应力场,模拟基坑开挖引起盾构隧道产生纵向差异变形。
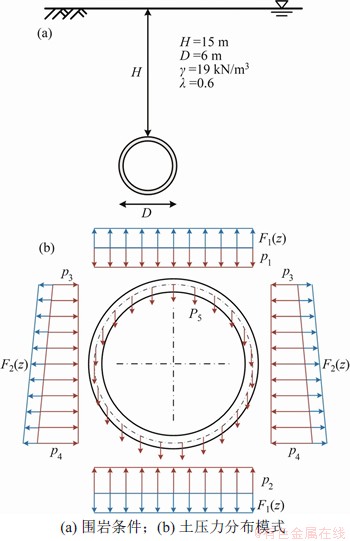
图4 土压力计算模型
Fig. 4 Calculation model of earth pressure around tunnel
3 计算结果
3.1 混凝土管片损伤特性
图5和图6所示分别为卸载作用下通缝和错缝拼装盾构隧道混凝土管片拉/压损伤云图,考虑到模型的对称性,图中仅展示半侧精细化模型(环18~34)的损伤云图。
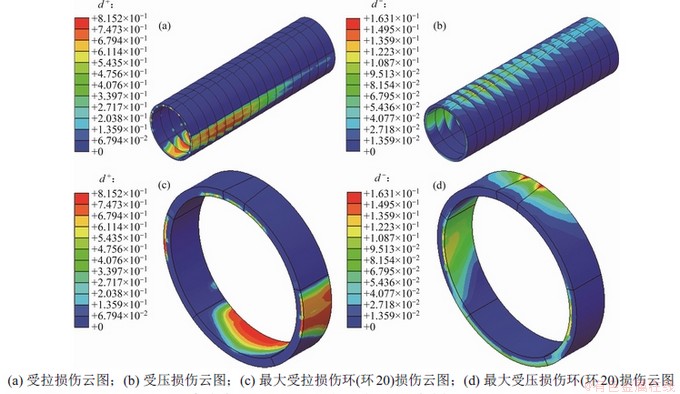
图5 卸载作用下通缝拼装盾构隧道混凝土管片拉/压损伤云图
Fig. 5 Tension/compression damage nephogram of straight joint assembled shield tunnel in unloading case
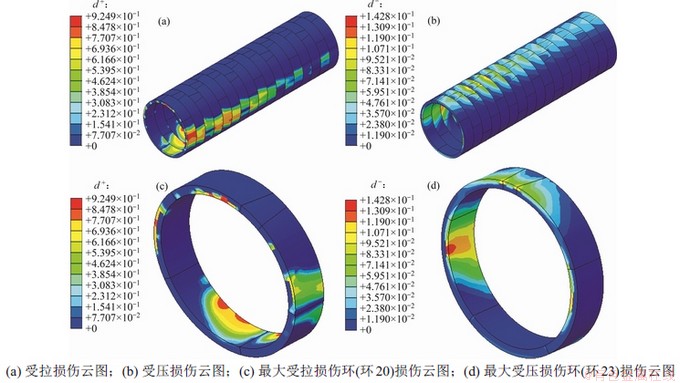
图6 卸载作用下错缝拼装盾构隧道混凝土管片拉/压损伤云图
Fig. 6 Tension/compression damage nephogram of staggered joint assembled shield tunnel in unloading case
由图5和图6可知:卸载作用下,通缝和错缝拼装盾构隧道管片均以受拉损伤为主而受压损伤相对较小,这是由混凝土抗压强度远高于抗拉强度所致。拉损伤主要出现在管环拱顶和拱底内缘、拱腰外缘以及受拉螺栓连接处(图5(a)和图6(a)环18上半部分纵向螺栓连接处存在明显局部拉损伤);压损伤则出现在拱顶、拱底外缘以及拱腰内缘,封顶块与邻接块接头位置存在应力集中,压损伤较明显。从图5和图6也可观察到:拉、压损伤分布不均,拐点附近管环受损较严重,中间及两端管环受损较小。
通缝拼装最大拉损伤和压损伤分别为0.82和0.16,均出现在环20,其中最大拉损伤出现在环20拱底与环21纵向螺栓连接处,最大压损伤出现在环20封顶块与邻接块的接头外缘位置,出现较大局部挤压应力,容易发生受压损伤。错缝拼装最大拉损伤和最大压损伤则分别为0.92和0.14左右,其中最大拉损伤出现在环20拱顶与环19纵向连接螺栓处,最大压损伤出现在环23拱腰内缘位置,且存在偏压现象。
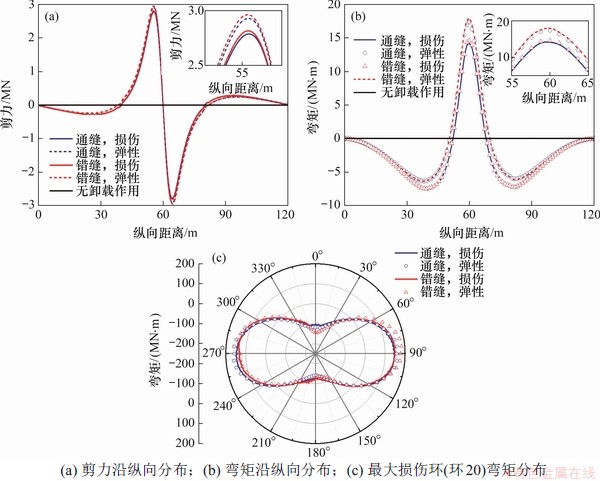
图7 卸载作用下盾构隧道内力分布
Fig. 7 Internal forces distribution of shield tunnel in unloading case
3.2 内力及应力
图7所示为卸载作用下盾构隧道内力分布曲线。由图7可知:卸载作用会引起盾构隧道产生对称分布的附加剪力和弯矩,隧道中心位置剪力为0 MN时,弯矩达到最大,与LIANG等[11-12]研究结果类似。
由图7(a)可知:几种工况计算出的附加剪力分布基本一致,最大剪力出现在拐点附近,采用本文混凝土损伤本构计算出的通缝和错缝拼装盾构隧道最大附加剪力分别为2.771 MN和2.803 MN,而采用弹性本构计算出的通缝和错缝拼装盾构隧道最大附加剪力则分别为2.916 MN和2.954 MN,可见盾构隧道的拼装形式和考虑混凝土损伤劣化对其抗剪承载力的影响比较有限。混凝土损伤本构模型由于考虑材料受损后的刚度退化和材料力学性能劣化,剪切刚度较小,抗剪承载力受限,计算结果略小于采用弹性本构的计算结果,采用弹性本构计算出的通/错缝拼装盾构隧道会略微高估隧道抗剪承载力,分别达5.23%和5.39%。而错缝拼装的附加剪力略大于通缝拼装的附加剪力,表明其抗剪承载力稍大于通缝拼装的抗剪承载力,但可以忽略。
由7(b)可见:当纵向距离在50~70 m范围内,盾构隧道表现为上侧受拉,该部分管环出现拱顶环缝张开,在此范围之外出现反弯,盾构隧道下侧受拉,拱底环缝张开。采用损伤本构计算出的通缝和错缝拼装盾构隧道最大附加弯矩分别为14.16 MN·m和14.63 MN·m,而采用弹性本构计算出的通缝和错缝拼装盾构隧道最大附加弯矩则分别为17.41 MN·m和17.96 MN·m,可见盾构隧道的拼装形式对附加弯矩影响较小,即错缝拼装盾构隧道抗弯承载力稍大于通缝拼装的抗弯承载力,但影响十分有限,最大差别仅3.32%。另一方面,所采用的混凝土材料本构模型对附加弯矩影响较明显,通缝和错缝拼装形式计算出的附加弯矩最大差别分别达22.95%和22.76%,由此可见,忽视混凝土材料损伤劣化会明显高估其抗弯承载力。
图7(c)所示为最大损伤环(环20)弯矩分布曲线,4种分析工况下不同位置处的弯矩如表2所示。综合图7(c)和表2可知:损伤对通缝拼装盾构隧道管环弯矩的影响较有限,不考虑混凝土材料劣化的影响会高估管环的承载能力,最大相对误差出现在拱顶位置,工况1和工况3计算的弯矩分别为-103.8 MN·m和-118.2 MN·m,相对误差为10.3%。比较工况2和工况4的结果可以看出,混凝土力学性能劣化对错缝拼装管环弯矩的影响比较明显,尤其表现在拱顶和拱腰位置,工况2和工况4得到的拱顶处的弯矩分别为-114.5 MN·m和-145.0 MN·m,拱腰处的弯矩分别为145.7 MN·m和177.0 MN·m,相对误差分别为26.64%和21.48%,可见不考虑混凝土力学性能非线性劣化会高估盾构隧道环向抗弯承载力。
表2 4种工况下环20不同位置处弯矩
Table 2 Bending moments at different positions of Ring 20 in four analysis cases
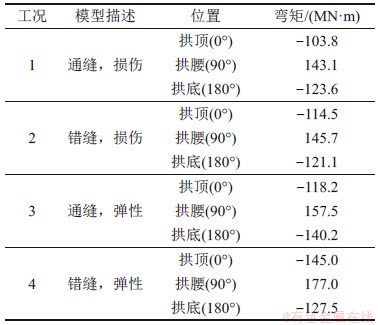
图8所示为2种拼装形式盾构隧道最大损伤环的钢筋及连接螺栓最大主应力云图。由图8可见:计算结果中所有的钢筋均未屈服,拱顶、拱底内缘和拱腰外缘处钢筋承受较大拉应力,基于损伤本构计算的通缝和错缝拼装形式钢筋最大主应力均出现在最大损伤环(环20)拱底(通缝)和拱顶(错缝)位置,分别为97.53 MPa和136.50 MPa。而不考虑混凝土损伤劣化计算的通/错缝拼装盾构隧道钢筋最大主应力则分别为65.78 MPa和72.30 MPa,可见将混凝土管片假定为弹塑性体会分担本该由钢筋承受的部分荷载,弱化钢筋的承载作用。通缝和错缝拼装盾构隧道仅在环14~环21之间上半侧的纵向连接螺栓发生屈服,在卸载作用下,盾构隧道整体表现为隆起,中间管环表现为上侧受拉,环缝张开,纵向连接螺栓承受较大拉力而发生屈服。通缝和错缝拼装形式的盾构隧道仅在环17和环18中心2个环邻接块与标准块之间的环向连接螺栓发生屈服,其余管环的环向螺栓均为屈服。
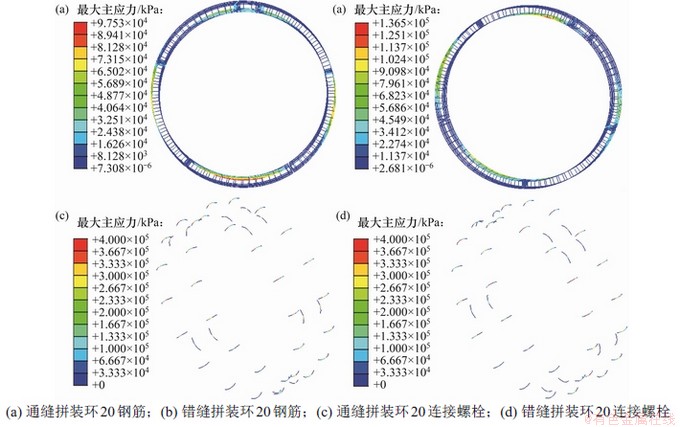
图8 卸载作用下通缝和错缝拼装盾构隧道最大损伤环钢筋及螺栓最大主应力云图
Fig. 8 Rebar and bolt nephogram of maximum principal stress in the severest damaged segmental ring of straight/staggered joint assembled shield tunnel in unloading cases
3.3 盾构隧道变形
图9所示为卸载作用下盾构隧道纵向变形和水平收敛变形。由图9可知:卸载作用会引起盾构隧道产生高斯或类高斯曲线形式的隆起变形,采用损伤本构计算出的通缝和错缝拼装盾构隧道最大挠度分别为24.20 mm和23.82 mm,而采用弹性本构计算出的通缝和错缝拼装盾构隧道最大挠度结果则分别为22.57 mm和22.26 mm,无论考虑混凝土损伤与否,错缝拼装盾构纵向变形均略小于通缝拼装的纵向变形,可见错缝拼装盾构隧道的整体纵向刚度略高于通缝拼装的整体纵向刚度,抵抗纵向变形的能力较强。另一方面,相较于基于弹性本构的计算结果而言,考虑损伤劣化计算出的纵向变形偏大,相对误差分别为7.22%(通缝)和7.01%(错缝)。这是由于管片混凝土局部已出现较大损伤,材料已进入刚度退化和劣化阶段,将混凝土管片假定为弹性体会高估隧道抵抗纵向变形的能力,随着纵向变形增大,损伤范围进一步扩大,这种差异会更加显著。
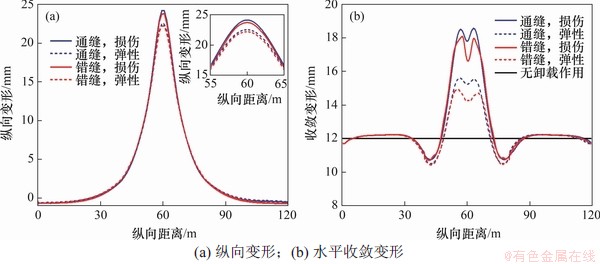
图9 卸载作用下盾构隧道纵向变形和水平收敛变形
Fig. 9 Longitudinal and circumferential deformation of shield tunnel in unloading case
图9(b)中,几种工况计算出的水平收敛变形沿纵向的分布规律一致且关于隧道中心左右对称。卸载作用会引起盾构隧道椭圆度沿纵向发生变化,这主要是由于卸载作用引起的附加剪力和弯矩对横截面的变形具有“剪切效应”和“扁平效应”[31]。最大收敛变形出现在拐点附近管环,隧道横截面表现为“横鸭蛋”,结合图7可知,拐点附近管环附加剪力最大,同时承受较大的附加弯矩作用,“剪切效应”和“扁平效应”比较明显,二者叠加后致使该部位管环产生较大收敛变形,这也可以解释为何在拐点位置管环损伤最严重;而在隧道中心位置,管环椭圆度稍小但仍明显高于无卸载作用时的管环椭圆度,这是由于隧道中心处虽无“剪切效应”(附加剪力为0),但具有最大附加弯矩,“扁平效应”起决定性作用。另一方面可以看到,中间部位管环横截面椭圆度由大到小排列依次为工况1、工况2、工况3和工况4,可见混凝土损伤会减小盾构隧道的环向刚度,减弱其抵抗收敛变形的能力,而错缝拼装的环向刚度略高于通缝拼装的环向刚度。
4 结论
1) 盾构隧道在卸载作用下,管片混凝土以局部拉损伤为主而压损伤较小,拉损伤主要出现在管环拱顶和拱底内缘、拱腰外缘以及螺栓连接处,压损伤则出现在拱顶、拱底外缘以及拱腰内缘。最大拉/压损伤均发生于加载曲线拐点附近管环。
2) 卸载作用下,盾构隧道会产生附加剪力和弯矩,最大剪力和弯矩分别出现在加载曲线拐点附近和模型中心位置。此外,也会造成盾构隧道横截面椭圆度沿纵向发生变化,拐点附近管环椭圆度最大。
3) 混凝土材料损伤劣化会降低盾构隧道纵向刚度和环向刚度,降低其承载能力。错缝拼装盾构隧道纵向刚度和环向刚度略高于通缝拼装的纵向刚度和环向刚度,抵抗变形的能力稍强。
4) 管片钢筋较难屈服,而中间部位管环上半侧纵向连接螺栓较易屈服。通缝和错缝拼装形式的盾构隧道仅在环17和环18中心2个环邻接块与标准块之间的环向连接螺栓发生屈服,其余管环的环向螺栓均未屈服。
5) 加载曲线拐点附近管环受损最严重,环向刚度衰减较大,且承受较大弯矩和剪力,水平收敛变形最大,应特别予以关注。
参考文献:
[1] LEI Mingfeng, LIN Dayong, SHI Chenghua, et al. A structural calculation model of shield tunnel segment: heterogeneous equivalent beam model[J]. Advances in Civil Engineering, 2018(5): 1-16.
[2] LEI Mingfeng, PENG Limin, SHI Chenghua. An experimental study on durability of shield segments under load and chloride environment coupling effect[J]. Tunnelling and Underground Space Technology, 2014, 42: 15-24.
[3] WU Huaina, SHEN Shuilong, YANG Jun, et al. Soil-tunnel interaction modelling for shield tunnels considering shearing dislocation in longitudinal joints[J]. Tunnelling and Underground Space Technology, 2018, 78: 168-177.
[4] CHANG Chite, SUN C W, DUANN S W, et al. Response of a Taipei Rapid Transit System(TRTS) tunnel to adjacent excavation[J]. Tunnelling and Underground Space Technology, 2001, 16(3): 151-158.
[5] SIMPSON B, VARDANEGA P J. Results of monitoring at the British Library excavation[J]. Proceedings of the Institution of Civil Engineers-Geotechnical Engineering, 2014, 167(2): 99-116.
[6] CAO Chengyong, SHI Chenghua, LEI Mingfeng, et al. Deformation characteristics and countermeasures of shallow and large-span tunnel under-crossing the existing highway in soft soil: a case study[J]. KSCE Journal of Civil Engineering, 2018, 22(8): 3170-3181.
[7] 朱叶艇, 张桓, 张子新, 等. 盾构隧道推进对邻近地下管线影响的物理模型试验研究 [J]. 岩土力学, 2016, 37(S2): 151-160.
ZHU Yeting, ZHANG Huan, ZHANG Zixin, et al. Physical model test study of influence of advance of shield tunnel on adjacent underground pipelines[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2016, 37(S2): 151-160.
[8] NG C W W, SHI Jiangwei, HONG Yi. Three-dimensional centrifuge modelling of basement excavation effects on an existing tunnel in dry sand[J]. Canadian Geotechnical Journal, 2013, 50(8): 874-888.
[9] SHI Jiangwei, NG C W W, CHEN Yonghui. Three-dimensional numerical parametric study of the influence of basement excavation on existing tunnel[J]. Computers and Geotechnics, 2015, 63: 146-158.
[10] SHI Chenghua, CAO Chengyong, LEI Mingfeng, et al. Effects of lateral unloading on the mechanical and deformation performance of shield tunnel segment joints[J]. Tunnelling and Underground Space Technology, 2016, 51: 175-188.
[11] LIANG Rongzhu, WU Wenbing, YU Feng, et al. Simplified method for evaluating shield tunnel deformation due to adjacent excavation[J]. Tunnelling and Underground Space Technology, 2018, 71: 94-105.
[12] LIANG Rongzhu, XIA Tangdai, HUANG Maosong, et al. Simplified analytical method for evaluating the effects of adjacent excavation on shield tunnel considering the shearing effect[J]. Computers and Geotechnics, 2017, 81: 167-187.
[13] ZHANG Zhiguo, ZHANG Mengxi, ZHAO Qihua. A simplified analysis for deformation behavior of buried pipelines considering disturbance effects of underground excavation in soft clays[J]. Arabian Journal of Geosciences, 2015, 8(10): 7771-7785.
[14] ZHANG Zhiguo, HUANG Maosong, WANG Weidong. Evaluation of deformation response for adjacent tunnels due to soil unloading in excavation engineering[J]. Tunnelling and Underground Space Technology, 2013, 38: 244-253.
[15] SHEN Shuilong, WU Huaina, CUI Yujun, et al. Long-term settlement behaviour of metro tunnels in the soft deposits of Shanghai[J]. Tunnelling and Underground Space Technology, 2014, 40: 309-323.
[16] 廖少明, 白廷辉, 彭芳乐, 等. 盾构隧道纵向沉降模式及其结构响应[J]. 地下空间与工程学报, 2006, 2(4): 566-570.
LIAO Shaoming, BAI Tinghui, PENG Fangle, et al. Longitudinal settlement forms and structural response of shield tunnel[J]. Chinese Journal of Underground Space and Engineering, 2006, 2(4): 566-570.
[17] WU Huaina, SHEN Shuilong, LIAO Shaoming, et al. Longitudinal structural modelling of shield tunnels considering shearing dislocation between segmental rings[J]. Tunnelling and Underground Space Technology, 2015, 50: 317-323.
[18] ZHANG Dongmei, HUANG Zhongkai, LI Zili, et al. Analytical solution for the response of an existing tunnel to a new tunnel excavation underneath[J]. Computers and Geotechnics, 2019, 108: 197-211.
[19] 刘建文, 施成华, 雷明锋, 等. 基坑开挖对下卧地铁隧道影响的解析计算方法[J]. 中南大学学报(自然科学版), 2019, 50(9): 2215-2225.
LIU Jianwen, SHI Chenghua, LEI Mingfeng, et al. Analytical method for influence analysis of foundation pit excavation on underlying metro tunnel[J]. Journal of Central South University(Science and Technology), 2019, 50(9): 2215-2225.
[20] HUANG Xu, SCHWEIGER H F, HUANG Hongwei. Influence of deep excavations on nearby existing tunnels[J]. International Journal of Geomechanics, 2013, 13(2): 170-180.
[21] LIU Hanlong, LI Ping, LIU Jinyuan. Numerical investigation of underlying tunnel heave during a new tunnel construction[J]. Tunnelling and Underground Space Technology, 2011, 26(2): 276-283.
[22] 艾辉军, 彭立敏, 施成华. 基于三维非连续接触模型的管片接头静动力特性分析[J]. 岩土工程学报, 2013, 35(11): 2023-2029.
AI Huijun, PENG Limin, SHI Chenghua. Static and dynamic characteristic analysis of segment joints based on three-dimensional discontinuous contact model[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 2013, 35(11): 2023-2029.
[23] YAN Qixiang, SONG Leyang, CHEN Hang, et al. Dynamic response of segment lining of overlapped shield tunnels under train-induced vibration loads[J]. Arabian Journal for Science and Engineering, 2018, 43(10): 5439-5455.
[24] 施成华, 刘建文, 李翔, 等. 差异变形下地铁盾构隧道内行车舒适性研究[J]. 中南大学学报(自然科学版), 2020, 51(5): 1279-1288.
SHI Chenghua, LIU Jianwen, LI Xiang, et al. Study on traffic comfort in metro shield tunnel during differential deformation[J]. Journal of Central South University(Science and Technology), 2020, 51(5): 1279-1288.
[25] 李杰, 吴建营. 混凝土弹塑性损伤本构模型研究 I: 基本公式[J]. 土木工程学报, 2005, 38(9): 14-20.
LI Jie, WU Jianying. Elastoplastic damage constitutive model for concrete based on damage energy release rates, part I: basic formulations[J]. China Civil Engineering Journal, 2005, 38(9): 14-20.
[26] WU Jianying, LI Jie, FARIA R. An energy release rate-based plastic-damage model for concrete[J]. International Journal of Solids and Structures, 2006, 43(3/4): 583-612.
[27] ORTIZ M. A constitutive theory for the inelastic behavior of concrete[J]. Mechanics of Materials, 1985, 4(1): 67-93.
[28] CAROL I, WILLAM K. Spurious energy dissipation/generation in stiffness recovery models for elastic degradation and damage[J]. International Journal of Solids and Structures, 1996, 33(20/21/22): 2939-2957.
[29] GB 50010—2010. 混凝土结构设计规范[S].
GB 50010—2010. Code for design of concrete structures[S].
[30] FARIA R, OLIVER J, CERVERA M. A strain-based plastic viscous-damage model for massive concrete structures[J]. International Journal of Solids and Structures, 1998, 35(14): 1533-1558.
[31] GONG Wenping, JUANG C H, HUANG Hongwei, et al. Improved analytical model for circumferential behavior of jointed shield tunnels considering the longitudinal differential settlement[J]. Tunnelling and Underground Space Technology, 2015, 45: 153-165.
(编辑 秦明阳)
收稿日期: 2020 -05 -26; 修回日期: 2020 -07 -30
基金项目(Foundation item):国家自然科学基金资助项目(51778636);国家重点研发计划项目(2017YFB1201204);中南大学中央高校基本科研业务费专项资金资助项目(2019zzts072)
funding:(Project(51778636) supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China, Project(2017YFB1201204) supported by the National Key Research & Development Program of China; Project(2019zzts072) supported by the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities of Central South University)
作者简介:施成华,教授,从事隧道与地下工程研究;E-mail: csusch@163.com
引用格式: 刘建文, 施成华, 雷明锋, 等. 基于混凝土损伤模型的卸载作用下盾构隧道损伤机理[J]. 中南大学学报(自然科学版), 2021, 52(3): 758-769.
Citation: LIU Jianwen, SHI Chenghua, LEI Mingfeng, et al. Damage mechanism of shield tunnel under unloading based on elastoplastic damage model of concrete[J]. Journal of Central South University(Science and Technology), 2021, 52(3): 758-769.