DOI: 10.11817/j.issn.1672-7207.2015.05.051
大脚岭铅锌尾矿库重金属迁移规律与污染评价
周科平,林允,胡建华,何川,高峰
(中南大学 资源与安全工程学院,湖南 长沙,410083)
摘要:为了保护东江湖的水质生态,以湖区大脚岭铅锌尾矿库为对象,采用工程取样、荧光成分分析技术对重金属迁移规律、迁移机理及污染特征进行分析与评价。研究结果表明:尾矿库复垦区、尾砂层和深部区的重金属元素质量分数均超过国家背景值,重金属污染表现为从上游到下游以及从复垦区到深部区污染程度逐渐变大的趋势;尾矿库重金属迁移机理主要是土壤的吸附作用和雨水的淋滤作用;尾矿库复垦区、尾砂层和深部区的重金属综合污染等级达到了五级,属于重度污染,因此,应针对重金属迁移规律和机理及时采取措施对该尾矿库进行无害化处理。
关键词:尾矿库;重金属污染;迁移规律;迁移机理;淋滤;吸附
中图分类号:X705 文献标志码:A 文章编号:1672-7207(2015)05-1953-06
Migration disciplinarian and pollution assessment of heavy metal of Dajiaoling tailings reservoir of lead and zinc
ZHOU Keping, LIN Yun, HU Jianhua, HE Chuan, GAO Feng
(School of Resources and Safety Engineering, Central South University, Changsha 410083, China)
Abstract: To protect the water quality and environmental ecology, taking Dajiaoling lead-zinc tailings reservoir in lake ridge as an object, the heavy metal migration patterns, the migration mechanism and pollution characteristics were analyzed and evaluated using engineering sampling and fluorescent composition analysis technology. The results show that the mass fraction of heavy metal element in reclamation area, backfilling materials and deep layer of tailings reservoir is more than the background value of countries. Heavy metal pollution gradually expands from upstream to downstream and from reclamation area to the deep area. Heavy metal migration mechanism of the tailings reservoir is mainly the adsorption effect of soil and the leaching effect of the rain. The comprehensive pollution levels of heavy metals in reclamation area, backfilling materials and deep layer in the tailings reservoir reach grade 5, which belongs to high levels of pollution. Therefore, it is necessary to take measures on heavy metal migration disciplinarian and mechanism timely to make the tailing reservoir harmless.
Key words: tailings reservoir; heavy metal pollution; migration disciplinarian; migration mechanism; leaching; absorption
资源与环境是人类赖以生存和发展的基本条件[1]。金属矿山尾矿库是亟待开发利用的土地资源,同时也是潜在的环境污染源,如何有效防治重金属对土壤和水体的污染是目前国际上普遍关注的问题[2-3]。自20世纪70年代以来,有色金属的生产和污染治理技术一直是多学科研究的活跃领域,其中,尾矿库周围土壤的重金属污染及治理技术的研究较多[4-10]。王国贤等[5]通过对内蒙古东部污灌区的分析认为重金属在土壤中的迁移是随着土层厚度增加而减弱的。张明亮等[6-7]分析发现:在尾矿库周围土壤中重金属元素的质量分数随土层加深而减少,土壤对重金属元素表现出吸附和淋滤作用。重金属元素在土层积累的状况是由重金属本身的质量分数、迁移性和土壤自然环境等因素共同决定的。韩雪冰等[8]通过对石墨尾矿库和周围土壤的重金属污染分析发现:下层土壤的污染程度高于上层,且不同重金属的迁移能力存在差异。目前,针对尾矿库这一污染源的相关研究还较少。大脚岭铅锌尾矿库距东江湖仅有2.5 km,对东江湖的生态环境构成严重威胁,因此,研究该尾矿库的重金属质量分数变化情况和迁移特征及规律对尾矿库的生态恢复和东江湖的污染治理具有重要意义。本文作者以湖南资兴大脚岭铅锌尾矿库为研究对象,分析尾矿库内的重金属迁移规律、迁移机理及污染特征。
1 工程概况
大脚岭铅锌尾矿库位于湖南省资兴市清江镇,地处东江湖上游,其东侧有河流经过,该河流在距尾矿库下游2.5 km处汇入东江湖。尾矿库现已废弃,库内无积水,其下部为尾砂,上部复垦,并生长许多杂草。
1.1 样品采集
应用洛阳铲采样。设3个采样点:1号点和2号点位于尾矿库下游,且1号点位于尾矿库东侧,靠近河流;2号点在尾矿库中部;3号点位于尾矿库上游。3个采样点位置示意图见图1。其中,1号点和2号点取样深度为4.0 m,0~60 cm为复垦区,60 cm处为复垦土与尾砂的交界面,60~250 cm 为尾砂层,250~400 cm为深部区;3号点的取样深度为1.6 m,0~60 cm为复垦区,60 cm处为复垦土与尾砂的交界面,60~130 cm为尾砂层,130~160 cm为深部区。

图1 采样点示意图
Fig. 1 Diagram of cross-section sampling point
1.2 重元素分析
将采集回来的尾矿砂和表层土壤样品在实验室内常温风干,并将风干后的样品碾碎,通过1 mm孔径尼龙筛,以除去砂砾和生物残体。采用X线荧光(XRF)测试法[11]测试样品的重金属元素铅(Pb)、铜(Cu)、锌(Zn)、砷(As)的质量分数。
2 结果分析
2.1 测试结果
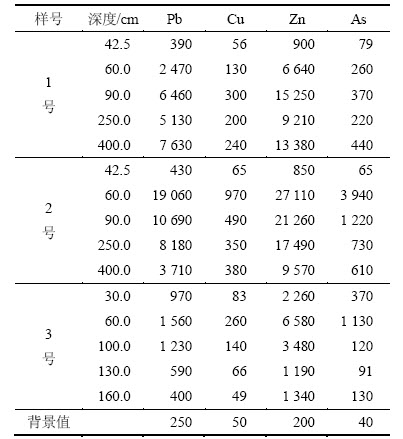
根据对采集的尾矿库样品的测试分析,对不同深度Pb,Cu,Zn和As这4种重金属元素进行测试分析,其质量分数见表1。土壤重金属质量分数背景值采用中华人民共和国国家标准之土壤环境质量标准(GB 15618—1995)中二类标准值[12]。
表1 重金属元素质量分数
Table 1 Mass fraction of heavy metal mg/kg
2.2 迁移规律
研究尾矿库重金属迁移规律是重金属污染无害化处理的关键[13]。根据对所采集样品中重金属质量分数的测试,经origin8软件统计分析,得出尾矿库各采样点中4种重金属元素的质量分数随深度变化的曲线如图2所示。
综合对比分析测试数据和各采样点重金属元素质量分数的变化曲线图,得出重金属迁移规律如下:
1) 空间分布。在各采样点垂向上,从复垦表土到复垦土与尾砂交界面,重金属元素的质量分数随深度增加而增加,并在交界面处出现富集现象;在尾砂层,重金属元素的质量分数随深度增加而减少;在深部区,1号点重金属元素的质量分数随深度的增加而增加,2号点重金属元素的质量分数随深度的增加而减少。在垂向的迁移规律总体表现为重金属元素质量分数随深度增加而减少。对比3个点可以发现:在相同土层中,位于上游的3号点中的重金属元素质量分数比下游的1和2号点的低,表明重金属元素有从上游向下游迁移的趋势。
2) 时间分布。尾矿库中深部区尾砂堆积时间比尾砂层的长。由3个点重金属元素质量分数从尾砂层到深部区逐渐减少的趋势表明:重金属元素的质量分数与尾砂堆积时间呈负相关。
3) 离子分布。样品检测分析结果表明:尾矿库中的4种重金属元素表现出的价键分别为Pb2+,Zn2+,Cu2+和As3+,它们与土壤中的负离子结合成为化合物或被吸附固定或溶于水而迁移。其中,Cu元素主要是以有机络合物的形式存在,迁移活性低,易出现富集现象[14]。
2.3 迁移机理
尾矿库重金属元素的迁移机理主要包括雨水淋滤作用与地下水径流作用以及土壤吸附作用,其中土壤吸附作用又包括毛细吸附作用、生物化学吸附作用和物理吸附作用。
1) 雨水淋滤作用和地下水径流作用主要包括2个方面:一是以离子键形式存在的重金属元素在水介质作用下发生水解反应而溶于水[15],并随雨水和地下水迁移;二是雨水通过影响土壤的pH[16]来改变重金属元素的迁移能力,一般pH越小(即酸性越强),重金属元素的迁移能力越大。郴州地处南方,酸雨较多,雨水降低了土壤的pH,使得尾矿库中的重金属元素迁移活性增加。
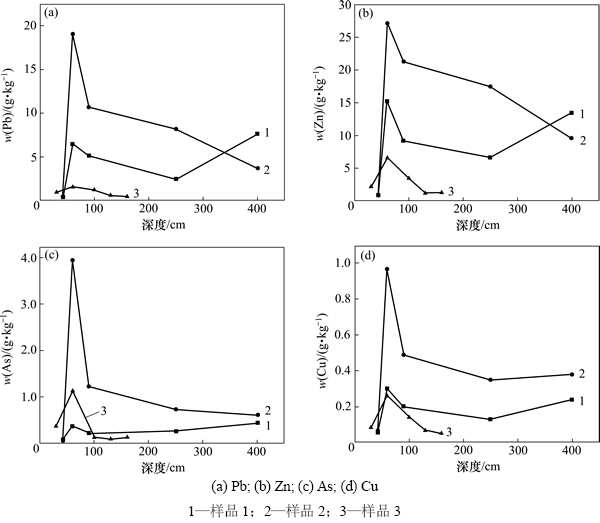
图2 不同深度重金属元素质量分数变化曲线
Fig. 2 Mass fraction of heavy metal at different depths
2) 毛细吸附作用主要是植物根系及土壤中多孔颗粒对重金属元素的吸附。植物的生长需要从土壤中吸收水分和营养元素,尾砂层中重金属元素发生水解作用而溶于水,进而被植物根系所吸收;在重金属元素向植物根系迁移的过程中,土壤多孔颗粒对重金属元素的动力吸附作用使得部分重金属元素被固定而沉淀下来,因而,复垦区的重金属元素质量分数会超标且在交界面处出现富集现象。
3) 生物化学吸附作用。重金属元素被土壤中的微生物吸收并转变为有机体而固定下来。主要过程是以离子态存在的重金属元素被OH-,CO32-和SO42-等离子结合为化合物而沉淀或固定[17-18],从而导致重金属元素的迁移能力发生改变。
4) 物理吸附作用。土壤中存在许多有机质、铁铝等的水合氧化物以及碳酸盐等对重金属元素有一定的吸附固定作用,而且各组分存在复杂的相互作用,尤其是铁氧化物发生化学反应后会形成各种胶体和黏性物质,对重金属元素有吸附作用,从而改变重金属的迁移能力。
由此可以预测:在未来一段时间内,尾矿库上游重金属质量分数会持续下降,复垦区重金属元素质量分数会因毛细吸附作用而增加;在雨水淋滤和地下水径流作用下,尾砂层和尾矿库中心点深部区的重金属元素质量分数会有所减少,靠近河流的点深部区质量分数会有所增加。
3 重金属污染评价
3.1 评价标准
重金属污染采用单因子指数法和内梅罗综合污染指数法进行分析评价[19]。
单因子指数法是目前国内普遍的方法之一,是评价土壤、土壤环境质量等级所用的一种相对的量纲一的指数,能全面反映各污染的污染程度,其计算公式为:
Pi=Ci/Si (1)
内梅罗综合污染指数法兼顾了单因子污染指数的平均值和最大值,突出污染较重的重金属污染物的作用,其计算公式为:
Pz={[(Ci/Si)2max+(Ci/Si)2ave]/2}1/2 (2)
式中:Pi为尾矿库中i污染物的单因子污染指数;Ci为i污染物的实测质量分数(mg/kg);Si为尾矿库中i污染物的背景值(mg/kg);Pz为内梅罗综合污染指数;(Ci/Si)max为尾矿库污染指数中的最大值;(Ci/Si)ave为尾矿库污染指数的平均值。
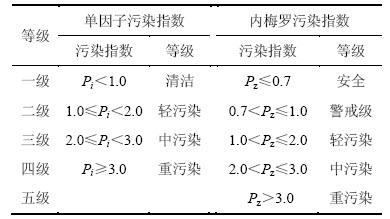
重金属污染程度分级标准[8]见表2。
表2 重金属污染等级划分标准
Table 2 Division standard of heavy metal pollution
3.2 重金属污染评价分级
尾矿库重金属污染程度采用单因子指数法和内梅罗综合污染指数法来进行评价,不同深度重金属元素单因子污染指数和内梅罗综合污染指数如表3所示。
表3 重金属污染指数
Table 3 Pollution index of heavy metal
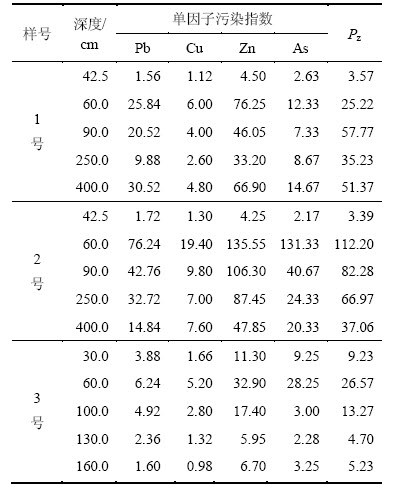
由表3可知:在尾矿库复垦区、尾砂层和深部区,Pb,Cu,Zn和As这4种重金属元素的单因子污染指数均大于1.00,且不同深度重金属元素的内梅罗综合污染指数都大于3.00,表明尾矿库重金属污染上下都有发展且综合污染等级达到5级,已造成严重污染。对比分析各采样点中4种重金属元素的单因子污染指数可知:在复垦区,4种重金属元素的污染程度由高到低依次为Zn,As,Pb,Cu;在尾砂层中,4种重金属的污染程度由高到低分别为Pb,Zn,As,Cu;在深部区,4种重金属元素的污染程度由高到低分别为Zn,Pb,As,Cu。
根据表3中尾矿库复垦区、尾砂层和深部区的内梅罗综合污染指数得到3点不同深度重金属元素的内梅罗综合污染指数的变化趋势,如图3所示。

图3 不同深度重金属平均内梅罗污染指数
Fig. 3 Average Nerrow pollution index of heavy metal taken at different depths
由图3可知:污染程度由大到小依次为复垦土与尾砂交界面、尾砂层、深部区、复垦表土区。
3.3 工程措施建议
通过对尾矿库复垦区、尾砂层和深部区的重金属污染定性与定量分析可知,大脚岭铅锌尾矿库重金属元素质量分数严重超标,污染情况十分严重,严重威胁东江湖区生态环境安全,应及时采取治理措施。针对尾矿库重金属污染特征和迁移规律,建议采取以下措施进行治理:1) 栽种对重金属吸收作用较强的植物,考虑到重金属易在植物内富集,宜栽种建材和风景林木等非人食性的植物[20]以达到控制雨水淋滤与径流作用、固化表层的目的;2) 在尾矿库下游构筑防渗墙,阻止库内重金属元素随地下水和河流进入东江湖。重金属元素已迁移到尾矿库下游深部区4 m处,因此,防渗墙深度应大于4 m。
4 结论
1) 重金属元素呈现出沿径流方向从西向东、从上游向下游、从尾砂层向深部区迁移的趋势,并且影响到东江湖的重金属污染,对东江湖区的生态环境构成极大的威胁。
2) 尾矿库重金属元素的迁移主要是受重金属元素的迁移性、雨水的淋滤作用、地下水的径流作用和土壤吸附作用的共同影响。
3) 尾矿库复垦区、尾砂层和深部区的Pb,Zn,As,Cu这4种重金属元素的质量分数均超过国家土壤重金属质量分数的背景值,重金属综合污染等级达到五级,污染十分严重,污染程度高低依次为复垦区与尾砂交界面、尾砂层、深部区、复垦区。
参考文献:
[1] 廖国礼. 典型有色金属矿山重金属迁移规律与污染评价研究[D]. 长沙: 中南大学资源与安全工程学院, 2005: 16-77.
LIAO Guoli. The transport characteristics and pollution assessment of heavy metal of typical nonferrous metal mine[D]. Changsha: Central South University. School of Resources and Safety Engineering, 2005: 16-77.
[2] 周元祥. 安徽铜陵典型尾矿库地球化学和环境地球化学效应[D]. 合肥: 合肥工业大学资源与环境工程学院, 2009: 5-152.
ZHOU Yuanxiang. Geochemical and environment geochemical effects of typical tailings impoundment in Tongling, Anhui[D]. Hefei: Hefei University of Technology. School of Resources and Environment Engineering, 2009: 5-152.
[3] 何书海, 林彰文, 杨安富, 等. 海南昌江石碌钴铜矿尾矿库重金属污染环境现状调查[J]. 环境监测管理与技术, 2012, 24(3): 41-45.
HE Shuhai, LIN Zhangwen, YANG Anfu, et al. Investigation on heavy metal pollution of Co and Cu mine waste dump in Changjiang, Hainan Province of China[J]. The Administration and Technique of Environmental Monitoring, 2012, 24(3): 41-45.
[4] 刘剑锋, 谷宁, 张可慧. 土壤重金属空间分异及迁移研究进展与展望[J]. 地理与地理信息科学, 2012, 28(2): 100-101.
LIU Jianfeng, GU Ning, ZHANG Kehui. Progress and prospect of soil heavy metal spatial differentiation and migration[J]. Geography and Geo-Information Science, 2012, 28(2): 100-101.
[5] 王国贤, 陈宝林, 任桂萍, 等. 内蒙古东部污灌区土壤重金属迁移律的研究[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 2007, 26: 30-32.
WANG Guoxian, CHEN Baolin, REN Guiping, et al. Migration of heavy metals in siol receiving effluent irrigation in eastern Inner-Mongolia[J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 2007, 26: 30-32.
[6] 张明亮, 王海霞. 煤矿区矸石山周边土壤重金属污染特征与规律[J]. 水土保持学报, 2007, 21(4): 189-192.
ZHANG Mingliang, WANG Haixia. Characteristics on soil heave metal pollution around coal mine waste piles[J]. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 2007, 21(4): 189-192.
[7] 胡瑞雪, 高柏, 胡宝群, 等. 某铀矿山尾矿堆积区周边土壤中重金属迁移规律初探[J]. 铀矿冶, 2009, 28(1): 16-17.
HU Ruixia, GAO Bai, HU Baoqun, et al. Migration of heavy metals in soils in a uranium mining area[J]. Uranium Mining and Metallurgy, 2009, 28(1): 16-17.
[8] 韩雪冰, 王笑峰, 蔡体久. 石墨尾矿库及周围土壤重金属污染特征与评价[J]. 黑龙江大学工程学报, 2011, 2(2): 59-62.
HAN Xuebing, WANG Xiaofeng, CAI Tijiu. Characteristics and evaluation of heavy metal pollution of graphite tailings reservoir and its surrounding soil[J]. Journal of Engineering of Heilongjiang University, 2011, 2(2): 59-62.
[9] 徐晓春, 王军, 李援, 等. 安徽铜陵林冲尾矿库重金属元素分布与迁移[J]. 岩石矿物学杂志, 2003, 22(4): 433-436.
XU Xiaochun, WANG Jun, LI Yuan, et al.The distribution and migration of heavy metal elements of Linchong tailings reservoir in Tongling, Anhui Province, and their environment effects[J]. Acta Petrologica et Mineralogica, 2003, 22(4): 433-436.
[10] 马智宏, 王纪华, 陆安详, 等. 京郊不同点土壤重金属的分布与迁移[J]. 河北农业大学报, 2007, 30(6): 12-15.
MA Zhihong, WANG Jihua, LU Anxiang, et al. Distribution and transfer of main heavy metals in different soil sections in Beijing suburb[J]. Journal of Agricultural University of Hebei, 2007, 30(6): 12-15.
[11] 邢宁, 吴平霄, 李媛媛, 等. 大宝山尾矿重金属形态及其潜在迁移能力分析[J]. 环境工程学报, 2011, 5(6): 1370-1374.
XING Ning, WU Pingxiao, LI Yuanyuan, et al. Analysis of chemical forms and potential mobility ability of heavy metals in tailings from Dabaoshan mine[J]. Chinese Journal of Environment Engineering, 2011, 5(6): 1370-1374.
[12] GB 15618—1995. 土壤环境质量标准[S].
GB 15618—1995. Environmental quality standard for soils[S].
[13] 隋红建, 吴璇, 崔岩山. 土壤重金属迁移模拟研究的现状与展望[J]. 农业工程学报, 2006, 22(6): 197-199.
SUI Hongjian, WU Xuan, CUI Yanshan. Modeling heavy metal movement in soil: Review and further study directions[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 2006, 22(6): 197-199.
[14] ZHANG Xiuying, LING Zaiying, ZHONG Taiyang, et al. Simulation of the availability index of soil copper content using general regression neural network[J]. Environ Earth Sci, 2011, 64: 1697-1702.
[15] 包汉峰, 杨维薇, 张立秋, 等. 污泥基活性炭去除水中重金属离子效能与动力学研究[J]. 中国环境科学, 2013, 33(1): 69-74.
BAO Hanfeng, YANG Weiwei, ZHANG Liqiu, et al. Efficiency and kinetics of heavy metal removal from water by sludge-based activated carbon[J]. China Environmental Science, 2013, 33(1): 69-74.
[16] 董霁红. 矿区充填复垦土壤重金属分布规律及主要农作物污染评价[M]. 徐州: 中国矿业大学出版社, 2009: 78-135.
DONG Jihong. Filling reclamation soil heavy metal distribution, and the evaluation of the main crop pollution[M]. Xuzhou: China University of Mining and Technology Press, 2009: 78-135.
[17] 刘红磊, 尹澄清, 唐运平. 太湖梅梁湾岸边带底泥中重金属的形态与分布[J]. 中国环境科学, 2010, 30(3): 389-394.
LIU Honglei, YI Chengqing, TANG Yunping. Distribution and speciation of heavy metals in sediments at a littoral zone of Meiliang Bay of Taihu Lake[J]. China Environment Science, 2010, 30(3): 389-394.
[18] Mott H V. Association of hydrophobic organic contaminants with soluble organic matter, evaluation of the database of K-doc values[J]. Advances in Environmental Research, 2002, 6(4): 577-593.
[19] 魏世强. 环境系统中重金属镉的迁移—机理、影响因素与建模[D]. 重庆: 西南农业大学资源环境学院, 2001: 9-18.
WEI Shiqiang. Cadmium in environmental system migration mechanism, influence factors and modeling[D]. Chongqing: Southwest Agricultural University. School of Resources and Environment, 2001: 9-18.
[20] 胡振琪, 魏忠义, 秦萍. 塌陷地粉煤灰充填复垦土壤的污染性分析[J]. 中国环境科学, 2004, 23(3): 311-315.
HU Zhenqi, WEI Zhongyi, QIN Ping. Contamination character analysis of filling reclaimed soil with fly ash in subsided land[J]. China Environment Science, 2004, 23(3): 311-315.
(编辑 赵俊)
收稿日期:2014-05-10;修回日期:2014-08-26
基金项目(Foundation item):国家“十二五”科技支撑计划项目(2012BAC09B02);国家自然科学基金资助项目(51204205);中央高校基本科研业务费专项资金资助项目(2013zzts261) (Project(2012BAC09B02) supported by the National Science and Technology Pillar Program during the “Five-year” Plan Period; Project(51204205) supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China; Project(2013zzts261) supported by the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities)
通信作者:胡建华,博士,副教授,从事高效安全采矿与岩土工程稳定性分析的研究;E-mail: hujh21@csu.edu.cn