从复合离子液体中电沉积制备铱
来源期刊:中国有色金属学报(英文版)2015年第5期
论文作者:钱建刚 殷 英 李 鑫 李铁军
文章页码:1685 - 1691
关键词:复合离子液体;铱;N, N-二甲基乙酰胺;电沉积
Key words:composite ionic liquid; iridium; N, N-dimethylacetamide; electrodeposition
摘 要:为研究复合离子液体中电沉积制备Ir的工艺过程,探讨添加剂N, N-二甲基乙酰胺(DMAC)对BMIC-BMIBF4复合离子液体黏度、电导率及电化学稳定性的影响,分析IrCl3在该复合体系中的电化学行为,并在不同电位下恒电位电沉积Ir层。采用扫描电镜及X射线衍射仪对沉积层形貌及组成进行表征。结果表明:DMAC的加入使复合体系的黏度降低、电导率升高、电化学稳定性提高;金电极上的循环伏安测试表明,Ir3+通过一步还原反应生成单质Ir的过程是受扩散速率控制的不可逆过程,其平均转移系数为0.170,扩散系数为1.096×10-6 cm2/s;SEM显示,在还原峰电位处可以获得较为致密、平整的Ir层,而XRD谱表明Ir层为多晶结构。
Abstract: In order to study the electrodeposition process of iridium in composite ionic liquid, the effects of N, N-dimethylacetamide (DMAC) on the viscosity, conductivity and electrochemical stability of composite ionic liquid BMIC-BMIBF4, as well as the electrochemical behavior of IrCl3 in this system were studied. Iridium (Ir) coatings were deposited at different constant potentials and characterized by SEM and XRD. The results show that the addition of DMAC can evidently decrease the viscosity of the composite system, increase conductivity and improve electrochemical stability of the composite system. Cyclic voltammograms of a Au electrode illustrate that the process controlled by diffusion rate is irreversible with the average charge transfer coefficient of 0.170 and average diffusion coefficient of 1.096×10-6 cm2/s. In addition, SEM image shows that Ir film deposited at the reduction peak potential is dense and even, while XRD pattern shows that Ir deposit is polycrystalline structure.
Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 25(2015) 1685-1691
Jian-gang QIAN, Ying YIN, Xin LI, Tie-jun LI
Key Laboratory of Bio-inspired Smart Interfacial Science and Technology of Ministry of Education, School of Chemistry and Environment, Beihang University, Beijing 100191, China
Received 3 June 2014; accepted 1 November 2014
Abstract: In order to study the electrodeposition process of iridium in composite ionic liquid, the effects of N, N-dimethylacetamide (DMAC) on the viscosity, conductivity and electrochemical stability of composite ionic liquid BMIC-BMIBF4, as well as the electrochemical behavior of IrCl3 in this system were studied. Iridium (Ir) coatings were deposited at different constant potentials and characterized by SEM and XRD. The results show that the addition of DMAC can evidently decrease the viscosity of the composite system, increase conductivity and improve electrochemical stability of the composite system. Cyclic voltammograms of a Au electrode illustrate that the process controlled by diffusion rate is irreversible with the average charge transfer coefficient of 0.170 and average diffusion coefficient of 1.096×10-6 cm2/s. In addition, SEM image shows that Ir film deposited at the reduction peak potential is dense and even, while XRD pattern shows that Ir deposit is polycrystalline structure.
Key words: composite ionic liquid; iridium; N, N-dimethylacetamide; electrodeposition
1 Introduction
Much interest in the preparation of iridium coatings is due to their variety of applications in aerospace, defense, energy and many other areas, which results from their excellent performance, such as high melting point (up to 2400 °C), high elastic modulus, high strength, good chemical inertness. Iridium coatings are generally deposited by chemical vapor deposition [1,2], sputter physical vapor deposition [3], double glow plasma method [4,5], plasma spraying [6] and electro- deposition [7-10]. Among them, electrodeposition is one of the most potential methods to prepare iridium coatings because of its low cost, strong controllability and flexibility to select the shape of the cathode material. However, the iridium coatings have been electrodeposited either in molten salts or in aqueous solution so far. The electrochemical deposition from molten salt system needs a large amount of energy in order to achieve very high temperature, which is highly corrosive and very dangerous for operator. The iridium coatings from aqueous solution system are usually loose and easy to crack, which may result from the poor stability and side reactions of aqueous solution. Therefore, good iridium coatings can hardly be deposited from aqueous solution despite its low cost and low viscosity.
Room-temperature ionic liquids (RTILs), by contrast, have been expected to take the place of various molten salts and aqueous solution in many areas [11], especially in electroplating, because they use much less energy than molten salts, and have wider electrochemical potential window, better thermal stability and chemical stability as well as lower vapor pressure [12-14] than aqueous solutions. It has been reported that some light metals such as Al [15] or Al-Zn alloy, which cannot be electrodeposited from aqueous solution, have been successfully electroplated from ionic liquids. And some refractory metals like Pt, Mo and Pd can also be deposited from RTILs whose temperature is much lower than that of molten salts. What’s more, since there is no water in ionic liquids and some are even hydrophobic, hydrogen evolution reaction can be prevented, which greatly improves the quality of the deposited layer [16,17]. Even and compact iridium layer was once prepared on a platinum substrate by electrodeposition under constant potential in 1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium chloride (BMIC) for the first time by our group, which shows great potential of electrodeposition iridium layer from ionic liquids.
However, the low solubility of IrCl3 in a single ionic liquid hinders the research process of electrodeposition. Thus, we used composite ionic liquids to increase the solubility of IrCl3, in order to promote the process of electrodeposition. So far, few studies have been conducted on electrodeposition in composite ionic liquids. CHEN and SUN [18] have reported the positive effects of composite ionic liquid EMI-Cl-BF4 composed of EMIC and EMIBF4 on the solubility of ion pairs Cu+/Cu2+. We have also found that the solubility of IrCl3 in composite ionic liquid BMIC-BMIBF4 is much higher than that in a single ionic liquid, which means that composite ionic liquids may have the unique excellent properties to promote the process of electrodeposition.
In the present study, the metal Ir was electrodeposited in the composite ionic liquid BMIC- BMIBF4. N, N-dimethylacetamide (DMAC) was added into the media above as organic additive to reduce the viscosity of ionic liquids, forming the new electrodeposition composite system DMAC-BMIC- BMIBF4. The effects of DMAC on the viscosity, conductivity and electrochemical stability of ionic liquids, as well as the electrochemical behavior of IrCl3 in DMAC-BMIC-BMIBF4 composite ionic liquid were studied.
2 Experimental
BMIC (Shanghai Chengjie Chemical Co., Ltd., >99%), BMIBF4 (Shanghai Chengjie Chemical Co., Ltd., >99%) and IrCl3 (Shanxi Kaida, >99.5%) were dried under vacuum for 30 min to remove its moisture before the experiment. All the electrochemical experiments and handing of hygroscopic reagents were performed in an argon-filled glove box with a continuous gas purification apparatus. The BMIC and BMIBF4 were fully mixed after stirring for 2 h, and then adequate addictive DMAC (Beijing Chemical Plant, China, AR) was added, forming the new composite system of DMAC-BMIC-BMIBF4. The conductivity and dynamic viscosity of the new composite system with or without the addictive at different temperatures were measured respectively by conductivity meter (Shanghai Leici Instrument Factory, China, DDS-307) and rotation viscometer (Shanghai Changji Geological Instrument Co., Ltd., China, NDJ-1). The absorption spectra of IrCl3 in BMIC-BMIBF4 and DMAC-BMIC-BMIBF4 were measured respectively by UV-Vis spectrometer (UV-3600).
Firstly, constant potential deposition experiments and electrochemical measurements were carried out using a standard three-electrode cell and electrochemical workstation (Shanghai Chenhua Instrument Co., Ltd., China, CHI660D). A Au electrode (d2 mm) was employed as working electrode. A platinum wire electrode (d0.5 mm) was used as a quasireference electrode. A graphite rod electrode (spectrally pure, d3 mm) was used as a counter electrode [19]. Then, Mo electrode (immersed area of 15 mm × 2 mm, >99%) was employed as working electrode and deposited Ir layer. After being washed with acetone and dried in the air, the Ir layer was characterized by scanning electron microscope (SEM, Quanta 250 FEG), energy-dispersive spectrometry (EDS in JSM 7500F) and X-ray diffractometer (XRD-6000).
3 Results and discussion
3.1 Viscosity and conductivity of ionic liquids
Table 1 shows the viscosity of composite ionic liquids at different temperatures. It is clear that the viscosities of composite ionic liquids BMIC-BMIBF4 and DMAC-BMIC-BMIBF4 decrease with the increase of temperature, respectively. Between them, the viscosity reduction of BMIC-BMIBF4 is larger. The viscosity of BMIC-BMIBF4 is 0.604 Pa·s at 20 °C, almost in still state, while it decreases to 0.0202 Pa·s at 90 °C, about 1/30 of the original. After equivoluminal DMAC was added to composite ionic liquid, the viscosity of the system declines to 0.0138 Pa·s at 20 °C, about 1/44 of that in BMIC-BMIBF4, while 0.0036 Pa·s at 90 °C, about 1/5 of that in BMIC-BMIBF4. This change results from strong intramolecular hydrogen bonds and van der Waals forces in ionic liquids, which may lead to high viscosity [20]. After soluble additive was added, the system became dispersed and intramolecular hydrogen bonds and van der Waals forces turned weak. Such a low viscosity system contributed to increasing the ion diffusion rate and improving electrodeposition process.
Table 1 Viscosity of composite ionic liquids at different temperatures
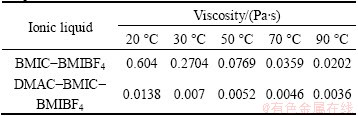
Table 2 Conductivity of composite ionic liquids at different temperatures
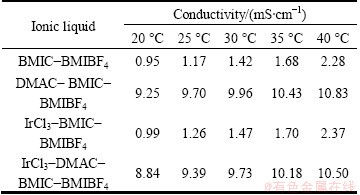
Table 2 shows the conductivity of composite ionic liquids at different temperatures. It shows that the conductivities of different composite ionic liquids all increase with the rising of temperature. They increase markedly from 0.95 to 9.25 mS/cm at 20 °C, while they increase from 2.28 to 10.83 mS/cm at 40 °C when DMAC is added. The inadequate dissociation of cation and anion in composite ionic liquid and ion association under the combined effects of hydrogen bondings, van der Waals forces and static electricity, etc., forming ion pairs, ion network structure and so on, leads to the low viscosity and high conductivity of BMIC-BMIBF4. The addition of DMAC leads to the salvation of ionic liquid, which decreases the quantity of ion pairs and increases the degree of ionization of the ionic liquid, thereby increasing the conductivity of system [21]. It is noteworthy that, the addition of 0.05 mol/L IrCl3 can increase the conductivity of BMIC-BMIBF4, but decrease the conductivity of DMAC-BMIC-BMIBF4. The UV-Vis absorption spectra of Ir(III) in BMIC- BMIBF4 and DMAC-BMIC-BMIBF4 are given in Fig. 1. Figure 1 shows three absorption maxima at about 370, 430 and 500 nm. These values agree well with those reported by POULSEN and GARNER [22] for [IrCl6]3- and the final result has something in common with Ref. [18]. Since Ir(III) exists mainly as [IrCl6]3- [22] and keeps balance as follows: IrCl3 + 3Cl- [IrCl6]3-, the addition of IrCl3 will promote the dissociation of ionic liquid by forming [IrCl6]3- and increase the total number of ions and conductivity of system, while ionic liquid will not dissociate adequately without the addition of IrCl3 in BMIC-BMIBF4. However, in DMAC-BMIC- BMIBF4, ionic liquid dissociates relatively thoroughly. Therefore, the formation of [IrCl6]3- will decrease the total number of ions as well as the conductivity of composite system.
[IrCl6]3-, the addition of IrCl3 will promote the dissociation of ionic liquid by forming [IrCl6]3- and increase the total number of ions and conductivity of system, while ionic liquid will not dissociate adequately without the addition of IrCl3 in BMIC-BMIBF4. However, in DMAC-BMIC- BMIBF4, ionic liquid dissociates relatively thoroughly. Therefore, the formation of [IrCl6]3- will decrease the total number of ions as well as the conductivity of composite system.
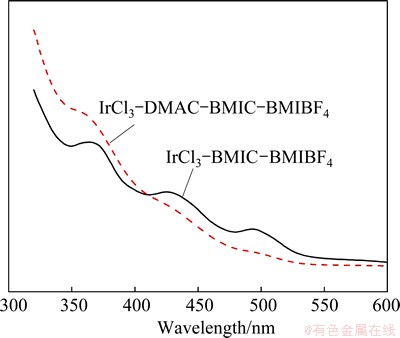
Fig. 1 UV-Vis absorption spectra of 0.05 mol/L IrCl3 in BMIC-BMIBF4 and DMAC-BMIC-BMIBF4
3.2 Electrochemical window in different ionic liquid systems
Figure 2 shows the cyclic voltammograms of a Au electrode in different ionic liquid systems at 90 °C. It is clear that the electrochemical window of BMIBF4 (from -2.25 to 1.20 V, about 3.45 V) is the widest, while those of BMIC (from -2.0 to 0 V, about 2.0 V) and BMIC-BMIBF4 (2.0 V) are narrower. After adding DMAC to BMIC-BMIBF4, the electrochemical window is from -2.2 to -0.1 V and similar to the original without DMAC. Meanwhile, the addition of DMAC can lower the current density, which indicates that the DMAC- BMIC-BMIBF4 composite system has better chemical stability within its range of electrochemical window. Therefore, the addition of DMAC can not only improve the stability of system, but also lower the viscosity of composite ionic liquid and increase its conductivity evidently, and then promote the electrodeposition process.
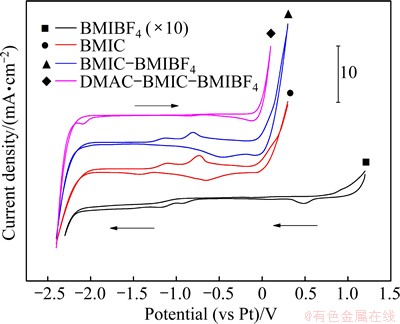
Fig. 2 Cyclic voltammograms of Au electrode in different ionic liquid systems at 90 °C
3.3 Electrochemical behavior of IrCl3 in DMAC- BMIC-BMIBF4
Figure 3 shows the cyclic voltammograms of a Au electrode in DMAC-BMIC-BMIBF4 with or without 0.05 mol/L IrCl3 at 90 °C and scan rate of 50 mV/s. There is a remarkable reduction peak at -1.35 V, which may be caused by the reduction of [IrCl6]3-, and an oxidation peak at -0.9 V after the addition of IrCl3.
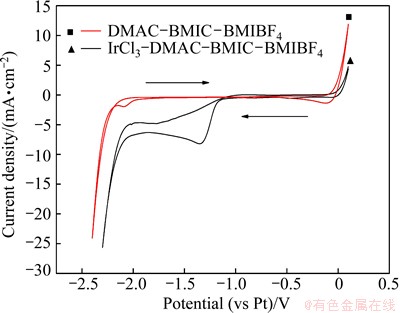
Fig. 3 Cyclic voltammograms of Au electrode in DMAC- BMIC-BMIBF4 with or without IrCl3 at 90 °C
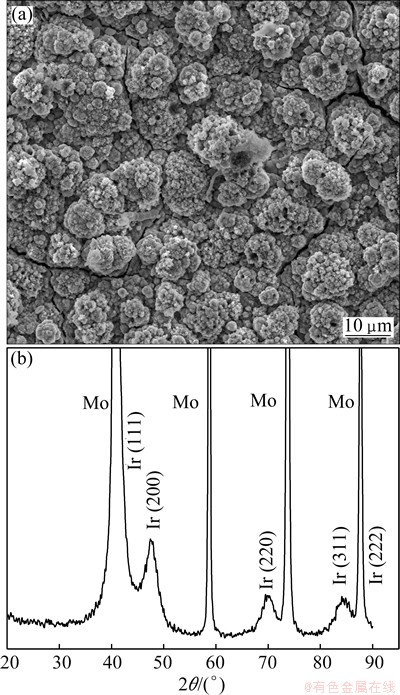
Fig. 4 SEM image (a) and XRD pattern (b) of Ir deposit prepared by constant potential deposition on Mo electrode in DMAC-BMIC-BMIBF4 containing 0.05 mol/L IrCl3 at 90 °C and deposition potential of -1.35 V (vs Pt) for 12 h
Figure 4 shows the SEM image and XRD pattern of Ir deposit prepared at constant potential of -1.35 V (vs Pt) for 12 h on Mo electrode in DMAC-BMIC-BMIBF4 containing 0.05 mol/L IrCl3 at 90 °C. Figure 4 indicates that dense deposit can be obtained at peak potential of -1.35 V by constant potential deposition. The deposit consists of many particle clusters gathered by small particles, and the diameter of particle clusters is about 10 μm. XRD pattern shows that there are three evident diffraction peaks at 47.34°, 69.36° and 84.50°, which correspond to three crystal faces of Ir: (200), (220) and (311), respectively, according to the XRD standard card(JCPDS, 43-0144). Crystal faces (111) and (222) of Ir at 40.68° and 88.00° respectively coincide with relatively strong Mo diffraction peaks. In addition, XRD pattern illustrates that Ir deposit has polycrystalline structure [8]. It can be inferred that [IrCl6]3- can be reduced to Ir0 by one step at this potential. Its electrode reaction is as follows:
[IrCl6]3-+3e=Ir0+6Cl- (1)
In addition, the oxidation peak current density is much smaller than the reduction peak current density, which indicates that the electrode process is irreversible.
Figure 5 shows the SEM image and line scanning analysis of cross section of Ir coating/Mo substrate prepared under the condition above. The yellow direct line in the middle of the picture is the path of line scanning. This exhibits good adherence between Ir coating and Mo substrate with no evident delamination. The thickness of Ir layer is about 1 μm according to the line scanning analysis of the cross section of the sample.
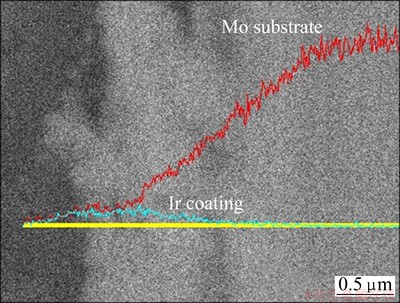
Fig. 5 SEM image and line scanning analysis of cross section of Ir coating/Mo substrate
Figure 6 shows the cyclic voltammograms of a Au electrode at different scan rates in DMAC-BMIC- BMIBF4 containing 0.05 mol/L IrCl3 at 90 °C. There is an evident reduction peak in the range from -1.25 to -1.40 V in every cyclic voltammogram. With the increase of scan rate, the reduction peak current density Jp gradually increases and the peak potential φp shifts to the more negative side.
Figure 7 shows the variation of the peak potential φp with scan rate. It is clear that φp and the natural logarithm of scan rate ln ν are in good linear relationship, which implies that this electrode reaction is irreversible.
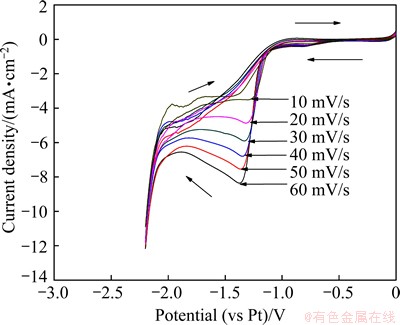
Fig. 6 Cyclic voltammograms of Au electrode at different scan rates in DMAC-BMIC-BMIBF4 containing 0.05 mol/L IrCl3 at 90 °C
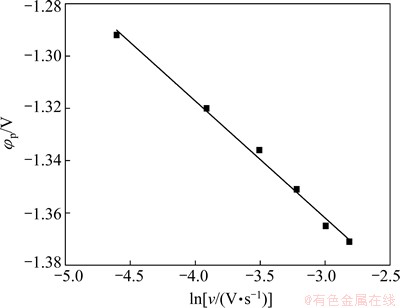
Fig. 7 Relationship between peak potential and scan rate in DMAC-BMIC-BMIBF4 containing 0.05 mol/L IrCl3 at 90 °C
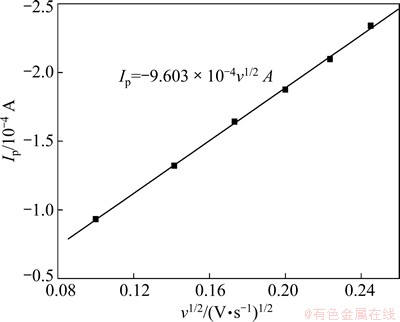
Fig. 8 Relationship between cathodic peak current and scan rate in DMAC-BMIC-BMIBF4 containing 0.05 mol/L IrCl3 at 90 °C
Figure 8 shows the variation of peak current Ip with ν1/2. It is clear that Ip and ν1/2 are in linear relationship, and the straight line goes though the origin of coordinates, which implies this electrode reaction is controlled by diffusion [23]. The following relations exist in the irreversible process controlled by diffusion [24]:
|φp-φp/2|=1.857RT/(αnF) (2)
Ip=-0.4958nFAC0D1/2ν1/2[αnF/(RT)]1/2 (3)
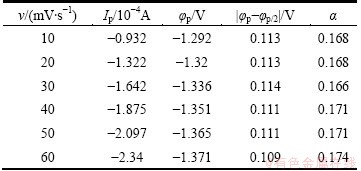
where φp denotes the reduction peak potential, φp/2 denotes the half peak potential (V), α denotes the transfer coefficient, n denotes the number of transferred electrons, F denotes the Faraday constant (C/mol), Ip denotes the peak current (A), A denotes the surface area of working electrode (cm2), C0 denotes the concentration of the material body (mol/cm3), D denotes the diffusion coefficient (cm2/s), and ν denotes the scan rate (V/s). According to Eq. (2), the transfer coefficients of ionic liquid are listed in Table 3. It is easy to know that the average transfer coefficient is 0.170. According to Eq. (3) and the relation between Ip and ν1/2 in Fig. 8, the diffusion coefficient of DMAC-BMIC-BMIBF4 of 1.096×10-6 cm2/s is obtained.
Table 3 Data of cyclic voltammograms at different potential scan rates
3.4 Ir coatings prepared by constant potential electrodeposition
In order to obtain even and dense Ir coatings, constant potential electrodeposition was conducted at different potentials. Figure 9 shows the microstructures of Ir coatings deposited at -1.35 and -1.45 V respectively on Mo electrode in DMAC-BMIC- BMIBF4 containing 0.05 mol/L IrCl3 at 90 °C. As can be seen from Fig. 9(a), Ir coatings deposited at -1.35 V are dense and even, with the diameter of the particle cluster being 10 μm as well as fewer cracks on the outer surface. This can be attributed to the equilibrium between nucleation rate and growth rate of the particles when Ir coatings are deposited near peak potential. Therefore, Ir particles grow evenly and Ir coatings are deposited densely. However, Ir coatings deposited at -1.45 V have uneven surface and big particle clusters, about 50 μm, with incompact arrangement. This results from the large driving force during the process of nucleation and growth, which can easily damage the balance between them and lead to the intensive growth of particles, and the larger the diameter of particle clusters is, the more uneven and looser the coatings are eventually.
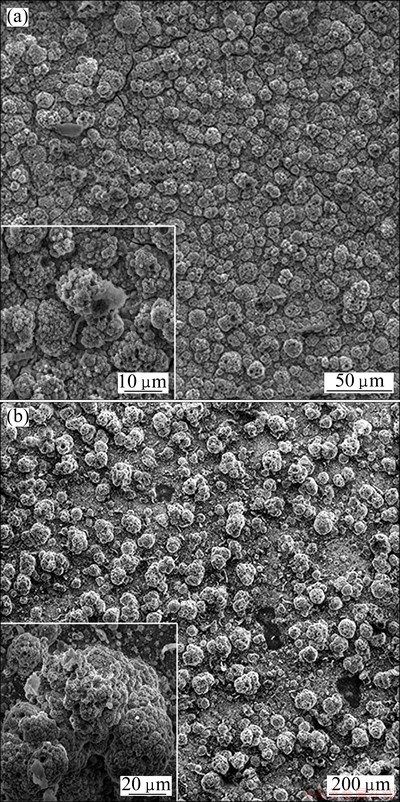
Fig. 9 SEM images of Ir coatings obtained at -1.35 V (a) and -1.45 V (b) on Mo electrode in DMAC-BMIC-BMIBF4 containing 0.05 mol/L IrCl3 at 90 °C and deposition time of 12 h
4 Conclusions
1) The effects of DMAC on the viscosity, conductivity and electrochemical window of composite ionic liquid BMIC-BMIBF4 were studied. It shows that the addition of DMAC can evidently decrease the viscosity, increase the conductivity and improve the electrochemical stability along with little change in electrochemical window. This will promote the electrodeposition experiments if this composite system is used for electrolyte.
2) IrCl3 is reduced to Ir by one step at -1.35 V in DMAC-BMIC-BMIBF4 at 90 °C, which is irreversible process controlled by diffusion. Analysis of cyclic voltammograms of a Au electrode illustrates that the average charge transfer coefficient is 0.170 and average diffusion coefficient is 1.096×10-6 cm2/s.
3) SEM images show that Ir coatings deposited at the reduction peak potential are dense and even, while they are loose and uneven at the overpotential.
References
[1] YAN Xin, ZHANG Qiu-yu, FAN Xiao-dong. New MOCVD precursor for iridium thin films deposition[J]. Materials Letters, 2007, 61(1): 216-218.
[2] BRYSKIN B, KOSTYLEV A, POKROVSKY J. Chemical vapor deposition of iridium and rhodium coatings from hydridotetrakis (trifluorophosphine) complexes [J]. JOM, 2012, 64(6): 682-687.
[3] MUMTAZ K, ECHIGOYA J, ENOKI H, HIRAI T, SHINDO Y. Thermal cycling of iridium coatings on isotropic graphite [J]. Journal of Materials Science, 1995, 30(2): 465-472.
[4] WANG Liang-bing, CHEN Zhao-feng, ZHANG Ping-ze, WU Wang-ping, ZHANG Ying. Ir coating prepared on Mo substrate by double glow plasma [J]. Journal of Coatings Technology and Research, 2009, 6(4): 517-522.
[5] WU Wang-ping, CHEN Zhao-feng, LIU Yong. Iridium coating deposited by double glow plasma technique—Effect of glow plasma on structure of coating at single substrate edge [J]. Plasma Science and Technology, 2012, 14(10): 909-914.
[6] SEKIGAWA T, TAKEDA F, TAGUCHITAL M. High temperature oxidation protection coating for C/C composites [C]//Proceedings of the 8th Symposium on High Performance Materials for Severe Environments. Tokyo, 1997: 307-315.
[7] ETENKO A, MCKECHNIE T, SHCHETKOVSKIY A, SMIRNOV A. Oxidation-protective iridium and iridium-rhodium coating produced by electrodeposition from molten salts [J]. ECS Transactions, 2007, 3(14): 151-157.
[8] ZHU Li-an, BAI Shu-xin, ZHANG Hong. Iridium coating prepared on rhenium substrate by electrodeposition in molten salt in the air atmosphere [J]. Surface and Coatings Technology, 2011, 206(6): 1351-1354.
[9] QIAN Jian-gang, XIAO Shi-ming, ZHAO Tian, LUAN Hai-jing. Effect of technical parameters on surface morphology of electrodeposition of iridium layer in aqueous system [J]. Rare Metal Materials and Engineering, 2012, 41(7): 1139-1143.
[10] QIAN Jian-gang, ZHAO Tian. Electrodeposition of Ir on platinum in NaCl-KCl molten salt [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2012, 22(11): 2855-2862.
[11] TIAN Guo-cai, LI Jian, HUA Yi-xin. Application of ionic liquids in hydrometallurgy of nonferrous metals [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2010, 20(3): 513-520.
[12] BONHOTE P, DIAS A P, PAPAGEORGIOU N, KALYANASUNDARAM K, GRATZEL M. Hydrophobic, highly conductive ambient-temperature molten salts [J]. Inorganic Chemistry, 1996, 35(5): 1168-1178.
[13] ROGERS R D, SEDDON K R. Ionic liquids—Solvents of the future? [J]. Science, 2003, 302(5646): 792-793.
[14] OHNO H. Electrochemical aspects of ionic liquids [M]. 2nd ed. Hoboken, NJ: John Wiley & Sons Inc, 2005.
[15] LIU Kai-ren, LIU Quan, HAN Qing, TU Gan-feng. Electrodeposition of Al on AZ31 magnesium alloy in TMPAC-AlCl3 ionic liquids [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2011, 21(9): 2104-2110.
[16] BOMPAROLA R, CAPORALI S, LAVACCHI A, BARDI U. Silver electrodeposition from air and water-stable ionic liquid: An environmentally friendly alternative to cyanide baths[J]. Surface and Coatings Technology, 2007, 201(24): 9485-9490.
[17] ABEDIN S Z E, ENDRES F. Electrodeposition of nanocrystalline silver films and nanowires from the ionic liquid 1-ethyl-3- methylimidazolium trifluoromethylsulfonate[J]. Electrochimica Acta, 2009, 54(24): 5673-5677.
[18] CHEN Po-yu, SUN I-wen. Electrochemical study of copper in a basic 1-ethyl-3-methylimidazolium tetrafluoroborate room temperature molten salt [J]. Electrochimica acta, 1999, 45(3): 441-450.
[19] RAZ O, COHN G, FREYLAND W, MANN O, EIN E Y. Ruthenium electrodeposition on silicon from a room-temperature ionic liquid [J]. Electrochimica Acta, 2009, 54(25): 6042-6045.
[20] FANNIN J A A, FLOREANI D A, KING L A, LANDERS J S, PIERSMA B J, STECH D J, VAUGHN R L, WILKES J S, WILLIAMS J L. Properties of 1,3-dialkylimidazolium chloride- aluminum chloride ionic liquids. 2: Phase transitions, densities, electrical conductivities, and viscosities [J]. The Journal of Physical Chemistry, 1984, 88(12): 2614-2621.
[21] PERRY R L, JONES K M, SCOTT W D, LIAO Q, HUSSEY C L. Densities, viscosities, and conductivities of mixtures of selected organic cosolvents with the Lewis basic aluminum chloride+ 1-methyl-3-ethylimidazolium chloride molten salt [J]. Journal of Chemical and Engineering Data, 1995, 40(3): 615-619.
[22] POULSEN I A, GARNER C S. A thermodynamic and kinetic study of hexachloro and aquopentachloro complexes of iridium (III) in aqueous solutions [J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 1962, 84(11): 2032-2037.
[23] GUNAWARDENA G, HILLS G, MONTENEGRO I, SCHARIFKER B. Electrochemical nucleation. Part I: General considerations [J]. Journal of Electroanalytical Chemistry and Interfacial Electrochemistry, 1982, 138(2): 225-239.
[24] BARD A J, FAULKNER L R. Electrochemical methods: Fundamentals and applications [M]. 2nd ed. New York: John Wiley & Sons Inc, 2001.
钱建刚,殷 英,李 鑫,李铁军
北京航空航天大学 化学与环境学院 仿生智能界面科学与技术教育部重点实验室,北京 100191
摘 要:为研究复合离子液体中电沉积制备Ir的工艺过程,探讨添加剂N, N-二甲基乙酰胺(DMAC)对BMIC-BMIBF4复合离子液体黏度、电导率及电化学稳定性的影响,分析IrCl3在该复合体系中的电化学行为,并在不同电位下恒电位电沉积Ir层。采用扫描电镜及X射线衍射仪对沉积层形貌及组成进行表征。结果表明:DMAC的加入使复合体系的黏度降低、电导率升高、电化学稳定性提高;金电极上的循环伏安测试表明,Ir3+通过一步还原反应生成单质Ir的过程是受扩散速率控制的不可逆过程,其平均转移系数为0.170,扩散系数为1.096×10-6 cm2/s;SEM显示,在还原峰电位处可以获得较为致密、平整的Ir层,而XRD谱表明Ir层为多晶结构。
关键词:复合离子液体;铱;N, N-二甲基乙酰胺;电沉积
(Edited by Wei-ping CHEN)
Foundation item: Project (51071014) supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China; Project (2010ZE51055) supported by the Aviation Science Foundation of China
Corresponding author: Jian-gang QIAN; Tel: +86-10-82339870; E-mail: qianjg@buaa.edu.cn
DOI: 10.1016/S1003-6326(15)63773-6

