
Effect of hydrogen content and stress state on room-temperature mechanical properties of Ti-6Al-4V alloy
YUAN Bao-guo(袁宝国), LI Chun-feng(李春峰), YU Hai-ping(于海平), SUN Dong-li(孙东立)
School of Materials Science and Engineering, Harbin Institute of Technology, Harbin 150001, China
Received 10 June 2009; accepted 15 August 2009
Abstract: This work aims to investigate the effects of hydrogen content (in the range of 0%-0.5%, mass fraction) and stress state (tension and compression) on the room-temperature mechanical properties of Ti-6Al-4V alloy through mechanical properties tests. The effects of hydrogen content on microstructure evolution of Ti-6Al-4V alloy is also examined by optical microscopy, X-ray diffractometry, transmission electron microscopy and scanning electron microscopy. The results show that hydrogen content and stress state have important effects on the room-temperature mechanical properties of Ti-6Al-4V alloy. Tensile strength and ultimate elongation decrease with increasing the hydrogen content, while compressive strength and ultimate reduction are improved after hydrogenation. The reason is that the intergranular deformation dominates at the state of tension. Hydrogen atoms in solid solution and hydrides at grain boundaries increase with increasing the hydrogen content and they can promote the initiation and propagation of cracks along grain boundaries. While the intragranular deformation dominates at the state of compression. The plastic beta phase and hydrides increase with increasing the hydrogen content and they improve the ultimate reduction and compressive strength.
Key words: Ti-6Al-4V alloy; hydrogen content; stress state; mechanical properties
1 Introduction
Hydrogen is a beta-stabilizing element in titanium alloys and can be easily introduced in a hydrogen environment at an elevated temperature and removed by vacuum annealing treatment[1-3]. The addition of hydrogen has a considerable effect on the microstructure and mechanical properties of titanium alloys. High hydrogen content can cause degradation in titanium alloys[4-6]. Therefore, hydrogen has been considered as a harmful alloying element for a long time, and much attention has been directed to the restriction of hydrogen content in titanium alloys. On the other hand, many researchers have recently found that hydrogen has some beneficial effects on the microstructure and mechanical properties of titanium alloys[7-12]. So the mechanism of hydrogen effects on the microstructure and mechanical properties of titanium alloys attracts much interest of materials scientists.
Until now, little work has been reported on the cold workability of hydrogenated titanium alloys. The aim of the present work is to investigate the effects of hydrogen content in the range of 0%-0.5% (mass fraction) on room-temperature mechanical properties of Ti-6Al-4V alloy under different stress state, including tensile and compressive stresses.
2 Experimental
The materials used in the experiment were Ti-6Al-4V alloy plate and bar with an initial microstructure consisting of alpha phase and beta phase. The beta transus temperature is about 1 263 K.
The hydrogenation treatment of the specimens was carried out in a tube-type furnace. Its procedure is as follows. The specimens were hydrogenated in an atmosphere of hydrogen at 1 023 K for 1 h, air cooled to room temperature, and then solution treated at 1 123 K for 0.5 h followed by furnace cooling to 973 K, and finally quenched into water at room temperature. The hydrogen contents in the hydrogenated specimens were controlled by changing the hydrogen pressure and determined by weighing the specimens before and after hydrogenation using an electronic balance providing an accuracy of 0.01 mg. The specimens with 0.1%, 0.2%, 0.3%, 0.4% and 0.5% (in mass fraction) hydrogen were obtained.
To investigate the effects of hydrogen content and stress state on mechanical properties of specimens, tensile and compressive tests were carried out at room temperature. Tensile tests were performed on an Instron 5569 machine with a constant crosshead speed of 0.5 mm/min, and the tensile specimens are 1 mm-thick plates. Compressive tests were carried out using a Zwick Z100 machine with a constant crosshead speed of 0.5 mm/min, and the compressive specimens are cylinders of 4 mm in diameter and 6 mm in height, and MoS2 was used as a lubricant. Microstructure evolution was investigated by optical microscopy (OM, Olympus BHM-2UM). Phase analysis was identified by X-ray diffractometry (XRD, Philips X’pert) and transmission electron microscopy (TEM, Philips CM-12). Fracture surfaces were observed by scanning electron microscopy (SEM, S-570).
3 Results and discussion
3.1 Effects of hydrogen content on mechanical properties of Ti-6Al-4V alloy
Tensile and compressive true stress—strain curves of specimens with different hydrogen contents are presented in Fig.1 and Fig.2, respectively. It can be seen that hydrogen content has different effects on room-temperature tensile and compressive properties. Tensile properties, such as tensile strength and ultimate elongation, reduce with increasing hydrogen content (Fig.1), while compressive properties, such as compressive strength and ultimate reduction that is the compressive amount when the first macroscopical crack appears at the cylindrical surface of specimen, are improved after hydrogenation (Fig.2).
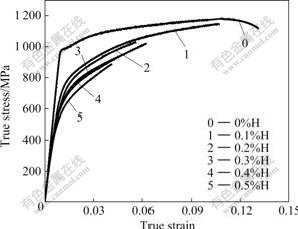
Fig.1 Tensile true stress—strain curves of Ti-6Al-4V-xH alloys
3.2 Effects of hydrogen content on microstructure of Ti-6Al-4V alloy
The microstructures of specimens with different hydrogen contents are shown in Fig.3. It can be seen that the specimen containing 0.1% hydrogen has an equiaxed alpha phase and beta phase (Fig.3(a)), similar to the non-hydrogenated specimen. When the hydrogen content equals or exceeds 0.2%, the needle-like martensite appears in the specimens. The martensite structure is a mixture of hexagonal α′ and orthorhombic α″ martensites that is supported by XRD analysis subsequently. The amount of equiaxed alpha phase decreases with an increase in the hydrogen content and the phase is not observed in the specimens when the hydrogen content exceeds 0.3% (Figs.3(c) and (d)). The observation indicates that the specimens containing 0.1% and 0.2% hydrogen were quenched below the beta transus temperature and those containing 0.3% and 0.5% hydrogen were quenched above the beta transus temperature.
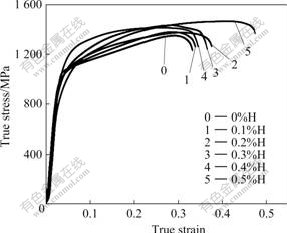
Fig.2 Compressive true stress—strain curves of Ti-6Al-4V-xH alloys
Fig.4 presents the XRD patterns of specimens with varied hydrogen contents. It can be seen that before hydrogenation the specimen contains alpha phase and beta phase. After hydrogenation, XRD patterns change obviously. The peaks of hexagonal α′ and orthorhombic α″ martensites appear in the hydrogenated specimens. Orthorhombic α″ martensite forms more easily in alpha and beta type titanium alloys with a large amount of beta-stabilizing alloying elements, which has been reported previously by QAZI et al[13], FANG and WANG[14] and NIINOMI et al[15]. The peaks of retained beta phase are strengthened, which means the amount of beta phase increases with the hydrogen content. It is because hydrogen, as a beta-stabilizing element, decreases the beta transus temperature. The more the hydrogen content, the more the amount of beta phase.
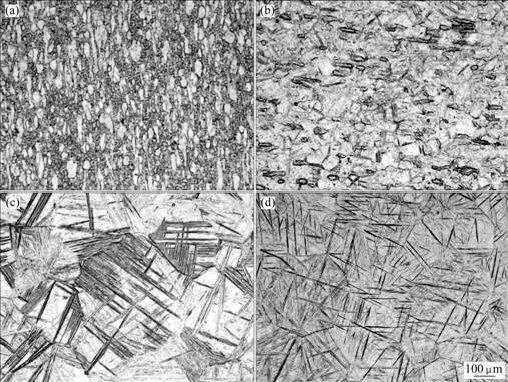
Fig.3 Optical micrographs of Ti-6Al-4V-xH alloys: (a) 0.1% H; (b) 0.2% H; (c) 0.3% H; (d) 0.5% H
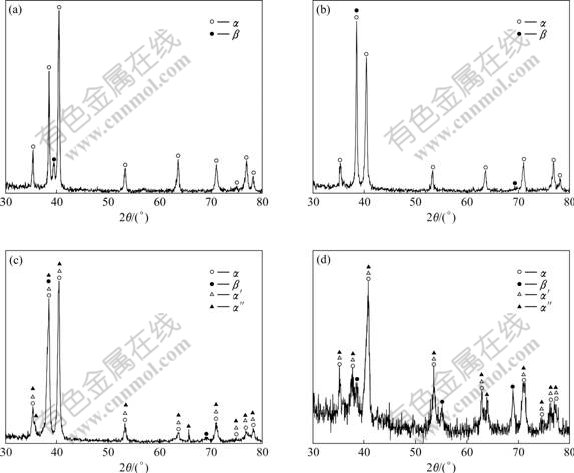
Fig.4 XRD patterns of Ti-6Al-4V-xH alloys: (a) 0% H; (b) 0.1% H; (c) 0.3% H; (d) 0.5% H
More detailed features of microstructure in the hydrogenated specimens can be identified by TEM analysis, and a face-centered cubic δ titanium hydride phase is detected in the hydrogenated specimen, as shown in Fig.5. Fig.5(a) shows a bright field (BF) image of the δ hydride and Fig.5(b) shows the corresponding selected-area electron diffraction (SAED) pattern along the zone axis of [001]δ.
3.3 Effects of hydrogen content on tensile fractograph of Ti-6Al-4V alloy
SEM micrographs of the tensile fracture surfaces of specimens with different hydrogen contents are presented in Fig.6. Slight necking is found near the fracture tip, and there are dimples on the whole fracture surface in the non-hydrogenated specimen, indicating transgranular rupture behavior. Fracture surfaces become flatter with increasing the hydrogen content. For the specimen containing 0.5% hydrogen, there is no necking during tension at room temperature and the specimen exhibits intergranular rupture behavior. The morphology reveals the ductile fracture in the non-hydrogenated specimen and the brittle fracture in those hydrogenated specimens. The observation above indicates that hydrogen changes the tensile fracture mode of Ti-6Al-4V alloy from the ductile transgranular fracture to the brittle intergranular fracture. Hydrogen atoms dissolved into the alloy aggregate along the grain boundaries and hydrides precipitate at grain boundaries. Consequently, the stress concentration near grain boundaries decreases the interface binding force, destroys the continuity of grain boundaries and promotes the initiation and propagation of cracks along grain boundaries. The reasons mentioned above cause the intergranular fracture in the hydrogenated specimens.
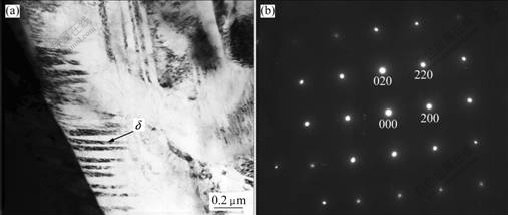
Fig.5 TEM images of Ti-6Al-4V alloy containing 0.2% hydrogen: (a) Hydride laths; (b) Corresponding SAED pattern of hydride
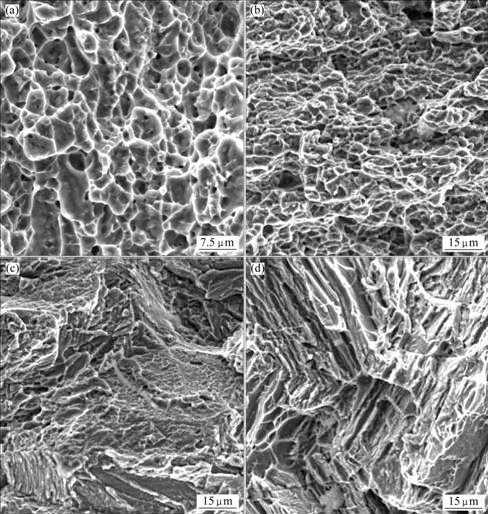
Fig.6 SEM micrographs of tensile fracture surfaces of Ti-6Al-4V-xH alloys: (a) 0% H; (b) 0.1% H; (c) 0.3% H; (d) 0.5% H
3.4 Discussion
On the basis of mechanical properties and microstructure analysis conducted in the present work, hydrogen content has different effects on the mechanical properties of specimens under the varied stress states. Hydrogen degrades the mechanical properties of specimens under tensile stress, but enhances the mechanical properties under compressive stress. Tensile stress can promote solid solution which aggregate along grain boundaries and hydrides which precipitate at grain boundaries may increase with increasing the hydrogen content in specimens, and they can decrease the interface binding force, moreover, promote the initiation and propagation of cracks along grain boundaries. The main influencing factor of mechanical properties under tensile stress is intergranular deformation and the specimens exhibit brittle fracture; therefore, the strength and elongation of specimens decrease with increasing the hydrogen content under tensile stress. On the other hand, although hydrogen atoms and hydrides exist at grain boundaries, the compressive stress can restrain or weaken the initiation and propagation of cracks along grain boundaries, so it can lessen the intergranular fracture. The main influencing factor of mechanical properties under compressive stress is intragranular deformation. The plastic beta phase and hydrides increase with the hydrogen content and they improve the plasticity and strength of specimens. The corresponding schematic diagram illustrating the deformation process of Ti-6Al-4V alloy with hydrogen under tensile and compressive stresses is shown in Fig.7.
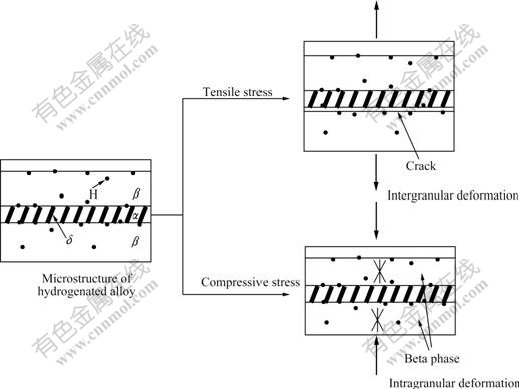
Fig.7 Schematic diagram illustrating deformation process of Ti-6Al-4V alloy with hydrogen under tensile and compressive stresses
4 Conclusions
1) Hydrogen content and stress state have important effects on mechanical properties of Ti-6Al-4V alloy. As the hydrogen content increases, the tensile strength and ultimate elongation decrease gradually, while the compressive strength and ultimate reduction that is the compressive amount when the first macroscopical crack appears at the cylindrical surface of specimen are improved. At the state of tension the intergranular deformation dominates, while the intragranular deformation dominates at the state of compression.
2) After hydrogenation treatment, the tensile fracture mode of Ti-6Al-4V alloy is changed from the ductile transgranular type to the brittle intergranular one, which is caused by the hydrogen atoms which aggregate along grain boundaries and the hydrides which precipitate at grain boundaries.
References
[1] SENKOV O N, FROES F H. Thermohydrogen processing of titanium alloys [J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 1999, 24(6): 565?576.
[2] ELIEZER D, ELIAZ N, SENKOV O N, FROES F H. Positive effects of hydrogen in metals [J]. Mater Sci Eng A, 2000, 280(1): 220?224.
[3] BHOSLE V, BABURAJ E G, MIRANOVA M, SALAMA K. Dehydrogenation of TiH2 [J]. Mater Sci Eng A, 2003, 356(1/2): 190?199.
[4] ALVAREZ A M, ROBERTSON I M, BIRNBAUM H K. Hydrogen embrittlement of a metastable beta-titanium alloy [J]. Acta Materialia, 2004, 52(14): 4161?4175.
[5] BRIANT C L, WANG Z F, CHOLLOCOOP N. Hydrogen embrittlement of commercial purity titanium [J]. Corrosion Science, 2002, 44(8): 1875?1888.
[6] TAL-GUTELMACHER E, ELIEZER D, EYLON D. The effects of low fugacity hydrogen in duplex- and beta-annealed Ti-6Al-4V alloy [J]. Mater Sci Eng A, 2004, 381(1/2): 230?236.
[7] LIN Ying-ying, PAN Hong-si, LI Miao-quan. Hydrogen treatment and its effect on superplasticity of titanium alloys [J]. Journal of Materials Engineering, 2005, 5: 60?64. (in Chinese)
[8] SUN D L, Li Z H, HAN X, WANG Q. Influence of hydrogen on tensile property of Ti-6Al-4V [J]. Key Engineering Materials, 2005, 297/300: 1133?1138.
[9] ZONG Y Y, SHAN D B, LU Y, GUO B. Effect of 0.3wt%H addition on the high temperature deformation behaviors of Ti-6Al-4V alloy [J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2007, 32(16): 3936?3940.
[10] LI M Q, ZHANG W F. Effect of hydrogenation content on high temperature deformation behavior of Ti-6Al-4V alloy in isothermal compression [J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2008, 33(11): 2714?2720.
[11] CHEN Y X, WAN X J, LI F, WANG Q J, LIU Y Y. The behavior of hydrogen in high temperature titanium alloy Ti-60 [J]. Mater Sci Eng A, 2007, 466(1/2): 156?159.
[12] FROES F H, SENKOV O N, QAZI J O. Hydrogen as a temporary alloying element in titanium alloys: thermohydrogen processing [J]. International Materials Reviews, 2004, 49(3/4): 227?245.
[13] QAZI J I, SENKOV O N, RAHIM J, FROES F H. Kinetics of martensite decomposition in Ti-6Al-4V-xH alloys [J]. Mater Sci Eng A, 2003, 359(1/2): 137?149.
[14] FANG T Y, WANG W H. Microstructural features of thermochemical processing in a Ti-6Al-4V alloy [J]. Materials Chemistry and Physics, 1998, 56(1): 35?47.
[15] NIINOMI M, GONG B, KOBAYASHI T, OHYABU Y, TORIYAMA O. Fracture characteristics of Ti-6Al-4V and Ti-5Al-2.5Fe with refined microstructure using hydrogen [J]. Metallurgical and Materials Transactions A, 1995, 26: 1141?1151.
(Edited by HE Xue-feng)
Corresponding author: YUAN Bao-guo; Tel: +86-451-86413970; E-mail: yuanbaoguo@163.com