文章编号:1004-0609(2008)08-1414-07
置氢Ti-6Al-4V合金显微组织演变与高温变形行为
李晓华1,牛 勇2,侯红亮1,李志强1
(1. 北京航空制造工程研究所,北京 100024;
2. 西北工业大学 材料学院,西安 710072)
摘 要:利用Gleeble高温压缩模拟实验研究置氢对Ti-6Al-4V合金微观组织和高温变形行为的影响,并探讨组织与高温塑性的关系。结果表明:适量的氢可显著降低钛合金的高温变形流变应力,Ti-6Al-4V合金氢含量为0.3%时,流变应力降低36%~60%,最小峰值应力对应的氢含量随温度的增加向低氢方向移动,并且在保持相同应力水平下,高温变形温度降低50 ℃;氢还可以促进钛合金热变形过程中的动态回复和动态再结晶,有利于降低变形抗力,其应力—应变曲线无明显硬化阶段;此外,由于氢引起的高温变形组织变化与在更高温度压缩时所引起的组织变化相当。
关键词:置氢Ti-6Al-4V合金;显微组织;高温变形
中图分类号:TG 146.2 文献标识码:A
Microstructure evolution and high temperature deforming behavior of hydrogenated Ti-6Al-4V alloy
LI Xiao-hua1, NIU Yong2, HOU Hong-liang1, LI Zhi-qiang1
(1. Beijing Aeronautical Manufacturing Technology Research Institute, Beijing 100024, China
2. Materials School, Northwestern Polytechnical University, Xi’an 710072, China)
Abstract: The effect of hydrogenation on the microstructure and high temperature deforming behavior of Ti-6Al-4V alloy was investigated by Gleeble thermal simulation test. The correlation between microstructure and high temperature behavior has been explored too. The results show that a certain amount of hydrogen in Ti-6Al-4V alloy can significantly reduce the flow stress of high temperature deformation. Adding 0.3% hydrogen in Ti-6Al-4V alloy allows a reduction of 36%?60% in forging stress and the hydrogen content that corresponds to the minimum flow stress generally decreases when the temperature increases. While keeping the same stress level, the deformation temperature decreases about 50 ℃. Hydrogen can promote the dynamic recrystallization and dynamic recovery during deformation, as a result, the flow stress may decrease and the true strain-true stress curves of hydrogenated alloy don’t show hardening stage obviously. Furthermore, the microstructure changes produced by increasing hydrogen content that happens during hot compression at a fixed temperature are equal to that obtained at higher temperature.
Key words: hydrogenated Ti-6Al-4V alloy; microstructure; high temperature deformation
人们把钛及其合金称作“21世纪的金属”、“新金属”,它在国民经济的各个领域,特别是高技术领域有广阔的应用前景[1?2]。但由于绝大多数钛合金必须在热态下成形,其热变形温度高、应变速率低等原因给模具选材、制造和成形设备都提出了较高的要求,大大地限制了钛合金的应用[3]。近年来,通过钛合金置氢处理以达到改性和改善工艺性能的研究在国内外受到了广泛的重视,其中,高温增塑是最早受到关注并得到深入研究的热氢处理技术方向[4?6]。KERR等[7]对置氢Ti-6Al-4V合金进行了等温锻造实验研究,张勇等[8]对Ti3Al基Ti-25Al-10Nb-3V-1Mo铸态和锻态合金进行了热压缩行为研究。研究表明[7?11],钛合金加氢可使合金的热压力加工性能得到改善,表现为热变形流动应力的降低和塑性的提高,使热变形更容易在较低温度下实现轧制、热锻等工序,且置氢改善高温塑性的效应对高铝含量的热强钛合金及Ti3Al合金的作用特别明显,对近α和(α+β)合金也是适用的,但对近β合金几乎没有作用。氢对钛合金组织影响的研究主要集中于钛合金的变质加工[12?15],而关于置氢后合金组织演变与其高温压缩变形行为的相关性研究尚属空白。本文作者研究了置氢对Ti-6Al-4V合金微观组织和高温压缩变形行为的影响,并探索了组织与高温塑性的相关性,从而为置氢钛合金的塑性分析提供另一个的参考或途径,以实现由微观组织预测置氢钛合金的塑性性能,并从微观组织的角度为氢与塑性的关系提供更深层的解释,对深入研究钛合金置氢变质加工改性机理将有重要的参考价值。
1 实验
实验用原材料为Ti-6Al-4V合金棒材,合金组织形态为典型的双态组织,如图1所示,高温压缩用试样尺寸为d 8 mm×12 mm。
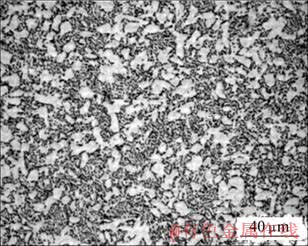
图1 原始Ti-6Al-4V合金的显微组织
Fig.1 Microstructure of as received Ti-6Al-4V alloy
采用高温气相充氢法获得置氢试样。试样经表面处理无氧化层和油污,置入自制的管式氢处理炉后加热,加热过程中用分子泵抽真空保持高真空度,温度至750 ℃后充入高纯氢气,炉内氢分压趋于平衡时炉冷至室温。氢含量是利用高精度物理天平通过称量法测定,精密分析天平的感量为1×10?5 g。
高温压缩实验在Gleeble?1500热加工模拟实验机上完成。压缩温度范围为750~900 ℃,压缩速率为0.01 /s,压缩最大变形量为50%,试样两端加垫石磨作为润滑剂,试样表面均涂有防氧化涂层,采用电阻加热法直接加热试样,升温速度为20 ℃/min,保温3 min后进行压缩实验,压缩变形后空冷。
用Olympus BX41M型光学显微镜观察高温变形后不同氢含量Ti-6Al-4V合金的微观组织。采用AJEM?2000Fx型透射电子显微镜观察置氢合金变形前后的微观组织。透射试样从平行压缩轴线的方向截取,用线切割方法切取1 mm薄片,机械抛光至50 μm,然后采用电解双喷减薄将其制备成直径3 mm的透射试样。
2 结果与讨论
2.1 光学显微组织分析
高温压缩变形后的显微组织如图2~4所示。分析表明,变形温度与氢含量均是影响合金组织形貌的重要因素。750 ℃变形后合金始终为(α+β)双态组织,但β相比例随氢含量增加而增加,氢含量为0.45%时,有片状次生α相生成;850 ℃变形后,氢含量为0.1%时已有片状次生α相出现,氢含量为0.3%时,保留了少量的初生α相和未完全转变的β相,同时生成了大量的马氏体α′,氢含量增至0.45%时则生成针状马氏体α″。由于氢的加入使α和β两相电势相近而且不易被腐蚀,因此光学显微镜下很难辨别微观组织形貌,而在扫描电镜中则可以较好的观察到针状马氏体α″,如图3(d)所示;900 ℃变形后,除了未置氢合金为有明显片状次生α相的(α+β)双态组织,置氢合金变形后均生成了大量的马氏体,且随氢含量的增加,马氏体由位向相同或相互交错呈编织状的针状马氏体α′转变为无明显位向关系的针状马氏体α″。
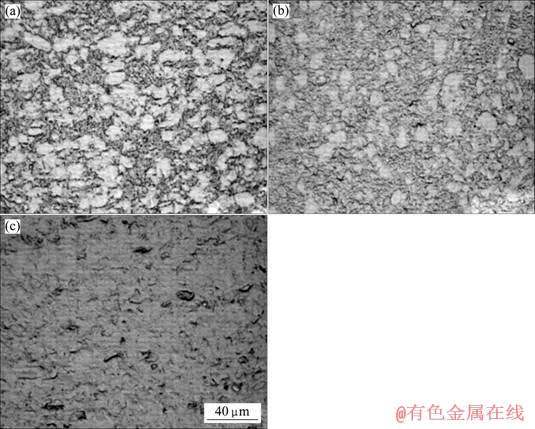
图2 不同氢含量合金750 ℃高温变形后的显微组织
Fig.2 Microstructures of as received and hydrogenated Ti-6Al-4V alloy after deformation at 750 ℃: (a) As received Ti-6Al-4V alloy; (b) 0.1%H; (c) 0.45%H
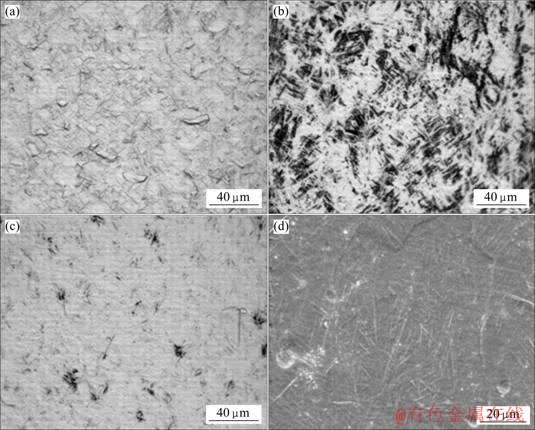
图3 不同氢含量合金850 ℃高温变形后的显微组织
Fig.3 Microstructures of as received and hydrogenated Ti-6Al-4V alloy after deformation at 850 ℃: (a) 0.1%H; (b) 0.3%H; (c) 0.45%H; (d) 0.45%H (SEM)
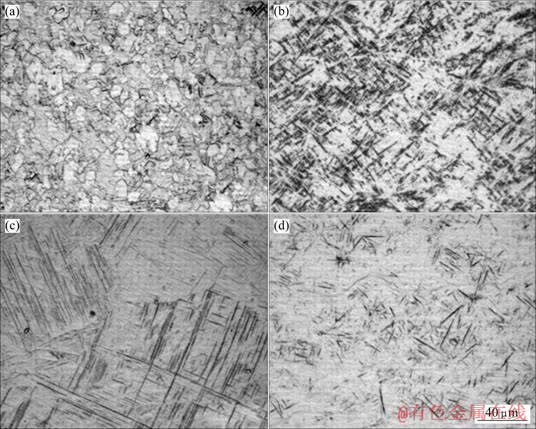
图4 不同氢含量合金900 ℃高温变形后的显微组织
Fig.4 Microstructures of as received and hydrogenated Ti-6Al-4V alloy after deformation at 900 ℃: (a) As received Ti-6Al-4V alloy; (b) 0.1%H; (c) 0.3%H; (d) 0.45%H
进一步分析表明,变形温度为750 ℃且氢含量小于0.45%,或变形温度为850 ℃且氢含量小于0.1%,或变形温度达到900 ℃的原始棒料,压缩变形后合金组织均为(α+β)两相双态组织;变形温度达到850 ℃且氢含量达到0.3%,或变形温度达到900 ℃而氢含量仅为0.1%,变形后合金组织形貌均显示出β相区变形特征,出现大量的马氏体。因此,等温压缩时由于氢含量增加所引起的组织变化相当于在更高温度压缩所引起的组织变化。
置氢钛合金高温变形后产生大量的马氏体,是由于氢的加入降低了β相转变温度,使变形得以在相变点附近或以上进行,而且氢增加了β相的稳定性,降低了临界冷却速率和马氏体转变的特征温度,因此合金可以在较低的温度和较低的冷却速率下获得大量的马氏体。变形温度较低而且氢含量较低时,能够生成马氏体α′,而变形温度较高且氢含量较高时,氢的作用效果更大,而生成马氏体α″。
2.2 TEM显微组织分析
置氢0.45%的Ti-6Al-4V合金的透射电镜显微组织如图5所示。分析表明,置氢合金中析出了层片状δ氢化物(图5(a)),氢化物的形成主要通过原子扩散的方式进行,在β相区形成富H区和贫H区,贫H区形成层片状α相,富H区则形成层片状δ氢化物[16]。

图5 置氢钛合金的TEM像
Fig.5 TEM image of hydrogenated alloy (0.45%H)
置氢0.45%的Ti-6Al-4V合金在900 ℃高温压缩变形后的透射电镜显微组织如图6所示。置氢0.45%合金变形后形成更为明显的层片状δ氢化物,如图6(a)所示,氢化物的存在及增多有强化合金的作用,从而增大变形抗力、降低塑性。图6(b)中细小的α相说明在900 ℃高温压缩变形中部分晶粒发生了动态再结晶,氢的加入促进了动态回复和动态再结晶的产生,因而提高了高温塑性和降低了变形抗力。此外,氢还诱发了孪晶的产生,具有协调塑性变形的作用,如图6(c)中的针状马氏体α″,马氏体中存在大量密集的 孪晶。
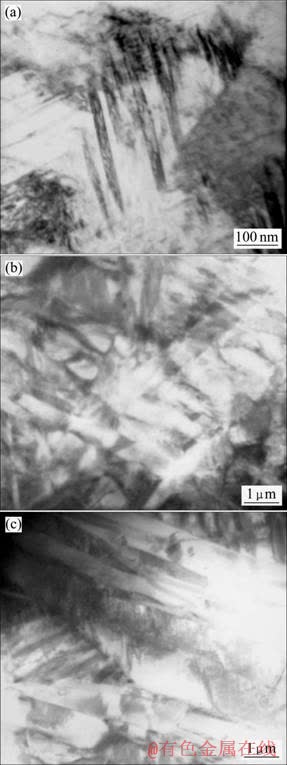
图6 含0.45%H的置氢合金于900 ℃压缩变形后的TEM像
Fig.6 TEM images of hydrogenated alloy with 0.45%H after deformation at 900 ℃: (a) Bright field image of δ hydride; (b) Small secondary α phase; (c) Acicular martensite
2.3 置氢对合金高温变形行为的影响
原始合金和置氢0.45%的Ti-6Al-4V合金在不同温度高温压缩变形的真应力—真应变曲线如图7所示。分析表明,合金的真应力—真应变曲线基本符合动态再结晶应力—应变曲线特征。原始合金的曲线在开始阶段流动应力随应变量的增加而增加,屈服后表现出明显的加工硬化,达峰值应力之后,由于再结晶作用的加强,流动应力逐渐降低,最终动态再结晶造成的软化与加工硬化达到动态平衡,进入稳态流变阶段,流动应力将不随应变的增加而增大。与原始钛合金相比,置氢合金的曲线则无明显的加工硬化阶段,且等应变条件下应力水平显著降低,变形温度超过800 ℃时,呈现相对稳定的流变阶段。这主要是由于氢的加入降低了Ti-6Al-4V合金的β相转变温度,同时降低了再结晶温度,800 ℃对于含氢0.45%的试样可能已超过其再结晶终了温度,因此在变形过程中不发生动态再结晶,而由于温度较高,合金原子容易扩散,发生动态回复软化,这种软化过程与合金的粘滞阻力及相变阻力相平衡,而使流变应力相对稳定。此外,变形温度的升高也使软化速率加快,可见氢化与升高变形温度对应力—应变曲线的作用效果相似。
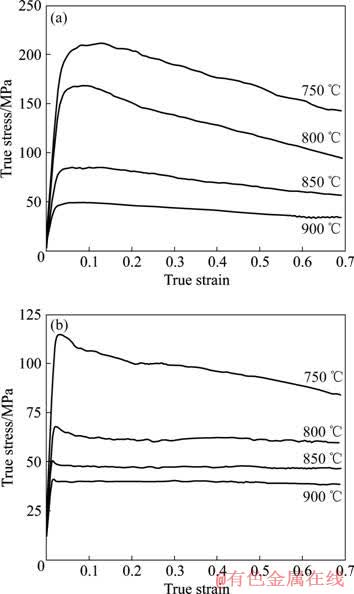
图7 原始与置氢合金的高温压缩真应力—真应变曲线
Fig.7 High temperature compression σ—ε curves of as received and hydrogenated Ti-6Al-4V alloy: (a) As received Ti-6Al-4V alloy; (b) 0.45%H
图8所示为不同温度下氢与高温压缩变形峰值流变应力的关系。结果表明,氢含量相同时,随着变形温度升高,应力峰值明显减小;变形温度相同时,氢的加入也可以显著降低峰值流变应力,且峰值流变应力最小值对应的氢含量随温度增加向低氢方向移动。在750~900 ℃范围内,含氢0.3%试样的峰值流动应力比未置氢试样降低了36%~60%,其中在800 ℃变形时,应力峰值最小值为67.8 MPa,比同样工艺高温压缩未置氢试样降低60%。
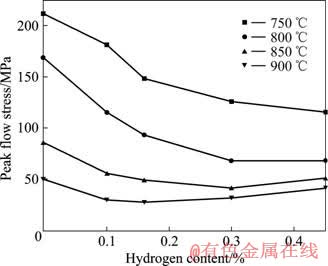
图8 氢含量与高温压缩峰值流变应力的关系
Fig.8 Relations of hydrogen content and peak flow stress
进一步分析表明,850 ℃高温压缩0.3%置氢试样时的峰值应力为41.3 MPa,小于900 ℃未置氢试样的49.3 MPa;同样,800和750 ℃高温压缩0.3%置氢试样时的峰值应力为67.8和125.8 MPa,分别小于850 ℃和800 ℃未置氢试样的85.2和168.5 MPa。这意味着从流变应力的角度出发,氢含量为0.3%的试样在850 ℃高温压缩时的效果与未置氢试样在900 ℃高温压缩时的效果相当,同样,在800 ℃和750 ℃高温压缩时的效果分别与未置氢试样在850 ℃和800 ℃高温压缩时的效果相当。因此,Ti6Al-4V合金中置氢0.3%可以在750~900 ℃范围内使高温压缩温度降低 约50 ℃。
此外,在不同温度变形时,随着氢含量的增加,流变应力先下降后升高,升高的原因可能是一方面随着氢含量增加,晶格畸变增大而产生强化,另一方面随着氢含量增加,氢化物出现并增多而产生强化。
3 结论
1) 钛合金加入适量的氢可以显著降低其流变应力和变形温度。从流变应力的角度出发,Ti-6Al-4V加入0.3%的氢,峰值流变应力降低36%~60%,变形温度降低约50 ℃。
2) 氢可以促进钛合金热变形过程动态回复和动态再结晶,有利于降低变形抗力,其应力-应变曲线无明显硬化阶段。
3) 氢对钛合金高温塑性变形过程组织演变的影响,与原始合金在更高温度变形引起的组织变化相当。
REFERENCES
[1] 王向东, 郝 斌, 逯福生, 贾 翊, 马云风. 钛的基本性质、应用及我国钛工业概况[J]. 钛工业进展, 2004, 21(1): 6?10.
WANG Xiang-dong, HAO Bin, LU Fu-sheng, JA Yi, MA Yun-feng. The basic properties and application situation of titanium in China[J]. Titanium Industry Progress, 2004, 21(1): 6?10.
[2] 刘 莹, 曲周德, 王本贤. 钛合金TC4的研究开发与应用[J]. 兵器材料科学与工程, 2005, 28(1): 47?50.
LIU Ying, QU Zhou-de, WANG Ben-xian. Research development and application of Ti6Al4V alloy[J]. Ordnance Material Science and Engineering, 2005, 28(1): 47?50.
[3] 侯红亮, 李志强, 王亚军. 钛合金热氢处理技术及其应用前景[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2003, 13(3): 533?549.
HOU Hong-liang, Li Zhi-qiang, WANG Ya-jun. Technology of hydrogen treatment for titanium alloy and its application prospect[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrons Metals, 2003, 13(3): 533?549.
[4] 韩明臣. 钛合金的热氢处理[J]. 宇航材料工艺, 1999(1): 23?27.
HAN Ming-chen. Thermohydrogen treatment of titanium alloys[J]. Aerospace Materials and Technology, 1999(1): 23?27.
[5] ILYIN A A, POLKIN I S, MOAMONOV A M, NOSOV V K. Thermohydrogen treament—the base of hydrogen technology of titanium alloys[C]// Titanium'95: Science and Technology. 1996: 2462?2469.
[6] 张少卿. 氢在钛合金热加工中的作用[J]. 材料工程, 1992(2): 24?29.
ZHANG Shao-qing. Effect of hydrogen on hot working for titanium alloys[J]. Materials Engineering, 1992(2): 24?29.
[7] KERR W R, GURNEY F J. Pilot plant forging of hydrogenated Ti-6-Al-4V[R]. AD A089107, Air Force Wright Aeronautical Laboratories, 1980.
[8] SENKOV J J. Effect of phase composition and hydrogen level on the deformation behavior of titanium hydrogen alloys[J]. Metall Mater Trans, 1996, 27: 1869?1877.
[9] 王天生, 寥 波, 苑 辉. 氢对Super-α2合金β固溶处理后时效组织的影响[J]. 材料研究学报, 1996(10): 588?592.
WANG Tian-sheng, LIAO Bo, YUAN Hui. The influence of hydrogen on aging microstructure for super-α2 alloy after β solution[J]. Journal of Materials Research, 1996(10): 588?592.
[10] YANG K, EDMONDS D V. Effect of hydrogen as a temporary alloying element on the microstructure of Ti3Al intermetallic[J]. Scripta Metal Mater, 1993, 28(1): 71?77.
[11] 张 勇. 钛合金及Ti3Al基合金的氢处理研究[D]. 北京: 北京航空材料研究院, 1996.
ZHANG Yong. Research on hydrogen treatment of titanium and Ti3Al base alloys[D]. Beijing: Beijing Aerospace Materials Institute, 1996.
[12] ZHANG Shao-qing, PAN Feng. Hydrogen treatment of Ti-6Al-4V alloy[J]. Chin J Met Sci Technol, 1990(6): 187?192.
[13] ZHANG Y, ZHANG S Q. Hydrogen characteristics of Ti-6Al-4V cast alloy and its microstructure modification by hydrogen treatment[J]. Int J Hydrogen Energy, 1997, 22(2): 161?168.
[14] 潘 峰, 张少卿. Ti-6Al-4V铸造合金在氢处理过程中Ti3Al的析出[J]. 机械工程学报, 1990, 26(4): 38?41.
PAN Feng, ZHANG Shao-qing. Precipitation of Ti3Al phase in Ti-6Al-4V cast alloy during hydrogen treatment[J]. Chinese Journal of Mechanical Engineering, 1990, 26(4): 38?41.
[15] 徐振声, 宫 波, 赖祖涵. 用氢细化Ti-6Al-4V合金显微组织的研究[J]. 有色矿冶, 1990(2): 45?48.
XU Zhen-sheng, GONG Bo, LAI Zhu-han. Research of microstructure refinement of Ti-6Al-4V by hydrogen[J]. Nonferrous Mineral and Metallurgy, 1990(2): 45?48.
[16] 苏彦庆, 骆良顺, 郭景杰, 贾 均, 傅恒志. Ti6Al4V合金渗氢氢化组织及氢脆机制的研究[J]. 稀有金属材料与工程, 2005, 34(4): 526?530.
SU Yan-qing, LUO Liang-shun, GUO Jing-jie, JA Jun, FU Heng-zhi. Investigation on the microstructures and hydrogen embrittlement mechanism of hydrogenated Ti6Al4V[J]. Rare Metal Materials and Engineering, 2005, 34(4): 526?530.
收稿日期:2007-11-10;修订日期:2008-03-10
通讯作者:侯红亮,研究员,博士;电话:010-85701497;E-mail: hou_hl@163.com
(编辑 陈爱华)