基于Hoek-Brown准则的层状岩体隧道开挖响应分析
钟正强1, 2,彭振斌1,彭文祥1
(1. 中南大学 地学与环境工程学院,湖南 长沙,410083;
2. 长沙理工大学 土木与建筑学院,湖南 长沙,410114)
摘 要:利用Hoek-Brown准则描述岩体的强度特征,并建立相应隧道开挖的数值计算模型,分析不同侧压系数时层状岩体的变形破坏特征。研究结果表明,隧道边墙水平位移随侧压系数K的增大而增大,但当K为2.0~2.5时,位移随侧压系数的变化幅度逐渐减小;顺层岩体一侧的水平位移大于逆层一侧的水平位移;当侧压系数较小时,顶板沉降量大于底板回弹量,当侧压系数较大时,二者之间的差别较小;隧道围岩的破坏形式包括剪切破坏和拉伸破坏,当侧压系数较小时,破坏区域较小,主要位于隧道的左上部;随着侧压系数的增大,围岩的破坏区域逐渐增大,但主要部位仍位于隧道的左上部,而右上部的破坏区域较小。
关键词:层状岩体;隧道;侧压系数;变形
中图分类号:U451 文献标志码:A 文章编号:1672-7207(2009)06-1689-06
Excavation response of tunnel in stratified rock mass based on Hoek-Brown criterion
ZHONG Zheng-qiang1, 2, PENG Zhen-bin1, PENG Wen-xiang1
(1. School of Geoscience and Environmental Engineering, Central South University, Changsha 410083, China;
2. Department of Architecture and Civil Engineering, Changsha University of Science and Technology, Changsha 410114, China)
Abstract: Hoek-Brown criterion was used to describe the strength characteristic of rock mass, and the numerical simulation model of tunnel was built to analyze the deformation and failure characterisitc of stratified rock mass with different side-pressure coefficients K. The results show that the maximum horizontal displacements of side wall as well as maximum vertical displacements of roof and floor of surrounding rock mass increase with the increase of K, but when K varies in 2.0-2.5, the increase range of displacement reduces gradually. The horizontal displacement for the inclined stratified rock mass is larger than that for the inverse inclined rock mass. When K is small, the settlement of the roof is larger than that of the floor rebound of tunnel, and the difference between them is smaller when K becomes larger. The failure mode of surrounding rock mass for tunnel consists of shear failure and tensile failure. When K is small, the failure area is small and exists in the top left of tunnel, the failure areas of rock mass become larger with the increase of K, and the main areas are located on the top left of tunnel with few failure areas located on the top right.
Key words: stratified rock mass; tunnel; side-pressure coefficient; deformation
层状岩体广泛存在于隧道工程中,其具有明显的横观各向同性,岩体强度不仅与完整岩石本身的强度有关,而且与岩体中结构面的产状和性质有关[1-2],因此,研究地下结构在层状岩体中开挖的变形和破坏特征对于工程实践具有重要意义。另外,由于地下工程所处位置不同,导致岩体的构造应力存在差异,从而引起岩体的变形破坏形式也不相同,表现出来的力学行为较复杂[3-5]。贾蓬等[6]采用RFPA 数值模拟软件对深埋垂直板裂结构岩体中洞室围岩失稳破坏过程进行了模拟,研究了在不同侧压力系数条件下板裂围岩的失稳破坏特点,并与完整岩体中相同条件下的洞室失稳破坏情况进行了对比;王汉鹏等[7]应用三维地质力学模型试验和三维快速拉格朗日方法模拟了分岔隧道连拱段和小间距段的施工全过程,研究了隧道在不同侧压系数情况下的受力及稳定性。这些研究主要基于Mohr-Coulomb等线性破坏准则,较少考虑非线性破坏准则,不能真实反映出实际工程中岩体的固有特点和非线性破坏特征。Tien等[8-10]采用Hoek-Brown准则较好地描述了层状岩体非线性破坏特征,以及岩石强度、结构面组数、所处应力状态对岩体强度的影响。研究基于非线性破坏准则的层状岩体开挖响应特征具有重要的理论意义和实际工程价值。在此,本文作者首先采用数值方法[11-13],建立基于Hoek-Brown准则的层状岩体隧道开挖计算模型,然后,分析侧压系数(水平应力与竖直应力之比)不同时隧道围岩的变形情况,探讨倾斜层状岩体中隧道的开挖稳定性,以便为工程实践提供参考。
1 数值模型与计算方法
1.1 计算模型
由于三维有限差分程序(一种工程计算处理程序)适用于绝大多数的工程力学问题,尤其适用于材料弹塑性以及几何边界复杂情况的数值模拟,但其在建模以及单元网格划分等处理问题上存在一定困难[14-15],为此,首先利用ANSYS建立数值模型,然后,通过自编的ANSYS-FLAC3D转换程序,导入FLAC3D进行计算。
模型隧道跨度为10 m,高为12 m,边墙高为8 m;考虑到隧道开挖的影响范围,整体模型长×宽×高为70 m×70 m×1 m,层理面按照软弱结构面进行考虑,利用实体单元建立软弱结构面;采用平面应变分析模式,共20 958个单元,6 892个节点,如图1所示。模型分为4个组:base_rock, base_weak,tunnel_rock和tunnel_weak;边界条件为:模型下部固定约束,侧面约束法向位移。计算得到的水平位移规定:向左为负,向右为正。竖直位移规定:向下为负,向上为正;隧道开挖完毕后,为了监测不同位置的位移变化情况,布设监测点2~27(图1(b)),记录开挖后的位移分布和扰动过程中的位移变化情况(本文称为动态位移)。采用Hoek-Brown准则对岩土体进行分析,岩土体计算参数如表1所示,其中:m为完整岩石的岩体强度指标;s为岩体特性系数。
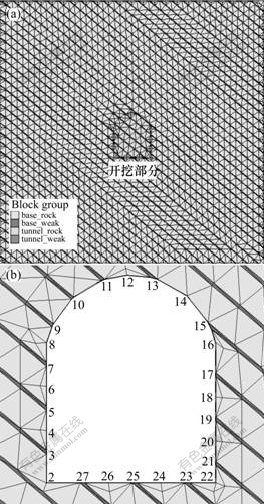
(a) 计算模型;(b) 监测点布置
图1 数值模型
Fig.1 Numerical model
表1 计算参数
Table 1 Calculation parameters

1.2 Hoek-Brown准则的数值实现
岩石破坏判据除了适用于结构完整且各向同性的均质岩石外,还应适用于碎裂岩体及各向异性的非均质岩体等。通过岩石抛物线型破坏包络线的系统,提出Hoek-Brown破坏经验判据的表达式为[16-18]:
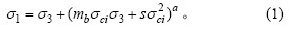
式中:σ1为岩体破坏时的最大主应力;σ3为作用在岩体上的最小主应力;σci为完整岩石单轴抗压强度;mb为岩体常数,与完整岩石的mi有关;s和a取决于岩体特性的系数。这些参数均可表述为地质强度指标GSI的函数,具体形式如下:
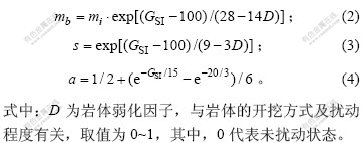
在数值计算过程中,首先采用弹性增量理论,应力及其变形的增量表达式为[19]:

由弹性增量理论可得估算应力分量:
根据塑性状态下的应变增量为弹性应变增量和塑性应变增量之和,推导应力分量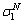 ,
,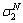 和
和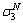 :
:

2 计算结果与分析
2.1 不平衡力
在计算过程中,计算系统的最大不平衡力变化情况如图2所示。在计算过程中,由于外荷载的作用,模型节点将产生不平衡力,而该不平衡力随着时间的推移,逐渐消散到周围节点中,直至系统达到平衡状态为止。另外,侧压系数K越大,开挖完毕时引起的扰动越大,产生的系统最大不平衡力也越大,最大不平衡力的变化范围为612.71~1 301.77 kN。单元弹性应变能的计算公式为[19]:


图2 计算过程中节点的最大不平衡力
Fig.2 Maximal unbalance force of node during calculation
由于σ1=σ3=Kσ1,因而,当侧压系数越大时,σ2和σ3也越大,从而导致在隧道开挖前,岩土体蓄积的弹性应变能也越大,隧道被开挖后,原先隧道位置岩体对周围岩体的支撑作用消失,使该部分岩体弹性应变能得到释放,从而引起更大的岩土体应力响应。
2.2 隧道最大位移
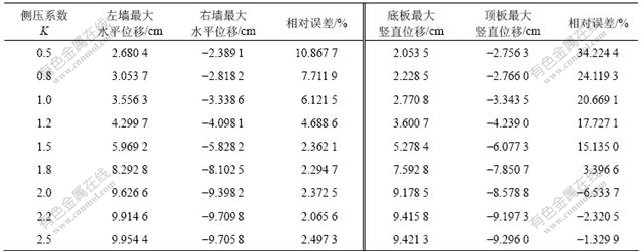
隧道围岩最大位移与侧压系数的关系见表2。从表2可以看出,隧道左墙和右墙的水平位移以及顶板和底板的竖直位移均随侧压系数K的增大而增大,但当K位于2.0~2.5时,位移随侧压系数的变化幅度逐渐减小,说明当K达到一定程度后,对隧道最大位移的影响变得较小。左墙的最大水平位移大于右墙的最大水平位移。这是由于左墙围岩属于顺层结构,而右墙围岩属于逆层结构,顺层结构更易于滑动,从而产生更大的水平位移,二者的相对误差随着侧压系数的增大呈现逐渐减小的态势,说明侧压系数增大,使岩体的各向异性特征逐渐消除。另外,隧道开挖引起顶板岩体竖直位移向下,底板竖直位移由于回弹呈现向上的趋势,当侧压系数较小时,二者的差别较大,顶板位移明显大于底板位移;但随着侧压系数的增大,隧道围岩受水平应力的影响,二者的差别逐渐减小,最终出现底板回弹量大于顶板岩体的沉降量。
表2 隧道围岩最大位移与侧压系数的关系
Table 2 Relationship between the maximum displacement of tunnel surrounding rock mass and side-pressure coefficient
2.3 位移变化趋势
从不同侧压系数下监测点的动态水平位移见图3。可见,隧道开挖完毕后,随着时间的推移,左右墙监测点的水平位移首先迅速增大,然后,逐渐趋于稳定,并且侧压系数越大,曲线的峰值越大,斜率也越大。这是由于侧压系数越大,在相同自重应力情况下,隧道围岩受到的构造应力较大,当隧道开挖完毕后,构造应力引起的隧道变形也越大;但当侧压系数增大到一定值后,其变化对于隧道围岩的变形影响变得较小。从图3可以看出,当K为0.5~1.2时,侧压系数的变化引起曲线峰值的变化较小;当K为1.2~2.0时,曲线的峰值变化幅度发生突变。可见,该范围内的侧压系数对于位移的影响较大,此时,隧道围岩变形对于侧压系数的敏感度较高;当K为2.0~2.5时,位移曲线峰值基本没有变化。对于动态竖直位移(图4),位移曲线随着K的变化规律与水平位移的变化规律相同。这是由于侧压系数越大,隧道围岩沿层面滑移的趋势也越大,从而引起较大的竖直位移。
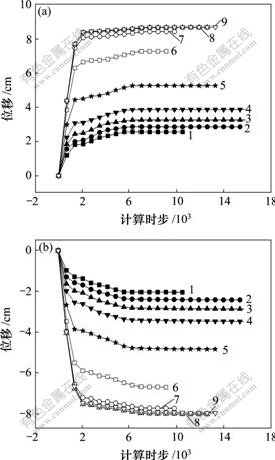
侧压系数K:1—0.5; 2—0.8; 3—1.0; 4—1.2; 5—1.5; 6—1.8; 7—2.0; 8—2.2; 9—2.5
(a) 不同侧压系数下第5监测点的动态水平位移;(b) 不同侧压系数下第19监测点的动态水平位移
图3 不同侧压系数下监测点的动态水平位移
Fig.3 Dynamic horizontal displacement of monitoring point with different side-pressure coefficients

(a) 第25监测点的动态竖直位移;(b) 第12监测点的动态竖直位移
侧压系数K:1—0.5; 2—0.8; 3—1.0; 4—1.2; 5—1.5; 6—1.8; 7—2.0; 8—2.2; 9—2.5
图4 不同侧压系数下监测点的动态竖直位移
Fig.4 Dynamic vertical displacements of monitoring point with different side-pressure coefficients
为了对比不同监测点的位移变化趋势,以侧压系数K为1.5为例,记录不同监测点的水平位移和竖直位移随时间推移的变化情况(图5)。从图5(a)可以看出,左右侧墙监测点的位移变化趋势除了在峰值上存在一定差别外,曲线的形态大致相同,即侧墙和隧道顶部监测点位移曲线均在6 000时步后达到稳定状态,并且最大水平位移出现在边墙中部;而顶底板监测点的动态竖直位移曲线则存在较大差别,底板位移较快达到稳定状态,大约需1 800计算时步;而顶板位移达到稳定状态的时间较长,大约需8 000计算时步。可见,隧道开挖后,底部围岩受到开挖的影响较小。这是由于隧道的层状岩体特征存在沿层面滑移的趋势,并且顶板位移的绝对值明显大于底板位移,顶底板最大位移均出现在中间部位。
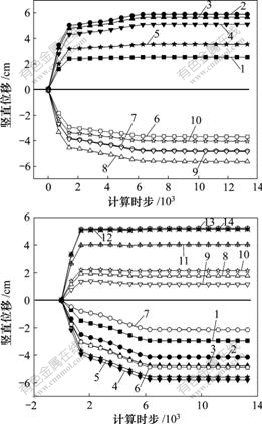
(a) 动态水平位移:1—监测点2; 2—监测点4; 3—监测点6; 4—监测点8; 5—监测点10; 6—监测点14; 7—监测点16;
8—监测点18; 9—监测点20; 10—监测点22
(b) 动态竖直位移:1—监测点9; 2—监测点10; 3—监测点11; 4—监测点12; 5—监测点13; 6—监测点14; 7—监测点15; 8—监测点2; 9—监测点22; 10—监测点23; 11—监测点24; 12—监测点25; 13—监测点26; 14—监测点27
图5 相同侧压系数下不同监测点的动态位移
Fig.5 Dynamic displacements of different monitoring points with the same side-pressure coefficients
2.4 塑性区分布
图6所示为隧道开挖后,围岩的塑性区分布。可以看出,隧道围岩的破坏形式包括剪切破坏和拉伸破坏,以及二者的复合破坏形式;当侧压系数较小时,破坏区域较小,主要位于隧道的左上部,此时,由于顺层岩体的滑移而产生剪切破坏;随着侧压系数的增大,围岩的破坏区域逐渐增大,但主要部位仍位于隧道的左上部,而右上部的破坏区域较小;隧道顶板附近出现拉伸破坏。
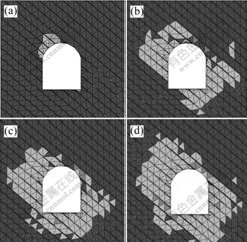
(a) K=0.5; (b) K=1.0; (c) K=1.5; (d) K=2.0
图6 塑性区分布
Fig.6 Distributions of plastic areas
3 结 论
a. 隧道左墙和右墙的水平位移以及顶板和底板的竖直位移,均随侧压系数K的增大而增大,但当K为2.0~2.5时,位移随侧压系数的变化幅度逐渐减小;顺层岩体一侧的水平位移大于逆层一侧的水平位移。
b. 当侧压系数较小时,顶板沉降量大于底板回弹量;当侧压系数较大时,二者之间的差别较小。
c. 隧道围岩的破坏形式包括剪切破坏和拉伸破坏;当侧压系数较小时,破坏区域较小,主要位于隧道的左上部;随着侧压系数的增大,围岩的破坏区域逐渐增大,但主要部位仍位于隧道的左上部,而右上部的破坏区域较小。
参考文献:
[1] Kwasniewski M A. Mechanical behavior of anisotropic rocks[M]. Oxford: Pergamon Press, 1993.
[2] 鲜学福. 层状岩体破坏机理[M]. 重庆: 重庆大学出版社, 1989.
XIAN Xue-fu. Failure mechanism of stratified rock mass[M]. Chongqing: Chongqing University Press, 1989.
[3] 郭 群. 层状岩石强度特征及其数值实现[J]. 科技导报, 2008, 26(16): 68-71.
GUO Qun. Strength characteristic of stratified rock and its numerical application[J]. Science and Technology Review, 2008, 26(16): 68-71.
[4] 刘 君, 孔宪京. 节理岩体中隧道开挖与支护的数值模拟[J]. 岩土力学, 2007, 28(2): 321-326.
LIU Jun, KONG Xian-jing. Numerical simulation of behavior of jointed rock masses during tunneling and lining of tunnels[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2007, 28(2): 321-326.
[5] 倪国荣, 叶梅新. 板裂结构岩体的力学分析法[J]. 岩土工程学报, 1987, 9(1): 99-108.
NI Guo-rong, YE Mei-xin. Mechanical analysis of rock mass with the plate fracture structure[J]. Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 1987, 9(1): 99-108.
[6] 贾 蓬, 唐春安, 张国联. 深埋垂直板裂结构岩体中洞室失稳破坏机制[J]. 东北大学学报, 2008, 29(6): 893-896.
JIA Peng, TANG Chun-an, ZHANG Guo-lian. Failure mechanism study on vertically stratified rock mass around deep tunnel[J]. Journal of Northeastern University, 2008, 29(6): 893-896.
[7] 王汉鹏, 李术才, 张强勇. 分岔隧道模型试验与数值模拟超载安全度研究[J]. 岩土力学, 2008, 29(9): 2521-2526.
WANG Han-peng, LI Shu-cai, ZHANG Qiang-yong. Model test and numerical simulation of overload safety of forked tunnel[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2008, 29(9): 2521-2526.
[8] Tien Y M, Kuo M C. A failure criterion for transversely isotropic rocks[J]. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci, 2001, 38: 399-412.
[9] Tien Y M, Tsao P F. Preparation and mechanical properties of artificial transversely isotropic rock [J]. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci, 2000, 37(6): 1001-1012.
[10] Tien Y M, Kuo M C, Juang C H. An experimental investigation of the failure mechanism of simulated transversely isotropic rocks[J]. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci, 2006, 43(8): 1163-1181.
[11] XU Guo-yuan, YAN Chang-bin. Numerical simulation for influence of excavation and blasting vibration on stability of mined-out area[J]. Journal of Central South University of Technology, 2006, 13(5): 577-583.
[12] LIU Jin-zhi, WU Ai-xiang, YANG Bao-hua, et al. Dynamic experiment and numerical simulation of solute transmission in heap leaching processing[J]. Journal of Central South University of Technology, 2007, 14(6): 838-841.
[13] 林 杭, 曹 平, 赵延林, 等. 强度折减法在Hoek-Brown准则中的应用[J]. 中南大学学报: 自然科学版, 2007, 38(6): 1219-1224.
LIN Hang, CAO Ping, ZHAO Yan-lin, et al. The application of strength reduction method in Hoek-Brown criterion[J]. Journal of Central South University: Science and Technology, 2007, 38(6): 1219-1224.
[14] 廖秋林, 曾钱帮, 刘 彤, 等. 基于ANSYS 平台复杂地质体FLAC3D 模型的自动生成[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 2005, 24(6): 1010-1013.
LIAO Qiu-lin, ZENG Qian-bang, LIU Tong, et al. Automatic model generation of complex geologic body with FLAC3D based on ANSYS platform[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2005, 24(6): 1010-1013.
[15] 林 杭, 曹 平, 李江腾, 等. 基于SURPAC的FLAC3D三维模型自动构建[J]. 中国矿业大学学报, 2008, 37(3): 339-342.
LIN Hang, CAO Ping, LI Jiang-teng, et al. Automatic generation of FLAC3D model based on SURPAC[J]. Journal of China University of Mining and Technology, 2008, 37(3): 339-342.
[16] Hoek E, Carranza-Torres C, Corkum B. Hoek-Brown failure criterion–2002 Edition[C]//Proc NARMS-TAC Conference. Toronto, 2002: 267-273.
[17] YANG Xiao-li, YIN Jian-hua. Slope stability analysis with nonlinear failure criterion[J]. Journal of Engineering Mechanics, 2004, 130(3): 267-273.
[18] YANG Xiao-li, YIN Jian-hua. Stability analysis of rock slopes with a modified Hoek-Brown failure criterion[J]. International Journal for Numerical and Analytical, 2004, 28(2): 181-190.
[19] Itasca Consulting Group Inc. FLAC3D (Fast Lagrangian Analysis of Continua in Three-dimensions), version 2.1, User’s Manual[R]. Itasca Consulting Group Inc, 2002.
收稿日期:2009-01-25;修回日期:2009-04-09
基金项目:国家自然科学基金资助项目(50878212)
通信作者:钟正强(1968-),男,湖南长沙人,副教授,从事隧道稳定性的分析与评价工作;电话:13607316010;E-mail: zzqcslg@126.com