文章编号:1004-0609(2010)03-0469-07
不同拉伸温度下SiC颗粒增强Al-Fe-V-Si复合材料的断裂行为
贺毅强1,乔 斌1,王 娜3,杨建明1,徐政坤2,尚 峰1,陈振华4
(1. 淮海工学院 机械工程系,连云港 222005;
2. 张家界航空工业职业技术学院 机械工程系,张家界 427000;
3. 淮海工学院 人事处,连云港222005;
4. 湖南大学 材料科学与工程学院,长沙 410082)
摘 要:采用喷射沉积工艺制备SiCP/Al-11.7Fe-1.15V-2.4Si复合材料,并通过热压工艺对复合材料进行致密化,再通过热轧加工成板材。对复合材料的显微组织以及不同温度下复合材料的断裂性能和断口形貌进行研究。结果表明:采用热压致密后再热轧工艺能使SiC颗粒分布均匀,长轴方向平行于轧制方向,有利于增强复合材料的力学性能,复合材料的断裂性能和断面形貌与拉伸温度以及SiC的分布和取向相关,随着拉伸温度升高,SiC/Al界面强度减弱,拔断的SiC颗粒逐渐减少,SiC颗粒的拔出成为主要的裂纹源;与基体金属不同的是,复合材料的塑性随着温度升高而降低。
关键词:SiC颗粒;耐热合金;复合材料;喷射沉积;断裂行为
中图分类号:TG146.2 文献标识码:A
Facture behavior of Al-Fe-V-Si composite reinforced with SiC particles at different tensile temperatures
HE Yi-qiang1, QIAO Bin1, WANG Na3, YANG Jian-ming1, XU Zheng-kun2, SHANG Feng1, CHEN Zhen-hua4
(1. College of Mechanical Engineering, Huaihai Institute of Technology, Lianyungang 222005, China;
2. Department of Mechanical Engineering, Zhangjiajie Institute of Aviation Industry Vocational,
Zhangjiajie 427000, China;
3. Department of Human Resource, Huaihai Institute of Technology, Lianyungang 222005, China;
4. College of Materials Science and Engineering, Hunan University, Changsha 410082, China)
Abstract: SiCP/Al-11.7Fe-1.15V-2.4Si composite was prepared by spray deposition and densified by hot pressing, and then were rolled into sheets. The microstructures, fracture properties and fractographies of the composite at different tensile temperatures were investigated. The results show that the uniform distribution of the SiC particles with their longitudinal direction parallel to the rolling direction is achieved by rolling after hot pressing, which contributes to the elevation of the mechanical properties of the composite. Fracture properties and fractographies of the composite are affected by the tensile temperature and distribution and orientation of SiC particles. The bonding between SiC particles and the matrix becomes weak, and the breakable particles reduce as the tensile temperature; the debonding of SiC/Al becomes the dominant fracture mechanism, the plasticity of the composite decreases as the tensile temperature increases, which is different from the matrix alloy.
Key words: SiC particle; heat resistant alloy; composite; spray deposition; fracture behavior
速凝固Al-Fe-V-S合金是美国Allied-Signal公司在20世纪80年代开发的新型耐热高铝合金。该材料具有高的室温和高温强度、高刚度、良好的断裂韧性和低的析出相颗粒粗化速率等性能[1]。陶瓷颗粒的多层喷射共沉积技术是开发高性能金属基复合材料的有效方法。快速凝固耐热铝合金坯料过去多采用平流铸造法和雾化制粉结合粉末冶金工艺来制备。喷射沉积技术作为一种新型近净成形工艺,也被用来制备这种高合金化铝合金[2]。为了进一步提高该系合金的力学性能,在该系合金中加入第二相进行增强,主要添加SiC颗粒、SiC晶须、Si3N4 Al18B4O33以及原位生成的TiC。因此,在汽车、电子以及航空工业等领域该合金有着广泛应用[3?4]。过去的研究主要是关于金属基复合材料的基体硬化、残余应力的影响、界面性能以及室温下的断裂行为[5?7],集中于Al-Fe-V-Si和SiCP/Al-11.7Fe-1.15V-2.4Si的室温力学性能和断裂行为[8?14],很少有研究涉及高温下金属基复合材料的断裂行为。金属基复合材料的力学性能取决于其显微组织,如裂纹扩展和断裂性能与增强颗粒的空间分布和体积分数相关,因此,要考虑加工过程中增强颗粒的分布和取向。此外,显微组织的均匀性对于金属基复合材料的影响很大。热压工艺能够改善采用传统挤压工艺加工的SiCP/Al-Fe-V-Si复合材料中SiC颗粒分布不均匀的问题。通过热压还可以解决因为设备限制难以制备大尺寸薄板的问题。
SiCP/Al-Fe-V-Si复合材料有很多优点,但因具有较低的延展性和断裂韧性使其应用受到限制,特别是SiC颗粒聚集的SiCP/Al-Fe-V-Si,加载早期的突然断裂(颗粒与基体之间的塑性断裂、脆性断裂和脱层)制约了其力学性能的提高和应用。因此,研究不同温度下SiCP/Al-Fe-V-Si复合材料的断裂性能和断裂形貌的关系,以及提高SiC颗粒的均匀性、基体合金与SiC颗粒之间的结合强度是有必要的。
1 实验
1.1 原料及成分设计
本试验以名义成分为15SiCP/Al-11.7Fe-1.15V- 2.4Si/的复合材料为研究对象(其中SiC的计量为体积分数,其他的为质量分数),基体合金中的Fe和V分别以Al-40Fe和Al-40Fe-10V的形式加入。首先,在中频感应炉中熔配Al-40Fe和Al-40Fe-10V中间合金,再添加适量的纯铝和纯硅在1 020 ℃熔配Al-11.7Fe-1.15V-2.4Si母合金。SiC颗粒为β-SiC,平均粒径约为10 μm,在复合材料中体积分数约为15%。将Al-11.7Fe-1.15V- 2.4Si母合金和SiC粉末在湖南大学材料学院的多层喷射沉积制备圆坯装置上进行喷射共沉积得到复合材料圆坯料。
1.2 塑性加工
将沉积锭坯车削成直径为155 mm的圆柱形坯料。然后,在1 025 t挤压机的挤压筒内进行热模压,锭坯加热温度为450 ℃,保温1 h;模具及挤压筒加热温度为400 ℃,保温1 h。热压得到的坯料垂直于高向锯成圆片,再将圆片锯成矩形板材进行轧制,轧制温度为480 ℃,其他轧制工艺参数与挤压后热轧的工艺参数相同。将热压的复合材料板材进行热轧,轧制温度为480 ℃,轧制前保温1 h,道次间退火保温20 min,采用石墨+机油润滑,轧速为0.43 m/s。
1.3 性能检测
常温拉伸试验在CSS?44100型电子万能试验机上进行,拉伸速率为0.5 mm/min,拉伸方向平行于板材轧制方向。金相样品用Keller试剂浸蚀后在XJL?03大型金相显微镜下进行组织观察。在JSM?5600扫描电镜下观察拉伸试样的断口形貌。
2 实验结果
2.1 SiC颗粒的分布
SiC颗粒具有高熔点、高硬度和高弹性模量。近年来,以SiC陶瓷颗粒为增强相的金属基复合材料得到了广泛的研究[15?17]。复合材料中的SiC颗粒通过机械破碎获得,因此,呈尖角不规则形状。SiC颗粒主要是六角密堆结构,因而,β-Al/SiC界面是非共格的。SiC颗粒在复合材料中的形态和分布随着加工工艺和加工状态变化而发生变化。
图1所示为SiCP/Al-11.7Fe-1.15V-2.4Si复合材料中的SiC颗粒在热压态和热压后再轧制的形状及分布状况。从图1(a)可以看到沉积态的SiC颗粒分布不均匀,且有较明显的团聚现象。这是因为在喷射沉积喷嘴的扫描过程中,SiC颗粒呈层状分布。因SiC和Al基体塑性变形能力的差异,挤压后,SiC颗粒偏聚于板材的板面。热压工艺的塑性流动小,因此,SiC颗粒的聚集和分层也没有得到明显改善(图1(b))。热压工艺没有造成这种SiC颗粒板材表面的聚集,通过后续的多道次热轧后,SiC颗粒的层间距减小,从而达到均匀化的效果。从图1(c)可以看出,SiC颗粒与基体结合状况良好。经过多道次热轧后,由于SiC颗粒的转动和滑动,使得总体上SiC颗粒的纵向平行于轧制平面。从微观角度,SiC增强颗粒的转动是由基体的塑性变形引起的,因此,塑性变形微观机制如位错滑移和攀移等将对SiC增强颗粒的转动起主导作用。这与?ADEK等[18]发现的情况一致,复合材料中的Al12(Fe,V)3Si颗粒和SiC颗粒几乎都沿挤压方向排列,且基体呈现出弱织构。
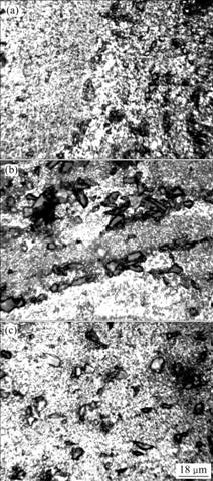
图1 SiCP/Al-Fe-V-Si复合材料在加工过程中的显微组织
Fig.1 Microstructures of composites during work process: (a) As-deposited; (b) As-hot pressed; (c) As-rolled after hot pressing
2.2 拉伸断口形貌
图2所示为先热压再轧制试样在不同温度下拉伸的断口形貌。对应的拉伸断口侧面形貌如图3所示。从图2(a)和(b)可以看出,在较低的拉伸温度下,SiC增强颗粒与基体结合良好,界面强度高。在拉伸过程中,由于SiC颗粒与基体金属的模量差以及热膨胀系数的不同,应力集中于SiC颗粒,SiC颗粒被拉断呈平整脆性断裂。当拉伸温度较低时,多数SiC颗粒被拉断,只有少数较小颗粒或长径比较小的颗粒在拉伸过程中被拔出。从图2(a)对应的断口侧面形貌(图3(a))可以看到SiC颗粒被拔断后留在金属基体断面上的半截SiC 颗粒,未见有SiC颗粒被拔出后的凹坑。从图3(b)也可以看出,在100 ℃拉伸断口的附近,基体中有被拉断的SiC颗粒,断口垂直于拉伸方向。随着拉伸温度的升高,被拉断的SiC颗粒减少,而被拔出的SiC颗粒逐渐增多。当拉伸温度为200 ℃(图2(c)和3(c))时,被拔断的SiC颗粒约为35%,而当拉伸温度升高到300 ℃(图2(d)和3(d))时,被拔断的SiC颗粒只有20%左右。当拉伸温度升高到400 ℃(图2(e)和3(e))时,少量的SiC颗粒被拔断,绝大部分SiC颗粒被拔出。从其对应的断口侧面金相可以看到SiC颗粒与基体金属的界面脱粘产生裂纹,并且基体也产生开裂。当拉伸温度进一步升高到450 ℃(图2(f)和3(f))时,只有极少的SiC颗粒被拔断,从其对应的断口侧面金相也可以看到SiC颗粒与基体界面的脱粘以及SiC颗粒被拔出后形成的凹坑。
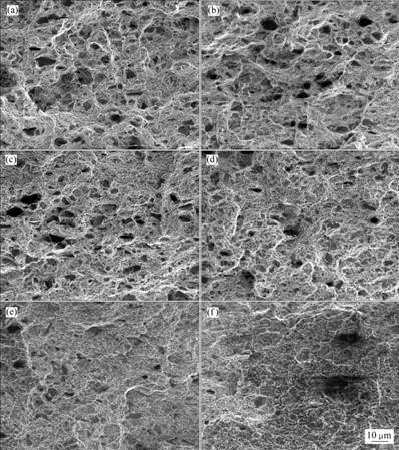
图2 SiCP/Al-Fe-V-Si复合材料在不同温度下拉伸的断口形貌
Fig.2 Fractographies of composite at different tensile temperatures: (a) 25 ℃; (b) 100 ℃; (c) 200 ℃; (d) 300 ℃; (e) 400 ℃; (f) 450 ℃
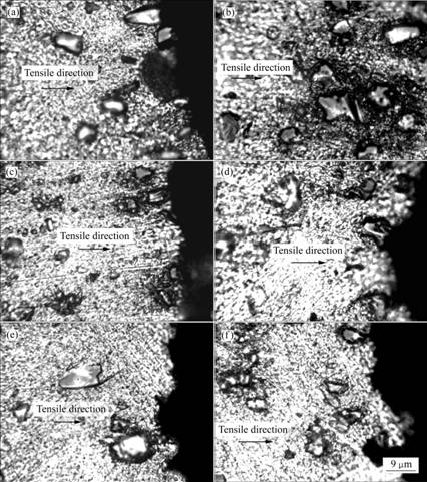
图3 SiCP/Al-Fe-V-Si复合材料在不同温度下的拉伸断面侧面形貌
Fig.3 Morphologies of fracture sides of composites at different tensile temperatures: (a) 25 ℃; (b) 100 ℃; (c) 200 ℃; (d) 300 ℃; (e) 400 ℃; (f) 450 ℃
2.3 断裂行为
SiCP/Al-Fe-V-Si复合材料在不同温度下变形行为不同。图4所示为SiCP/Al-11.7Fe-1.15V-2.4Si复合材料薄板在不同温度下的应力—应变曲线,拉伸速率为0.5 mm/min,标距为10 mm。在相同的拉伸速率下,SiCP/Al-11.7Fe-1.15V-2.4Si复合材料的抗拉强度随着拉伸温度的升高,其抗拉强度下降;断裂应变也随着拉伸温度的上升而下降。这与未添加SiC的合金材料不同。合金材料在100~150 ℃存在中温脆性区,所以,合金材料的断裂应变量随着拉伸温度的升高先下降,在100~150 ℃最低;当拉伸温度超过脆性温度后,材料的断裂应变量又上升[19]。而添加SiC增强颗粒的SiCP/Al-Fe-V-Si复合材料的断裂应变量随着拉伸温度的升高而一直下降,SiCP/Al-11.7Fe-1.15V-2.4Si在室温应力—应变曲线在强度达到极限抗拉强度后,流变应力下降,呈加工软化,断裂应变量为7.7%。当拉伸温度升高到100 ℃时,其软化现象有所减弱,断裂应变量减少到7.1%。随着拉伸温度的升高,软化现象进一步减弱。当拉伸温度为200 ℃和300 ℃时,材料的断裂应变量分别为6.5%和6.4%。当拉伸温度升高到400 ℃时,复合材料经过加工硬化阶段达到极限抗拉强度后即断裂,断裂应变量降低到5.1%。断裂应变量随拉伸升高的变化规律与表1所示的其断后伸长率随拉伸温度升高的变化规律一致。可以看出,复合材料的抗拉强度和伸长率随着拉伸温度的升高而降低,室温抗拉强度为581.2 MPa,伸长率为4.5%;随着拉伸温度升高到100、200、300和400 ℃时,抗拉强度下降到461.5、372.2、315.8和232.6 MPa,伸长率下降到4.2%、3.3%、2.5%和1.4%。与图2和3一致,复合材料没有出现合金材料的中温脆性现象。
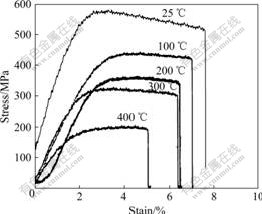
图4 SiCP/Al-11.7Fe-1.15V-2.4Si薄板在不同温度下的应力?应变曲线(应变速率为5×10-4)
Fig.4 Stress—strain curves of SiCP/Al-11.7Fe-1.15V-2.4Si sheets at different tensile temperatures(Stain rate: 5×10-4)
表1 SiCP/Al-11.7Fe-1.15V-2.4Si薄板在不同温度下的力学性能
Table 1 Mechanical properties of SiCP/Al-11.7Fe-1.15V- 2.4Si sheets at different tensile temperatures
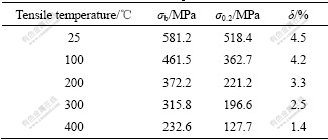
Every datum in Table 1 was taken as an average value from more than five data
3 分析与讨论
Al-Fe-V-Si合金基体和SiC颗粒之间的弹性模量失配度大,坚硬、脆性的SiC颗粒抑制了相对柔软的基体合金的塑性流变。因此,复合材料呈总体上的脆性断裂和局部韧性断裂相结合的复合断裂。复合材料的塑性差是因为基体合金的塑性变形受到非连续的SiC增强颗粒的阻碍,而非基体合金的塑性差。
SiC颗粒增强复合材料存在3种失效方式:SiC颗粒断裂、界面脱粘和基体开裂。复合材料的断裂方式和SiC与基体金属界面强度相关外,而界面强度与变形温度相关。当拉伸温度升高300 ℃以上时,被拉断的SiC颗粒越来越小,SiC颗粒被拔出而形成的凹坑越来越多。当拉伸温度为400 ℃时,断面上的SiC颗粒几乎没有被拉断,是基体和SiC颗粒的界面被破坏,SiC颗粒被拔出,断面上留下SiC被拔出而形成的韧窝或突出的SiC颗粒。SiC颗粒和基体界面的脱粘以及基体的开裂成为裂纹形核的主要机制。界面的脱粘是复合材料高温下延展性差的重要原因。在不同的拉伸温度下,复合材料都是呈基体的韧性断裂和总体上的脆性断裂相结合的复合断裂。脆性断裂作为主要的断裂方式不是因为基体合金的塑性有限,而是因
为非连续的SiC增强颗粒对基体合金塑性流动的限制,并在SiC颗粒周围形成撕裂棱。受SiC的空间分布、体积分数的影响,SiC颗粒捕获位错限制塑性流动,在周围形成高密度位错区域,在SiC颗粒之间的基体产生撕裂棱。在拉伸过程中,随着变形程度的增大,SiC颗粒周围的应力集中程度增高。从室温到300 ℃,较大的SiC颗粒首先被拉断,然后,相对较小的SiC颗粒被拉断。具有高纵横比的SiC颗粒更趋向于这种断裂。SiC颗粒断裂后产生的微裂纹迅速扩展并相互连接,因而,使复合材料突然脆性断裂。要让SiC颗粒完全被拉断,则SiC 颗粒要被加载到它们的断裂应力,这主要通过拉应力来实现,还有部分来自于颗粒与基体界面的剪切力。通过界面剪切力来加载的程度取决于SiC颗粒的纵横比(S)。假设基体中的SiC颗粒理想分布,则纵横比与SiC的强度(σ(SiC))以及界面剪切强度(τi)之间的关系如式(1)所示[20]。

从式(1)可以看出,SiC是否被拉断还与界面剪切强度相关。当拉伸温度超过400 ℃时,由于温度的升高,SiC颗粒和基体合金的界面变弱,SiC颗粒被拔出界面的破坏以及基体金属的开裂成为裂纹源,微裂纹扩展并连接而导致复合材料失效。此外,复合材料的断裂方式还受SiC的空间分布的影响,SiC颗粒聚集的区域更容易引起应力集中,SiC颗粒也更容易断裂。热挤压后,板坯中存在严重的SiC颗粒表面聚集,从而造成SiC颗粒的过早断裂而降低复合材料的力学性能。热压再轧制工艺能使SiC颗粒分布更加均匀,因此,可以避免SiC颗粒在拉伸过程中的过早突然断裂,从而提高复合材料的力学性能。
随着拉伸温度的升高,复合材料的抗拉强度和屈服强度下降,导致伸长率降低,比同成分的合金材料的性能差。随着拉伸温度的升高,基体合金的软化以及SiC颗粒与基体界面的减弱是引起复合材料强度下降的主要原因。复合材料的塑性主要取决于变形过程中能够塑性流动的基体材料的体积分数,能够塑性流动的基体的体积分数越高,塑性就越好。在复合材料中,基体的塑性流动又受到SiC颗粒的制约,塑性流动的基体减少,因此,塑性下降,比同成分的合金材料的性能差。
在颗粒增强的金属基复合材料中,主要的裂纹形核机制是增强颗粒的开裂和增强颗粒与基体界面的脱粘。对于给定增强颗粒粒度和体积分数的复合材料,裂纹形核方式取决于界面结合的强度。当拉伸温度低于400 ℃时,由于SiC增强颗粒与Al基体界面的结合较强,主要通过SiC增强颗粒的开裂形核。在SiC开裂以前,基体金属在变形过程中经过加工硬化阶段,并产生软化,材料塑性较好。当拉伸温度达到400 ℃时,SiC增强颗粒与Al基体界面的结合较弱,界面的脱粘成为裂纹形核的主要机制,在材料产生软化以前已经断裂。从室温到400 ℃,随着温度的升高,界面结合强度逐渐减弱,被拉断的SiC颗粒越来越少,被拔出的SiC颗粒越来越多,加工软化现象越来越弱,复合材料的塑性也越来越差。
4 结论
1) 对喷射沉积SiCP/Al-11.7Fe-1.15V-2.4Si复合材料采用热压致密,能使SiC颗粒在基体合金中分布均匀,有利于基体的结合。
2) 复合材料的断裂方式取决于拉伸温度。从室温到300 ℃,SiC颗粒的断裂成为最主要的裂纹源;拉伸温度为400℃,SiC颗粒与基体的界面脱粘成为主要的裂纹源。此外,复合材料的断裂方式还受SiC的空间分布的影响,SiC颗粒聚集的区域更容易引起应力集中,SiC颗粒也更容易断裂,具有高纵横比的SiC颗粒也更容易被拉断。
3) 随着拉伸温度的升高,复合材料的抗拉强度和屈服强度下降,断后伸长率也下降。室温下的抗拉强度为581.2 MPa,100 ℃时下降为461.5 MPa,再到200 ℃时的372.2 MPa,300 ℃时的315.8 MPa,400 ℃时的232.6 MPa。伸长率在室温下为4.5%,100 ℃时下降为4.2%,200 ℃时为3.3%,到300 ℃时为2.5%,400 ℃时为1.4%。
REFERENCES
[1] SKINNER D J, BYE R L, RAYBOULD D, BROWN A M. Dispersion strengthened Al-Fe-V-Si alloys[J]. Scripta Metal Mater, 1986, 20(6): 867?872.
[2] HARIPRASAD S, SASTRY S M L. Processing maps for optimizing gas atomization and spray deposition[J]. Journal of Metals, 1995, 10: 56?59.
[3] LEE J C, PARK S B, SEOK H K, OH C K, LEE H I. Prediction of Si contents to suppress the interfacial reaction in the SiCp/2014Al composites[J]. Acta Mater, 1998, 46(8): 2635?2643.
[4] LEE J C, BYUN J Y, PARK S B, LEE H I. Prediction of Si contents to suppress the formation of Al4C3 in the SiCp/Al composite[J]. Acta Mater, 1998, 46(5): 1771?1780.
[5] LEE J C, SEOK H K, LEE H I. Alloy design of thixoformable wrought SiC/Al alloy composites[J]. Materials Research Bulletin, 1999, 34(1): 35?42.
[6] SRIVATSAN T S, LAVERNIA E J. Use of spray techniques to synthesize particulate-reinforced metal-matrix composites[J]. Journal of Materials Science, 1992, 27(22): 5965?5981.
[7] GAO N F, MIYAMOTO Y, ZHANG D. Dense Ti3SiC2 prepared by reactive HIP[J]. J Mater Sci, 1999, 34(18): 4385?4392.
[8] CHEN Zhen-hua, HE Yi-qiang, YAN Hong-ge, CHEN Zhi-gang, YIN Xian-jue, CHEN Gang. Ambient temperature mechanical properties of Al-11.7Fe-1.15V-2.4Si/SiCP composite[J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2007, 460/461: 180?185.
[9] CHEN Zhen-hua, HE Yi-qiang, YAN Hong-ge, HAO Liang, CHEN Zhi-gang, CHEN Gang. Microstructure and mechanical properties of Al-Fe-V-Si/SiCP composites[J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2007, 17(S1): s238?s243.
[10] 肖于德, 钟 掘, 黎文献, 马正青. 快速凝固Al-Fe-V-Si 合金喷射沉积坯的显微组织与力学性能[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2006, 16(11): 1869?1875.
XIAO Yu-de, ZHONG Jue, LI Wen-xian, MA Zheng-qing. Microstructural features and mechanical properties of spray deposited billets of rapidly solidified Al-Fe-V-Si aluminum alloy[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2006, 16(11): 1869?1875.
[11] 熊柏青, 朱宝宏, 张永安, 韦 强, 石力开, 孙玉峰, 沈宁福. 喷射成形Al-F-V-Si系耐热铝合金的制备工艺和性能[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2002, 12(2): 250?254.
XIONG Bo-qing, ZHU Bao-hong, ZHANG Yong-an, WEI Qiang, SHI Li-kai, SUN Yu-feng, SHEN Ning-fu. Technique and property of heat resisting Al-Fe-V-Si alloys prepared by spray forming process[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2002, 12(2): 250?254.
[12] 陈振华, 贺毅强, 陈志钢, 尹显觉, 陈 刚. SiCP/Al-11.7Fe-1.15V-2.4Si复合材料的显微组织及室温力学性能研究[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2007, 17(6): 858?863.
CHEN Zhen-hua, HE Yi-qiang, CHEN Zhi-gang, YIN Xian-jue, CHEN Gang. Microstructure and ambient temperature mechanical properties of SiCp/Al-11.7Fe-1.15V-2.4Si composite [J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2007, 17(6): 858?863.
[13] 贺毅强, 陈振华, 王 娜, 郝 亮, 陈志钢, 陈 刚. SiCP/Al-Fe-V-Si复合材料组织与性能的热稳定性[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2008, 18(3): 432?438.
HE Yi-qiang, CHEN Zhen-hua, WANG Na, HAO Liang, CHEN Zhi-gang, CHEN Gang. Thermostability of hardness and microstructure of SiCp/Al-Fe-V-Si composite[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2008, 18(3): 432?438.
[14] 詹美燕, 陈振华, 夏伟军. 喷射沉积?轧制工艺制备的FVS0812薄板的高温组织和力学性能[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2004, 14(8): 1348?1352.
ZHAN Mei-yan, CHEN Zhen-hua, XIA Wei-jun. Microstructure and properties of spray-deposited heat-resistant FVS0812 aluminum alloy at high temperature[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2004, 14(8): 1348?1352.
[15] HAMBLETON R, JONES H, RAINFORTH W M. Effect of alloy composition and reinforcement with silicon carbide on the microstructure and mechanical properties of three silicide dispersion strengthened aluminium alloys[J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2001, 304/306: 524?528.
[16] ?ADEK J, KUCHA?OR? K, ZHU S J. Creep behaviour of an Al-11.7Fe-1.15V-2.4Si-15SiCP composite at temperatures ranging from 873 to 948 K[J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2002, 328: 283?290.
[17] KIM I S, KIM N J, NAM S W. Temperature dependence of the optimum particle size for the dislocation detachment controlled creep of Al-Fe-V-Si/SiCP composite[J]. Scripta Metallurgical et Materials, 1995, 32(11): 1813?1814.
[18] ?ADEK J, KUCHA?OR? K, ZHU S J. High temperature creep behaviour of an Al-11.7Fe-1.15V-2.4Si alloy reinforced with silicon carbide particulates[J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2000, 283: 172?180.
[19] MITRA S. Elevated temperature mechanical properties of a rapidly solidified Al-Fe-V-Si alloy[J]. Scripta Metallurgica et Materialia, 1992, 27(5): 521?526.
[20] LLOYD D J. Particle reinforced aluminium and magnesium matrix composites[J]. International Materials Reviews, 1994, 39(1): 1?23.
基金项目:江苏省高校自然科学研究资助项目(09KJD430001);江苏省高校重点建设学科资助项目
收稿日期:2009-03-09;修订日期:2009-08-25
通信作者:贺毅强,讲师,博士;电话:0518-85895330;E-mail: ant210@sina.com
(编辑 杨 华)