CO2化学刺激剂对增强地热系统热储层的改造作用
那金1,冯波1,兰乘宇2,许天福1,鲍新华1
(1. 吉林大学 地下水资源与环境教育部重点实验室,吉林 长春,130021;
2. 大庆油田有限责任公司 井下作业分公司,黑龙江 大庆,163453)
摘要:基于松辽盆地徐家围子地区大庆油田钻井的地球物理和地球化学参数,建立反应性溶质运移模型,模拟CO2化学刺激剂对热储层渗透性的改造作用,分析不同地层压力、温度下的刺激效果,并讨论注入水的化学成分对刺激效果的影响。研究结果表明:孔隙度的增加主要源于原生碳酸盐矿物的溶蚀;通过高温高压反应釜模拟不同温度、压力、水化学条件下CO2化学刺激剂与方解石(主要碳酸盐矿物)的化学反应,实验结果反映出的碳酸盐矿物溶蚀规律与数值模拟结果基本一致。
关键词:增强型地热系统(EGS);化学刺激剂;超临界CO2;数值模拟;室内实验
中图分类号:P641 文献标志码:A 文章编号:1672-7207(2014)07-2447-12
Effectiveness of using supercritical CO2 as stimulation agent for enhanced geothermal systems
NA Jin1, FENG Bo1, LAN Chengyu2, XU Tianfu1, BAO Xinhua1
(1. Key Lab of Groundwater Resources and Environment, Ministry of Education, Jilin University,
Changchun 130021, China;
2. Downhole Operation Company, Daqing Oil Field, Daqing 163453, China)
Abstract: A number of reactive transport simulations were performed to study CO2-induced mineral dissolution and porosity enhancement. Geophysical parameters and geochemical parameters were extracted from a well of Xingcheng oilfield of Xujiaweizi in Songliao Basin. The effects of chemical stimulation in the reservoir of different formation pressures and temperatures were investigated. Ways in which chemical composition of water within CO2 was injected to enhance porosity were examined. The results indicate that the increase of porosity of fractured channel is mainly caused by calcite dissolution. Laboratory experiments on chemical interaction between CO2 stimulation agent and calcite (a major carbonate mineral) are also conducted at different temperatures,pressures and water chemistry conditions with a high-temperature reactor. The information currently available for the mineral alteration at laboratory experiment is generally consistent with that of the simulation.
Key words: enhanced geothermal systems (EGS); stimulation agent; supercritical CO2; numerical simulation; laboratory experiments
增强型地热系统(enhanced geothermal system, EGS)是从地下深部低渗透性岩体通过人工压裂技术后,经济地采出相当数量深层热能的人工地热系统[1]。在EGS工程中,经常会遇到生产井/注入井与人工地热储层裂隙网络的水力联系较差,无法满足EGS的产能需求。为了拓展裂隙网络,增大裂隙渗透性,通常利用EGS化学刺激,即以低于地层破裂压力的注入压力向井附近热储层裂隙注入化学刺激液,依靠其化学溶蚀作用使矿物溶解来增加地层的渗透性[2-4]。传统石油天然气领域的化学刺激工艺一般选取土酸(HCl溶液+HF溶液)和螯合剂(NTA溶液)作为化学刺激液[5]。然而,在EGS热储层高温高压的地质环境下,这2组化学刺激液和岩体矿物反应速度过快,只对注入井附近的岩体进行溶蚀,稍微进入储层即消耗殆尽,无法保持理想的穿透距离[6]。鉴于上述问题,一些学者[6-7]提出用CO2作为化学刺激剂。Xu[6]通过数值模拟技术探讨化学刺激过程中的反应机理,研究结果显示CO2和水混合注入热储层后,一部分溶解于水并转化为碳酸对岩体矿物进行溶蚀[6-7]。将HF和NaOH与NTA混合液相比,CO2-水的混合流体和岩体矿物的反应速度较慢,在地层中的穿透距离较长,具有良好的刺激效果。曲希玉等[8-9]通过水热实验探讨CO2-地层水-岩石间相互作用,研究成果表明CO2-水对砂岩中的方解石、长石、石英等矿物都具有溶蚀能力。本文作者以中国松辽盆地徐家围子断陷营城组火成岩为研究目的层,通过数值模拟技术探讨CO2化学刺激剂使用过程中热储层的裂隙通道矿物组分、孔隙度的变化特征,通过敏感性分析讨论热储层温度、压力和注入水化学组分对化学刺激效果的影响。并通过室内实验模拟热储层高温高压环境,将实验结果和数值模拟结果进行对比,探索CO2化学刺激剂与热储层主要碳酸盐堵塞物方解石的化学反应特征。
1 模型建立
1.1 地质概况
兴城油田位于中国黑龙江省大庆市徐家围子地区,深层火山岩发育广泛主要为上侏罗—下白垩统岩层, 自下而上分为火石岭组、沙河子组、营城组等,其上不整合覆盖登娄库组[10-11]。地质资料分析表明:兴城油田埋深3 400 m处为营城组流纹质凝灰岩,地层压力约为34 MPa,地温梯度约为4.1 ℃/(100 m),以此估算地层温度可达到140 ℃,具有一定的地热开发价值。营城组流纹质凝灰岩的天然裂隙开度较小,连通性较差,岩层的孔隙度和渗透率较低,分别为0.034 5和0.810×10-15 m2,无法直接汲取地热流体[12]。所以,需要通过水力压裂扩展天然裂缝的开度,提高岩层的渗透率和孔隙度。本次研究把“储层改造”后的营城组流纹质凝灰岩组作为EGS目标热储层。
1.2 概念模型
本次研究建立一维反应性溶质运移模型模拟EGS运行中的热量运移和物质运移及其引发的化学组分、孔隙度和渗透率参数变化。假定EGS注入井和生产井间的距离为600 m,井间被剖分成72个计算网格, 网格的间离由注入井处的0.1 m逐渐增至生产井处的20 m(图1)。理想的EGS储层裂隙分布较密且具有良好的连通性,裂隙网络中的流体可看作一个连续统一体处理。因此,本次研究中采用Pruess等[13]提出的多重介质连续模型(MINC)探讨流体在裂隙多孔介质的流动过程。假定流体仅通过被认定为连续的裂隙系统,基质间并无直接的水力联系,仅与其相邻的裂隙进行能量交换和物质交换(图2)。参考文献[6]的研究成果,热储层的人工裂隙概化成正交裂隙系统,相邻裂隙间距设定为10 m。
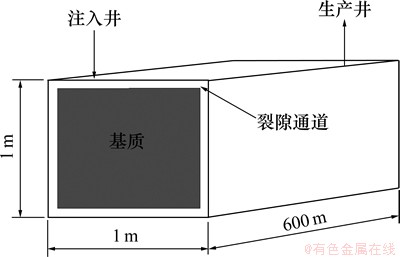
图1 一维地质模型模示意图
Fig. 1 Schematic representation for 1D model
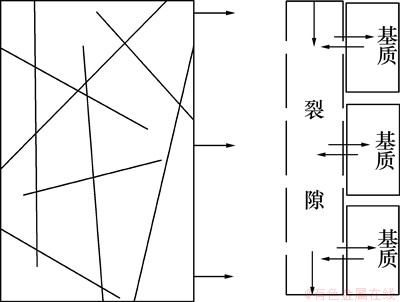
图2 裂隙多孔介质概化示意图
Fig. 2 Schematic representation for “multiple interacting continua” (MINC) method
由于营城组流纹质凝灰岩中地下水流动滞缓,本研究忽略了人工地热储层的初始水动力条件,储层中热流体只会在注入流体的驱动下由注入井向生产井运动。人工地热储层顶底板为低渗透性岩层,与人工地热储层仅存在能(热)量交换而不存在质量交换,所以模型的上下边界被设定为隔水传热边界,传热量根据Vinsome和Westerveld的经验解析公式进行计算[13]。
1.3 水文地质参数
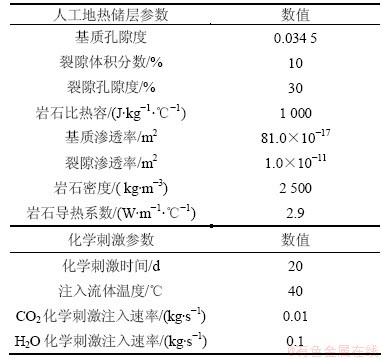
根据研究区的地质资料,人工地热储层的相关参数见表1。参考目标层的实际情况,设定储层的地层温度为140 ℃,地层压力为34 MPa[12]。初始时储层为均质、各向同性。参考前人的研究成果,基质孔隙度被设定为0.034 5,渗透率为81.0×10-17 m2 [10]。参考国外深部地热系统的研究成果,水力压裂后的裂隙孔隙度被设定为0.3,渗透率为1.0×10-11 m2。在化学刺激过程中,将40 ℃时以速度0.01 kg/s CO2和0.1 kg/s蒸汽冷凝液注入裂隙通道, 化学刺激时间定为20 d。
表1 人工地热储层参数
Table 1 Basic parameters of artificial geothermal reservoir
1.4 地球化学参数
模型中矿物组成及含量参考钻井CS1-2岩样的矿物相对质量X线衍射分析结果见表2[14]。兴城油田营城组火成岩矿物组分以石英和长石为主,并含有一部分碳酸盐矿物,黏土矿物的含量极少。模拟中使用的反应动力学公式见文献[15],矿物动力学数据见表3,主要来源于资料搜集[6, 16]。本研究利用Kozeny-Caeman球体颗粒模型将计算由孔隙度改变导致的渗透率的变化,具体表达式如下[17]:
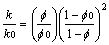 (1)
(1)
式中:k0为初始渗透系数;k为渗透系数; 为初始孔隙度;
为初始孔隙度;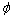 为孔隙度。
为孔隙度。
表2 原生矿物初始体积分数及可能产生的次生矿物
Table 2 Initial mineral volume fractions and possible secondary mineral
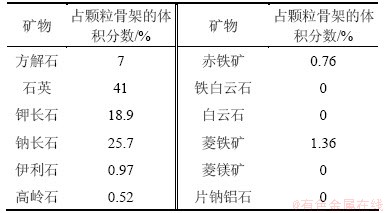
表3 砂岩各种矿物反应动力学参数表
Table 3 Parameters for kinetic rate constants of minerals
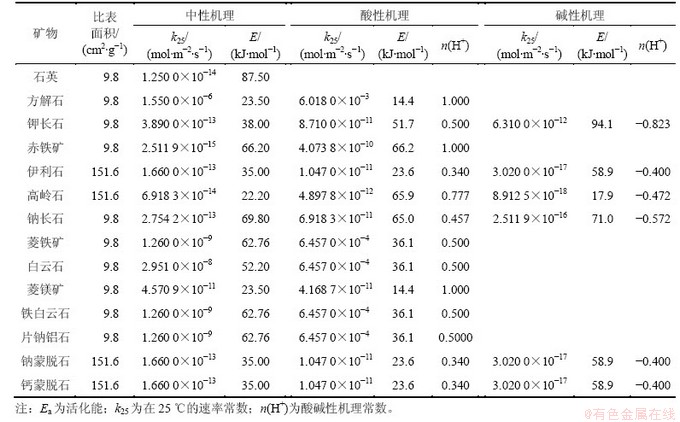
热储层液相组分和矿物组分基本处于化学平衡状态。鉴于此,本研究通过收集水化学资料和化学平衡相结合的方法获得储层液相组分的初始浓度,见表4。Na+和Cl-是松辽盆地流纹质凝灰岩地层水重要的液相组分,兴城油田一带NaCl浓度可达到0.28 mol/L[18]。热储层水化学成分采用0.28 mol/L的NaCl溶液与地层原生矿物在相应的地层温度进行化学平衡得到。注入流体蒸汽冷凝液,其化学成分与蒸馏水的一致[6]。
表4 模型热储层水化学组分初始浓度
Table 4 Initial total dissolved component concentrations for geothermal reservoir water mol/L
1.5 模拟工具
本文采用的反应传输模拟器为美国劳伦斯伯克利国家重点实验室开发的多相流多组分软件TOUGHREACT[6]。目前该软件使用的数据库是EQ3/6,适用于不同温度(0~300 ℃)、压力(0.1 MPa到几十MPa之间)、水饱和度、离子强度(最高可达到6 mol/kg)、pH和氧化还原电位(EH)等水文地质和地球化学条件下的热-物理-化学过程;还可以应用于一维、二维或三维非均质(物理和化学的)多孔隙或裂隙介质中的相关数值模拟研究。
2 数值模拟结果与讨论
2.1 模拟结果分析
低温CO2化学刺激剂注入后被地层加热,储层因发生热损耗而温度降低,至20 d化学刺激剂的温度影响范围可达到400 m(见图3,其中x为距注入井距离)。超临界状态CO2被注入热储层后,溶于水进而解离生成H+和HCO3-,从而降低地下水的pH。至10 d时,裂隙通道地下水的pH降低至小于4.7,注入点处pH降低幅度尤为明显,可降低至3.9(见图4)。
低温CO2化学刺激剂改变了储层的温度场和化学场,打破了原有的水化学平衡,影响了母岩中矿物质的溶解度,矿物的体积分数相应发生变化。裂隙通道中的方解石和菱铁矿物发生溶蚀作用,在注入点处最为强烈,见图4。由于沿着化学刺激方向地层温度逐渐升高,碳酸盐矿物的溶解度降低,在方解石和菱铁矿溶解区的前沿2种矿物发生少量沉淀。与曲希玉等[8]的研究成果一致,CO2注入后钠长石和钾长石发生溶蚀作用[19],但是溶解体积分数远小于方解石和菱铁矿溶解体积分数,见图4和图5。长石的溶解提供了Al和Si等液相组分,导致高岭石发生微量沉淀。赤铁矿和石英等其他矿物也有微小变化,但体积分数变化均小于1×10-6,与主要反应矿物相比可以忽略。尽管上述原生矿物的溶解为次生碳酸盐矿物的生成提供了Ca,Fe,Na和Al等液相组分,但是,化学刺激过程水-岩-气作用的时间较短,并且地下水始终保持较低的pH,裂隙通道中并未出现次生碳酸盐矿物的 沉淀。
矿物的溶解和沉淀导致裂隙通道的孔隙度和渗透率发生变化。由图4和图6可见:裂隙通道孔隙度的变化趋势和碳酸盐矿物体积分数的变化趋势相似。至20 d时,储层裂隙通道最高孔隙度为0.326 5,比初始孔隙度(0.300 0)高0.026 5,其中方解石和菱铁矿的溶解体积分数分别为0.018 0和0.007 6,由此可见裂隙通道储层孔隙度的增加几乎全部源于方解石的溶解。由于模拟过程中选择的孔隙度-渗透率相互关联的模型没有考虑到孔隙大小、形状、连通性等多方面因素的影响,孔隙度和渗透率的关联性较好。至20 d时,储层裂隙的最大渗透率可达到1.392×10-11 m2,高于初始渗透率39.2%。由此可见,CO2化学刺激剂注入后裂隙通道的孔隙度和渗透率增加明显。
CO2化学刺激剂注入地层后形成酸性较弱的碳酸,对原生碳酸盐矿物具有良好的溶蚀能力,但是对长石等硅铝矿物溶蚀能力较弱,注入热储层后不会被注入井附近的矿物消耗殆尽,可对EGS热储层的人工裂隙通道进行深部穿透。如图3和4所示,化学刺激进行至20 d,CO2化学刺激剂的有效穿透距离可达到110 m。
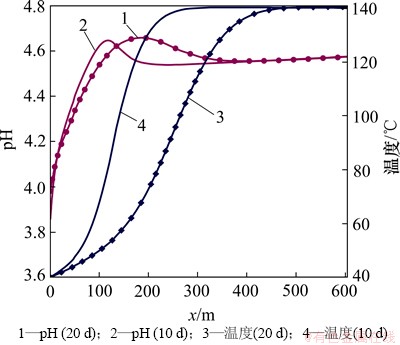
图3 裂隙通道pH和温度分布图
Fig. 3 pH and temperature in fracture
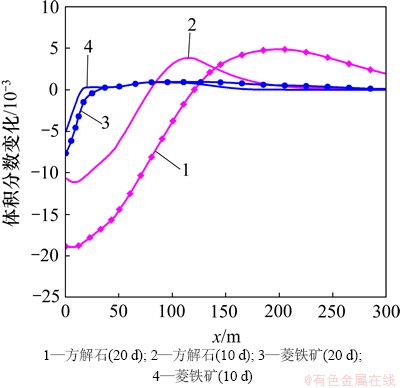
图4 裂隙通道碳酸盐矿物体积分数变化分布图
Fig. 4 Carbonate mineral volume fraction changes in fracture
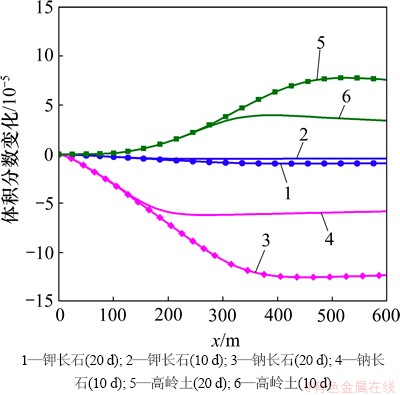
图5 裂隙通道硅酸盐矿物体积分数变化分布图
Fig. 5 Silicate mineral volume fraction changes in fracture
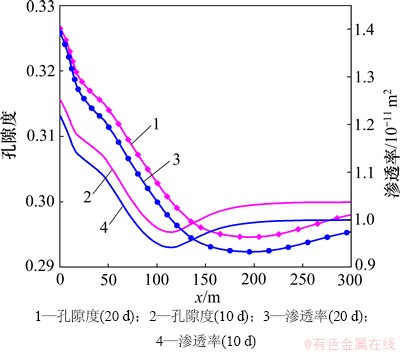
图6 裂隙通道孔隙度和渗透率分布图
Fig. 6 Porosity and permeability in fracture
2.2 敏感性分析
在目前的EGS工程中,各研究场地的热储层地层温度和地层压力相差较大,且化学刺激剂注入水的化学成分具有多样性,使CO2化学刺激剂的应有效果具有不确定性。本研究通过敏感性分析讨论上述3种因素对CO2化学刺激剂应用效果的影响。
2.2.1 温度
研究资料表明国外主要EGS场地的热储层温度范围为150~250 ℃。本研究将地层温度分别设定为170 ℃和210 ℃,考查地层温度对CO2化学刺激剂使用效果的影响。
如图7所示,受到化学刺激剂和热储层热传递作用的影响,至20 d时,不同地层温度模型在距注入井30 m范围内的地层温度相差不大,都降低至40 ℃左右,但是在30 m以外地层温度出现明显差异。距注入井30~200 m范围内,裂隙通道地下水的pH分布随着地层温度的降低而降低,这是因为较低的地层温度有利于超临界CO2的溶解,加剧CO2(aq)分解H+。
至20 d时,距注入井30 m范围内碳酸盐岩的溶蚀量随地层温度的增加而增加(图8)。这是因为根据TOUGHREACT数据库,地层温度为140,170和210 ℃时,方解石初始lg K(平衡常数K的对数值)分别为0.095,0.050和-0.600,注入井附近的地层温度降低至40 ℃后方解石的平衡常数值升高至1.5。地层温度为140,170和210 ℃时,菱铁矿的初始lg K分别为-2.12,-2.50和-3.08,注入井附近的地层温度降低至40 ℃后菱铁矿的lg K都升高至-0.500。由此可见:注入同样温度的化学刺激剂,注入井附近的碳酸盐矿物lg K增量随地层温度的增加而增强,导致碳酸盐矿物的溶蚀作用增强。30 m以外地层温度出现差异,碳酸盐岩的溶蚀量和溶蚀区域随温度的增加而减小。这是因为温度的增加会降低超临界CO2和碳酸盐矿物的溶解度,抑制化学刺激过程中碳酸盐矿物的溶蚀作用。
CO2化学刺激剂使用效果受原生碳酸盐矿物溶蚀作用的控制。距注入井30 m范围内裂隙通道的孔隙度和渗透率随着地层温度的增加而增加(图9和图10),30 m外裂隙通道的孔隙度和渗透率增量随着地层温度的增加而降低。地层温度由140 ℃增加至170 ℃,CO2化学刺激剂的有效距离由110 m降低至100 m,地层温度增加至210 ℃后CO2化学刺激剂的有效距离降低至90 m。
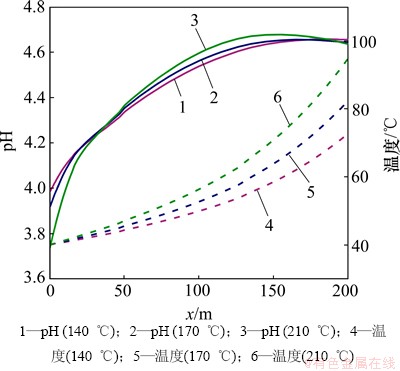
图7 不同地层温度裂隙通道pH和温度分布图
Fig. 7 pH and temperature in fracture considering different formation temperatures
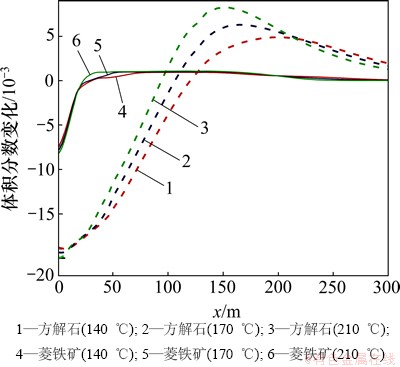
图8 不同地层温度碳酸盐矿物体积分数变化分布图
Fig. 8 Carbonate mineral volume fraction changes in fracture considering different formation temperatures
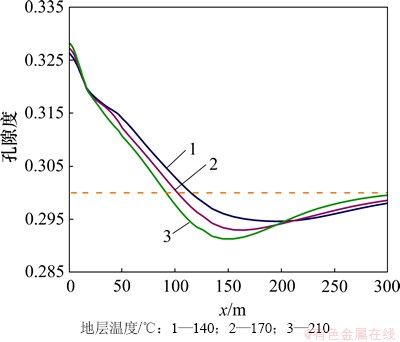
图9 不同地层温度孔隙度分布图
Fig. 9 Porosity in fracture considering different formation temperatures
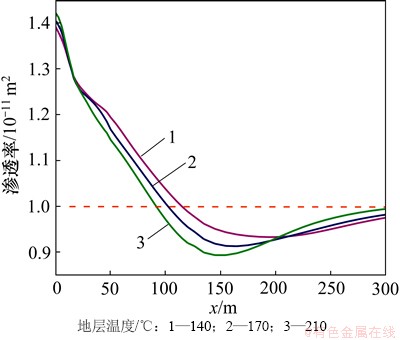
图10 不同地层温度渗透率分布图
Fig. 10 Permeability in fracture considering different formation temperatures
2.2.2 压力
研究资料表明国外EGS场地的热储层埋深范围为1 000~4 500 m,地层压力为10~45 MPa。本研究将地层压力设定为20 MPa和34 MPa,考查地层压力对CO2化学刺激剂使用效果的影响。
地层压力的增加有利于超临界CO2的溶解,加剧CO2(aq)分解为H+和HCO3-,从而降低裂隙通道地下水的pH(图11),加剧碳酸盐矿物的溶蚀作用。至20 d时,裂隙通道方解石和菱铁矿的溶蚀量及溶蚀范围随着地层压力的增加而增大(图12)。受这2种矿物溶蚀作用的影响,CO2化学刺激剂对裂隙通道孔隙度和渗透率的刺激效果随着地层压力的增加而增大。地层压力由34 MPa降低至20 MPa,CO2化学刺激剂的有效距离由110 m降低至108 m,地层压力增加至40 MPa后CO2化学刺激剂的有效距离增加至115 m(图13和图14)。
2.2.3 水化学
反应性溶质运移模型中化学刺激剂的注入水被设定为蒸汽冷凝水[6]。蒸汽冷凝水的矿化度远小于热储层地下水,注入热储层后易引发“水敏”效应,导致岩层中的钻井泥浆、黏土矿物膨胀而堵塞孔隙,因此CO2化学刺激剂注入水需要具有一定的盐度。本研究先是将注入水化学成分由蒸馏水改为地层水,然后将注入水化学成分设定为1 mol/L的NaCl溶液,考查不同注入水化学成分对CO2化学刺激剂作用效果的影响。
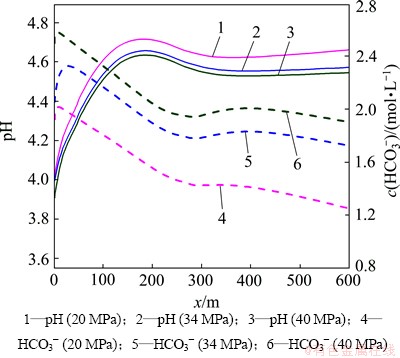
图11 不同地层压力裂隙通道pH和HCO3-浓度分布图
Fig. 11 pH and HCO3- concentration in fracture considering different formation pressures
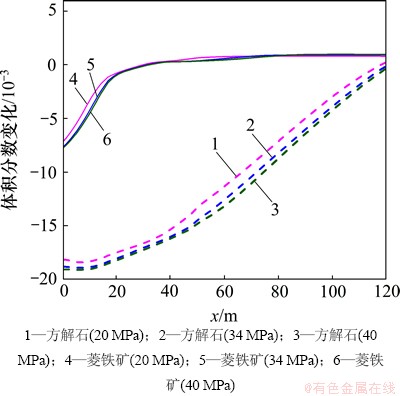
图12 不同地层压力裂隙通道碳酸盐矿物体积分数变化分布图
Fig. 12 Carbonate mineral volume fraction changes in fracture considering different formation pressures
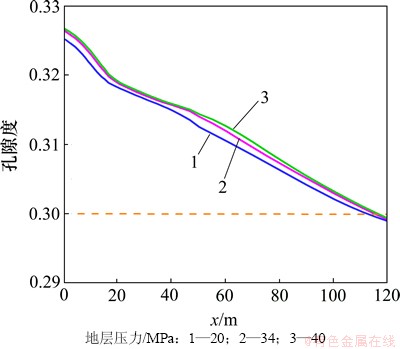
图13 不同地层压力裂隙通道孔隙度分布图
Fig. 13 Porosity in fracture considering different formation pressures
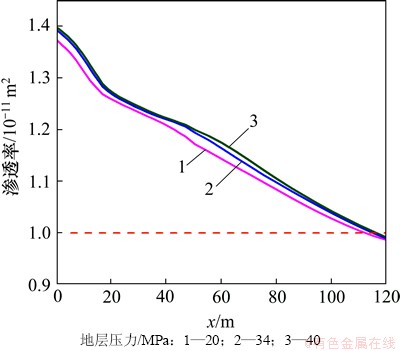
图14 不同地层压力裂隙通道渗透率分布图
Fig. 14 Permeability in fracture considering different formation pressures
由图15和图16可见:CO2化学刺激剂对原生碳酸盐矿物的溶蚀能力、裂隙通道的刺激能力随注入水盐度的增加而增强。注入蒸馏水模型、注入地层水模型和注入1 mol/L NaCl溶液模型的CO2化学刺激剂有效距离分别为110,126和145 m,可见有效距离随着注入水盐度的增加而增长。
在化学刺激过程中,注入水化学成分的变化对CO2化学刺激效果的影响主要在于盐效应和同离子效应。地层水的钙、铁等液相组分远比蒸馏水的高,对碳酸盐矿物的溶解起抑制作用。但是,其注入水的钠、氯等非碳酸盐岩液组分远比初始方案的高,导致地下水的离子积增加,有利于方解石和菱铁矿的溶解。国内学者普遍认为“与同离子效应相比盐效应对水-岩反应的影响可以忽略”[20],但是,注入地层水模型碳酸盐矿物的溶蚀量和溶蚀区域明显比注入蒸馏水的高,至20 d时孔隙度、渗透率及化学刺激有效距离明显较大。由此可见在本研究中盐效应对化学刺激效果的影响大于同离子效应的影响。当注入水由地层水(NaCl浓度为0.281 mol/L)变为1 mol/L的NaCl溶液后,CO2化学刺激剂的作用效果再次增强,裂隙通道孔渗参数和刺激有效距离明显增加。由此可见“与同离子效应相比盐效应对水-岩反应的影响可以忽略”的说法是值得商榷的。这是因为EGS热储层地下水一般埋藏较深,与浅层低盐度地下水相比含盐量较大,盐效应对水-岩作用的影响更为明显。况且EGS热储层地下水温度较高,地下水盐效应随着温度的升高而增强[21]。
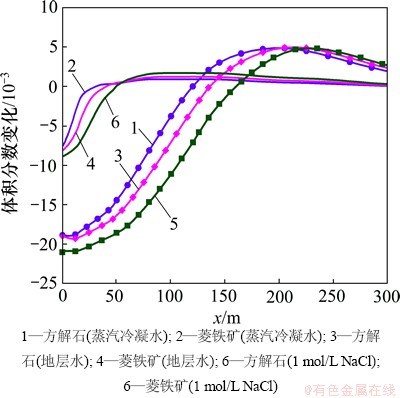
图15 注入水化学成分不同时裂隙通道碳酸盐矿物体积分数变化分布图
Fig. 15 Carbonate mineral volume fraction changes in fracture considering different injected water compositions
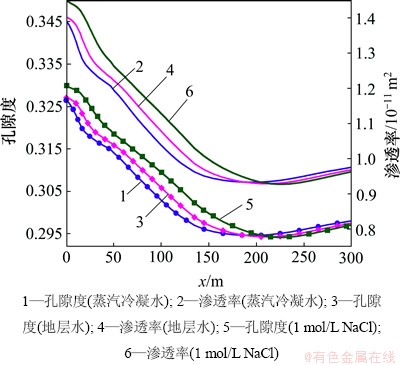
图16 注入水化学成分不同时裂隙通道孔隙度和渗透率分布图
Fig. 16 Porosity and permeability in fracture considering different injected water compositions
3 室内实验对比分析
通过数值模拟结果分析可知:碳酸盐矿物的溶蚀是使裂隙通道孔渗特征发生变化的主要因素。方解石是最常见的碳酸钙矿物,也是EGS热储层裂隙通道的重要堵塞物。本次研究通过室内实验模拟EGS热储层的高温高压环境,讨论在CO2化学刺激剂注入热储层后方解石在不同地层温度、压力和水化学条件下溶蚀作用的差异,并将实验结果与数值模拟结果进行对比。
3.1 实验方案
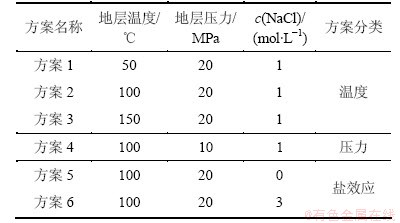
实验方案设计如表5所示。实验温度设定为50~150 ℃,地层压力设定为10~20 MPa,溶液的NaCl浓度设定为0~3 mol/L。
3.2 实验设备及材料
本实验采用FYX-1型高压釜。实验中,利用恒温控制仪和气-液增压泵分别对实验的温度和压力进行控制。
表5 方案设计表
Table 5 Scheme designing table
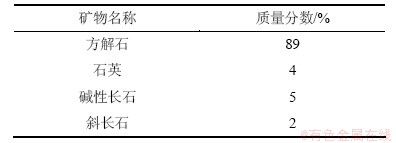
本研究采用的方解石样取自兴城地区天然方解石脉,其矿物成分见表6。实验前对方解石进行碎样,岩块的粒径为2.0~5.0 mm,并用X线荧光光谱射线衍射仪测定样品的化学成分。岩样的表面特征用JSM-6700F型扫描电子显微镜观察。
表6 岩样矿物相对质量X线衍射分析表
Table 6 Mineral abundance in calcite with XRD
3.3 实验步骤
将岩样用蒸馏水冲洗、烘干(80 ℃,8 h)、称量。将一定方解石岩样及实验溶液(固液质量比为1:20)放入反应釜内,密闭。通过气-液增压泵通入超临界CO2,使釜内压力到达所设定的地层压力,通过恒温控制仪使釜内温度达到所设定的温度,反应时间为48 h。当反应结束后打开反应釜,取出样品和反应剩余溶液。待反应液冷却至室温,测定其pH和溶液中HCO3-浓度。岩样用蒸馏水冲洗,烘干至恒量后对其称量并计算溶蚀率(反应损失质量/装入岩样质量),并进行扫描电镜分析。
3.4 实验结果与讨论
3.4.1 温度因素
方案1、方案2和方案3实验后溶液的pH随着实验温度的增加而增加,HCO3-浓度随着实验温度的增加而降低(图17)。这再次证明了溶液温度增加后,CO2溶解度降低,不利于H+和HCO3-的分解。由于溶液的pH和HCO3-浓度是从实验环境移至常温常压环境下的变化后值,故不能精确反映实验室条件下的试剂浓度,但是可以反映出其在不同实验环境下(温度、压力和水化学成分)的变化趋势。
与图7所示的结果一致,方解石的溶蚀率随着实验温度的增加而降低(图18)。由图19可知:在50 ℃环境下方解石溶蚀作用强烈,岩体表面溶洞发育;在150 ℃环境下方解石溶蚀作用较弱,岩体表面较为平整,在节理处发生微溶蚀,形成少量溶缝。其主要原因包括:(1) 实验温升高后,CO2在水中的溶解度减少,溶液的CO2(溶解)分解产生的H+降低,不利于方解石的溶解。(2) 方解石在水中的溶解度随着温度增加而减少。(3) 较高的实验温度加剧水的蒸发,水蒸气和超临界CO2混合,减小了超临界CO2和液相水的接触面积,不利于方解石的溶蚀。曲希玉等[8]通过扫面电镜技术观测CO2-水对砂岩不同矿物的溶蚀效果,结果表明方解石溶蚀强度随温度的升高而增大,和本次研究成果有所不同。这主要是由于扫描电镜技术只能对矿物的变化进行局部定性观测,无法定量描述单矿物的变化特征。
3.4.2 压力因素
与图11所示的结果一致,方案4和方案2实验后溶液的pH随着实验压力的增加而降低,HCO3-浓度随着实验压力的增加而增加(图20)。再次证明地层压力的增加有利于超临界CO2的溶解,加剧CO2(aq)对H+和HCO3-的分解作用。
同样方解石的溶蚀率随着实验压力的增加而增加(图21)。20 MPa环境下方解石溶蚀作用强烈,岩石表面溶缝发育,并含有少量小孔洞。10 MPa环境下方解石溶蚀作用较弱,岩石表面较为平整,仅形成少量溶缝(图22)。实验结果再次证明了地层压力的增加会加剧原生碳酸盐矿物的溶蚀作用,有利于CO2化学刺激剂的应用。
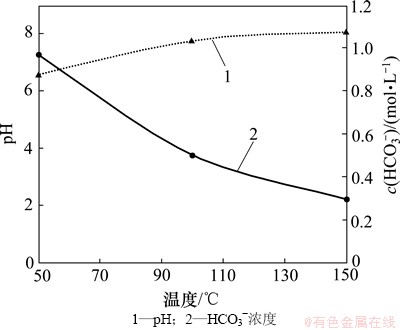
图17 不同温度下pH和HCO3-浓度变化图
Fig. 17 pH and HCO3- concentration considering different temperatures
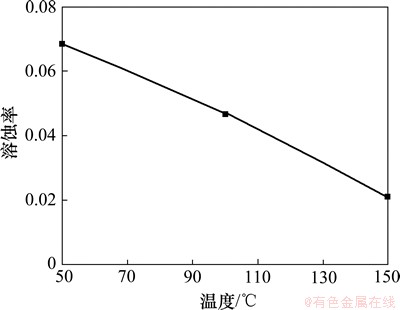
图18 不同温度下方解石溶蚀率变化图
Fig. 18 Solution ratio of calcite considering different temperatures
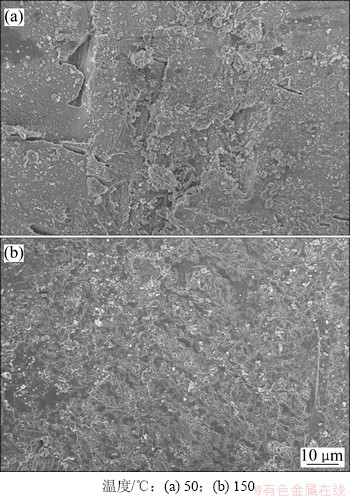
图19 不同温度下方解石溶蚀扫描电镜照片
Fig. 19 SEM images of corroded calcite at different temperatures
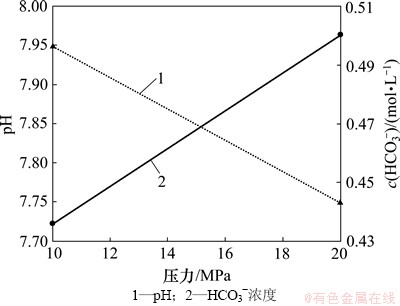
图20 不同压力下pH和HCO3-浓度变化图
Fig. 20 pH and HCO3- concentration considering different pressures
3.4.3 水化学因素
CO2在水中的溶解度一般随着溶液盐度的增加而减小,不利于CO2(溶解)对游离H+和HCO3-的分解[22]。然而,在本研究中,游离H+和HCO3-浓度随着NaCl浓度的增加而增加(图23)。这可能是因为NaCl浓度的增加促进了CO2(溶解)的分解作用,导致溶液pH降低和HCO3-浓度增加。
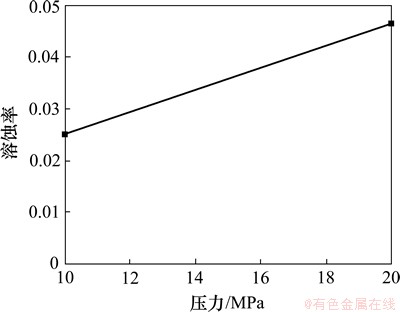
图21 不同压力下方解石溶蚀率变化图
Fig. 21 Solution ratio of calcite considering different pressures
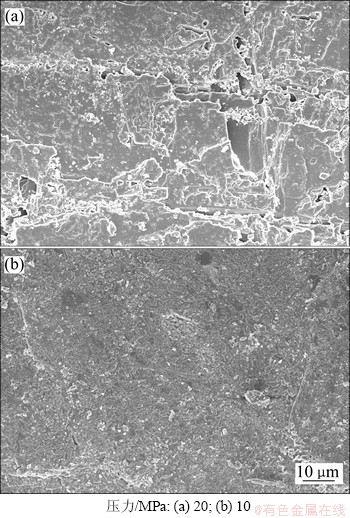
图22 不同压力下方解石溶蚀扫描电镜照片
Fig. 24 SEM images of corroded calcite at different pressures
方解石的溶蚀率随着溶液盐度的增加而增加(图24)。当NaCl浓度为3 mol/L时,方解石溶蚀作用强烈,岩石表面被溶蚀至片状破碎。当NaCl浓度为0 mol/L时,方解石溶蚀作用微弱,岩石表面仅发育少量溶缝(图25)。实验结果证明溶液中NaCl浓度增加,地下水的离子积增加,活度系数变小,有利于pH降低和方解石溶解度增加。通过上述分析可见,EGS热储层中地下水的盐效应对水-岩-气化学反应的影响不能被忽略。
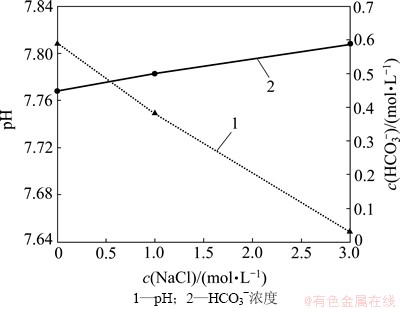
图23 不同盐度下pH和HCO3-浓度变化图
Fig. 23 pH and HCO3- concentrations considering different salinity
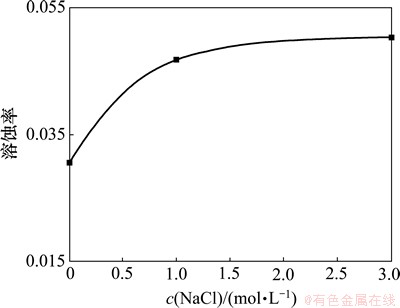
图24 不同盐度下方解石溶蚀率变化图
Fig. 24 Solution ratio of calcite considering different salinity
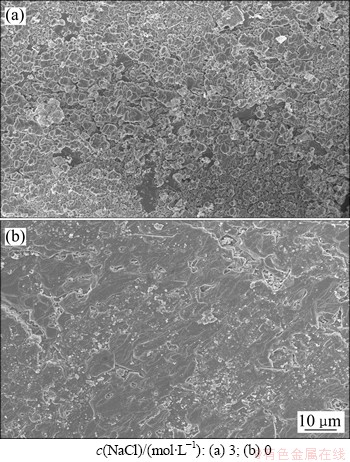
图25 不同盐度下方解石溶蚀扫描电镜照片
Fig. 25 SEM images of corroded calcite at different NaCl concentrations
4 结论
(1) CO2化学刺激剂被注入热储层后,裂隙通道孔隙度、渗透率的增加主要源自于原生碳酸盐矿物的溶解。CO2化学刺激剂对硅酸盐、硅铝酸盐的溶蚀性较弱。由于CO2溶与水形成弱酸,可以保持较大的穿透距离。
(2) 地层温度增加,CO2化学刺激剂对原生碳酸盐矿物的溶蚀能力减弱,热储层裂隙通道的化学刺激效果减弱。地层压力增加,地层水中溶解CO2含量增加,原生碳酸盐矿物的溶蚀作用加强,CO2化学刺激剂对热储层裂隙通道的作用效果增强。
(3) 受到盐效应的影响,CO2化学刺激剂对原生碳酸盐矿物的溶蚀作用随着注入水NaCl浓度的增加而增加。注入水的盐效应对刺激效果的影响不能被忽略。
(4) 本研究中用于计算渗透率的Kozeny-Caeman方程在一定程度上较好地反映地质介质中孔隙度和渗透率的关系,但由于渗透率的变化不但取决于孔隙度的整体变化,而且受到其他因素的影响,如孔径的分布、孔隙形状和连通性,还需要对其计算方法进一步改进;此次研究假定为均质条件,但实际的地质条件是非常复杂的,需要进一步探讨。在化学刺激中,热储层岩石在温度发生变化可能产生新裂纹,使热储层渗透率发生改变,这有待进一步研究。
参考文献:
[1] Armstead H C H. The future of geothermal energy[J]. Institute Fuel Journal, 1978, 51: 109-118.
[2] Rose P, Xu T, Kovac K, et al. Chemical stimulation in near-wellbore geothermal formations: Silica dissolution in the presence of calcite at high temperature and high pH[EB/OL]. [2007-07-22]. http://www.geothermal-energy.org/pdf/IGAstandard/ SGW/2007/rose.pdf.
[3] Xu T, Rose P, Fayer S, et al. On modeling of chemical stimulation of an enhanced geothermal system using a high pH solution with chelating agent[J]. Geofluids, 2009, 9(2): 167-177.
[4] Portier S, Vuataz F D, Nami P, et al. Chemical stimulation techniques for geothermal wells: experiments on the three-well EGS system at  , France[J]. Geothermics, 2009, 38(4): 349-359.
, France[J]. Geothermics, 2009, 38(4): 349-359.
[5] Portier S,  L, Vuataz F D. Review on chemical stimulation techniques in oil industry and applications to geothermal systems[J]. Engine, Work Package, 2007, 32(4): 1-30.
L, Vuataz F D. Review on chemical stimulation techniques in oil industry and applications to geothermal systems[J]. Engine, Work Package, 2007, 32(4): 1-30.
[6] Xu T. Numerical simulation to study the feasibility of using CO2 as a stimulation agent for enhanced geothermal systems[R]. Berkeley: Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory, 2010: 1-8.
[7] Rosenbauer R J, Koksalan T, Palandri J L. Experimental investigation of CO2-brine-rock interactions at elevated temperature and pressure: Implications for CO2 sequestration in deep-saline aquifers[J]. Fuel Processing Technology, 2005, 8(6): 1581-1597.
[8] 曲希玉, 刘立, 马瑞, 等. CO2流体对岩屑长石砂岩改造作用的实验[J]. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版), 2008, 38(6): 959-964.
QU Xiyu, LIU Li, MA Rui, et al. Experiment on debris-arkosic sandstone reformation by CO2 fluid[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Earth Science Edition), 2008, 38(6): 959-964.
[9] 王广华, 赵静, 张凤君, 等. 砂岩储层中CO2-地层水-岩石的相互作用[J]. 中南大学学报(自然科学版), 2013, 44(3): 1168-1173.
WANG Guanghua, ZHAO Jing, ZHANG Fengjun, et al. Interactions of CO2-brine-rock in sandstone reservoir[J]. Journal of Central South University (Science and Technology), 2013, 44(3): 1168-1173.
[10] Huang H P, Yang J, Yang Y F. Geochemistry of natural gases in deep strata of the Songliao Basin, NE China[J]. Int J Coal Geo, 2004, 5(8): 231-244.
[11] Hu W S, Cai C F, Wu Z Y. Structural style and its relation to hydrocarbon exploration in the Songliao Basin, northeast China[J]. Mar Petrol Geol, 1998: 15: 41-55.
[12] 潘昊. 徐家围子断陷营城组火山岩储层特征研究[D]. 大庆: 东北石油大学地球科学学院, 2010: 17-20.
PAN Hao. Research on the volcanic reservoir characteristics of Yingcheng formation of Xujiaweizi fault depression[D]. Daqing: Northeast Petroleum University. College of Geoscience, 2010: 17-20.
[13] Pruess K, Moridis G J, Oldenburg C. TOUGH2 user's guide, version 2.0[M]. Berkeley: Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory, 1999: 2-9.
[14] 王百坤. 火山岩储层酸化体系研究[D]. 合肥: 合肥工业大学化学工程学院, 2010: 1-4.
WANG Baikun. Research on acidified system for the volcanic reservoir[D]. Hefei: Hefei University of Technology. College of Chemistry Engineering, 2010: 1-4.
[15] Xu T, Sonnenthal E, Spycher N, et al. TOUGHREACT: A simulation program for non-isothermal multiphase reactive geochemical transport in variably saturated geologic media: Applications to geothermal injectivity and CO2 geological sequestration[J]. Computers & Geosciences, 2006, 32(2): 145-165.
[16] Zhang W, Li Y, Xu T, et al. Long-term variations of CO2 trapped in different mechanisms in deep saline formations: A case study of the Songliao Basin, China[J]. International Journal of Greenhouse Gas Control, 2009, 3(2): 161-180.
[17] Xu T, Sonnenthal E, Spycher N, et al. TOUGHREACT user’s guide: A simulation program for non-isothermal multiphase reactive geochemical transport in variably saturated geologic media, V1.2.1[R]. Berkeley, CA, US: Ernest Orlando Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory, 2008: 8-18.
[18] 刘伟. 大庆徐家围子地区水性分布规律及预测[D]. 杭州: 浙江大学地球科学系, 2010: 28-34.
LIU Wei. Water distribution and prediction in Xujiaweizi Daqing[D]. Hangzhou: Zhejiang University. Department of Earth Sciences, 2010: 28-34.
[19] Ueda A, Kato K, Ohsumi T, et al. Experimental studies of CO2-rock interaction at elevated temperatures under hydrothermal conditions[J]. Geochemical Journal, 2005, 39(5): 417-425.
[20] 刘再华, Reybrodt R D, 韩军. CaCO3-CO2-H2O岩溶系统的平衡化学及其分析[J]. 中国岩溶, 2005, 24(1): 1-4.
LIU Zaihua, Reybrodt R D, HAN Jun. Equilibrium chrmistry of the CaCO3-CO2-H2O system and discussion[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 2005, 24(1): 1-4.
[21] 梁冰, 陈楠, 姜利国. 盐酸盐溶液中温度对方解石和白云石溶解度的影响[J]. 水资源与水工程学报, 2011, 22(4): 21-24.
LING Bing, CHEN Nan, JIANG Liguo. Influence of temperature on dissolving degree of calcite and domomite in hydrochloride solution[J]. Journal of Water Resources and Water Engineering, 2011, 22(4): 22-30.
[22] Pruess K, Spycher N. ECO2N: A fluid property module for the TOUGH2 code for studies of CO2 storage in saline aquifers[J]. Energy Conversion and Management, 2007, 48(6): 1761-1767.
(编辑 杨幼平)
收稿日期:2013-07-26;修回日期:2013-10-11
基金项目:国家高技术研究发展计划(“863”计划)项目(2012AA052801);教育部博士点基金资助项目(20110061110057)
通信作者:冯波(1982-),男,吉林长春人,博士,讲师,从事增强型地热储层改造研究;电话:18686692355;E-mail: fengbo82@126.com