DOI: 10.11817/j.issn.1672-7207.2015.01.047
反应结晶法处理含锌废水
周秋生,张芳,李小斌,齐天贵,刘桂华,彭志宏
(中南大学 冶金与环境学院,湖南 长沙,410083)
摘要:基于结晶学原理,采用低温反应结晶法处理含锌废水,利用扫描电镜、粒度分析和红外光谱等分析手段考察结晶操作方式、添加剂、Ostwald熟化对含锌废水净化过程及颗粒结晶行为的影响。研究结果表明:连续无溢流操作方式下主要以初级成核为主,反应产物粒度较小,而采用连续溢流操作有利于颗粒附聚和长大;添加相对分子质量适中的聚乙二醇(PEG)系列添加剂能明显提高除锌效果,所得反应产物颗粒粗、结构相对致密且形貌规整;熟化能改善反应结晶产物的粒度分布并增大其平均粒径。
关键词:反应结晶;含锌废水;操作方式;添加剂;熟化
中图分类号:O781;X522 文献标志码:A 文章编号:1672-7207(2015)01-0351-07
Treatment of zinc-containing wastewater by reaction crystallization method
ZHOU Qiusheng, ZHANG Fang, LI Xiaobin, QI Tiangui, LIU Guihua, PENG Zhihong
(School of Metallurgy and Environment, Central South University, Changsha 410083, China)
Abstract: The zinc-containing wastewater was treated by reactive precipitation method based on crystallization principles. Influences of operation mode, additives and Ostwald ripening on the wastewater treatment and the crystallization behavior of zinc hydroxide particles were investigated by the scanning electron microscope, particle size distribution and infrared spectrum analysis. The results show that the primary nucleation is dominant in the continuous operations without overflow, while the crystal growth and agglomeration are primary in continuous operations with overflow. Additives of polyethylene glycol (PEG) with appropriate relative molecular mass can obviously increase Zn2+ removal efficiency and large particles with compact structure and regular morphology can be obtained. Moreover, Ostwald ripening can improve the particle size distribution and increase the mean particle size of the reaction crystallization products.
Key words: reaction crystallization; zinc-containing wastewater; operation mode; additive; ripening
有色金属选冶及加工过程产生的废水中常含有大量的重金属离子,其中含锌废水具有来源广、残留时间长和毒性大等特点,若进入到环境中将严重污染生态环境、威胁水生动植物的生存及人类健康[1]。电镀行业、矿山开采、有色金属冶炼等企业均会产生大量含锌废水。以某铅锌冶炼厂为例,其产生的废水中锌含量高达70~350 mg/L,远远超过了工业废水排放国家标准(2 mg/L)。化学沉淀法是工业上含锌废水处理的主要应用方法,具有工艺简单、操作方便和技术成熟等优点[2]。但该法存在易生成细小颗粒或无定形絮状沉淀[3]、沉降性能差、难以快速高效分离、处理后的废水难以稳定达标等问题,导致其处理成本高且效果不稳定[4]。因此,含锌等重金属废水的经济高效处理仍然是一个亟待解决的问题。反应结晶是一复杂的多相反应与结晶过程的耦合技术,同时涉及化学反应、成核、晶体生长以及附聚、破裂、熟化等子过程,目前已广泛应用于制药、精细化工、矿物分离提纯[5-6]等诸多领域。但迄今有关重金属废水反应结晶净化过程的研究报道甚少。这可能是由于以下2方面的原因:1) 重金属的氢氧化物沉淀的溶解度很低,溶液过饱和度高,易穿越介稳区爆发成核形成细小颗粒;2) 重金属废水中锌等重金属离子浓度低,生成的沉淀量少,反应区晶浆悬浮密度低,不利于传质,颗粒难以长大。为此,本文作者基于结晶学原理,自制了适于重金属废水反应结晶处理的结晶器,以实验室合成的含锌模拟废水为研究对象,采用反应结晶法对其进行净化处理。试图通过研究模拟废水反应结晶净化过程中化学反应、成核、晶体长大、附聚和熟化等子过程,以期获得颗粒粗大、形貌规整的反应结晶产物,从而可通过简单的沉降分离过程实现重金属废水的经济高效净化。
1 实验
1.1 实验原料及装置
试验所用含锌模拟废水由分析纯Zn(NO3)2和蒸馏水在实验室配制而成,用分析纯盐酸调节废水的pH,沉淀剂为分析纯NaOH的水溶液。
实验装置如图1所示,主要由反应器、温度控制仪器、搅拌装置及pH检测仪器组成。结晶器(见图2)为实验室自制,主要由内筒(反应区)、外筒和溢流口等3部分组成。内筒直径为6 cm,底面与外筒相通,废水和沉淀剂加入到内筒中,外筒中经反应处理后的溶液达到一定的液位后由溢流口流出。

图1 实验装置图
Fig. 1 Schematic diagram of experimental equipment
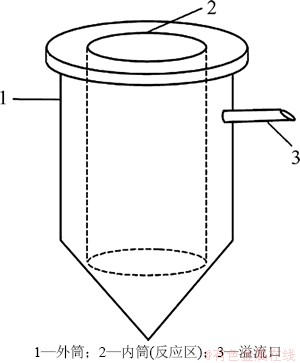
图2 自制结晶器示意图
Fig. 2 Schematic diagram of self-made crystallizer
1.2 实验方法
根据某重金属冶炼厂含锌废水的浓度,准确称取一定质量的Zn(NO3)2并加入到蒸馏水中使其完全溶解,配制成含锌模拟废水;称取一定质量的分析纯NaOH并加入到蒸馏水中使其溶解,配制成沉淀剂。将废水和沉淀剂分别加入自制结晶器的反应区内,并通入空气进行搅拌。结晶器置于水浴槽中保温,用pH计控制反应过程的pH,通过温度控制器控制反应过程的温度。由于冶炼过程排放的废水含少量余热,试验中反应结晶过程的温度定为40 ℃;根据Zn2+最佳沉淀pH范围,反应的pH定为9。
1.3 分析方法
利用Mastersizer 2000激光粒度分析仪(英国Marwin公司)对反应结晶产物进行粒度分析,采用JSM-6360LV扫描电镜(日本JEOL公司)观察结晶产物的形貌和粒度,利用Nicolet 6700红外光谱仪(美国ThermoFisher公司)分析反应产物的结构变化。
2 结果与讨论
2.1 反应结晶操作方式对含锌废水净化过程中颗粒结晶行为的影响
间歇操作是工业上处理含锌废水常用的操作方式,即废水预先装入反应池中,将沉淀剂一次性投加到反应池中与废水反应。这种操作方式虽然方便、简单,但存在如下问题:由于局部过饱和度高易形成絮状沉淀,颗粒细、含水率高、沉降性能差、分离效率低,通常还需要进行进一步的絮凝或膜分离处理,从而增加了处理流程及成本。反应结晶过程中为获得较低的局部过饱和度,常采用连续操作方式,即废水和沉淀剂分别连续逐渐加入反应器中。
针对废水中锌离子浓度低、反应所得的晶浆悬浮密度(单位体积溶液中所含晶体的质量)小,不利于颗粒传质生长的问题,实验室自制了结晶器,并对自制结晶器进行的连续溢流操作与连续无溢流操作方式进行了对比,通过计算单位质量反应产物的颗粒数探讨不同操作方式下颗粒的结晶行为。
实验中含锌废水流量为4 mL/min,废水中锌离子质量浓度为316.59 mg/L,每隔12 h取一次反应产物,对其进行粒度分析。根据粒度分析结果,调用pmassnum.m计算程序[7](其中Zn(OH)2的密度为3.053 g/cm3)来计算单位质量反应产物的颗粒数,得出其随时间的变化关系,如图3所示。由图3可知:由于沉淀颗粒的尺寸主要集中在0~45 μm,为了进一步明晰颗粒的结晶行为,将粒度细分为0~10,10~20和20~45 μm 3个区间进行分析,得到的各粒度区间内单位质量产物的颗粒数随时间的变化关系如图4所示。
单位质量颗粒的粒子数不仅可以反映体系中颗粒的粒度,也可以反映颗粒形成过程的行为。单位质量产品中颗粒数较多时,表明颗粒粒度较小,体系以成核为主;反之,单位质量产物中颗粒数较少时,表明产品颗粒较粗,晶体长大或发生附聚。结合图3和图4可以看出:连续溢流方式下单位质量产物中总颗粒数和细粒子(0~10 μm)数均比连续无溢流操作方式下少,而粗粒子(20~45 μm)数比连续无溢流方式下的多,说明前者得到的颗粒较后者得到的粗。在0~36 h内,2种方式下单位质量产物中总粒子数的变化趋势相似:先升高再急剧降低、随后又缓慢上升。反应初期(0~12 h内),由于溶液过饱和度高,体系以初级成核为主,生成大量细小晶核,因而2种方式下单位质量产物的总颗粒数增加。12~24 h内,单位质量反应产物中总粒子数减少时,0~10 μm粒度区间内颗粒减少,而20~45 μm范围内的颗粒数增加。这主要是由于体系中的晶核发生了附聚,使粒度增大。随着反应的进行,36~72 h内,连续无溢流操作方式下单位质量反应产物中总颗粒数急剧增加,生成大量细粒子;而连续溢流操作方式下单位质量产物的总粒子数增加平缓并开始减少,且10~20 μm范围内的颗粒数增加,该体系下细粒子向粗颗粒转变。

图3 不同操作方式下单位质量反应产物中总颗粒数
Fig. 3 Particle number per unit mass of products by different operation modes

图4 不同操作方式下单位质量反应产物中各粒度区间的颗粒数变化
Fig. 4 Variation of particle number per unit mass in each particle size interval of product by different operation modes
由上述分析可知:连续无溢流操作方式下,体系以初级成核为主、成核量大、细粒子数多;而连续溢流操作方式下,体系中伴随着晶体的附聚和长大,使总粒子数减少。这是由于废水中Zn2+质量浓度低、生成氢氧化物沉淀的悬浮密度很小。采用自制结晶器进行连续溢流操作时,反应区体积一定,随反应的进行,沉淀集中在反应区(内筒)内,增加了沉淀的悬浮密度,使晶粒间距离减小,由于邻近效应而使固相传质所需的推动力降低。此外,沉淀浓度的增加使新生成的溶质与晶核接触的概率增加,更易在晶核表面析出而生长或颗粒之间因附聚而长大。而采用连续无溢流操作时,结晶区域体积较大,沉淀的悬浮密度低,晶体长大所需的生长表面小。新生成的溶质与晶核及晶核与晶核之间接触的概率小,溶质扩散到晶核表面并在其上生长的难度也相应增大。若新生成核无附着点,则在过饱和度的推动下继续成核而减小反应产物的粒度。
2.2 添加剂对含锌废水反应结晶净化过程的影响
结晶过程中微量的添加剂即能对成核、晶体生长和晶体形貌产生很大的影响[8-9]。非离子型表面活性剂具有在水中不电离的特点,决定了它在某些方面较离子型表面活性剂优越。为此,本实验研究了不同相对分子质量的聚乙二醇(PEG)系列添加剂对含锌废水反应结晶净化过程的影响。将一定量的PEG溶解于NaOH溶液中,添加量为30 mg/L。表1所示为添加不同相对分子质量的PEG时溢流中检测到的Zn2+的质量浓度。
表1 添加不同相对分子质量的PEG对溢流中Zn2+ 质量浓度的影响
Table 1 Influence of PEG with various relative molecular masses on concentration of Zn2+ in overflow mg/L

由表1可以看出:加入PEG系列添加剂后,废水的除锌效果得到明显提高,溢流中Zn2+质量浓度基本上能达到铅、锌工业企业中重金属的排放标准(GB 25466—2010)[10]。PEG系列添加剂中,加入PEG 20 000后除锌效果相对较差;添加PEG 6 000后除锌效果最好,溢流中Zn2+质量浓度低于1.56 mg/L。对上述条件下得到的反应结晶产物进行扫描电镜分析,结果如图5所示。
由图5可知:添加PEG 600和PEG 20 000所得反应结晶产物的形貌不规则、颗粒细小、疏松多孔,这种颗粒通常含水率高、沉降性能差;而添加PEG 2 000和PEG 6 000时所得反应结晶产物的粒度较大、呈近球形,且颗粒表面光滑致密。
添加剂改变结晶行为的机理,一般认为是添加剂与生长基元相互竞争而吸附到晶体表面上,进而影响晶体生长方式[11-12]。为了研究添加剂与所得反应产物的相互作用,对添加PEG 6 000所得反应结晶产物进行了红外光谱分析,结果如图6所示。
图6所示的曲线2中3 450 cm-1和1 643 cm-1处以及曲线1中的3 363 cm-1处为羟基振动带,曲线1中1 386 cm-1处是Zn(OH)2中羟基桥联产生的振动带。在曲线2中2 862 cm-1和1 469 cm-1处为—CH2的振动带,1 113 cm-1处是C—O键特征伸缩振动带[13],在曲线1即反应结晶产物的红外光谱图中也出现了这几种特征峰,说明有PEG 6 000吸附于反应产物中。而曲线1中C—O键特征伸缩振动带发生了明显的红移(移至1 043 cm-1处),主要是由于C—O键中氧原子与Zn(OH)2表面的—OH中的氢原子形成氢键,导致C—O键的吸收峰发生偏移。此外,曲线2中1 469 cm-1处的振动带在曲线1中移至1 508 cm-1处,可能是由于Zn(OH)2的—OH与PEG 6 000的C—O键中的氧以及C—H键通过氢键结合形成环结构而引起的。
综上所述可知:在含锌废水反应结晶净化过程中PEG系列添加剂以化学吸附的形式与颗粒发生作用,不但提高了除锌效果,而且改善了反应产物的粒度和形貌。但这种促进作用受PEG相对分子质量大小的影响,当PEG相对分子质量过大或过小时,所得反应结晶产物的粒度小、颗粒形貌较差;当PEG相对分子质量适中(如PEG 2 000和PEG 6 000)时,所得反应结晶产物粒度大、颗粒形貌好。这主要是由于在相同质量浓度下,相对分子质量适中的PEG主链可稳定吸附于颗粒上,官能团吸附更多细小晶粒,从而使颗粒长大,且其选择性吸附抑制了颗粒某些方向的生长,促进了颗粒间的交互生长,从而改善了反应结晶产物的形貌。而相对分子质量小的PEG在水溶液中能较好地呈锯齿长链状铺展,易以单层复合物的形式覆盖在刚形成的颗粒表面[14-15],形成“隔离层”,从而阻碍了颗粒的生长;而相对分子质量过大的PEG,由于其分子链长、空间位阻大、稳定性差,导致其对颗粒的吸附性能较差。此外,化学吸附主要是依靠氢键和分子间力的作用对产物进行吸附,链越长,氢键和分子间力的作用越弱,吸附作用也相应减弱。
2.3 Ostwald熟化对含锌废水反应结晶净化过程的 影响
当两相混合系统达到平衡时,系统中总的相界面积达到最小。当相界面积的减小是通过从高界面曲率区域向低界面曲率区域质量传递时,这种相界面积减小的过程称为Ostwald熟化。Ostwald熟化的结果是使晶体粒度增大,小颗粒的溶解,大颗粒依靠摄取小粒子的质量而生长[16-17]。为此,实验将添加十二烷基苯磺酸钠及PEG 6 000条件下反应结晶48 h所得反应产物置于40 ℃烘箱中保温处理,考察熟化时间对最终产物粒度的影响。不同保温时间下所得最终产物的粒度分析和扫描电镜分析结果分别如图7和图8所示。
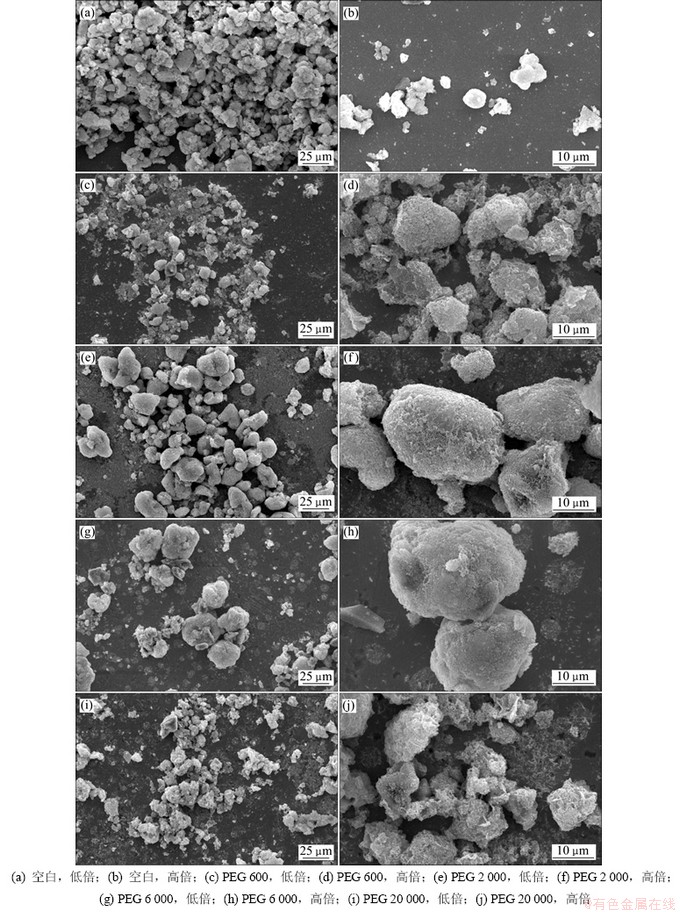

图5 添加不同相对分子质量的PEG后所得反应结晶产物的SEM像
Fig. 5 SEM images of products by reaction crystallization of zinc-containing wastewater by adding different PEG
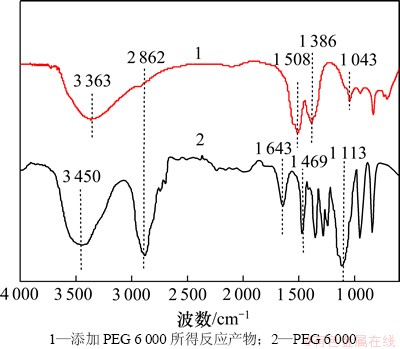
图6 PEG 6 000及添加PEG 6 000所得结晶反应产物的红外光谱图
Fig. 6 Infrared spectra of PEG 6 000 and precipitation products with PEG 6 000
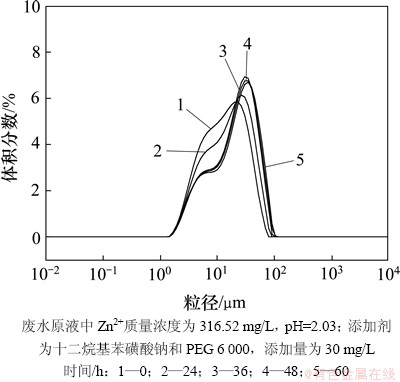
图7 不同熟化时间下所得反应产物的粒度分布曲线
Fig. 7 Curves of particle size distribution of products with different ripening time
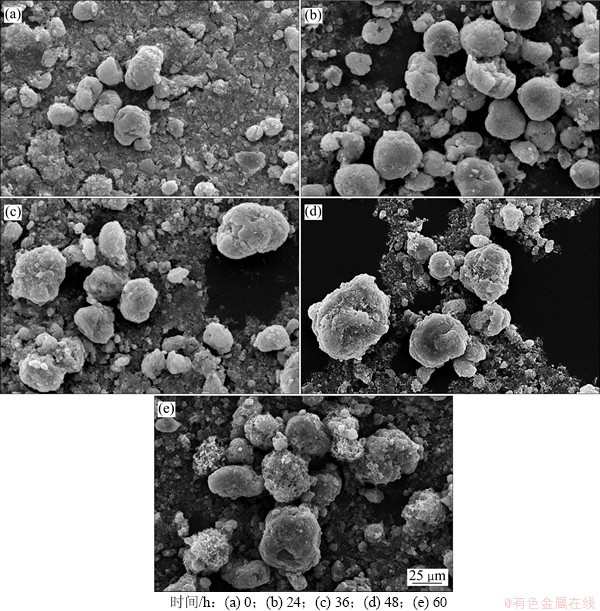

图8 不同熟化时间下所得反应产物的SEM像
Fig. 8 SEM images of products with different ripening time
结合图7和图8可知:在0~36 h内,随熟化时间的延长,颗粒的平均粒径增加,熟化时间为0,24和36 h时,反应产物的平均粒径分别为16.29,19.52和23.99 μm,且随熟化时间延长粒度分布范围变窄。但随熟化时间的继续延长,36~60 h范围内反应产物的粒度变化不明显,约为24.00 μm。这说明熟化作用可增大产物的平均粒径并改善其粒度分布,但当熟化体系趋近平衡时,熟化作用减弱。
3 结论
1) 在连续无溢流操作方式下,体系中单位质量颗粒数增加,体系以初级成核为主;而在连续溢流操作方式下,体系中细粒子数减少,粗粒子数增加,有利于颗粒的附聚和长大。
2) PEG系列添加剂对含锌废水的反应结晶过程有明显影响。当PEG的相对分子质量适中(如PEG2 000和PEG 6 000)时,所得颗粒粒度大、表面光滑致密,而当其相对分子质量过大或过小时,不利于颗粒的生长和结晶形貌的改善。
3) 熟化作用可使含锌废水反应结晶过程所得产物中细粒子溶解并在粗粒子上生长,从而使粗粒子继续长大,进而改善颗粒的粒度分布。
参考文献:
[1] Karvelas M, Katsoyiannis A, Samara C. Occurrence and fate of heavy metals in the wastewater treatment process[J]. Chemosphere, 2003, 53(10): 1201-1210.
[2] Adhoum N, Monser L, Bellakhal N, et al. Treatment of electroplating wastewater containing Cu2+, Zn2+ and Cr(Ⅵ) by electrocoagulation[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2004, 112(3): 207-213.
[3] Jones A, Rigopoulos S, Zauner R. Crystallization and precipitation engineering[J]. Computers & Chemical Engineering, 2005, 29(6): 1159-1166.
[4] Fu F, Wang Q. Removal of heavy metal ions from wastewaters: A review[J]. Journal of Environmental Management, 2011, 92(3): 407-418.
[5] Shekunov B Y, York P. Crystallization processes in pharmaceutical technology and drug delivery design[J]. Journal of Crystal Growth, 2000, 211(1): 122-136.
[6] 林丹. 硝酸硫胺反应结晶(沉淀)研究[D]. 天津: 天津大学化工学院, 2002: 4-6.
LIN Dan. The research on the reactive crystallization processes (precipitation) of thiamine nitrate[D]. Tianjin: Tianjin University. School of Chemical Engineering and Technology, 2002: 4-6.
[7] 彭殿军. 铝酸钠溶液碳分过程中的颗粒生长[D]. 长沙: 中南大学冶金科学与工程学院, 2009:14-16.
PENG Dianjun. The particle growth in carbonation of sodium aluminate solution[D]. Changsha: Central South University. School of Metallurgical Science and Engineering, 2009: 14-16.
[8] Thompson C, Davies M C, Roberts C J, et al. The effects of additives on the growth and morphology of paracetamol (acetaminophen) crystals[J]. International Journal of Pharmaceutics, 2004, 280(1): 137-150.
[9] Xu C, Wang F, Liu D, et al. Effect of additive EDTA on crystallization process of magnesium hydroxide precipitation[J]. Chinese Journal of Chemical Engineering, 2010, 18(5): 761-766.
[10] GB 25466—2010, 铅、锌工业污染物排放标准[S].
GB 25466—2010, Emission standard of pollutants for lead and zinc industry[S].
[11] Gong J, Wang J, Wei H. Effect of Mixed Solvents and Additives on the Habit Modification of 6-APA Crystals[J]. Transaction of Tianjin University, 2005, 11(3): 157-161.
[12] Black S N, Davey R J, Halcrow M. The kinetics of crystal growth in the presence of tailor-made additives[J]. Journal of Crystal Growth, 1986, 79(1): 765-774.
[13] 贝拉米 L J, 黄维垣, 聂崇实. 复杂分子的红外光谱[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 1975: 120-122.
Ballamy L J, HUANG Weiheng, LIE Congshi. The infra-red spectra of complex molecules[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 1975: 120-122.
[14] 邓姝皓. 聚乙二醇的缓蚀、阻垢机理研究[D]. 长沙: 湖南大学化学化工学院, 2000: 26-30.
DENG Shuhao. Research on inhibition and scale inhibition mechanism of polyethylene glycol[D]. Changsha: Hunan University. College of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, 2000: 26-30.
[15] 万牡华, 王淼, 邓兰青, 等. 不同分子质量聚乙二醇对一水草酸钙成核和生长的调控作用[J]. 人工晶体学报, 2008, 32(2): 106-108.
WANG Muhua, WANG Miao, DENG Lanqing, et al. Modulation of polyethylene glycol with different molecular weight on nucleation and growth of calcium oxalate monohydrate[J]. Journal of Synthetic Crystals, 2008, 32(2): 106-108.
[16] Madras G, Mccoy B J. Transition from nucleation and growth to Ostwald ripening[J]. Chemical Engineering Science, 2002, 57(18): 3809-3818.
[17]  M, et al. The kinetics of industrial crystallization[M]. Amsterdam: Elsevier, 1985: 311-315.
M, et al. The kinetics of industrial crystallization[M]. Amsterdam: Elsevier, 1985: 311-315.
(编辑 杨幼平)
收稿日期:2014-02-12;修回日期:2014-04-28
基金项目(Foundation item):国家自然科学基金资助项目(51274243) (Project(51274243) supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China)
通信作者:齐天贵,博士,从事有色金属冶金研究;E-mail: qitiangui@csu.edu.cn