DOI: 10.11817/j.issn.1672-7207.2020.07.013
正交异性钢桥面板的疲劳裂纹扩展规律
汪珍,王莹
(东南大学 江苏省工程力学分析重点实验室,江苏 南京,211189)
摘要:为了研究正交异性钢桥面板U肋-横隔板的连接部位的疲劳问题,基于扩展有限元方法分析典型疲劳裂纹的扩展机理,并引入U肋-横隔板焊缝的残余应力,分析残余应力对疲劳裂纹扩展的影响。研究结果表明:萌生于横隔板开孔处的疲劳裂纹未考虑残余应力时不会扩展,加入残余应力后会改变裂纹的应力状态,裂尖应力可以驱动横隔板开孔处的裂纹扩展,裂纹扩展类型为Ⅰ型裂纹;萌生于U肋焊趾处的疲劳裂纹为Ⅰ型主导的Ⅰ-Ⅱ-Ⅲ复合型裂纹,残余应力会影响裂纹扩展角度;对于萌生于横隔板焊趾处的裂纹,相比于不考虑残余应力的情况,考虑残余应力的裂纹扩展规律与实桥开裂规律相符,说明对于焊缝疲劳裂纹,在疲劳评估时应考虑焊接过程中残余应力对评估结果的影响。
关键词:正交异性钢桥面板;扩展有限元法;疲劳裂纹;残余应力;应变能释放率
中图分类号:U441.4 文献标志码:A
文章编号:1672-7207(2020)07-1873-10
Analysis of fatigue crack propagation on orthotropic steel bridge deck
WANG Zhen, WANG Ying
(Jiangsu Key Laboratory of Engineering Mechanics, Southeast University, Nanjing 211189, China)
Abstract: In order to study the fatigue problem of the welded joint of U-rib-to-diaphragm in orthotropic steel bridge deck, the propagation mechanism of the typical fatigue crack was analyzed based on the extended finite element method, and the residual stress of the U-rib-to-diaphragm weld was introduced to qualitatively analyze the impact of the residual stress on the fatigue crack propagation. The results show that fatigue crack initiating from free edge of cutout in the diaphragm can not propagate without residual stress, and the stress state of crack details will be changed when residual stress is added, then the stress of crack tip can drive the crack at the cutout in the diaphragm to grow, and the crack extension type is mode Ⅰ crack; fatigue crack initiating from U-rib weld toe is mode Ⅰ dominant with mode Ⅰ-Ⅱ-Ⅲ, and residual stress can affect the crack propagation angle. For cracks arising at the toe of diaphragm welding, compared with the case without residual stress, the crack propagation rule of residual stress is more consistent with the test results, which indirectly indicates that the impact of residual stress on the evaluation results of welding seam fatigue crack should be considered in the fatigue evaluation of welding seam.
Key words: orthotropic bridge deck; extended finite element method; fatigue crack; residual stress; strain energy release rate
正交异性钢桥面板作为大跨钢桥首选的桥面板结构形式,被广泛应用于现代桥梁结构。然而,由于其构造中的众多焊缝存在较大的残余应力,通过改变平均应力和循环应力的最大值影响桥面板的疲劳破坏行为,导致正交异性桥面板疲劳问题显著。近年来,国内外学者多基于断裂力学法分析钢桥疲劳问题,诸多研究[1-3]表明,断裂力学法由于充分考虑正交异性桥面板结构中存在的初始缺陷,可有效预测钢桥的疲劳裂纹扩展和寿命。断裂力学法常用的数值分析方法有边界配置法、边界元法和有限元法,其中扩展有限元法(extended finite element method, XFEM)由于在处理不连续问题的巨大优势,被广泛应用于疲劳裂纹断裂分析中[4]。DA等[5]基于扩展有限元方法对钢箱梁疲劳裂纹萌生和扩展阶段进行疲劳寿命预测,预测结果与实验结果相吻合。NACY等[6]采用线弹性断裂力学和扩展有限元方法,分析了萌生于U肋-顶板焊缝处疲劳裂纹的寿命,研究了顶板厚度和U肋厚度对疲劳寿命的影响。WANG等[7]基于等效裂纹扩展长度准则,对正交异性桥面板焊缝处随机缺陷进行了均质化处理,基于扩展有限元方法提出了一种多尺度方法,用来预测含孔隙夹杂的焊接接头在随机车辆流作用下宏观裂纹萌生寿命。许华翔[8]通过XFEM对裂纹扩展进行数值模拟,得到疲劳裂纹开裂的应力强度因子幅值变化规律、裂纹扩展速率以及开裂疲劳寿命,进而分析了横隔板切割误差的疲劳劣化效应。王春生等[9]通过正交异性钢桥面板足尺疲劳试验发现受焊接残余应力影响,处于疲劳荷载压应力区的腹板与横隔板连接焊缝端部会萌生疲劳裂纹。随后,王春生等[10]在钢桥面板节段模型中引入焊接残余应力场,基于扩展有限元方法,对桥面板典型细节进行了裂纹断裂的数值模拟。现有研究分析了板厚、焊缝缺陷和切割误差等因素对钢箱梁的疲劳寿命的影响,研究了车辆载荷和残余应力作用下的疲劳裂纹扩展机理,但针对残余应力对疲劳裂纹扩展规律的影响缺乏细致分析。为此,本文作者基于扩展有限元方法揭示正交异性钢桥面板萌生于U肋-横隔板焊缝的3类典型疲劳裂纹的扩展机理。采用多尺度建模方法,建立含拉索、桥墩、正交异性钢桥面板和裂纹的全桥多尺度有限元模型,在跨中部位的桥面板上施加标准疲劳载荷,利用J积分计算静态裂纹的应力强度因子以确定裂纹开裂最不利工况,再基于扩展有限元法分析车辆载荷作用下未考虑残余应力和考虑残余应力的疲劳裂纹扩展,对比无残余应力和考虑残余应力时疲劳裂纹的扩展形态,研究焊接残余应力对疲劳裂纹的影响。
1 数值模拟模型及理论
1.1 多尺度有限元模型
以某公路斜拉桥为工程背景,全桥长756 m,宽37.1 m,钢箱梁高3 m。桥面结构采用正交异性桥面板,桥面板顶板厚14 mm,腹板厚16 mm,U肋间距600 mm,桥面板材料采用Q345钢。参照此斜拉桥建立全桥多尺度有限元模型。首先,建立尺度特征为102 m的桥梁整体模型(见图1),以梁单元建立桥墩、杆单元建立悬索、壳单元建立钢箱梁桥面板,并对跨中40 m的桥面板进行精细化建模,建立尺度特征为100 m,包含顶板、底板、斜腹板、U肋和横隔板的壳单元模型(见图2)。其中,U肋-横隔板连接体采用实体单元建模,建立含尺度特征为10-3 m裂纹的U肋-横隔板实体单元有限元模型(见图3),单元长×宽×高为1 mm×1 mm×1 mm,在实体单元模型中插入3类实际工程中常见的椭圆形疲劳裂纹(分别见图3(b),(c)和(d))。
多尺度有限元模型的连接方式为:桥梁整体模型和精细化模型以节点位移耦合方式连接,精细化模型和实体模型采用壳-实体耦合方式连接。在数值模拟时,对4对桥墩进行固定约束。

图1 桥梁整体模型
Fig. 1 Global bridge model
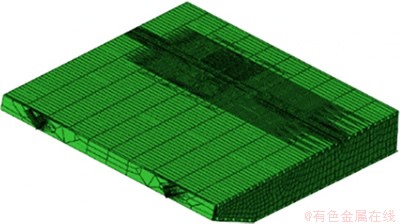
图2 正交异性桥面板的精细化模型
Fig. 2 Detailed model of orthotropic bridge deck
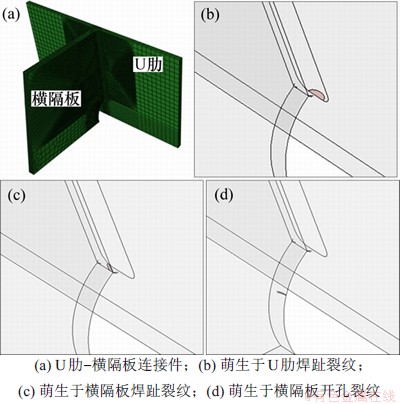
图3 U肋-横隔板连接部位
Fig. 3 U-rid-to-diaphragm joint part
1.2 焊接有限元模型
U肋-横隔板连接构件的焊接有限元分析模型如图4所示。利用生死单元技术进行热-结构耦合分析,热分析采用点热源进行加热,热源电压为250 V,电流为25 A,热效率为0.75,加热速度为10 mm/s;结构分析在U肋的一端约束x方向位移,在横隔板截断部位采用z方向对称约束,在U肋和横隔板底端约束y方向位移。
焊接分析中钢材热物理与热力学特征值主要参考文献[11],结合文献[12]对高温度的热力学参数进行适当修正,得到焊接模型的参数,如图5所示。
1.3 扩展有限元方法(XFEM)
扩展有限元方法由BELYTSCHKO等[13]提出,可简单有效地处理不连续问题。扩展有限元方法采用单位分解法思想,在常规有限元的位移函数基础上,增加能反映裂纹面位移不连续和裂尖位移的富集函数,提高了计算效率[14-16],位移函数表达式为
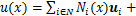
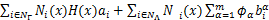 (1)
(1)
式中:ui为连续的节点位移向量;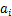 和
和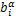 为节点附加自由度;m为裂尖富集基函数的数目;NΓ为被裂纹贯穿单元节点集;NΛ为含裂尖单元节点集;H(x)为阶跃函数,
为节点附加自由度;m为裂尖富集基函数的数目;NΓ为被裂纹贯穿单元节点集;NΛ为含裂尖单元节点集;H(x)为阶跃函数,
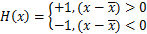 (2)
(2)
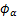 为描述裂纹尖端位移的富集函数:
为描述裂纹尖端位移的富集函数:
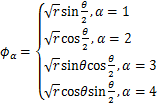 (3)
(3)
式中:(r,θ)表示裂纹尖端的极坐标。
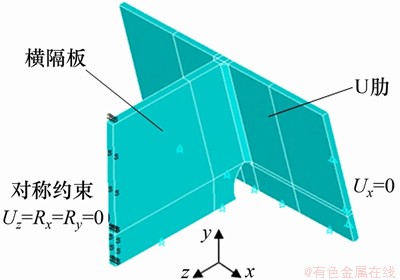
图4 U肋-横隔板连接构件焊接分析模型
Fig. 4 Welding analysis model of U-rib-to-diaphragm joint
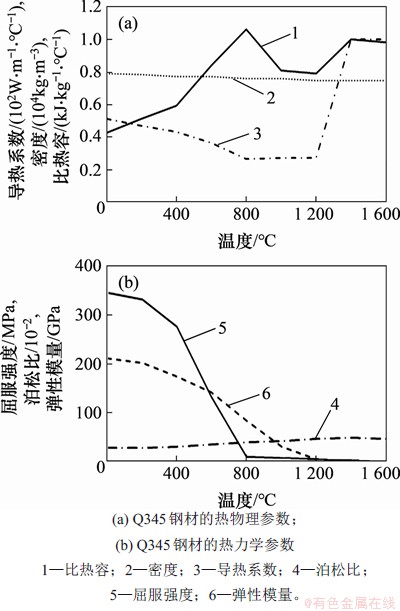
图5 Q345钢材的热力学分析参数
Fig. 5 Thermodynamic analysis parameters of Q345 steel
式(1)中,右边第一项为常规有限元位移函数,第二项为裂纹贯穿单元的位移,通过加入阶跃函数H(x)来反映位移不连续性;第三项反映裂纹尖端的奇异性。
1.4 疲劳裂纹扩展实现方法
线弹性断裂力学理论中,描述疲劳裂纹扩展常用Paris公式:
 (4)
(4)
但在ABAQUS有限元软件中,改变了Paris公式中应力强度因子增量,以能量释放率增量代替:
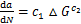 (5)
(5)
式中: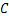 ,m,
,m, 和
和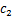 为材料常数,m=2.67,C=1.58×10-11[17];a为裂纹长度;N为循环次数;△K为应力强度因子幅值;△G为能量释放率幅值。
为材料常数,m=2.67,C=1.58×10-11[17];a为裂纹长度;N为循环次数;△K为应力强度因子幅值;△G为能量释放率幅值。
以Ⅰ型裂纹为例,其能量释放率GⅠ和应力强度因子KⅠ的关系为
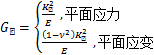 (6)
(6)
其中:E为材料弹性模量;υ为泊松比。
当裂纹尖端能量释放率满足Gth<△Gpl时,疲劳裂纹开始扩展,其中,Gpl为能量释放率最大值,接近钢材断裂韧度GC;Gth为能量释放率阈值,参考文献[18]中桥梁结构钢的应力强度因子Kth=92 MPa·mm1/2,通过式(6)得到能量释放率阈值Gth。
当最大的能量释放率大于其阈值时,疲劳裂纹启裂,其流程如图6所示。裂纹启裂后,ABAQUS设定裂纹沿最大主应力方向扩展。假设裂纹尖端第i个单元沿裂纹扩展方向扩展,根据水平集函数追踪虚拟裂纹并确定裂纹扩展增量△ɑi,利用虚拟裂纹闭合法(virtual crack closure technique,VCCT)计算能量释放率△Gi,再由Paris公式得到△Ni。循环次数最小的单元为最终断裂单元,记录断裂单元k的裂纹扩展增量△ɑk和循环次数△Nk,更新累计循环次数和裂纹长度,进入下一轮循环,直至循环次数达到最大值为止。
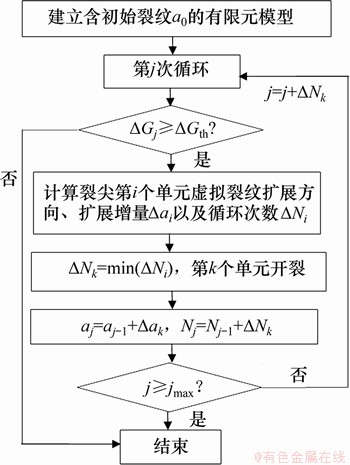
图6 疲劳裂纹扩展模拟流程
Fig. 6 Simulation flow of fatigue crack propagation process
2 静态裂纹的数值模拟
本文只分析疲劳裂纹的扩展形态和裂纹类型,未计算疲劳寿命,故采用简化车辆载荷即可达到研究目的。选用的车辆载荷为“公路钢结构桥梁设计规范”中的疲劳载荷模型Ⅲ[19],其加载方式如图7所示。疲劳载荷模型Ⅲ由4个标准轴组成,其纵向两长轴的距离为6 m,间距较大,对于桥面板上的某个具体节点而言,当前面两轴的轮载作用于该节点附近时,后面两轴尚远离该点,对该部位的疲劳应力的贡献不显著,故本文仅考虑纵向轴距为1.2 m的短轴轮载作为施加于多尺度模型的疲劳荷载,即以轮载作用面的长×宽为0.6 m×0.2 m,总重力为2×120 kN的车辆载荷模型作为移动的车辆载荷。
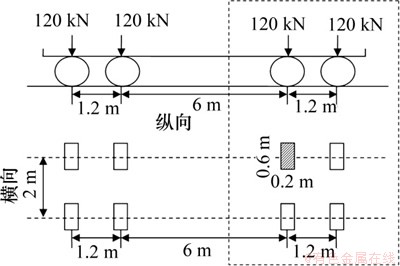
图7 疲劳载荷模型III
Fig. 7 Fatigue load model-III
为确定促进裂纹开裂的最不利加载位置,U肋-横隔板细节加载方式采用多分析步加载,车辆载荷移动位置如图8所示。疲劳载荷模型分别以H1~H7为车道沿桥梁纵向移动,纵向移动位置如图8(b)所示,分为37个位置工况加载。其中,横向位置H1~H7的距离间隔为100 mm,纵向起始位置为后轮距离裂纹位置为3.75 m,终止位置为车轮前轮远离裂纹位置长度3.75 m;当远离U肋-横隔板处裂纹时,每个加载位置距离间隔为200 mm;接近U肋-横隔板处裂纹时,间隔为100 mm,形成37个纵向加载位置Z1~Z37。
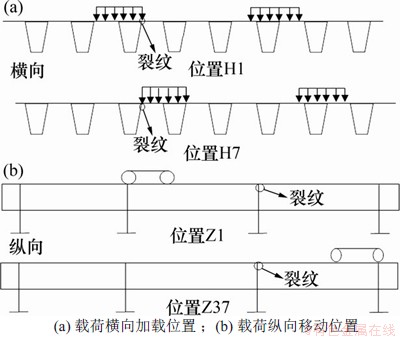
图8 移动车辆载荷
Fig. 8 Moving vehicle load
以图8所示的移动载荷进行加载,在裂尖选取多个积分半径计算J积分,通过J积分计算各工况下U肋-横隔板疲劳裂纹的应力强度因子,确定最不利工况。考虑U肋-横隔板细节的3类典型疲劳裂纹:萌生于横隔板焊趾的裂纹、萌生于U肋焊趾的裂纹和萌生于横隔板开孔的裂纹。假设初始椭圆裂纹短轴长a0和长轴长c0分别为2.5 mm和5.0 mm,a0/c0=1/2,其中,萌生于U肋焊趾的裂纹为半椭圆裂纹,萌生于横隔板焊趾和横隔板开孔处裂纹为1/4椭圆裂纹,得到U肋-横隔板焊缝裂纹KⅠ影响线如图9所示。
图9(a)所示为横隔板焊趾处裂纹的应力强度因子影响线。从图9(a)可看出:此处裂纹的KⅠ峰值约为117.9 MPa·mm1/2,对应的车辆载荷加载位置为Z7-H2。图9(b)所示为U肋焊趾处裂纹的应力强度因子影响线,可见U肋焊趾裂纹KⅠ峰值为105.1 MPa·mm1/2,对应车辆载荷加载位置为Z20-H3。图9(c)所示为横隔板开孔处裂纹的应力强度因子影响线,可见应力强度因子始终小于0 MPa·mm1/2,表明裂纹区域处于受压状态。
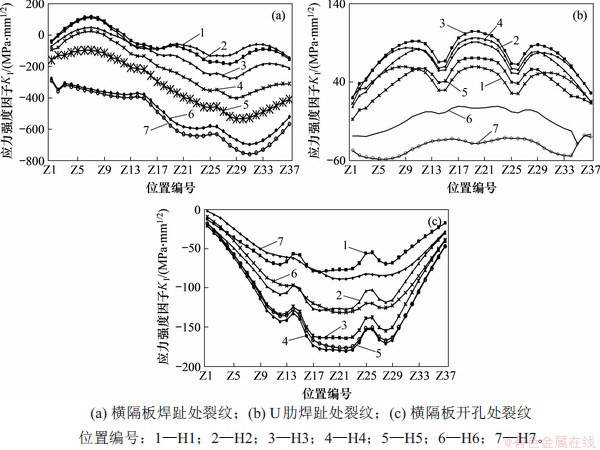
图9 U肋-横隔板焊缝裂纹KⅠ影响线
Fig. 9 Influence line of KⅠ of cracks at welding of U-rid-to-diaphragm
3 未考虑残余应力的疲劳裂纹扩展
由以上分析可知,车辆载荷作用不考虑残余应力时,横隔板开孔处静态裂纹的应力强度因子始终小于0 MPa·mm1/2,即疲劳裂纹无法扩展;横隔板焊趾和U肋焊趾的静态裂纹分析得到最大的应力强度因子为117.9 MPa·mm1/2和105.1 MPa·mm1/2,均大于应力强度因子阈值Kth=92 MPa·mm1/2。故在车辆载荷作用下,当不考虑残余应力时,横隔板焊趾和U肋焊趾的疲劳裂纹会扩展。
3.1 横隔板焊趾处疲劳裂纹扩展
横隔板焊趾的初始裂纹设为1/4椭圆裂纹,短轴长度a0与长轴长度c0分别为2.5 mm和5.0 mm。在车辆载荷作用下,未考虑残余应力时的疲劳裂纹扩展路径如图10所示。从图10可看出:裂纹向焊缝区域扩展,经测量裂纹扩展方向与初始裂纹长度方向角度约为56°,这与文献[20]得到的裂纹扩展路径相悖。
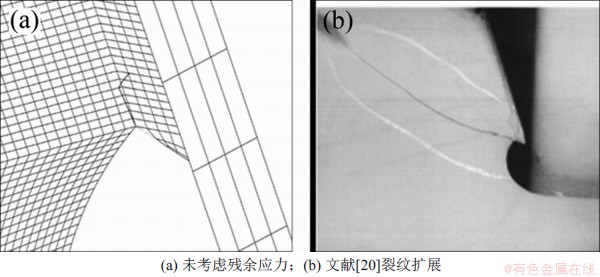
图10 横隔板焊趾处裂纹扩展
Fig. 10 Fatigue crack propagation of diaphragm welding toe
横隔板焊趾处疲劳裂纹扩展过程中的累计应变能释放率如图11所示,其中,GⅠ,GⅡ和GⅢ分别为Ⅰ型裂纹、Ⅱ型裂纹和Ⅲ型裂纹的累计应变能释放率。从图11可见:GⅠ与GⅡ和GⅢ相差不大,说明Ⅱ型裂纹和Ⅲ型裂纹对疲劳裂纹扩展的影响较大,会驱使裂纹以较大偏转角向焊缝扩展。
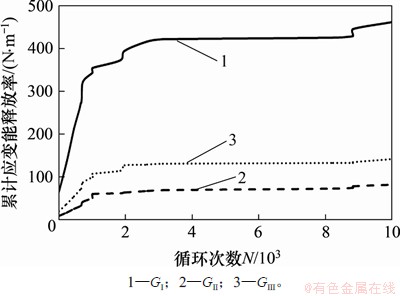
图11 横隔板焊趾处裂纹累计应变能释放率
Fig. 11 Cumulative strain energy release rate of crack propagation at diaphragm welding toe
3.2 U肋焊趾处疲劳裂纹扩展
U肋焊趾的初始裂纹设为半椭圆裂纹,短轴与2倍长轴之比a0/(2c0)=1/4,车辆载荷作用未考虑残余应力时,疲劳裂纹扩展路径如图12所示。从图12可见:右侧裂尖的裂纹长度增量比左侧裂尖的更大,裂纹扩展角度较小,约为0°,明显小于文献[20]的疲劳裂纹扩展角度。
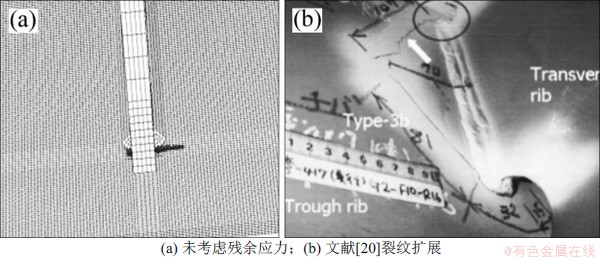
图12 U肋焊趾处裂纹扩展
Fig. 12 Fatigue crack propagation of U-rid welding toe
裂纹扩展过程的累计应变能释放率如图13所示。从图13可见:Ⅰ型裂纹占绝对主导地位;Ⅱ型和Ⅲ型裂纹应变能释放率相当,约占Ⅰ型裂纹的应变能释放率的0.1。Ⅱ型和Ⅲ型裂纹对裂纹扩展影响不可忽略,主要体现在裂纹扩展路径以微小角度向U肋腹板顶部扩展。
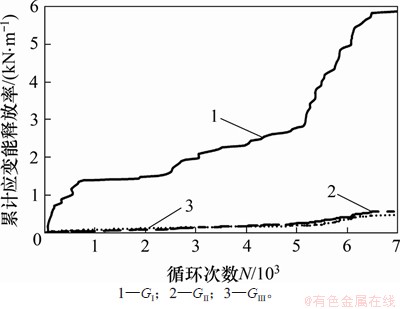
图13 U肋焊趾处裂纹累计应变能释放率
Fig. 13 Cumulative strain energy release rate of crack propagation at U-rid welding toe
4 考虑残余应力的疲劳裂纹扩展
4.1 焊接残余应力分析
钢桥面板焊接过程中U肋-横隔板连接构件的热量在时间和空间上会急剧变化,是典型的非线性瞬态传热问题。对U肋-横隔板连接构件进行热弹塑性分析,利用增量法逐步求解U肋-横隔板的温度场、应力场等。
通过生死单元技术分析有限元模型(图4),得到U肋-横隔板连接构件的焊接残余应力场,如图14所示。从图14(a)可见:整个焊缝区域的等效应力达到钢材的屈服应力,焊缝起始和终止位置残余应力较小,焊缝中间区域处于残余拉应力状态,分布均匀且已达到钢材屈服应力。从图14(b)可知:U肋焊趾沿横隔板厚度方向残余应力为残余拉应力,横隔板焊趾沿横隔板厚度方向残余应力为残余压应力。横隔板焊趾残余应力分布曲线如图15所示。从图15可见:焊趾中间地段为残余应力稳定区,沿纵向和横向的残余应力几乎全为拉应力。本文的纵、横向残余应力曲线的分布规律与文献[12]中的分布规律基本一致,故认为此残余应力结果是准确的,后续将此残余应力场加入多尺度模型中,分析U肋-横隔板三类裂纹在车辆载荷和残余应力场作用下的疲劳裂纹扩展规律。
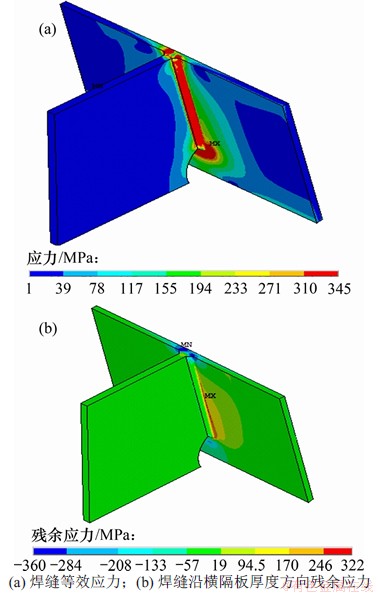
图14 U肋-横隔板连接构件焊接残余应力
Fig. 14 Residual stress distribution of U-rid-to-diaphragm weld
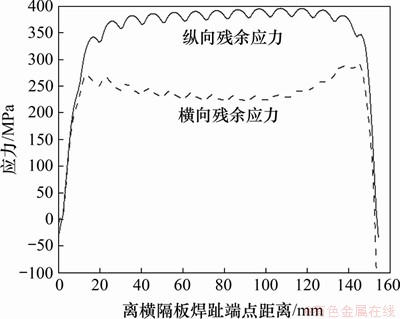
图15 横隔板焊趾残余应力分布
Fig. 15 Distribution of longitudinal and transverse residual stress at welded toe of diaphragm
4.2 横隔板开孔处疲劳裂纹扩展
多尺度模型中加入焊接残余应力后,开孔处的残余拉应力将开孔裂纹处应力状态由压应力状态转变为拉应力状态,使裂尖应力有足够驱动力驱动横隔板开孔处裂纹扩展,得到疲劳裂纹扩展如图16所示。从图16可知:裂纹沿着初始裂纹的长度和深度方向扩展,扩展后的裂纹面和初始裂纹面基本在同一平面上,与文献[20]中的疲劳裂纹扩展路径相似。
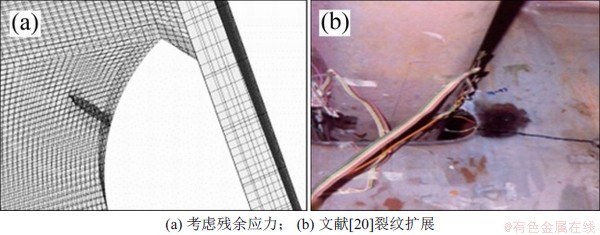
图16 考虑残余应力的横隔板开孔处裂纹扩展
Fig. 16 Fatigue crack propagation in diaphragm cutout edge with residual stress
裂纹扩展过程中的累计应变能释放率如图17所示。从图17可见:Ι型裂纹占绝对的主导地位,Ⅱ型和Ⅲ型裂纹应变能释放率远远小于GⅠ,可以忽略,故此处疲劳裂纹为Ι型裂纹。
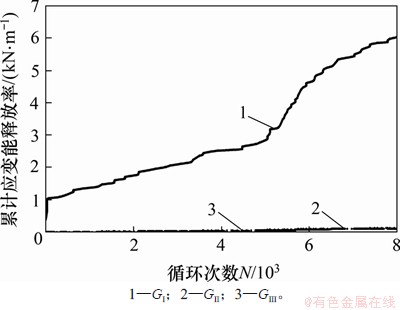
图17 考虑残余应力的横隔板开孔处裂纹累计应变能释放率
Fig. 17 Cumulative strain energy release rate of crack propagation in diaphragm cutout edge with residual stress
4.3 横隔板焊趾处疲劳裂纹扩展
与未考虑残余应力时的初始裂纹和车辆加载形式相同,仅在含横隔板焊趾裂纹的多尺度模型中加入焊接残余应力,得到疲劳裂纹扩展路径如图18所示。由图18可知:考虑残余应力的疲劳裂纹以一定角度沿着横隔板扩展,相比于未考虑残余应力的疲劳裂纹(以56°角向焊缝区域扩展),考虑残余应力的疲劳裂纹扩展路径与文献[20]中试验路径更相符。
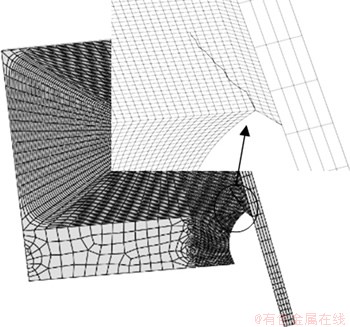
图18 考虑残余应力的横隔板焊趾疲劳裂纹扩展
Fig. 18 Fatigue crack propagation in diaphragm welding toe with residual stress
未考虑残余应力和考虑残余应力的累计应变能释放率的比值GⅡ/GⅠ和GⅢ/GⅠ如图19所示。从图19可见:与未考虑残余应力时相比,考虑残余应力时的GⅡ/GⅠ增大,GⅢ/GⅠ减小。其原因是横隔板焊趾的纵向残余拉应力增大了平行于裂纹面的切应力,即与Ⅱ型裂纹对应的面内切应力增大,相应的GⅡ增大;而由图14(b)可知:横隔板焊趾沿板厚方向残余应力为压应力,减小了与Ⅲ型裂纹对应的面外切应力,导致GⅢ减小。考虑残余应力的Ⅱ型裂纹的累计应变能释放率与Ⅰ型的累计应变能释放率比值较大,最大值约为0.35,GⅢ占比较小,所以,考虑残余应力的疲劳裂纹为Ⅰ型主导的Ⅰ-Ⅱ复合型裂纹。
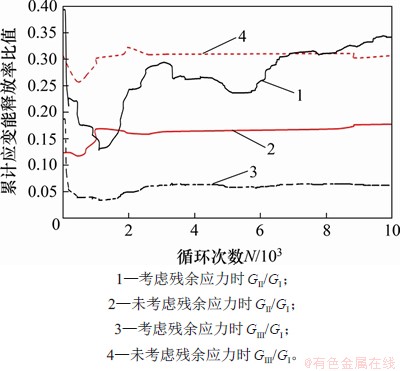
图19 横隔板焊趾处裂纹累计应变能释放率比值
Fig. 19 Cumulative strain energy release rate ratio of crack propagation in diaphragm welding toe
4.4 U肋焊趾处疲劳裂纹扩展
考虑残余应力的U肋焊趾处疲劳裂纹扩展路径如图20所示。从图20可见:疲劳裂纹两侧裂尖的裂纹长度增量相当,以横隔板为对称轴对称增大。与未考虑残余应力的疲劳裂纹扩展路径(图12)对比可发现:考虑残余应力的裂纹扩展角度更大,其裂纹扩展路径更符合文献[20]中的裂纹扩展路径。
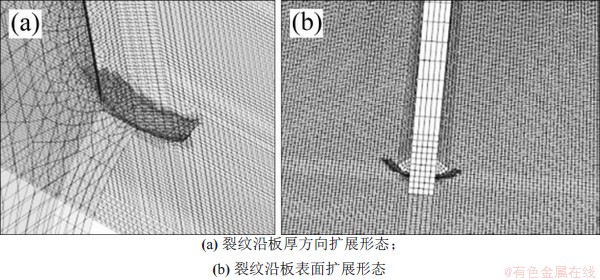
图20 考虑残余应力的U肋焊趾疲劳裂纹扩展
Fig. 20 Fatigue crack propagation of U-rid weld toe with residual stress
裂纹扩展过程中的累计应变能释放率比值如图21所示。从图21可见:无论是否考虑残余应力,Ⅱ型和Ⅲ型裂纹应变能释放率均相当,且数值较大无法忽略,说明U肋焊趾处裂纹为Ⅰ主导的Ⅰ-Ⅱ-Ⅲ复合型裂纹。但考虑残余应力时,GⅡ/GⅠ和GⅢ/GⅠ更大,主要是因为U肋焊趾处纵向和板厚方向皆为残余拉应力,增加了与Ⅱ型、Ⅲ型裂纹对应的面内、面外切应力,相应的GⅡ和GⅢ增大。GⅡ/GⅠ和GⅢ/GⅠ变化也体现在裂纹扩展路径上,考虑残余应力的裂纹扩展角度比未考虑残余应力的扩展角度更大,且裂纹以横隔板为对称轴对称增长,更符合实桥裂纹扩展情况。
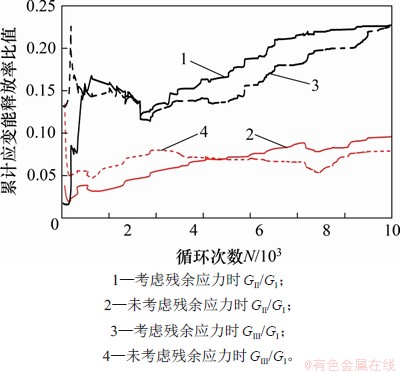
图21 U肋焊趾处裂纹累计应变能释放率比值
Fig. 21 Cumulative strain energy release rate ratio of crack propagation in U-rid welding toe
5 结论
1) 当车辆载荷作用未考虑残余应力时,萌生于横隔板开孔处的疲劳裂纹始终保持闭合,横隔板焊趾处的疲劳裂纹扩展形式与实际情况相悖,萌生于U肋焊趾处的疲劳裂纹以微小角度沿U肋板扩展,为Ⅰ型主导的Ⅰ-Ⅱ-Ⅲ复合型裂纹,裂纹扩展角度与其他开裂角度略有偏差。
2) 对于萌生于横隔板开孔处的疲劳裂纹,考虑残余应力后改变了裂纹细节处的应力状态,增大的裂纹尖端应力足以驱动裂纹扩展,裂纹类型为Ⅰ型裂纹;对于萌生于横隔板焊趾处疲劳裂纹,考虑残余应力后改变了Ⅱ型和Ⅲ裂纹对疲劳裂纹扩展的影响,使得扩展路径基本一致,形成的裂纹为Ⅰ型主导的Ⅰ-Ⅱ复合型裂纹;对于萌生于U肋焊趾处的疲劳裂纹,考虑残余应力后,Ⅱ型和Ⅲ裂纹对疲劳裂纹扩展的影响更显著,促使裂纹扩展角度增大,扩展路径和扩展角度更符合实桥裂纹开裂情况。
3) 残余应力会显著影响U肋-横隔板焊缝处的疲劳裂纹扩展规律,考虑残余应力的疲劳裂纹扩展规律与实桥开裂规律更相符。说明对于焊缝疲劳裂纹,在疲劳评估时应考虑焊接过程中残余应力对评估结果的影响。
参考文献:
[1] 卫星, 姜苏. 基于断裂力学的钢桥面肋-板接头疲劳寿命预测[J]. 西南交通大学学报, 2017, 52(1): 16-22
WEI Xing, JIANG Su. Fatigue life prediction on rib-to-deck welded joints of steel bridge deck based on lefm[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2017, 52(1): 16-22.
[2] 李明, 刘杨, 唐雪松. 疲劳裂纹的跨尺度分析[J]. 浙江大学学报(工学版), 2017, 51(3): 524-530.
LI Ming, LIU Yang, TANG Xuesong. Trans-scale analysis for fatigue crack[J]. Journal of Zhejiang University(Engineering Science), 2017, 51(3): 524-530.
[3] 刘中祥. 大跨钢桥疲劳裂纹扩展的数值模拟研究[D]. 南京:东南大学土木工程学院, 2015: 53-61.
LIU Zhongxiang. Research in numerical simulation of fatigue crack propagation in long-span steel bridge[D]. Nanjing: Southeast University. School of Civil Engineering, 2015: 53-61.
[4] 谭高托. 基于扩展有限元法的钢桥疲劳寿命可靠度方法研究[D]. 广州: 华南理工大学土木与交通学院, 2017: 7-9.
TAN Gaotuo. Research on fatigue reliability evaluation of steel bridges based on extended finite element method[D]. Guangzhou: South China University of Technology. School of Civil Engineering and Transportation, 2017: 7-9.
[5] DA SILVA A L L , CORREIA J A F O, DE JESUS A M P, et al. Influence of fillet end geometry on fatigue behaviour of welded joints[J]. International Journal of Fatigue, 2019, 123: 196-212.
[6] NAGY W, SCHOTTE K, VAN BOGAERT P, et al. Fatigue strength application of fracture mechanics to orthotropic steel decks[J]. Advances in Structural Engineering, 2016, 19(11): 1696-1709.
[7] WANG Benjin, ZHOU Xiaoyi, DE BACKER H, et al. Macro-crack initiation life for orthotropic steel decks considering weld heterogeneity and random traffic loading[J]. Structure and Infrastructure Engineering, 2017, 13(12): 1639-1652.
[8] 许华翔. 两类制造误差对纵肋与横隔板焊接细节疲劳抗力的劣化效应研究[D]. 成都:西南交通大学土木工程学院, 2018: 27-51.
XU Huaxiang. Study on deterioration effect of two manufacturing errors of steel bridges on fatigue resistance of rib-to-diaphragm welding details[D]. Chengdu: Southwest Jiaotong University. School of Civil Engineering, 2018: 27-51.
[9] 王春生, 付炳宁, 张芹, 等. 正交异性钢桥面板足尺疲劳试验[J]. 中国公路学报, 2013, 26(2): 69-76.
WANG Chunsheng, FU Bingning, ZHANG Qin, et al. Fatigue test on full-scale orthotropic steel bridge deck[J]. China Journal of Highway and Transport, 2013, 26(2): 69-76.
[10] 王春生, 翟慕赛, 唐友明, 等. 钢桥面板疲劳裂纹耦合扩展机理的数值断裂力学模拟[J]. 中国公路学报, 2017, 30(3): 82-95.
WANG Chunsheng, ZHAI Musai, TANG Youming, et al. Numerical fracture mechanical simulation of fatigue crack coupled propagation mechanism for steel bridge deck[J]. China Journal of Highway and Transport, 2017, 30(3): 82-95.
[11] 赵秋, 吴冲. U肋加劲板焊接残余应力数值模拟分析[J]. 工程力学, 2012, 29(8): 262-268.
ZHAO Qiu, WU Chong. Numerical analysis of welding residual stress of U-rib stiffened plate[J]. Engineering Mechanics, 2012, 29(8): 262-268.
[12] 康玲. 正交异性钢桥面板纵、 横肋焊接残余应力数值模拟[D]. 成都: 西南交通大学土木工程学院, 2015: 31-41, 62-64.
KANG Ling. Numerical simulation of welding residual stress in both longitudinal and transverse ribs of orthotropic steel deck[D]. Chengdu: Southwest Jiaotong University. School of Civil Engineering, 2015: 31-41, 62-64.
[13] BELYTSCHKO T, BLACK T. Elastic crack growth in finite elements with minimal remeshing[J]. International Journal for Numerical Methods in Engineering, 1999, 45(5): 601-620.
[14] SINGH I V, MISHRA B K, BHATTACHARYA S, et al. The numerical simulation of fatigue crack growth using extended finite element method[J]. International Journal of Fatigue, 2012, 36(1): 109-119.
[15] 余天堂. 扩展有限单元法—理论、 应用及程序[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2014: 47-75.
YU Tiantang. The extended finite element method:thory, applications and program[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2014: 47-75.
[16] 郭历伦, 陈忠富, 罗景润, 等. 扩展有限元方法及应用综述[J]. 力学季刊, 2011, 32(4): 612-625.
GUO Lilun, CHEN Zhongfu, LUO Jingrun, et al. A review of the extended finite element method and its applications[J]. Chinese Quarterly of Mechanics, 2011, 32(4): 612-625.
[17] 宗亮, 施刚, 王元清, 等. Q345qD桥梁钢疲劳裂纹扩展速率试验研究[J]. 中国铁道科学, 2015,36(3): 37-44.
ZONG Liang, SHI Gang, WANG Yuanqing, et al. Experimental study on fatigue crack growth rate of Q345qD bridge steel[J]. China Railway Science, 2015,36(3): 37-44.
[18] JSS IV-09—2010. Fatigue design recommendations for steel structures and commentary [S].
[19] JTG D64—2015. 公路桥梁钢结构设计规范[S].
JTG D64—2015. Specification for design of highway steel bridge [S].
[20] KOLSTEIN M H. Fatigue classification of welded joints in orthotropic steel bridge decks[D]. Delft: Delft University of Technology. Fauity of Civil Engineering and Geosciences, 2007.
(编辑 赵俊)
收稿日期: 2019 -09 -06; 修回日期: 2019 -11 -06
基金项目(Foundation item):国家自然科学基金资助项目(51678135);江苏省自然科学基金资助项目(BK20171350) (Project(51678135) supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China; Project(BK20171350) supported by the Natural Science Foundation of Jiangsu Province)
通信作者:王莹,博士,副教授,从事结构健康监测、状态评估、疲劳、损伤与断裂研究;E-mail:civil_wangying@seu.edu.cn