金属材料塑性参数仪器化压入识别方法
来源期刊:中国有色金属学报2014年第4期
论文作者:马德军 陈 伟 宋仲康 郭俊宏
文章页码:958 - 974
关键词:塑性;仪器化压入;屈服强度;应变硬化指数;特征应力;特征应变
Key words:plastic properties; instrumented indentation; yield strength; strain hardening exponent; representative stress; representative strain
摘 要:采用有限元数值仿真结合仪器化压入实验的方法,选择Vickers压头和面角为172°的四棱锥压头用于金属材料塑性参数的仪器化识别,通过量纲分析和有限元数值仿真建立基于压入比功We/Wt的金属材料塑性参数仪器化压入识别方法和基于名义硬度Hn的金属材料塑性参数仪器化压入识别方法。根据识别方法的精度分析结果,确定条件屈服强度σ0.2和应变硬化指数n作为金属材料塑性参数识别的目标参数。6061铝合金、S45C碳钢、SS316不锈钢、SS304不锈钢和黄铜5种金属材料条件屈服强度σ0.2的识别误差为-17.5%~4%,基本满足工程需要,验证本研究中建立的金属材料塑性参数仪器化压入识别方法的有效性。
Abstract: The instrumented indentation is a useful tool to probe the plastic properties of metals. The finite element computations combined with instrumented indentation experiments were applied to choose the diamond indenters which were used to estimate the plastic properties of metals. The methods for determining the plastic properties of metals based on the ratio of indentation work We/Wt and nominal hardness Hn were established with the aid of dimensional analysis and finite element computations. 0.2% yield strength (σ0.2) and strain hardening exponent (Hn) were suggested to be the target parameters based on the accuracy analysis of the methods. The errors of σ0.2 of 6061 aluminum alloy, S45C carbon steel, SS316 stainless steel, SS304 stainless steel and brass are from -17.5% to 4%, which satisfies the need of engineering application. This verifies the effectiveness of the methods.
文章编号:1004-0609(2014)04-0958-16
马德军,陈 伟,宋仲康,郭俊宏
(装甲兵工程学院 机械工程系,北京 100072)
摘 要:采用有限元数值仿真结合仪器化压入实验的方法,选择Vickers压头和面角为172°的四棱锥压头用于金属材料塑性参数的仪器化识别,通过量纲分析和有限元数值仿真建立基于压入比功We/Wt的金属材料塑性参数仪器化压入识别方法和基于名义硬度Hn的金属材料塑性参数仪器化压入识别方法。根据识别方法的精度分析结果,确定条件屈服强度σ0.2和应变硬化指数n作为金属材料塑性参数识别的目标参数。6061铝合金、S45C碳钢、SS316不锈钢、SS304不锈钢和黄铜5种金属材料条件屈服强度σ0.2的识别误差为-17.5%~4%,基本满足工程需要,验证本研究中建立的金属材料塑性参数仪器化压入识别方法的有效性。
关键词:塑性;仪器化压入;屈服强度;应变硬化指数;特征应力;特征应变
中图分类号:TH140 文献标志码:A
MA De-jun, CHEN Wei, SONG Zhong-kang, GUO Jun-hong
(Department of Mechanical Engineering, Academy of Armored Force Engineering, Beijing 100072, China)
Abstract: The instrumented indentation is a useful tool to probe the plastic properties of metals. The finite element computations combined with instrumented indentation experiments were applied to choose the diamond indenters which were used to estimate the plastic properties of metals. The methods for determining the plastic properties of metals based on the ratio of indentation work We/Wt and nominal hardness Hn were established with the aid of dimensional analysis and finite element computations. 0.2% yield strength (σ0.2) and strain hardening exponent (Hn) were suggested to be the target parameters based on the accuracy analysis of the methods. The errors of σ0.2 of 6061 aluminum alloy, S45C carbon steel, SS316 stainless steel, SS304 stainless steel and brass are from -17.5% to 4%, which satisfies the need of engineering application. This verifies the effectiveness of the methods.
Key words: plastic properties; instrumented indentation; yield strength; strain hardening exponent; representative stress; representative strain
仪器化压入因所需试样尺寸小、测试接近无损、操作简单方便等特点,广泛应用于材料力学性能测试,尤其是在小尺度材料力学性能测试方面具有显著优势[1-8]。利用仪器化压入识别金属材料的塑性参数已成为仪器化压入测试领域的热点问题[9-18]。人们采用量纲分析和有限元数值仿真的方法针对这个问题进行了广泛、深入的研究。目前,代表性的金属材料塑性参数仪器化压入识别方法是基于特征应力和特征应变建立的,且使用多个具有不同锥角的金刚石压头。
值得注意的是,仍有两个核心问题需要更为深入的讨论。一是金刚石压头的选用。人们在选择金刚石压头时考虑的主要因素为金刚石压头与金属材料之间的摩擦。研究表明:随着金刚石压头锥角的增加,摩擦对金属材料压入响应的影响降低[19-21]。BUCAILLE等[22]假设不同的摩擦因数,对具有不同锥角的圆锥压头仪器化压入铝合金(弹性模量为70 GPa,屈服强度为500 MPa,应变硬化指数为0.122)的压入响应进行数值仿真,发现圆锥压头锥半角为60°和70.3°时相同最大压入深度所对应的最大压入载荷变化不超过3%。因此,BUCAILLE等[22]建议选用锥半角大于60°的圆锥压头用于金属材料塑性参数的压入识别。研究者们也是根据上述建议进行金刚石压头的选择,甚至直接选择锥半角为60°的圆锥压头[12, 14, 23-26]。LE[27]发现摩擦因数为0和0.15时,锥半角为60°的圆锥压头仪器化压入上述铝合金的另一个压入响应参数-压入总功与弹性功的比值(压入总功与弹性功分别为金刚石压头在加载和卸载过程中所做的功)的差别达到7%,这说明锥半角为60°的圆锥压头并不适用于金属材料塑性参数的压入识别。因此,需要重新选择用于金属材料塑性参数识别的合理的金刚石压头,并对其进行实验考察。
二是金属材料塑性参数识别方法有效性的实验验证。人们通常以理想幂硬化金属材料或者真实金属材料的真实应力—应变曲线为输入参数,通过有限元数值仿真确定不同锥角金刚石压头仪器化压入该材料的压入响应,应用提出的塑性参数识别方法确定该材料塑性参数的识别结果,通过与输入参数进行比较,以检验识别方法的有效性[12-14, 22-27]。显然,这种识别缺少仪器化压入实验,而仅采用有限元数值仿真不能够全面检验金属材料塑性参数识别方法的有效性。
针对上述两个问题,本文作者采用有限元数值仿真结合仪器化压入实验的方法来选择用于识别金属材料塑性参数的金刚石压头,以此为基础建立新的基于特征应力和特征应变的金属材料塑性参数仪器化压入识别方法,并用实验验证该方法的有效性。
1 金刚石压头的选用
仪器化压入涉及复杂的材料、几何和接触边界条件非线性,因此,人们至今无法获得准确的解析解,而只能通过有限元数值仿真的办法来确定被测材料的压入响应[28]。但是,有限元数值仿真得到的材料压入响应是理想化的结果,并不能全面地反映压入问题。因此,本文作者采用有限元数值仿真结合仪器化压入实验的方法来选择用于识别金属材料塑性参数的金刚石压头。
本研究中选择面角为120°的四棱锥压头、Vickers压头、面角为172°的四棱锥压头为待研究的金刚石压头,选择SS304不锈钢作为被测材料。相关研究表明,对于同一被测材料,采用四棱锥压头和与其具有相同面积函数的圆锥压头可以获得相同的仪器化压入加载、卸载曲线[11, 29]。面角为120°的四棱锥压头、Vickers压头和面角为172°的四棱锥压头所对应的圆锥压头锥半角分别为62.9°、70.3°和86.45°。应用有限元软件ABAQUS建立理想圆锥压头压入半无限空间体的轴对称模型对3种四棱锥压头仪器化压入SS304不锈钢的压入响应进行数值仿真。图1所示为有限元划分的压头与被测材料的总体网格和靠近压头尖端的局部网格。压头和被测材料分别划分了3600个和10000个四边形单元。有限元模型的网格收敛性和远场无关性均符合要求。被测材料与压头之间的摩擦因数μ分别设为0和0.15。以SS304不锈钢的真实应力—应变曲线为输入参数,可得SS304不锈钢对应3种圆锥压头的仪器化压入加载、卸载曲线。
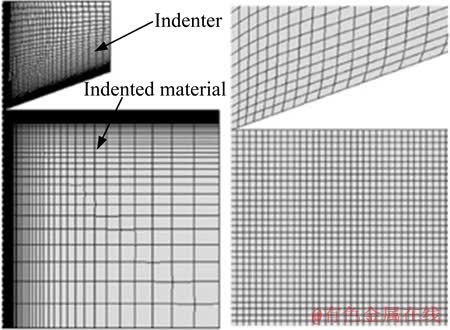
图1 压头与被测材料的有限元网格划分
Fig. 1 FEM mesh of indenter and indented material
利用高精度仪器化压入仪[30-31]结合面角为120°的四棱锥压头、Vickers压头、面角为172°的四棱锥压头对SS304不锈钢实施最大压入载荷设定为50N的仪器化压入实验,材料不同位置重复进行5次实验。图2所示为SS304不锈钢采用面角为120°的四棱锥压头5次实验测得的压入载荷—深度曲线和锥半角为62.9°圆锥压头数值仿真得到的压入载荷—深度曲线。
由图2可以看出,SS304不锈钢采用面角为120°的四棱锥压头5次实验测得的压入载荷—深度曲线基本重合;SS304不锈钢采用锥半角为62.9°的圆锥压头数值仿真得到的对应摩擦因数μ分别为0和0.15的压入载荷—深度曲线重合性较好;SS304不锈钢实验所得压入载荷—深度曲线和数值仿真所得压入载荷—深度曲线存在较大差别。
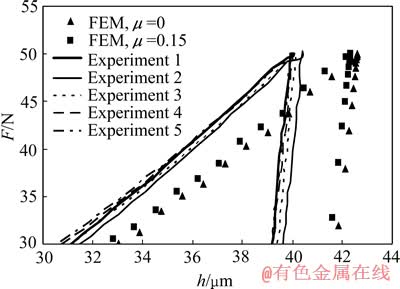
图2 面角为120°的四棱锥压头情况下SS304不锈钢实验及数值仿真所得压入载荷—深度曲线
Fig. 2 Experimental (four-sided pyramidal indenter with 120° included angle) and computational (62.9° conical indenter) indentation load—depth curves of SS304 stainless steel
SS304不锈钢采用锥半角为62.9°的圆锥压头数值仿真得到的对应摩擦因数μ分别为0和0.15的最大压入载荷相差1.26%,压入总功与弹性功的比值相差4.23%。这表明,对于锥半角为62.9°的圆锥压头,摩擦对压入总功与弹性功的比值仍存在一定影响。最大压入深度相等情况下,SS304不锈钢5次实验的最大压入载荷平均值和压入总功与弹性功的平均比值与摩擦因数μ为0和0.15的数值仿真结果的差别分别为16.97%和6.96%,15.5%和2.85%。这将严重限制锥半角为62.9°的圆锥压头在金属材料塑性参数识别方面的应用。上述结果也从侧面证明锥半角为60°的圆锥压头不适合用于金属材料塑性参数的识别。因此,只能选择锥角更大的金刚石压头以实现金属材料塑性参数的精确测试。
图3和4所示为SS304不锈钢采用Vickers压头和面角为172°的四棱锥压头5次仪器化压入实验测得的压入载荷—深度曲线和锥半角为70.3°和86.45°的圆锥压头仪器化压入数值仿真得到的压入载荷—深度曲线。
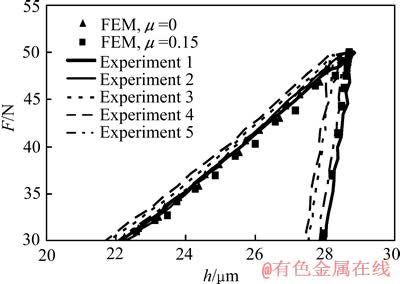
图3 Vickers压头情况下SS304不锈钢实验及数值仿真所得压入载荷—深度曲线
Fig. 3 Experimental (Vickers indenter) and computational (70.3° conical indenter) indentation load—depth curves of SS304 stainless steel
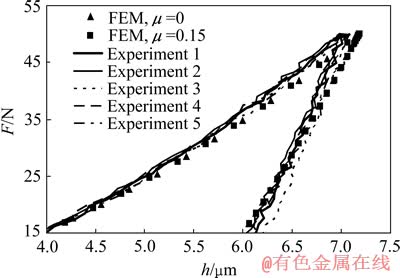
图4 面角为172°的四棱锥压头情况下SS304不锈钢实验及数值仿真所得压入载荷—深度曲线
Fig. 4 Experimental (four-sided pyramidal indenter with 172° included angle) and computational (86.45°conical indenter) indentation load—depth curves of SS304 stainless steel
由图3可以看出,SS304不锈钢采用Vickers压头5次实验测得的压入载荷—深度曲线基本重合;SS304不锈钢采用锥半角为70.3°的圆锥压头数值仿真得到的对应摩擦因数μ为0和0.15的压入载荷—深度曲线重合性较好;SS304不锈钢实验所得压入载荷—深度曲线和数值仿真所得压入载荷—深度曲线能够较好的重合。由图4可以看出,SS304不锈钢采用面角为172°的四棱锥压头5次实验测得的压入载荷—深度曲线基本重合;SS304不锈钢采用锥半角为86.45°的圆锥压头数值仿真得到的对应摩擦因数μ为0和0.15的压入载荷—深度曲线重合性较好;SS304不锈钢实验所得压入载荷—深度曲线和数值仿真所得压入载荷—深度曲线能够较好的重合。由此可知,Vickers压头和面角为172°的四棱锥压头排除了摩擦等因素对仪器化压入响应的影响,从而保证了实验所得压入载荷—深度曲线与数值仿真所得压入载荷—深度曲线的一致性。
鉴于上述结果,本文作者选择Vickers压头和面角为172°的四棱锥压头用于金属材料塑性参数的压入识别。
2 仪器化压入问题的量纲分析及有限元数值仿真
假设金属材料的真实应力—应变曲线由线弹性和Hollomon幂硬化函数组成,即
 (1)
(1)
式中: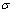 和
和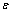 为真实应力和真实应变;E为弹性模量;
为真实应力和真实应变;E为弹性模量;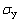 和
和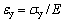 为屈服强度和屈服应变;n为应变硬化指数。
为屈服强度和屈服应变;n为应变硬化指数。
相关研究表明,对于确定角度的金刚石压头,存在多种具有不同屈服强度和应变硬化指数组合的材料,其仪器化压入加、卸载曲线几乎相同[32-33]。这些材料的真实应力—应变曲线绘制于同一直角坐标系时几乎通过同一个应力—应变数据点,该数据点所对应的应力和应变分别称为特征应力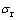 和特征应变
和特征应变 ,如图5所示。
,如图5所示。
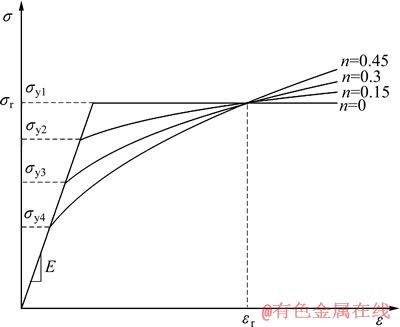
图5 特征应力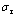 和特征应变
和特征应变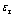 示意图
示意图
Fig. 5 Schematic illustration of representative stress and representative strain
根据仪器化压入载荷—深度曲线定义名义硬度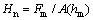 ,Fm为最大压入载荷,A(hm)为最大压入深度hm所对应的金刚石压头横截面积;压入总功Wt和弹性功We分别为金刚石压头在加载和卸载过程中所做的功,其数值等于加载曲线和卸载曲线与压入载荷—深度曲线横坐标所围面积;压入比功We/Wt为弹性功We与压入总功Wt的比值。
,Fm为最大压入载荷,A(hm)为最大压入深度hm所对应的金刚石压头横截面积;压入总功Wt和弹性功We分别为金刚石压头在加载和卸载过程中所做的功,其数值等于加载曲线和卸载曲线与压入载荷—深度曲线横坐标所围面积;压入比功We/Wt为弹性功We与压入总功Wt的比值。
假设金刚石压头为纯弹性体,其弹性模量为Ei,泊松比为 ,且金刚石压头与被测材料之间无摩擦。名义硬度
,且金刚石压头与被测材料之间无摩擦。名义硬度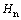 和压入比功We/Wt可表示为被测材料的弹性模量E、泊松比
和压入比功We/Wt可表示为被测材料的弹性模量E、泊松比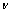 、屈服强度
、屈服强度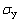 、应变硬化指数n、金刚石压头的弹性模量Ei和泊松比
、应变硬化指数n、金刚石压头的弹性模量Ei和泊松比 、压头角度
、压头角度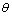 及最大压入深度hm的函数关系:
及最大压入深度hm的函数关系:
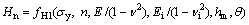 (2)
(2)
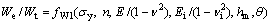 (3)
(3)
式中: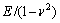 和
和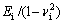 为被测材料和金刚石压头的平面应变弹性模量。
为被测材料和金刚石压头的平面应变弹性模量。
广泛使用的折合弹性模量为
 (4)
(4)
平面应变弹性模量之比为
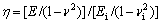 (5)
(5)
结合式(4)和式(5),式(2)和(3)可改写为
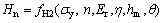 (6)
(6)
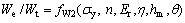 (7)
(7)
应用量纲 定理,式(6)和(7)可简化为
定理,式(6)和(7)可简化为
 (8)
(8)
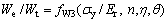 (9)
(9)
针对式(8)和(9),利用特征应力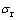 代替屈服强度
代替屈服强度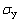 可得
可得
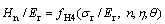 (10)
(10)
 (11)
(11)
根据式(10)和(11), 可表示为
可表示为
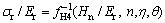 (12)
(12)
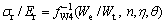 (13)
(13)
同理,特征应变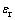 可表示为
可表示为
 (14)
(14)
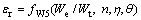 (15)
(15)
为获得式(12)~(15)的显式表达式,采用圆锥压头锥半角分别为70.3°和86.45°的轴对称模型对Vickers压头和面角为172°四棱锥压头仪器化压入广泛的纯金属和金属合金材料的压入响应进行数值仿真。金刚石压头的弹性模量Ei=1141 GPa,泊松比 =0.07。被测材料弹性模量E取值为70、200和400 GPa;屈服强度
=0.07。被测材料弹性模量E取值为70、200和400 GPa;屈服强度 取值范围为50 MPa~160 GPa;应变硬化指数
取值范围为50 MPa~160 GPa;应变硬化指数 取值为0、0.15、0.3和0.45;泊松比
取值为0、0.15、0.3和0.45;泊松比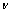 取固定值0.3。金刚石压头和被测材料的平面应变弹性模量之比
取固定值0.3。金刚石压头和被测材料的平面应变弹性模量之比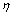 分别为0.0671、0.1917和0.3834。
分别为0.0671、0.1917和0.3834。
图6所示为圆锥压头锥半角为70.3°情况下平面应变弹性模量之比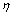 分别取0.0671、0.1917和0.3834所对应的特征应力
分别取0.0671、0.1917和0.3834所对应的特征应力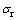 与折合弹性模量
与折合弹性模量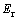 之比
之比 和压入比功
和压入比功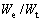 的关系。由图6可以看出,平面应变弹性模量之比
的关系。由图6可以看出,平面应变弹性模量之比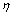 对
对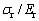 和
和 关系存在影响。这表明折合弹性模量
关系存在影响。这表明折合弹性模量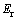 并不能精确反映金刚石压头和被测材料的联合弹性效应。为此,定义联合弹性模量
并不能精确反映金刚石压头和被测材料的联合弹性效应。为此,定义联合弹性模量 代替折合弹性模量
代替折合弹性模量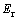 ,从而得到
,从而得到 和
和 的关系,如图7所示。显然,平面应变弹性模量之比
的关系,如图7所示。显然,平面应变弹性模量之比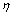 对
对 和
和 关系不构成影响。图8所示为特征应变
关系不构成影响。图8所示为特征应变 和压入比功
和压入比功 的关系。圆锥压头锥半角为86.45°情况下,对应于不同平面应变弹性模量之比
的关系。圆锥压头锥半角为86.45°情况下,对应于不同平面应变弹性模量之比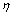 的
的 和
和 关系以及
关系以及 和
和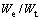 关系,如图9和10所示,其中联合弹性模量为
关系,如图9和10所示,其中联合弹性模量为
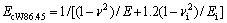 (16)
(16)
利用多项式函数对圆锥压头锥半角为70.3°和86.45°情况下的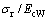 和
和 的关系以及
的关系以及 和
和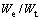 关系进行拟合,可得上述关系的解析表达式:
关系进行拟合,可得上述关系的解析表达式:
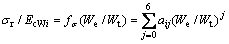 (17)
(17)
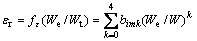 (18)
(18)
式中: ;i=1,2对应锥半角为70.3°和86.45°的圆锥压头;m=1,2,3对应平面应变弹性模量之比
;i=1,2对应锥半角为70.3°和86.45°的圆锥压头;m=1,2,3对应平面应变弹性模量之比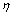 为0.0671、0.1917和0.3834。系数
为0.0671、0.1917和0.3834。系数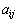 和
和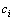 的取值见表1,系数
的取值见表1,系数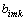 的取值见表2。
的取值见表2。
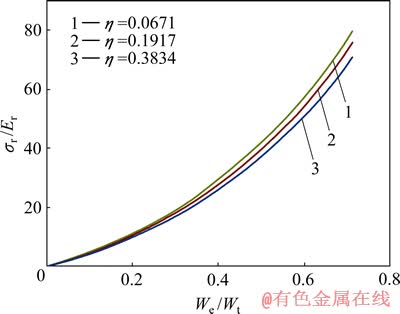
图6 圆锥压头锥半角为70.3°、不同平面应变弹性模量之比η的条件下σr/Er与We/Wt的关系
Fig. 6 Relationship between σr/Er and We/Wt at conical indenter of 70.3° and different η values
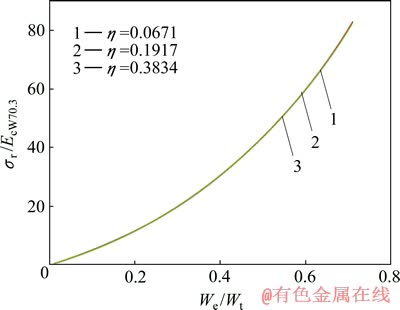
图7 圆锥压头锥半角为70.3°、不同平面应变弹性模量之比η的条件下σr/EcW70.3与We/Wt的关系
Fig. 7 Relationship between σr/EcW70.3 and We/Wt at conical indenter of 70.3° and different η values
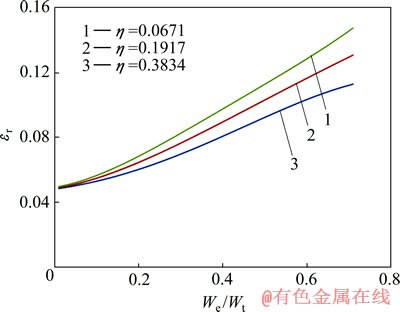
图8 圆锥压头锥半角为70.3°、不同平面应变弹性模量之比η的条件下εr与We/Wt的关系
Fig. 8 Relationship between εr and We/Wt at conical indenter of 70.3° and different η values
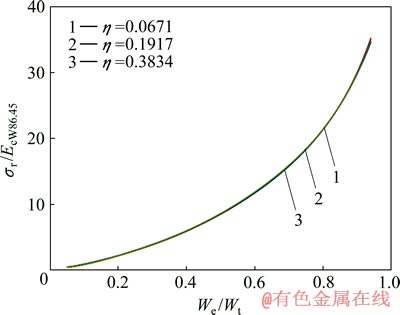
图9 圆锥压头锥半角为86.45°、不同平面应变弹性模量之比η的条件下σr/EcW86.45与We/Wt的关系
Fig. 9 Relationship between σr/EcW86.45 and We/Wt at conical indenter of 86.45° and different η values
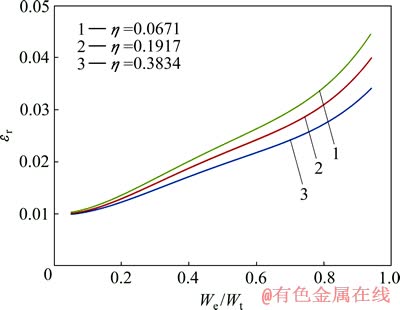
图10 圆锥压头锥半角为86.45°、不同平面应变弹性模量之比η 条件下εr与We/Wt的关系
Fig.10 Relationship between εr and We/Wt at conical indenter of 86.45° and different η values
图11和12所示为圆锥压头锥半角为70.3°情况下特征应力 与折合弹性模量Er之比
与折合弹性模量Er之比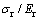 和名义硬度Hn与折合弹性模量Er之比Hn/Er的关系,及特征应变
和名义硬度Hn与折合弹性模量Er之比Hn/Er的关系,及特征应变 和名义硬度Hn与折合弹性模量Er之比Hn/Er的关系。由图11和12可以看出,平面应变弹性模量之比
和名义硬度Hn与折合弹性模量Er之比Hn/Er的关系。由图11和12可以看出,平面应变弹性模量之比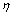 对
对 和
和 关系存在影响。定义联合弹性模量
关系存在影响。定义联合弹性模量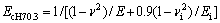 代替折合弹性模量Er,从而得到对应于不同平面应变弹性模量之比
代替折合弹性模量Er,从而得到对应于不同平面应变弹性模量之比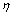 的
的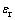 与
与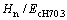 关系,如图13所示。显然,平面应变弹性模量之比
关系,如图13所示。显然,平面应变弹性模量之比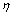 对
对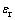 和
和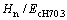 关系不构成影响。圆锥压头锥半角为86.45°情况下,对应于不同平面应变弹性模量之比
关系不构成影响。圆锥压头锥半角为86.45°情况下,对应于不同平面应变弹性模量之比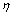 的特征应力
的特征应力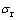 与折合弹性模量Er之比
与折合弹性模量Er之比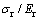 和名义硬度Hn与折合弹性模量Er之比
和名义硬度Hn与折合弹性模量Er之比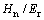 的关系,及特征应变
的关系,及特征应变 和名义硬度Hn与联合弹性模量
和名义硬度Hn与联合弹性模量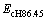 之比
之比 的关系,如图14和15所示,其中联合弹性模量
的关系,如图14和15所示,其中联合弹性模量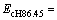
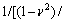
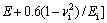 。显然,平面应变弹性模量之比
。显然,平面应变弹性模量之比 对
对 和
和 关系不构成影响。
关系不构成影响。
表1 系数aij和ci的取值
Table 1 Values of aij and ci

表2 系数bimk的取值
Table 2 Values of bimk
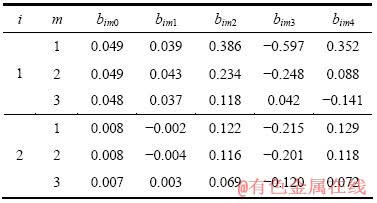
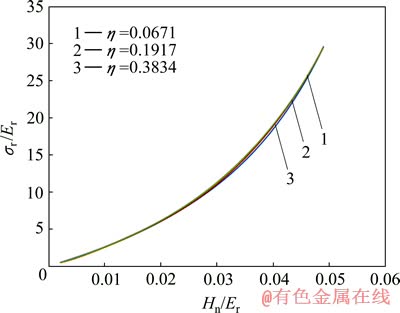
图11 圆锥压头锥半角为70.3°、不同平面应变弹性模量之比η条件下σr/Er和Hn/Er的关系
Fig. 11 Relationship between σr/Er and Hn/Er at conical indenter of 70.3° and different η values
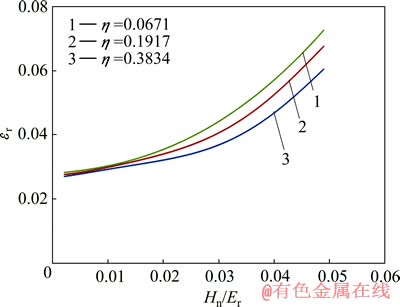
图12 圆锥压头锥半角为70.3°、不同平面应变弹性模量之比η条件下εr和Hn/Er的关系
Fig. 12 Relationship between εr and Hn/Er at conical indenter of 70.3° and different η values
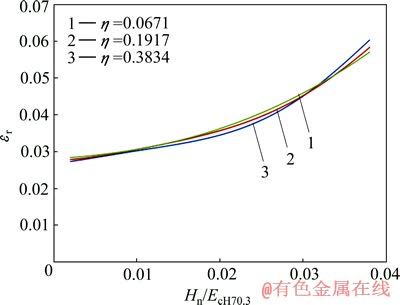
图13 圆锥压头锥半角为70.3°、不同平面应变弹性模量之比η条件下εr和Hn/EcH70.3的关系
Fig. 13 Relationship between εr and Hn/EcH70.3 at conical indenter of 70.3° and different η values
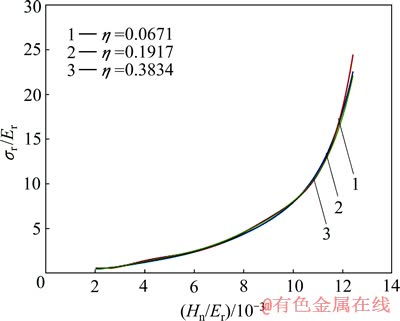
图14 圆锥压头锥半角为86.45°、不同平面应变弹性模量之比η条件下σr/Er和H n/Er的关系
Fig. 14 Relationship between σr/Er and H n/Er at conical indenter of 86.45° and different η values
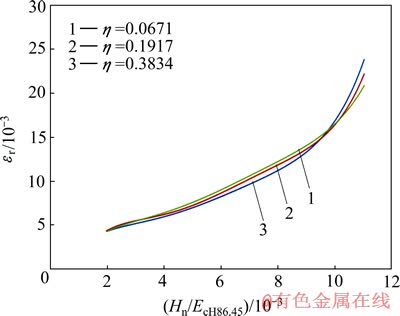
图15 圆锥压头锥半角为86.45°、不同平面应变弹性模量之比η条件下εr和Hn/EcH86.45的关系
Fig. 15 Relationship between εr and Hn/EcH86.45 at conical indenter of 86.45° and different η values
折合弹性模量Er可看做一种特殊形式的联合弹性模量Ec,这样,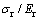 和
和 关系转化为
关系转化为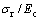 和
和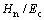 关系。利用多项式函数对圆锥压头锥半角为70.3°和86.45°情况下的
关系。利用多项式函数对圆锥压头锥半角为70.3°和86.45°情况下的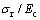 和
和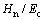 关系以及
关系以及 和
和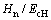 关系进行拟合,可得上述关系的解析表达式:
关系进行拟合,可得上述关系的解析表达式:
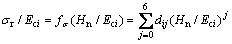 (19)
(19)
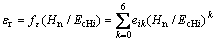 (20)
(20)
式中: ,
,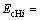
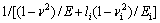 ;i=1,2对应锥半角为70.3°和86.45°的圆锥压头。系数
;i=1,2对应锥半角为70.3°和86.45°的圆锥压头。系数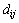 和系数
和系数 的取值见表3,系数
的取值见表3,系数 和系数
和系数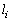 的取值见表4。
的取值见表4。
表3 系数dij和gi的取值
Table 3 Values of dij and gi

表4 系数eik和li的取值
Table 4 Values of eik and li
3 方法的建立
根据式(17)和(18),建立基于压入比功We/Wt的金属材料塑性参数仪器化压入识别方法,该方法由以下步骤组成。
1) 利用高精度仪器化压入仪和Vickers压头(Berkovich压头或者锥半角为70.3°的圆锥压头)对被测材料实施最大压入深度大于3 μm的仪器化压入测试,获得压入载荷—深度曲线。根据该曲线计算名义硬度Hn70.3和压入比功(We/Wt)70.3,进而根据“纯能量法”[34-35]得到被测材料的弹性模量E,从而确定联合弹性模量EcW70.3及平面应变弹性模量之比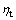 。
。
2) 将联合弹性模量EcW70.3和压入比功(We/Wt)70.3代入关系式(17),可得特征应力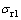 。
。
3) 将压入比功(We/Wt)70.3代入关系式(18),可得与平面应变弹性模量之比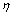 取0.0671、0.1917和0.3834相对应的特征应变
取0.0671、0.1917和0.3834相对应的特征应变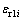 (i=1, 2, 3)。应用拉格朗日插值可得与平面应变弹性模量之比
(i=1, 2, 3)。应用拉格朗日插值可得与平面应变弹性模量之比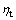 相对应的特征应变
相对应的特征应变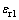 。
。
4) 将步骤1)中的Vickers压头(Berkovich压头或者锥半角为70.3°的圆锥压头)更换为面角为172°的四棱锥压头(锥半角为86.45°的圆锥压头),重复执行步骤1到步骤3的操作,获得与面角为172°的四棱锥压头相对应的特征应力 和特征应变
和特征应变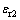 。
。
5) 利用Hollomon幂硬化函数对两组特征应变—特征应力数据点 和
和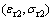 进行拟合,结合弹性模量识别结果E,可得被测材料的屈服强度
进行拟合,结合弹性模量识别结果E,可得被测材料的屈服强度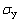 和应变硬化指数n,进而可确定条件屈服强度
和应变硬化指数n,进而可确定条件屈服强度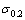 。
。
根据式(19)和(20),建立基于名义硬度Hn的金属材料塑性参数仪器化压入识别方法,该方法由以下步骤组成。
1) 利用高精度仪器化压入仪和Vickers压头(Berkovich压头或者锥半角为70.3°的圆锥压头)对被测材料实施最大压入深度大于3 μm的仪器化压入测试,获得压入载荷—深度曲线。根据该曲线计算名义硬度Hn70.3和压入比功(We/Wt)70.3,进而根据“纯能量法”得到被测材料的弹性模量E,从而确定联合弹性模量Ec70.3和EcH70.3。
2) 将名义硬度Hn70.3和联合弹性模量Ec70.3代入关系式(19),可得特征应力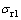 。
。
3) 将名义硬度Hn70.3和联合弹性模量EcH70.3代入关系式(20),可得特征应变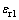 。
。
4) 将步骤1)中的Vickers压头(Berkovich压头或者锥半角为70.3°的圆锥压头)更换为面角为172°的四棱锥压头(锥半角为86.45°的圆锥压头),重复执行步骤1到步骤3的操作,获得与面角为172°的四棱锥压头相对应的特征应力 和特征应变
和特征应变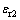 。
。
5) 利用Hollomon幂硬化函数对两组特征应变—特征应力数据点 和
和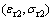 进行拟合,结合弹性模量识别结果E,可得被测材料的屈服强度
进行拟合,结合弹性模量识别结果E,可得被测材料的屈服强度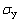 和应变硬化指数n,进而可确定条件屈服强度
和应变硬化指数n,进而可确定条件屈服强度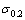 。
。
4 金属材料塑性参数识别方法精度分析
采用工程上常用的金属结构材料对本研究中建立的金属材料塑性参数仪器化压入识别方法的识别精度进行分析。假设该类材料为标准幂硬化材料,且针对Vickers压头的仪器化压入比功(We/Wt)70.3处于0.04到0.4之间。定义金属材料屈服强度识别误差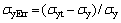 ,
, 为屈服强度的识别结果,
为屈服强度的识别结果,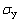 为屈服强度的真实值;定义金属材料条件屈服强度识别误差
为屈服强度的真实值;定义金属材料条件屈服强度识别误差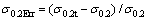 ,
,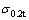 为条件屈服强度的识别结果,
为条件屈服强度的识别结果,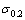 为条件屈服强度的真实值;定义金属材料应变硬化指数绝对识别误差
为条件屈服强度的真实值;定义金属材料应变硬化指数绝对识别误差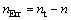 ,
, 为应变硬化指数的识别结果,n为应变硬化指数的真实值。
为应变硬化指数的识别结果,n为应变硬化指数的真实值。
4.1 基于压入比功We/Wt的金属材料塑性参数仪器化压入识别方法精度分析
图16所示为金属材料屈服强度识别误差 的分布。总体上看,金属材料屈服强度识别误差
的分布。总体上看,金属材料屈服强度识别误差 分布在-5%~15%之间,应变硬化指数n为0和0.45的金属材料屈服强度识别误差为屈服强度识别误差带的下边界和上边界。由图16可以看出,随着平面应变弹性模量之比
分布在-5%~15%之间,应变硬化指数n为0和0.45的金属材料屈服强度识别误差为屈服强度识别误差带的下边界和上边界。由图16可以看出,随着平面应变弹性模量之比 的增加,屈服强度识别误差带的宽度增加,误差带相对于坐标横轴上移。这说明弹性模量越大的材料,屈服强度的识别误差越大。随着压入比功
的增加,屈服强度识别误差带的宽度增加,误差带相对于坐标横轴上移。这说明弹性模量越大的材料,屈服强度的识别误差越大。随着压入比功 的增加,屈服强度识别误差带的宽度减小。
的增加,屈服强度识别误差带的宽度减小。
图17所示为金属材料应变硬化指数绝对识别误差nErr的分布。总体上看,金属材料应变硬化指数绝对识别误差nErr分布在-0.05~0.08之间,应变硬化指数n为0和0.45的金属材料应变硬化指数绝对识别误差为应变硬化指数绝对识别误差带的上边界和下边界,且应变硬化指数n为0.15和0.3的金属材料应变硬化指数绝对识别误差明显小于应变硬化指数n为0 和0.45的金属材料应变硬化指数绝对识别误差。平面应变弹性模量之比 对应变硬化指数绝对识别误差带的宽度和相对于坐标横轴的位置几乎不构成影响。
对应变硬化指数绝对识别误差带的宽度和相对于坐标横轴的位置几乎不构成影响。
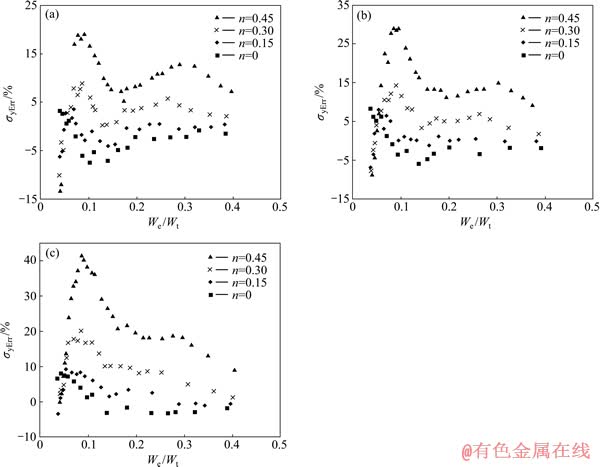
图16 金属材料屈服强度识别误差σyErr的 分布
Fig. 16 Illustration relative determination error of metal field strength (σyErr) at η= 0.0671(a), η=0.1917(b), η=0.3834(c)
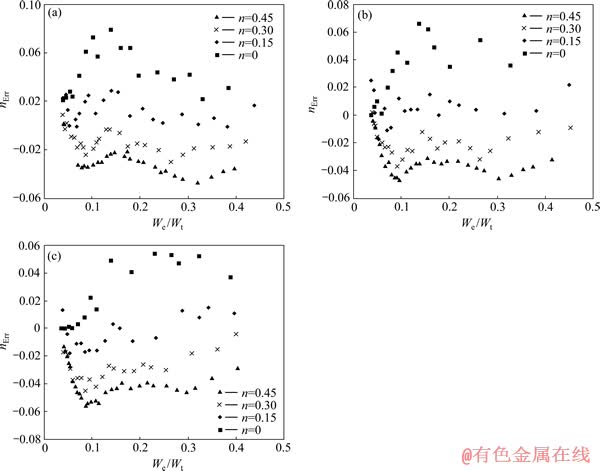
图17 金属材料应变硬化指数绝对识别误差nErr的分布
Fig. 17 Illustration of absolution determination error of metal strain hardening exponent (nErr) at η=0.0671(a), η=0.1917(b), η=0.3834(c)
图18所示为金属材料条件屈服强度识别误差 的分布。总体上看,金属材料条件屈服强度识别误差
的分布。总体上看,金属材料条件屈服强度识别误差 分布在-5%~5%之间,应变硬化指数n为0和0.45的金属材料条件屈服强度识别误差为条件屈服强度识别误差带的下边界和上边界。金属材料条件屈服强度识别误差带的宽度明显小于屈服强度识别误差带的宽度,这表明该方法在识别金属材料条件屈服强度方面更具有优势。
分布在-5%~5%之间,应变硬化指数n为0和0.45的金属材料条件屈服强度识别误差为条件屈服强度识别误差带的下边界和上边界。金属材料条件屈服强度识别误差带的宽度明显小于屈服强度识别误差带的宽度,这表明该方法在识别金属材料条件屈服强度方面更具有优势。
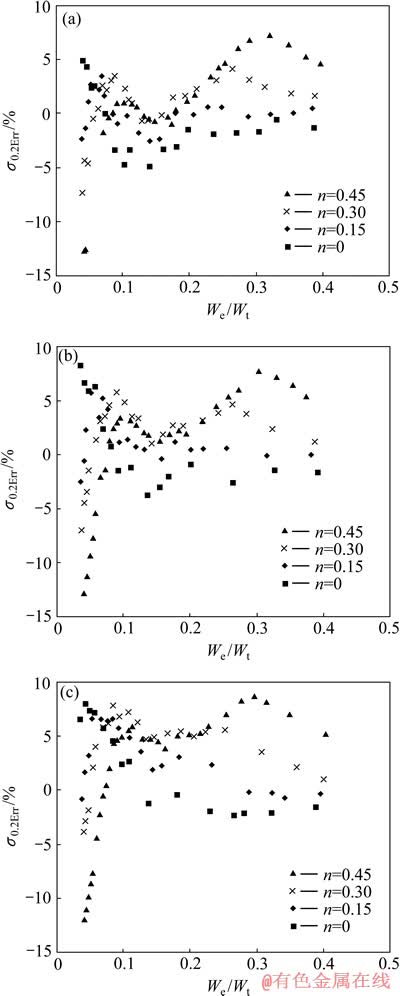
图18 金属材料条件屈服强度识别误差σ0.2Err的分布
Fig. 18 Illustration of relative determination error of metal yield strength (σ0.2Err) at η=0.0671(a), η=0.1917(b), η=0.3834(c)
4.2 基于名义硬度Hn的金属材料塑性参数仪器化压入识别方法精度分析
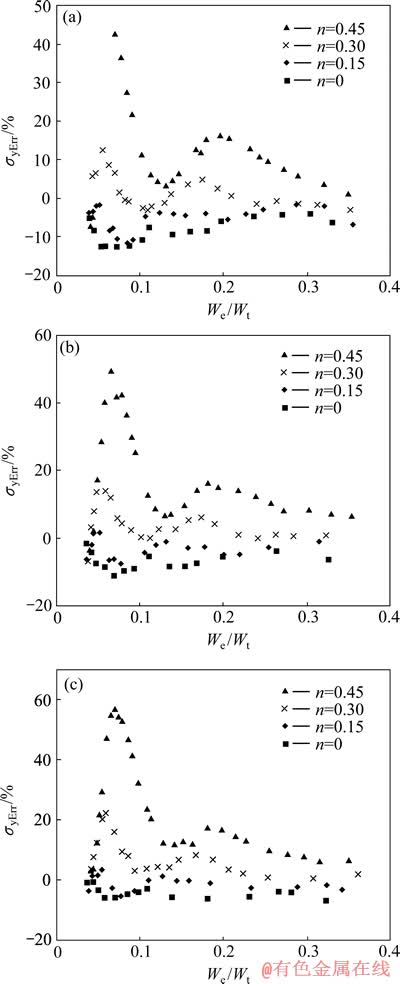
图19 金属材料屈服强度识别误差σyErr的分布
Fig. 19 Illustration of relative determination error of metal yield strength (σyErr) at η=0.0671(a), η=0.1917(b), η=0.3834(c)
图19所示为金属材料屈服强度识别误差 的分布。总体上看,金属材料屈服强度识别误差
的分布。总体上看,金属材料屈服强度识别误差 分布在-10%~15%之间,应变硬化指数n为0和0.45的金属材料屈服强度识别误差为屈服强度识别误差带的下边界和上边界。平面应变弹性模量之比
分布在-10%~15%之间,应变硬化指数n为0和0.45的金属材料屈服强度识别误差为屈服强度识别误差带的下边界和上边界。平面应变弹性模量之比 对屈服强度识别误差带的宽度和相对于坐标横轴的位置几乎不构成影响。随着压入比功
对屈服强度识别误差带的宽度和相对于坐标横轴的位置几乎不构成影响。随着压入比功 的逐渐增加,屈服强度识别误差带的宽度有较为明显的变化,总体来看,识别误差带的宽度逐渐变小。
的逐渐增加,屈服强度识别误差带的宽度有较为明显的变化,总体来看,识别误差带的宽度逐渐变小。
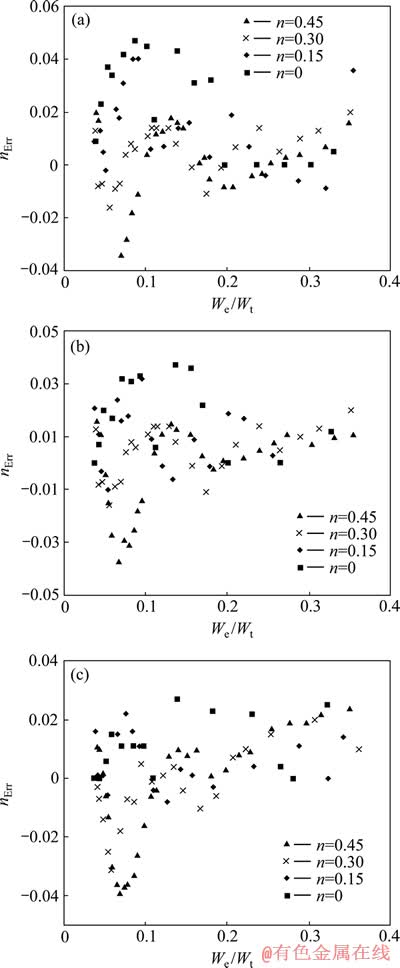
图20 金属材料应变硬化指数绝对识别误差nErr的分布
Fig. 20 Illustration of absolute determination error of metal strain hardening exponent (nErr) at η=0.0671(a), η=0.1917(b), η=0.3834(c)
图20所示为金属材料应变硬化指数绝对识别误差nErr的分布。总体上看,金属材料应变硬化指数绝对识别误差nErr分布在-0.01~0.04之间,且应变硬化指数n为0、0.15、0.3和0.45的金属材料应变硬化指数绝对识别误差相互交叉。随着压入比功We/Wt的增加,识别误差带的宽度变小。
图21所示为金属材料条件屈服强度识别误差 的分布。总体上看,金属材料条件屈服强度识别误差
的分布。总体上看,金属材料条件屈服强度识别误差 分布在-10%~10%之间,应变硬化指数n为0和0.45的金属材料条件屈服强度识别误差为条件屈服强度识别误差带的下边界和上边界。金属材料条件屈服强度识别误差带的宽度明显小于屈服强度识别误差带的宽度,这表明该方法在识别金属材料条件屈服强度方面更具优势。平面应变弹性模量之比
分布在-10%~10%之间,应变硬化指数n为0和0.45的金属材料条件屈服强度识别误差为条件屈服强度识别误差带的下边界和上边界。金属材料条件屈服强度识别误差带的宽度明显小于屈服强度识别误差带的宽度,这表明该方法在识别金属材料条件屈服强度方面更具优势。平面应变弹性模量之比 和压入比功
和压入比功 对条件屈服强度识别误差带的宽度和相对于坐标横轴的位置几乎不构成影响。
对条件屈服强度识别误差带的宽度和相对于坐标横轴的位置几乎不构成影响。
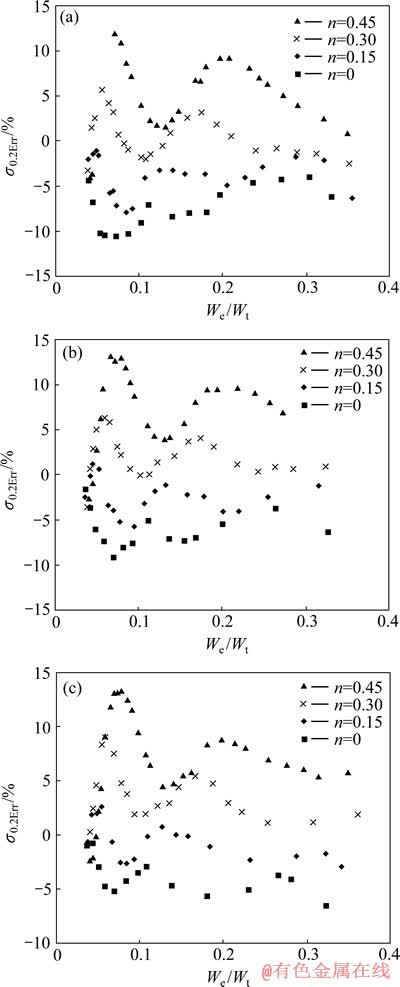
图21 金属材料条件屈服强度识别误差σ0.2Err的分布
Fig. 21 Illustration of relative determination error of metal yield strength (σ0.2Err) at η=0.0671(a), η=0.1917(b), η=0.3834(c)
基于压入比功We/Wt的金属材料塑性参数仪器化压入识别方法和基于名义硬度Hn的金属材料塑性参数仪器化压入识别方法的精度分析结果,相对于识别金属材料的屈服强度 ,本研究所建立的金属材料塑性参数识别方法在识别条件屈服强度
,本研究所建立的金属材料塑性参数识别方法在识别条件屈服强度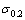 方面更具有优势。因此,确定条件屈服强度
方面更具有优势。因此,确定条件屈服强度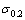 为金属材料塑性参数识别的目标参数。基于压入比功We/Wt的金属材料塑性参数仪器化压入识别方法在条件屈服强度
为金属材料塑性参数识别的目标参数。基于压入比功We/Wt的金属材料塑性参数仪器化压入识别方法在条件屈服强度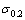 识别方面较基于名义硬度Hn的金属材料塑性参数仪器化压入识别方法优势明显。
识别方面较基于名义硬度Hn的金属材料塑性参数仪器化压入识别方法优势明显。
5 实验验证
本研究中建立金属材料塑性参数仪器化压入识别方法时假设金属材料为标准幂硬化材料,而实际上,大多数金属材料的真实应力—应变曲线并不严格符合标准幂硬化形式。因此,有必要对本研究提出的金属材料塑性参数识别方法的有效性进行实验验证。选择6061铝合金、S45C碳钢、SS316不锈钢、SS304不锈钢和黄铜5种金属材料用于检验方法的有效性。利用高精度仪器化压入仪和Vickers压头及面角为172°的四棱锥压头对上述5种金属材料实施最大压入载荷为50 N的仪器化压入实验。为保证实验结果的可靠性,每种压头在材料表面不同位置重复进行5次实验。图22所示为Vickers压头及面角为172°的四棱锥压头对6061铝合金、S45C碳钢、SS316不锈钢、SS304不锈钢和黄铜5种金属材料进行5次压入实验得到的压入载荷—深度曲线。
表5所列为5种金属材料对应上述两种金刚石压头的5次压入实验结果均值,其中Et70.3为利用“纯能量法”识别的金属材料的弹性模量。表6所列为分别应用基于压入比功We/Wt的金属材料塑性参数仪器化压入识别方法和基于名义硬度Hn的金属材料塑性参数仪器化压入识别方法确定的5种金属材料的塑性参数。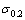 和
和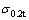 为金属材料条件屈服强度单轴拉伸试验测试结果和仪器化压入实验识别结果,
为金属材料条件屈服强度单轴拉伸试验测试结果和仪器化压入实验识别结果, 为条件屈服强度识别误差,
为条件屈服强度识别误差,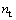 为应变硬化指数的识别结果。
为应变硬化指数的识别结果。
总体来看,5种金属材料条件屈服强度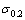 的识别结果小于真实值,是对真实值的保守估计。5种金属材料条件屈服强度识别误差为-17.5%~4%,基本满足工程需要,验证本研究提出的金属材料塑性参数仪器化压入识别方法的有效性。基于压入比功We/Wt 识别5种金属材料条件屈服强度的误差水平低于基于名义硬度Hn识别结果的误差水平,这一点与识别方法精度分析结果相符合。
的识别结果小于真实值,是对真实值的保守估计。5种金属材料条件屈服强度识别误差为-17.5%~4%,基本满足工程需要,验证本研究提出的金属材料塑性参数仪器化压入识别方法的有效性。基于压入比功We/Wt 识别5种金属材料条件屈服强度的误差水平低于基于名义硬度Hn识别结果的误差水平,这一点与识别方法精度分析结果相符合。
表5 金属材料仪器化压入实验测试结果
Table 5 Average values of experimental parameters
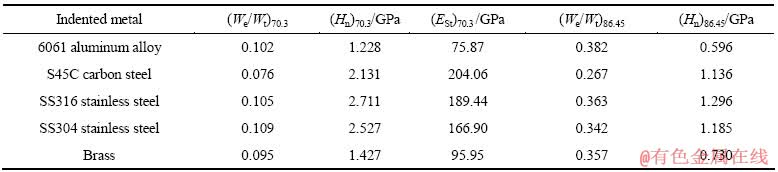
表6 金属材料塑性参数仪器化压入识别结果
Table 6 Plastic parameters determined by instrumented indentation
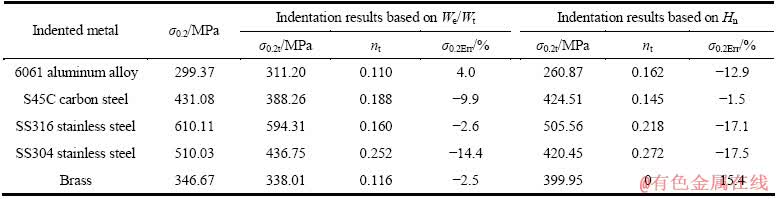
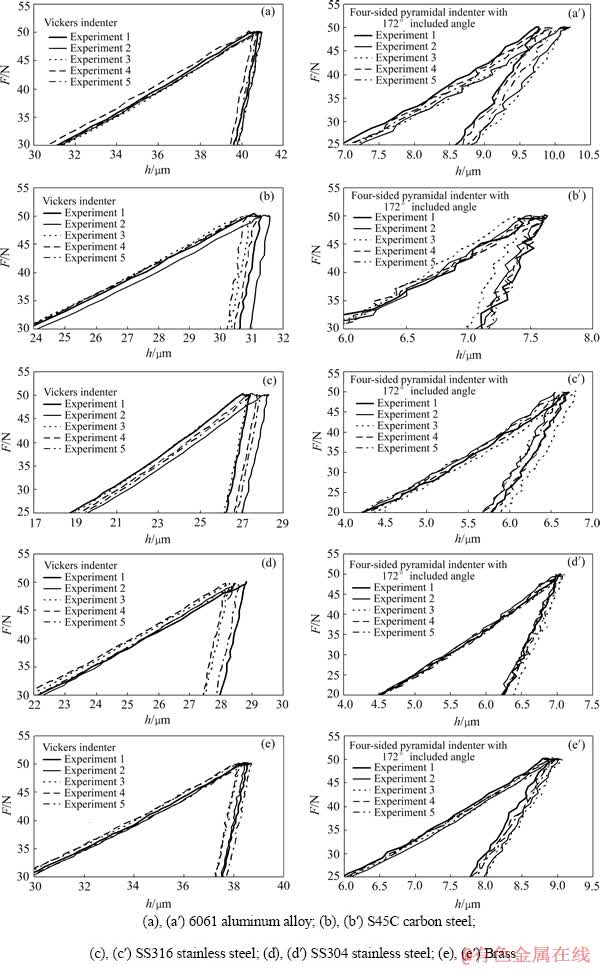
图22 5种金属材料仪器化压入载荷—深度曲线
Fig. 22 Experimental indentation load—depth curves (Vickers indenter and four-sided pyramidal indenter with 172° included angle)
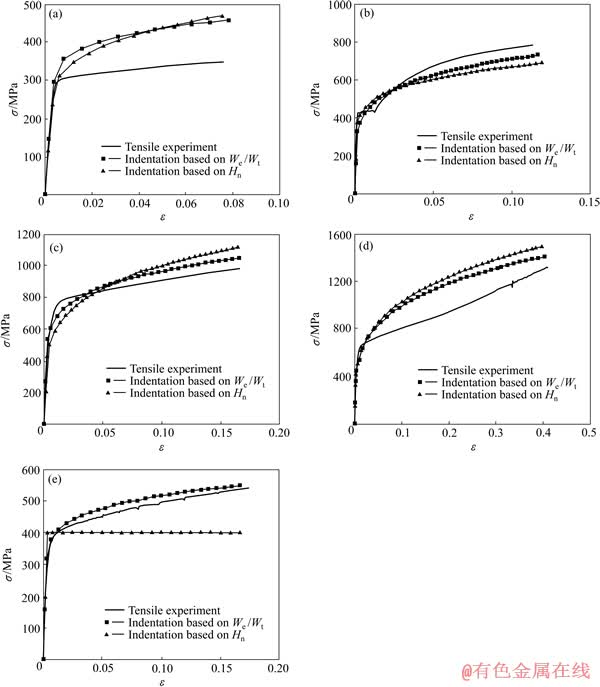
图23 5种金属材料仪器化压入实验所得真实应力—应变曲线与单轴拉伸实验所得真实应力—应变曲线
Fig. 23 True stress—strain curves obtained by instrumented indentation versus tensile true stress—strain curves of 6061 aluminum alloy(a), S45C carbon steel(b); SS316 stainless steel(c), SS304 stainless steel(d) and brass(e)
为了更直观地说明5种金属材料塑性参数识别结果与单轴拉伸试验测试结果的差别,将仪器化压入实验得到的5种金属材料的真实应力—应变曲线与单轴拉伸试验所得真实应力—应变曲线放置于同一直角坐标系下,如图23所示。
6 结论
1) 锥半角小于62.9°的圆锥压头及具有相同面积函数的棱锥压头不适用于金属材料塑性参数的压入识别;锥半角为70.3°、86.45°的圆锥压头及具有面积函数的Vickers压头、面角为172°的四棱锥压头可以满足金属材料塑性参数识别的需要。
2) 金属材料塑性参数仪器化压入识别方法精度分析表明,条件屈服强度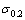 的识别精度明显高于屈服强度
的识别精度明显高于屈服强度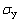 的的识别精度。考虑到工程实际应用,确定将条件屈服强度
的的识别精度。考虑到工程实际应用,确定将条件屈服强度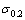 和应变硬化指数n作为金属材料塑性参数识别的目标参数。
和应变硬化指数n作为金属材料塑性参数识别的目标参数。
3) 6061铝合金、S45C碳钢、SS316不锈钢、SS304不锈钢和黄铜5种金属材料的条件屈服强度识别误差为-17.5%~4%,基本满足工程需要,验证了本研究提出的金属材料塑性参数仪器化压入识别方法的有效性。
REFERENCES
[1] OLIVER W C, PHARR G M. An improved technique for determining hardness and elastic-modulus using load and displacement sensing indentation experiments[J]. Journal of Materials Research, 1992, 7(6): 1564-1583.
[2] FISCHER-CRIPPS A C. Nanoindentation[M]. New York: Springer-Verlag, 2004.
[3] ZHANG T H, FENG Y H, YANG R, JIANG P. A method to determine fracture toughness using cube-corner indentation[J]. Scripta Materialia, 2010, 62(4): 199-201.
[4] TRICOTEAUX A, DUARTE G, CHICOT D, BOURHIS L, BEMPORAD E, LESAGE J. Depth-sensing indentation modeling for determination of elastic modulus of thin films[J]. Mechanics of Materials, 2010, 42(2): 166-174.
[5] 任明星, 李邦盛, 杨 闯, 傅恒志. 纳米压痕法测定微铸件硬度及弹性模[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2008, 18(2): 231-236.
RENG Ming-xing, LI Bang-shen, YANG Chuang, FU Heng-zhi. Hardness and elastic modulus of microcastings by nanoindentation[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2008, 18(2): 231-236.
[6] 崔 航, 陈怀宁, 陈 静, 黄春玲, 吴昌忠. 球形压痕法评价材料屈服强度和应变硬化指数的有限元分析[J]. 金属学报, 2009, 45(2): 189-194.
CUI Hang, CHEN Huai-ning, CHEN Jing, HUANG Chun-ling, WU Chang-zhong. FEA of evaluating material yield strength and strain hardening exponent using a spherical indentation[J]. Acta Metallurgica Sinica, 2009, 45(2): 189-194.
[7] 马德军. 材料弹性模量的仪器化压入测试方法[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2010, 20(12): 2336-2343.
MA De-jun. Method for determining elastic modulus by instrumented indentation test[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2010, 20(12): 2336-2343.
[8] 宋仲康, 马德军, 郭俊宏, 陈 伟. 一种改进的纳米压入测试方法[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2012, 22(2): 520-525.
SONG Zhong-kang, MA De-jun, GUO Jun-hong, CHEN Wei. A modified method of nanoindentation testing method[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2012, 22(2): 520-525.
[9] CHENG Y T, CHENG C M. Can stress-strain relationships be obtained from indentation curves using conical and pyramidal indenters?[J]. Journal of Materials Research, 1999, 14(9): 3493-3496.
[10] FUTAKAWA M, WAKUI T, TANABE Y, LOKA I. Identification of the constitutive equation by the indentation technique using plural indenters with different apex angles[J]. Journal of Materials Research, 2001, 16(8): 2283-2292.
[11] DAO M, CHOLLACOOP N, VAN K J, VENKATESH T A, SURESH S. Computational modelling of the forward and reverse problems in instrumented sharp indentation[J]. Acta Materialia, 2001, 49: 3899-3918.
[12] CHOLLACOOP N, DAO M, SURESH S. Depth-sensing instrumented indentation with dual sharp indenters[J]. Acta Materialia, 2003, 51: 3713-3729.
[13] CAO Y P, QIAN X Q, LU J, YAO Z H. An energy-based method to extract plastic properties of metal materials from conical indentation tests[J]. Journal of Materials Research, 2005, 20(5): 1194-1206.
[14] LUO J, LIN J. A study on the determination of plastic properties of metals by instrumented indentation using two sharp indenters[J]. International Journal of Solids and Structures, 2007, 44(18/19): 5803-5817.
[15] HEINRICH C, WAAS AM, WINEMAN A S. Determination of material properties using nanoindentation and multiple indenter tips[J]. International Journal of Solids and Structures, 2009, 46: 364-376.
[16] HUANG Y L, LIU X F, ZHOU Y C, MA Z S, LU C S. Mathematical analysis on the uniqueness of reverse algorithm for measuring elastic-plastic properties by sharp indentation[J]. Journal of Materials Science & Technology, 2011, 27(7): 577-584.
[17] MA Z S, ZHOU Y C, LONG S G, LU C S. A new method to determine the elastoplastic properties of ductile materials by conical indentation[J]. Science China: Physics Mechanics & Astronomy, 2012, 55: 1032-1036.
[18] HASANOV A, MURADOGLU Z. Fast inversion algorithm for identification of elastoplastic properties of power hardening materials from limited spherical indentation tests[J]. International Journal of Non-Linear Mechanics, 2012, 47(5): 526-536.
[19] TABOR D. The hardness of metals[M]. Oxford: Clarendon Press, 1951.
[20] DICARLA A, YANG H T, CHANDRASEKAR S. Prediction of stress—strain relation using cone indentation: Effect of friction[J]. International Journal of Numerical Method Engineering, 2004, 60(3): 661-674.
[21] HARSONA E, SWADDIWUDHIPONG S, LIU Z S. The effect of friction on indentation test results[J]. Modeling and Simulation in Materials Science and Engineering, 2008, 16(6): 1-11.
[22] BUCAILLE J L, STAUSS S, FELDER E, MICHLER J. Determination of plastic properties of metals by instrumented indentation using different sharp indenters[J]. Acta Materialia, 2003, 51(6): 1663-1678.
[23] SWADDIWUDHIPONG S, THO K K, LIU Z S, ZENG K. Material characterization based on dual indenters[J]. International Journal of Solids and Structures, 2005, 42: 69-83.
[24] YAN J, KARLSSON A M, CHEN X. Determining plastic properties of a material with residual stress by using conical indentation[J]. International Journal of Solids and Structures, 2007, 44: 3720-3737.
[25] LAN H Z, VENKATESH T A. Determination of the elastic and plastic properties of materials through instrumented indentation with reduced sensitivity[J]. Acta Materialia, 2007, 55: 2025-2041.
[26] LE M Q. A computational study on the instrumented sharp indentations with dual indenters[J]. International Journal of Solids and Structures, 2008, 45: 2818-2835.
[27] LE M Q. Improved reverse analysis for material characterization with dual sharp indenters[J]. International Journal of Solids and Structures, 2011, 48: 1600-1609.
[28] 马德军. 材料力学性能仪器化压入测试原理[M]. 北京: 国防工业出版社, 2010.
MA De-jun. Principles of measuring mechanical properties of materials by instrumented indentation[M]. Beijing: National Defense Industry Press, 2010.
[29] PELLEETIER H, KRIER J, CORNET. Limits of using bilinear stress—strain curve for finite element modeling of nanoindentation response on bulk materials[J]. Thin Solid Films, 2000, 379(1): 147-155.
[30] 马德军, 郭俊宏, 陈 伟, 宋仲康. 高精度仪器化压入仪设计与应用[J]. 仪器仪表学报, 2012, 33(8): 1889-1897.
MA De-jun, GUO Jun-hong, CHEN Wei, SONG Zhong-kang. Design and application of high accuracy instrumented indentation tester[J]. Chinese Journal of Scientific Instrument, 2012, 33(8): 1889-1897.
[31] 马德军, 宋仲康, 郭俊宏, 陈 伟. 一种高精度压入仪及金刚石压头压入试样深度的计算方法: 中国专利, 201110118464.9[P]. 2011-05-09.
MA De-jun, SONG Zhong-kang, GUO Jun-hong, CHEN Wei. High accuracy instrumented indentation tester and method for determining the indentation depth: China. 201110118464.9 [P]. 2011-05-09.
[32] CHEN X, OGASAWARA N, ZHAO M H, CHIBA N. On the uniqueness of measuring elastoplastic properties from indentation: The indistinguishable mystical materials[J]. Journal of Mechanics and Physics of Solids, 2007, 55: 1618-1660.
[33] OGASAWARA N, CHIBA N, CHEN X. Representative strain of indentation analysis[J]. Journal of Materials Research, 2005, 20(8): 2225-2234.
[34] MA D, ONG C W. Analytical relationship among nominal hardness, reduced Young’s modulus, the work of indentation, and strain hardening exponent[J]. Journal of Materials Science, 2010, 45(9): 2530-2533.
[35] MA D, ONG C W. Further analysis of energy-based indentation relationship among Young’s modulus, nominal hardness, and indentation work[J]. Journal of Materials Research, 2010, 25(6): 1131-1136.
(编辑 李艳红)
收稿日期:2013-07-22;修订日期:2013-12-25
通信作者:马德军,教授,博士;电话:010-66717048;传真:010-66717048;E-mail: dejunma@yahoo.com

