文章编号:1004-0609(2014)05-1311-08
铝合金基体上含化学镀过渡层的二氧化锆热障涂层失效机制
陆冠雄1, 2,郝利军1, 2,刘 彻1, 2,叶福兴1, 2
(1. 天津大学 材料科学与工程学院,天津 300072;
2. 天津大学 天津市现代连接技术重点实验室,天津 300072)
摘 要:为了缓解涂层和基体之间的热失配应力,采用化学镀方法在2A70铝合金表面上制备Ni-P和Ni-Cu-P过渡层;然后在镀层表面依次制备CoNiCrAlY粘结层和ZrO2-8%Y2O3(8YSZ)陶瓷层(质量分数),获得复合热障涂层;并采用热循环方法评定该涂层体系的抗热震性能。结果表明,采用Ni-P镀层和Ni-Cu-P镀层作为过渡层的试样的热震寿命分别约为1000次和500次;Ni和Al元素的互扩散使过渡层与基体界面区域形成了扩散层和岛状颗粒,一些颗粒与扩散层连通后提高了涂层与基体的结合强度,但孤立的颗粒由于变形能力差,对涂层的寿命有不利影响;在交变应力下颗粒与基体界面处会形成裂纹,并最终导致涂层剥离。
关键词:热障涂层;大气等离子喷涂;化学镀;失效机制
中图分类号:TG174 文献标志码:A
Failure mechanism of ZrO2-8%Y2O3 thermal barrier coatings on
aluminum alloy with electroless plating interlayer
LU Guan-xiong1, 2, HAO Li-jun1, 2, LIU Che1, 2, YE Fu-xing1, 2
(1. School of Materials Science and Engineering, Tianjin University, Tianjin 300072, China;
2. Tianjin Key Laboratory of Advanced Joining Technology, Tianjin University, Tianjin 300072, China)
Abstract: To relieve the thermal mismatch stress between coatings and substrate, Ni-P and Ni-Cu-P electroless platings were fabricated onto 2A70 aluminum as interlayers. Subsequently, the specimen with plating was covered by CoNiCrAlY bond coat and ZrO2-8%Y2O3(8YSZ) top coat (mass fraction), then a novel thermal barrier coating (TBC) was produced. The thermal shock resistance of TBCs was evaluated by heat cycle test. The results indicate that the lifetimes of TBC with Ni-P interlayer and Ni-Cu-P interlayer are about 1000 cycles and 500 cycles, respectively. The interdiffusion of Ni and Al results in the formation of diffusion layers and island particles at the interface between interlayers and substrate. The connection between particles and diffusion layers improves the adhesion of coatings with substrate, while isolate particles are harmful to the lifetime of coatings due to their poor deformation ability under alternative stress. Crack initiation happens at the interfaces between particles and substrate, which leads to coatings spallation.
Key words: thermal barrier coating; air plasma spray; electroless plating; failure mechanism
铝合金材料价格低廉,比强度高,耐蚀性好,因此已被广泛应用于车辆工程,飞机制造等领域[1-3]。但是,铝合金熔点和高温强度都较低[4],这给铝合金在高温结构领域的应用带来极大限制。热障涂层材料(如陶瓷和金属间化合物)能在高温下长期稳定工作,并可以通过喷涂、电镀、气相沉积等方法覆盖在铝合金基体上[5-6]。含该类涂层材料的热导率较低,可以通过减小热输入来有效降低铝合金零件的工作温度。此外,热障涂层能够有效阻挡氧化性气体对基体的侵蚀,延长零件的使用寿命。
经过国内外科研人员多年的努力,热障涂层已经被成功应用于高温合金零件的防护。在航空发动机和
地面汽轮机等高温工况下,热障涂层能够保证零件在高温环境中的长期稳定工作。典型的热障涂层体系为双层结构,分别是陶瓷隔热层和高温合金材质的粘结层[5]。生产中最常用的陶瓷隔热层是以Y2O3作为相变稳定剂的ZrO2涂层,常温下其热膨胀系数为9.0×10-6 K-1,而MCrAlYX(其中M=Ni/Co,X=Si,Ha,Ta)粘结层的热膨胀系数13.6×10-6 K-1[7],介于陶瓷隔热层和高温合金基体的之间,可以有效减小涂层和基体之间热失配引起的应力。相比之下,铝合金基体的热膨胀系数常温下为21.0×10-6 K-1,比高温合金的大得多。因此,直接在铝合金基体表面制备的热障涂层服役时会在涂层与基体界面处产生较大的应力,导致涂层的热震寿命降低[8]。对于该问题国内外很多学者进行了相关了研究,赵海涛等[9]采用梯度涂层代替传统的双层结构,有效地减小了涂层与基体之间的热失配应力。SAAD等[10]则在铝合金基体上制备了热导率比氧化锆更低的高温聚合物涂层,通过进一步降低基体温度来降低界面处的热应力。MARR等[11]使用新型热电偶测得了涂层界面处的温度变化曲线,通过优化涂层厚度来控制界面应力。CERIT等[12]则运用有限元分析的方法估算了涂层与基体界面处的热应力水平,为建立涂层寿命的模型提供了参考。本文作者在热膨胀系数相差最大的粘结层和基体之间通过制备过渡层以减小热失配引起的应力。过渡层采用化学镀方法进行制备,化学镀工艺成本低、设备简单、沉积效率高、污染小、与基体结合强度高[13]。在化学镀层的沉积过程中,Ni2+离子被H2PO2-还原,生成单质Ni与P一起混合沉积到基体上,形成一种非平衡态的Ni-P二元合金。当P含量大于7%时,沉积得到的化学镀层都是非晶态的,具有良好的耐蚀性。在Ni-P合金中加入Cu元素,可以进一步改善镀层的热稳定性和耐蚀性[14]。据相关文献的报道[15-16],Ni-P和Ni-Cu-P合金镀层的线膨胀系数分别为17×10-6 K-1和14×10-6 K-1,介于粘结层的线膨胀系数和基体的之间,预期可以有效地缓解热失配引起的应力,延长涂层的服役寿命。
1 实验
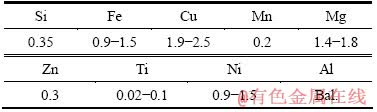
实验中采用Al-Cu-Mg系的2A70铝合金作为基体,该型铝合金不仅强度高,而且具有良好的耐热性能,常被用于制造发动机零部件。该合金的名义成分列于表1中[17]。8YSZ陶瓷层和CoNiCrAlY粘结层的喷涂粉末分别采用Sulzer Metco公司生产的204B-NS粉末(粒度为45~75 μm)和AMDRY9951粉末(粒度为5~37 μm)。陶瓷层选用APS-2000型等离子喷涂系统制备,涂层厚度约为300 μm,喷涂电压70 V,电流600 A。粘结层采用天津大学研制的TJ-9000型超音速火焰喷涂系统制备,涂层厚度约为200 μm,喷涂参数设定为燃气流速20 L/min,助燃气流速220 L/min。
表1 2A70铝合金的名义成分[17]
Table 1 Nominal composition of 2A70 aluminum alloy[17] (mass fraction, %)
施镀前对铝合金试样进行碱洗和酸洗,然后镀锌以避免其在空气中氧化[18]。通过化学镀方法,在基体表面制备了约30 μm厚的非晶合金层。为了消除在热震过程中镀层晶化引起的生长应力对涂层的不利影响,在制备热障涂层前,首先将试样放入大气气氛炉中在400 ℃下保温1 h,以便去氢和使镀层晶化[14, 19]。
镀层的相组成分析通过Bruker D8 X射线衍射仪来进行,扫描采用铜靶,扫描速度为10 (°)/min。采用HITACHI S-4800扫描电子显微镜来对镀层的组织形貌和能谱进行分析。两种复合涂层的结合强度测试在单轴拉伸试验机上进行。抗热震性能测试过程中,采取火焰烧蚀和压缩空气冷却循环进行的方法来模拟涂层的热循环工况。试样表面温度由红外测温仪测定,试样正面陶瓷层最高温度为650 ℃,基体背面的最高温度约为330 ℃。热循环周期为4 min,实验中测得的试样表面温度循环曲线如图1所示。当试样表面出

图1 热震测试时试样正面和背面热循环曲线
Fig. 1 Thermal cycling curves of TC surface and back surface of substrate during thermal shock test
现明显的裂纹或是涂层剥离面积达到15 %以上时即可判定涂层失效。
2 结果与讨论
2.1 化学镀层成分和相组成分析
两种合金镀层的EDS结果如图2中所示。两者的P含量都较高,该类涂层有着良好的耐腐蚀性能,硬度较高[20]。图3所示为400 ℃热处理前后Ni-P和Ni-Cu-P化学镀层的XRD谱。从图3可以看出,通过化学镀方法制备的两种合金镀层均为非晶态。经过400 ℃大气气氛保温1 h的热处理后,化学镀层的组织已经充分晶化。对于Ni-P二元合金镀层,晶化后的组织以稳定相Ni3P为主,也存在少量的Ni相。根据MARTYAK[21]的研究,化学镀制备的高P镀层起始晶化温度约为330 ℃,晶化初期过程中主要析出相为Ni3P、Ni以及Ni5P2,而亚稳相Ni5P2约在400 ℃以上转变为稳定相。Ni-Cu-P三元合金在沉积过程中,Cu2+在镀液中起到稳定剂和加速剂的作用[22],Cu以共沉积
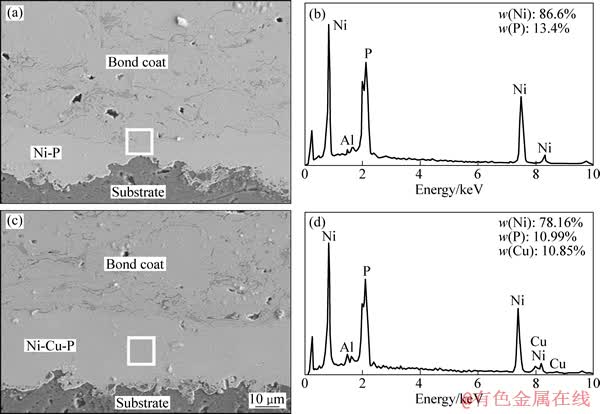
图2 热处理后Ni-P(a和b)和 Ni-Cu-P(c和d)化学镀层的显微结构和EDS结果
Fig. 2 Microstructures and EDS results of Ni-P ((a) and (b)) and Ni-Cu-P ((c) and (d)) electroless platings after heat treatment
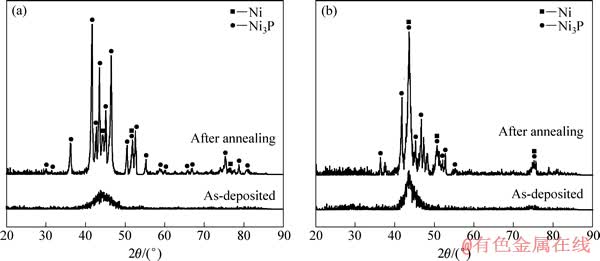
图3 400 ℃热处理前后Ni-P和Ni-Cu-P化学镀层的XRD谱
Fig. 3 XRD patterns of Ni-P(a) and Ni-Cu-P(b) electroless platings before and after annealing at 400 ℃ for 1 h
的方式加入到Ni-P二元合金中,可以有效提高镀层的耐蚀性[18]。Cu的存在提高了镀层的热稳定性,使得Ni5P2和Ni12P5等亚稳相的存在时间延长,提高了其转变为稳定相Ni3P的起始温度[14]。
2.2 复合涂层的结合强度测试
为了减小随机误差对实验结果的影响,每组选取5个试样进行拉伸测试,拉伸试样的断裂面均位于粘结层和镀层的界面处,实验结果示于图4中。从图4可以看出,两种复合涂层的整体强度都在30 MPa左右,复合涂层与基体的结合强度能基本满足使用要求。
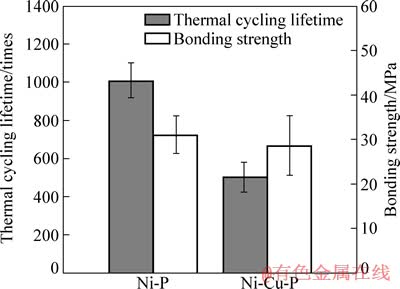
图4 分别含Ni-P和Ni-Cu-P过渡层的复合涂层的热循环寿命和结合强度
Fig. 4 Thermal cycling lifetime and bond strength of Ni-P and Ni-Cu-P composite coatings
2.3 抗热震性能测试和结果分析
如图4所示,采用Ni-Cu-P合金过渡层的试样平均热震寿命约为500次,而采用Ni-P合金过渡层的试样平均热震寿命约为1000次,两种试样的失效部位都位于镀层和基体的界面区域,两种试样失效后的涂层截面形貌如图5所示,两种合金镀层内部都没有较大的变形,也没有出现明显的裂纹等缺陷,说明镀层的强度和韧性都很高。从图5(a)和5(b)可以看出,以Ni-P合金为过渡层的试样陶瓷层(TC)比较完整,裂纹和缺陷较少,而以Ni-Cu-P合金为过渡层的试样陶瓷层中生成了大量的网状裂纹和孔洞,说明Ni-P镀层对热应力的缓解作用明显优于Ni-Cu-P镀层的。由图5(c)和5(d)可知,对于以Ni-P合金为过渡层的试样,在其粘结层(BC)表面可以观察到一层明显的厚度约为1.04 μm的TGO层。而以Ni-Cu-P合金为过渡层的试样,粘结层表面TGO的厚度只有0.43 μm。对于前者的粘结层,氧已经扩散至扁平粒子内部,形成内氧化物的层状网络。而对于以Ni-Cu-P合金为过渡层的试样,内氧化只发生在扁平粒子的结合界面缺陷处。这是由于镀层中的Cu扩散到了粘结层中,提高了粘结层的抗氧化性能。
如图6和图7所示,在两种试样的断裂处,都聚集着大量的Mg、Al和O元素。而Ni、Cr等元素含量较低,说明化学镀层能有效阻止粘结层中的合金元

图5 含Ni-P镀层和Ni-Cu-P镀层的热震失效试样的横截面显微形貌
Fig. 5 Cross-sectional morphologies of fractured specimens with Ni-P ((a), (c)) and Ni-Cu-P ((b), (d)) interlayer after thermal shock test ((c) is higher magnification image of TC/BC interface in (a); (d) is higher magnification image of TC/BC interface in (b))
图6 带有Ni-P过渡层的试样失效处横截面的SEM像,元素分布以及A和B区域的EDS分析结果
Fig. 6 SEM image of cross section of fracture zone and corresponding elemental distrilaition maps, ((a)-(f)) EDS of results of areas A (g) and B (h) in specimen with Ni-P interlayer
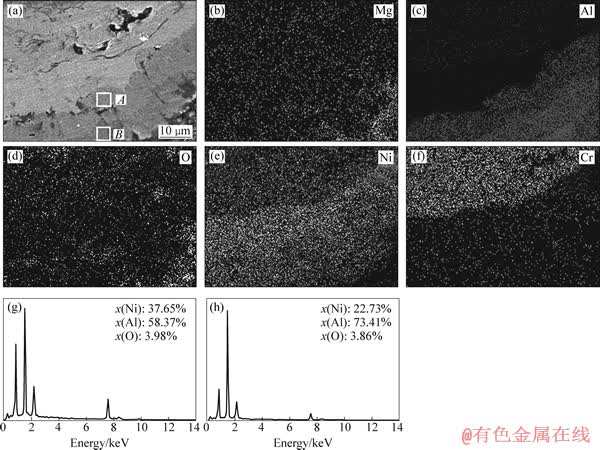
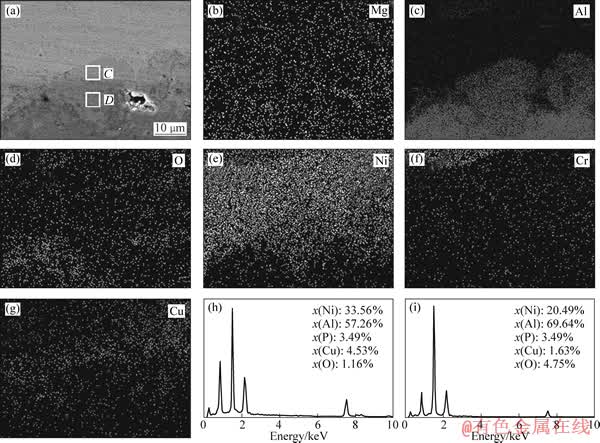
图7 带有Ni-Cu-P过渡层的试样失效处横截面的SEM像,元素分布以及C和D区域的EDS分析结果
Fig. 7 SEM image of cross section of fracture zone and corresponding elemental distribution maps ((a)-(g)), EDS results of areas C (h) and D (i) in specimen with Ni-Cu-P interlayer
素向基体中扩散,对于保持粘结层中合金元素的含量有着明显的作用。当界面处出现裂纹时,渗入的O元素易偏聚于缺陷处,Mg和Al元素比体系中其他元素更活泼,会率先和O结合形成氧化物。这些氧化物逐渐增多,连通后在基体表面形成保护性的氧化膜。由于基体中存在丰富的Mg和Al元素,所以在整个氧化过程中没有贫Al阶段出现,这与在高温合金基体上制备热障涂层时界面处氧化物的生长情况是不同的[5]。由于浓度差的作用,Mg和Al等活性高的小尺寸元素逐渐向镀层和粘结层中扩散,导致基体中形成空穴。镀层中Ni的自腐蚀电位比Al的高,造成了对铝合金基体的接触腐蚀,进一步提高了界面处空位的浓度,这些空位聚集后会形成微裂纹源。
基体中的Al元素和镀层中的Ni元素在浓度差的作用下发生互扩散。Ni—Ni化学键的离解能比Al—Al化学键的高,Ni—Al之间形成化学键有利于体系的稳定[23]。随着热循环的进行,化学镀层与基体的界面区域形成了层状的不同Ni/Al比例的扩散层。图6所示为含Ni—P过渡层的试样失效处横截面的元素分布和A和B区域的EDS分析结果。图7所示为带有Ni-Cu-P过渡层的试样失效处横截面的元素分布和C和D区域的EDS分析结果。从图6和图7可以看出,两种试样中形成的扩散层都可分为两个亚层,通过EDS能谱分析可知,这两层依次主要是由Ni2Al3相和NiAl3相组成的。Ni-Al金属间化合物相熔点高,抗热腐蚀能力强,从能谱分析结果来看,扩散层中O元素的含量都在5%(摩尔分数)以下,说明在本实验的工作温度下Ni-Al化合物层对基体有着良好的阻氧保护作用。但是Ni-Al金属间化合物中Ni-Al的化学键很稳定,造成其在热循环引起的交变应力作用下很难滑移变形,这样的结构导致其本征脆性,室温下尤为明 显[24]。在交变应力的作用下,扩散层的内部、层与层界面处以及其与基体的界面处都会成为微裂纹的起裂点。
经过1000次热循环以后,Ni-P镀层中出现的两扩散层的厚度都在10 μm左右。而对于Ni-Cu-P镀层,Cu元素的加入提高了镀层的热稳定性,降低了扩散层的形成速度。失效时两扩散层的厚度分别为4和10 μm左右。其上层扩散层的厚度明显小于Ni-P镀层中的对应扩散层,这导致双层结构Ni-Al化合物层对应力的缓解作用减弱。
除了形成层状扩散层外,镀层中的Ni元素扩散至基体中,偏聚于晶界和缺陷等区域,与Al结合形成大量的Ni-Al金属间化合物相晶核。如图8所示,这些晶核长大后首先在界面区域形成许多孤立的Ni-Al金属间化合物岛状颗粒。这些颗粒聚集长大后,其中一些与扩散层连通,增加了扩散层与基体界面的粗糙度,因而提高了整体涂层与基体的结合强度。另一些则仍然独立地存在于基体中,这些孤立的颗粒在形成初期体积较小,对基体起到第二相强化的作用。但随着其
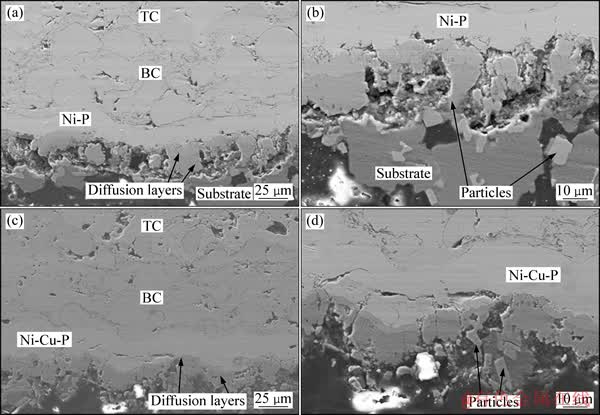

图8 采用Ni-P和Ni-Cu-P合金作为过渡层的试样失效处横截面显微形貌
Fig. 8 Cross sectional morphologies of fracture zone of specimens with Ni-P interlayer ((a), (b)) and Ni-Cu-P interlayer ((c), (d))
体积的增大,在交变载荷作用下,这些颗粒不能与基体一起进行同步的较大变形,导致其与基体的界面处成为微裂纹的萌生处。由图8(d)所示,在Ni-Cu-P合金与基体的界面处,出现大量带有棱角的Ni-Al颗粒,造成其与基体界面处易产生应力集中,加剧了颗粒与基体界面的开裂倾向。
除此之外,热循环对于基体强度也有重要的影响。2A70铝合金组织中主要起强化作用的析出相是S(Al2CuMg)相和θ(CuAl2)相[25]。热震过程中,试样背面瞬时最高温度为340 ℃,已达到合金元素固溶温度,部分强化相会溶入基体中。进入冷却阶段,基体中的合金元素又会以亚稳的θ″和S″相形式析出,但由于保温时间短,强化相不能充分长大,且新析出的S″相和θ″相呈均匀细小的片状分布[26],导致其对基体的强化作用减弱。基体强度的下降有利于裂纹在基体内部的扩展。在交变应力的作用下,裂纹逐渐连通,并最终导致涂层的失效与剥离。
3 结论
1) Ni-P镀层的热膨胀系数比Ni-Cu-P镀层的更大,对涂层和基体之间的热失配应力的缓解作用优于对Ni-Cu-P镀层的。以Ni-P镀层和Ni-Cu-P镀层为过渡层的试样热循环寿命分别约为1000次和500次。
2) 化学镀层能有效阻止粘结层中的合金元素向基体中扩散,对于保持粘结层中合金元素的含量有明显作用。由于Mg和Al元素比体系中其他元素更活 泼,会率先和O结合形成氧化物膜,有利于阻止基体的氧化,但是Mg和Al的扩散留下大量空穴,空穴聚集后成为裂纹源。
3) Ni和Al元素的互扩散使过渡层与基体界面区域形成了双层结构的Ni-Al化合物扩散层以及岛状颗粒。一些颗粒与扩散层连通后提高了镀层与基体的结合强度,但孤立的颗粒变形能力差,其与基体界面处易形成裂纹。
4) 热循环改变了基体中析出相的形态,导致其对基体的强化作用减弱。基体强度的下降有利于裂纹在基体内部的扩展,在交变应力的作用下,裂纹逐渐连通,并最终导致涂层的失效与剥离。
REFERENCES
[1] HIRSCH J. Automotive trends in aluminum—The European perspective[J]. Materials Forum, 2004, 28: 15-23.
[2] 刘 兵, 彭超群, 王日初, 王小锋, 李婷婷. 大飞机用铝合金的研究现状及展望[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2010, 20(9): 1704-1715.
LIU Bing, PENG Chao-qun, WANG Ri-chu, WANG Xiao-feng, LI Ting-ting. Recent development and prospects for giant plane aluminum alloys[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2010, 20(9): 1704-1715.
[3] LI Zhan-ming, ZHU You-li, DU Xiao-kun, HUANG Yuan-lin. Microstructures and mechanical properties of 2024 aluminum alloy welded joint after ultrasonic peening treatment[J]. Rare Metal Materials and Engineering, 2012, 41(s2): 307-311.
[4] 郭海龙, 孙志超, 杨 合. 挤压态7075铝合金再结晶经验模型及应用[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2013, 23(6): 1507-1515.
GUO Hai-long, SUN Zhi-chao, YANG He. Empirical recrystallization model and its application of as-extruded aluminum alloy 7075[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2013, 23(6): 1507-1515.
[5] EVANS A G, MUMM D R, HUTCHINSON J W, MEIER G H, PETTIT F S. Mechanisms controlling the durability of thermal barrier coatings[J]. Progress in Materials Science, 2001, 46: 505-553.
[6] 刘纯波, 林 锋, 蒋显亮. 热障涂层的研究现状与发展趋势[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2007, 17(1): 1-13.
LIU Chun-bo, LIN Feng, JIANG Xian-liang. Current state and future development of thermal barrier coating[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2007, 17(1): 1-13.
[7] ZHOU Y C, HASHIDA T. Coupled effects of temperature gradient and oxidation on thermal stress in thermal barrier coating system[J]. International Journal of Solids and Structures, 2001, 38: 4235-4264.
[8] HEJWOWSKI T. Comparative study of thermal barrier coatings for internal combustion engine[J]. Vacuum, 2010, 85: 610-616.
[9] 赵海涛, 贾 薇, 张学萍. 等离子喷涂梯度涂层的显微组织结构和性能[J]. 沈阳工业大学学报, 2003, 25(6): 468-470.
ZHAO Hai-tao, JIA Wei, ZHANG Xue-ping. Microstructure and property of gradient coatings fabricated with plasma spraying[J]. Journal of Shenyang University of Technology, 2003, 25(6): 468-470.
[10] SAAD D, SAAD P, KAMO L. Thermal barrier coatings for high output turbocharged diesel engine[J]. SAE Technical Paper, 2007, 1(1): 1-11.
[11] MARR M, WALLACE J S, MEMME S, CHANDRA S, PERSHIN L, MOSTAGHIMI J. An investigation of metal and ceramic thermal barrier coatings in a spark-ignition engine[J]. SAE Technical Paper, 2010, 3(2): 115-125.
[12] CERIT M, AYHAN V, PARLAK A, YASAR H. Thermal analysis of a partially ceramic coated piston: effect on cold start HC emission in a spark ignition engine[J]. Applied Thermal Engineering, 2011, 31: 336-341.
[13] BALARAJU J N, RAJAM K S. Electroless deposition of Ni-Cu-P, Ni-W-P and Ni-W-Cu-P alloys[J]. Surface and Coatings Technology, 2005, 195: 154-161.
[14] YU Hui-sheng, LUO Shou-fu, WANG Yong-rui. A comparative study on the crystallization behavior of electroless Ni-P and Ni-Cu-P deposits[J]. Surface & Coatings Technology, 2001, 148: 143-148.
[15] SUI M L, LU K. Thermal expansion behavior of nanocrystalline Ni-P alloys of different grain sizes[J]. Nanostructured Materials, 1995, 6: 651-654.
[16] GU Li-jian, CHEN Xiao-long, FAN Xi-zhi, LIU Yang-jia, ZOU Bing-lin, WANG Ying, CAO Xue-qiang. Improvement of thermal shock resistance for thermal barrier coating on aluminum alloy with various electroless interlayers[J]. Surface and Coatings Technology, 2011, 206: 29-36.
[17] 高艳华, 郭鸿镇, 王晓晨, 姚泽坤. 等温锻造温度对2A70 铝合金组织性能的影响[J]. 热加工工艺, 2009, 38(23): 27-29.
GAO Yan-hua, GUO Hong-zhen, WANG Xiao-chen, YAO Ze-kun. Influence of isothermal forging temperature on microstructure and mechanical property of 2A70 aluminum alloy[J]. Hot Working Technology, 2009, 38(23): 27-29.
[18] HINO M, MURAKAMI K, MITOOKA Y, MURAOKA K, KANADANI T. Effects of zincate treatment on adhesion of electroless Ni-P coating onto various aluminum alloys[J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2009, 19: 814-818.
[19] ASHASSI-SORKHABI H, DOLATI H, PARVINI-AHMADI N, MANZOORI J. Electroless deposition of Ni-Cu-P alloy and study of the influences of some parameters on the properties of deposits[J]. Applied Surface Science, 2002, 185: 155-160.
[20] 胡光辉, 吴辉煌, 杨防祖. 镍磷化学镀层的耐蚀性及其与磷含量的关系[J]. 物理化学学报, 2005, 21(11): 1299-1302.
HU Guang-hui, WU Hui-huang, YANG Fang-zu. Corrosion resistance of electroless Ni-P deposits and its relation to P contents[J]. Acta Physico-Chimica Sinica, 2005, 21(11): 1299-1302.
[21] MARTYAK N M. Characterization of thin electroless nickel coatings[J]. Chemistry of Materials, 1994, 6: 1667-1674.
[22] ARMYANOV S, GEORGIEVA J, TACHEV D, VALOVA E, NYAGOLOVA N, MEHTA S, LEIBMAN D, RUFFINI A. Electroless deposition of Ni-Cu-P alloys in acidic solutions[J]. Electrochemical and Solid-State Letters, 1999, 2(7): 323-325.
[23] DEAN J A. Lange’s handbook of chemistry[M]. New York: McGraw-Hill Inc, 1992: 315-322.
[24] WANG Hua-bin,HAN Jie-cai, DU Shan-yi, NORTHWOOD D O. Reaction synthesis of nickel/aluminide multilayer composites using Ni and Al foils: Microstructures, tensile properties, and deformation behavior[J]. Metallurgical and Materials Transactions A, 2007, 38: 409-419.
[25] 刘志义, 李云涛, 刘延斌, 夏卿坤. Al-Cu-Mg-Ag合金析出相的研究进展[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2007, 17(12): 1905-1915.
LIU Zhi-yi, LI Yun-tao, LIU Yan-bin, XIA Qing-kun. Development of Al-Cu-Mg-Ag alloys[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2007, 17(12): 1905-1915.
[26] RYLANDS L M, WILKES D M J, RAINFORTH W M, JONES H. Coarsening of precipitates and dispersoids in aluminium alloy matrices: A consolidation of the available experimental data[J]. Journal of Materials Science, 1994, 29: 1895-1900.
(编辑 龙怀中)
基金项目:天津市自然科学基金资助项目(12JCYBJC12300)
收稿日期:2013-07-02;修订日期:2013-12-17
通信作者:叶福兴,教授,博士;电话:022-27406261;E-mail:yefx@tju.edu.cn