文章编号:1004-0609(2015)-07-2015-07
聚乙二醇对氧化亚铁硫杆菌浸出黄铜矿的影响
张瑞洋,魏德洲,刘文刚,卢 涛,沈岩柏,崔宝玉
(东北大学 资源与土木工程学院,沈阳 110819)
摘要:为提高黄铜矿生物浸出率,研究聚乙二醇(PEG)对Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans strain XZ11 Fe2+氧化活性和黄铜矿生物浸出过程的影响,并采用SEM和EDS对浸出后矿物表面形貌和相组成进行表征。结果表明:相对分子质量大于200的PEG对Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans Fe2+氧化活性具有一定的促进作用,添加30 mg/L PEG 2000时,浸出20 d后,铜浸出量高达451.70 mg/L,较不添加FEG时提高了1.11倍;添加PEG时,黄铜矿表面的侵蚀面呈沟壑状,出现溶蚀坑,并生成Fe3+的羟基化多聚物Fe(Ⅲ)—O—OH。PEG的添加提高了浸出体系中细菌浓度和Fe3+浓度,加速了黄铜矿的溶解。
关键词:黄铜矿;聚乙二醇;氧化亚铁硫杆菌;生物浸出;表面活性剂
中图分类号:TF111.31 文献标志码:A
Effect of polyethylene glycol on chalcopyrite bioleaching with Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans
ZHANG Rui-yang, WEI De-zhou, LIU Wen-gang, LU Tao, SHEN Yan-bai, CUI Bao-yu
(College of Resources and Civil Engineering, Northeastern University, Shenyang 110819, China)
Abstract: Polyethylene glycol (PEG) was used to improve the bioleaching rate of chalcopyrite by Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans (At.f) strain XZ11. The effect of PEG on the Fe2+ oxidizing activities of Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidan and bioleaching of chalcopyrite were investigated. The surface morphologies and phase composition of chalcopyrite after bioleaching were characterized by SEM and EDS. The results show that PEG with relative molecular mass greater than 200 can promote the Fe2+ oxidizing activities of Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidan After bioleaching for 20 d, the copper extraction yield of chalcopyrite with 30 mg/L PEG 2000 is 451.70 mg/L, which increases by about 1.11 times compared with the bioleaching without PEG. Native-like structure, holes and Fe(III)—O—OH form on the erosion surface of chalcopyrite. PEG can increase the cell density of Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidan and Fe3+ concentration in the leaching solution, consequently, accelerates the chalcopyrite oxidation dissolution.
Key words: chalcopyrite; polyethylene glycol; Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans; bioleaching; surfactant
黄铜矿(CuFeS2)是自然界储量最丰富的铜矿资源,也是最难溶浸的铜矿物[1]。黄铜矿难以进行生物浸出的主要原因如下:1) 黄铜矿的高晶格能使氧化腐蚀难以进行;2) 生物浸出过程中易于生成的“钝化物”如黄钾铁矾和单质硫等,阻碍了黄铜矿的细菌氧化浸出[2-3];3) 黄铜矿表面的疏水行为削弱了浸出液与矿物的界面作用[4-6]。目前,国内外研究者提出的强化黄铜矿生物浸出方法主要有控制浸出过程pH与氧化还原电位法[7]、中高温菌的生物浸出法[8]、金属阳离子催化法[9]等,但上述方法均存在局限性,难以投入到实际应用中。
近年来,研究者发现[10-11],添加表面活性剂可降低浸出液的表面张力,增强黄铜矿的亲水性,从而促进黄铜矿的溶浸。由于阳离子表面活性剂杀菌作用极强,阴离子表面活性剂的杀菌作用次之,非离子表面活性剂的毒性最低[12],因此,表面活性剂在黄铜矿细菌浸出中的应用研究主要集中在温和的吐温类非离子表面活性剂上。研究表明[13-15],吐温类表面活性剂仅仅缩短了生物浸出过程中的“滞后期”,并没有明显改善黄铜矿的浸出效果。因此,探索开发适用于黄铜矿生物浸出的表面活性剂可为解决黄铜矿生物浸出效率低的问题提供一种新方法。
聚乙二醇(PEG)是一种非离子性表面活性剂[16],结构式为H(CH2CH2O)nOH,特殊的线性原子结构使其具有强极化性及亲水性,还具有良好的润湿性、低毒性、热稳定性及生物可降解性等优点[17]。目前,已有研究表明[18],PEG的添加可促进微生物催化木质纤维素的水解,但PEG在生物浸矿方面的应用还未见报道。为此,本文作者以Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans strain XZ11纯菌株和黄铜矿单矿物为研究对象,考察了PEG对Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans Fe2+氧化活性及黄铜矿浸出效果的影响,探讨了PEG在黄铜矿生物浸出过程的作用行为。
1 实验
1.1 菌种和培养基
研究所用菌株是从西藏甲玛地区酸性矿坑水中富集、筛选、分离出来的纯菌株,菌体呈杆状、直径为0.2~0.4 μm、长度为0.7~1.5 μm,呈革兰氏阴性,经16SrDNA鉴定为嗜酸氧化亚铁硫杆菌,命名为Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans strain XZ11(以下简称At.f菌),GenBank登录号为KJ573102。图1所示为Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans strain XZ11菌的SEM像。

图1 Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans strain XZ11的SEM像
Fig. 1 SEM image of Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans strain XZ11
实验所用菌株生长培养基为9 K培养基,其组成如下:(NH4)2SO4 3.0 g/L,KCl 0.1 g/L, K2HPO4 0.5 g/L,MgSO4·7H2O 0.5 g/L,Ca(NO3)2 0.01 g/L,FeSO4·7H2O 44.2 g/L,用5 mol/L H2SO4调节pH 2.0。所用浸矿培养基为不添加Fe2+的9 K培养基,即无铁0 K培养基。
1.2 黄铜矿单矿物的制备
实验所用黄铜矿单矿物是从某铜矿山采集的标本级黄铜矿,矿石破碎后经人工挑选,再经摇床抛除少量杂质后,干磨并筛分出粒径小于0.045 mm的精矿作为实验样品。黄铜矿矿样各元素质量分数为32.84% Cu、29.62% Fe、33.1% S,黄铜矿单矿物的XRD谱见图2。
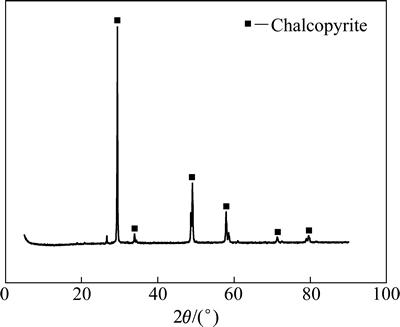
图2 黄铜矿单矿物的XRD谱
Fig. 2 XRD pattern of pure chalcopyrite
1.3 菌种制备及实验
1.3.1 浸矿菌种的制备
生长至对数期的At.f菌悬浮液经Whatman 42号滤纸过滤除去铁矾沉淀,离心15 min(10000 r/min)后收集菌体,再用pH=2.0的H2SO4溶液清洗3次以去除菌体表面残留金属离子,所得菌体作为浸矿接种菌。
1.3.2 PEG对细菌Fe2+氧化活性的影响
在95 mL 9K培养基中分别加入30 mg/L不同相对分子质量的PEG(化学纯)作为培养体系,分别接种5 mL对数期的At.f菌悬浮液,于温度为30 ℃、转速为160 r/min气浴恒温振荡器(ZD-85A)中培养,定期取样检测培养液中Fe2+浓度。Fe2+浓度采用重铬酸钾滴定法测量,Fe2+氧化率(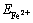 )由式(1)计算所得:
)由式(1)计算所得:
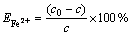 (1)
(1)
式中:c0为初始Fe2+浓度;c为培养液中Fe2+浓度。
1.3.3 生物浸出实验
取1 g灭菌后的黄铜矿单矿物于三角瓶中,加入灭菌后的100 mL无铁0K培养基,在初始At.f菌接种量为1.0×107 mL-1的条件下,在温度为30 ℃、转速为160 r/min的气浴恒温振荡器中振荡浸出。在添加30 mg/L PEG与不添加PEG的条件下进行对比试验,并以不加At.f菌、不添加PEG的酸浸作为空白对照组。定期取样检测浸出液中氧化还原电位、细菌浓度、Fe2+、Cu2+及全铁含量,用去离子水补充蒸发水。浸出液中细菌浓度采用血球计数板于显微镜下计数,浸出液氧化还原电位采用ORP复合电极(雷磁)测定,浸出液中Cu2+及全铁的含量采用全谱直读等离子发射光谱仪进行测定;浸出液中Fe3+浓度为全铁浓度与Fe2+浓度之差。
1.3.4 浸出作用后黄铜矿形貌与表面化学成分分析
浸出作用后的黄铜矿经pH=2.0的H2SO4溶液淋洗后,自然晾干,采用场发射扫描式电子显微镜(UltraPlus)进行形貌观察,表面能谱仪(EDX-GENESIS 60S)进行表面化学成分分析。
2 结果与讨论
2.1 PEG相对分子质量对At.f菌Fe2+氧化活性的影响
At.f菌在9 K培养基中生长,唯一的能源物质是硫酸亚铁,以氧化Fe2+来获取生长所需能量。因此,培养基中Fe2+氧化速度反映出At.f菌的生长速度,本实验中采用Fe2+氧化率来表征At.f菌的生长特性。当添加30 mg/L相对分子质量分别为200、1000、2000和6000的PEG时,At.f菌的Fe2+氧化活性如图3所示。
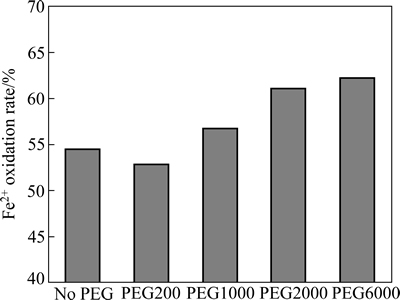
图3 不同相对分子质量PEG对Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans菌Fe2+氧化活性的影响(培养36 h)
Fig. 3 Influences of PEG with different relative molecular mass on Fe2+ oxidation rate of Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans strain (culturing for 36 h)
从图3可以看出,低相对分子质量的PEG 200对At.f菌生长有一定的抑制作用,与未添加PEG时相比,PEG200使At.f菌的Fe2+氧化率由54.44%降低至52.78%,主要原因如下:PEG含有大量的醚键—O—,含有未成键的孤对电子,在酸性溶液中与H+结合而带正电,小分子PEG易穿透细菌细胞膜,而At.f菌细胞内是接近中性的,带电PEG分子进入细胞后,引起细胞液酸化,从而破坏了细菌生长所需的pH梯度[19-20]。高相对分子质量PEG(≥1000)对At.f菌生长不仅未产生抑制作用,反而有一定的促进作用,PEG6000的加入使At.f菌对Fe2+氧化率提高了7.78%,可能是由于PEG改变了At.f菌细胞膜的性质,提高了细胞膜的通透性,加快了At.f菌对Fe2+的氧化[21-22]。
2.2 PEG相对分子质量对黄铜矿生物浸出效果的影响
当添加30 mg/L相对分子质量分别为200、1000、2000和6000的PEG时,黄铜矿生物浸出铜浸出量的变化如图4所示。由图4可知,PEG 200对At.f菌浸出黄铜矿产生了不利影响,与不加PEG时相比,20d后,铜浸出量降低了15.58 mg/L,这主要是因为PEG200对At.f菌的生长产生抑制作用。PEG的相对分子质量分别为1000、2000和6000时,铜的浸出量比不加时均有所提高,其中添加PEG 2000的浸出效果最佳,20 d后铜浸出量高达451.70 mg/L,较不加时的(214.38 mg/L)提高了1.11倍。
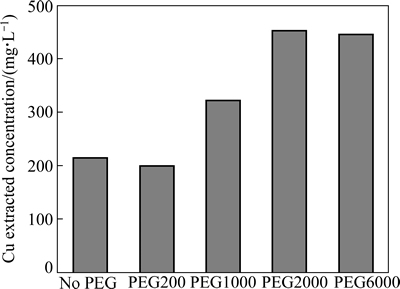
图4 PEG相对分子质量对铜浸出量的影响(生物浸出20 d)
Fig. 4 Influences of PEG with different relative molecular mass on Cu extraction concentration of chalcopyrite (bioleaching for 20 d)
2.3 PEG2000对黄铜矿生物浸出过程的影响
添加30 mg/L PEG2000对黄铜矿生物浸出过程中铁离子浓度、氧化还原电位、细菌浓度和铜浸出量的影响如图5所示。根据图5所示结果,将黄铜矿的浸出过程按时间分为浸出初期、浸出中期和浸出后期进行分析。
浸出初期(0~3 d),由图5(c)可见,添加与未添加PEG时,浸出液中At.f菌的浓度均较低,细菌处于“停滞期”,黄铜矿中的铁以Fe2+的形式溶出,黄铜矿表面的微孔裂隙、晶格缺陷等活性区域优先与H+作用按照式(2)进行分解[23]。由图5(a)可知,浸出3 d,不加菌不加PEG(酸浸)与加菌不加PEG时的Fe2+浓度相近,分别为63和65 mg/L,PEG的添加使Fe2+浓度上升至90 mg/L,这是因为黄铜矿由于表面弛豫作用使其表面硫原子相对富余,出现富硫表面,因而具有较强的疏水性[6];PEG中羟基氧原子与黄铜矿表面硫原子可产生分子间配位作用[24],因此,PEG的加入改变了黄铜矿的表面性质,增强了黄铜矿的亲水性,从而促进了黄铜矿的溶解作用:
CuFeS2+4H++O2→Cu2++Fe2++2S0+2H2O (2)
浸出中期(3~12 d),由图5(c)可知,PEG的加入使浸出液中细菌的浓度大幅度提高,不添加PEG浸出9 d时,细菌浓度由初始1.0×107 mL-1升高至9.6×107 mL-1;而添加PEG时,细菌浓度在12 d时达到最大值,为2.34×108 mL-1,PEG的加入使浸出体系中细菌浓度的极值提高了1.44倍。细菌浓度的升高加快了Fe2+的氧化速度(见式(3)),[Fe3+]/[Fe2+]比值增大,进而氧化还原电位上升速度较未添加时的更快(见图5(b)),然而添加PEG时,黄铜矿的浸出速率高于未添加时的浸出速率(见图5(d));这表明黄铜矿浸出动力学并非直接取决于氧化还原电位,而主要由Fe2+和Fe3+浓度控制,这一观点与HIROYOSHI等[25]和彭安安等[26]的研究结果相一致。
4Fe2++O2+4H+→4Fe3++2H2O (3)
由图5(d)可见,添加PEG时,黄铜矿的铜浸出量明显高于未添加时的浸出量,这是因为PEG的加入促进了黄铜矿的化学浸出作用,黄铜矿的溶解为At.f菌的生长提供了更多的能源物质,使浸出液中细菌浓度大幅度提高,细菌浓度的提高反过来又加速了黄铜矿的生物氧化,二者相互促进形成良性循环。

图5 PEG 对黄铜矿浸出过程中铁离子浓度、氧化还原电位、细菌浓度和铜浸出量的影响
Fig. 5 Effect of PEG on Fe ion concentration(a), redox potential(b), bacterial density(c) and Cu extraction (d) of leaching of chalcopyrite
浸出后期(12~20 d),由图5(a)可知,未添加PEG时,浸出12 d后,浸出液中Fe3+浓度开始下降;浸出20 d时,下降至41 mg/L,这是因为Fe3+水解生成了铁矾沉淀(见式(4)),添加PEG条件下,Fe3+浓度呈持续上升趋势,浸出20 d时,高达242 mg/L。由图5(a)和(d)可见,添加PEG时,在整个浸出过程,溶液中Fe3+浓度均高于未添加时PEG溶液中Fe3+浓度,Fe3+是细菌浸出黄铜矿过程中重要的氧化剂,因而Fe3+浓度的升高有利于黄铜矿的氧化作用,如反应(5)所示:
3Fe3++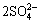 +6H2O+M+→MFe3(SO4)2(OH)6+6H+ (4)
+6H2O+M+→MFe3(SO4)2(OH)6+6H+ (4)
式中:M为正一价的阳离子,如K+、Na+和NH4+等。
CuFeS2+4Fe3+→Cu2++5Fe2++2S0 (5)
2.4 黄铜矿浸出后表面形貌及化学成分分析
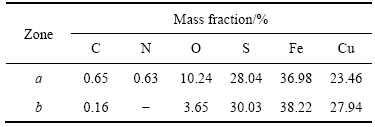
添加PEG对黄铜矿生物浸出后表面形貌及化学成分分析的影响如图6和表1所示。由图6和表1可知,未添加PEG时,浸出20 d后,黄铜矿表面未出现明显的溶蚀现象;虽经过稀硫酸冲洗,矿物表面仍附着大量的絮状铁矾沉淀,这是因为矿石表面上吸附的细菌或分泌物为铁矾沉淀的生长与形成提供了成核中心,使沉淀牢固地附着在矿物表面,相应的矿物表面并未检测出K元素,矿物表面N与O质量比约为1:16.25,与黄铵铁矾中N与O质量比理论值1:15.98相近,推断絮状沉淀为黄铵铁矾。PEG的加入增强了浸出液在黄铜矿微孔裂隙的渗透作用,有利于侵蚀的纵向深入,黄铜矿表面侵蚀明显,侵蚀面呈有规则的沟壑状,出现溶蚀坑和溶蚀沟,未发现有絮状沉淀的生成,表面Cu、Fe、S质量比为1:1.37:1.07,同时浸出液中全Fe浓度小于Cu离子浓度(见图5(a)和图5(d)),这说明黄铜矿表面呈富铁状态,且矿物表面含有一定量的氧,推测矿物表面生成了铁的羟基化多聚物Fe3+—O—OH[3, 27]。
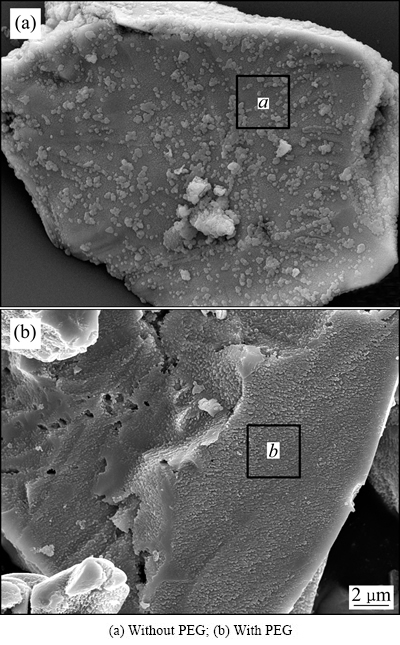

图6 生物浸出20d后黄铜矿的SEM像
Fig. 6 SEM images of chalcopyrite after bioleaching for 20 d
表1 图6中黄铜矿表面EDS分析结果
Table 1 Composition of chalcopyrite surface by EDS shown in Fig. 6
3 结论
1) PEG的添加对At.f菌Fe2+氧化活性具有一定的影响,低相对分子质量PEG200对At.f菌Fe2+氧化活性有一定的抑制作用,与未添加PEG时相比,PEG 200使At.f菌的Fe2+氧化率由54.44%降低至52.78%。相对分子质量大于200的PEG对At.f菌Fe2+氧化活性具有促进作用,PEG6000的加入使At.f菌对Fe2+氧化率提高了7.78%。
2) 加入相对分子质量大于200的PEG可明显改善黄铜矿生物浸出效果,PEG相对分子质量为2000时浸出效果最佳,在添加量为30 mg/L时,浸出20 d后,铜浸出量高达451.70 mg/L,较不添加时的浸出量(214.38 mg/L)提高了1.11倍。
3) 未添加PEG时,生物浸出20 d后,黄铜矿表面未见明显的侵蚀现象,表面附着大量絮状黄铵铁矾沉淀;PEG的加入有利于侵蚀的纵向深入,黄铜矿表面氧化侵蚀明显,侵蚀面呈有规则的沟壑状,出现溶蚀坑和溶蚀沟,表面生成了铁的羟基化多聚物Fe(III)—O—OH。
4) PEG提高黄铜矿生物浸出率的主要原因如下:一方面PEG增强了黄铜矿的亲水性,增强了浸出液在黄铜矿微孔裂隙的渗透作用,促进了黄铜矿的溶解;另一方面PEG的加入提高了浸出体系中细菌浓度和Fe3+浓度,从而加速了黄铜矿的氧化过程。
REFERENCES
[1] WATLING H R. The bioleaching of sulphide minerals with emphasis on copper sulphides—A review[J]. Hydrometallurgy, 2006, 84(1/2): 81-108.
[2] ZHAO Xin-qing, WANG Ru-cheng, LU Xian-cai, LU Jian-jun, LI Cheng-xiang, LI Juan. Bioleaching of chalcopyrite by Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans[J]. Minerals Engineering, 2013, 53(6): 184-192.
[3] 马鹏程, 杨洪英, 佟琳琳, 韩战旗, 宋 言. 黄铜矿生物浸出过程中Fe(II)和Fe(III)的行为[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2013, 23(6): 1694-1699.
MA Peng-cheng, YANG Hong-ying, TONG Lin-lin, HAN Zhan-qi, SONG Yan. Behaviour of Fe(II) and Fe(III) in chalcopyrite bioleaching process[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2013, 23(6): 1694-1699.
[4] 梁长利, 夏金兰, 杨 益, 聂珍媛, 邱冠周. 黄铜矿生物浸出过程的硫形态转化研究进展[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2012, 22(1): 265-270.
LIANG Chang-li, XIA Jin-lan, YANG Yi, NIE Zhen-yuan, QIU Guan-zhou. Progress in sulfur speciation transformation during chalcopyrite bioleaching[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2012, 22(1): 265-270.
[5] KLAUBER C. A critical review of the surface chemistry of acidic ferric sulphate dissolution of chalcopyrite with regards to hindered dissolution[J]. International Journal of Mineral Processing, 2008, 86(1/4): 1-17.
[6] WEN Shu-ming, DENG Jiu-shuai, XIAN Yong-jun, DAN Liu. Theory analysis and vestigial information of surface relaxation of natural chalcopyrite mineral crystal[J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2013, 23(3): 796-802.
[7] VILC EZ J, SUTO K, INOUE C. Bioleaching of chalcopyrite with thermophiles: Temperature pH ORP dependence[J]. International Journal of Mineral Processing, 2008, 88(1/2): 37-44.
EZ J, SUTO K, INOUE C. Bioleaching of chalcopyrite with thermophiles: Temperature pH ORP dependence[J]. International Journal of Mineral Processing, 2008, 88(1/2): 37-44.
[8] CHEN Bo-wei, WU Biao, LIU Xing-yu, WEN Jian-kang. Comparison of microbial diversity during column bioleaching of chalcopyrite at different temperatures[J]. Journal of Basic Microbiology, 2014, 54(6): 491-499.
[9] NAZARI G, DIXON D G, DREISINGER D B. The role of silver-enhanced pyrite in enhancing the electrical conductivity of sulfur product layer during chalcopyrite leaching in the GalvanoxTM process[J]. Hydrometallurgy, 2012, 113/114: 117-184.
[10] 吴爱祥, 艾纯明, 王贻明, 李希雯. 表面活性剂强化铜矿石的浸出[J]. 北京科技大学学报, 2013, 35(6): 709-713.
WU Ai-xiang, AI Chun-ming, WANG Yi-ming, LI Xi-wen. Surfactant accelerating leaching of copper ores[J]. Journal of University of Science and Technology Beijing, 2013, 35(6): 709-713.
[11] SHARMA S D, SINGH M. Effect of surfactant on leaching of pendimethalin in Florida candler fine sand[J]. Bulletin of Environmental Contamination & Toxicology, 2007, 78(1): 91-94.
[12] 赵国玺. 表面活性剂物理化学[M]. 北京: 北京大学出版社, 1991: 35-64.
ZHAO Guo-xi. Physico-chemistry of surfactants[M]. Beijing: Beijing University Press, 1991: 35-64.
[13] KINGMA J G, SILVER M. Autotrophic growth of thiobacillus acidophilus in the presence of a surface-active agent, Tween 80[J]. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 1979, 38(5): 795-799.
[14] ZHANG Cheng-gui, XIA Jin-lan, ZHANG Rui-yong, PENG An-an, NIE Zhen-yuan, QIU Guan-zhou. Comparative study on effects of Tween-80 and sodium isobutyl-xanthate on growth and sulfur-oxidizing activities of Acidithiobacillus albertensis BY-05[J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2008, 18(4): 1003-1007.
[15] 张德诚, 朱 莉, 罗学刚. 低温下非离子表面活性剂加速细菌浸出黄铜矿[J]. 化工进展, 2008, 27(4): 540-543.
ZHANG De-cheng, ZHU Li, LUO Xue-gang. Effect of non-ionic surfactants in bacteria leaching of chalcopyrite at low temperature[J]. Chemical Industry and Engineering Progress, 2008, 27(4): 540-543.
[16] NOURMORADI H, NIKAEEN M, KHIADANI M. Removal of benzene, toluene, ethylbenzene and xylene(BTEX) from aqueous solutions by montmorillonite modified with nonionic surfactant: Equilibrium, kinetic and thermodynamic study[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2012, 191(19): 341-348.
[17] CHEN Shen-fu, LI Ling-yan, ZHAO Chao, ZHENG Jie. Surface hydration: Principles and applications toward low-fouling/ nonfouling biomaterials[J]. Polymer, 2010, 51(23): 5283-5293.
[18] PARDO A G. Effect of surfactants on cellulose production by Nectria catalinensis[J]. Current Microbiology, 1996, 33(4): 275-278.
[19] MCINTYRE N S, ZETARUK D G. X-ray photoelectron spectroscopic studies of iron oxides[J]. Analytical Chemistry, 1977, 49(11): 1521-1529.
[20] TUTTLE J H, DUGAN P R. Inhibition of growth, iron, and sulfur oxidation in Thiobacillus ferrooxidans by simple organic compounds[J]. Canadian Journal of Microbiology, 1976, 22(5): 719-730.
[21] ALEXANDER B, LEACH S, INGLEDE W J. The relationship between chemiosmotic parameters and sensitivity to anions and organic acids in the acidophile Thiobacillus ferrooxidans[J]. Microbiology, 1987, 133(5): 1171-1179.
[22] MCPHERSON T, KIDANE A, SZLEIFER I, PARK K. Prevention of protein adsorption by tethered poly(ethylene oxide) layers: experiments and single-chain mean-field analysis[J]. Langmuir, 1998, 14(1): 176-186.
[23] 邓久帅, 文书明, 先永骏, 刘 建, 刘 丹. 黄铜矿在水溶液中的溶解特性和表面性质谱学表征[J]. 光谱学与光谱分析, 2012,32(2): 519-524.
DENG Jiu-shuai, WEN Shu-ming, XIAN Yong-jun, LIU Jian, LIU Dan. Spectroscopic characterization of dissolubility and surface properties of chalcopyrite in aqueous solution[J]. Spectroscopy and Spectral Analysis, 2012, 32(2): 519-524.
[24] 张建斌, 李 强, 刘占英, 白 杰, 张 通, 魏雄辉. 聚乙二醇及其水溶液吸收SO2机理研究[J]. 化学工程, 2010, 38(12): 76-79.
ZHANG Jian-bin, LI Qiang, LIU Zhan-ying, BAI Jie, ZHANG Tong, WEI Xiong-hui. Absorption mechanism of SO2 in polyethylene glycol and its aqueous solution[J]. Chemical Engineering, 2010, 38(12): 76-79.
[25] HIROYOSHI N, MIKI H, HIRAJIMA T, TSUNEKAWA M. A model for ferrous-promoted chalcopyrite leaching[J]. Hydrometallurgy, 2000, 57(1): 31-38.
[26] 彭安安, 汤 露, 夏金兰, 夏乐先, 赵小娟, 聂珍媛, 朱薇. 3种典型能量代谢菌浸出黄铜矿及其硫形态的转化[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2012, 22(10): 2930-2937.
PENG An-an, TANG Lu, XIA Jin-lan, XIA Le-xian, ZHAO Xiao-juan, NIE Zhen-yuan, ZHU Wei. Sulfur/iron oxidation activity of three typical bioleaching bacteria and sulfur speciation in bioleaching of chalcopyrite[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2012, 22(10): 2930-2937.
[27] HARMER S L, THOMAS J E, FORNASIERO D, GERSON A R. The evolution of surface layers formed during chalcopyrite leaching[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2006, 70(17): 4392-4402.
(编辑 龙怀中)
基金项目:国家“十二五”科技支撑计划项目(2012BAB01B03);中央高校基本科研业务费研究生创新项目(N120601005)
收稿日期:2014-12-15;修订日期:2015-04-30
通信作者:魏德洲,教授,博士;电话:024-83673863;E-mail:dzwei@mail.neu.edu.cn