文章编号:1004-0609(2007)09-1475-06
Al元素对Ti40阻燃钛合金550 ℃热稳定性的影响
辛社伟1,2,赵永庆2,曾卫东1
(1. 西北工业大学 材料学院,西安 710012;
2. 西北有色金属研究院 钛合金研究所,西安 710016)
摘 要:研究Ti-25V-15Cr-0.2Si和Ti-25V-15Cr-2Al-0.2Si两种阻燃钛合金在550 ℃热暴露不同时间后的力学性能,并应用光学显微镜、X射线衍射、透射电镜对合金组织进行分析。结果表明,Al元素使Ti40阻燃钛合金在550 ℃的热稳定性能显著降低;对相的分析表明,Al元素可促进合金中Ti5Si3和a相的形成。在550 ℃热暴露200 h条件下,出现明显的TiCr2有序相。降低组织的稳定性及使合金在热暴露过程中生成过多的第二相是Al元素降低合金热稳定性能的主要原因。
关键词:Ti40阻燃钛合金;热暴露;析出物;力学性能
中图分类号:TG 146.23 文献标识码:A
Effect of alloying element Al on thermal stability of Ti40 burn-resistant titanium at 550 ℃
XIN She-wei1, 2, ZHAO Yong-qing1, 2, ZENG Wei-dong1
(1. School of Materials Science, Northwestern Polytechnical University, Xi’an 710012, China;
2. Titanium Alloy Research Center, Northwest Institute for Nonferrous Metal Research, Xi’an 710016, China)
Abstract: The mechanical properties of Ti-25V-15Cr-0.2Si and Ti-25V-15Cr-2Al-0.2Si after thermal exposure at 550 ℃ for different times were studied, and their microstructures were analyzed by OM, XRD and TEM. The results show that the thermal stability of the alloy decreases obviously with the addition of Al element during thermal exposure process. The analysis results of microstructures indicate that the addition of Al improves the precipitation of Ti5Si3 and a phase, and after 550 ℃ thermal exposed for 200 h there formed TiCr2 ordered phases in the alloy with the addition of Al element. The decrease of structure stability and much more precipitated phases are the main reasons of the effect of alloying element Al on the thermal stability.
Key words: Ti40 burn-resistant titanium alloy; thermal exposure; precipitated phases; mechanical property
Ti40合金作为我国自主研发的阻燃钛合金已研究多年,取得了一定成果[1?2]。该合金的主要特点是具有优良的阻燃性和综合力学性能,高温和承载的综合服役条件要求该合金也要具有较好的高温性能,它决定了合金的使用寿命和工件的安全可靠性。热稳定性能是高温性能的一个重要指标,对热稳定性能的研究是Ti40合金的一个重要方向。在Ti40合金的研究中,Al元素是钛合金的一种重要合金元素,由于它的加入,不但可以降低成本(通过Al-V中间合金的使用),还可以提高相变点,有望提高或不降低合金的热稳定。对此,英国剑桥大学Li[3?4]和中国北京航空材料研究院的黄旭等[5?6]也进行过研究,使用的合金名义成分主要为英国Rolls-Royce公司的Ti-25V-15Cr-xAl-xC合金,但是在研究中主要是就合金本身进行论述,没有对Al元素的作用进行对比研究。本文作者旨在进一步探讨Al元素在全b合金中的作用,这将为以后该类合金的设计和成分调整提供更全面的理论基础。
1 实 验
实验用合金采用自制中间合金经真空自耗电弧炉3次熔炼,制成5 kg的铸锭,开坯锻造成d 25 mm的圆棒,然后再旋锻成d 12 mm的棒材,热处理后加工成d 5 mm的标准拉伸试样进行热稳定实验(即实验结果为带氧化皮的力学性能)。热处理工艺为实验室推荐的合金最佳热处理工艺:820 ℃、0.5 h,水淬+ 600 ℃、5.0 h,空冷。热稳定实验工艺为550 ℃分别热暴露0,50,100和200 h后再测试室温拉伸性能。所有的力学性能均在Instro?1185拉伸机上进行测试。在OLMPUS PMG光学显微镜、PW1700型X射线衍射仪和TECNAl G2 20型透射电子显微镜上进行显微组织观察和分析。
实验所配制两种合金的名义成分分别为: Ti-25V-15Cr-0.2Si(1号合金);Ti-25V-15Cr-2Al-0.2Si (2号合金)。其中1号合金名义成分为西北有色金属研究院研制的Ti40合金的名义成分。
2 结果与分析
2.1 力学性能
表1所列为合金在550 ℃热暴露不同时间的力学性能。对于热稳定性的研究,主要分为两个方面:一是表面稳定性的研究,二是组织稳定性的研究。文献[7?8]已证明Ti40合金在600 ℃以下工作时,组织因素起决定因素,表面氧化对力学性能影响很小。本文实验合金接近于Ti40成分,实验温度在600 ℃以下,可以不考虑表面氧化的影响,认为组织稳定性是合金550 ℃热暴露力学性能的控制因素。如果不考虑表面稳定性的影响,热暴露过程也是一个过时效过程,其力学性能符合一般钛合金热处理的时效特点[9],即随时效时间的延长,合金强度先升高,达到一个最大值后下降,此过程中塑性基本一直处于下降趋势。在本实验中,从表1的力学性能可以看出,无论对于1号还是2号合金,在热暴露过程中,合金塑性都严重降低,这是因为合金热暴露是在热处理的基础上进行的一个完全的过时效行为,此过程是第二相继续析出、粗化的过程。当热暴露时间超过50 h后塑性变化缓慢,这从一定程度反映了合金组织逐渐趋于稳定。对比1号和2号合金在不同热暴露时间的性能,发现Al元素对合金室温性能有较为明显的强化作用,但降低合金的热稳定性能。在相同处理条件下,2号合金的塑性都低于1号合金,特别是当热暴露时间延长到200 h后,由于完全的脆性断裂,合金的屈服强度及延伸率都无法测出。对Ti40合金来说,塑性的降低主要是因为晶界析出物所致[10?12],长时间高温热暴露过程中在晶界形成连续的析出物弱化合金的晶界强度,使合金强度降低并呈现完全的脆性断裂。2号合金的强度和塑性严重降低,证明这种组织的变化对2号合金产生的影响更大。
表1 合金550 ℃热暴露不同时间的力学性能
Table 1 Mechanical properties of two alloys after thermal exposure at 550 ℃ for different times

2.2 组织分析
2.2.1 金相显微组织
图1所示为合金在不同热暴露时间的显微组织。从组织对比可以看到,随热暴露时间的延长,两种合金晶粒都有明显的粗化倾向,析出物也略呈增加的趋势,这符合一般钛合金的时效特点[9]。两种合金在热暴露过程中,析出物增加趋势不明显,也证明了合金的组织具有相当的稳定性;对比1号和2号合金的组织发现,2号合金在热暴露过程中析出物增加相对更多,这反映了Al元素在合金热暴露过程中,降低组织的稳定性,使合金组织对热暴露过程更为敏感。
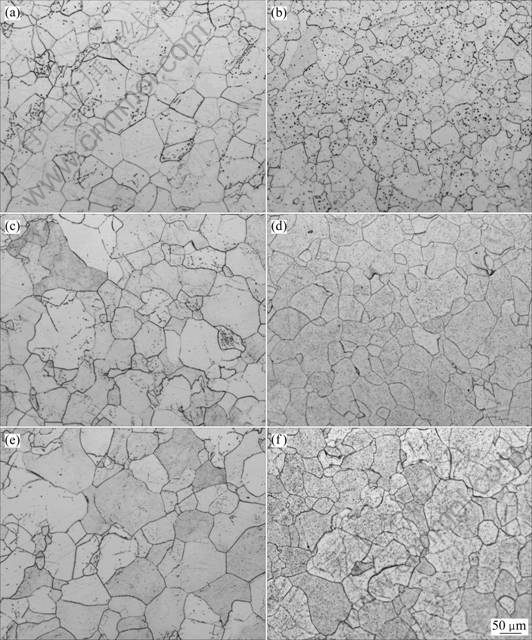
图1 合金热处理与550 ℃热暴露不同时间的显微组织
Fig.1 Microstructures of alloys after thermal exposure at 550 ℃ for different times: (a), (c) and (e) are respectively alloy 1 for 0, 50 and 200 h; (b), (d) and (f) are respectively alloy 2 for 0, 50 and 200 h
2.2.2 X射线衍射分析
图2所示为合金在不同热暴露时间的X射线衍射谱。可以看出,虽然进行高温长时间的热暴露实验,两种合金中都仅有b相和Ti5Si3相的衍射峰,没有a峰和其他过渡相衍射峰,证明在X射线衍射检测范围内,合金组织具有相当的稳定性,热暴露过程中仅有少量的b相分解。这是由于Ti40合金属于全β合金,具有极高的Mo当量,使得β组织有高度的热稳定性,热稳定过程中保持相当的组织稳定性也是该合金的一个特点。
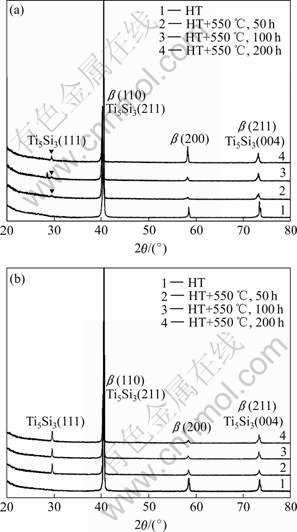
图2 合金550 ℃热暴露不同时间的X射线衍射谱
Fig.2 XRD patterns of alloys after thermal exposure at 550 ℃ for different times: (a) Alloy 1; (b) Alloy 2
对比1号和2号合金的X射线衍射谱可知,2号合金Ti5Si3(111)衍射峰的出现比1号合金的要早,1号合金在热暴露100 h后才有出现的迹象,而2号合金在50 h后就有明显的峰,并且明显要强于1号合金的,这从一定程度反映了Al元素促进Ti5Si3相的形成。由图2可见,在热暴露过程中1号和2号合金都观察到了Ti5Si3相,目前,尚无有效检测手段能够得到它们在各自合金中的准确含量,但是,Al元素促进Ti5Si3相的析出是可以理解的。首先,Al元素促进a相的生成是必然的,文献[10, 12]已经指出,在Ti40合金热暴露过程中,析出物主要为a相,而作为a相稳定元素,Al元素的加入必然会增加b相向a相转变的量。由于Si元素在b相中的固溶度远大于在a相中的固溶度,b相向a相转变的过程其实就是Ti5Si3析出的过程。其次,Al元素的加入,从一定程度降低了Ti40合金的组织稳定性,对于快共析型元素Si,合金组织越不稳定,越容易析出。
2.2.3 透射电镜分析
在透射电镜下观察,热暴露50和100 h后的组织除析出物群数量有所不同外,析出相的种类基本相同,或许也存在着析出相种类的不同,但是很难观察到,为此,着重对热暴露200 h后的组织进行了分析,通过典型相的分析可知合金在热暴露过程中组织的变化。图3(a)、3(c)所示为1号、2号合金热暴露200 h后析出相的典型明场像和衍射斑点,图3(b)、3(d)所示为它们主衍射斑点的暗场像,图3(g)、3(h)所示为衍射斑点的标定。从透射电镜明暗场像可以看出,析出物一旦形成,基本都是成群析出,a相和Ti5Si3相互作用,形核长大;从暗场相可以看到析出相的形貌,a相既有板条状,又有块状,Ti5Si3相基本都是颗粒状析出,并且沿析出群有呈线状分布的趋势。通过分析可知,Ti40合金的析出物主要产生在晶界,而这些析出物一旦形成,将互相依助,形核长大,形成析出物群,这些沿晶界产生的析出物群是合金热稳定性降低的主要原因。

图3 合金550 ℃不同热暴露时间的TEM像和衍射斑点
Fig.3 TEM bright and dark field images after thermal exposure at 550 ℃ for 200 h: (a), (b) Bright and dark field micrographs of a phase in b matrix of alloy 1; (c), (d) Ti5Si3 in alloy 2; (e), (f) hcp TiCr2 in alloy 2; (g) b[310] and a[322] diffraction patterns of (a); (h) a and Ti5Si3 diffraction pattern of (c); (i) hcp TiCr2[010] diffraction pattern of (e)
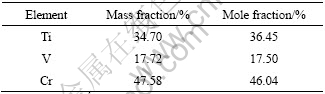
在透射电镜分析中,除了都能看到a相Ti5Si3相外,在2号合金中还观察到了重要的未知相,其形貌、衍射斑点如图3(e)、3(f)所示,成分分析见表2。通过对斑点的标定和成分分析,判定该相为六方TiCr2有序相,晶格常数为:a=0.491 2 nm, c=1.600 4 nm, 具体衍射斑点分析见图3(i)。TiCr2相在该合金系中是一个非常重要的相。在2号合金中观察到了TiCr2相有两种意义:一是TiCr2相作为脆性有序相,本身降低合金的塑性,所以在一般的钛合金设计中,Cr元素的含量都控制在一定范围内。目前,Ti40合金中尚未发现该相[10?12],主要原因除了Cr属于慢共析元素外,合金中高的V含量也会抑制TiCr2相的形成;二是TiCr2相的形成,反映了Al元素降低组织稳定性达到一定的程度,因为在钛合金中,Cr元素属于慢共析元素,TiCr2相的形成受多种因素影响,比如较长时效时间或较高时效温度等,在相同条件下,2号合金中出现较明显TiCr2相,证明Al元素降低Ti40合金组织稳定性达到一定的度。
表2 未知相的成分分析
Table 2 Elements analysis of unknown phase
3 讨 论
1号和2号合金都属于全β合金,热处理后室温为全β组织,具有较低相变点,设计时Al元素的加入,主要是考虑到降低合金的成本(通过Al-V中间合金的使用),同时由于Al元素提高合金相变点,使Tβ转变温度较远离合金工作温度,有望提高或不降低合金热稳定性,但从实验结果看Al元素对于热稳定性有害。这是因为对于热稳定性而言,Al元素的加入有双重作用:其一,提高相变点,对热稳定性有益;其二,使β相稳定性降低,对热稳定性有害。实验结果取决于何种机制起主导作用。对于普通的近a、a+β合金,由于含有较多的Al元素,使得合金室温组织中β相含量较少,保证了热暴露过程中β分解对合金性能影响不大;而对于普通的近β、β合金,Al元素使β相在热暴露过程中的稳定性降低起主导作用。本实验中1号合金有着极高Mo当量,室温下保留稳定的全β相是其重要的特点,这决定了在热暴露过程中β相的稳定对其热稳定性能起主导作用。Al元素的加入促进a相和Ti5Si3相形成,特别是在550 ℃热暴露200 h后出现了TiCr2相,说明Al元素的加入,较显著地降低Ti40合金的组织稳定性,给合金高温使用带来不利的影响。
4 结 论
1) 在热暴露过程中,Al元素促进Ti40合金中a相和Ti5Si3相的析出,并促进TiCr2相的形成;在 550 ℃热暴露200 h的条件下,加入Al元素的Ti40合金中形成了较为明显的TiCr2有序相。
2) Al元素降低Ti40合金热稳定性能的主要原因是降低组织的稳定性,使合金在热暴露过程中生成过多的第二相。
REFERENCES
[1] ZHAO Yong-qing, ZHOU Lian, ZHU Kang-ying, et al. Mechanism of burn resistant titanium alloy Ti-40[J]. Journal of Materials Science and Technology, 2001(6): 677?682.
[2] Zhao Y Q, Zhou L. High temperature deformation mechanism and constitutive equation of Ti40 alloy[J]. Acta Metallurgic Sinica, 2001, 37(1): 406?411.
[3] Li Y G., Blenkinsop P A, Loretto M H, et al. The structure and stability of precipitates in TiV25V15Cr-xAl alloys exposed at 550 ℃[J]. Acta Mater, 1998,14(8): 732?737.
[4] Li Y G, Loretto M H, Rugg D, et al. Effect of heat treatment and exposure on microstructure and mechanical properties of Ti-25V-15Cr-2Al-0.2C (wt%)[J]. Acta Mater, 2001, 49: 3011?3017.
[5] 雷力明, 黄 旭, 孙福生, 等. 热暴露对Ti-25V-15Cr- 2Al-0.2C合金微观组织的影响[J]. 稀有金属, 2003, 27(1): 207?209.
LEI Li-ming, HUANG Xu, SUN Fu-sheng, et al. Effect of thermal exposure on microstructure of Ti-25V-15Cr-0.2C alloy[J]. Chinese Journal of Rare Metals, 2003, 27(1): 207?209.
[6] 黄 旭, 雷力明, 孙福生, 等. Ti-25V-15Cr-2Al-0.2C合金微观组织和相组成研究[J]. 稀有金属材料与工程, 2004, 33(2): 218?230.
HUANG Xu, LEI Li-ming, SUN Fu-sheng, et al. Study of microstructure and phase constituent of Ti-25V-15Cr-2Al-0.2C alloy[J]. Rare Metal Materials and Engineering, 2004, 33(2): 218?230.
[7] Zhao Y Q, Qu H L, Zhu K Y, et al. Oxidation behavior of a burn resistant highly stabilized b titanium alloy[J]. Mater Sci Eng A, 2001, A316: 211?216.
[8] 吴 欢, 赵永庆, 曲恒磊, 等. 两种Ti-V-Cr系阻燃钛合金在450~650 ℃下高温氧化行为[J]. 稀有金属材料与工程, 2003, 32(1): 45?49.
WU Huan, ZHAO Yong-qing, QU Heng-lei, et al. The oxidation behavior at 450~650 ℃ for two Ti-V-Cr b-stabilized titanium alloys[J]. Rare Metal Materials and Engineering, 2003, 32(1): 45?49.
[9] 辛社伟, 赵永庆. 关于钛合金热处理和析出相的研究与讨论[J]. 金属热处理, 2006, 31(9): 39?42.
XIN She-wei, ZHAO Yong-qing. Discussion about the heat treatment and precipitated phases of titanium alloy[J]. Heat Treatment of Metals, 2006, 31(9): 39?42.
[10] Zhao Y Q, Qu H L, Zhu KY, et al. The second phase in Ti40 burn resistant alloy after high temperature exposure for a long time[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2002, 333: 165?169.
[11] Zhao Y Q, Qu H L, Zhu K Y, et al. The second phases in a burn resistant stable beta titanium alloy-Ti40[J]. Journal of Materials Science, 2003, 38: 1579?1584.
[12] Zhu K Y, Zhao Y Q, Qu H L, et al. Thermal stability of Ti-V-Cr burn-resistant alloys[J]. Journal of Materials Science, 2004, 39: 2387?2394.
基金项目:国家重点民口配套资助项目(MKPT-01-101 (ZD));国防“973”资助项目(51333)
收稿日期:2006-12-21;修订日期:2007-06-19
通讯作者:赵永庆,教授;电话:029-86266577;E-mail: trc@c-nin.com
(编辑 陈爱华)