文章编号:1004-0609(2008)07-1216-07
钒和铬对Ti40阻燃钛合金力学性能的影响机制
辛社伟1, 2,赵永庆2,曾卫东1
(1. 西北工业大学 材料学院,西安 710012;
2. 西北有色金属研究院 钛合金研究所,西安 710016)
摘 要:以Ti40合金为基础,配制4种不同V和Cr含量的合金,测试其在锻造、热处理、热暴露和蠕变条件下的相关力学性能,并观察其组织。结果表明:合金元素V和Cr对Ti40合金室温力学性能、蠕变行为和组织的影响具有相似性,即随V和Cr含量的降低,合金室温综合力学性能变化不明显、抗蠕变能力减弱、组织粗化;这与V和Cr同属于β稳定元素、且原子半径都小于Ti原子有关;而V和Cr对于热稳定性能的影响则完全相反,V含量的增加或Cr含量的降低合金热稳定性能优化,其主要原因可能与V属于同晶型β稳定元素而Cr属于共析型β稳定元素有关。
关键词:Ti40阻燃钛合金;V;Cr;热稳定性;蠕变行为;力学性能
中图分类号:TG 146.23 文献标识码:A
Mechanism of V and Cr on mechanical properties of
Ti40 burn resistant titanium alloy
XIN She-wei1, 2, ZHAO Yong-qing2, ZENG Wei-dong1
(1. School of Materials Science and Engineering, Northwestern Polytechnical University, Xi’an 710012, China;
2. Titanium Alloy Research Center, Northwest Institute for Nonferrous Metal Research, Xi’an 710016, China)
Abstract: Four alloys with different contents of V and Cr were prepared on the base of Ti40 alloy. Their properties and microstructures after forging, heat treatment, thermal exposure and creep treatment were tested. The results indicate that the effect of alloying elements V and Cr on mechanical properties at room-temperature, creep behavior and microstructures are similar. With increasing contents of V and Cr, their mechanical properties produce little change, the creep resistant property decreases and microstructure grows, which is mainly due to their characteristics of β-stability element and smaller atomic radius compared with Ti. On the contrary, the effects of V and Cr on the thermal stability are quite different. With increasing V content or decreasing Cr content the thermal stability for the alloy becomes better, which may be due to the different solution characteristics of V and Cr element in titanium alloy that V belongs to isomorphous β-stability element and Cr belongs to eutectoid β-stability element.
Key words: Ti40 burn resistant titanium alloy; V; Cr; thermal stability; creep behavior; mechanical properties
Ti40合金作为我国具有自主知识产权的阻燃钛合金已经研究多年。目前,就合金的阻燃机理[1?2],变形机制[3?4],组织特点[5?6]及高温使用性能[7?8]等方面已经进行广泛研究,取得一定成果。但是,关于合金元素对力学性能方面的影响却鲜见报道,在已有的合金 元素影响机制方面的论述中,仅局限于其阻燃性能[1]。
众所周知,在我国推出Ti40(Ti-25V-15Cr-0.2Si)以前,美国已研制Alloy C(Ti-35V-15Cr)阻燃钛合金,现在发展为Alloy C+合金
[9?10],其名义成分差别仅在于V含量和微量元素的添加。赵永庆等的研究结果表明,Ti40合金和Alloy C合金同样具有优异的阻燃性能,而Ti40合金由于降低V含量而节约了成本。同时V和Cr作为最重要的β稳定元素之一被广泛应用于β钛合金设计中,本文作者的研究成果也可以为以后高β稳定元素(V、Cr含量)合金的设计提供指导。
1 实验
实验用4种合金采用自制中间合金经真空自耗电弧炉3次熔炼,制成5 kg的铸锭,开坯锻造成d 25 mm的圆棒,然后再旋锻成d 12 mm的棒材,热处理后加工成d 5 mm的标准拉伸试样。热处理实验在箱式电阻炉中进行,热处理工艺为820 ℃、0.5 h,水淬+600 ℃、5.0 h,空冷。合金的热稳定实验(500 ℃暴露100 h)和蠕变实验(温度为500 ℃,应力为250 MPa,持续时间为100 h)都是在热处理后进行的。所有拉伸力学性能在Instro?1185拉伸实验机上进行测试,蠕变实验在RD2型蠕变实验机上进行。金相组织、X射线衍射分析、断口扫描电镜和透射电镜分析分别在OLMPUS PMG光学显微镜、PW1700型X射线衍射仪、S?2700型扫描电镜和JEM?200CX型透射电镜下进行,金相腐蚀剂为10%HF+30%HNO3+50%H2O。
不同V和Cr含量的4种合金的名义成分见表1。其中2#合金为西北有色金属研究设计的Ti40合金。
2 结果及分析
2.1 合金的力学性能
表1所列为4种不同合金分别在锻态、热处理态、热暴露和蠕变情况下的性能参数,其中2#合金为Ti40合金的名义成分。
表1 4种合金的名义成分和合金元素V、Cr对合金力学性能的影响
Table 1 Nominal compositions of four alloys and effects of alloying element V, Cr on mechanical properties of Ti40 alloy
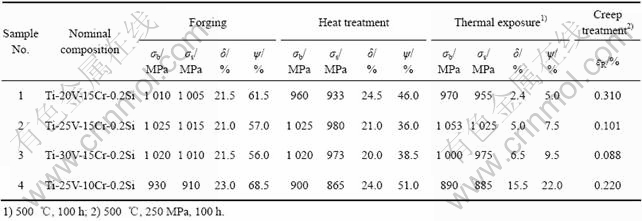
从表1中可以看出,当V含量(质量分数)在20%~ 30%变化时,合金锻态和热处理态的室温力学性能差别不是很大,相对来说,含25%V的2#合金和含30%V的3#合金性能几乎相同,而含20%V的1#合金热处理态的强度有一定程度的降低,这从一定程度反映V含量对室温力学性能影响不是很大。但是,相对来说,高温力学性能参数变化明显,无论是热暴露后的力学性能,还是蠕变性能,当V含量为20%时,性能降低明显,同样,2#合金和3#合金性能却变化不大,这说明这存在一个V元素的临界含量,这个含量是成分与力学性能曲线的拐点,当V元素含量高于这个临界含量时,力学性能统一较好,当在这个临界含量上下取值时力学性能变化明显,从表1中所示的力学性能结果看,这个临界值应该在20%~25%之间。因此从力学性能方面来讲,Ti40合金的V含量为25%也有一定的合理性。对比表1中4#合金和2#合金的力学性能,可以看到Cr含量的降低对Ti40合金力学性能影响较为明显。当Cr含量从15%降低到10%,锻造和热处理后的室温力学性能中,塑性的提高不大,而强度降低明显;合金热暴露后,其强度承接了热处理后的特点(相对不高),而塑性却仍然保持相当的程度;蠕变性能降低也很明显。从这里不难得出,Cr含量的降低,降低合金的强度和蠕变性能,提高合金塑性和热稳定性能。
2.2 合金的晶格常数
图1 所示为Ti40合金(2#合金)经热处理(820 ℃、0.5 h WQ+550 ℃、6 h AC)后的XRD谱。图中直线为标准卡片中β钛合金相应晶面对应的衍射线位置。由图1可知:Ti40合金热处理后仍然为全β组织,析出的第二相很少。Ti40合金的β相衍射峰较标准卡片有较大偏移,合金的(110)、(200)和(211)晶面对应衍射峰的衍射角与标准卡片相差分别是1.990?、2.909?和3.815?,如果将测量误差考虑在内,这种角度差别的递增性正好反应了他们正弦值差别的不变性,是实际衍射结果的体现。通过Brag方程可以计算出Ti40合金的晶格常数约为0.316 8 nm,相对于标准卡片提供的晶格常数0.330 6 nm,减小0.013 8 nm。这主要是因为合金中固溶大量的V和Cr,V和Cr的原子半径都小于Ti,在高温下,合金元素具有高度的活性,使得V和Cr可以均匀地固溶到Ti基体中,并且对晶格能影响不大,但是在低温下,必然对合金的相关性能产生重要影响。
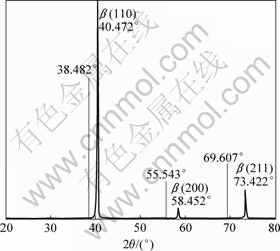
图1 2#合金(Ti40)热处理后的XRD谱
Fig.1 XRD patterns of alloy 2 after heat treatment (Upright line shown in figure is corresponding sites of crystal face β(110), β(200) and β(211) in standard card of β phase)
2.3 合金的组织分析
2.3.1 合金的金相组织
图2所示分别为4种合金在热处理和热暴露状态下的光学显微组织。对比不同合金的组织,可以清楚地看到合金元素对晶粒大小的影响,随V含量的增加,合金组织明显得到细化;而当Cr含量从15%降低到10%,合金组织粗化明显,由此可以认为V和Cr对合金组织的晶粒大小有着重要影响,相比较而言,Cr的影响更为显著;对比不同合金的热处理和热暴露组织,可以看到相差不大,热暴露组织承接了热处理组织,并没有体现出析出物多少的不同,而且不同合金的热暴露组织之间,也看不到析出物多少的差别,仅能观察到晶粒大小的不同,这并不是说明热暴露对合金组织没有影响,赵永庆 等[6?7]及辛社伟等[11?12]的研究结果表明,热暴露后合金塑性降低的结果主要是由于晶界析出物所致,Ti40合金的成分特点决定了在热暴露过程中析出物很少,并且主要分布在晶界,这些都无法在OM组织中得到体现,蠕变的OM组织的特点和热暴露组织相似。

图2 4种合金热处理和热暴露后的金相组织
Fig.2 OM micrographs after heat treatment and thermal exposure for four alloys: (a), (c), (e), (g) and (b), (d), (f), (h) are respectively microstructures of alloys 1, 2, 3 and 4 after heat treatment and thermal exposure at 500 ℃ for 100 h
2.3.2 合金的TEM组织
辛社伟等[6, 11?12]对Ti40合金的热稳定性能进行过系统分析,通过对透射电镜组织的观察指出,虽然Ti40合金在热暴露过程中产生的析出物很少,但是它们大都在晶界形成,从而较严重地影响合金热稳定性能,本实验具有相同的结果。对于不同V、Cr含量的合金,热暴露后力学性能不同的主要原因除了晶粒大小差别之外,与晶界析出物数量的多少也有很大关系,但这些都不能在透射电镜中得到体现(透射电镜照片略)。图3所示为Ti40合金(2#合金)蠕变后的典型TEM组织,其他合金组织具有相似性。从图中可以观察到蠕变过程中位错的分解或合并反应(图3(a)的分叉位错)和由于位错攀移而形成的位错阵列,在析出物周围存在着位错塞积(图3(b)),但这些都很难体现合金元素含量不同的影响,所以合金元素含量对热稳定性能和蠕变性能影响需从机理上进行分析。

图3 Ti40(2#)合金的蠕变组织
Fig.3 TEM bright images of Ti40 alloy after creep treatment: (a) Dislocations and dislocation wall; (b) Precipitates and dislocations
2.3.3 合金的SEM断口形貌
图4所示为4种合金在热暴露后拉伸试样的断口组织,这些断口形貌不但体现不同合金元素含量对晶粒大小的影响,也反映晶界析出物多少的不同。4种合金的断口都既有延晶的脆性断裂,又有穿晶的塑性断裂。裂纹萌生于晶界并沿晶界扩展,随后穿晶形成二次韧窝是合金保持一定塑性的重要原因。对比图4(a)~(c)可以看到,随V含量的增加,合金中穿晶韧性断裂相对增多,证明晶界析出物对合金晶界弱化作用降低,也反映晶界析出物的减少;同样,4#合金的断口组织中展现最多的穿晶韧窝,这与表1中所列的力学性能是对应的,证明Cr含量的降低使晶界弱化明显降低,从而得到更好的塑性。
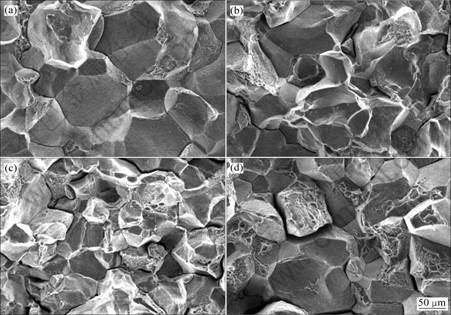
图4 合金热暴露后的断口形貌
Fig.4 SEM fractographs for four alloys after thermal exposure at 500 ℃ for 100 h: (a) Alloy 1; (b) Alloy 2; (c) Alloy 3; (d) Alloy 4
3 讨论
3.1 V元素的影响
从上述试验结果可以看到,V含量的增加,不但可以细化合金组织,而且提高合金的热稳定性和蠕变性能。对于V细化组织,这和一般合金元素作用相似,几乎所有的合金元素都有细化组织的作用[13],V细化Ti40合金组织可能与其稳定β晶格,增加合金键强有关。V对热稳定性能的影响主要与晶界析出物有关,作为同晶型β稳定元素,V含量增加,必然β相稳定能力增强,这样在热暴露过程中第二相就更不容易析出,降低了析出物的总量;其次,V细化组织,增加了合金中的晶界数量,也会降低单位晶界析出物的数量。这样,无论是从析出物的总量,还是单位析出物的数量方面都呈下降趋势(强度相对较低),从而减少晶界析出物,降低晶界析出物对合金晶界的弱化作用(塑性相对较高),提高了热稳定性能;V提高蠕变性能主要是与其在钛合金中的固溶性质有关。在3.2节的分析中已经指出,由于V和Cr的固溶,造成合金晶格常数的降低,V的原子半径小于Ti原子,V的加入必然造成β晶格的畸变,并且V属于β稳定元 素,稳定β晶格能力较强,由此可以推测在β晶格中,βTi—V的键强要强于βTi—Ti键强[14?16]。也就是说,V的加入,不但使β发生畸变,而且加强了畸变晶格中原子之间的结合力,这种稳定的畸变晶格(在蠕变温度下依然能够得到保持)产生的应力场可以有效的阻碍蠕变过程中的位错滑移和攀移,对晶界的滑移也有一定的阻碍作用;并且由于原子之间键强的增强,有效的降低了蠕变过程中原子和空位的形成和扩散能力[17],从而提高了合金的蠕变强度。
3.2 Cr元素的影响
从图2的组织对比可以得出,随Cr含量的增加,合金组织也会得到细化,这与V的作用效果是相似的。但是Cr含量的降低,却能有效提高合金的热稳定性能(热暴露后合金仍然保持良好的塑性),这可能与Cr在钛合金中属于共析元素的性质有关。对于Ti40合金,当Cr含量变化时,由于β晶格稳定能力不同造成的在热暴露过程中析出物量的不同将不起主要作用,而起关键作用的可能是由Cr共析性质决定的形成的一些Cr的初级偏聚区。虽然到目前为止,Ti40合金500 ℃热暴露100 h组织中没有发现Ti-Cr元素的共析有序相—TiCr2相,但是相信经长时间热暴露后,必然会在合金中产生一些Cr的初级偏聚区,这些偏聚区会严重影响合金的热稳定性能,Cr含量的降低,减少或消除了这些偏聚区,从而提高了合金的热稳定性能。也或许是这个原因,Ti40和Alloy C都选择了15%的Cr含量,因为当Cr含量过低时,根据赵永庆等人的研究,合金阻燃性能将得不到满足,并且室温强度也较低,而当Cr含量较高,室温塑性和热稳定性能必然急剧下降。
3.3 V元素和Cr元素的影响比较
同样作为β稳定元素,V和Cr对Ti40合金力学性能的影响既具有相似性,也有不同性,这正好是V和Cr在钛合金中作用性质的体现。由于他们同属于β稳定元素,而且原子半径都小于Ti的原子半径,所以它们对合金晶粒细化作用和蠕变强化作用相似,但是在这种相似性的前提条件下,存在着影响程度的不同。从表1中的力学性能和图2与图4中的组织特点都可以看出,Cr对力学性能和晶粒大小的影响明显强于V,这正好体现了V和Cr对β晶格稳定能力和原子半径的不同。从β稳定元素的临界浓度(V为15%,Cr为6.4%)或它们的Mo当量系数(V的Mo当量系数为0.699;Cr的Mo当量系数为1.613)可以看出,Cr的稳定β相能力约为V元素的2.3倍;而且,Cr的原子半径比Ti的原子半径更小(Ti的原子半径为0.145 nm;V的原子半径为0.135 nm;Cr的原子半径为0.127 nm),所以,Cr的加入造成的晶格畸变更严重,形成的应力场更强,因此,对力学性能和晶粒大小的影响更明显。然而,同作为β稳定元素,V和Cr元素对热稳定性的影响却完全相反,本文作者认为这是由于它们在βTi晶格中的同晶和共析性质决定的。V作为β同晶型合金元素,它固溶到βTi中将不会析出任何析出物,稳定地存在于βTi晶格中;而Cr是共析型合金元素,虽然它和Ti元素形成的共析产物TiCr2需要一定的温度和相当长的时间(在Ti合金中Cr属于慢共析元素),但是这证明了Cr在βTi中固溶的不稳定性,在长时时效或热暴露过程中它有形成TiCr2相的趋势,即先形成Cr的初级偏聚区,进而向有序TiCr2相转变。这或许是Cr和V对热稳定性能影响不同的根本原因。
4 结论
1) V和Cr对Ti40合金的组织有不同程度的细化作用,随V和Cr含量的增加,合金组织呈现一定细化倾向,相对于V而言,Cr的细化作用更为明显。
2) V含量的变化对Ti40合金室温力学性能影响不大,Cr的影响较为显著,随Cr含量的降低,合金强度降低,塑性升高。
3) 随V和Cr含量的降低,合金抗蠕变能力都减弱,但Cr的作用强于V,这是由于它们同属于β稳定元素,而原子半径和对β相的稳定能力又不同,从而在合金中造成不同的畸变应力场所致。
4) V和Cr对于合金热稳定性能的影响表现出不同的结果,V的增加或Cr的降低使合金热稳定性能得到优化,这可能与V属于同晶型元素而Cr属于共析型元素有关。
REFERENCES
[1] ZHAO Y Q, ZHOU L. Mechanism of burn resistant titanium alloy Ti-40[J]. Journal of Materials Science and Technology, 2001, 17(6): 677?682.
[2] ZHAO Y Q, ZHOU L, DENG J. The role of interface in the burning of titanium alloys[J]. Mater Sci Eng A, 1999, 267: 167?171.
[3] ZHAO Y Q, ZHOU L. High temperature deformation mechanism and constitutive equation of Ti40 alloy[J]. Acta Metallurgica Sinica, 2001, 13(1): 406?411.
[4] 赵永庆. Ti40阻燃钛合金的变形机理和阻燃机理研究[D]. 沈阳: 东北大学, 1998.
ZHAO Yong-qing. Deformation mechanism of Ti40 burn resistant mechanical of Ti40 burn resistant titanium alloy[D]. Shenyang: Northeast University, 1998.
[5] ZHAO Y Q, QU H L, ZHU K Y, WU H, ZHOU L. The second phases in a burn resistant stable beta titanium alloy-Ti40[J]. Journal of Materials Science, 2003, 38: 1579?1584.
[6] ZHAO Y Q, QU H L, ZHU K Y, WU H, LIU C L, ZHOU L. The second phase in Ti40 burn resistant alloy after high temperature exposure for a long time[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2002, 333: 165?169.
[7] ZHU K Y, ZHAO Y Q, QU H L, WU H. Thermal stability of Ti-V-Cr burn-resistant alloys[J]. Journal of Materials Science, 2004, 39: 2387?2394.
[8] ZHAO Y Q, QU H L, ZHU K Y, WU H. Oxidation behavior of a burn resistant highly stabilized β titanium alloy[J]. Mater Sci Eng A, 2001, 316: 211?216.
[9] WORD C H, SPANOS G, BRODERICK T F,RESHAD J. Isothermal transformation of precipitates in Alloy C+[C]//BLENKINSOP P A, EVANS W J, FLOWER H M. Titanium’95 Science and Technology. UK: The Institute of Materials, 1995: 2377?2379.
[10] BRODERICK T F, RESHAD J, WARD C H, SCHELTENS F J. Solvus temperature of various phase in Alloy C+[C]//BLENKINSOP P A, EVANS W J, FLOWER H M. Titanium’95: Science and Technology. UK: The Institute of Materials, 1995: 2377?2379.
[11] 辛社伟, 赵永庆, 曾卫东, 吴 欢, 杨海瑛, 李 倩. 550 ℃热暴露对Ti40阻燃钛合金力学性能的影响[J]. 金属热处理, 2007, 32(9): 55?58.
XIN She-wei, ZHAO Yong-qing, ZENG Wei-dong, WU Huan, YANG Hai-ying, LI Qian. Effect of thermal exposure at 550 ℃ on mechanical properties of Ti40 burn resistant titanium alloy[J]. Heat Treatment of Metals, 2007, 32(9): 55?58.
[12] XIN S W, ZHAO Y Q, ZENG W D,WU H. Research on thermal stability of Ti40 alloy at 550 ℃[J]. Mater Sci Eng A, 2008, 477: 372?378.
[13] HAYES R W, VISWANATHAN G B, MILLS M J. Creep behavior of Ti-6Al-2Sn-4Zr-2Mo (Ⅰ): The effect of nickel on creep deformation and microstructure[J]. Acta Mater, 2002, 50: 4953?4963.
[14] 刘伟东, 刘志林, 屈 华, 刘 艳. 高合金化β钛合金拉伸延性的价电子理论分析[J]. 金属学报, 2002, 38(10): 1037?1041.
LIU Wei-dong, LIU Zhi-lin, QU Hua, LIU Yan. Study on the tensile ductility of high alloying β-titanium alloy with the valence electron theory[J]. Acta Metallurgica Sinica, 2002, 38(10): 1037?1041.
[15] MORINAGA M, YUKAWA N, MAYA T, SONE K, ADACHI H. Theoretical design of β-type titanium alloys[C]//LACOMBE P, TRICOT R, B?RANGER G. Sixth World Conference on Titanium. France: Société Francaise de Métallurgie, 1988: 217?224.
[16] 张济山, 崔 华, 胡壮麒. d电子合金理论及其在合金设计中的应用[J]. 材料科学与工程, 1993, 11(3): 1?10.
ZHANG Ji-shan, CUI Hua, HU Zhuang-qi. d-electrons alloy theory and its application in alloy design[J]. Mater Sci Eng, 1993, 11(3): 1?10
[17] K?PPERS M, HERZIG C, FRESEL M, MISHIN Y. Intrinsic self-diffusion and substitutional Al diffusion in α-Ti[J]. Acta Mater, 1997, 45(10): 4181?4191.
基金项目:国家重点民口配套基金资助项目(MKPT?01?101(ZD));国家重点基础研究发展计划资助项目(2007CB613807)
收稿日期:2007-08-27;修订日期:2007-12-05
通讯作者:赵永庆,教授,博士;电话:029-86231078-435;E-mail: trc@c-nin.com
(编辑 龙怀中)