DOI: 10.11817/j.ysxb.1004.0609.2021-39726
β转变组织TA15钛合金的流动软化行为
董显娟1,胡生双2,徐 勇1,鲁世强1
(1. 南昌航空大学 轻合金加工科学与技术国防重点学科实验室,南昌 330036;
2. 航空工业西安飞机工业(集团)有限责任公司,西安 710089)
摘 要:利用等温压缩实验研究了β转变组织TA15钛合金在变形温度750~950 ℃、应变速率0.001~10 s-1范围内的流动软化行为,定量分析了变形热效应和微观组织演变对流动软化行为的影响。结果表明:变形热效应是β转变组织TA15钛合金流动软化的重要机制,变形热软化程度随着变形温度的下降和应变速率的增大而增强,最高占到总流动软化程度的48.2%;动态再结晶、动态回复和流动失稳缺陷等形式的微观组织演变是流动软化的主要机制。基于动态材料模型,利用应变速率敏感性指数预测了3种微观组织演化形式主导的软化区域,并通过微观组织观测进行了验证。
关键词:TA15钛合金;流动软化;变形热效应;微观组织演变
文章编号:1004-0609(2021)-04-0858-10 中图分类号:TG146 文献标志码:A
引文格式:董显娟, 胡生双, 徐 勇, 等. β转变组织TA15钛合金的流动软化行为[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2021, 31(4): 858-867. DOI: 10.11817/j.ysxb.1004.0609.2021-39726
DONG Xian-juan, HU Sheng-shuang, XU Yong, et al. Flow softening behavior of TA15 titanium alloy with lamellar microstructure[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2021, 31(4): 858-867. DOI: 10.11817/j.ysxb.1004.0609.2021-39726
钛合金具有比强度高、耐热性能好和抗腐蚀性好等优异性能,是航空航天领域重要的轻质结构材料。钛合金加热到相变点以上,因冷却速度不同可得到针状、细片状或粗片状β转变组织[1]。在后续的热加工过程中,这种转变组织对合金的加工性能和变形机理有重要影响[2-4]。合金在热加工过程中,由于加工硬化与流动软化的交互作用导致流变应力对变形工艺参数的响应呈现高度的非线性[5]。一方面,由于塑性变形使位错密度迅速增加,形成位错塞积或缠结,流动应力增大,呈现加工硬化现象;另一方面,由于动态回复(Dynamic recovery, DRV)或动态再结晶(Dynamic recrystallization, DRX)引起的位错湮灭等原因,材料发生流动软化。
由于DRV与DRX的交互作用、变形热效应等原因,金属材料在热变形时的主要流动软化机制有所不同。AZ80镁合金在变形温度200~400 ℃、应变速率0.001~1 s-1范围内热变形时,其流动软化行为由DRX主导[6];253MA不锈钢在高应变速率条件下变形时主要流动软化机制是变形热效应,DRX对流动软化有重要影响[7];在变形温度300~500 ℃、应变速率0.01~10 s-1条件变形时,6061铝合金流动应力在达到峰值应力后呈现连续流动软化,软化机制以DRV为主[8];Ti-22Al-26Nb合金在温度950~1050 ℃、应变速率0.01~1 s-1范围内热变形时,其流动软化机制为DRX[9]。针对钛合金的流动软化行为,国内外研究人员也开展了广泛的研究。GHASEMI等[10]研究变形温度1000~1100 ℃、应变速率0.001~0.1 s-1范围内BT9钛合金的热变形行为时,发现其流动软化由DRV和DRX共同引起,DRX仅发生在1000 ℃、0.1 s-1条件下,其他变形条件下以DRV为主;赵慧俊等[11]认为DRX主导的动态球化是双态Ti-6Al-2Zr-1Mo-1V合金的流动软化机制;MILLER等[12]提出片层组织的扭曲与塑性屈服是片层Ti-6Al-4V钛合金流动软化的主要机制;LIU等[13]认为Ti-1.5Fe-2.25Mo-0.6Y合金流动软化机制是连续动态再结晶;梁后权等[14-15]在TC18钛合金高温变形行为的研究中发现:低应变速率(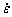 ≤0.001 s-1)条件下,软化机制以动态再结晶为主;而高应变速率(
≤0.001 s-1)条件下,软化机制以动态再结晶为主;而高应变速率(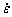 >0.001 s-1)条件下,软化机制以动态回复为主;并且在较高温度范围内,软化行为选择对变形温度并不敏感。由此可知,钛合金的流动软化行为较为复杂,它与变形温度、应变速率和变形量等参数密切相关。一般认为,随着变形温度升高和应变速率降低,DRX软化效应增强。当应变速率较高时,变形时间不充分,不利于DRX进行,但是高应变速率产生的变形热提高了材料的温度,又有利于DRX的发生。对热传导性较差的钛合金来说,高应变速率变形时极易导致局部流动、微裂纹等塑性失稳,也会引起流动软化[16]。因此,为提高钛合金塑性成形性能、确定热加工载荷及改善合金微观组织,有必要对其热变形过程流动软化机制开展深入的研究。另外,变形热效应和微观组织演变对钛合金流动软化行为定量影响的研究目前还未见相关报道。
>0.001 s-1)条件下,软化机制以动态回复为主;并且在较高温度范围内,软化行为选择对变形温度并不敏感。由此可知,钛合金的流动软化行为较为复杂,它与变形温度、应变速率和变形量等参数密切相关。一般认为,随着变形温度升高和应变速率降低,DRX软化效应增强。当应变速率较高时,变形时间不充分,不利于DRX进行,但是高应变速率产生的变形热提高了材料的温度,又有利于DRX的发生。对热传导性较差的钛合金来说,高应变速率变形时极易导致局部流动、微裂纹等塑性失稳,也会引起流动软化[16]。因此,为提高钛合金塑性成形性能、确定热加工载荷及改善合金微观组织,有必要对其热变形过程流动软化机制开展深入的研究。另外,变形热效应和微观组织演变对钛合金流动软化行为定量影响的研究目前还未见相关报道。
本工作通过β转变组织TA15钛合金等温恒应变速率压缩实验,基于流动软化特征与微观组织演变对其变形行为进行描述,分析其热变形过程的变形热效应、微观组织演变对流动软化行为的影响。研究结果对优化TA15钛合金加工参数和改善合金微观组织具有重要的工程应用价值和理论指导意义。
1 实验
实验用TA15钛合金棒料化学成分(质量分数,%)为:Al 6.3,Zr 1.97,Mo 1.4,V 1.4,O 0.08,N 0.01,Ti余量。金相法测得其(α+β)/β相变点为990 ℃。材料在1020 ℃保温30 min后随炉冷却,微观组织如图1所示。由图1可知,微观组织中原始β晶粒轮廓清晰,晶界α片层厚度较大,约6 μm;晶内α相呈集束状分布,α相平均片层厚度约4.3 μm。压缩试样沿棒料长度方向取样,尺寸为直径8 mm×12 mm圆柱体,两端刻有0.2 mm深的凹槽,用来储存玻璃粉润滑剂以减小摩擦。
图1 TA15钛合金原始组织
Fig. 1 Initial microstructure of TA15 titanium alloy
压缩实验在THERMECMASTOR-Z型热加工模拟实验机上进行,变形温度为750~950 ℃,应变速率为0.001~10 s-1,压下量为50% (真应变0.69)。实验采用真空感应加热,升温速度为10 ℃/s,加热至设定温度后保温210 s,变形完成后氦气冷却,冷却速度30 ℃/s。变形后试样沿压缩方向对半切开,经机械研磨、抛光后选用Kroll试剂腐蚀。腐蚀后的试样在XJP-6A型金相显微镜上进行微观组织观察,透射电镜实验在Tecnai G2 20ST型透射电子显微镜上进行。
2 流动软化行为
2.1 应力-应变曲线
图2所示为不同变形温度和变形速率条件下TA15合金的应力-应变曲线,反映了变形温度、应变速率和应变对流变应力的影响。由图2可以看出,流变应力随着变形温度的升高而下降,随着应变速率的加快而增大。这是因为变形温度的升高提高了金属材料原子间的活动能力,原子扩散加速,热激活作用加强,增强了动态软化效应,从而导致流变应力减小;而应变速率的增大导致材料发生相同变形程度下的变形时间缩短,位错的滑移或攀移运动进行不充分,削弱了软化效应,从而流变应力增加。由图2还可以看出,在所有变形温度和应变速率条件下,流变应力达到峰值后表现出连续流动软化特征,并呈现逐渐趋于稳定的趋势。
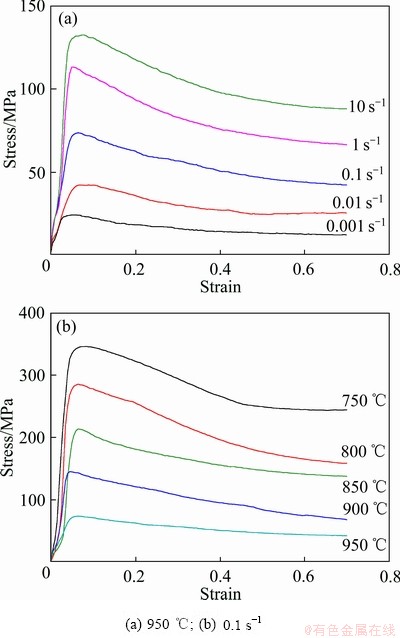
图2 TA15合金的应力-应变曲线
Fig. 2 Stress-strain curves of TA15 alloy
2.2 流动软化程度
为分析不同变形条件下TA15合金热变形过程中的流动软化行为,定义流动软化程度(Decline ratio of flow stress, DRFS),表示如下:
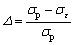 (1)
(1)
式中: 为流动软化程度;
为流动软化程度; 为峰值应力;
为峰值应力;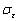 为某应变时的流动应力。
为某应变时的流动应力。
图3所示为应变为0.69时不同变形温度和应变速率条件下TA15钛合金的  曲线。从图3(a)可知,当应变速率恒定时,在750~900 ℃范围内
曲线。从图3(a)可知,当应变速率恒定时,在750~900 ℃范围内 随着变形温度的上升而增大,在900 ℃时
随着变形温度的上升而增大,在900 ℃时 达到峰值,随后当继续温度上升,
达到峰值,随后当继续温度上升, 反而有所下降,;在应变速率为0.001 s-1变形时,
反而有所下降,;在应变速率为0.001 s-1变形时, 较高。从图3(b)可以看出,在较低温度变形(750~850 ℃)时,随着应变速率的提高,
较高。从图3(b)可以看出,在较低温度变形(750~850 ℃)时,随着应变速率的提高, 先降低而后又增大,在应变速率0.1 s-1时最大;在较高温度变形(900~950 ℃)时,
先降低而后又增大,在应变速率0.1 s-1时最大;在较高温度变形(900~950 ℃)时, 随着应变速率的提高而下降,在应变速率10 s-1时最小。
随着应变速率的提高而下降,在应变速率10 s-1时最小。
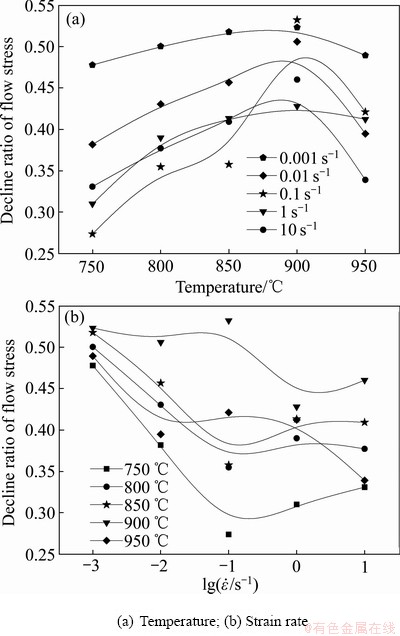
图3 应变0.69时变形参数对TA15合金DRFS的影响
Fig. 3 Effect of deformation temperature on decline ratio of flow stress of TA15 alloy at true strain of 0.69
 随变形温度和应速率变化的复杂性说明在不同的变形条件下,材料流动软化机制发生了变化。
随变形温度和应速率变化的复杂性说明在不同的变形条件下,材料流动软化机制发生了变化。
3 流动软化机制
3.1 变形热效应
材料的热变形过程中,大约仅有5%的塑性变形功储存在材料中,而大约95%的塑性变形功转化为热能,塑性变形导致的变形热会导致材料的温度上升,这种温度上升现象受塑性变形应变速率和变形温度的影响,通常可采用式(2)计算温升(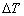 )[17]:
)[17]:
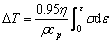 (2)
(2)
式中:0.95是机械能转换为热能的效率;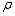 是材料密度;cp是材料的定压比热容(J/g·K);
是材料密度;cp是材料的定压比热容(J/g·K); 是Taylore- Quinney绝热修正系数,可由式(3)计算[18]:
是Taylore- Quinney绝热修正系数,可由式(3)计算[18]:
 (3)
(3)
式中:TA15钛合金密度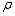 为4.45 g/cm3,根据其不同温度下的定压比热容[19]可由插值式(4)计算本实验温度范围内的定压比热容:
为4.45 g/cm3,根据其不同温度下的定压比热容[19]可由插值式(4)计算本实验温度范围内的定压比热容:
 (4)
(4)
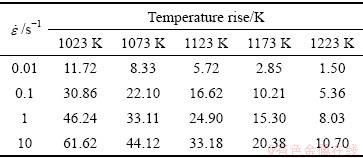
根据式(2)~(4),可以计算出TA15钛合金在不同变形条件下因变形热导致的温升。表1所示为应变0.69时、不同应变速率和变形温度下TA15钛合金的温度上升情况。由表1可以看出,在高温、低应变速率条件下,变形热导致的温升效应较小,在950 ℃、0.01 s-1条件下,温升仅为1.50 ℃;而在低温、高应变速率条件下,温升则较大,在750 ℃、10 s-1条件下,温升达到为61.62 ℃。因为变形温度低,材料的变形抗力增大,更多的变形功转化为热能;而高的应变速率,使得变形热向外扩散的时间缩短。因此,低温、高应变速率条件下,材料的变形热效应更明显。
表1 应变0.69时TA15合金试样的温升
Table 1 Temperature rise of TA15 alloy during deformation at different temperatures and true strain of 0.69
变形热引起的试样温度上升,必然会导致流动应力下降。在金属材料变形热导致流动软化的研究中,DEVADAS等[20]建立的模型应用较为广泛:
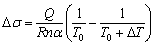 (5)
(5)
式中:Q为变形激活能;R为摩尔气体常数;n和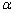 为材料常数。但是,参数Q、n和
为材料常数。但是,参数Q、n和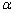 通常不是恒定的,受到变形温度、应变速率等条件的影响。实验采集的应力数据已经包含了变形热的影响,因此,利用实验采集的应力应变数据计算得来的Q、n和
通常不是恒定的,受到变形温度、应变速率等条件的影响。实验采集的应力数据已经包含了变形热的影响,因此,利用实验采集的应力应变数据计算得来的Q、n和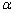 值,再去计算变形热导致的流动软化,其误差在计算过程中被二次放大,可能会影响结果的准确性。
值,再去计算变形热导致的流动软化,其误差在计算过程中被二次放大,可能会影响结果的准确性。

图4 应变速率10 s-1、应变0.69时变形热修正流动应力的计算
Fig. 4 Stress correction for deformation heating at strain rate of 10 s-1 and strain of 0.69
本工作采用ZHANG等[7]提出的方法来计算变形热导致的流动软化。图4所示为应变速率10 s-1、应变0.69时计算变形热修正流动应力方法的示意图。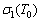 为未修正的流动应力值,由于变形热导致试样温度上升(
为未修正的流动应力值,由于变形热导致试样温度上升( ),试样内部实际温度高于实验值。由图4可知,变形温度850 ℃时实验所得流动应力
),试样内部实际温度高于实验值。由图4可知,变形温度850 ℃时实验所得流动应力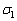 (850),修正后,变形温度为
(850),修正后,变形温度为 ℃。因此,修正后,
℃。因此,修正后, ℃变形时的流动应力
℃变形时的流动应力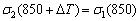 。由于
。由于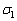 (T0)、
(T0)、 数据呈现良好的线性关系,由图4可知,
数据呈现良好的线性关系,由图4可知,
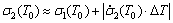 (6)
(6)
根据式(6),可计算出不同变形温度和应变速率条件下,由于变形热导致的流动应力软化值。图5所示为TA15合金在不同变形条件下变形热修正的应力-应变曲线。由图5可以看出,在低温、高应变速率条件下,变形热对流动应力有显著的影响。在温度750 ℃、应变速率10 s-1变形条件下,真应变达到0.69时,因变形热引起的流动软化为75.6 MPa。从变形热修正后的应力-应变曲线可以看出,应力达到峰值后随应变增大仍然表现出逐渐减小并趋于稳定的趋势,说明还存在变形热之外的流动软化机制。根据动态材料模型理论,热变形过程中工件单位体积吸收的机械功率可通过两个方面进行耗散:即大部分转变为粘塑性热、少量以晶格畸变能的形式存储,另一部分与动态回复、动态再结晶、微裂纹及超塑性变形等组织演变相关。将流动软化机制分为变形热效应和微观组织演变两种形式,根据变形热修正的应力应变数据可定量计算出两种机制的软化效果。如图5(a)所示,在温度750 ℃、应变速率10 s-1的变形条件下,真应变达到0.69时,变形热导致的流动软化占总流动软化的比例可通过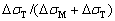 计算。不同变形条件下,TA15钛合金变形热软化占总流动软化的比例如表2所示。在低温、高应变速率区域,变形热效应软化明显,如750 ℃、10 s-1变形时,变形热效应软化达到48.2%,与微观组织演变软化相当;随着温度的升高和应变速率的降低,变形热效应软化占比逐渐下降,微观组织演变软化占比逐渐增加。
计算。不同变形条件下,TA15钛合金变形热软化占总流动软化的比例如表2所示。在低温、高应变速率区域,变形热效应软化明显,如750 ℃、10 s-1变形时,变形热效应软化达到48.2%,与微观组织演变软化相当;随着温度的升高和应变速率的降低,变形热效应软化占比逐渐下降,微观组织演变软化占比逐渐增加。

图5 变形热修正后的TA15试样应力-应变曲线
Fig. 5 Stress-strain curves corrected for deformation heating of TA15 alloy at temperature of 750 ℃(a), 800 ℃(b), 900 ℃(c), 950 ℃(d)
3.2 微观组织演变
图6所示为TA15钛合金在不同变形条件下试样心部大变形区的金相组织。从图6(a)可以看出,在750 ℃、0.001 s-1变形时,还存在明显的原始β晶界,α片层发生了小幅度弯折,大部分仍保持集束状分布。随着变形温度升高(见图6(b)~(d)),α片层弯折、等轴化程度增大,等轴α晶粒明显增多。当变形温度为950 ℃时,片层α组织基本转化为短棒状和等轴状晶粒,等轴α相约占45%(体积分数),晶粒尺寸明显减小,少量存在的片层α相平均厚度也从原始的5 μm降为3 μm。另一方面,随着变形温度的升高α相体积分数明显减少,当变形温度为750~900 ℃时,α相体积分数约70%~80%;当温度达到950 ℃时,α相的体积分数下降到30%~40%。同时,片层α相的等轴化对应变速率有较大的敏感性,随着应变速率增大,α相的等轴化程度减小(见图6(c)、(e)和(f))。当应变速率为0.001 s-1时,等轴α相比例约为33%,大部分α相呈短棒状,还有少量晶界α相呈长条状。当应变速率为0.01~10 s-1时,随应变速率增大,α相的等轴化百分比逐渐减小,片层α相的长宽比逐渐增大,原始β晶粒边界趋于平直完整。
表2 不同变形温度下TA15钛合金变形热软化占总流动软化的比例
Table 2 Ratio of deformation heating softening to total flow softening of TA15 titanium alloy at different temperatures
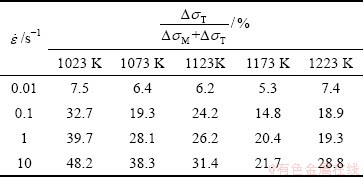
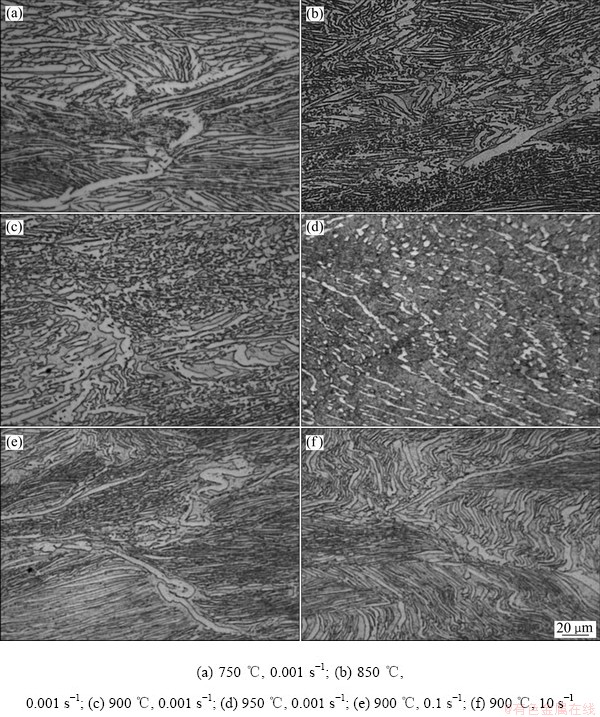
图6 不同变形温度和应变速率时TA15钛合金的微观组织
Fig. 6 Microstructures of TA15 alloy at different temperatures and strain rates (ε=0.69)
研究表明[21-22],不同类型的组织软化机制对应不同的功率耗散效率η。根据动态材料模型理论,热变形过程中工件单位体积吸收的机械功率P可通过两个方面进行耗散:即功率耗散量G和与功率耗散协量J。
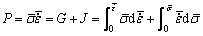 (7)
(7)
式中: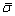 为等效应力;
为等效应力; 为等效应变速率。根据η的定义,可知:
为等效应变速率。根据η的定义,可知:
 (8)
(8)
式中:m为应变速率敏感性指数。
材料在稳定塑性变形时,m值在DRV软化区维持一个恒定的值,而DRX软化区具有更明显的应变速率敏感性,对应的m值更大[15]。如ZK60镁合金DRV软化区对应的m值为0.16~0.22[23],而m值大于0.22以上区域为AZ80镁合金的DRX软化区[6],AA7075铝合金DRV软化区对应的m值为0.17~0.40[24]。对于钛合金来说,研究表明[21-22, 25] η值介于0.1~0.3为DRV软化区,大于0.35为DRX软化区。结合式(8),m值介于0.05~0.21之间的区域可认为是TA15钛合金的DRV软化区,m大于0.21的区域为DRX软化区。图7所示为TA15钛合金不同变形温度和应变速率时m值分布图。由图7可知,阴影部分为DRX软化区,可以看出,DRX软化区位于低应变速率区域,随着变形温度的升高,软化区的应变速率上限增加。变形温度为750 ℃应变速率宜控制在0.005 s-1以下,当变形温度上升为890 ℃后,应变速率可增大到0.056 s-1;当温度进一步上升到930~950 ℃,应变速率可增大至0.2 s-1以内。但是在低应变速率区域(0.001~0.018 s-1) 变形温度890~930 ℃范围存在一个低m值区域,即DRV软化区。这可能是因为m值在850 ℃附近达到峰值后,随着温度的上升,相转变α+β→β开始大量发生,使得β相的体积分数明显增大,变形以较软的β相为主,大量相转变降低了组织的稳定性,使得m值下降至0.1左右。
图8所示为TA15钛合金在DRX软化区和DRV软化区压缩变形后的TEM像。从图8(a)可以看出,片层α相中发生了连续DRX,片状α相内的亚晶界通过聚集位错提高位错密度使小角度晶界转为大角度晶界,或者通过β相沿亚晶界楔入形成等轴状α晶粒。等轴状α晶界呈圆弧形,这正是发生DRX以及晶界原子发生长时间扩散的结果。类似的微观组织特征,在一些动态再结晶或球化行为的研究中也被发现[11, 26]。图8(b)中位错通过滑移和攀移而发生多边形化,形成亚晶界,产生大量规则排列的位错胞。由于钛合金的层错能较高,在热变形过程中,通过位错滑移形成位错墙和位错缠结,动态回复容易发生,动态回复降低了储存能从而降低了再结晶的驱动力。另外,α+β→β转变的大量发生,进一步消耗了再结晶的驱动力。因此,在850 ℃、0.001 s-1的变形条件下,组织软化以DRX为主,而在900 ℃、0.01 s-1的变形条件下,组织软化以DRV为主。
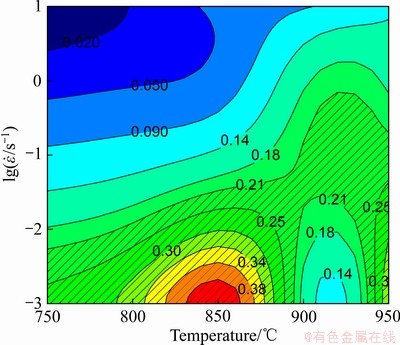
图7 TA15钛合金不同变形温度和应变速率时的m值
Fig. 7 Contour map of strain rate sensitivity index m of TA15 alloy at different temperatures and strain rates (ε=0.69)
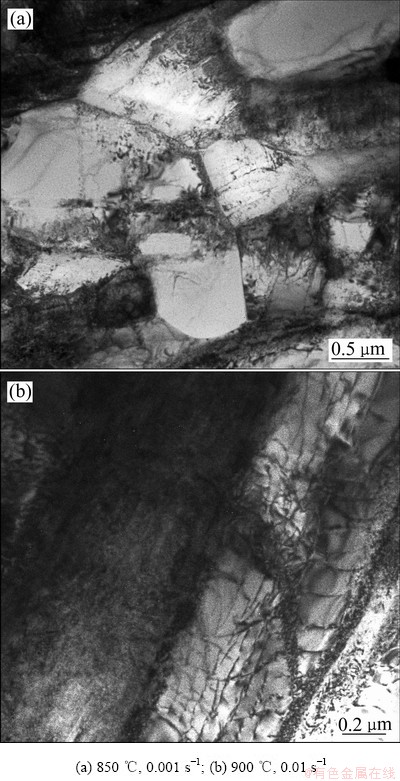

图8 TA15钛合金的TEM像
Fig. 8 TEM images of TA15 alloy at different temperatures and strain rates (ε=0.69)
m值在0.05以下的区域,对应于低温、高应变速率(750~850 ℃、1~10 s-1)区,TA15钛合金在该区域变形时会发生流动失稳现象,在微观组织中产生局部流动、微孔洞和微裂纹等缺陷,甚至试样表面出现宏观剪切裂纹。研究表明,随着m值的减小,局部流动指数增大[22],微孔洞生长指数增大[27]。对于炉冷态片层组织TA15钛合金,其变形过程中的局部流动在较大的变形参数范围内都存在(见图6(a)、(b)、(e)和(f)中深灰色条带)。局部流动随应变速率增大和变形温度降低而增大,尤其是在低温、高应变速率区这种局部流动更加剧烈,并形成微孔洞甚至微裂纹。图9所示为TA15钛合金在低温、高应变速率条件下变形时产生的微孔洞和微裂纹。由图9可见,低温、高应变速率变形时产生局部流动、微孔洞及微裂纹等缺陷也会导致材料发生流动软化,流动应力下降。
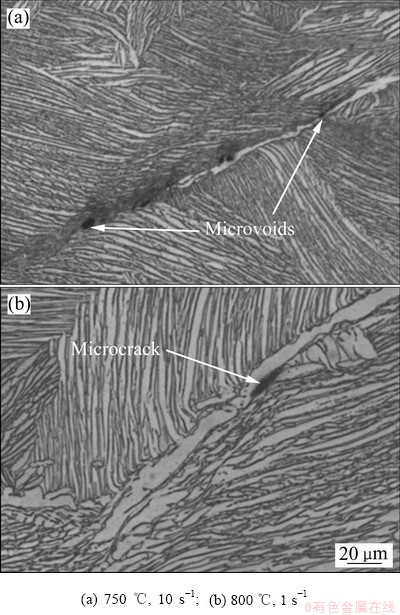
图9 TA15钛合金变形试样中的微孔洞和微裂纹
Fig. 9 Microviods and microcrack of TA15 alloy at different temperatures and strain rates
4 结论
1) β转变组织TA15钛合金在温度750~950 ℃、应变速率0.001~10 s-1范围内变形时,呈现出明显的流动软化行为。流动软化程度受变形温度和应变速率的影响,软化机制为微观组织演变和变形热效应。
2) 变形热效应是β相转变组织TA15钛合金流动软化的重要机制。变形热效应导致的流动软化程度随变形温度下降和应变速率加快而增强,在750 ℃、10 s-1变形时,变形热软化程度最大,占总流动软化程度的48.2%。
3) 微观组织演变是β转变组织TA15钛合金流动软化的主要机制。DRX、DRV和局部流动、微孔洞、微裂纹等流动失稳缺陷是导致流动软化的微观组织演变形式,m值大于0.21的区域为DRX软化区,m值介于0.05~0.21之间的区域为DRV软化区,m值小于0.05的区域为流动失稳软化区。
REFERENCES
[1] 陈慧琴, 曹春晓, 郭 灵, 等. TC11钛合金片层组织热变形球化机制[J]. 稀有金属材料与工程, 2009, 38(3): 421-425.
Chen Hui-qin, Cao Chun-xiao, Guo Ling, et al. Globularization mechanisms during hot deformation processes of TC11 alloy with lamellar structure[J]. Rare Metal Materials and Engineering, 2009, 38(3): 421-425.
[2] Kar S K, Suman S, Shivaprasad S, et al. Processing-microstructure-yield strength correlation in a near β Ti alloy, Ti-5Al-5Mo-5V-3Cr[J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2014, 610: 171-180.
[3] LI C, Zhang X, Li Z, et al. Hot deformation of Ti-5Al-5Mo-5V-1Cr-1Fe near β titanium alloys containing thin and thick lamellar α phase[J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2013, 573: 75-83.
[4] Ning Y, Fu M W, Hou H, et al. Hot deformation behavior of Ti-5.0Al-2.40Sn-2.02Zr-3.86Mo-3.91Cr alloy with an initial lamellar microstructure in the α+β phase field[J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2011, 528(3): 1812-1818.
[5] Xu J, Zeng W, Zhou D, et al. Analysis of flow softening during hot deformation of Ti-17 alloy with the lamellar structure[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2018, 767: 285-292.
[6] 蔡 贇, 孙朝阳, 万 李, 等. AZ80镁合金动态再结晶软化行为研究[J]. 金属学报, 2016, 52(9): 1123-1132.
CAI Yun, SUN Chao-yang, WAN Li, et al. Study on the dynamic recrystallization softening behavior of AZ80 magnesium alloy[J]. Acta Metallurgica Sinica, 2016, 52(9): 1123-1132.
[7] Zhang J, DI H,Wang X. Flow softening of 253 MA austenitic stainless steel during hot compression at higher strain rates[J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2016, 650: 483-491.
[8] WANG Guan, LOU Lin-yuan, LIU Zhi-wen, et al. Flow softening behavior and microstructure evolution of aluminum alloy 6061 due to dynamic recovery[J]. Materials Research Express, 2019, 6(5): 056555.
[9] 李 萍, 左 标, 郭威威, 等. Ti-22Al-26Nb 合金热变形本构方程建立及软化行为研究[J]. 稀有金属材料与工程, 2018, 47(12): 3811-3815.
Li Ping, Zuo Biao, Guo Wei-wei, et al. Establishment of constitutive equation and research on softening behavior of Ti-22Al-26Nb alloy during hot deformation[J]. Rare Metal Materials and Engineering, 2018, 47(12): 3811-3815.
[10] Ghasemi E, Zarei-Hanzaki A, Farabi E, et al. Flow softening and dynamic recrystallization behavior of BT9 titanium alloy: A study using process map development[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2017, 695: 1706-1718.
[11] ZHAO Hui-jun, WANG Bao-yu, JU Dong-ying, et al. Hot tensile deformation behavior and globularization mechanism of bimodal microstructured Ti-6Al-2Zr-1Mo-1V alloy[J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2018, 28(12): 2449-2459.
[12] MILLER R M, BIELER T R, SEMIATIN S L. Flow softening during hot working of Ti-6Al-4V with a lamellar colony microstructure[J]. Scripta Materialia, 1999, 40: 1387-1393.
[13] LIU B, LI Y P, MATSUMOTO H, et al. Thermomechanical characterization of P/M Ti-Fe-Mo-Y alloy with a fine lamellar microstructure[J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2011, 528(6): 2345-2352.
[14] 梁后权, 郭鸿镇, 宁永权, 等. 基于软化机制的TC18钛合金本构关系研究[J]. 金属学报, 2014, 50(7): 871-878.
LIANG Hou-quan, GUO Hong-zhen, NING Yong-quan, et al. Analysis on the constitutive relationship of TC18 titaniumalloybased on the softening mechanism[J]. Acta Metallurgica Sinica, 2014, 50(7): 871-878.
[15] Liang H Q, Nan Y, Ning Y Q, et al. Correlation between strain-rate sensitivity and dynamic softening behavior during hot processing[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2015, 632: 478-485.
[16] Zhu Y C, Zeng W D, Liu J L, et al. Effect of processing parameters on the hot deformation behavior of as-cast TC21 titanium alloy[J]. Materials and Design, 2012, 33: 264-272.
[17] GOETZ R L, SEMIATIN S L. The adiabatic correction factor for deformation heating during the uniaxial compression test[J]. Journal of Materials Engineering and Performance, 2001, 10(6): 710-717.
[18] Mataya M C, Sackschewsky V E. Effect of internal heating during hot compression on the stress-strain behavior of alloy 304L[J]. Metallurgical and Materials Transactions A, 1994, 25(12): 2737-2752.
[19] 黄 旭, 朱知寿, 王红红. 先进航空钛合金材料与应用[M]. 北京: 国防工业出版社, 2012: 44.
HUANG Xu, ZHU Zhi-shou, WANG Hong-hong. Advanced aeronautical titanium alloys and applications[M]. Beijing: National Defense Industry Press, 2012: 44.
[20] Devadas C, Baragar D, Ruddle G, et al. The thermal and metallurgical state of steel strip during hot rolling: Part II. Factors influencing rolling loads[J]. Metallurgical Transactions A, 1991, 22(2): 335-349.
[21] Seshacharyulu T, Medeiros S C, Morgan J T, et al. Hot deformation mechanisms in eli grade Ti-6A1-4V[J]. Scripta Materialia, 1999, 41(3): 283-288.
[22] Murty S V S N, Rao B N. On the flow localization concepts in the processing maps of titanium alloy Ti-24Al-20Nb[J]. Journal of Materials Processing Technology, 2000, 104: 103-109.
[23] Galiyev A, Kaibyshev R, Gottstein G. Correlation of plastic deformation and dynamic recrystallization in magnesium alloy ZK60[J]. Acta Materialia, 2001, 49(7): 1199-1207.
[24] Jenab A, Karimi Taheri A. Experimental investigation of the hot deformation behavior of AA7075: Development and comparison of flow localization parameter and dynamic material model processing maps[J]. International Journal of Mechanical Sciences, 2014, 78: 97-105.
[25] Ning Y Q, Xie B C, Liang H Q, et al. Dynamic softening behavior of TC18 titanium alloy during hot deformation[J]. Materials and Design, 2015, 71: 68-77.
[26] Zherebtsov S, Murzinova M, Salishchev G, et al. Spheroidization of the lamellar microstructure in Ti-6Al-4V alloy during warm deformation and annealing[J]. Acta Materialia, 2011, 59(10): 4138-4150.
[27] Cocks A C F, Ashby M F. Creep fracture by coupled power-law creep and diffusion under multiaxial stress[J]. Metal Science, 1982, 16(10): 465-474.
Flow softening behavior ofTA15 titanium alloy with beta transformed microstructure
DONG Xian-juan1, HU Sheng-shuang2, XU Yong1, LU Shi-qiang1
(1. National Defense Key Disciplines Laboratory of Light Alloy Processing Science and Technology, Nanchang Hangkong University, Nanchang 330063, China;
2. Aviation Xi’an Aircraft Industry Croup Co., Ltd., Xi’an 710089, China)
Abstract: The flow softening of TA15 titanium alloy with beta transformed microstructure was investigated by means of hot compression tests performed at the temperature range of 750-950 ℃ and strain rate of 0.001-10 s-1. The effect of deformation temperature and strain rate on the flow softening and the flow softening mechanisms were examined. The thermal softening due to deformation heating is an important mechanism of flow softening. The degree of thermal softening increases with the decrease of deformation temperature and the increase of strain rate, and the maximum is 48.2% to the total flow softening degree. The microstructural evolution, including dynamic recrystallization, dynamic recovery and flow instability defects, is the main mechanism of flow softening. Three types of softening regions dominated by microstructure evolution were identified by strain rate sensitivity index based on the dynamic material model, and verified by microstructure observation.
Key words: TA15 titanium alloy; flow softening; deformation heating; microstructural evolution
Foundation item: Project(51864035) supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China; Project (2019ZE056009; 2020Z047056003) supported by the Aeronautical Science Foundation of China; Project (20202BBEL53012) supported by the Key Research and Development Program of Jiangxi Province, China
Received date: 2020-05-29; Accepted date: 2020-12-05
Corresponding author: XU Yong; Tel: +86-791-83863103; E-mail: xuyong@nchu.edu.cn
(编辑 龙怀中)
基金项目:国家自然科学基金资助项目(51864035);航空科学基金资助项目(2019ZE056009;2020Z047056003);江西省重点研发计划资助项目(20202BBEL53012)
收稿日期:2020-05-29;修订日期:2020-12-05
通信作者:徐 勇,副教授,博士;电话:0791-83863103;E-mail:xuyong@nchu.edu.cn