In-situ investigation of atmospheric corrosion behavior of bronze under thin electrolyte layers using electrochemical technique
来源期刊:中国有色金属学报(英文版)2012年第5期
论文作者:廖晓宁 曹发和 陈安娜 刘文娟 张鉴清 曹楚南
文章页码:1239 - 1249
关键词:青铜;薄液膜;原位研究;大气腐蚀;电化学技术
Key words:bronze; thin electrolyte layer; in-situ investigation; atmospheric corrosion; electrochemical technique
摘 要:采用阴极极化曲线、开路电位和电化学阻抗谱,监测青铜在不同薄液膜厚度下的大气腐蚀行为。阴极极化曲线结果表明,阴极极限电流密度随着液膜的减薄而增大。电化学阻抗谱结果表明,在腐蚀初期,腐蚀速率随着液膜的减薄而增加,这主要是由于腐蚀速率是由阴极过程控制的;随着时间的延长,腐蚀程度随着液膜厚度的变化从强到弱的趋势为:150 μm,310 μm,100 μm,本体溶液,57 μm。开路电位和电化学阻抗谱实验较好地再现了原位电化学腐蚀信息,且电化学结果与物理表征具有良好的一致性。
Abstract:
The atmospheric corrosion behavior of bronze under thin electrolyte layer (TEL) with different thicknesses was monitored using cathodic polarization curves, open circuit potential (OCP) and electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS). Cathodic polarization result indicates that the cathodic limiting current density increases with decreasing the TEL thickness. EIS result shows that the corrosion rate increases with decreasing the TEL thickness at the initial stage because the corrosion is dominated by the cathodic process, whereas after long immersion time, the corrosion degree with the TEL thickness is in the sequence of 150 μm > 310 μm >100 μm ≈ bulk solution > 57 μm. The measurements of OCP and EIS present in-situ electrochemical corrosion information and their results are in good agreement with that of physical characterizations.

![]()

Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 22(2012) 1239-1249
LIAO Xiao-ning1,2, CAO Fa-he1, CHEN An-na1, LIU Wen-juan1, ZHANG Jian-qing1,3, CAO Chu-nan1,3
1. Department of Chemistry, Zhejiang University, Hangzhou 310027, China;
2. College of Science, Jiangxi Agricultural University, Nanchang 330045, China;
3. State Key Laboratory for Corrosion and Protection, Institute of Metal Research,
Chinese Academy of Sciences, Shenyang 110016, China
Received 13 September 2011; accepted 12 January 2012
Abstract: The atmospheric corrosion behavior of bronze under thin electrolyte layer (TEL) with different thicknesses was monitored using cathodic polarization curves, open circuit potential (OCP) and electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS). Cathodic polarization result indicates that the cathodic limiting current density increases with decreasing the TEL thickness. EIS result shows that the corrosion rate increases with decreasing the TEL thickness at the initial stage because the corrosion is dominated by the cathodic process, whereas after long immersion time, the corrosion degree with the TEL thickness is in the sequence of 150 μm > 310 μm >100 μm ≈ bulk solution > 57 μm. The measurements of OCP and EIS present in-situ electrochemical corrosion information and their results are in good agreement with that of physical characterizations.
Key words: bronze; thin electrolyte layer; in-situ investigation; atmospheric corrosion; electrochemical technique
1 Introduction
Bronzes, i.e., copper alloys containing tin and sometimes some other elements, are usually employed to cast sculptures and artifacts. Nowadays, these archaeological bronze materials undergo serious corrosion process due to the increasing air pollutions. In order to classify the corrosion mechanism and further to preserve these cultural heritages, the corrosion behavior of bronze materials exposed to atmospheric environments has been extensively studied through laboratory or field studies [1-3].
A detailed description on behavior can be done by the investigation of the bronze/atmospheric interface from beginning of exposure to the corrosive environment [4]. This task can be fulfilled either by performing the reaction or by subsequent investigation of the changes, or by in-situ observations of the ongoing reaction. In-situ investigations are advantageous due to the possibility of direct observation of the surface processes, thus reducing the possibility of artifacts.
Up to now, many physical characterizations including the scanning tunneling microscopy (STM) [5], atomic force microscopy (AFM) [6], synchrotron X-ray diffraction (SR-XRD) [7] and quartz crystal microbalance (QCM) [8] have been developed to investigate the atmospheric corrosion behavior of historical objects (including copper and bronzes). These methods have provided in-situ information on, e.g., surface morphology, surface chemical composition or even on the kinetics of surface reactions by prediction. However, physical characterizations have their respective limitations. For example, STM as a tool for the in-situ investigation of electrochemical behavior is seriously limited by the requirement that the surface under study must be electronically conductive. Furthermore, the presence of the tunneling current between the surface and the tip may interfere with the faradic currents associated with the electrochemical reactions [9]. AFM overcomes both of these limitations and appears to be a more reliable tool for investigating morphological changes during electrochemical process [1,9]. But the roughness and cleanliness of the initial surface must be checked carefully. As a consequence, the AFM technique can only be used in the investigation of the initial corrosion stage. In addition, all these physical characterization methods fail to give the direct instantaneous electrochemical reaction information, such as corrosion rate, corrosion potential, which is closely related to the atmospheric corrosion behavior.
Electrochemical techniques, such as dynamic polarization curve, open circuit potential (OCP) measurement, electrochemical impedance spectrometry (EIS), have been proved to be reliable and convenient methods in the investigation of bronze corrosion behavior [10,11]. Nevertheless, all these studies have been made only in bulk solutions where the corrosion behavior is always significantly different from that in atmospheric environment. In atmospheric environment the thickness of TEL on the metal is always lower than 1 mm [12]. Under such thin electrolyte layers, the thickness plays important role in the corrosion behavior. A change of the electrolyte layer thickness affects the mass transport of the dissolved oxygen, the accumulation of corrosion products and the hydration of dissolved metal ions.
Since the atmospheric corrosion commonly occurs under TEL and this kind of corrosion can be regarded as an electrochemical nature [13], the general electrochemical laws which hold for metal corrosion in bulk electrolytes also hold for the special case of atmospheric corrosion. So, the electrochemical methods used in bulk solutions for bronzes can obviously be used under TEL after major modification.
However, the use of electrochemical techniques to investigate atmospheric corrosion behavior of bronzes is significantly constrained. Consequently, the electrochemical corrosion behavior of bronze in atmospheric environment is still not clear. The most significant challenge in its application is that the solution resistance becomes extremely high when the thickness of electrolyte layer is very thin. In such a condition, an extremely high ohmic drop and a non-uniform current distribution over the working electrode produce serious errors in the measurement of electrochemical corrosion rate. Inspired by NISHIKTA et al [14], this limitation was broken through in our previous work [15,16], achieving precise electrochemical corrosion behavior of aluminum alloy 2024-T3 and copper under TEL by modified electrochemical set-ups. In these set-up, the working electrode was positioned over the counter and reference electrode, which assures that even if the electrolyte film is ultra thin on the working electrode, the counter and reference electrode are still immersed in the bulk electrolyte. In this way, the ohmic drop between the reference electrode and the working electrode can be minimized.
Based on our previous work, the electrochemical techniques including cathodic polarization curve, OCP and EIS were employed to investigate the electrochemical corrosion behavior of bronze under TEL in the current work. The emphasis was put on the effect of TEL thickness on the atmospheric corrosion behavior of bronze. The OCP and EIS measurements provide in-situ electrochemical corrosion information of bronze. Physical characterizations, such as optical microscopy (OM), scanning electron microscopy (SEM), energy dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (EDS) and X-ray diffraction (XRD) were also performed to further verify the corrosion behavior of bronze under TEL.
2 Experimental
2.1 Materials
The bronze used in this study was a mono α phase alloy. Its composition, determined by EDS, was 96.13% Cu (mole fraction) and 3.87% Sn, which is similar to that of bronze commonly used in ancient times for artistic casting [17]. The working electrode made from this alloy was embedded into nylon, leaving an exposed surface area of 0.5 cm2. Prior to experiment, each electrode was abraded gradually to 1000 grit with emery paper and polished with alumina powder down to 2.5 μm, degreased in ethanol in an ultrasonic bath, rinsed with distilled water and dried in a stream of nitrogen gas. A 3.5% (mass fraction) sodium chloride solution (pH 6.70), prepared from deionized water and analytical grade reagent (Sinopharm Chemical Reagent Co., Ltd., Shanghai, China), was used here to simulate the ocean climate.
2.2 Electrochemical measurements
All the electrochemical measurements were performed on a VMP2 multichannel potentiostat (PARC Corporation, USA). A three-electrode electrochemical cell, fabricated with high precision, was used. The set-up in electrochemical measurement is the same as that in our previous work [16]. Briefly, the working electrode bronze was inserted in the centre of a Teflon cylinder and fixed firmly in the cell, leaving only the upper surface exposed. A Pt wire circling the working electrode was used as the counter electrode and was positioned lower than the working electrode surface. A saturated calomel electrode (SCE) was used as the reference electrode and was inserted into the bulk solution. The TEL thickness on the working electrode was determined using an equipment consisting of a sharp Pt needle, an iron support with a micrometer and an ohmmeter, which was also reported in detail in our previous work [16]. To keep the thickness of the TEL constant for a long time during electrochemical measurements, the cell and a sodium chloride solution of the same concentration with the test solution was placed inside the vacuum desiccator. EIS measurements were performed at the OCP after different immersion time in a frequency from 100 kHz to 10 mHz with a potential perturbation 10 mV (6 points per decade). The evolution of OCP with immersion time was monitored every 2 h in the first 24 h, then was recorded every 12 h. The cathodic polarization test was started from the OCP after immersion for 30 min, and performed with scan rate of 0.5 mV/s. All measurements were performed at room temperature (26±1) °C.
2.3 Surface analysis and structure characterization
The morphologies of the corrosion products were characterized with XTL 3400 OM (Cany Precision Instrument Co., Ltd., Shanghai, China) and FEI SIRION-100 SEM. The surface compositions of all samples were studied with a GENESIS 4000 quantitative EDS, attached to the SEM. Phase identification of the products was carried out by XRD using an ARL X'TRA X-ray diffractometer with Cu Kα radiation (λ=0.15406 nm), in 2θ range of 10°-80°.
3 Results and discussion
3.1 Cathodic polarization behavior
The anodic polarization curve is useful for the electrochemical corrosion mechanism analysis in the bulk solution. However, our pre-experiments showed that the reproducibility of the anodic polarization curves of bronze covered with TEL was poor because the current density was concentrated on the brim of the electrode. Therefore, only cathodic polarization curves have been performed in this study. For the cathodic process, the cathodic current is mainly attributed to the reduction of oxygen, which diffuses perpendicularly to the electrode surface, which facilitates the charge transferring on the whole electrode surface. Therefore, the cathodic current distributes uniformly on the whole electrode [18].
Figure 1 presents the cathodic polarization curves of bronze covered with various thicknesses of electrolyte layers after a immersion time of 30 min. It can be seen that all the cathodic polarization curves can be divided into three regions. Region Ι is the polarization region from OCP to the potential of about -0.5 V (vs SCE). In this region, a peak which perturbates the linear region is found. This peak can be attributed to the reduction of corrosion product nantokite (CuCl) [19]. Region II, at the more negative potentials a plateau ascribed to the oxygen reduction under mass-transfer control can be observed. In this region, peak 2 between -0.7 and -0.8 V, which superimposes on the diffusion-limited current of O2 reduction, may be attributed to the reduction of absorbed layer copper hydroxide compounds (Cu(OH)-) [16], Peak 3, only can be found below 200 μm TEL, is attributed to the reduction of cuprite (Cu2O) formed by the hydrolysis of cuprous corrosion products [20]. Region III, rising at the negative potentials between -1.2 and -1.4 V can be attributed to the hydrogen evolution reaction. The potential of hydrogen evolution as shown in Fig. 2 is shifted towards negative direction with decreasing the TEL thickness, suggesting the increase of hydroxyl ions (OH-) concentration with decreasing the TEL thickness. These results indicate that the cathodic reaction is enhanced by decreasing the TEL thickness.
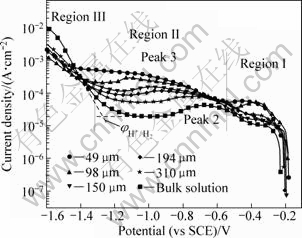
Fig. 1 Cathodic polarization curves of bronze under TEL with various thicknesses and in bulk solution containing chloride ions
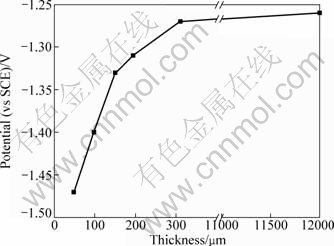
Fig. 2 Dependence of hydrogen evolution potential and TEL thickness of bronze covered with various thicknesses of electrolyte layers
The cathodic current densities under different thickness taken at -1.0 V from Fig. 1 are listed in Table 1. It is shown that all the current densities under TEL are greater than that in the bulk solution, suggesting that the current distribution on the bronze electrode under TEL is uniform. Furthermore, the current densities under TEL increase with decreasing the thickness, indicating that the corrosion process under TEL is under the control of the reduction of oxygen at the initial stage. This cathodic polarization behavior of bronze is also similar with that of copper in sodium chloride or sodium sulfate solutions [13,21].
Table 1 Cathodic current densities of bronze under TEL with different thickness and in bulk solution at -1.0 V (vs SCE)

3.2 Evolution of OCP
Figure 3 presents the evolution of OCP with immersion time for the bronze covered with various thicknesses of electrolyte layers, recorded after immersion for 30 min. The evolution depends strongly on the thickness of electrolyte layer. For the bronze under an ultra TEL of 57 μm, the OCP rapidly shifts towards positive direction from -199.6 to -161.0 mV in the first 6 h of immersion, and then attains a quite steady state (about -153.0 mV) during the rest period. The rapid increase of OCP suggests a rapid formation process of passivation layer, whereas the steady OCP value means that the corrosion reaction occurs in a slow rate [22]. For the bronze under TEL of 150 μm, a similar behavior in comparison to the case of 57 μm is observed in 22 h of immersion, whereas a big fluctuation of OCP occurs in the rest exposure time. The big fluctuation can be attributed to a rapid corrosion (dissolution/passivation) process occurring on the bronze surface. For the bronze immersed in the bulk solution, the variations of OCP can be divided into three stages: a decrease of OCP due to the dissolution of the air-formed passive film in the first 4 h, a continuous increase process from 6 h to 24 h attributing to the increase of thickness in the passivation layer and an evident fluctuation process for the rest immersion time owning to the dissolution/repassivation process.
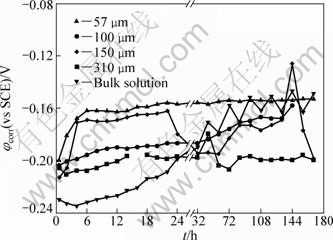
Fig. 3 Evolution of OCP with immersion time for bronze covered with different thicknesses of electrolyte layers
3.3 EIS behavior
EIS is a powerful technique for characterizing electrochemical reactions at the metal/electrolyte interface as it not only provides an assessment of the corrosion rate with non-destructive way but also enables the reaction process to be determined in a mechanistic pathway [23]. Electrochemical impedance responses of bronze surfaces under chloride-containing TEL and in the bulk solution were investigated for different exposure time up to 168 h (Fig. 4). At the initial stage, the curves in Nyquist diagrams for all cases show only one capacitive loop at high and intermediate frequencies (HFs and IFs) and a diffusion tail at low frequencies (LFs). For a longer time of immersion, all the curves in the Nyquist diagrams present two overlapped capacitive loops at HFs and IFs followed by a diffusion tail at LFs. But the analysis of Bode plots indicates the existence of three resolved relaxation phenomena. The evolution of impedance curves shows that a film of corrosion products is gradually formed on the bronze surface. Generally, the HF loop is attributed to the response of deposited corrosion products. The second loop (at IFs) is normally attributed to the metal dissolution during corrosion attack, whereas the diffusion tail is the response of diffusion process for cuprous chloride complexes, chloride ions and oxygen [24].
Equivalent circuits given in Fig. 5 are used to fit the EIS data in Fig. 4 to quantitatively account for the corrosion behavior of bronze under TEL. The circuit elements are defined as follows: Rs is the solution resistance, Rf and Cf correspond to the capacitance and resistance of surface film respectively; Rct and Cdl are the double layer capacitance and charge-transfer resistance; ZW represents the Warburg diffusion impedance in the LF region; nf and ndl represent respectively the depressed feature of the capacitive loop in Nyquist diagram. It is seen that the equivalent circuits fit the experimental data well, indicating that the equivalent circuits of Fig. 5 are suitable.
The parameters obtained by non-linear least square fitting of data presented in Fig. 4 are listed in Table 2. The values of Rs range from 5.8 to 270.2 Ω·cm2 at different TEL thickness and exposure time. The value of Rs is relatively small, meaning that the experimental setup minimizes the ohmic drop between the working electrode and reference electrode though the thickness of TEL is extremely thin. The change of Cdl is attributed to the change of real area of the corroded electrode during the corrosion process. The Rf evolution indicates the change of protective performance for the corrosion products. For the bronze under 57 mm, the value of Rf is relatively stable, especially after 72 h, indicating a stable process occurring through the formed layer. However, for others Rf evolution exhibits an obvious fluctuation process and its amplitude is strongly dependent on the TEL thickness, showing that a dissolution/repassivation process occurs on the bronze surface with different corrosion degrees. It is also interesting to note that in the case of 150 mm the value of Rf is lower than that of others, indicating that the formed layer has poorer protection or suffers more serious attack in comparison with others.
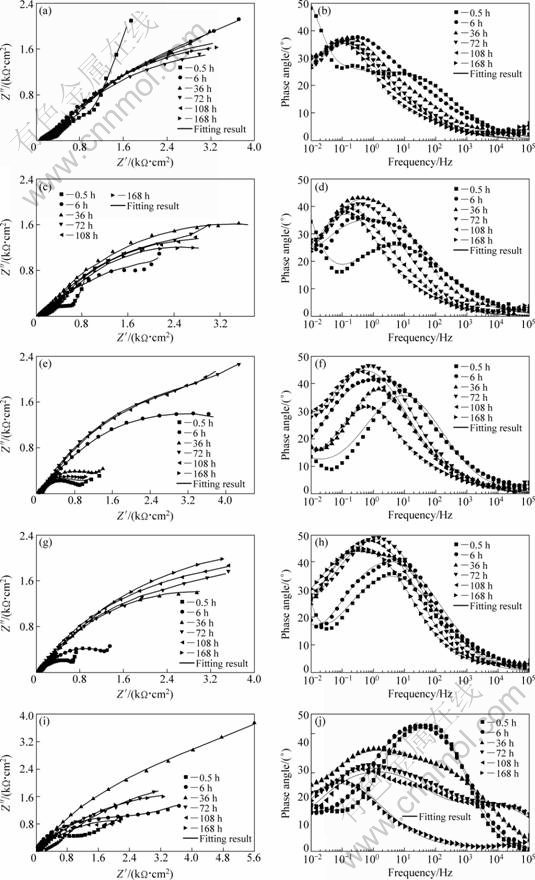
Fig. 4 Nyquist diagrams (a, c, e, g, i) and Bode plots (b, d, f, h, j) of bronze covered with various thickness of electrolyte layers containing chloride ions during 168 h immersion time: (a, b) 57 μm; (c, d) 100 μm; (e, f) 150 μm; (g, h) 310 μm; (i, j) Bulk solution
Table 2 Fitting parameters of EIS for bronze under TEL with various thickness and in bulk solution for different immersion time
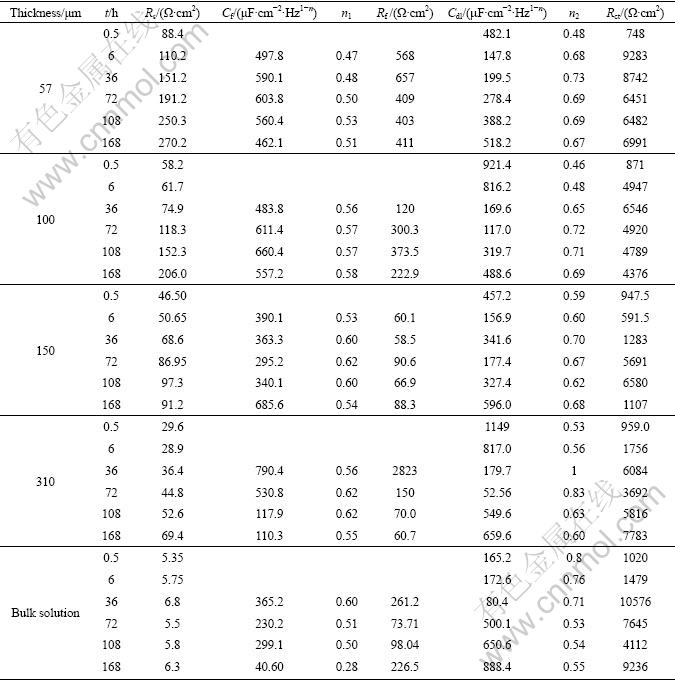
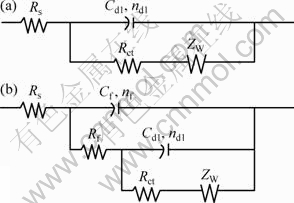
Fig. 5 Equivalent circuits used to fit experimental impedance data for bronze covered with electrolyte layers containing chloride ions: (a) At the initial stage; (b) After long time of immersion
Figure 6 presents the evolution of 1/Rct with time for bronze covered with various thicknesses of electrolyte layers. In the current study, the 1/Rct (but not the 1/Rp) is taken as a parameter to characterize the corrosion rate because Rct is the entity more correlated with corrosion rate when there is more than one constant or diffusion impedance [23,25]. It can be seen that the corrosion rate of bronze under TEL at the initial stage (0.5 h) increases with the decrease of TEL and is higher than that in the bulk solution, indicating that the bronze corrosion during this stage is controlled by the diffuse process of oxygen through the electrolyte layer to the surface of electrode. A similar phenomenon was also observed by NISHIKATA et al [14] for the copper in sodium sulfate solutions. After 0.5 h of immersion, the curve of corrosion rate can be divided into decreasing part and increasing one for each case with immersion time. The increase of corrosion rate can be attributed to the disrupting of passivation film, whereas the decrease one is due to the repassivation process. The change of corrosion rate is closely dependent on the TEL thickness.
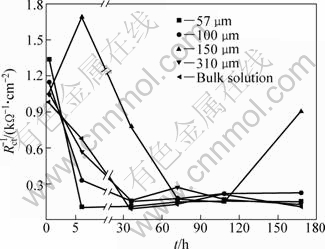
Fig. 6 Evolution of 1/Rct with immersion time for bronze under TEL with various thickness and in bulk solution
For the bronze under TEL of 57 μm, the 1/Rct decreases markedly in the first immersion time (0.5-6 h), then achieves a quite steady state for longer immersion time. The dramatic decrease of 1/Rct suggests a rapid formation of protective layer in 0.5-6 h, while steady state means that the corrosion rate is low after a long time of immersion, which is in well agreement with the analysis result of OCP measurement. In the case of 150 μm, the 1/Rct value increases from 0.5 h to 6 h due to the dissolution of passivation film, then decreases rapidly followed by a pronounce increase with time. The rapid change of 1/Rct indicates a rapid corrosion (dissolution/ repassivation) process occurring on the bronze surface. In the bulk solution, the bronze shows a similar behavior to that in the 100 and 310 μm cases. The corrosion rate for these cases shows a decrease evolution process at the initial stage due to the deposition of passivation film, and then it is disrupted by a small irregular variation, which indicates that the attack on the protective layer occurs in a moderate way.
3.4 Characterization
Evidence of the different corrosion behavior of the bronze with various thicknesses of TEL was also supported by the characterization, performed at the end of the electrochemical test.
Figure 7 presents the OM images for bronze surface with various thicknesses of TEL after immersion for 168 h. The visual appearance of all five samples is quite different. For the copper with 57 μm TEL or in the bulk solution, the appearance is homogenous with reddish color and slightly bluish patches after long immersion time of 168 h, while for the bronze with TEL of 100 and 310 μm, it is strongly inhomogeneous with reddish and bluish patches. As for the bronze covered with 150 μm TEL, a homogeneous bluish outer layer is developed on the surface. From the broken part of the bluish layer, a reddish inner layer is observed. The reddish layer is mainly the corrosion products of cuprite (Cu2O) and tin compounds [11]. The bluish patina can be attributed to the mixture of corrosion products atacamite (Cu2(OH)3Cl) and malachite (Cu2(OH)2CO3), as verified by XRD profiles shown in Fig. 8. This result indicates that the patina formation preceded from an internal oxidation of the bronze substrate, as observed by MURESAN et al [26]. The evolution of bronze surface morphology indicates that the bronze covered with 150 μm TEL underwent the most serious corrosion.
Figure 8 shows XRD patterns from the surface of bronze samples with various thicknesses of TEL and in the bulk solution after immersion for 168 h. For the samples under 57 μm film and in the bulk solution, only corrosion product cuprite is detected. While for the other samples, in addition to cuprite, atacamite and malachite are identified. The spectra show that the copper peaks are less intense and atacamite, nantokite and malachite peaks are more intense for the bronze covered with 150 μm TEL, indicating that a thicker corrosion layer formed on the bronze surface. Generally, cuprite is the first corrosion product for bronze atmospheric corrosion, then it is further transferred into atacamite in the presence of chloride ions [27]. This result suggests that the bronze covered with 150 μm film underwent the most severe corrosion, which is consistent with the result of OM. In addition, no crystalline Sn compound is detected for all samples, indicating that Sn compounds on samples only exist as non-crystalline tin hydroxide (Sn(OH)x) or tin oxide (SnO2), as also widely reported in literature [28-30].
Figure 9 shows the SEM morphologies of bronze surfaces with various thicknesses of TEL and in the bulk solution after immersion for 168 h. In the bulk solution, some cube corrosion products are deposited on the bronze surface, which are Cu-Sn compound revealed by point EDS analysis. Whereas in the case of TEL, only some amorphous corrosion products are observed, suggesting that the corrosion mechanism of bronze in the bulk solution is different from that under TEL. It is also clear that the deposited amount of corrosion products on the bronze surface is dependent on the thicknesses of the TEL. The amount of corrosion products for the bronze covered with 150 μm of TEL is the largest, showing that the most severe attack occurs in this case, which is also consistent with the results of OM, XRD, OCP and EIS.
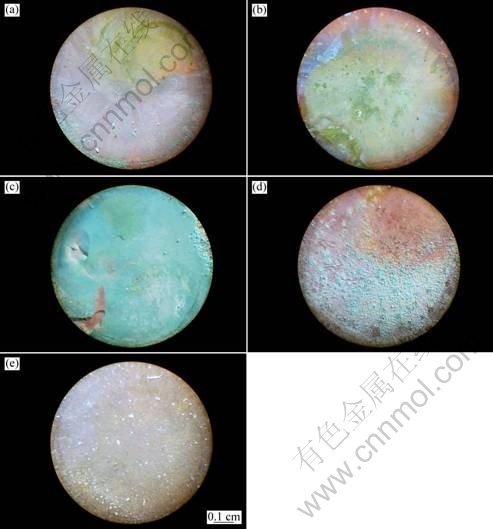
Fig. 7 OM images for bronze surface with various thicknesses of TEL after immersion of 168 h: (a) 57 μm; (b) 100 μm; (c) 150 μm; (d) 310 μm; (e) Bulk solution
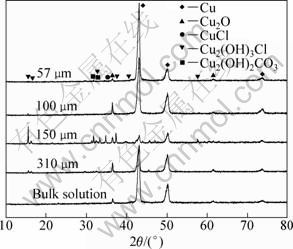
Fig. 8 XRD patterns of bronze surface with various thicknesses of TEL and in bulk solution with immersion time of 168 h
Table 3 presents the EDS results for bronze surfaces covered with different thicknesses of electrolyte layers after immersion for 168 h. The EDS analysis was performed on the whole bronze surface for these samples. The result indicates that the corrosion products are composed of copper, oxide, carbon, chloride and tin elements. No sodium is detected. Combined with the XRD result (Fig. 8), the corrosion layer can be determined to be a mixture of cuprite, nantokite, atacamite, malachite and amorphous Sn compounds. The corrosion layer is characterized by a noticeably lower copper content than that in the alloy, which is called the decuprification phenomenon of Cu-Sn alloys corrosion, i.e., a preferential dissolution of copper compared with other alloy element, as reported in Refs. [26,27,29]. The difference of copper amount in the corrosion layer among different samples shows that the corrosion degree is different for the bronze covered with different thicknesses of TEL.
Table 3 EDS results for bronze surfaces covered with different thicknesses of electrolyte layers after immersion for 168 h
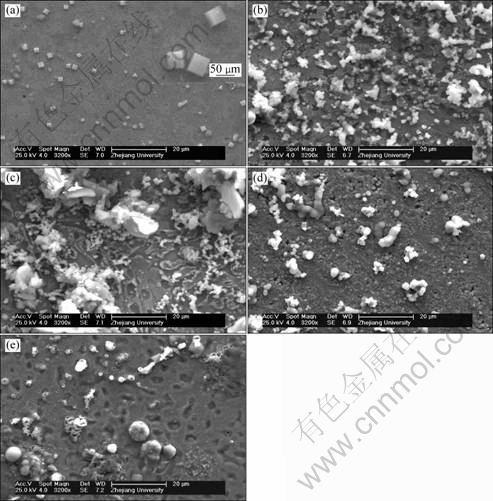
Fig. 9 SEM images of bronze surfaces with various thicknesses TEL and in bulk solution after immersion for 168 h: (a) Bulk solution; (b) 310 μm; (c) 150 μm; (d) 100 μm; (e) 57 μm
Figure 10 presents the comparison of corrosion degree between the EDS results and EIS results. The corrosion degree derived from the EIS measurement is calculated by the integration of t/Rct from Fig. 6 as follows:
![]() (1)
(1)
While for the EDS result, the corrosion degree is assessed by a dissolution factor fCu. The parameter fCu, which was proposed for archaeological bronzes by CHIAVARI et al [28] and ROBBIOLA et al [31], is used to quantify the selective dissolution of bronzes elements in the corrosive environment, defined as follows:
![]() (2)
(2)
where xalloy and xlayer are the molar fraction of the element A in the alloy and corrosion layer, respectively. Considering that the dissolution of Sn can be neglected compared with that of copper [31,32], therefore, it is reasonable to take fCu as the corrosion degree in this case. The calculated values of fCu for bronze covered with different thicknesses of electrolyte layers shown in Fig. 10 follow the order of 150 μm > 310 μm > 100 μm ≈ bulk solution > 57 μm, which means the order of corrosion degree is 150 μm > 310 μm > 100 μm ≈ bulk solution > 57 μm. The result is consistent with that of EIS result, further confirming that the corrosion rate obtained by EIS is accurate.
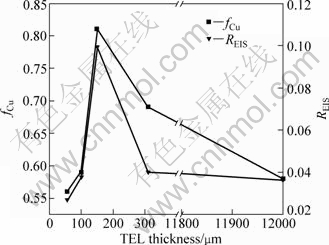
Fig. 10 Comparison of corrosion degree between EDS results and EIS results
In general, the corrosion is determined by both the anodic and cathodic processes after a long immersion time because of the accumulation of corrosion products. Therefore, the dependence of bronze corrosion degree with TEL thickness after a long immersion time can be elucidated on how the thickness affects the cathodic and anodic processes. As for the relatively thick electrolyte layer, the diffusion processes of corrosion products (such as cuprous chloride from bronze surface to the bulk solution) and chloride ions (from the bulk solution to the bronze surface) are relatively easy, thus the corrosion is still under the control of oxygen diffusion process. As a result, the corrosion degree in the bulk solution and under 310 μm film is smaller than that under 150 μm film. When the TEL is lower than 150 μm, although the diffusion of oxygen is easier, the diffusion of chloride ions and corrosion product becomes difficult, i.e., the anodic process is inhibited, resulting in the inhibition of corrosion. According to TOMASHOV’s model [12], the maximum corrosion is at the point of the transition from cathodic to anodic control, which corresponds to the 150 μm film in the current study. The bronze corrosion covered with TEL less than 150 μm was under anodic control and the corrosion degree decreases with decreasing TEL thickness. For the 57 μm TEL, the corrosion is even lower than that in the bulk solution due to the strong inhibition of the anodic process. For such a thin layer, the diffusion of the corrosion products and chloride ions is extremely difficult.
4 Conclusions
1) The cathodic current densities of bronze under TEL increase with decreasing the thickness of TEL and are higher than those in the bulk solution.
2) The corrosion rate of bronze under TEL increases with the decrease of TEL thickness at the initial stage. After a long immersion time, the corrosion degree of bronze covered with various thicknesses of electrolyte layers during the exposure time of 168 h is ranked as 150 μm > 310 μm > 100 μm ≈ bulk solution > 57 μm, which is in well agreement with the EDS results.
References
[1] WADSAK M, AASTRUP T, ODNEVALL WALLINDER I, LEYGRAF C, SCHREINER M. Multianalytical in situ investigation of the initial atmospheric corrosion of bronze [J]. Corrosion Science, 2002, 44(4): 791-802.
[2] FANG C Z, WANG Y S, WANG C S, WANG S J, HU K L, ZHAO H Z. The kinetics of growth process of powdery rust of bronze [J]. Science China B, 1992, 22(5): 470-477. (in Chinese)
[3] WANG Ju-ling, XU Chun-chun. Mechanism of formation process of pure Cu crystals in bronze corrosion [J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2004, 14(11): 1869-1874. (in Chinese)
[4] KORSHIN G V, FERGUSON J F, LANCASTER A N. Influence of natural organic matter on the corrosion of leaded brass in potable water [J]. Corrosion Science, 2000, 42(1): 53-66.
[5] ZHANG X G, STIMMING U. Scanning tunneling microscopy of copper corrosion in aqueous perchloric acid [J]. Corrosion Science, 1990, 30(8-9): 951-954.
[6] KLEBER C, SCHREINER M. In situ TM-AFM investigations of the influence of zinc and tin as alloy constituents of copper to the early stages of corrosion [J]. Applied Surface Science, 2003, 217(1-4): 294-301.
[7] LEYSSENS K, ADRIAENS A, DOWSETT M G, SCHOTTE B, OLOFF I, PANTOS E, BELL A M T, THOMPSON S P. Simultaneous in situ time resolved SR-XRD and corrosion potential analyses to monitor the corrosion on copper [J]. Electrochemical Communication, 2005, 7(12): 1265-1270.
[8] AASTRUP T, WADSAK M, SCHREINER M, LEYGRAF C. Experimental in situ studies of copper exposed to humidified air [J]. Corrosion Science, 2000, 42(6): 957-967.
[9] BERTRAND G, ROCCA E, SAVALL C, RAPIN C, LABRUNE J C, STEINMETZ P. In-situ electrochemical atomic force microscopy studies of aqueous corrosion and inhibition of copper [J]. Journal of Electroanalytical Chemistry, 2000, 489(12): 38-45.
[10] ZHU Xiao-ling, LI Ren-shun, WU Reng, ZHOU De-rui. The initial corrosion mechanism of α-phase aluminum bronze in NaCl solution [J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 1992, 2(1): 61-62. (in Chineses)
[11] ROBBIOLA L, TRAN T T M, DUBOT P, MAJERUS O, RAHMOUNI K. Characterization of anodic layers on Cu-10Sn bronze (RDE) in aerated NaCl solution [J]. Corrosion Science, 2008, 50(8): 2205-2215.
[12] TOMASHOV N D. Development of electrochemical theory of metallic corrosion [J]. Corrosion, 1964, 20: 7-14.
[13] ZHANG S H, LYON S B. The electrochemistry of iron, zinc and copper in thin layer electrolytes [J]. Corrosion Science, 1993, 35(1-4): 713-718.
[14] NISHIKATA A, ICHHARA Y, TSURU T. Electrochemical impedence spectroscopy of metals covered with a thin electrolyte layer [J]. Electrochimica Acta, 1995, 41(7-8): 1057-1062.
[15] CHENG Y L, ZHANG Z, CAO F H, LI J F, ZHANG J Q, WANG J. M, CAO C N. A study of the corrosion of aluminum alloy 2024-T3 under thin electrolyte layers [J]. Corrosion Science, 2004, 46(7): 1649-1667.
[16] LIAO X N, CAO F H, ZHENG L Y, LIU W J, CHEN A N, ZHANG J Q, CAO C N. Corrosion behaviour of copper under chloride-containing thin electrolyte layer [J]. Corrosion Science, 2011, 53(10): 3289-3298.
[17] LAGUZZI G, LUVIDI L, BRUNORO G. Atmospheric corrosion of B6 bronze evaluated by the thin layer activation technique [J]. Corrosion Science, 2001, 43(4): 747-753.
[18] STRATMANN M, STRECKEL H, KIM K. T, CROCKETT S. On the atmospheric corroison of metals which are covered with thin electrolyte layers. 3. The measurement of polarization curves on metal-surface which are covered by thin lelctolyte layers [J]. Corrosion Science, 1990, 30(6-7): 715-734.
[19] DESLOUIS C, TRIBOLLET B, MENGOLI G, MUSIANI M M. Elelctrochemical behavior of copper in neutrl aerated chloride solution. 1. Steady-state inverstigation [J]. Journal of Applied Electrochemistry, 1988, 18(3): 374-383.
[20] KEAR G, BARKER B D, WALSH F C. Electrochemical corrosion of unalloyed copper in chloride media—A critical review [J]. Corrosion Science, 2004, 46(1): 109-135.
[21] HUANG H, DONG Z, CHEN Z, GUO X. The effects of Cl- ion concentration and relative humidity on atmospheric corrosion behaviour of PCB-Cu under adsorbed thin electrolyte layer [J]. Corrosion Science, 2011, 53: 1230-1236.
[22] EL-NAGGAR M M. Bis-triazole as a new corrosion inhibitor for copper in sulfate solution. A model for synergistic inhibition action [J]. Journal of Materirals Science, 2000, 35(24): 6189-6195.
[23] LORENZ W J, MANSFELD F. Determination of corrosion rates by electrochemical DC and AC methods [J]. Corrosion Science, 1981, 21(9-10): 647-672.
[24] van INGELGEM Y, TOURW? E, VEREECKEN J, HUBIN A. Application of multisine impedance spectroscopy, FE-AES and FE-SEM to study the early stages of copper corrosion [J]. Electrochimica Acta, 2008, 53(25): 7523-7530.
[25] EPELBOIN I, KEDDAM M, TAKENOUTI H. Use of impedance measurements for the determination of the instant rate of metal corrosion [J]. Journal of Applied Electrochemistry, 1972, 2(1): 71-79.
[26] MURESAN L, VARVARA S, STUPNISEK-LISAC E, OTMACIC H, MARUSIC K, HORVAT-KURBEGOVIC S, ROBBIOLA L, RAHMOUNI K, TAKENOUTI H. Protection of bronze covered with patina by innoxious organic substances [J]. Electrochimica Acta, 2007, 52(27): 7770-7779.
[27] CHIAVARI C, BERNARDI E, MARTINI C, PASSARINI F, OSPITALI F, ROBBIOLA L. The atmospheric corrosion of quaternary bronzes: The action of stagnant rain water [J]. Corrosion Sciece, 2010, 52(9): 3002-3010.
[28] CHIAVARI C, RAHMOUNI K, TAKENOUTI H, JOIRET S, VERMAUT P, ROBBIOLA L. Composition and electrochemical properties of natural patinas of outdoor bronze monuments [J]. Electrochimica Acta, 2007, 52(27): 7760-7769.
[29] BERNARDI E, CHIAVARI C, LENZA B, MARTINI C, MORSELLI L, OSPITALI F, ROBBIOLA L. The atmospheric corrosion of quaternary bronzes: The leaching action of acid rain [J]. Corrosion Science, 2009, 51(1): 159-170.
[30] BERNARD M C, JOIRET S. Understanding corrosion of ancient metals for the conservation of cultural heritage [J]. Electrochimica Acta, 2009, 54(22): 5199-5205.
[31] ROBBIOLA L, BLENGINO J M, FIAUD C. Morphology and mechanisms of formation of natural patinas on archaeological Cu-Sn alloys [J]. Corrosion Science, 1998, 40(12): 2083-2111.
[32] BERNARDI E, CHIAVARI C , MARTINI C, MORSELLI L. The atmospheric corrosion of quaternary bronzes: An evaluation of the dissolution rate of the alloying elements [J]. Applied Physics A—Materals Science Process, 2008, 92(1): 83-89.
廖晓宁1,2,曹发和1,陈安娜1,刘文娟1,张鉴清1,3,曹楚南1,3
1. 浙江大学 化学系,杭州 310027;
2. 江西农业大学 理学院,南昌 330045;
3. 中国科学院 金属研究所 腐蚀与防护国家重点实验室,沈阳 110016
摘 要:采用阴极极化曲线、开路电位和电化学阻抗谱,监测青铜在不同薄液膜厚度下的大气腐蚀行为。阴极极化曲线结果表明,阴极极限电流密度随着液膜的减薄而增大。电化学阻抗谱结果表明,在腐蚀初期,腐蚀速率随着液膜的减薄而增加,这主要是由于腐蚀速率是由阴极过程控制的;随着时间的延长,腐蚀程度随着液膜厚度的变化从强到弱的趋势为:150 μm,310 μm,100 μm,本体溶液,57 μm。开路电位和电化学阻抗谱实验较好地再现了原位电化学腐蚀信息,且电化学结果与物理表征具有良好的一致性。
关键词:青铜;薄液膜;原位研究;大气腐蚀;电化学技术
(Edited by YANG Hua)
Foundation item: Projects (51131005, 51171172, 50801056) supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China; Project (Y4110074) supported by Natural Science Foundation of Zhejiang Province, China
Corresponding author: CAO Fa-he; Tel: +86-571-87952318; Fax: +86-571-87951895; E-mail: nelson_cao@zju.edu.cn
DOI: 10.1016/S1003-6326(11)61311-3

