
J. Cent. South Univ. (2018) 25: 1701-1707
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11771-018-3861-1
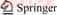
Breakdown mechanism of CF4 and N2 binary gas in refrigeration temperature range
LI Wei-guo(李卫国), HOU Meng-xi(侯孟希), YUAN Chuang-ye(袁创业),CHENG Yu-di(程宇頔), TU You-ping(屠幼萍)
School of Electrical and Electronic Engineering, North China Electric Power University,Beijing 102206, China
 Central South University Press and Springer-Verlag GmbH Germany, part of Springer Nature 2018
Central South University Press and Springer-Verlag GmbH Germany, part of Springer Nature 2018
Abstract: The mechanism of gas discharge in refrigeration temperature range is still not clear. N2, CF4, 20% CF4+N2 and 50%CF4+50%N2 binary gas mixtures were tested under the conditions of –153–25 °C and 50–2000 Pa. The experimental results show that the minimum of Paschen curves of all test samples shifts to low pressure, from 500 Pa to 200 Pa. The value of Paschen curve minimum of N2 shows remarkable fluctuation. This fluctuation is explained by molecule agglomeration and electronic mean energy. The fluctuation decreases with the increasing mixing ratio of CF4. What’s more, the value of Paschen curve minimum of CF4 decreases with temperature. This phenomenon is ascribed to attach-radiation and secondary process.
Key words: CF4; N2; agglomeration; attach-radition; breakdown mechanism; refrigeration temperature range
Cite this article as: LI Wei-guo, HOU Meng-xi, YUAN Chuang-ye, CHENG Yu-di, TU You-ping. Breakdown mechanism of CF4 and N2 binary gas in refrigeration temperature range [J]. Journal of Central South University, 2018, 25(7): 1701–1707. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11771-018-3861-1.
1 Introduction
SF6 is widely used in high-voltage equipment because of its remarkable arc quenching capability and dielectric insulating properties. With the help of SF6, the measurement of equipment is reduced and the margin of safety of equipment has also been improved. But SF6 is a kind of powerful greenhouse gas, and its global warming potential index is 23900 times than that of CO2. The environmental problems caused by SF6 have attracted wide attention. What’s more, with the development of global energy interconnection, key substations and power lines will be built in extremely cold regions and SF6 which can not normally work in extremely cold regions has relatively high liquefaction temperature.
The study of SF6 substitution is mainly divided into two directions. On one hand, mixtures containing SF6 are studied. On the other hand, new dielectric insulation materials are also studied. In the short term, under room temperature, SF6/N2 mixture has relatively strong dielectric strength and low liquefaction temperature which is the most effective substitution for SF6 [1]. In the long run, under room temperature, c-C4F8 [2], CF3I [3] and CnF2nO [4] are popular research subjects.
In cold regions, few gases can maintain their insulation properties. G3 gas (green gas for gird), i-C3F7CN which is developed by GE and Alstom [5] is a new substitution for SF6. G3 gas can work normally at –30 °C. Its dielectric strength is 90% of SF6, but its global warming potential (GWP) index is only 10% of SF6.
In cryogenic engineering, He and N2 are used as coolants and dielectrics. However, some current devices of high temperature superconducting work in refrigeration temperature range (–153–25 °C), which is higher than cryogenic temperature range. But common insulation gas SF6 cannot be used. This temperature range shows its special feature.
Recent researches prove that the temperature influence on gas discharge mechanism is still not clear at low temperatures. IRMISH et al [6] and MEATS [7] reported that the breakdown voltage of pressurise-helium has positive correlation with the gas pressure at low temperatures. The shape of test curves follows the Paschen law under the conditions of low pressure at low temperatures. Meanwhile, the minimum of Paschen curve at low temperatures is higher than that at room temperature. But this deviation was attributed to gas impurity. The investigations of XIAO [8, 9] showed that the pressure and the shape of electrode have influence on N2 breakdown properties, but the deviations are not explained from the gas discharge mechanism. HEARTMEAN [10] found that the materials of electrode have influence on N2 discharge character, and this influence is interpreted that cathode material has influence on secondary discharge.
RABIE et al [11] studied the liquefaction temperature and toxicity of thousands of compounds which consist of C, H, O, N, F and S. They found that some compounds of C, F are non-toxic and they have relatively low liquefaction temperature. Therefore, they can be used in refrigeration temperature range.
CF4 is used as coolant in industrial production, so it is a potential gas which can be used in refrigeration temperature range. GENG et al [12] reported the property and power frequency breakdown property of CF4, and they found that its dielectric strength is about 50% of SF6. HUANG [13] and XU et al [14] reported that arc extinction property of CF4 is about 50% of SF6. LI et al [15] previously reported the breakdown characteristics of CF4 and CF4/N2 hybrid gas in slightly non- uniform electric field under lighting impulse, which shows 20%CF4/80%N2 hybrid gas has excellent insulation property, low GWP index and low liquefaction temperature. Furthermore, LI et al [16] also studied breakdown characteristics of CF4 and CF4/N2 mixture gas in refrigeration temperature range, which shows that 20%CF4/80%N2 mixtures have great potential to be used under this condition. Aiming at studying the low temperature influence on CF4 and CF4/N2 binary gas discharge mechanism, series of low temperature DC breakdown tests are designed and temperature influence on Pashcen curve is analyzed.
2 Experimental
In order to obtain the breakdown data of the dielectric gases, a low temperature-air-tight test system was designed [17].
The test chamber is divided into two major parts. The inner part made of red copper is the test zone, which is covered by nickel-plating thermal shield, aiming for reducing the thermal radiation. The outer sphere made of stainless steel is used to build vacuum environment. There is a 30 cm gap between the inner part and the outer sphere. This annular area was dynamically vacuated by mechanical pump and molecular pump in the course of the experiment. The structure of test chamber, thermal shield, and the whole test system are shown in Figures1–3, respectively.

Figure 1 Structure of test chamber
KDE415-KDC6000 cryostat was used to cool the test chamber. The heat leakage rate of the test system is estimated by one dimensional Fourier heat flow equation [18], approximately 0.62 W. The fluctuation of temperature of the test chamber is less than 1 K within 2 h, so the temperature during breakdown test is constant.

Figure 2 Nickel-plating thermal shield
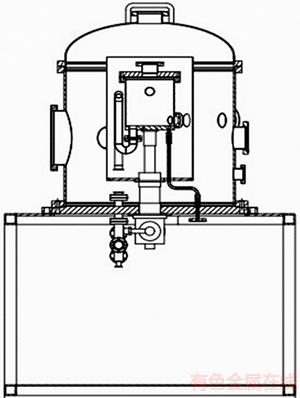
Figure 3 Structure of test cage
Plane-plane electrode made of red copper is adopted, and the interelectrode gap is 1 mm. The electrodes were always sandblasted prior to use in order to minimize the influence of previous discharges in measurements. The test pressure changed from 50 Pa to 2000 Pa on both sides of the Paschen minimum. The test temperature is altered from –150 °C to 25 °C.
Before a new test, the former sample was vacuated and the test chamber would be vacuated to 10–5 Pa, then the new test sample was injected. Minority proportion gas was injected before majority proportion gas when mixture gases were tested. After mixture gases were tested, it should stand 4 h before test. The applied voltage rose at the rate of 5 V/s. 2 min breaks punctuate the whole series of measurements. The test sample is CF4 and N2, and the mixing ratio is 100%CF4, 50%CF4/50%N2, 20%CF4/80%N2 and 100%N2. Each group of gases was tested 10 times, and the average value of 10 test measurements were taken as the final breakdown voltage of dielectric.
3 Results and discussion
3.1 Test results
The DC breakdown characteristics of N2, CF4, 20%CF4/N2 and 50%CF4/N2 were investigated. Their Paschen curves in refrigeration temperature range are shown in Figures 4–7.
As is shown in Figure 4, the shape of test curves of N2 follows Paschen law. The Paschen minimum of N2 at low temperatures is higher than that at room temperature, and this matches the result of Irmisch. Moreover, the minimum of Paschen curves shifts to the left from 300–500 Pa to 200–300 Pa, with the temperature decreasing. And under the same condition of (pd), the breakdown voltage of N2 rises with temperature decreasing from 25 °C to –100 °C. But when p is lower than 1300 Pa, the breakdown voltage at –150 °C is lower than that at –100 °C.
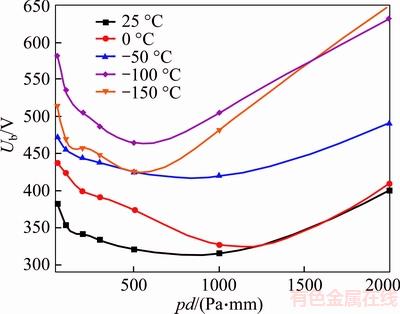
Figure 4 N2 breakdown voltage in refrigeration temperature range (d=1 mm)
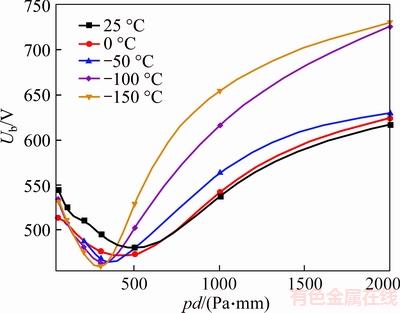
Figure 5 CF4 breakdown voltage in refrigeration temperature range (d=1 mm)
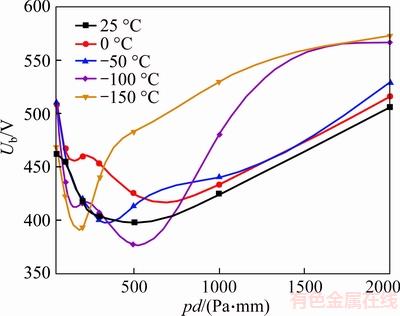
Figure 6 20%CF4/80%N2 breakdown voltage in refrigeration temperature range (d=1 mm)
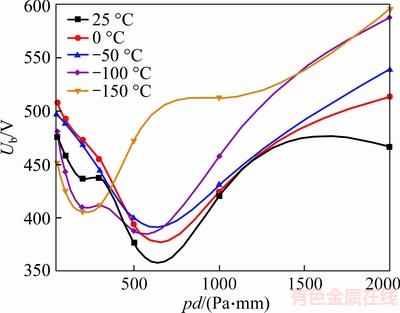
Figure 7 50%CF4/50%N2 breakdown voltage in refrigeration temperature range (d=1 mm)
CF4 DC breakdown voltage in low temperatures is shown in Figure 5. It is remarkable that the minimum of Paschen curves shift to the left from 500–1000 Pa to 300–500 Pa, with the temperature decreasing. The value of Paschen minimum of CF4 rises with temperature, and this is different from N2. On the right side of the minimum point, the breakdown voltage of CF4 rises with temperature decreasing. While the breakdown voltage of CF4 has no rules to follow on the left side of the minimum point.
20%CF4/80%N2 breakdown voltage in refrigeration temperature range is shown in Figure 6. The minimum breakdown voltage still appears at 25 °C, which is the same as N2. And the minimum breakdown voltage is approximately 15% higher than that of the pure N2, which means adding a spot of CF4 can increase the dielectric strength of N2 a lot. And it is also remarkable that the minimum of Paschen curves shifts to the left from 300–500 Pa to 200–300 Pa, with the temperature decreasing. But when adding a handful of CF4 to N2, the shape of curves is totally different from the pure N2, and several cross points are found in Figure 6.
As is shown in Figure 7, adding CF4 mixing ratio from 20% to 50%, the minimum breakdown voltage appears at –100 °C instead of 25 °C. And the minimum breakdown voltage is approximately 35% higher than that of N2. Moreover, the minimum of Paschen curves shifts to the left from 300–500 Pa to 200–300 Pa, with the temperature decreasing.
3.2 Common points of Paschen curves
In refrigeration temperature range, gas discharge mechanism differs to room temperature. There are two common points based on the analyses of the four pictures. One is that the Paschen curves minimum shifts to the left with temperature decreasing. The other is, on the right side of Paschen curves, the breakdown voltage rises with temperature decreasing.
The offset value of test samples is shown in Table 1. The electrical breakdown of any gas is the result of self-sustained avalanche processes and depends on the relative activity of electron generation-and-loss mechanisms [19]. The DC breakdown voltage is determined by Townsend criterion [20]:
Table 1 Corresponding pressure (100 Pa) of sample’s Paschen minimum
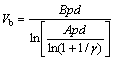 (1)
(1)
where A=kσ/T; B=AUi; k is Boltzmann constant; Ui is ionisation potential; γ is the number of electrons generated from secondary process; T is temperature. Take partials of (pd):
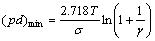 (2)
(2)
Neglecting the influence of T on σ and γ, (pd)min is the function of T, i.e., (pd)min decreases with temperature.
Actually, it is assumed that the Paschen minimum U0 at room temperature of the test sample located at p0. The pressure p0 is kept to cool and the test chamber is used to cool to T1 (T1 lower than room temperature). Aiming at keeping the pressure, more samples should be injected in the test chamber. The density of the test sample will increase at T1. Free path length of electron decreases because of the molecule density increase, which means, before collision with molecule, electrons obtain less energy at T1 than at room temperature. So, the DC breakdown voltage of test sample at T1 is higher than U0. If we hold the temperature T1, then decrease p0 to pressure p1(p1
0), the free path length of electron will heighten again and the DC breakdown voltage of testing sample U1 will be lower than U0.
If p1 is appropriate, the new Paschen minimum of test sample at T1 appears, i.e., the temperature influence on electron free path is the reason why the Paschen minimum shifts to the left.
And also on the right side of the off-peak point, all curves show that the breakdown voltage increases with the temperature falling. This phenomenon can be explained by free-path length.
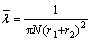
Under certain conditions of pressure, molecular density(N) is inversely proportional to temperature, which means shorter free-path length to electronics. So, the breakdown voltage is inversely proportional to temperature.
3.3 Fluctuation of Paschen curve minimum
It is remarkable that the value of Paschen minimum of N2 fluctuates with temperature. The maximum of Paschen minimum appears at –100 °C. Similar fluctuations are also observed in 20% and 50% CF4/N2 mixtures. But the increase of CF4 mixing ratio diminishes this kind of fluctuation, i.e., the fluctuations will not be observed in pure CF4, which matches Figure 8.
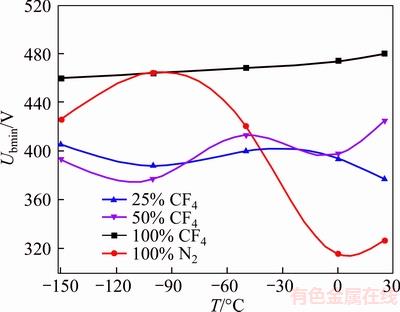
Figure 8 Paschen curve minimum fluctuation
Simultaneously, the result shows that the Paschen minimum of CF4 decreases with temperature. The Paschen minimum of CF4 at low temperature is lower than that at room temperature which is opposite to N2. The mechanism of this phenomenon is not known to us at the moment. This phenomenon results from the following conjectures.
On the one hand, CF4 is electronegative gas. The major radiation pattern of electronegative gas is attach-radiation, which is expressed as
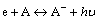
Attach-radiation will generate photon. The emission of photon can accelerate ionization, which leads to lower Paschen minimum of CF4. Under the conditions of low temperatures and low pressure, it is easier to generate stable anion [21], i.e., the lower the temperature is, the more the photon will be, thus Paschen minimum of CF4 decreases with temperature.
On the other hand, the red copper electrodes are always sandblasted prior to use, but red copper is easily oxidized after sandblasted, when test chamber vacuated, and oxidization might occur. The materials of electrode are not pure substance with dopant in it. After breakdown several times, the trace-oxide prevents positron recombination with cathode. On the contrary, positron aggregate on the surface of oxide, which can form a very strong electric field. The strength of this additional electric field can reach 106 V/m, sometimes even higher. This phenomenon is called Malter effect [22]. Additional strong electric field caused by Malter effect can reduce Schottky barrier [23] of cathode. This will enhance secondary process, leading to the decrease of Paschen minimum of CF4. But the influence of temperature on Malter effect and Schottky effect at low temperatures still have to be confirmed in further investigation.
However, the two hypotheses mentioned above is used to explain that the monotonicity of CF4 (electronegativity gas). N2 is electroneutrality molecule, which has less attach-radiation. Here we attribute a fraction of fluctuation to molecule agglomeration and this process is shown in Figure 9.
The velocity of Brownian movement decreases with temperature which is determined as
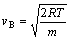
With the temperature decreasing, approaching to liquefaction temperature, electroneutrality molecule will gradually agglomerate. Increasing of N2 cross section helps to enhancing ionization. At the same time the rate of collision decreases crippling ionization. By the actions of these two factors, the Paschen minimum of N2 has extremum.
But the Paschen minimum curves of N2 and mixing gases have more than one extremum points, which means molecule agglomeration is not the only influence factor. ANA et al [24] mentioned that the mobility is equal to drift velocity in N2. And both of them are function of E/p. While drift velocity is inversely proportional to E/p and the mobility is proportion to E/p. That is to say, under weak electric field, mean energy of electronic is fluctuating. So under the condition of different temperatures, the N2 minimum of Paschen curves fluctuates.
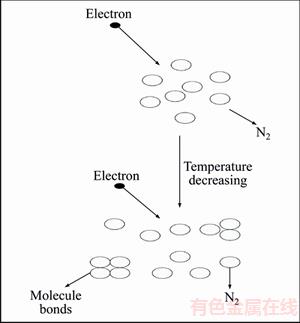
Figure 9 N2 molecule agglomeration process
4 Conclusions
1) Temperature decrease leads to the shift of Paschen minimum to low pressure, from 500 Pa to 200 Pa. The mechanism of this phenomenon is that temperature has influence on free path length.
2) Temperature decrease has influence on attach-radiation and secondary process, causing the value of Paschen minimum of CF4 decrease with temperature.
3) The value of Paschen minimum of N2 fluctuates with temperature decrease, and this probably relates to molecule agglomeration and electronic mean energy.
References
[1] KIEFFEL Y, BIQUEZ F. SF6 alternative development for high voltage switchgears [C]// Electrical Insulation Conference. Denver: CO, 2015: 1–5. DOI: 10.1109/PESGM. 2015.7286096.
[2] WU Bian-tao, XIAO Deng-ming. Analysis of insulation characteristics of c-C4F8 and N2 gas mixtures by Monte Carlo method [J]. Journal of Physics D-Applied Physics, 2006, 39(19): 4204–4207. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1088/0022-3727/ 39/19/012.
[3] YOKOMIZU Y, OCHIAI R. Electrical and thermal conductivities of high-temperature CO2-CF3I mixture and transient conductance of residual are during its extinction process [J]. Journal of Physics D-Applied Physics, 2009, 42(21): 5204–5217. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1088/0022-3727/ 42/21/215204.
[4] YUSUKE K, KENJI I. CF3 fragmentation by electron impact ionization of perfluoro-propyl-vinyl-ethers, C5F10O, in gas phase [J]. Japanese Journal of Applied physics, 2015, 54(4): 3312–3320. DOI: https://doi.org/10.7567/JJAP.54.040301.
[5] YANNICK K, TODD I. Green gas to replace SF6 in electrical grids [J]. IEEE Power and energy magazine, 2016, 14(2): 32–39. DOI: 10.1109/MPE.2016.2542645.
[6] IRMISH M, ZWECKER V, JAARAH M. Breakdown characteristics of He gas at cryogenic temperature and low pressure [J]. IEEE Transactions on Electrical Insulation, 1993, 28(4): 507–511. DOI: 10.1109/14.231533.
[7] MEATS R J. Pressurised-helium breakdown at very low temperature [J]. Electrical Engineers, 1972, 6(119): 760–765. DOI: 10.1049/piee.1972.0158.
[8] XIAO Li-ye. Recent progress of power application of superconductor in China [J]. IEEE Transactions on Applied Superconductivity, 2007, 17(2): 2355–2360. DOI: 10.1109/ TASC.2007.898160.
[9] XIAO Li-ye. Development of the world's first HTS power substation [J]. IEEE Transactions on Applied Superconductivity, 2012, 22(3): 504–504. DOI: 10.1109/ TASC.2011.2176089.
[10] HEARTMEAN P. Effect of different elementary processes on the breakdown in low-pressure helium gas [J]. Plasma Sources Science & Technology. 2000, 2(2): 43–50. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1088/0963-0252/9/2/311.
[11] RABIE M, FRANCK M. Computational screening of new high voltage insulation gases with low global warming potential [J]. IEEE Transactions on Dielectrics and Electrical Insulation, 2001, 22(1): 296–302. DOI: 10.1109/TDEI. 2014.004474.
[12] GENG Zhen-xin, LIN Xin. Experimental study of CF4 insulation performance [C]// Electric Power Equipment Switching Technology. Busan: ICEPE, 2015: 394–397. DOI: 10.1109/ICEPE-ST.2015.7368401.
[13] HUANG Yi-bin. Research of the ARC interruption capability of CF4 [D]. Shanghai: Shanghai Jiao Tong University, 2010. (in Chinese)
[14] XU Guo-zhen, LI Qing-min. Investigation of SF6/CF4 mixture as the insulating and cooling medium of gas insulated transformer [J]. Journal of Tsinghua University, 1997,18(9): 18–21. DOI: 10.16511/j.cnki.qhdxxb.1997.09. 005. (in Chinese)
[15] LI Wei-guo, HOU Meng-xi. Breakdown characteristics of CF4/N2 in slightly non-uniform electric field under lighting impulse [J]. High Voltage Apparatus, 2016, 52(12): 128–133. DOI: 10.13296/j.1001-1609.hva.2016.12.020. (in Chinese)
[16] LI Wei-guo, HOU Meng-xi. Study on AC breakdown characteristics of CF4 and its N2 mixtures [J]. Journal of Guangxi University, 2016, 41(6): 1863–1868. DOI: 10.13624/j.cnki.issn.1001-7445.2016.1863. (in Chinese)
[17] TAN R. Electrical test system for insulation materials in low temperature superconducting [D]. Beijing: North China Electric Power University, 2013. (in Chinese)
[18] CHENG Guo-bin. Low temperature thermal transmission and isolation technique [M]. Beijing: China Science Press, 2004. (in Chinese)
[19] OSMOKROVIC P. Mechanism of electrical breakdown of gases at very low pressure and interelectrode gap values [J]. IEEE Transactions on Plasma Science, 1993, 21(6): 645–653. DOI: 10.1109/27.256784.
[20] SATIR M. Characteristics of an argon DC glow discharge and effect of cathode on Paschen curve and cathode temperature [C]// International Conference on Plasma Science. Antalya: ICOPS, 2015: 1–4. DOI: 10.1109/PLASMA.2015. 7179581.
[21] YANG Jin-ji. Gas discharge [M]. Beijing: China Science Press, 1983. (in Chinese)
[22] FREDERICKSON O. Measurement of conductivity and charge storage in insulators related to spacecraft charging [J]. Electrical Insulation and Dielectric Phenomena, 2003, 18(7): 24–27. DOI: 10.1109/TNS.2003.821397.
[23] KITTLE C. Introduction to solid physics [M]. New York, Marcel Dekker Inc, 1986.
[24] ANA B, SASA D. Positron transport in CF4 and N2/CF4 mixtures [J]. European Physical Journal D, 2014, 68(5): 1–10. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1140/epjd/e2014-50087-5.
(Edited by HE Yun-bin)
中文导读
CF4及其N2混合物在普冷温区下绝缘机理分析
摘要:普冷温区环境下气体绝缘机理依然不够明朗。本文在温度–153~25 °C,气压50~2000 Pa的范围内对CF4、N2、20%CF4/N2以及50%CF4/N2混合气体进行了绝缘击穿试验。试验结果表明:气体临界击穿电压出现位置随着温度的降低向低气压偏移;N2临界击穿电压随着温度的变化呈现明显的波动性,随着气体中CF4含量的增高,混合气体临界击穿电压随着温度变化的波动性降低,纯CF4气体临界击穿电压随着温度的降低呈单调下降趋势。这一现象与分子电负性强弱、附着效应、分子团以及二代电子崩的形成有关。
关键词:CF4;N2;分子团;附着效应;击穿机理;普冷温区
Foundation item: Project(51277063) supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China; Project(51407013) supported in part by the National Natural Science Foundation of China
Received date: 2017-02-17; Accepted date: 2017-04-12
Corresponding author: LI Wei-guo, PhD, Professor; Tel: +86–18701289872; E-mail:18810102619@139.com; ORCID: 0000-0003- 2550-7513