川东北飞仙关组高含H2S气藏油田水地球化学特征
赵兴齐1, 2,陈践发2,郭望3,何大祥2,陈斐然2,刘高志2
(1. 核工业北京地质研究院 中核集团铀资源勘查与评价技术重点实验室,北京,100029;
2. 中国石油大学(北京) 油气资源与探测国家重点实验室,北京,102249;
3. 中国地质调查局 西安地质调查中心,陕西 西安,710054)
摘要:根据川东北地区飞仙关组气藏中油田水的分析测试资料及实际地质情况,探讨该区高含H2S气藏中油田水的成因及地球化学特征、影响油田水化学性质的因素及与油气聚集、保存的关系。研究结果表明:川东北地区飞仙关组油田水是以阴、阳离子分别为Cl-和(Na++K+)为主的Na2SO4型水,只有少数是CaCl2型和NaHCO3型;地层水度矿化度分布范围较宽主要与碳酸盐岩储层具有较强的非均质性有关,导致TSR反应过程中产生的淡水与原生油田水混合不均匀,同时TSR作用过程中产生的淡水会降低原始油田水矿化度。研究区高含H2S地层和高含SO42-油田水分布特征基本相似,高值区主要分布在海槽东侧蒸发台地相,而海槽相及海槽西侧开阔台地相SO42-含量低,油田水中SO42-质量浓度分布控制了气藏中H2S和溶解H2S质量浓度的分布。高含H2S气藏油田水中阳离子质量浓度基本比低含H2S气藏的小,阴离子中Cl-含量也明显较其他低含H2S气藏油田水的低,而SO42-含量远远比低含H2S气藏的高。该区油田水水型、钠氯系数、脱硫系数出现异常及阴离子中Cl-含量明显偏低都主要与储层中膏质盐类的溶蚀导致油田水中SO42-质量浓度增高密切相关,因此,研究区这种高矿化度的Na2SO4型油田水并不代表地层对油气的保存不利,相反为该区天然气的有利富集区。研究区高含H2S气藏和低含H2S气藏油田水最主要差别在于SO42-含量,微观上典型气藏产气层和产水层油田水中SO42-和溶解H2S之间存在此消彼长的关系与TSR反应有关,气-水界面及附近水层中更有利于TSR反应的发生。
关键词:硫化氢;气藏;油田水;地球化学特征;飞仙关组;川东北
中图分类号:TE122.1 文献标志码:A 文章编号:1672-7207(2014)10-3477-12
Geochemical characteristics of oilfield waters with high H2S gas reservoirs in Feixianguan formation, Northeastern Sichuan Basin
ZHAO Xingqi1, 2, CHEN Jianfa2, GUO Wang3, HE Daxiang2, CHEN Feiran2, LIU Gaozhi2
(1. CNNC Key Laboratory of Uranium Resources Exploration and Evaluation Technology,
Beijing Research Institute of Uranium Geology, Beijing 100029, China;
2. State Key Laboratory of Petroleum Resources and Prospecting, China University of Petroleum, Beijing 102249, China;
3. Xi’an Center of Geological Survey, China Geological Survey, Xi'an 710054, China)
Abstract: Based on the geochemical analysis of oilfield water from gas reservoir with high-content of H2S and local geological characteristics of Feixianguan formation, the origin, geochemical characters of oilfield water and factors influencing the attributes of oilfield water and gas accumulation were analyzed. The results show that the main chemical composition is dominated by Cl- and (Na++K+), which can be classified as Na2SO4 type water, and only a few samples belongs to CaCl2 type and NaHCO3 type water. The wide distribution of oilfield water salinity are mainly related with significant heterogeneity of carbonate reservoirs, which leads the primary oilfield water to be mixed by fresh water derived from TSR and its salinity can be decreased. The distributional characteristic of high content of H2S reservoir is consistent with the distribution of oilfield water with high content of SO42-. The high value areas are mainly located in the east side of trough with evaporate platform facies, while trough facies and open-platform facies in the west side of trough are characterized by low level of SO42-. Besides, the distribution of SO42- controls the distribution of free H2S and dissolved H2S in gas reservoir. The content of cation and Cl- from oilfield water with high level of H2S is lower than the counterparts from gas reservoir with lower level of H2S. But the situation of SO42- is intensely opposite. The geochemical analysis about oilfield water shows that the types of water, sodium to chloride coefficient and desulfurization coefficient are abnormally affected by the gypsum rocks dissolution that arouses the high content of SO42-, and therefore, it can not be concluded that the formation, with high content of H2S in oilfield water, in study area is against gas accumulating, on the contrary, there may be the favorable zone. The significant difference between low H2S area and high H2S area is the content of SO42-, the reciprocal relationship between SO42- and dissolved H2S in oilfield waters of typical gas reservoir production gas and water yield formation are related with TSR reaction. The TSR are more likely to occur in gas-water interface and the nearby water zone.
Key words: hydrogen sulphide; gas reservoir; oilfield waters; geochemical characteristics; Feixianguan formation; Northeastern Sichuan Basin
油田水是指在储集层中与油气相伴生的地下水,是油气藏流体系统中一个不可缺少的重要组成部分,其形成和运动规律与油气的生成、运移、聚集以及油气藏的形成、保存和破坏紧密相关[1-5]。在油气成藏过程中,油田水与围岩、油气之间存在物质和能量的交换,其中蕴含了丰富的油气藏形成和保存的信息。油田水化学组分及相应的化学指标可以直接或间接指示沉积盆地流体系统的开放性和封闭性以及不同程度地反映油气聚集、保存条件,不同沉积背景条件下形成的含油气盆地往往具有不同特征的油田水:因此,研究地层中油田水对指导油气勘探具有十分重大的意义。而对于天然气成藏来说,保存条件更是制约着天然气气藏勘探成功的重要因素。近年来,关于油气藏中油田水的研究相对较多,取得了许多重要的认识[6-12],并建立了利用油田水判断油气聚集及保存条件的相关参数指标。但关于高含H2S气藏中油田水的地球化学特征鲜有报道,江兴福等[13-15]通过对川东北飞仙关组地层水特征研究认为,该区Na2SO4型地层水的形成主要与膏岩的溶滤作用有关,且认为这种类型地层水对油气藏的形成有利,但文中均未考虑到TSR作用对地层水的影响。地层中高含H2S主要是烃类-矿物发生TSR反应的产物,但是这种反应并不是单纯的气-固两相反应,实验室已经证明这种TSR作用大部分情况下是发生在油田水中的均相反应[16]。随着反应的进行,不论反应物和生成物的变化必将导致油田水化学性质发生变化,例如TSR反应生成的H2S和CO2气体的溶解、石膏层的溶蚀以及反应导致pH的变化,这些必将形成高含H2S地层特有的油田水模式。因此,本文作者通过对川东北地区高含H2S气藏中油田水的研究,探讨该区油田水地球化学特征和成因以及H2S气藏油田水的组成模式,以深化研究区天然气聚集、保存规律的认识,以期为川东北地区天然气的进一步勘探与开发提供地质—地球化学依据。
1 区域地质概况
四川盆地是扬子准地台西部1个呈北东向延展的菱形构造兼沉积型含油气盆地,震旦纪至中三叠世的海相碳酸盐岩和晚三叠世至始新世的陆相碎屑岩沉积组合的大型复合含油气盆地。根据基底性质、沉积盖层、气藏(田)特征及天然气类型等,把四川盆地划分为4个油气聚集区,即川东气区、川南气区(包括川南和川西南)、川西气区和川中油气区[17-18](图1)。气田分布较分散,在各区块都有,其中川东和川南气田气藏最多,约占总数的70%,川南的气田和气藏规模都比较小,而川东大、中型气田最多[19]。由于沉降中心的迁移和演化过程的不均一性,使得各区块具有不同的沉积组合和油气分布规律。其中,油田主要分布在川中地区,其他区块几乎没有工业规模的油田,均为气田。川东北地区位于四川盆地东北部,在地理位置上属于达州市(开江、宣汉、达县)、万源市境内,在传统的大地构造上属于上扬子地台的一部分,该区主体构造为NW向大巴山弧形构造带及其前缘带和NE—NEE向川东弧形褶皱带,米仓山构造带南缘褶皱基底与盖层的接触带。目前研究区已发现金珠坪、渡口河、罗家寨、滚子坪、黃龙场、清溪场、铁山坡、普光、毛坝、大湾、东岳寨、铁山、龙岗、元坝、河坝、金溪、射箭河等17个长兴组—飞仙关组气田或含气圈闭,已探明的大型气田主要有渡口河、铁山坡、罗家寨、普光和大湾气田,其有效储产层都主要分布在长兴—飞仙关组的碳酸盐岩地层中。
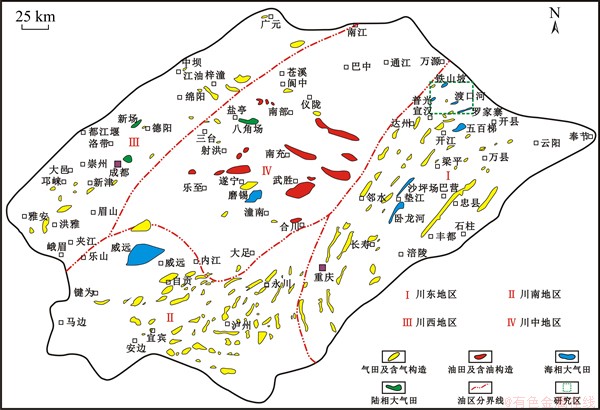
图1 四川盆地油气田平面分布图(据文献[17-18]修改)
Fig. 1 Distribution of oil and gas field in Sichuan basin (revised according to Refs. [17-18])
近年来,在川东北地区下三叠统飞仙关组(T1f)储层中发现高含H2S天然气,已发现了普光、罗家寨、渡口河和铁山坡等高含硫化氢气田,这些气藏H2S多数占气体组分的10%~15%[20],其中普光和渡口河气田H2S含量最高,其H2S含量平均占气体组分的16%左右,罗家寨和铁山坡气田H2S含量分别平均占各自气体组分的12%和14%左右[21]。从古地理环境来看,飞仙关组沉积早期,川东北地区发育开江—梁平陆棚和城口—鄂西陆棚,2个陆棚之间发育川东北孤立台地沉积,而开江—梁平陆棚西南侧则以一套与陆地相连的碳酸盐岩沉积为特征[22]。从研究区H2S分布特征来看:高含H2S气田主要分布在开江—梁平海槽东侧的蒸发台地相,由于沉积旋回及滩坝的障壁作用,沉积了少量薄层膏质盐类,累计厚度为5~10 m,为该区形成高含H2S提供了硫源,次生孔隙十分发育,可能与硫化氢对碳酸盐岩的溶蚀改造作用有关,而陆棚相区和陆棚西侧开阔台地相飞仙关组由于不发育膏质盐类,储层性质较差,主要以裂缝型储层为主,故天然气中H2S含量明显较蒸发台地相低[21]。前人对川东北地区高含硫化氢的成因开展了大量地质—地球化学研究及模拟实验分析,表明该区H2S主要为硫酸盐热化学还原反应成因(TSR),该区储层中膏岩的存在为形成高浓度H2S提供了必要条件[17, 19-25]。
2 油田水地球化学特征
2.1 油田水组成及矿化度
本次研究在中石化股份有限公司勘探南方分公司收集了川东北地区飞仙关组(T1f)28口井67组油田水实测数据。由于油田水在钻井和试气生产过程中易受到地表水、钻井液、完井液、酸化液或压裂液等残留液的污染,不能真实反映油气田中油田水的原始地球化学特征。在对本次油田水资料的实际分析过程中,为了尽量避免残留液对油田水的污染,对研究区飞仙关组高含硫化氢气藏典型井段测井解释结果、出水情况、取样时间及取样条件等资料进行系统分析,在此基础上排除了非正常油田水的测试数据资料。
对研究区14口飞仙关组高含H2S气田油田水的常规离子分析表明(表1),油田水中阳离子主要以(Na++K+)为主,其次为Ca2+和Mg2+;阴离子主体由大到小表现为Cl-,SO42-,HCO3-,CO32-,油田水中CO32-除了极个别井含有外,大多数不含CO32-;按照水型计算公式[r(Na+)+r(K+)-r(Cl-)]/[2r(SO42-)]几乎全小于1,总体属于Na2SO4型油田水,只有少部分是CaCl2型和NaHCO3型油田水。在常规离子中Na++K+,Ca2+,SO42-和HCO3-普遍都比现代海水平均值要高,但Mg2+含量明显比现代海水的低,这主要是由于Mg2+在成岩过程中参与了白云石化作用而大量消耗,这与研究区现今储层主要以白云岩为主的碳酸盐岩储层相对应。油田水中Na++K+和Cl-含量与矿化度有很好的正相关性,表明该区油田水矿化度主要受这2类离子的控制,说明研究区油田水矿化度受蒸发浓缩作用的影响较大。研究区油田水矿化度(TDS)变化范围较大,其值分布在24.850~81.010 g/L,平均质量浓度为44.510 g/L,大于海相油田水矿化度,表明研究区地层有利于油气的保存[26-27]。从研究区油田水类型来看,似乎表明川东北地区地表水与地下水交替频繁,封闭性差,不利于油气的保存,然而这些地区往往是高产天然气区。
2.2 油田水特征系数
油田水特征系数可以反映油田水所处的水文地球化学环境和水-岩相互作用强度。本文采用钠氯系数(r(Na+)/r(Cl-))、脱硫酸系数(r(SO42-)×100/r(Cl-))、氯镁系数(r(Cl-)/r(Mg2+))和钙镁系数(r(Ca2+)/r(Mg2+))对研究区油田水地球化学特征进行系统分析。一般认为,r(Na+)/r(Cl-)越小,地下水越浓缩,变质越深,水体环境趋于还原,越有利于油气保存。地层水的r(Na+)/r(Cl-)小于0.85,则油气保存条件好;若大于0.85,则表明有地下水渗入,油气保存条件差[7]。脱硫酸系数(r(SO42-)×100/r(Cl-))是表征脱硫酸作用的程度,一般认为,若油田水的脱硫系数小于3,则保存条件良好;若大于3,则认为还原作用不彻底,可能受到表层氧化作用的影响[28]。氯镁系数(r(Cl-)/r(Mg2+))是反映浓缩变质作用和阳离子吸附交换作用的重要水化学参数,油田水封闭越好、时间越长,浓缩变质越深,其r(Cl-)/r(Mg2+)越大,有利于油气的聚集与保存[28]。钙镁系数(r(Ca2+)/r(Mg2+))是表征浓缩变质作用和阳离子吸附交换作用强弱的水文地球化学重要参数之一。白云岩化作用越强、作用时间越长,油田水中Mg2+含量就越小,浓缩变质程度就越大,钙镁系数就越大,油田水封闭就越好,有利于油气聚集与保存。一般来说,油田水的钙镁系数大于3,封闭条件良好,有利于油气成藏[28]。川东北飞仙关组高含H2S油田水组特征参数见表1。从表1可知:川东北飞仙关组高含H2S地区油田水r(Na+)/r(Cl-)总体大于1.0,平均为1.17,可能是由于水中碱土金属与岩层中的碱金属离子发生交换时,因地层水中Na++K+含量的增加,从而导致Cl-含量低于(Na++K+)含量;r(SO42-)×100/r(Cl-)均大于3,最大可达202.29,这2个参数也似乎表明该区油田水受到大气降水淋滤作用的影响,地层封闭性差,不利于油气的保存。但从该区沉积环境来看,环开江—梁平海槽下三叠统飞仙关组(T1f)、嘉陵江组(T1j)和中三叠统雷口坡组(T2l)为连续沉积,中间没有明显的沉积间断或抬升剥蚀,次生方解石中具有很高的Fe、较高的Sr和很低的Mn含量及地层孔隙水中具有较高含量的Sr,表明飞仙关组地层整体形成于较强还原、缺乏大陆淡水影响的封闭性成岩环境中[29];假如飞仙关组地层在后期有地表水的作用,则地层中H2S含量不可能达到现今这么高,因为地表水中的重金属离子易于与H2S发生反应生成金属硫化物,不断消耗H2S。但值得注意的是该区油田水矿化度明显较其他海相含油气盆地偏低,这可能与该区H2S主要来源于TSR作用有关[19-24]。因为TSR作用是一个产生淡水的过程,而这些产生的淡水与原生油田水相混合,从而降低了油田水矿化度。研究区油田水矿化度分布范围较宽可能是由于碳酸盐岩储层具有较强的非均质性,导致TSR反应过程中产生的淡水与原生油田水混合不均匀。r(Cl-)/r(Mg2+)分布于154.63~522.58之间,平均可达184.80,r(Ca2+)/r(Mg2+)分布范围为1.37~16.65,平均为7.94,这2个参数反映研究区油田水封闭较好,储层有利于天然气的保存。
表1 川东北飞仙关组高含H2S油田水组特征参数
Table 1 Characteristic parameters of oilfield waters with high H2S gas reservoirs in Feixianguan formation, Northeastern Sichuan Basin
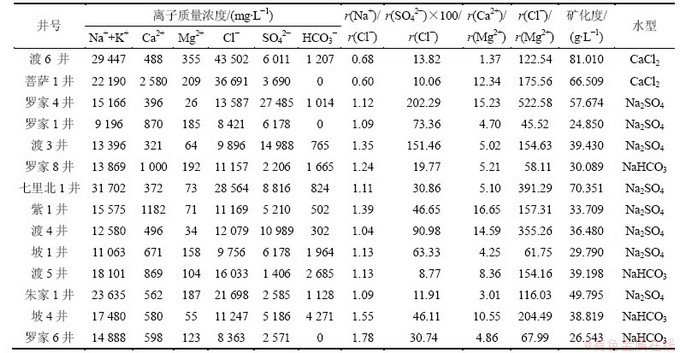
2.3 油田水SO42-和溶解H2S分布规律
统计分析川东北地区飞仙关组28口井油田水SO42-、溶解H2S浓度在平面上的变化特征。由SO42-分布图(图2)可以看出:SO42-质量浓度高值区位于海槽东侧,主要有罗家寨、渡口河、普光大中型气藏以及部分泻湖相微产气藏,总体上具有泻湖亚相油田水SO42-质量浓度稍比台缘鲕粒滩(坝)亚相的高,但二者SO42-质量浓度均远大于海槽相和西侧开阔台地相地层油田水SO42-质量浓度;而在东南部主要发育开阔台地相[21, 30],飞一到飞三段储层中不发育膏质盐类,因此该区气藏几乎不含H2S。由油田水溶解H2S质量浓度分布图(图3)可看出整个川东北地区溶解H2S质量浓度有2个相对高质量浓度区,主要分布于海槽的东侧和西侧,东侧蒸发台地相最高质量浓度位于菩萨1井、渡5井、朱家1井,最高溶解H2S达到6 174 mg/L;而西侧开阔台地相最高质量浓度位于天东55井处,但仅为3 381 mg/L,同SO42-分布相似,开阔台地相油田水溶解H2S质量浓度也明显比蒸发台地相的小。
从SO42-以及油田水溶解H2S质量浓度的分布特征来看:川东北高含H2S地层和高含SO42-油田水分布特征基本相似,高值区主要分布在海槽东侧蒸发台地相,同时该区气藏中H2S质量浓度及油田水溶解H2S质量浓度也较高;而海槽相及海槽西侧开阔台地相SO42-质量浓度低,油田水溶解H2S质量浓度及气藏中H2S质量浓度也较低。由此说明SO42-和油田水溶解H2S必然与气藏中H2S的生成有联系,即SO42-分布控制了气藏中H2S和油田水溶解H2S的分布,因此,海槽东侧蒸发台地相气藏中H2S质量浓度明显较海槽相及开阔台地相的高。
2.4 高含H2S气藏油田水与低含H2S气藏油田水特征对比
研究区内高含H2S气藏与其他低含H2S气藏地层水中主要组分的含量对比可以看出,飞仙关组高含H2S气藏油田水主要具有以下2方面特征:
1) 中国部分海相地层油田水类型见图4。由图4可见:川东北高含H2S气藏油田水的主要水型为Na2SO4型,但研究区内低含H2S气藏多为NaHCO3型油田水,下伏的石炭系海相地层以及塔里木盆地海相地层油田水多为CaCl2型。在一般情况下,烃类聚集与水型的关系由大到小顺序为:CaCl2,NaHCO3,MgCl2,Na2SO4。CaCl2型油田水交换能力差有利于油气的保存,是含油气区的主要水型;而Na2SO4型油田水反映保存条件差,通常表征地表连通的静水压力系统,一般油气聚集区不存在此类油田水[31]。然而,川东北高含H2S气藏油田水的主要水型为Na2SO4型,与一般天然气储层油田水类型为CaCl2型油田水这一规律相矛盾,因为目前川东北飞仙关组地层平均埋深在4 km左右,区域内无深大断裂与地表水系统相通,不可能出现Na2SO4油田水,且此区天然气储量巨大,必然保存环境较好,不可能与地表水系统连通,所以,此类油田水的存在必然有其特殊性。结合川东北飞仙关组地层矿物分析后发现这些高含H2S气藏储层主要是以白云岩组成为主的碳酸盐岩储集层,且储层中膏质盐类十分发育,同时这些储层中膏质盐类普遍发生过溶蚀作用,伴随着膏质盐类溶蚀作用的进行将不断产生SO42-,从而导致油田水中SO42-质量浓度增加[13-14];TSR作用及其他脱硫酸作用使一部分SO42-转化为H2S,但地层水中仍残余了大量的SO42-,这些SO42-与油田水阳离子中占绝对优势的Na+结合,使得研究区油田水呈现今的Na2SO4型。由于TSR作用对碳酸盐岩储层具有明显的溶蚀改造作用[32],造成储层孔隙度增大和储层物性变好,从而为后期油气藏的形成提供了有利聚集空间。因此,研究区这种特殊成因的Na2SO4型油田水并不代表该区地层不利于油气的保存,相反为研究区天然气的有利富集区。
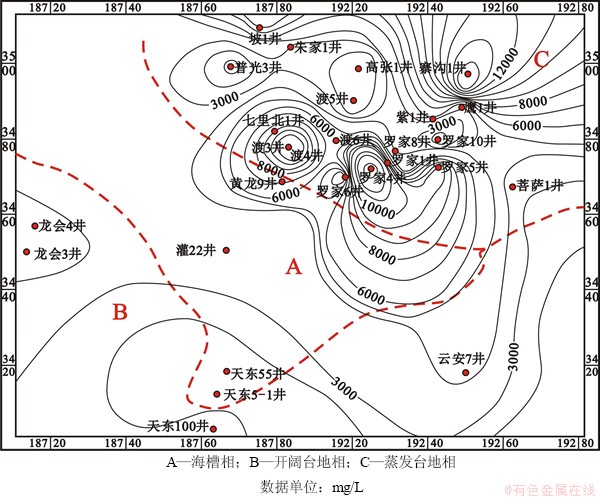
图2 川东北飞仙关组油田水SO42-质量浓度等值线图
Fig. 2 Isoline diagram showing concentration of SO42- of oilfield water in Feixianguan formation
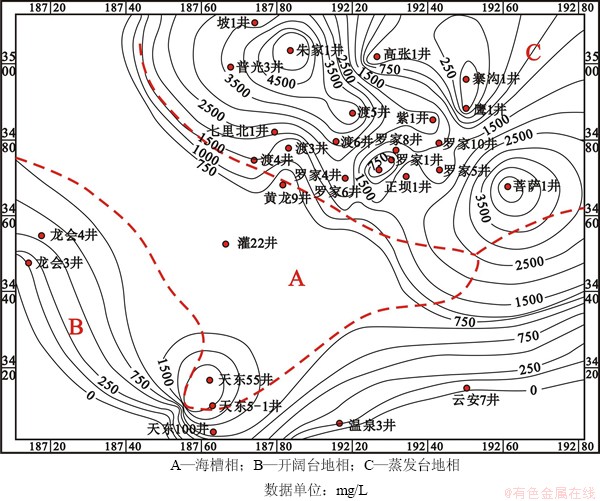
图3 川东北飞仙关组油田水溶解H2S质量浓度等值线图
Fig. 3 Isoline diagram showing concentration of H2S dissolved by oilfield water in Feixianguan formation
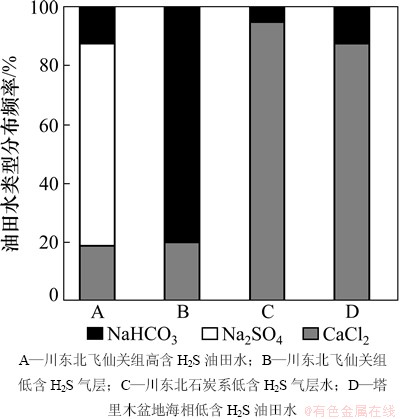
图4 中国部分海相地层油田水类型
Fig. 4 Types of oilfield water in some marine strata in China
2) 川东北飞仙关组高含H2S气藏油田水中阳离子含量基本都比其他低含H2S气藏油田水的小,阴离子中Cl-质量浓度也明显较其他低含H2S气藏油田水的低,Cl-含量的这种变化特征可能与膏质盐类溶解产生大量的SO42-有关。值得注意的是研究区高含H2S气藏油田水阴离子中SO42-质量浓度远远比其他低含H2S气藏的高,见图5,与特征1)相似,研究区高质量浓度的SO42-不仅来源于原始海水,更重要的是研究区地层中膏质盐类的不断溶蚀,为油田水提供了大量的SO42-,使油田水中SO42-质量浓度增加,同时也为TSR反应的持续进行提供了硫源,因此,地层中H2S质量浓度也相对较高。
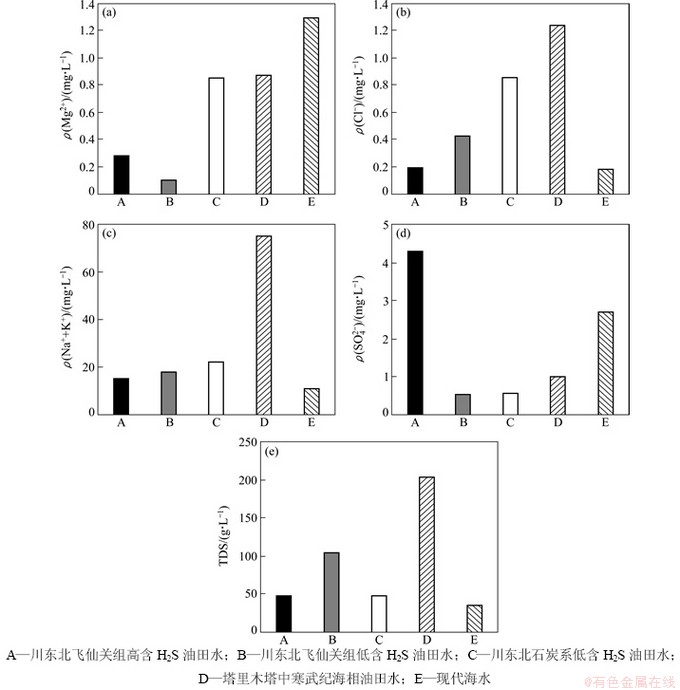
图5 中国部分海相盆地油田水数据分析图
Fig. 5 Data analysis of oilfield water in some marine basins in China
3 高含H2S气藏油田水地球化学解释
对比发现高含H2S气藏与低含H2S气藏油田水最重要的差别在于SO42-的质量浓度。宏观上油田水中SO42-质量浓度与产生的H2S气体含量之间存在正相关关系,然而对于这一现象的内在成因机制仍不清楚,还需开展进一步的研究工作。本文主要利用高含H2S气藏气-水关系和典型气藏的油田水地球化学证明了油田水中SO42-与烃类之间发生了TSR反应,地层中膏质盐类的溶解为地层水提供了大量的SO42-,而TSR反应过程中只消耗了部分SO42-,因此,油田水中的SO42-含量与气藏中H2S含量之间呈现出正相关关系。
3.1 气-水界面附近去膏化作用
川东北地区高含H2S气藏的碳酸盐岩储层中普遍有各种类型的次生方解石产出。川东北飞仙关组石膏溶蚀孔洞、次生方解石和黄铁矿晶体分布关系见图6。在储层微观观察中,发现一些板状石膏溶蚀,次生方解石在石膏溶蚀孔洞周围沉淀并与次生方解石相伴生(图6(a)~(f)),即石膏溶蚀提供TSR反应物,即硫酸根离子(SO42-),TSR反应后形成的CO2溶于水与Ca2+结合,形成次生方解石沉淀。另外,还见到非生物构型的次生黄铁矿晶体,其中黄铁矿晶体分布在石膏和次生方解石的缝合线处(图6(g)~(h)),是H2S与地层中的Fe2+结合形成的。粉晶白云石裂缝中初始充填矿物为石膏,后期发生去石膏化作用(膏质盐类的溶蚀作用)使得方解石交代了石膏,出现石膏与次生方解石相伴生的现象,次生方解石仍然具有石膏的晶形。同样,白云石中斑块状的孔洞原来充填的是石膏,而后期由于石膏发生去膏化作用而被方解石交代,其方解石的晶形仍具有石膏的放射状(图6(f))。在岩心中可见到大量白云岩的溶蚀孔洞,呈海绵状或蜂窝状的次生孔隙,并具有层状分布,连通性较好的特点(图6(i))。对储层矿物进行了系统的矿物岩石鉴定分析,共分析了19口高产气井940余个碳酸盐岩岩心薄片、5口微产气井220余个碳酸盐岩岩心薄片、12口水井775个碳酸盐岩岩心薄片、1口气水同产井的87个碳酸盐岩岩心薄片,观察这些井地层是否发生过去膏化作用。图7所示为川东北飞仙关组去膏化作用方解石统计图。从图7可以看出:在高产气井储层发生去膏化作用的样品井约为同类井的16%,微产气井储层去膏化作用样品井约占同类井的80%,产水井相应地层的去膏化样品井约占同类井的83%,气-水同产的井同样发生了去膏化作用,但达到100%。可以看出川东北地区飞仙关组地层有充分的去膏化作用方解石分布,但去膏化方解石在地层中存在很强的不均一性,去膏化作用主要集中在气-水界面及其附近的水层中,产气层去膏化作用远比其他几种类型地层的低。Machel[4]研究表明:在高含H2S地层中去膏化作用形成的次生方解石被认为是TSR发生的重要岩石矿物特征之一,且TSR反应主要在储层中的气水过渡带中进行,而现今飞仙关组高含H2S气藏中去膏化作用也主要集中在气-水界面及其附近的水层。因此,这种分布特征绝非偶然,气-水界面及附近的水层很可能是气藏中TSR作用的主要反应区。
表2所示为渡口河气藏部分特征参数。由表2可知:渡口河气藏去膏化作用与油田水的关系,渡5井、渡6井飞仙关组地层(T1f)均位于气-水界面下方,两口井均有去膏化方解石存在,油田水中溶解H2S质量浓度高达3 000 mg/L以上;渡1、渡2、渡3、渡4井飞仙关组地层均位于气-水界面以上,为工业产气层,油田水中溶解H2S含量均比渡5、渡6井的低,且在这几口产气井飞仙关组地层中未发现去膏化作用形成的次生方解石。显然,气-水界面附近含水地层中的H2S气体含量及油田水溶解H2S含量均比产气地层中的高,且去膏化作用在含水地层中出现频率也较高。Bildstein等[33]研究了其他一些高含H2S气藏后也指出TSR反应产物之一单质硫同样在气-水界面及其水层中相对富集。所以,除了去膏化作用,TSR反应的其他几个产物分布特征也进一步证明相对于含气层TSR作用很可能集中在气-水界面及其附近含水地层中。
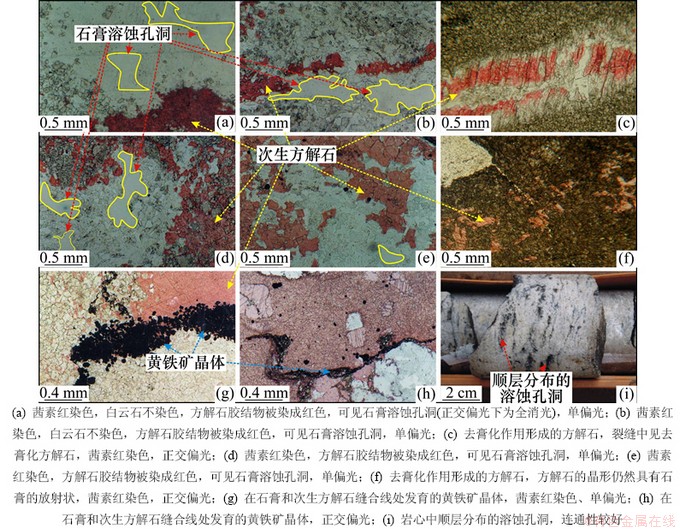
图6 川东北飞仙关组石膏溶蚀孔洞、次生方解石和黄铁矿晶体分布关系
Fig. 6 Distribution relationship of dissolved pores and cavities of gypsum, secondary calcite and pyrite crystals in Feixianguan formation, Northeastern Sichuan Basin
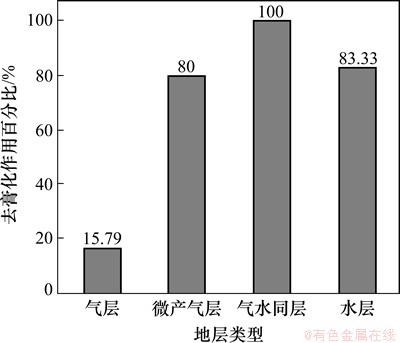
图7 川东北飞仙关组去膏化作用方解石统计图
Fig. 7 Statistics of calcite which undergo degypsification in Feixianguan Formation, Northeastern Sichuan basin
3.2 典型气藏的油田水地球化学解释
油田水的SO42-、溶解H2S以及Na++K+的总量等参数的变化,进一步揭示了在气-水界面及其附近水层中可能更有利于TSR反应的发生。渡口河气藏中油田水化学组成特征见表3。从表3可见:1) 含水层SO42-浓度远小于含气层,如位于气层井的束缚油田水中SO42-质量浓度可达10 000 mg/L,而位于水层的井(渡5井和渡6井)SO42-质量浓度仅为1 406 mg/L和6 011 mg/L;2) 含水层中的溶解H2S含量明显比气层的高,如位于气-水界面下方的渡5、渡6井SO42-质量浓度低,但H2S质量浓度却高达3 000 mg/L以上,而渡3、渡4井油田水的溶解H2S质量浓度则较低;3) 水层和气层中Na++K+的总质量浓度差别不大。渡5井、渡6井油田水的Na++K+质量浓度比渡3井、渡4井油田水的高,这可能与地层的沉积环境有关,因为越靠近泻湖亚相油田水的矿化度越高。无独有偶,与渡口河气藏相邻的罗家寨气藏油田水也表现出了相似的特征:1) 位于气-水界面下产水层的SO42-质量浓度最高仅2 206 mg/L,而气-水界面上产气层的油田水SO42-质量浓度最高可达 27 485 mg/L(表3),二者相差1个数量级;2) 产水井油田水中溶解H2S的质量浓度分别为1 044 mg/L和1 548 mg/L,而产气井油田水中溶解H2S质量浓度最高仅为880 mg/L,SO42-质量浓度和油田水中溶解H2S质量浓度有着明显的负相关关系(图8),即随着油田水中溶解H2S质量浓度的增大SO42-质量浓度相应地减少;3) 产气井和产水井油田水中的Na++K+质量浓度基本相同。
表2 渡口河气藏部分特征参数
Table 2 Part of characteristic parameters of Dukouhe gas reservoir
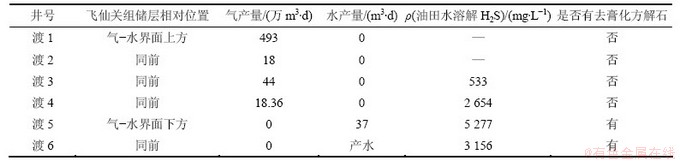
表3 渡口河及罗家寨气藏油田水化学组成特征
Table 3 Characteristics of chemical composition on oilfield water in Dukouhe and Luojiazhai gas reservoir
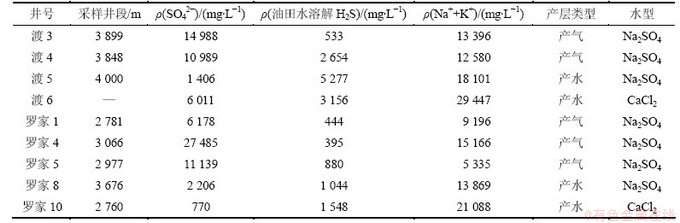
沉积环境分析表明:渡口河气藏中渡5井、渡6井和罗家寨气藏中罗家8井、罗家10井相对于其他几口产气井地层沉积环境更接近泻湖环境[19],其地层剖面中的膏盐质量浓度应明显比台缘鲕粒滩坝相的渡3、渡4井和罗家1、罗家4、罗家5井地层的高,相应膏岩溶解作用产生的SO42-质量浓度也高。但值得注意的是,渡5井、渡6井和罗家8井、罗家10井油田水中SO42-质量浓度与其膏盐质量浓度分布特征并不一致,这肯定与气-水界面及其附近油田水所发生的地球化学反应有关。
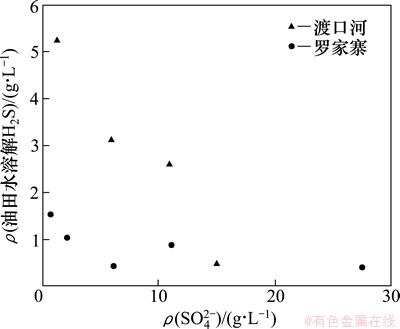
图8 渡口河及罗家寨气藏油田水SO42-与溶解H2S质量浓度的关系
Fig. 8 Relationship between mass concentration of SO42- and dissolved H2S in oilfield water of Dukouhe and Luojiazhai gas reservoir
由图8可知:油田水中SO42-含量和油田水溶解H2S含量之间存在很强的负相关关系。虽然产水井和产气井中油田水的Na++K+基本相同,但是产水层油田水的SO42-含量明显比产气层油田水的小,而产水层中溶解H2S的量却比产气层的大,这可能是SO42-的消耗与H2S产生是相辅相成的。对于一个发生TSR的封闭油田水体系来说,反应物SO42-必然会随着反应的进行而消耗,同时作为产物H2S溶解于油田水中的量也会相应增加;而Na+和K+因为没有参与反应则质量浓度可能没有明显的变化,仍然保持原始质量浓度。这些现象说明SO42-很有可能参与了TSR反应,是TSR反应的反应物之一,但油田水中SO42-很可能是石膏溶蚀的产物,石膏很可能是形成H2S的重要硫源,但不是直接反应物。因此,在满足TSR反应发生的条件下,油田水中只有提供了充足的SO42-的地区才有可能形成高含H2S气藏,这样也就解释了为什么川东北地区飞仙关组油田水SO42-质量浓度高的地区其气藏中H2S及油田水溶解H2S质量浓度也高,川东北飞仙关组油田水相比其他海相油田水SO42-质量浓度高同时H2S质量浓度也高的原因。
4 结论
1) 川东北地区飞仙关组高含H2S气藏油田水主要以Na2SO4型为主,只有少数是CaCl2型和NaHCO3型,地层水矿化度分布在24.850~81.010 g/L,平均达44.510 g/L,受蒸发浓缩作用的影响较大,TSR作用过程中产生的淡水会降低原始地层水矿化度。地层水矿化度分布范围较宽可能是由于碳酸盐岩储层具有较强的非均质性,导致TSR反应过程中产生的淡水与原生地层水混合不均匀。
2) 川东北地区高含H2S地层和高含SO42-油田水分布特征基本相似,高值区主要分布在海槽东侧蒸发台地相,而海槽相及海槽西侧开阔台地相SO42-含量低,油田水溶解H2S含量及气藏中H2S含量也较低;气藏中H2S和溶解H2S含量分布明显受控于SO42-含量的分布。研究区高含H2S气藏油田水中阳离子含量基本比低含H2S气藏的小,阴离子中Cl-质量浓度也明显较低含H2S气藏油田水低,而SO42-质量浓度远比低含H2S气藏的高,油田水水型、Cl-质量浓度及高含量的SO42-主要与该区膏质盐类的溶蚀作用有关;因此,研究区这种特殊成因的Na2SO4型油田水并不代表该区不利于油气的保存,相反为该区天然气的有利富集区。
3) 高含与低含H2S气藏油田水最主要的差别在于SO42-含量,宏观上普遍存在气藏中H2S质量浓度高的区域油田水中SO42-含量也相应较高,同时溶解H2S也高;但微观上典型气藏产气层和产水层油田水中SO42-和溶解H2S之间存在此消彼长的关系,但由于TSR作用过程中消耗的只是部分SO42-,油田水中仍残留了大量的SO42-,从而导致宏观上出现气藏中H2S含量与油田水中SO42-含量成正相关关系;研究区油田水中SO42-主要来源于的膏质盐类溶蚀,其气-水界面及其附近水层中更有利于TSR反应的发生。
参考文献:
[1] 刘方槐, 颜婉荪. 油气田水文地质学原理[M]. 北京: 石油工业出版社, 1991: 29-54.
LIU Fanghuai, YAN Wansun. The principle of hydrogeology in oilfield[M]. Beijing: Petroleum Industry Press, 1991: 29-54.
[2] Davisson M L, Presser T S, Criss R E. Geochemistry of tectonically expelled fluids from the northern Coast Ranges, Rumsey Hills[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1994, 58: 1687-1699.
[3] 李伟, 刘济民, 陈晓红. 吐鲁番坳陷油田水地化特征及其石油地质意义[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 1994, 12(5): 12-18.
LI Wei, LIU Jimin, CHEN Xiaohong. Characteristics of oil field water in Turpan depression and its petroleum geological significance[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 1994, 12(5): 12-18.
[4] Machel H G. Bacterial and thermochemical sulfate reduction in diagenetic settings: Old and new insights[J]. Sedimentary Geology, 2001, 140(1/2): 143-175.
[5] 钱一雄, 蔡立国, 顾忆. 塔里木盆地塔河油区油田水元素组成与形成[J]. 石油实验地质, 2003, 25(6): 751-757.
QIAN Yixiong, CAI Liguo, GU Yi. The oilfield water in Tahe area, Tarim Basin: Constraints from its element composition[J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 2003, 25(6): 751-757.
[6] 薛会, 张金川, 王毅, 等. 塔里木盆地塔中低凸起地层水与油气关系[J]. 石油实验地质, 2007, 29(6): 593-597.
XUE Hui, ZHANG Jinchuan,WANG Yi, et al. Relationship of formation fluid and hydrocarbon in Tazhong low uplift of the Tarim Basin[J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 2007, 29(6): 593-597.
[7] 曾溅辉, 吴琼, 杨海军, 等. 塔里木盆地塔中地区地层水化学特征及其石油地质意义[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2008, 29(4): 223-229.
ZENG Jianhui, WU Qiong, YANG Haijun, et al. Chemical characteristics of formation water in Tazhong area of the Tarim Basin and their petroleum geological significance[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2008, 29(4): 223-229.
[8] FU Yong, ZHAN Hongbin. On the origin of oil-field water in the Biyang depression of China[J]. Environmental Geology, 2009, 58: 1191-1196.
[9] LI Wei, YANG Jinlin, JIANG Junwei, et al. Origin of Upper Triassic formation water in middle Sichuan Basin and its natural gas significance[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2009, 36(4): 428-435.
[10] 徐德英, 周江羽, 王华, 等. 渤海湾盆地南堡凹陷东营组地层水化学特征的成藏指示意义[J]. 石油实验地质, 2010, 32(3): 285-289.
XU Deying, ZHOU Jiangyu, WANG Hua, et al. Chemical characteristics of formation water significant to oil reservoir in Dongying Formation, Nanpu Sag, Bohai Bay Basin[J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 2010, 32(3): 285-289.
[11] 王运所, 许化政, 王传刚, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地上古生界地层水分布与矿化度特征[J]. 石油学报, 2010, 31(5): 748-753.
WANG Yunsuo, XU Huazheng, WANG Chuangang, et al. Characteristics of the salinity and distribution of the Neopaleozoic formation water in Ordos Basin[J]. Acta Petroleum Sinica, 2010, 31(5): 748-753.
[12] 林晓英, 曾溅辉, 杨海军, 等. 塔里木盆地哈得逊油田石炭系地层水化学特征及成因[J]. 现代地质, 2012, 26(2): 377-383.
LIN Xiaoying, ZENG Jianhui, YANG Haijun, et al. Geochemical characteristics and origin of formation water from the carboniferous in Hadexun Oil Field, Tarim Basin[J]. Geoscience, 2012, 26(2): 377-383.
[13] 江兴福, 谷志东, 赵容容, 等. 四川盆地环开江—梁平海槽飞仙关组地层水的地化特征及成因研究[J]. 天然气勘探开发, 2009, 32(1): 5-17.
JIANG Xingfu, GU Zhidong, ZHAO Rongrong, et al. Geochemical characteristics and origin of formation water in Feixianguan formation around Kaijiang-Liangping trough, Sichuan Basin[J]. Natural Gas Exploration and Development, 2009, 32(1): 5-17.
[14] 关云梅, 王兰生, 张鉴, 等. 四川盆地高含硫气藏地层水地化特征分析[J]. 天然气勘探开发, 2011, 34(3): 21-23.
GUAN Yunmei, WANG Lansheng, ZHANG Jian, et al. Geochemical characteristics of formation water in high H2S gas reservoirs, Sichuan Basin[J]. Natural Gas Exploration and Development, 2011, 34(3): 21-23.
[15] 徐振平, 梅廉夫. 川东北地区不同构造带地层水化学特征与油气保存的关系[J]. 海相油气地质, 2006, 11(4): 29-33.
XU Zhenping, MEI Lianfu. Relationship between chemical features of formation water and hydrocarbon preservation in different structural areas in ortheast part of Sichuan Basin[J]. Marine oil and Gas Geological, 2006, 11(4): 29-33.
[16] Machel H G. Bacterial and thermo chemical sulfate reduction indiagenetic settings-old and new insights[J]. Sedimentary Geology, 2001, 140(1/2): 143-175.
[17] 朱光有, 张水昌, 梁英波, 等. 四川盆地H2S的硫同位素组成及其成因探讨[J]. 地球化学, 2006, 35(4): 333-345.
ZHU Guangyou, ZHANG Shuichang, LIANG Yingbo, et al. Stable sulfur isotopic composition of hydrogen sulfide and its genesis in Sichuan Basin[J]. Geochimica, 2006, 35(4): 333-345.
[18] 赫云兰, 付孝悦, 刘波, 等. 川东北飞仙关组鲕滩沉积与成岩对储集层的控制[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2012, 39(4): 434-443.
HE Yunlan, FU Xiaoyue, LIU Bo, et al. Control of oolitic beaches sedimentation and diagenesis on reservoirs in Feixianguan Formation, northeastern Sichuan Basin[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2012, 39(4): 434-443.
[19] ZHANG Shuichang, ZHU Guangyou, CHEN Jianpin, et al. A discussion on gas sources of the Feixianguan Formation H2S rich giant gas fields in the northeastern Sichuan Basin[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2007, 52(SupplⅠ): 86-94.
[20] 朱光有, 张水昌, 李剑, 等. 中国高含硫化氢天然气田的特征及其分布[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2004, 31(4): 18-21.
ZHU Guangyou, ZHANG Shuichang, LI Jian, et al. Formation and occurrence of hydrogen sulfide bearing gas in China[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2004, 31(4): 18-21.
[21] 朱光有, 张水昌, 梁英波, 等. 川东北地区飞仙关组高含H2S天然气TSR成因的同位素证据[J]. 中国科学(D辑), 2005, 35(11): 1037-1046.
ZHU Guangyou, ZHANG Shuichang, LIANG Yingbo, et al. Isotopic evidence of TSR origin for natural gas bearing high H2S contents within the Feixianguan Formation of the northeastern Sichuan Basin, southwestern China[J]. Science in China (Series D), 2005, 35(11): 1037-1046.
[22] 蔡春芳, 蔡镠璐, 张俊, 等. 川东北飞仙关组甲烷为主的TSR及其同位素分馏作用[J]. 岩石学报, 2012, 28(3): 889-894.
CAI Chunfang, CAI Liulu, ZHANG Jun, et al. H2S-generation by methane-dominated TSR and carbon isotope fractionation in Lower Triassic Feixianguan Formation, Northeast Sichuan Basin[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2012, 28(3): 889-894.
[23] 王一刚, 窦立荣, 文应初, 等. 四川盆地东北部三叠系飞仙关组高含硫气藏H2S成因研究[J]. 地球化学, 2002, 31(6): 517-523.
WANG Yigang, DOU Lirong, WEN Yingchu, et al. Origin of H2S in Triassic Feixianguan Formation gas pool, northeastern Sichuan basin, China[J]. Geochemical, 2002, 31(6): 517-523.
[24] 黄士鹏, 廖凤蓉, 吴小奇, 等. 四川盆地含硫化氢气藏分布特征及硫化氢成因探讨[J]. 天然气地球科学, 2010, 21(5): 705-714.
HUANG Shipeng, LIAO Fengrong, WU Xiaoqi, et al. Distribution characteristics of hydrogen sulphide-bearing gas pools and the genesis of hydrogen sulphide in Sichuan Basin[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 2010, 21(5): 705-714.
[25] CAI Chunfang, LI Kaikai, ZHU Yangming, et al. TSR origin of sulfur in the Permian and Triassic reservoir bitumen in East Sichuan Basin, China[J]. Organic Geochemistry, 2010, 41: 871-878.
[26] 郭彤楼, 楼章华, 马永生. 南方海相油气保存条件评价和勘探决策中应注意的几个问题[J]. 石油实验地质, 2003, 25(1): 3-9.
GUO Tonglou, LOU Zhanghua, MA Yongsheng. Several problems on oil and gas preservation and their commercial prospecting in marine sequences of South China[J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 2003, 25(1): 3-9.
[27] 李继宏, 李荣西, 韩天佑, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地西缘马家滩地区地层水与油气成藏关系研究[J]. 石油实验地质, 2009, 31(3): 253-257.
LI Jihong, LI Rongxi, HAN Tianyou, et al. study of stratum water and oil gas accumulation relations of Majiatan area in the western Ordos Basin[J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 2009, 31(3): 253-257.
[28] 陈建平, 查明, 周瑶琪, 等. 准噶尔盆地西北缘地层水化学特征与油气关系研究[J]. 地质地球化学, 2000, 28(3): 54-58.
CHEN Jianping, CHA Ming, ZHOU Yaoqi. Chemical characteristics of formation water in relation with oil and gas in the Northwester parts of Junggar Basin [J]. Geology-Geochemistry, 2000, 28(3): 54-58.
[29] 郑荣才, 党录瑞, 文华国, 等. 川东北地区飞仙关组白云岩成岩作用与系统划分[J]. 地球科学—中国地质大学学报, 2011, 36(4): 659-669.
ZHENG Rongcai, DANG Lurui, WEN Huaguo, et al. Diagenesis characteristics and system for dolostone in Feixianguan formation of Northeast Sichuan[J]. Earth Science—Journal of China University of Geosciences, 2011, 36(4): 659-669.
[30] CAI Chunfang, Worden R H, HU Guoyi, et al. Methane-dominated thermochemical sulphate reduction in the Triassic Feixianguan Formation East Sichuan Basin, China: towards prediction of fatal H2S concentrations[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2004, 21: 1265-1279.
[31] 李贤庆, 侯读杰, 张爱云. 油田水地球化学研究进展[J]. 地质科技情报, 2001, 20(2): 51-54.
LI Xianqing, HOU Dujie, ZHANG Aiyun. Advancement of the geochemical study of oilfield water[J]. Geological Science and Technology Information, 2001, 20(2): 51-54.
[32] 张水昌, 朱光有, 何坤. 硫酸盐热化学还原作用对原油裂解成气和碳酸盐岩储层改造的影响及作用机制[J]. 岩石学报, 2011, 27(3): 809-826.
ZHANG Shuichang,ZHU Guangyou, HE Kun. The effects of thermochemical sulfate reduction on occurrence of oil-cracking gas and reformation of deep carbonate reservoir and the interaction mechanisms[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2011, 27(3): 809-826.
[33] Bildstein O, Worden R H, Brosse E. Assessment of anhydrite dissolution as the rate-limiting step during thermochemical sulfate reduction [J]. Chemical Geology, 2001, 176: 173-189.
(编辑 杨幼平)
收稿日期:2013-10-21;修回日期:2014-03-05
基金项目(Foundation item):国家自然科学基金资助项目(40773039);国家重点基础研究发展计划(“973”计划)项目(2011CB201102)(Project (40773039) supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China; Project (2011CB201102) supported by Major State Basic Research Development Program)
通信作者:赵兴齐(1984-),男,贵州福泉人,博士,从事油气地球化学、石油地质学、铀矿地质学的研究;电话:13401108479;E-mail:zhaoxingqi_77@126.com