DOI: 10.11817/j.issn.1672-7207.2016.04.046
电动力学技术回收废旧印刷线路板中的铜
王蓉1,陈梦君2,黄金秀2,陈海焱2,谌书2,王彬2
(1. 西南科技大学 国防科技学院,四川 绵阳,621010;
2. 西南科技大学 固体废物处理与资源化教育部重点实验室,四川 绵阳,621010)
摘要:采用电动力学技术,研究废旧印刷线路板(WPCBs)投加量、离子液体体积分数、电流密度、电动力学时间以及H2O2用量等对Cu回收率的影响以及电动力学过程中铜的分布特性。研究结果表明:Cu基本集中于阴极区,并以粉末的形式回收;各因素对Cu回收率均有不同程度的影响,其中电动力学时间的影响最为显著;电流密度过高会导致电流效率的下降而降低Cu的回收率;加入2 g WPCBs,当离子液体体积分数为10%,电流密度为 20 mA/cm2,H2O2体积为2 mL时,处理24 h,Cu的总回收率为84.6%;所得金属粉末主要以Cu和Cu2O的形式存在,含量为97.86%。此法可以直接在组成极其复杂的WPCBs 中回收金属铜,为其资源化提供了新的途径。
关键词:废旧印刷线路板;电动力学;铜;离子液体;回收
中图分类号:TF131,X705 文献标志码:A 文章编号:1672-7207(2016)04-1436-05
Copper recycling from waste printed circuit boards by electrokinetics
WANG rong1, Chen Menjun2, HUANg Jinxiu2, CHEN Haiyan2, CHEN Shu2, WANF Bin2
(1. School of National Defense Science and Technology,Southwest University of Science and Technology, Mianyang 621010, China;
2. Key Laboratory of Solid Waste Treatment and Resource Recycle, Ministry of Education,Southwest University of Science and Technology, Mianyang 621010, China)
Abstract: A new technology, called electrokinetics, was applied to recovery copper from WPCBs. Factors, such as WPCBs adding amount, ionic liquid concentration, current density, time and H2O2 amount, which affect Cu recycling rate as well as Cu distribution during the process were examined. The results show that Cu is mainly concentrated in cathode chamber and recycled as powder. All the factors can affect Cu recycling rate, especially time. A relatively higher current density will lower the current efficiency, making Cu recycling rate down. When 2 g WPCBs powders are used, the ionic liquid volume fraction is 10%, H2O2 adding amount is 2 mL, Cu recycling rate will reach 84.6% with current density of 20 mA/cm2 for 24 h. And the obtained powders are mainly Cu and Cu2O with a Cu purity of 97.86%. Electrokinetics can be successfully used for recycling Cu from such a complex system as WPCBs, which provides a novel and prospective solution for WPCBs reutilization.
Key words: waste printed circuit boards (WPCBs); electrokinetics (EK); copper; ionic liquid; recycling
电子废弃物(E-waste)是近10 a增长最为迅速的固体废物,为普通城市生活垃圾的3倍[1],其中废旧印刷线路板(WPCBs)约占电子废弃物总量的4%[2],我国每年需处理的WPCBs 达50万t以上[3]。WPCBs的资源性与毒害性,尤其是在自然资源供求矛盾日益尖锐的今天,在确保环境安全的同时实现WPCBs的资源化,越来越受到人们的关注。自1969 年美国矿业局最先回收WPCBs 以来,其资源化处理处置技术如机械处理[4-5]、火法冶金[6]、湿法冶金[7]、微生物冶金[8]、超临界液体技术等[9]得到长足发展。虽然这些技术在一定程度上可以满足资源化的要求,但总体上仍存在着设备要求高、处理时间长、能量消耗大、产品附加值低的缺点。将电动力学体系应用于WPCBs 资源化处理处置,可为WPCBs的绿色资源化处理提供一种新的选择。电动力学技术(EK)或电动力学修复技术(EKR)[10],是将阴阳电极分别插入彼此分离的阴极室和阳极室,中间室放置固体废弃物,阴极室和阳极室里的电解质可以不断循环,重金属在阴阳极室得到富集并进行后续处理,电流密度较低时就可以完成EK过程,离子交换膜控制离子流动方向和数量,从而使被分离物质得到富集和回收[11]。目前,EK主要用于污染土壤及固体废物中重金属的去除修复。如PERDERSEN[12]通过研究发现EK能有效地去除飞灰中的有毒有害重金属。GUILLAUME等[13]利用EK法从富锌废渣中回收金属锌,将EK法应用于固体废物的资源化处理处置。受此启发,XIU等[14-15]将电动力学技术应用于经超临界水处理的WPCBs残渣中得到Cu2O纳米颗粒粉末。实验结果表明,经超临界水处理后WPCBs中的覆层金属转化为相应的氧化物或含氧酸盐,进行EK处理后,铜以单质的形式沉积在阴极上,其余贵重金属以浓缩液的形式在阳极区或阴极区富集[14];在阴极区加入PVP纳米粒子稳定剂后,此法可在阴极区一步合成得到均一的球形Cu2O纳米颗 粒[15]。但此法需通过超临界水氧化以彻底地去除WPCBs所含有机物,很难实现工业化应用。HUANG等[16]研究发现,因WPCBs中Cu等覆层金属的金属活性低于氢,一步EK过程中阴极氢气优先析出,很难实现Cu等覆层金属资源化回收。利用离子液体体系([bmim]HSO4,1-丁基-3-甲基咪唑硫酸氢盐)可以有效地解决这一难题[16]。针对这一问题,本文作者提出利用电动力学法一步法直接从WPCBs中回收金属铜,研究WPCBs投加量、离子液体浓度、电流密度、电动力学时间以及H2O2用量等对Cu回收率的影响以及电动力学过程中铜的分布特性。
1 材料与方法
1.1 WPCBs样品准备
将WPCBs样品切成长×宽为50 mm×50 mm的小块后,用万能粉碎机(SM2000 smf/UpM,Retsch,德国)粉碎至粒度为0.5~1.0 mm。利用“HNO3-H2O-HF”[17]体系进行微波(Mars 240/50,CEM,美国)消解后,采用等离子体光谱仪(ICP-OES, OPTIMA 2000, PerkinElmer,美国)进行分析。Cu质量分数为20.4%,Fe为8.0%,Sn为4.0%,Ni,Pb,Zn,Ag和Au分别为2.0%,2.0%,1.0%,0.2%和0.1%。
1.2 电动力学回收实验
电动力学反应装置如图1所示。反应装置长 15 cm,宽6 cm,高6 cm,材质为有机玻璃。用2个玻璃砂芯膜将整个反应装置分隔成3个室(阳极室I、中间室II和阴极室III)。
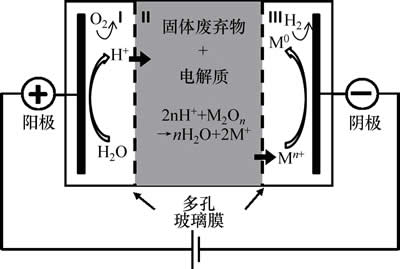
图1 电动力学技术示意图
Fig. 1 Schematic chart of electrokinetics
取一定质量WPCBs样品于250 mL锥形瓶中,依次加入H2O2和离子液体水溶液,置于水浴恒温振荡器中50 ℃震荡2 h。震荡结束后,将锥形瓶中的WPCBs残渣和浸出液同时加入电动力学反应装置的室II中,室I和室III中分别加20 mL离子液体水溶液。通电并用磁力搅拌器搅拌,使WPCBs粉末在电动力学装置中保持悬浮状态。阴极和阳极均使用钌涂层的钛电极板。反应中保持阴阳电极平行相对,极板间距为9.50 cm,极板的活性面积为5.88 cm2。实验中,每隔一段时间记录1次电位,恒电流密度分别保持在10,20,30,40和50 mA/cm2。
电动力学反应结束之后,取下电极,分别于5 mol/L HNO3溶液中浸泡12 h。采用ICP-OES分析浸泡液和电解液中的Cu2+质量浓度。收集阴极液离心 (10 000 r/min)、超声,并用质量分数为30%水/乙醇混合液冲洗所得沉积物3次,除去水溶性的杂质。最后,获得的产品在真空下干燥。阴极液中Cu2+质量浓度通过ICP-OES分析。
2 结果与讨论
2.1 WPCBs投加量
WPCBs投加量对Cu在阴极室、阳极室、中间室以及阴、阳极板迁移分布的影响如图2所示。由图2可知:Cu在各区域的回收率从大至小对应的区域依次为中间室、阴极室、阴极板、阳极室、阳极板。当WPCBs投中量为2.00 g时,Cu在中间室和阴极板的回收率最高,分别为19.70%和6.68%;当WPCBs投加量为3.00 g时,Cu在阴极室的回收率最高,为15.20%。此外,Cu在阳极板的回收率非常低,几乎可以忽略;而在阳极室的回收率保持在2.50%左右,这可以归因于扩散作用。
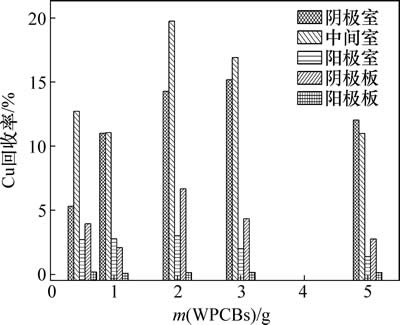
图2 WPCBs投加量对Cu回收率的影响
Fig. 2 Effect of WPCBs amount on copper recovery rate
当WPCBs的投加量分别为0.50,1.00,2.00,3.00和5.00 g时,Cu在各区域的总回收率分别为24.1%,46.2%,44.7%,37.9%和25.0%。因此,在电动力学反应过程中,合适的WPCBs投加量对Cu的回收率有显著影响。
2.2 离子液体体积分数
离子液体体积分数对Cu回收率的影响,结果如图3所示。由图3可知:当离子液体体积分数为10%时,Cu的回收率从大至小对应的区域依次为中间室、阴极室、阴极板、阳极室、阳极板。当离子液体体积分数为20%时,Cu在阴极室的回收率最高,为20.20%;当离子液体体积分数继续增大至40%,60%和80%时,Cu在各区域的回收率均不同程度地降低。显然,阳极板Cu回收率极低,为0.15%~0.43%;Cu在阳极室因扩散作用的存在,回收率维持在3.00%左右。
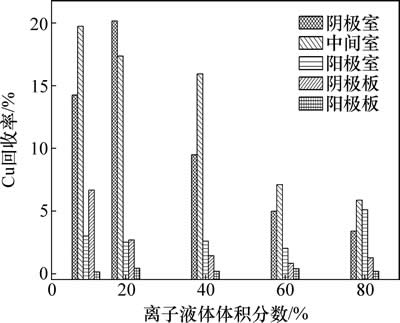
图3 离子液体体积分数对Cu回收率的影响
Fig. 3 Effect of ILs concentration on copper recovery rate
当离子液体体积分数分别为10%,20%,40%,60%和80%时,Cu的总回收率分别为44.70%,51.20%,43.10%,36.75%和31.90%(见图3)。由此看出,在以离子液体[bmim]HSO4为辅助试剂的电动力学反应过程中,离子液体体积分数的增加并不能提高Cu的回收率。这与文献[16]中的结果一致。离子液体的体积分数过高,其黏度也随之增大,不利于Cu2+扩散,也就会影响电动力学体系中Cu的回收率。因此,选用体积分数为10%的离子液体适用于进行后续的实验。
2.3 电流密度
电流密度对Cu回收率的影响如图4所示。电流密度由10 mA/cm2增大至40 mA/cm2时,Cu在各区域的回收率基本呈逐渐增大的趋势;当电流密度由10 mA/cm2增大至20 mA/cm2时,Cu在各区域的回收率迅速增大;而当电流密度由20 mA/cm2增大至40 mA/cm2时,Cu在各区域的回收率增长并不显著。
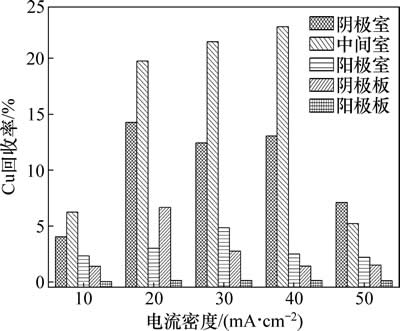
图4 电流密度对Cu回收率的影响
Fig. 4 Effect of current density on copper recovery rate
当电流密度为50 mA/cm2时,各区域Cu的回收率反而降低。当电流密度分别为10,30和40 mA/cm2时,Cu在各区域的回收率从大至小对应的区域依次为中间室、阴极室、阳极室、阴极板、阳极板;而当电流密度分别为20 mA/cm2和50 mA/cm2时,Cu的回收率从大至小对应的区域依次为中间室、阴极室、阴极板、阳极室、阳极板。
从图4可知:Cu的总回收率随着电流密度的增加而增加,同时也可以看到,在电动力学处理中,所使用的恒电流密度越高,那么体系的初始电位降也越高。当电流密度分别为10,20,30,40和50 mA/cm2时,电动力学体系初始电位降分别为0.75,1.49,1.74,2.15和2.37 V/cm。虽然当电流密度为40 mA/cm2时,Cu的总回收率达到最高,但电流密度越大,溶液中通过的电流越大,溶液的温度增加越快,电流做功一方面发生电化学反应,另一方面产生大量的热量,导致电流效率降低。除此之外,电流密度过高,体系的电位降也越高,而体系电位降的升高很容易导致其他副反应的增加,例如H+在阴极的还原反应,从而也会导致电流效率的降低,因此,合适的电流密度为20 mA/cm2。
2.4 电动力学反应时间
电动力学反应时间对Cu回收率的影响如图5所示。
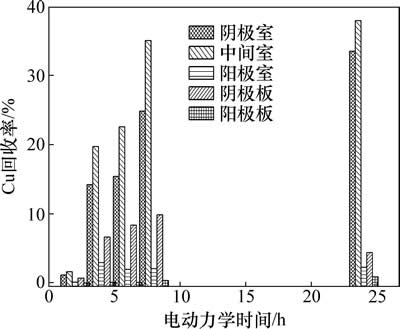
图5 电动力学反应时间对Cu回收率的影响
Fig. 5 Effect of EK time on copper recovery rate
从图5可知:随着电动力学反应时间的延长,Cu在各区域的回收率也呈增大的趋势。当电动力学反应时间小于6 h时,Cu的回收率明显较低,而当电动力学反应时间延长至24 h时,Cu在各区域的回收率显著提高。电动力学反应时间不同,Cu在各区域的回收规律大致相同,即由大至小对应的区域依次为中间室、阴极室、阴极板、阳极室、阳极板。当电动力学时间分别为2,4,6,8和24 h时,Cu在中间室的回收率分别为1.69%,19.70%,22.60%,35.00%和37.90%,Cu在阴极室的回收率分别为1.20%,14.30%,15.40%,24.90%和33.50%。因此,电动力学反应时间由2 h延长至4 h,Cu的回收率增大很快。
随着电动力学时间的延长,Cu在各区域的总回收率增大显著。当电动力学反应时间分别为2,4,6,8和24 h时,Cu在各区域的总回收率分别为:8.07%,44.70%,50.10%,76.60%和84.60%。因此,电动力学反应时间是影响Cu回收率的重要因素。当电动力学反应时间为2 h时,Cu在各区域的总回收率只有8.07%,原因是在这个阶段,反应器中Cu2+质量浓度很低,而H+的质量浓度反而很高,所以,H+在阴极的还原反应对Cu的还原产生强烈的竞争,导致在这个阶段铜的回收率很低。
2.5 H2O2用量
H2O2用量对Cu回收率的影响如图6所示。
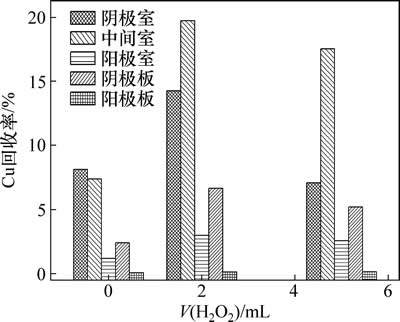
图6 H2O2用量对Cu回收率的影响
Fig. 6 Effect of H2O2 amount on copper recovery rate
H2O2用量不同时,Cu在各区域的回收规律大致相同,即由大至小对应的区域依次为中间室、阴极室、阴极板、阳极室、阳极板。当H2O2用量分别为0,2和5 mL时,Cu在中间室的回收率分别为7.39%,19.70%和17.50%,Cu在阴极室的回收率分别为8.15%,14.30%和7.11%。Cu在各区域的总回收率分别为32.10%,44.70%和40.10%。由此看出,适量地添加H2O2有利于Cu总回收率的提高。
2.6 回收所得铜粉特性
当[Bmim]HSO4的体积分数为10%,WPCBs投加量为2.00 g,电流密度为20 mA/cm2,H2O2用量为2 mL时,EK反应24 h,回收所得铜粉的XRD分析结果如图7所示。
由图7可知:回收所得铜粉主要物相为金属铜和氧化亚铜,没有观察到其他杂质元素如铅、锡等的存在。铜粉消解后ICP-OES测试结果表明:铜的质量分数达到97.86%,Sn为1.30%,Pb仅为0.01%。
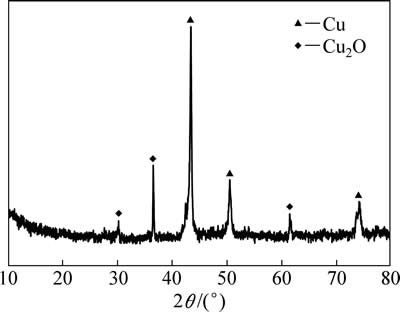
图7 回收所得铜粉的XRD图
Fig. 7 XRD patterns of Cu powder recycled by EK
3 结论
1) 在离子液体电动力学技术法回收WPCBs中Cu的过程中,Cu大多在阴极区加以回收,说明在反应过程中,Cu是以阳离子物种的形式存在于电动力学体系中。
2) 在离子液体电动力学技术法回收WPCBs中Cu的过程中,WPCBs投加量、离子液体体积分数、电流密度、电动力学时间以及H2O2用量对Cu回收率均有不同程度的影响。电动力学时间影响Cu回收率最显著,当电动力学时间为24 h时,WPCBs投加量为2.00 g,离子液体体积分数为10%,电流密度为 20 mA/cm2,H2O2用量为2 mL时,Cu在各区域的总回收率为84.6%。
3) 在离子液体电动力学技术法回收WPCBs中Cu的过程中,过高的电流密度不利于Cu的回收,反而会降低电流效率。
参考文献:
[1] ANDREOLA F, BARBIERI L, CORRADI A, et al. CRT glass state of the art-A case study: recycling in ceramic glazes[J]. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2007, 27(2/3): 1623-1629.
[2] ZHOU Lei, XU Zhenming. Response to waste electrical and electronic equipments in China: legislation, recycling system, and advanced integrated process[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2012, 46(9): 4713-4724.
[3] ELAINE Y L S. The recovery of metals from electronic scrap[J]. JOM, 1991, 43(4): 53-61.
[4] LI Jia, GAO Bei, XU Zhenming. New technology for separating resin powder and fiberglass powder from fiberglass-resin powder of waste printed circuit boards[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2014, 48(9): 5171-5178.
[5] LI Jia, XU Zhenming. Environmental friendly automatic line for recovering metal from waste printed circuit boards[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2010, 44(4): 1418-1423.
[6] ZHUAN Lu, XU Zhenming. Separating and recovering Pb from copper-rich particles of crushed waste printed circuit boards by evaporation and condensation[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2011, 45(12): 5359-5365.
[7] KIM E Y, KIM M S, LEE J C, et al. Leaching kinetics of copper from waste printed circuit boards by electro-generated chlorine in HCl solution[J]. Hydrometallurgy, 2011, 107(3/4): 124-132.
[8] YANG Yuankun, CHEN Shu, LI Shicheng, et al. Bioleaching waste printed circuit boards by Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans and its kinetics aspect[J]. Journal of Biotechnology, 2014, 173(10): 24-30.
[9] XIU Furong, ZHANG Fushen. Materials recovery from waste printed circuit boards by supercritical methanol[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2010, 178(1/3): 628-634.
[10] VELIZAROVA E, RIBEIRO A B, OTTOSEN L M. A comparative study on Cu, Cr and As removal from CCA-treated wood waste by dialytic and electrodialytic processes[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2002, 94(2): 147-160.
[11] ELEKTOROWICZ M, HABIBI S. Sustainable waste management: recovery of fuels from petroleum sludge[J]. Canadian Journal of Civil Engineering, 2005, 32(1): 164-169.
[12] PERDERSEN A J. Characterization and electrodialytic treatment of wood combustion fly ash for the removal of cadmium[J]. Biomass & Bioenergy, 2003, 25(4): 447-458.
[13] GUILLAUME P, LECLERC N, LAPICQUE F. Electroleaching and electrodeposition of Zinc in a single-cell process for the treatment of solid waste[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2008, 152(1): 85-92.
[14] XIU Furong, ZHANG Fushen. Recovery of copper and lead from waste printed circuit boards by supercritical water oxidation combined with electrokinetic process[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2009, 165(1/3): 1002-1007.
[15] XIU Furong, ZHANG Fushen. Preparation of nano-Cu2O/TiO2 photocatalyst from waste printed circuit boards by electrokinetic process[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2009, 172(2/3): 1458-1463.
[16] HUANG Jinxiu, CHEN Mengjun, CHEN Haiyan, et al. Leaching behavior of copper from waste printed circuit boards with  acidic ionic liquid[J]. Waste Management, 2014, 34(2): 483-488.
acidic ionic liquid[J]. Waste Management, 2014, 34(2): 483-488.
[17] CHEN Mengjun, ZHANG Fushen, ZHU Jianxin. Lead recovery and the feasibility of foam glass production from funnel glass of dismantled cathode ray tube through pyrovacuum process[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2009, 161(2/3): 1109-1113.
(编辑 罗金花)
收稿日期:2015-04-12;修回日期:2015-06-12
基金项目(Foundation item):国家自然科学基金资助项目(21377104);国家高技术研究发展计划(863计划)项目(2013AA040207)(Project (21377104) supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China; Project (2013AA040207) supported by National High Technology Research and Development Program (863 Program) of China)
通信作者:陈梦君,博士,副教授,从事固体废物(电子废弃物)污染控制原理与资源化理论研究;E-mail:kyling@swust.edu.cn