文章编号:1004-0609(2010)05-0891-07
Mg-Zn-Ca三元镁合金生物材料的腐蚀行为
欧阳春1,雷 霆1,王 丽1,李年丰1, 2,周乐山3
(1. 中南大学 粉末冶金国家重点实验室,长沙 410083;
2. 中南大学 湘雅医院,长沙 410008;
3. 中南大学 湘雅医学院,长沙 410013)
摘 要:以Zn与Ca为合金组元,采用熔融浇注法制备3种Ca含量分别为1%、2%和3%的Mg-Zn-Ca三元镁合金生物可降解材料,并对3种镁合金在Hank模拟体液中的质量损失腐蚀及电化学腐蚀行为进行研究。对不同腐蚀时间的合金表面形貌以及合金组织和相成分进行分析。结果表明:镁合金的腐蚀是从镁基相的点蚀开始的,含Ca量为1%的镁合金表现出良好的抗腐蚀性能;合金中Mg2Ca相的分布显著影响合金的耐腐蚀性能,合金体中Mg2Ca相的含量随着合金中Ca含量的增加而增加,导致合金的抗腐蚀性能变差。
关键词:Mg-Zn-Ca合金;Hank溶液;电化学腐蚀;Mg2Ca相;生物降解
中图分类号:TG146.23 文献标志码:A
Corrosion behaviours of ternary Mg-Zn-Ca alloy biomaterials
OUYANG Chun1, LEI Ting1, WANG Li1, LI Nian-feng1, 2, ZHOU Le-shan3
(1. State Key Laboratory of Powder Metallurgy, Central South University, Changsha 410083, China;
2. Xiangya Hospital, Central South University, Changsha 410008, China;
3. Xiangya School of Medicine, Central South University, Changsha 410013, China)
Abstract: With elements of Zn and Ca as alloy components, three kinds of degradable ternary Mg-Zn-Ca alloys with Ca contents of 1%, 2% and 3%(mass fraction), respectively, were fabricated by melting and casting. The mass loss measurement and electrochemical corrosion technique were employed to study their corrosion behaviours in Hank’s simulated body fluid. The results based on the SEM morphology observation and analyses of structures and phases show that the corrosion of Mg alloy begins from pitting corrosion at Mg matrix. The ternary alloy with 1% Ca shows an enhanced corrosion resistance, and the existence and distribution of Mg2Ca phase in alloy significantly affect its corrosion-resisting performance. The content of Mg2Ca phase in alloy increases with the increase of Ca content, leading to a poor corrosion resistance for alloy.
Key words: Mg-Zn-Ca alloy; Hank solution; electrochemical corrosion; Mg2Ca phase; biodegradation
近年来,镁及镁合金作为金属基生物材料受到越来越多的关注。镁是一种轻质金属,具有与人体骨膜相近的密度[1-2]和弹性模量[3],且无毒[4]、生物相容性好等优点。与目前临床上普遍采用的钛合金、不锈钢等金属植入材料相比,镁合金具有质量轻,弹性模量更加接近正常骨组织,避免应力遮挡[5]等优点,而且作为降解产物的镁离子能够通过新陈代谢完全排出体外[6]。因此,镁及镁合金作为硬组织修复材料和心血管支架材料在临床医学应用上具有广阔的前景。
镁的标准电极电位为-2.34 V,化学性质极为活泼,单纯的金属镁在介质中极易发生腐蚀,因此,通常采用合金化来增强镁的耐腐蚀性能。目前,生物医用镁合金的研究主要集中在镁铝合金和镁稀土Mg-RE合金系列。WITTE等[7]比较了AZ31、AZ91、WE43和LAE422这4种镁合金种植体在动物体内的腐蚀降解特点和骨组织对镁植入体的反应,发现镁合金具有比可降解聚合物更好的骨组织相容性和骨组织诱导性能。这些镁合金都采用了Ni、Al、Zr等合金元素来增强镁金属的耐蚀性。大量的研究数据指出这些元素具有致癌性、过敏性以及对细胞的慢性毒性[8-9],因此,开发具有更低细胞毒性和细胞相容性的新型镁基生物可降解吸收材料具有重要的医疗临床应用价值和广阔前景。近年来,我国学者也为此开展了广泛的研究。SONG[10]研究发现在纯镁中添加Zn元素能够显著减慢合金的腐蚀速度,对含Zn镁合金添加Mn元素后合金的腐蚀降解速率能够继续减慢。高家诚等[11]研究了纯镁及镁锌系列合金在仿生体液中的腐蚀行为。李子剑 等[12]观察镁钙合金对体外细胞生长的影响,发现镁钙合金浸出液没有表现出细胞毒性作用,呈现出良好的细胞相容性。
在此,本文作者以营养元素Zn和Ca作为合金组元,制备Mg-Zn-Ca 三元镁合金。其中,Zn可以与Mg形成MgZn相,具有固溶强化和时效强化的双重作用;Ca能够在铸造的过程中起阻燃作用,同时细化合金组织的晶粒,形成Mg2Ca相[13-14],从而提高镁的强度和塑性。并对三元镁合金在Hank模拟体液中的质量损失腐蚀及电化学腐蚀行为进行研究,通过对不同腐蚀时间合金表面形貌的观察以及合金组织及相成分的分析,探讨三元镁合金在模拟体液中的腐蚀机理。
1 实验
1.1 合金的制备
以纯度为99.99%的镁锭和锌粒以及纯度为99.8%的钙屑为原料。将设计量的镁锭放入石墨坩埚中,抽至真空,通入CO2和SF6混合气体作保护,在700~ 800 ℃加热10~20 min,待镁锭全部熔化后,加入设计量的锌和钙原料,设定加热温度为750 ℃,继续保温25~45 min,在保护气氛下趁热注入预热至200 ℃的金属模具中,浇铸成直径为50 mm的合金锭。
铸造样品用线切割法制成14 mm×5 mm的圆柱形试样块。
1.2 质量损失腐蚀
将3种合金的表面用砂纸打磨光滑,在丙酮溶液
中超声清洁10 min后干燥称量,浸入盛有100 mL Hank模拟体液的磨口瓶中(Hank模拟体液的组成[13]:NaC l8.0 g/L,KCl 0.4 g/L,CaCl2 0.14 g/L,NaHCO3 0.35 g/L,D-C6H6O6 0.35 g/L,MgSO4?7H2O 0.2 g/L,KH2PO4 0.1 g/L,Na2HPO4?12H2O 60 mg/L,用50 mmol/L稀HCl和(CH2OH)3CNH2调节pH值为7.2~7.4),(37±1)℃恒温,9 d后取出,然后在20%铬酸和1%硝酸银溶液中煮沸2 min,除去表面沉积的腐蚀产物,最后分别在丙酮和酒精中超声清洗10 min,室温干燥后在精度为0.1 mg的电子天平上称量。重复以上步骤将每种合金样品进行3组平行试验。
腐蚀速率根据公式v=Δm/(At)计算[15]。其中:Δm为腐蚀前、后样品的质量损失;A为合金浸泡前的几何面积;t为浸泡时间。
1.3 电化学腐蚀
将3种合金分别暴露一个面作为工作面,其余面用树脂密封并引出一根导线,对暴露的合金工作面进行砂纸打磨抛光和丙酮超声清洁后,置于三电极体系电解池中作为工作电极,参比电极采用饱和甘汞电极,将作为盐桥的鲁金毛细管的端口尽量靠近工作电极表面,以减小溶液电阻,铂丝作为对电极,在CHI660C电化学工作站上进行电化学腐蚀测试。在开路电位的-200~200 mV区间,以5 mV/s进行线性扫描获得塔菲尔曲线。
1.4 表面分析
用DMAX3C型X射线衍射仪(XRD)进行合金样品的成分分析,用HITACHI S-650型扫描电子显微镜 (SEM)观察合金在Hank模拟体液中分别浸泡5 h和3 d后的表面腐蚀形貌,并用EDAX能谱表征腐蚀产物的 成分。
2 结果与讨论
2.1 铸态样品的微观结构
图1所示为Mg-Zn-Ca三元铸态合金的SEM像,合金的元素组成如表1所列。从图1可知,随着合金中Ca含量的增加,合金的晶界变得更加清晰,晶粒尺寸也逐渐减小,晶界联通成网络状;在含Ca量为3%的合金C中可见明显的网状晶界结构,说明Ca元素的加入有利于合金的晶粒细化,此外,几乎没有出现第二相粒子的偏析。
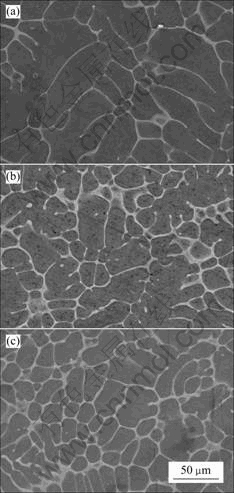
图1 3种合金的SEM像
Fig.1 SEM images of ternary casting alloys: (a) Alloy A; (b) Alloy B; (c) Alloy C
表1 3种合金的元素组成
Table 1 Compositions of three kinds of alloys
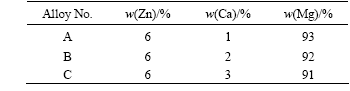
图2所示为三元合金的XRD谱。从图2可知,3种镁合金中除镁基相外,还有MgZn和Mg2Ca相。其中,MgZn相具有固溶强化和时效强化的双重作用,将有助于改善镁合金的耐腐蚀性能。随着Ca含量的增加,合金中Mg2Ca相的峰强度逐渐增强。图3所示为合金在扫描电镜下的晶界成分分析结果,表明在晶界处富集了更多的Ca成分。
2.2 质量损失腐蚀和电化学腐蚀
表2所列为3种合金在模拟体液中恒温37 ℃连续浸泡9 d后3组平行试验测量的平均腐蚀速率。
图2 3种合金的XRD谱
Fig.2 XRD patterns of ternary alloys: (a) Alloy C; (b) Alloy A; (c) Alloy B
表2 合金的质量损失腐蚀速率
Table 2 Mass loss rates of alloys for corrosion
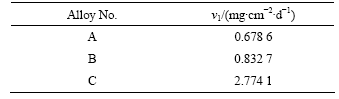
由表2可知合金A的耐腐蚀性能最好,其次是合金B,合金C的腐蚀降解速率比合金A的快了近4倍,说明Ca元素的加入显著影响三元镁合金的抗腐蚀 性能。
图4所示为3种合金的塔菲尔电化学腐蚀曲线。通常,阴极极化曲线表示水还原产生的阴极氢气析出过程,阳极极化曲线表示金属镁的溶解过程[16]。一般情况下,腐蚀电位越正,腐蚀电流密度越小,则材料的腐蚀速率越小,即材料的耐腐蚀能力越强。从塔菲尔曲线可知,3种合金的自腐蚀电位在-1.64 ~ -1.67 V,相对于镁的标准电极电位(-2.34 V(vs SHE)),腐蚀电位均有大幅度的正移,说明合金化显著改善和增强镁金属的耐腐蚀性能。由塔菲尔曲线的斜率交点所对应的电流密度即可以计算出被测试样的电化学腐蚀速率。
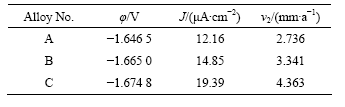
表3所列为根据塔菲尔曲线计算的自腐蚀电流密度、自腐蚀电位和腐蚀速率。从表3可见,随着合金中Ca含量的增加,合金表现出的抗腐蚀性能变差。3种合金的电化学腐蚀速率从高到低的顺序为合金C、合金B和合金A,合金A的耐腐蚀性能最好,与质量损失腐蚀法测定的结果一致。值得注意的是,当将阳极极
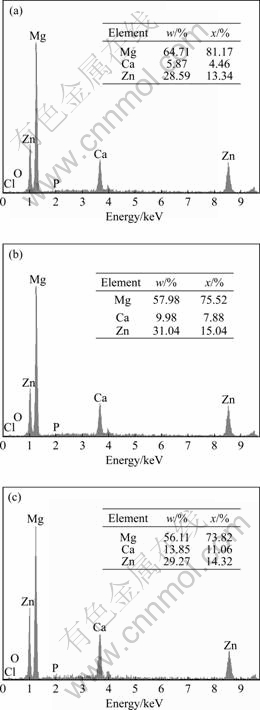
图3 合金晶界处的能谱图
Fig.3 EDAX spectra at grain boundary of alloys: (a) Alloy A; (b) Alloy B; (c) Alloy C
化曲线正向扫描到2.0 V时,极化曲线表现出合金的连续溶解而没有出现钝化区,这可能与Hank模拟体液中存在较高浓度的氯离子有关,说明在氯离子浓度高达0.145 mol/L的体液中,阳极极化的镁合金表面难以形成致密的钝化氧化膜或者一旦形成就被氯离子快速击穿[17-18],这也解释了在质量损失腐蚀测定时,延长浸泡时间所观察到镁合金表面层的大块脱落现象。
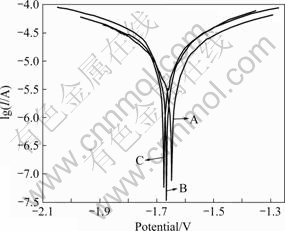
图4 合金电化学腐蚀的塔菲尔曲线
Fig.4 Tafel curves of alloys in electrochemical corrosion
表3 3种合金的电化学腐蚀数据
Table 3 Data of three kinds of alloys for electrochemical corrosion
由质量损失腐蚀和电化学腐蚀测定的结果可知,合金中Ca的加入量影响合金的耐腐蚀性能,结合2.1节合金的微观结构分析,合金B和C的耐腐蚀性较合金A差的原因应该归因于大量Mg2Ca相的存在,这一推测也被文献[13-14, 19-20]证实。KIM等[19]研究Mg-Ca二元合金时发现Mg2Ca的含量与分布能够控制合金的抗腐蚀性能和氢气的产生速率。文献[21]报道Mg2Ca相的腐蚀电位为-1.54 V(vs SCE),而金属镁 的平衡电位为-2.61 V(vs SCE)[22],因此,当Mg2Ca相存在于镁基合金体中时,在溶液与合金体的界面处,合金中的Mg2Ca相将作为阴极与金属镁基相作为阳极构成原电池,导致镁基相的腐蚀发生,生成镁离子进入溶液。随着合金中Ca含量的增加,Mg2Ca相的含量也相应增加,将有利于形成Mg-Mg2Ca原电池,从而加快镁基相的腐蚀,这就解释了含Ca量为3%的合金C最容易发生腐蚀降解的原因。由此可见,可以 通过控制Ca的加入量来有效调控镁合金的腐蚀降解速率。
2.3 合金在Hank模拟体液中的腐蚀机理
研究发现将合金样品浸入模拟体液中2~3 min后,合金表面很快就有气泡溢出,局部开始发生明显的点蚀,再继续浸泡到5 h,其SEM像如图5(a)所示。图5(b)所示为浸泡3 d后合金的SEM像,显示出合金表层的部分塌陷。结合实验观察与图5可知,在腐蚀初期,由于镁离子的形成并进入溶液,样品表面局部区域发生腐蚀破坏,同时伴随大量氢气的产生。图5(a)所示的表面裂纹是由于样品干燥过程中的脱水所致,但大部分表面仍然保持完整。随着浸泡时间的延长,蚀点数目逐渐增加,腐蚀破坏面积不断扩大,腐蚀进程从表面向内部深入,大量腐蚀产物在表面附着沉积析出,由于表层镁基体的完全腐蚀破坏,导致表层部分脱落。
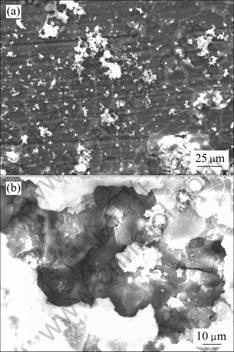
图5 合金A在模拟体液中浸泡5 h和3 d后的SEM像
Fig.5 SEM images of alloy A after being immersed in Hank’s SBF for 5 h (a) and 3 d (b)
在合金试样浸泡的初期,还观察到如图6(a)所示的结晶状沉淀物在合金表面的析出。图6(b)所示的EDAX能谱分析显示该沉淀物中富含大量的Cl-、CO32-和镁离子,几乎没有磷酸根离子,由此推测该结晶状沉淀物是含氯和碳酸根离子的镁盐,其可能的化学反应式如下:

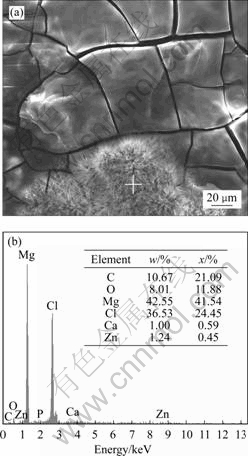
图6 合金A在模拟体液中浸泡5 h后的SEM像和EDAX谱
Fig.6 SEM image (a) and EDAX spectrum (b) of alloy A after being immersed in SBF for 5 h
图7所示为合金B在模拟体液中连续浸泡3 d后的SEM像以及对应于表层和内层沉积物的EDAX能谱。同图5(b)所示的合金A的腐蚀形貌一样,在合金B的表面沉积了大量沉淀物并出现了表面层的脱落和塌陷,能谱分析指出表层和内层沉积物的主要成分是含钙和镁的磷酸盐。虽然有研究[13]表明镁金属在模拟体液中浸泡一定时间后能生成少量的羟基磷灰石(HA),我们的结果显示表层磷酸钙盐沉淀物的Ca与P的量比为1.21,内层磷酸钙盐沉淀物的Ca与P的量比为1.18左右,均小于形成羟基磷灰石所需Ca与P的量比为1.67的条件。
综上所述,我们认为镁合金体的腐蚀,总体上是一种电化学反应过程。由于合金中Mg2Ca相的平衡电位较金属镁基相正得多,Mg2Ca相易与镁基相构成原电池Mg-Mg2Ca,镁合金的腐蚀过程可以表述如下。
1) 首先,合金中作为阳极的镁基相上的金属镁按式(4)所示的反应溶解成镁离子进入溶液中,表现为镁基相的点蚀;作为阴极的Mg2Ca相上则析出氢气,
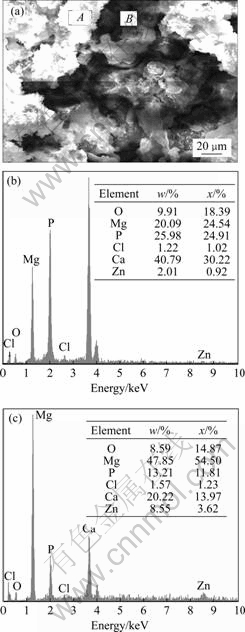
图7 合金B在模拟体液中浸泡3 d后的SEM像以及对应的EDAX谱
Fig.7 SEM image (a) and EDAX spectra ((b) and (c)) of alloy B after being immersed in SBF for 3 d corresponding to correlated areas A and B in Fig.7(a)
如式(5)的反应所示。同时,疏松的氢氧化镁白色沉积物按式(6)所示的反应在合金表面析出。
2) 在腐蚀初期,由于模拟体液中共存大量的Cl-和CO32-,部分氢氧化镁沉积物以及镁基相将与Cl-和CO32-反应形成MgCl2和MgCO3,随着腐蚀进程的继续,表面局部区域的MgCl2与MgCO3饱和度逐渐增大,至MgCl2和MgCO3成核时,MgCl2和MgCO3盐就会在合金样品表面结晶析出。
3) 随着腐蚀反应的进行,溶液会通过疏松的沉积物渗透进入内层的合金体,使内层镁金属继续发生腐蚀反应,溶解的镁离子也通过疏松的沉积物迁移到合金表面,同时溶液的pH值因腐蚀过程(如式(5)的反应)产生OH-而上升,合金表面呈局部碱化,这时Mg2 +与OH-会进一步生成Mg(OH)2沉淀。
4) 随着反应(4)~(6)的不断重复,Mg(OH)2沉积物变得越来越厚,溶液中存在的钙离子和磷酸根离子吸附在Mg(OH)2沉积物上形成磷酸钙盐析出,同时合金体因局部合金表面层镁基相的完全腐蚀而产生脱落或塌陷。
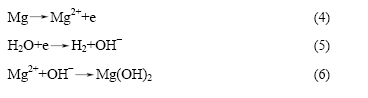
3 结论
1) 制备了Mg-Zn-Ca三元镁合金生物材料并发现合金元素Ca的加入能明显细化镁合金的晶粒,合金中形成的Mg2Ca相能显著影响合金的抗腐蚀性能。
2) 含Ca量为1%的镁合金表现出良好的抗腐蚀性能,过量Ca的加入会形成大量的Mg2Ca相,将可能弱化镁合金的耐腐蚀性能。
3) 镁合金的腐蚀是从镁基相的点蚀开始的,在腐蚀初期,镁的氯化物和碳酸盐结晶沉淀析出,随着腐蚀的深入,表面局部碱化,产生大量的氢氧化镁沉淀;在腐蚀后期,有大量含镁和钙的磷酸盐沉淀物析出,并伴随表面层的脱落。
REFERENCES
[1] 李世普. 生物医用材料导论[M]. 武汉: 武汉工业大学出版社, 2000: 52-71.
LI Shi-pu. Introduction of biomedical materials[M]. Wuhan: Wuhan University of Technology Press, 2000: 52-71
[2] 刘振东, 范清宇. 应力遮挡效应—寻找丢失的钥匙[J]. 中华创伤骨科杂志, 2002(4): 62-64.
LIU Zhen-dong, FAN Qing-yu. Stress shield effect—Search the lost key[J]. Chinese Wound and Bone, 2002(4): 62-64.
[3] KIM S G, INOUE A, MASUMOTO T. Increase of mechanical strength of a Mg85Zn12Ce3 amorphous alloy by dispersion of ultrafine hcp-Mg particles[J]. Mater Trans, 1991, 32(9): 875-878.
[4] KIM S R, LEE J H, KIM Y T. Synthesis of Si, Mg substituted hydroxyapatites and their sintering behaviors[J]. Biomaterials, 2003, 24(8): 1389-1398.
[5] 王勤涛, 张玉梅, 胡奈赛. 钛合金种植体临床断裂的原因分析[J]. 稀有金属材料与工程, 2004, 33(4): 442-444.
WANG Qing-tao, ZHANG Yu-mei, HU Nai-sai. Microstructure analysis of fractured Ti alloy implant[J]. Rare Metal Materials and Engineering, 2004, 33(4): 442-444.
[6] 颜廷亭, 谭丽丽, 熊党生, 张炳春, 杨 柯. 医用镁金属材料的研究进展[J]. 材料导报, 2008, 22(1): 110-129.
YAN Ting-ting, TAN Li-li, XIONG Dang-sheng, ZHANG Bing-chun, YANG Ke. Researching progress of biomedical Mg alloys[J]. Material Review, 2008, 22(1): 110-129.
[7] WITTE F, KAESE V, HAFERKAMP H, SWITZER E, MEYER L A, WIRTH C J, WINDHAGEN H. In vivo corrosion of four magnesium alloys and the associated bone response[J]. Biomaterials, 2005, 26: 3557-3563.
[8] HAUDRECHY P, FOUSSEREAU J, MANTOUT B, BAROUX B. Nickel release from 304 and 316 stainless steels in synthetic sweat: Comparison with nickel and nickel-plated metals[J]. Corros Science, 1993, 35: 329-336.
[9] K?STER R, SOMMERAUER M, K?HLER J, BALDUS S, MEINERTZ T, HAMM C W. Nickel and molybdenum contact allergies in patients with coronary in-stent restenosis[J]. The Lancet, 2000, 356(9245): 1895–1897.
[10] SONG G L. Control of biodegradation of biocompatible magnesium alloys[J]. Corrosion Science, 2007, 49: 1696–1701.
[11] 高家诚, 伍 沙, 乔丽英, 王 勇. 镁及镁合金在仿生体液中的腐蚀降解行为[J]. 中国组织工程研究与临床康复, 2007(18): 3584–3586.
GAO Jia-cheng, WU Sha, QIAO Li-ying, WANG Yong. Corrosion behavior of magnesium and its alloy in simulated body fluid[J]. Journal of Clinical Rehabilitative Tissue Engineering Research, 2007(18): 3584–3586.
[12] 李子剑, 张 克, 娄思权, 郑玉峰. 镁钙合金的细胞毒性研究[J]. 中国骨与关节损伤杂志, 2007, 9(22): 740–742.
LI Zi-jian, ZHANG Ke, LOU Si-quan, ZHENG Yu-feng. A cellular study on cytotoxicity of magnesium-calcium alloy[J]. Chinese Journal of Bone and Joint Injury, 2007, 9(22): 740–742.
[13] LI Z J, GU X N, LOU S Q, ZHENG Y F. The development of binary Mg-Ca alloys for use as biodegradable materials within bone[J]. Biomaterials, 2008, 29: 1329-1344.
[14] 刘生发, 范晓明, 王仲范. 钙在铸造镁合金中的作用[J]. 铸造, 2003, 54(14): 246-248.
LIU Sheng-fa, FAN Xiao-ming, WANG Zhong-fan. The effect of Ca in the process of casting Mg alloys[J]. Foundry, 2003, 54(14): 246-248.
[15] LIU C, XIN Y, TANG G, CHU P K. Influence of heat treatment on degradation behavior of bio-degradable die-cast AZ63 magnesium alloy in simulated fluid[J]. Mater Sci Eng A, 2007, 456: 350-357.
[16] JIAN W C, XING W G, PENG H F, LI M P, WEN J D. Effect of heat treatment on corrosion and electrochemical behavior of Mg-3Nd-0.2Zn-0.4Zr (wt%) alloy[J]. Electrochim Acta, 2007, 52: 3160-3167.
[17] 李龙川, 高家诚, 王 勇. 医用镁合金的腐蚀行为与表面改性[J]. 材料导报, 2003, 17(10): 29-32.
LI Long-chuan, GAO Jia-cheng, WANG Yong. The corrosion behavior and surface modification of biomedical Mg alloys[J]. Material Review, 2003, 17(10): 29-32.
[18] 任伊宾, 黄晶晶, 杨 柯, 张炳春, 姚志铭, 王 皓. 纯镁的生物腐蚀研究[J]. 金属学报, 2005, 41(11): 1228-1232
REN Yi-bing, HUANG Jing-jing, YANG Ke, ZHANG Bing-chun, YAO Zhi-ming, WANG Hao. Study of biocorrosion of pure magnesium[J]. Acta Metall Sinca, 2005, 41(11): 1228-1232.
[19] KIM W C, KIM J G, LEE J Y, SEOK H K. Influence of Ca on the corrosion properties of magnesium for biomaterials[J]. Materials Letters, 2008, 62: 4146-4148.
[20] ZHANG E L, YANG L. Microstructure, mechanical properties and bio-corrosion properties of Mg-Zn-Mn-Ca alloy for biomedical application[J]. Mater Sci Eng A, 2008, 497: 111-118.
[21] KIM J G, KIM Y W. Advanced Mg-Mn-Ca sacrificial anode materials for cathodic protection[J]. Mater Corros, 2001, 52: 137-139.
[22] JONES D A. Principles and prevention of corrosion[M]. 2nd ed. London: Prentice-Hall, 1996.
(编辑 杨 华)
基金项目:国家自然科学基金资助项目(50721003);中南大学粉末冶金国家重点实验室开放基金资助项目
收稿日期:2009-03-09;修订日期:2009-08-25
通信作者:雷 霆,教授,博士;电话:13203176590;E-mail: tlei@mail.csu.edu.cn